Unit 4
Global Issues
Globalization and MNCs
Globalisation refers to the continual process by which regional economies, societies and cultures have become integrated through a globe-spanning network of communication and trade. A multinational company (MNC) is an organisation that operates in two or more countries and plays a significant role in expanding globalized business.
Companies such as Apple, Coca-Cola, Exxon, HSBC, Microsoft, Nike, Samsung, Toyota, Walmart etc. are examples of MNCs which all excel within their industries in term of sales, profits, assets and market value.
The rise of MNCs including the ever-growing importance of international trade has intensified globalization.
Multinational corporations are agents of globalization. They reap the many benefits of globalization and at the same time, many multinational corporations also are adversely affected by globalization.
The effects of globalization can be studied as follows:
- Access to New Markets
Globalization gives businesses access to markets that might have been difficult to reach in the past. Because of the internet, customers from anywhere in the world can order products from companies anywhere else in the world, and have those products delivered by airplane in only a few weeks. This is naturally an incredible advantage to businesses, who stand to extend their potential customer base by millions by reaching bent foreign buyers.
2. Access to Labour at Cheaper Prices
Outsourcing and off-shoring allow businesses to recruit employees in foreign countries, where labour and assets costs could also be less than in the business' home country. While these practices can have negative effects on workers trying to find full-time jobs, there's little doubt that they decrease costs, and thus increase profits, for businesses.
3. Minimize Costs Through Partnership Formation
Companies stricken by globalization are able to form partnerships with organizations all over the world. There are a number of American, European, and Asian companies that have corporate partnerships that stretch across continents. For instance, tech giant Google partnered with South Korea's LG Electronics in 2014 and with Taiwan's HTC in 2017 to be able to offer its own line of cellular phones, including the Google Pixel. These sorts of partnerships minimize costs and maximize quality by playing to the strengths of teams all over the world.
4. Opportunities for Tax Reduction
Globalization gives multinational corporations the power to seek out foreign countries for their investments when their current country adopts a tax program they find to be unfavourable. Countries with low corporate tax rates are sometimes called "tax havens," as they permit corporations and individuals to lower their tax rates by moving assets offshore. These counties include Bermuda, Belize and Switzerland. The international financial structure, comprised of encrypted information systems and personal documents, makes all this possible
5. Coordination Challenges
One of the main drawbacks’ companies face in a globalized economy is coordination of resources. A company that operates in America, Japan and Europe, for instance, will need to hire employees who speak a number of different languages, and it could be difficult for that company to make sure all employees are on the same page when only some of them speak the same language. Translators could also be called upon to help in information coordination where language barriers exist. Problems in coordination may also arise from differences in cultural norms and business norms like managing logistics in countries with low-quality infrastructure.
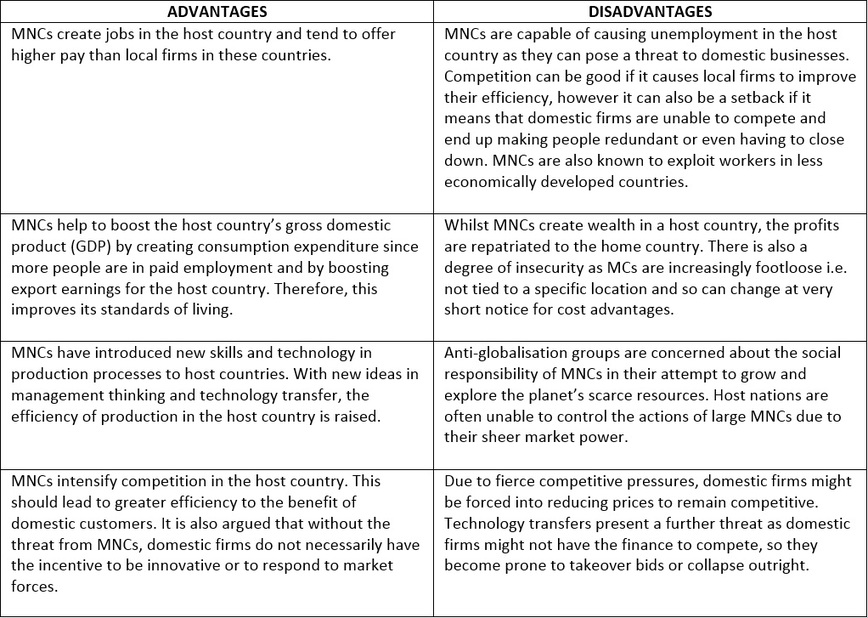
Advantages and Disadvantages of MNCs
Multinational Corporations (MNCs) also referred to as Transnational Corporation (TNC) or Multinational Enterprise (MNE) can be described as a business unit which operates simultaneously in numerous countries around the globe. In some cases, the manufacturing unit can be in one country, while the marketing and investment is in other country.
