Module-10
Plant physiology
10.1 Plant Physiology
A biological science that concerned with the plants and their general patterns governing the life processes happening in plants. Plant physiology includes the life of a plant and studies the ways in which plants absorb water and nutrients, grow and develop into a bigger plant, and bearflower and ultimately bear fruit. It also deals with concepts like mineral nutrition andrespiration, photosynthesis, that help the plant to grow and reproduce it includes biosynthesis and the accumulation of substances which together enable plants in all its processes. The Environmental condition is a major factor on which life processes of plants depend, plant physiology serves as the theoretical basis for increasing the total productivity of plants, improving their nutritional value, and raising the quality of their tissues and organs for use in industry. Research in plant physiology provides a scientific basis for the rational planting of crops in regard to soil and climatic conditions.
Plant physiology is a branch of study in Botany that deals with the functions of the plant and the various physiological processes that occur in plants. Specifically, it is ashow a descriptive study of structure and variation of plants at the cellular and molecular level leading to ecological, physiological and biochemistry related aspects of plants exploration.
As plants evolved on land, they required various methods to survive with the separation of carbon dioxide and water.
Plant physiology gives an account of the different parts of the plant and how they function.
Physiology of Plant Parts
Leaves
Leaves are the most important organ of the plant. The leaves help in photosynthesis. They have many veins and have the pigment chlorophyll;theleaves grow in a variety of shapes and sizes. They are the primary centre of photosynthesis where the food is prepared.
Stem
The stem is the backbone of the plant they provide support and structure to the plant. The stem is of different type in many species, they are branched or may be a single stem, they perform many important functions such as plant growth, compete and survive in different environments, etc.
Roots
The roots are the part of the plant that help the plant to fix in the soil, they help the plant to stand firmly. It helps in absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. Thus,they are an important part of the plant.
Xylem and Phloem
These form the vascular tissues of the plant. These are also known as sap. They transport water, sugars and other important substances between the roots, stem and leaves
Respiration in Plants
Food that is required for life processes comes from photosynthesis. Cellular respiration results in the release of energy which is used for the synthesis of ATP which involves glycolysis.
Aerobic respiration leads to complete oxidation of organic substances in the presence of oxygen which is common in higher organisms.
All living organism, containing plants, get their energy necessary for their survival from a series of chemical reactions termed respiration. The process of Respiration needs glucose to start the reactions which are changed into energy and later produce carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
The method by which cells get chemical energy by the consumption of oxygenand the liberation of carbondioxide is called respiration.in order to carry on respiration, plant cells require oxygen and a means of disposing of carbon dioxide just as animals cell do. In plants, every par such as root stem executes respiration as plants do not possess any particular organs for exchange of gases.
The method of respiration is written as:
Oxygen+glucose------water + carbon dioxide with energy.
As plants do not have any specialized organs like lungs to breathe, plants do not breathe they respire, they respire with the help of lenticels and stomata that east on stems and leaves which carry out the function of exchange of gases.
Types of respiration
There are two kinds of respiration which are categorize on the basis of presence or absence of oxygen.
Aerobic respiration
The respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen is called aerobic respiration due to air that which has oxygen. The aerobic respiration contains utilization of oxygen for the breaking of chemical bonds in Glucose to liberate energy in high volumes. It is the central source of energy for all organisms, Animals and plants that use oxygen for respiration are aerobes. Mostly all the animals have aerobic respiration.
C6H12O6+6O2-6CO2+6H2O+Energy
Aerobic respiration takes more energy because a complete breaking of glucose takes place during respiration with the use of oxygen.
Anaerobic Respiration
The respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen is known as anaerobic respiration. In this process, the incomplete oxidation of food substance is being made by carbon dioxide CO2 and alcohol (OH). Beside this other organic matter such as citric acid, oxalic acid,lactic acid etc. are produced.
Glucose-Alcohol+CO2+ (Energy)
Anaerobic respiration yields much less energy due to the partial breakdown of Glucose happens in anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen. All the organisms which gain energy by Anaerobic respiration can exist without oxygen. E.g. yeast can live in the absence of oxygen, yeast respires anaerobically and all through this process, yeast transforms into alcohol, therefore it is used to make alcohol and in fermentation industry.
