Unit - 4
Communication and Technical Writing
A public speaking presentation is different from an online presentation because the online presentation may be viewed and/or listened to at the viewer's convenience, while a public speech is typically limited to a specific time or place. Online presentations are often comprised of slideshows or pre-recorded videos of a speaker.
Most Group Discussions can be divided into 3 kinds:
A) Topical Group Discussions, which are based on current affairs or ‘static’ matters – for example, a GD on the topic of the recent demonetization of Rs 500 and Rs 1000 notes would be the former, whereas a GD on whether India should adopt a presidential model of democracy would be the latter, as it has no limitation of a time frame.
B) Case-studies, which present the group with a complex business situation that requires a decision to be made. Such cases usually have multiple problems embedded in the given situation, and both the individual participants and the group are required to analyses the situation, identify the problems, and suggest a way out.
C) Abstract Group Discussions, which are called so because they offer us no definite framework of the topic, and hence no definite direction to take in the discussion. Instead, the participants are required to interpret the topic in their own ways and demonstrate innovative thinking in doing so.
An oral presentation can be given as an individual or as part of a group. It also might add components of technology, such as a slide show, video clip or audio recording. An oral presentation is most often assigned as part of class coursework but can have other purposes as a teaching tool. A teacher might assign students an oral presentation on a particular topic or set of topics that requires them to learn more about the subject. The presenting students then take on a teaching role in sharing that new information to the class through their presentation.
It is a face-to-face interaction between interviewee and interviewer. If handled carefully, it can be a powerful technique in having accurate information of the interviewee otherwise unavailable. At the same time, if the interview is not handled carefully, it can be a source of bias, restricting or distorting the flow of communication.
Presentation aids are the resources beyond the speech itself that a speaker uses to enhance the message conveyed to the audience. The type of presentation aids that speakers most typically make use of are visual aids: pictures, diagrams, charts and graphs, maps, and the like. Audible aids include musical excerpts, audio speech excerpts, and sound effects. A speaker may also use fragrance samples or food samples as olfactory (sense of smell) or gustatory (sense of taste) aids.
Presentations can be enhanced by the effective use of visual aids. These include handouts, overhead transparencies, drawings on the whiteboard, PowerPoint slides, and many other types of props. Once you have chosen a topic, consider how you are going to show your audience what you are talking about. Visuals can provide a reference, illustration, or image to help the audience to understand and remember your point.
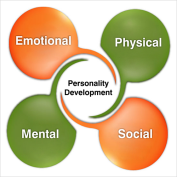
Benefits of personality development include the following keys:
Essentially, a report is a short, sharp, concise document which is written for a particular purpose and audience. It generally sets outs and analyses a situation or problem, often making recommendations for future action. It is a factual paper, and needs to be clear and well-structured.

Reports may contain some or all of the following elements:
Project proposals - write a project proposal helps you communicate your project's value to your clients, investors or an employer. This skill is essential for getting your project approved and funded. When writing a project proposal, you can follow some steps to make sure you write an effective one.
Project proposals are documents that tell stakeholders why your project ideas should be executed. Reading about your ideas in a well-written document should convince stakeholders to support them. You may use project proposals for the following purposes:
Brochures - A brochure is an informative paper document (often also used for advertising) that can be folded into a template, pamphlet, or leaflet. A brochure can also be a set of related unfolded papers put into a pocket folder or packet. Brochures are promotional documents, primarily used to introduce a company, organization, products or services and inform prospective customers or members of the public of the benefits.
Newsletters – is a written report, issued periodically, typically by a business, institution, or other organization, that presents information and news to people with a specific interest in the organization or subject. It is a newsletter is a printed or electronic report containing news concerning of the activities of a business or an organization that is sent to its members, customers, employees or other subscribers.
Technical articles - It is a written composition treating scientific or a technical subject distinctly. It is a systematic account of the result of some investigation, research, fieldwork and other activities.
It explores one area of interest and presents an objective analysis and interpretation of facts, findings, inferences, suggestions, recommendations and suggestions and conclusions.
Manuals - is a booklet or book, usually accompanying an appliance, device, computer game or vehicle, which contains written guidelines informing how to use it.
Official notes - An official letter is a formal letter written by one Official to another Official or to the government, semi-govt , Autonomous, Semi-Autonomous bodies or private organization. An Official letter maybe written by an Official to a non-official, from non- Official to an Official regarding any Official affair. In an Official letter, the designation with the name of the Office of the writer is used in the heading. In our country , Official letter are generally written their person and Govt. Offices
Business letters- A business letter is a letter from one company to another, or between such organizations and their customers, clients, or other external parties. The overall style of letter depends on the relationship between the parties concerned. A Business Letter is type of letter which serves as a means of communication written for various commercial purposes.
Memos - A memo is actually short for Memorandum. It is one of the most used means of official communication in the business world. Its main purpose is to serve as a reminder or to give some instructions. Again these like circulars are a means of mass communication, i.e. to communicate with a large number of people within the organization.
Progress reports- is an assessment that takes place during a project or process, that conveys details such as what sub-goals have been accomplished, what resources have been expended, what problems have been encountered, and whether the project or process is expected to be completed on time and within budget.Progress reports are used by management to determine whether changes are necessary to an ongoing effort.

Minutes of meetings- Also known as protocol or note, minutes are the live written record of a meeting. They include the list of attendees, issues raised, related responses, and final decisions taken to address the issues. Their purpose is to record what actions have been assigned to whom, along with the achievements and the deadlines.
Event report- Event reporting involves producing a report after an event has concluded in order to assess whether the objectives of the event were met. Event reports are sent to the sponsors of the event and should be tailored towards the needs and interests of the sponsor.
A post-event report pulls together relevant data, statistics and information that has been gathered in the lead up to, during and after an event.
References:
1. David F. Beer and David McMurrey, Guide to writing as an Engineer, John Willey. New York, 2004
2. Diane Hacker, Pocket Style Manual, Bedford Publication, New York, 2003. (ISBN 0312406843)
3. Shiv Khera, You Can Win, Macmillan Books, New York, 2003.
4. Raman Sharma, Technical Communications, Oxford Publication, London, 2004.
5. Dale Jungk, Applied Writing for Technicians, McGraw Hill, New York, 2004. (ISBN: 07828357-4)
6. Sharma, R. and Mohan, K. Business Correspondence and Report Writing, TMH New Delhi 2002.
7. Xebec, Presentation Book, TMH New Delhi, 2000. (ISBN 0402213)