Unit - 1
Introduction
- A disaster may be a unforeseen, unfortunate event that seriously disrupts the functioning of a community or society and causes human, material, and economic or environmental losses that exceed the community's or society's ability to cope exploitation its own resources. Although typically caused naturally, disasters will have human origins.
- Disaster Management are often outlined because the organization and management of resources and responsibilities for addressing all humanitarian aspects of emergencies, especially, readiness, response and recovery so as to reduce the impact of disasters.
- A disaster may be a serious disruption occurring over a brief or long amount of your time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss that exceeds the flexibility of the affected community or society to cope exploitation its own resources.
- Developing countries suffer the best prices once a disaster hits – quite ninety fifth of all deaths caused by hazards occur in developing countries, and losses because of natural hazards are twenty times bigger (as a proportion of GDP) in developing countries than in industrial countries. Regardless of what society disasters occur in, they have an inclination to induce amendment in government and social life.
- They will even alter the course of history by generally poignant entire populations and exposing management or corruption in spite of however tightly data is controlled during a society.

Fig. No. 1 Disaster
1.2.1 Disaster:
- A disaster is an occasion disrupting the traditional conditions of existence and inflicting tier of suffering that exceeds the capability of adjustment of the affected community.
- A disaster is an occasion disrupting the traditional conditions of existence and inflicting tier of suffering that exceeds the capability of adjustment of the affected community.
- A disaster may be a serious disruption occurring over a brief or long amount of your time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss that exceeds the flexibility of the affected community or society to cope exploitation its own resources.
- Developing countries suffer the best prices once a disaster hits – quite ninety fifth of all deaths caused by hazards occur in developing countries, and losses because of natural hazards ar twenty times bigger (as a proportion of GDP) in developing countries than in industrial countries.
- Regardless of what society disasters occur in, they have an inclination to induce amendment in government and social life. They will even alter the course of history by generally poignant entire populations and exposing management or corruption in spite of however tightly data is controlled during a society.
- Disasters are habitually divided into natural or human-made, though complicated disasters, wherever there's no single root cause, are a lot of common in developing countries. A particular disaster could spawn a secondary disaster that will increase the impact. A classic example is AN earthquake that causes a moving ridge, leading to coastal flooding. Some factory-made disasters are ascribed to nature.
- Some researchers additionally differentiate between continual events like seasonal flooding, and people thought of unpredictable.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- A disaster is an occasion disrupting the traditional conditions of existence and inflicting tier of suffering that exceeds the capability of adjustment of the affected community.
1.2.2 Hazard:
- Hazard is a happening that has potential for inflicting injury/ loss of life or injury to property/environment. Disaster is a happening that happens suddenly/unexpectedly in most cases and disrupts the traditional course of life in affected space. It leads to loss or injury to life, property or setting.
- A hazard may be a potential supply of damage. Substances, events, or circumstances will represent hazards once their nature would permit them, even simply on paper, to cause injury to health, life, property, or the other interest useful.
- The chance of that damage being complete during a specific incident, combined with the magnitude of potential damage, form up its risk, a term typically used synonymously in informal speech.
- Hazards are often classified in many ways in which. They'll be classified as natural, evolution, technological, or any combination so, like within the case of the phenomenon of inferno turning into a lot of common because of human-made global climate change or a lot of harmful because of changes in building practices.
- A standard theme across several kinds of hazard is that the presence of keep energy that, once discharged, will cause injury. Keep energy will occur in several forms: chemical, mechanical, thermal, hot, electrical, etc. things can even be dangerous, as for instance confined or restricted egress areas, oxygen-depleted atmospheres, awkward positions, repetitive motions, low-hanging or projecting objects, etc.
- They will even be classified as health or safety hazards, by the populations which will be affected, and therefore the severity of the associated risk. In most cases a hazard could have an effect on a spread of targets, and have very little or no result on others.