In other cases, all the business operations are administered is other countries, with the strategic headquarters in any part the planet. The MNCs are large corporate enterprises that extend their business operations beyond the country of origin through a network of industries and marketing operations.
Role of Multinational Corporations in the Indian Economy
Prior to 1991 Multinational companies failed to play much role within the Indian economy. The Indian economy was dominated by public enterprises in the pre-reform period.
To prevent concentration of economic power industrial policy 1956 didn't allow the private firms to grow in size beyond some extent. MNCs didn't play much role within the Indian economy where import-substitution development strategy was followed even though they played a significant role in the promotion of growth and trade in South-East Asian countries. After the adoption of business policy since of liberalization and privatization since 1991 rote of private foreign capital has been recognized as important for rapid development of the Indian economy.
Multinational Corporation have been allowed to work in the Indian economy subject to some regulations since source of bulk of foreign capital and investment lie in other countries. The following are the important reasons for this alteration in policy towards multinational companies during the post-reform period.
1. Promotion Foreign Investment:
External assistance to developing countries has been declining in recent years. This is because the investing developed countries have not been willing let go of larger proportion of their GDP for supporting developing countries. MNCs can act as a bridge between the needs of foreign capital for increasing foreign investment in India.
The liberalized foreign investment (1991) allows MNCs to make investment in India subject to different limits fixed for different industries or projects. Foreign investment has also a multiplier effect on income and employment in a country like domestic investment.
For instance, the effect of Suzuki firm’s investment in Maruti Udyog manufacturing cars is not confined to income and employment for the workers and employees of Maruti Udyog but goes beyond that. Many workers are employed in dealer firms who sell Maruti cars.
2. Non-Debt Creating Capital inflows:
Foreign direct investment by MNCs was discouraged in the pre-reform period, thus, India relied heavily on external commercial borrowing (ECB) which was of debt-creating capital inflows. This elevated the external debt and debt service payments reached the alarming figure of 35 per cent of India's current account receipts. This led to doubts about the country's ability to fulfill debt obligations which lead to the balance of payments crisis in 1991. MNCs can avoid the liability of debt-servicing payments as direct foreign investments by Multinational Corporation represents non-debt creating capital inflows. The benefits of investment by MNCs lies in the fact that servicing of non-debt capital begins only when the MNC firm reaches the stage of making profits to repatriate Therefore, MNCs can play a vital role in reducing stress strains and on India’s balance of payments (BOP).
3. Technology Transfer:
One of the most vital roles of an MNC is to transfer high sophisticated technology to developing countries which are crucial for raising productivity of working class and enabling them to start new productive ventures requiring high technology. MNCs not only import new equipment and machinery embodying new technology but also skills and technical know-how to use the new equipment and machinery whenever multinational firms set up their subsidiary production units or joint-venture units.
This leads to Indian workers' and engineers' increased knowledge of new superior technology and the way to use it. The corporate sector spends only few resources on Research and Development (R&D) in India. The larger MNCs tend to spend a lot on the development of new technologies which may greatly benefit the developing countries by transferring the new technology developed by them. Therefore, MNCs play a vital role in the technological advancement of the Indian economy.
