Unit - 5
Plastic Moulding, Glass Cutting
Plastic and non-metallic materials in the form of natural and synthetic resins and their compounds.
Limitations of plastics:
Plastics have made applications in the following areas:
Classification of plastics:
All the plastics are broadly classified into two main groups as under.
Fabrication of plastics:
Plastics are available in industry in the forms:
Commonly used method for fabrication:
Injection moulding, compression moulding, blog moulding, thermoforming, lamination, spreading, calendering etc.
Compressing moulding: Most of thermosetting plastics and few thermoplastics plastics can be moulded through this process. A correct amount of plastic compound is placed in a heated mould. A punch called force compressors the compound from top into the required shape and density. The mould is kept closed for sufficient time to allow the chemical change to complete, so that the product is sufficiently hardened.
Operating parameter:
Injection moulding: It is very commonly used for thermoplastic plastics .the Powder plastic compound is first heated to drive of moisture and then fit into the pauper. When the RAM is drawn back, some of the Powder drops down into the chamber. After closing the Mount, the RAM is moved forward. Applying pressure behind the Powder. during heating in the chamber, the temperature of the material rises to between 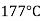 and
and 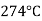 .After the plastic has been cooled and sufficiently hardened in the mould, the mould is opened and the produced part is not out. It is a faster process and suites best for large quantity production.
.After the plastic has been cooled and sufficiently hardened in the mould, the mould is opened and the produced part is not out. It is a faster process and suites best for large quantity production.
Blow moulding: It is used for producing narrow neck plastic containers, like bottles in this process a heated closed and thermoplastic tube is placed in the mould and air pressure is applied to inflate it for acquire the shape of mould cavity. After the plastic is cooled the mould is open and the product taken out.
Glass cutting:
Types of silicate glasses and their application
Properties of glass:
Glass cutting:
Steps:
Select proper work area.
- Dip the cutter in the oil to create a smooth score line.
- Layout a straight edge by using a thick yardstick or desk ruler.
- Apply pressure tooth class, pull the cutter along the surface by rolling the small carbide wheel.
- Run the cutter smoothly from one h to the other. Do not run back and forth.
- Wipe the oil, the score should look like a small scratch.
Bracking and smoothing:
Cutting a curve:
References:
1. Hajra Choudhury S.K., Hajra Choudhury A.K. And Nirjhar Roy S.K., “Elements of Workshop Technology”, Vol. I 2008 And Vol. Ii 2010, Media Promoters and Publishers Private Limited, Mumbai.
2. Kalpakjian S. And Steven S. Schmid, “Manufacturing Engineering and Technology”, 4th Edition, Pearson Education India Edition, 2002.
3. Gowri P. Hariharan and A. Suresh Babu,” Manufacturing Technology – I” Pearson Education, 2008.
4. Roy A. Lindberg, “Processes and Materials Of Manufacture”, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall India, 1998.
5. Rao P.N., “Manufacturing Technology”, Vol. I And Vol. Ii, Tata Mcgrawhill House, 2017.