- Identification of hazards assumes that the potential targets are outlined, and is that the commencement in playacting a risk assessment.
- Environmental hazards embody long run environmental deterioration like natural process of soils and build-up of region dioxide to communal and involuntary social hazards like crime and terrorist act to voluntary and private hazards like misuse and ice climbing.
- Environmental hazards sometimes have outlined or common characteristics together with their tendency to be fast onset events that means they occur with a brief warning time, they need a transparent supply of origin that is well known, impact are swift and losses suffered quickly throughout or shortly when on-set of the event, risk of exposure is typically involuntary because of location or proximity of individuals to the hazard and therefore the "disaster happens with AN intensity ANd scale that justifies an emergency response".
- Hazards could also be classified in keeping with their characteristics. These factors are associated with geology events that don't seem to be method specific:
- Areal extent of injury zone
- Intensity of impact at a point
- Duration of impact at a point
- Rate of onset of the event
- Predictability of the event

Fig. No. 2 Hazard
- Natural hazards could also be outlined as "extreme events that originate within the part, layer, layer or atmosphere" or "a potential threat to humans and their welfare" that embody earthquake, landslide, cyclone and tsunamis. Technological and simulated hazards embody explosions, unharness of noxious materials, episodes of severe contamination, structural collapses, and transportation, construction and producing accidents etc.
- A distinction also can be created between speedy onset natural hazards, technological hazards and social hazards that area unit represented as being of unexpected prevalence and comparatively short length, and therefore the consequences of long run environmental degradation like geologic process and drought.
- In process hazard Keith Smith argues that what could also be outlined as hazard is a hazard if there's the presence of humans to create it a hazard which it's otherwise merely an occasion of interest. During this sense the environmental conditions we tend to might think about hostile or risky is seen as neutral therein it's our perception, human location and actions that determine resources and hazards at intervals the vary of natural events.
- During this regard human sensitivity to environmental hazards could be a combination of each physical exposure (natural and/or technological events at a location associated with their applied mathematics variability) and human vulnerability (in respect to social and economic tolerance of identical location).
- Smith states that natural hazards area unit best seen in associate ecological framework so as to tell apart between natural events as natural hazards. He says "natural hazards, therefore, result from the conflict of geology processes with individuals and that they lie at the interface what has been known as the natural events system and therefore the human interface system."
- He says that "this interpretation of natural hazards offers humans a central role. First of all through location, as a result of it's only individuals and their possessions get within the approach of natural processes that hazard exists."
- A natural hazard is thought-about as a geology event that once it happens in extremes and a person's issue is concerned which will gift a risk.
- During this context we will see that there could also be an appropriate variation of magnitude which may vary from the calculable traditional or average vary with higher and lower limits or thresholds. In these extremes the natural prevalence might become an occasion that presents risk to the atmosphere or individuals.
- Smith says "most social and economic activities area unit intermeshed to some expectation of the 'average' conditions. As long because the variation of the environmental component remains fairly on the point of this expected performance, insignificant harm happens and therefore the component are perceived as helpful.
- But once the variability exceeds some threshold on the far side the conventional band of tolerance, identical variable starts to impose a stress on society and become a hazard."therefore higher than average wind speeds leading to a tropical depression or cyclone consistent with intensity measures on the Saffir–Simpson scale can give associate extreme occurrence which can be thought-about a hazard.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Identification of hazards assumes that the potential targets are outlined, and is that the commencement in playacting a risk assessment.
1.2.3 Vulnerability:
- Vulnerability is that the inability to resist a hazard or to retort once a disaster has occurred. As an example, people that go on plains area unit a lot of liable to floods than people that live in a higher place.
- Vulnerability refers to the shortcoming (of a system or a unit) to resist the consequences of a hostile atmosphere. A window of vulnerability (WOV) could be a timeframe at intervals that defensive measures area unit diminished, compromised or lacking.