4. Promotion of Exports:
Lower costs multinationals can play a significant role in promoting exports of a country in which they invest with extensive links all over the world and effective production. Historically in India, MNCs made large investment in industries whose products they exported. Japanese automobile company Suzuki made a large investment in Maruti Udyog with a joint collaboration with Government of India in recent years. This made Maruti cars available to be sold not only in the Indian domestic market but are exported in a large number to the foreign countries.
When giving permission to a multinational firm for investment in India, the Indian government granted the permission subject to the condition that the concerned multinational company would export the product so as to earn foreign exchange for India.
5. Investment in Infrastructure:
It is said that multinational corporations could invest in infrastructure such as power projects. Modernization of airports and posts, telecommunication with a large command over financial resources and their superior ability to raise resources both globally and inside India.
The investment in infrastructure will not only provide a significant boost to industrial growth but will also help in creating income and employment in the India economy. The external economies generated by investment in infrastructure by MNCs will therefore crowd in investment by the indigenous private sector and will therefore stimulate economic growth.
List of MNCs in India
Due to India’s growing economy, globalization and its potential in the market, many of the multinational companies are coming to India to extend their business. Below are the top Multinational Companies operating in India currently:
1. Microsoft
2. IBM
3. Nestle
4. Proctor & Gamble
5. Coca-Cola
6. PepsiCo
7. CITI Group
8. SONY Corporation
9. Hewlett Packard
10. Apple Inc
Environmental Ethics
Environmental ethics can be defined as the philosophical discipline that considers the moral and ethical relationship of human beings to the environment. In other words: what, if any, obligation does man have to the preservation and care of the non-human world?
While ethical issues concerning the environment have been debated for hundreds of years, environmental ethics failed to emerge as a philosophical discipline until the 1970s. Its emergence was the result of increased awareness of how the rapidly growing world population was impacting the environment and additionally with the environmental consequences that came with the growing use of pesticides, technology, and industry.
Environmental ethics as a discipline assists in defining man's moral and ethical obligations toward the environment. But human values become an element when observing environmental ethics. Human values are the items that are important to individuals that they then use to judge actions or events. In other words, humans assign value to certain things then use this assigned value to form decisions about whether something is correct or wrong. Human values are unique to every individual because not everyone places identical importance on each element of life. For instance, an individual living in poverty in an undeveloped country may find it morally acceptable to chop down the forest to create room for a farm where he can grow food for his family. However, an individual in a developed country may find this action ethically unacceptable as the destruction of forests increases carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere, which may negatively impact the environment.
Environmental ethics, in conjunction with human values, create challenging philosophical debates about man's interaction with the environment. Water and air pollution, the depletion of natural resources, loss of biodiversity, destruction of ecosystems, and global climate change are all issues concerned with the environmental ethics debate. It is often observed that within the discipline of environmental ethics there are tough ethical decisions humans must consider.
The fundamental principles of environmental ethics can be classified as follows:
Ecosphere and Ecosystems:
- We should not deplete or degrade the earth’s physical, chemical or biological capital, which supports all life and all human economic activities.
- We should attempt to understand and cooperate with nature as a whole.
- We should work with nature and natural resources to sustain the ecological integrity, biodiversity and adaptability of the earth’s life support systems.
- When we must alter nature to fulfil our needs or wants, we must always choose methods that do the minimum possible harm to us and other living things.
- Before we alter nature, we must always perform an Environmental Impact Assessment to gauge proposed actions and find out the way to inflict the minimum short – and long-term environmental harm.
Species and Cultures:
- Every species incorporates a right to live or at least struggle to live. Simply because it exists.
- We should work to preserve the maximum amount of the earth’s genetic variety as possible because it's the staple for all future evolution.
- We have the right to defend ourselves against individuals of species that do us harm and to use individuals of species to fulfil our vital needs but we must always strive not to cause premature extinction of any wild species.
- The best way to protect species and individuals of species is to safeguard the ecosystem within which they live and to assist restore those we've degraded.
- No human culture should become extinct as a result of our actions.