10.2 Transpiration
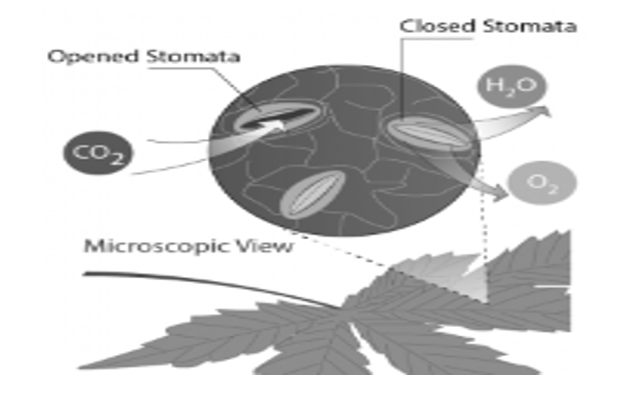
Transpiration, is a plantsloss of water, mainly through the stomataof leaves. Stomatal openings are present on the leaves, these stomata have openings that allow carbon dioxide inside the leaf and oxygen is given out through the leaves through photosynthesis. Therefore,Transpiration is a very important step in plants that accompany the real function of stomata. It has been observed that transpiration provides the energy to transport water in the plant. Excessive transpiration can be extremely injurious to a plant. When water loss exceeds water intake, it can retard the plant’s growth and ultimately lead to death by dehydration
Transpiration was first measured by Stephen Hales (1677–1761), an English botanist and physiologist. He noticed compared to animals’plants “imbibe” and “perspire” significant amounts of water compared to animals and therefore help measuring the emission of water vapour by plants. He found there was an upward flow of dissolved nutrients and water from the roots and that transpiration occurred from the leaves and he proposed that Transpiration occurred through leaves. Modern research has shown that as much as 99 percent of the water taken in by the roots of a plant is released into the air as water vapour.
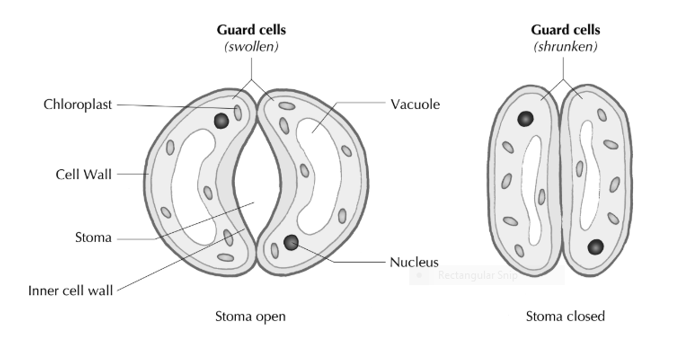
The primary sites for Transpiration are the leaf stomata’s. Stomata consist of two guard cells that have small openings. The opening and the closing of the stomata is controlled by the guard cells, this also further depends onenvironmental stimulus and the guard cells can regulate transpiration to reduce loss of water from leaves.Stomatas can sometimes close and transpiration can decrease due todarkness and internal water deficit, some factors that help opening of stomata are illumination, ample water supply, and optimum temperature open stomates and increase transpiration. Many plants close their stomates under high temperature conditions in order to reduce evaporation or under high concentrations of carbon dioxide gas, when the plant likely has sufficient quantities for photosynthesis
There are a few other adaptations which also help to reduce water loss through transpiration. Physically, plants that live in areas of low humidity have leaves with less surface area therefore evaporation is minimal or limited. On the other hand, plants in humid areas, which receive very less sunlight, have large leaves to receive sufficient sunlight and keep water loss low. Manydesert plants have minute leaves that eliminate water loss during the dry season theleaves are deciduous during drought periods, Sunken stomata waxy cuticle ,trichomesand other leaf adaptations help reduce transpiration rates by keeping the surface of the leaf cool, however cacti lack any form of leaves , when conditions are very hot and dry some plants including many succulents, open their stomates during the night to take in carbon dioxide and close them during the day time.
|
Fig1: Shows the presence of stomata on leaves, they have an opening for the opening of gases.
|
Fig 2: Shows the internal structure guard cells, they control the opening and closing of stomata, they have a cell wall and an inner cell wall, a vacuole and chloroplast.
10.3 Mineral Nutrition
The most naturally occurring inorganic nutrient that is found in soil and food is called as Mineral Nutrition, it is essential for the proper functioning of animal and plant body. They are the most vital elements necessary for the body. Both the plants and animals require minerals essentially. For example, for the manufacture of protein and cell division the nutrient Zinc is absolutely essential.
Nutrients which are required by plants in very small amounts are termed as Micro Elements or macronutrients. Some of them include copper, magnesium, iron, boron, chlorine, and molybdenum.
Plants which require Nutrients in large amounts are termed as Macronutrients. Some of them include nitrogen,sulphur, carbon, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
Role of Nutrients
Micronutrients
Functions of some of the Micronutrients are stated below:
Copper
Manganese
Zinc
Macronutrients
Functions of certain macronutrients are stated below:
Phosphorous
Nitrogen
Potassium
Potassium is an important micronutrient as it is the only monovalent cation that is essential for plants. It acts as an enzyme activator including DNA polymerase. Mottled chlorosis occurs due to the deficiency of potassium.
References:
1.Fundamentals of Plant Physiology –Dr. V.K. Jain
2. Plant Physiology—Lincoln Tiaz, Eduardo Zeiger.