- The understanding of social and environmental vulnerability, as a method approach, involves the analysis of the risks and assets of underprivileged teams, like the senior. The approach of vulnerability in itself brings nice expectations of policy and medical specialty coming up with.
- In regard to hazards and disasters, vulnerability could be a thought that links the connection that folks have with their atmosphere to social forces and establishments and therefore the cultural values that sustain and contest them. “The thought of vulnerability expresses the multi-dimensionality of disasters by focusing attention on the totality of relationships in an exceedingly given social scenario that represent a condition that, together with environmental forces, produces a disaster”.
- It's conjointly the extent to that changes might hurt a system, or to that the community is plagued by the impact of a hazard or exposed to the likelihood of being attacked or injured, either physically or emotionally: "we were in an exceedingly vulnerable position".
- Within the body of literature associated with vulnerability, major analysis streams embody queries of methodology, such as: measurement and assessing vulnerability, together with finding acceptable indicators for numerous aspects of vulnerability, up- and down scaling strategies, and democratic strategies[clarification needed]
- Vulnerability analysis covers a fancy, multidisciplinary field together with development and financial condition studies, public health, climate studies, security studies, engineering, geography, political ecology, and disaster risk management.
- This analysis is of importance and interest for organizations making an attempt to cut back vulnerability– particularly as associated with financial condition and different Millennium Development Goals.
- Several establishments area unit conducting knowledge domain analysis on vulnerability. A forum that brings several of this researchers on vulnerability along is that the professional social unit (EWG). Researchers area unit presently operating to refine definitions of “vulnerability”, mensuration and assessment strategies, and effective communication of analysis to call manufacturers.
- In its sense, social vulnerability is one dimension of vulnerability to multiple stressors (agent chargeable for stress) and shocks, together with abuse, social exclusion and natural hazards. Social vulnerability refers to the shortcoming of individuals, organizations, and societies to resist adverse impacts from multiple stressors to that they're exposed.
- These impacts area unit due partially to characteristics inherent in social interactions, establishments, and systems of cultural values. During this respect, there's a desire to put associate accrued stress on assets and entitlements for understanding ‘catastrophe’ as critical only the strength or severity of shocks.
- A psychological feature vulnerability, in psychology, is associate misconception, psychological feature bias, or pattern of thought that's believed to incline the individual to psychological issues.
- It's in situ before the symptoms of psychological disorders begin to seem, like high disturbance, and once the individual encounters a nerve-racking expertise, the psychological feature vulnerability shapes a maladaptive response which will result in a folie.
- In psychopathology, psychological feature vulnerability is made from schema models, despair models, and attachment theory. Bias is one mechanism resulting in faulty psychological feature bias that results in cognitive vulnerability. Allocating a danger level to a threat depends on the urgency or intensity of the edge. Anxiety isn't related to selective orientation.
- The definition of vulnerability, by Brene Brown, is "uncertainty, risk, and emotional exposure". Brown goes on to recommend that vulnerability is our most correct live of courage: to be vulnerable, to permit ourselves to be seen. Vulnerability is usually thought of because the center of emotions such as: grief, shame, fear, disappointment; however it conjointly the middle and birthplace of affection, belonging, credibleness, creativity, courage, and answerability.
- In military language, vulnerability may be a set of survivability, the others being susceptibleness and recoverability. Vulnerability is outlined in numerous ways that reckoning on the state and repair arm involved, however generally it refers to the near-instantaneous effects of a weapon attack. In aviation it's outlined because the inability of associate degree craft to resist the harm caused by the unreal hostile atmosphere.
- In some definitions, recoverability (damage management, firefighting, restoration of capability) is enclosed in vulnerability. Some military services develop their own idea of vulnerability.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Vulnerability analysis covers a fancy, multidisciplinary field together with development and financial condition studies, public health, climate studies, security studies, engineering, geography, political ecology, and disaster risk management.