Individual Responsibility:
- We should not inflict unnecessary suffering or pain on any animal we raise or hunt for food or use for scientific or other purposes.
- We should use no more of the earth’s resources than we require and not waste such resources.
- We should leave the planet nearly as good as—or better—than we found it.
- We should work with the world to help heal ecological wounds we've inflicted.
Computer ethics can be defined as a set of ethical principles that regulate the utilization of computers. Some of the computing ethics are to not use a computer to harm people or to steal. Some common problems with computer ethics include intellectual property rights, like copyrighted electronic material, privacy concerns and the way computers affect society. As technology continues to advance, computer ethics continue to create ethical standards that address the new issues caused by new technologies.
The importance of computer ethics has grown, thanks to the growth of the internet, in conjunction with privacy issues. Concerns regarding computing technologies, like spyware and browser cookies, have questioned ethical behaviour in technologies. Computer ethics are designed to grant and protect rights and freedoms along with protecting individuals from harm. It also intends to assist in the prevention of cybercrime. The ethics also help maintain a collection of guidelines for communication and interaction between individuals through the web.
Ten Commandments of Computer Ethics as a code of computer ethics are provided by the Computer Ethics Institute. They are:
1. One should not use a computer to harm people.
2. One should not interfere with other people’s computer work.
3. One should not look around in other people’s computer files that may be private.
4. One should not use steal information using a computer.
5. One should not use a computer to bear false witness.
6. One should not copy or use proprietary software for which one has not paid for.
7. One should not use other people’s computer resources without authorization or proper compensation.
8. One should not appropriate other people’s intellectual output.
9. One should think about the social consequences of the program they are writing or the system they are designing.
10. One should use a computer in ways in which ensure consideration and respect for fellow humans.
Issues Concerned with Computer Ethics
Privacy concerns, intellectual property rights and effects on the society are considered as some of the common issues associated with computer ethics.
Privacy Concerns
- Hacking – means the unlawful intrusion by an individual into a computer or a computer network to steal or jeopardize data.
- Malware – means malicious software which created with the purpose or aim to impair a computer system. Viruses, spyware, worms and trojan horses are some common types of malwares.
- Data Protection – referred to as information privacy or data privacy is the procedural safeguarding of sensitive data which intends to influence a balance between individual privacy rights while still authorizing data to be used for business purposes.
- Anonymity – is a method of keeping a user’s identity masked through various software.
Intellectual Property Rights
- Copyright – is a type of intellectual property that offers proprietary publication, distribution and usage rights for the author.
- Plagiarism – is an act of copying and publishing an individual's work without proper citation claiming it as one's own.
- Cracking – is a way of breaking into a system by getting past the safety features of the system.
- Software License – allows the utilization of digital material by following the license agreement.
Effects on Society
- Jobs – Some jobs are abolished while some jobs became simpler as computers have replaced physical tasks in companies and businesses. This change may be considered unethical as it limits the skills of the employees. There may also be ethical concerns on health and safety of employees getting sick from constant sitting, viewing computer screens and typing on the keyboard or clicking on the mouse.
- Environmental Impact – Environment has been greatly affected with the advent of computers and the internet since a large amount of time spent using computers increases energy usage which successively increases the emission of greenhouse gases.
- Social Impact – Computers and the internet help people stay connected with family and friends. Social media has been very popular nowadays.
Computer gaming influenced society both positively and negatively. Positive effects include improved hand-eye coordination, stress relief and improved strategic thinking among individuals. Negative effects may be addiction of gamers to video games and isolation from the real world.
Computer technology helps the government in improving services to its citizens. Advanced database can hold huge data being collected and analysed by the government.
Computer technology assists businesses through automatizing processes, reports and analysis.
Cybercrimes
Cybercrime is any form of illegal activity that takes place via digital means. Data theft is, of course, one among the foremost common kinds of cybercrime, but cybercrime also includes a vast range of malicious activity as well, like cyberbullying or planting worms or viruses. Cybercrimes are often divided into two distinct categories: those that cause intentional damage and those that cause unintentional damage. Financial damage is the one of the most common consequences of cybercrime along with loss of intellectual property, defamation etc.