1.2.4 Risks-severity
- Severity describes the best level of injury potential once associate degree accident happens from a specific hazard. For instance: technology hazards could lead to Negligible, Moderate, or perhaps crucial levels of accidents, reckoning on tasks (e.g., typewriting or lifting serious materials).
- Severity on the danger matrix represents the severity of the foremost doubtless consequence of specific hazard prevalence. In different words, if a hazard happens and isn't lessened, what's the severity of the foremost doubtless downside that may occurs. As UN agency says of severity, “the severity of a hazard’s projected consequence.”
- For example, within the event of a hazard “Runway incursion,” the foremost doubtless downside that may occur is maybe either associate degree Accident or mishap. If you identify that Accident is that the possibly probable concern, the severity would be “Catastrophic”. If you identify that mishap is that the most likely concern, then “Serious” would doubtless be your severity.
- So, once you are process criteria for severity in your risk matrix, detain mind that you just are process criteria for many doubtless safety incident following a hazard prevalence.
- What Is chance on Risk Matrix
Likelihood on a risk matrix represents the chance of the foremost doubtless consequence occurring within the event of hazard prevalence to place it in our own way, if a hazard happens, what are the probabilities the foremost doubtless safety mishap can occur.
- To use the instance from earlier, within the event of a hazard “Runway incursion,” the foremost doubtless downside that may occur is maybe Accident. The chance of this prevalence would be fairly low, as there are several management measures mitigating this downside.
- So, once you are process chance in your risk matrix, you ought to produce criteria that outline chance of the danger prevalence (not the chance of hazard occurrence).
- Ways to outline Criteria for Severity on Risk Matrix
It’s very necessary that you just use multiple totally different criteria to outline severity on your matrix. These criteria can offer you multiple modes of justification for every risk assessment’s severity.
- Each level of severity ought to use identical criteria however have in increase in “damages” for every rising level of severity.
- As Risk is set by a mix of likelihood and Severity, the most space of the Matrix reveals the danger Levels. The amounts are Low, Medium, High, and very high. Notice that a Hazard with Negligible Accident Severity is sometimes Low risk, however it might become a Medium Risk if it happens oft.
- Statistically, the amount of draw back risk are often calculated because the product of the likelihood that hurt happens (e.g., that associate degree accident happens) increased by the severity of that hurt (i.e., the typical quantity of hurt or additional guardedly the most credible quantity of harm).
- A risk matrix may be a matrix that's used throughout risk assessment to outline the amount of risk by considering the class of likelihood or chance against the class of consequence severity. This is often a straightforward mechanism to extend visibility of risks and assist management deciding.
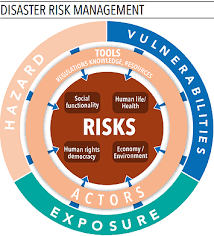
Fig. No. 3 Risks-severity
- Risk is that the lack of certainty regarding the result of creating a specific alternative. Statistically, the amount of draw back risk are often calculated because the product of the likelihood that hurt happens (e.g., that associate degree accident happens) increased by the severity of that hurt (i.e., the typical quantity of hurt or additional guardedly the most credible quantity of harm).
- In follow, the danger matrix may be a helpful approach wherever either the likelihood or the hurt severity can't be calculable with accuracy and exactitude.
- Although normal risk matrices exist in bound contexts (e.g. US DoD, NASA, ISO), individual comes associate degreed organizations may have to make their own or tailor an existing risk matrix. For example, the hurt severity are often classified as:
- Catastrophic – multiple deaths
- Critical – one death or multiple severe injuries
- Marginal – one severe injury or multiple minor injuries
- Negligible – one minor injury
- The likelihood of hurt occurring could be classified as 'certain', 'likely', 'possible', 'unlikely' and 'rare'. But it should be thought-about that terribly low possibilities might not be terribly reliable.
- The ensuing risk matrix might be:
- Negligible Marginal Critical Catastrophic
- Certain High High Extreme Extreme
- Likely Moderate High High Extreme
- Possible Low Moderate High Extreme
- Unlikely Low Low Moderate Extreme
- Rare Low Low Moderate High
- The company or organization then would calculate what levels of risk they will take with totally different events. This could be done by consideration the danger of an occasion occurring against the value to implement safety and therefore the profit gained from it.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Severity on the danger matrix represents the severity of the foremost doubtless consequence of specific hazard prevalence. In different words, if a hazard happens and isn't lessened, what's the severity of the foremost doubtless downside that may occurs. As UN agency says of severity, “the severity of a hazard’s projected consequence.”
1.2.5 Frequency and details:
- The frequency of a natural hazard event is that the variety of times it happens inside a such measure.
- The magnitude of a natural hazard event is expounded to the energy free by the event. It's distinguished from intensity that is expounded to the consequences at a particular location or space.
- The world is facing the impact of natural disasters on human lives and economy on a vast scale. In 2008, 321 disasters killed 235,816 people, affected 211 million others and value a complete of US$181 billion. Asia account for an oversized share of those figures. The foremost frequent disasters are floods and storms, accounting for seventieth of the natural disasters that occurred between 1950 and 2008.
- This chapter builds on the international Emergency Disasters information (EM-DAT) to supply an summary of each the prevalence and therefore the human and economic consequences of natural disasters across time and house.
- It additionally points out that statistics are essential for the understanding of risk profiles and severity of impact, and concerns additional standardized definitions and strategies. Above all, the economic damages of natural disasters are for the most part underreported.
- Natural disasters kill on the average sixty,000 individuals p.a., globally.
- Globally, disasters were liable for zero.1% of deaths over the past decade. This was extremely variable, starting from zero.01% to 0.4%.
- Deaths from natural disasters have seen an oversized decline over the past century – from, in some years, legion deaths p.a. To a median of sixty,000 over the past decade.
- Historically, droughts and floods were the foremost fatal disaster events. Deaths from these events ar currently terribly low – the foremost deadly events these days tend to be earthquakes.
- Disasters have an effect on those in financial condition most heavily: high death tolls tend to be targeted in low-to-middle financial gain countries while not the infrastructure to guard and reply to events.
- Natural disasters kill on the average sixty,000 individuals p.a. And are liable for zero.1% of world deaths
- The number of deaths from natural disasters may be extremely variable from year-to-year; some years pass with only a few deaths before an oversized disaster event claims several lives.
- If we glance at the typical over the past decade, around sixty, 000 individuals globally died from natural disasters every year. This represents zero.1% of world deaths.
- In the visualizations shown here we tend to see the annual variability within the variety and share of deaths from natural disasters in recent decades.
- What we tend to see is that in a few years, the quantity of deaths usually terribly low – often but ten,000, and accounting for as low as zero.01% of total deaths.
- However we tend to conjointly see the devastating impact of shock events: the 1983-85 famine and drought in Ethiopia; the 2004 ocean earthquake and tsunami; Cyclone Nargis that stricken Asian country in 2008; and therefore the 2010 Port-au-Prince earthquake in Haiti. All of those events pushed international disasters deaths over two hundred,000 – over zero.4% of deaths in these years.
- Low-frequency, high-impact events like earthquakes and tsunamis aren't preventable, however such high losses of human life ar. We all know from historical information that the globe has seen a big reduction in disaster deaths through earlier prediction, a lot of resilient infrastructure, emergency preparation, and response systems.
- Those at low incomes are typically the foremost susceptible to disaster events: up living standards, infrastructure and response systems within these regions are going to be key to preventing deaths from natural disasters in the returning decades.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- It additionally points out that statistics are essential for the understanding of risk profiles and severity of impact, and concerns additional standardized definitions and strategies. Above all, the economic damages of natural disasters are for the most part underreported.