Cyberbullying, for example, is unlawful when it constitutes a threat to an individual's physical safety, involves coercion or displays hate or bias against certain protected populations. In that case, the damage is not financial, but it's still considered a criminal offence. For instance, unintentional damage might be caused by a disgruntled employee planting a "harmless" virus that disrupts business in any way. While it should not cause a similar immediate financial damage as stealing proprietary or financial information, it still causes collateral financial damage because of both lost employee time and whatever money the corporate must spend to mend the problem.
Serious cases of cybercrimes include human trafficking, selling and buying illegal pornography or child phonography, forgery of legal documents, hacking into bank accounts and illegally transferring money to offshore accounts etc.
Types of Cybercrimes
Below are the most common types of cybercrimes:
- DDoS (Denial of Service) Attacks
These are employed to make a web service unavailable and take the network down by overwhelming a specific website with traffic from a range of sources. Botnets - Large networks of infected devices are created by depositing malware on users’ computers. Once the network is down, the hacker then hacks into the system.
2. Identity Theft
This type of activity takes place when a criminal gains access to a user’s personal information to steal funds, access confidential data, or participate in tax or insurance fraud. They can also open a phone/internet account in another individual's name, use their name to plan a criminal activity and claim government benefits in their name. They may attempt that by figuring out user’s passwords through hacking, retrieving personal information from social media, or sending phishing emails.
3. Cyberstalking
Here the user is subjected to a plethora of online messages and emails leading to online harassments. Usually, cyber-stalkers use social media, websites and search engines to intimidate a user and generate fear. In this type of cybercrime, the cyber-stalker knows their victim and makes the person feel afraid or concerned for his or her safety.
4. Social Engineering
Social engineering involves criminals making direct contact with the victim, typically by phone or email. They attempt to gain their confidence and usually pose as a customer service agent so they will give the information needed. This is typically a password, the company one is employed in, or bank information. Cybercriminals will determine what they can about their victim on the web and then try to add them as an acquaintance on social accounts. Once they gain access to an account, they will be able to sell the information or secure accounts in their victim's name.
5. PUPs
PUPS or Potentially Unwanted Program is a type of malware and is comparatively less threatening than other cybercrimes. They uninstall important software in the victim's system including search engines and pre-downloaded apps. They can include spyware or adware, so it’s a decent idea to install antivirus software to avoid the malicious download.
6. Phishing
This is a kind of cyber-attack which involves a hacker sending malicious email attachments or URLs to the users to gain access to their computers and personal accounts. Cybercriminals have become skilled and now many of the phasing emails are no more flagged as spam by email engines. Users are tricked into emails claiming they need to alter their password or update their billing information which provides the criminal access to their personal information.
7. Prohibited/Illegal Content
Here criminals share and distribute inappropriate content that may be considered highly disturbing, offensive and illegal. Offensive content may include, but isn't limited to, pornography, videos with intense violent and videos of criminal activity. Illegal content also includes materials advocating terrorism-related acts and child exploitation material. This type of content exists both on the everyday internet and on the dark web which is a hard to access anonymous network.
8. Online Scams
Online scams are typically in the form of ads or spam emails that include promises of rewards or offers of unrealistic amounts of money. Online scams include enchanting offers that are usually “too good to be true” which include links to win these rewards and when clicked on can cause malwares to enter the system and compromise information.
Ethical Living, in simple terms, can be described as the philosophy of making decisions for day to day life which take into account ethics and moral values, particularly with regard to consumerism, sustainability, environmentalism, wildlife, and animal welfare.
Ethical Living is often considered as a part of sustainable living in which the individual primarily makes a series of small lifestyle changes in order to limit their effect on the environment. Making the decision to start to live ethically can involve initial steps as simple as beginning to recycle, switching off lights when leaving a room, buying local organic or fair-trade produce, or eating less meat, etc.
Living with intention is one of the most important elements of ethical living. In intentional living a person is encouraged to become aware of their fundamental beliefs and be willing to make an effort to have their behaviour reflect those beliefs.