1.2.6 Capacity:
- Capacity refers to all or any the strengths, attributes and resources obtainable inside a community, organization or society to manage and cut back disaster risks and strengthen resilience.
- It is vital to emphasize people's capability to anticipate, cope with, resist and live through disasters, instead of merely specializing in the vulnerability that limits them. Like vulnerability, capability depends on social, economic, political, psychological, environmental and physical assets and therefore the wider governance regimes (DFID, 2004) - and like vulnerability it may be delineated victimization completely different terms.
- For instance, capability is typically delineated because the opposite of vulnerability, however this overlooks the very fact that even poor and vulnerable individuals have capacities (Wisner et al., 2012; Shepard et al., 2013).
- Indeed, the start line for capability development is that the existing data, strengths, attributes and resources people, organizations or society has. Capability could embody infrastructure, establishments, human data and skills, and collective attributes like social relationships, leadership and management (UNISDR, 2017).
- A connected idea is ‘coping capacity’, that is that the ability of individuals, organizations and systems, to use obtainable skills and resources, to manage adverse conditions, risk or disasters.
- The capability to cope needs continued awareness, resources and sensible management, each in traditional times likewise as throughout crises or adverse conditions (UNISDR, 2017). Cope capability conjointly depends on adequate unit assets and supportive social and governance relations (DFID, 2004) and might be thought of as a part of wider capability development for disaster risk reduction.
- Capacity development is that the method by which individuals, organizations and society consistently stimulate and develop their capacities over time to attain social and economic goals.
- Iit's an inspiration that extends the term of capability -building to comprehend all aspects of making and sustaining capability growth over time. It involves learning and numerous varieties of coaching, however conjointly continuous efforts to develop establishments, political awareness, monetary resources, technology systems and therefore the wider sanctioning atmosphere (UNISDR, 2017).
- It is vital to emphasise people's capability to anticipate, cope with, resist and live through disasters, instead of merely specializing in the vulnerability that limits them. Like vulnerability, capability depends on social, economic, political, psychological, environmental and physical assets and therefore the wider governance regimes (DFID, 2004) - and like vulnerability it may be delineated victimisation completely different terms.
- A connected idea is ‘coping capacity’, that is that the ability of individuals, organizations and systems, to use obtainable skills and resources, to manage adverse conditions, risk or disasters.
- Capacity development is that the method by which individuals, organizations and society consistently stimulate and develop their capacities over time to attain social and economic goals. It's an inspiration that extends the term of capability -building to comprehend all aspects of making and sustaining capability growth over time.
- It involves learning and numerous varieties of coaching, however conjointly continuous efforts to develop establishments, political awareness, monetary resources, technology systems and therefore the wider sanctioning atmosphere (UNISDR, 2017).
- How can we live capacity?
Capacity assessment is that the method by that the capability of a bunch is reviewed against desired goals, wherever existing capacities ar known for maintenance or strengthening and capability gaps ar known for more action. (UNISDR, 2017).
- Capability resides at 3 connected levels: in people, in organizations and within the overall operating atmosphere inside that people and organizations operate - ‘the sanctioning environment’ (UNDP, 2010), that powerfully relates to the idea of resilience. Every of those may be associate degree entry purpose for capability assessment:
Enabling atmosphere
- Sometimes mentioned because the ‘societal’ or ‘institutional’ level, capacities at the extent of the sanctionative atmosphere relate to the broader system among that people and organizations perform (UNDP, 2009). Understanding the sanctionative atmosphere will be obtained from the ‘institutional analysis’, ‘power analysis’ or ‘drivers of modification analysis’ more and more being undertaken by donor organizations because the basis for country help plans (OECD DAC, 2006).
- Capacities at the extent of the sanctionative atmosphere relate to any or all the principles, laws and legislation, policies, power relations and social norms (UNDP, 2009). Governments, civil society thus the non-public sector therefore have a chance and obligation to figure along to attempt to a safer future (UNISDR, 2015a), and so their capability for engagement will be assessed across all sectors (e.g. Global climate change, finance, planning) and levels (e.g. Little and medium enterprise, farmers, insurers).
- This level could be a common entry purpose for capability assessment (UNDP, 2008). This level relates to the interior structure, policies, systems ndd procedures that verify an organization's effectiveness and skill to deliver on its mandate and permit people to figure along (UNDP, 2009).
- Structure level capacities facilitate develop and apply internal policies, arrangements, procedures and frameworks, that is critical to deliver the organization's mandate (UNDP, 2010).
- Organizational level capacities facilitate develop and apply internal policies, arrangements, procedures and frameworks, that area unit necessary to deliver the organization's mandate (UNDP, 2010).
- It's not solely regarding skills, however conjointly incentives and governance. Folks and organizations will have sturdy or weak incentives to vary, develop and learn, as a results of their atmosphere or internal factors (Datta et al., 2012).
- The Individual Level
This level relates to the talents, expertise and information of individuals that enable them to perform. Capability assessment at this level is often enforced by researchers and non-governmental organizations functioning at the native level, furthermore as by some native level governments. However, individual capability has got to be understood among the context of each the structure level and sanctionative atmosphere.
Four key problems common to most capability assessments area unit institutional arrangements, leadership, information and responsibleness. Not each assessment must cowl all four of those problems, however they ought to be a minimum of thought of once shaping the scope of AN assessment.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Capacity refers to all or any the strengths, attributes and resources obtainable inside a community, organization or society to manage and cut back disaster risks and strengthen resilience.
1.2.7 Impact:
- Natural disasters cause destruction of property, loss of economic resources, and private injury or unwellness. The loss of resources, security and access to shelter will cause huge population migrations in lesser-developed countries.
- Natural disasters will have a life-altering impact on the people and families lucky enough to survive them. However the impact of natural disasters will be felt at the community, town and state level, or persistently will impact a whole country.
- Natural disasters will have immense environmental impacts furthermore, even once human communities area unit comparatively unaffected. However well the impact of a disaster event is absorbed has a lot of to try and do with the intensity of the impact and therefore the level of readiness and resilience of the topic wedged.
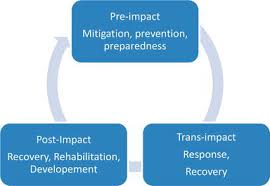
Fig no 4 Impact
Significance:
- Even before the industrial enterprise of the fashionable world, natural disasters are a truth of life. There area unit records of the migratory travels of Native Americans off from coastal Sunshine State specifically to avoid seasonal hurricanes.
- However, with the modernization of the many societies worldwide and therefore the changes our industrial activities have delivered to the atmosphere, several weather connected natural disasters have gained in each frequency and intensity. This interprets to in multiplied international impact of natural disasters in the slightest degree levels.
Individual Impact:
- At the individual level, the impact will typically be felt physically, mentally and showing emotion. Natural disasters cause destruction of property, loss of economic resources, and private injury or unwellness. The loss of resources, security and access to shelter will cause huge population migrations in lesser-developed countries.
- After experiencing a natural disaster, several people develop severe post-traumatic stress disorders or withdraw into states of depression. Others develop negative associations with the atmosphere, in additional developed nations; this will conjointly cause vital population migrations.
Community Impact:
SCIENCE
Biology
Cells
Molecular
Microorganisms
Genetics
Human Body
Ecology
Chemistry
Atomic & Molecular Structure
Bonds
Reactions
Stoichiometry
Solutions
Acids & Bases
Thermodynamics
Organic Chemistry
Physics
Fundamentals
Mechanics
Electronics
Waves
Energy
Fluid
Astronomy
Geology
Fundamentals
Minerals & Rocks
Earth Structure
Fossils
Natural Disasters
Nature
Ecosystems
Environment
Insects
Plants & Mushrooms
Animals
MATH
Arithmetic
Addition & Subtraction
Multiplication & Division
Decimals
Fractions
Conversions
The Impact of Natural Disasters
- Updated April nineteen, 2018
By leader Sharrieff
Natural disasters will have a life-altering impact on the people and families lucky enough to survive them. However the result of natural disasters are often felt at the community, town and state level, or persistently will impact a complete country.