In this way, instead of constantly being aware and concerned about the future effect of one's actions, a person is more focused on (and mindful of) the intent and inherent moral worth of that which they are currently doing. Rather than being focused on perceived success or failure, a person is more concentrated on and subsequently mindful of living with a sense of purpose, and thus, finds comfort and solace by living a purposeful life.
An individual strengthens their resilience and nurtures a will to succeed, thereby fulfilling the dictum that "no mountain is too great, when you have a reason to climb." with such a sense of purpose.
Concept of Harmony in Life
Marriam Webster defines harmony as, "a pleasing arrangement of parts". In other words, harmony means the co-existence and interdependence of different parts of a system that facilitate smooth functioning of the entity as a whole. The concept of harmony in life may be compared to living life as a forest does, where every element has a purpose in this giant organism. Each part has a specific purpose, and all the parts are connected to each other, and are dependent on each other for their survival.
The concept of harmony in life can be understood by the following principles:
1. Celebrate life - live life with passion.
It is important to celebrate your life every day. Live with passion and excitement. A harmonious life always begins with waking up in the morning and smiling: One should take a deep breath and say “It’s another great day to be alive!” to rejuvenate the often-forgotten sense of being alive. It is necessary to boost up your engines, caress your soul, honour your body, give peace and tranquillity to your mind! Be content in being yourself without trying to imitate someone else.
2. Show gratitude and appreciation.
Showing gratitude and appreciation to your loved ones nourishes your relationships. It is important to let your loved ones know how important and dear they are to you; how much better your life is for having them close.
It is often seen that many times one might be silent and only think about the words they’d like to say - but have no courage to say them out of fear. However, practicing gratitude and appreciation will help in getting rid of that fear.
Gratitude and appreciation must be used as return gifts to give in return for all the things you get.
3. Learn how to communicate.
It is often seen that people complain of failing relationships dude to a lack of communication. It is important to realize that even though you may not realize it, but you are sending a message every moment when you are in the presence of someone; perhaps there is no direct communication because you are busy doing something else. One of the best examples of indirect communication is with a pet. If you have a dog or cat you know that communication takes place all the time. Your dog, for instance, cannot say anything to you and yet, they can understand you and you can understand them.
If communication is not with words, it is carried out with body language. While speaking, the tone of your voice says more than your words. Therefore, it is imperative to be aware of all these elements for proper communication to lead a harmonious life.
4. Know what you want.
Define your goals in life. It is crucial to know where you are going and formulate a well-designed plan how to get there. To realize what your goal is you may ask yourself what will give purpose and meaning to your existence?
It is important to know the things you can achieve and how much more you can accomplish. Remind yourself that, at the end of your life, its not important how much money or fame one has amassed but how many lives one has touched.
5. Have compassion.
Having compassion is one of the most fundamental requirements for leading a harmonious life.
Having compassion includes, accepting people as they are and listening with the intention of finding out new things, to understand, to really see the person in front of you.
It is also essential that one must be compassionate oneself as well. One should accept their limitations and learn to forgive themselves for making mistakes.
6. Teach others how to treat you.
The way you treat yourself sets the standards of what you expect from others. One should always treat oneself with respect. When referring to yourself in a conversation, do not berate yourself. Being respectful towards yourself is necessary to protect your well-being, self-image, and future.
7. Stay positive.
Almost everything that happens in life has a positive aspect which is often overlooked. Therefore, one should always look for the positive side of things and be confident that whatever life puts in front of them, they’ll find your way. Be conscious of the fact that there is no problem without a solution. Be aware of how many possibilities and opportunities are opened up for you. Clean up your surroundings of negativity including negative people and things and pay attention, notice and acknowledge the bright side of life.
8. Harmony with Nature
Nature is the primary provider for all human needs. Therefore, you should consider yourself as an intrinsic part of nature and work as a single organism along with it. This includes, maintaining cleanliness, having respect for all living things, trying to be in the company of nature as much as possible etc.