Natural disasters will have immense environmental impacts moreover, even once human communities area unit comparatively unaffected. However well the impact of a disaster event is absorbed has abundant to try and do with the intensity of the impact and also the level of state and resilience of the topic wedged.
Significance
- Wind from cyclone Chief Executive whips past palm trees September twelve, 2008 in Galveston, Texas.
- Even before the manufacture of the fashionable world, natural disasters are a truth of life. There area unit records of the migratory travels of Native Americans aloof from coastal American state specifically to avoid seasonal hurricanes.
- However, with the modernization of the many societies worldwide and also the changes our industrial activities have dropped at the surroundings, several weather connected natural disasters have gained in each frequency and intensity. This interprets to in increased world impact of natural disasters in any respect levels.
Individual Impact
- People rest and charge devices at a shelter for those plagued by Superstorm Sandy at Saints Peter and Paul Church on All Saints' Day, 2012 in Hoboken, New Jersey.
- At the individual level, the impact will typically be felt physically, mentally and showing emotion. Natural disasters cause destruction of property, loss of monetary resources, and private injury or health problem. The loss of resources, security and access to shelter will result in large population migrations in lesser-developed countries.
- After experiencing a natural disaster, several people develop severe post-traumatic stress disorders or withdraw into states of depression. Others develop negative associations with the surroundings, in additional developed nations; this will conjointly result in important population migrations.
Community Impact
- Homes destroyed by the Waldo ravine hearth area unit seen from the air during a neighborhood on June thirty, 2012 in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
- Communities that have a natural disaster should conjointly absorb the impacts of those damaging events. Several native communities lose such a lot in economic resources that recovery becomes tough, if not virtually not possible.
- Some communities notice chance within the aftermath of a disaster to reconstruct higher and stronger communities than before. Communities should typically acknowledge population, demographic, and cultural shifts as a results of the impact of the natural disaster on their individual voters.
Economic Impact:
- In 2005, cyclone Katrina desolated city and also the Mississippi Gulf Coast. In city alone, quite two hundred,000 homes were destroyed; over seventy p.c of the resident population had to be a minimum of briefly settled outside of the bigger city space.
- Additionally, immense sums of federal help were necessary to assist jump begin recovery efforts within the town and close region. Estimates of over $105 to $150 billion in reduced tax income, loss of infrastructure, expense of reclamation efforts, and loss of traditional revenue were lost to the town.
- On the far side the economic losses to city, it's calculable that the u. s. Economy suffered a two p.c loss of overall gross domestic product at intervals one year of the disaster as a right away results of the cyclone and its impact on this vital international port town.
Environment
- Just as a natural will modification the landscape of our personal lives moreover as aspects of our community, thus can also differing kinds of disasters drastically alter the natural surroundings.
- The cyclones that occurred in Union of Burma in 2008, or the wildfires that unfold throughout California in 2009 area unit samples of however areas of land that detail whole ecosystems are often dramatically broken or reworked from one disaster event.
- On a bigger scale, the controversy concerning the way to address world temperature change and also the ensuing natural impacts is any punctuated by estimates of water level will increase which will fully swamp some island nations. What is more, the speedy chemical change of salt water oceans caused by melting glaciers might deprive the globe of thirty p.c or additional of its edible fish provide, and also the loss of coral reefs from an equivalent cause would place various coastal regions in risk of recurrent event waves and surges.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Natural disasters will have a life-altering impact on the people and families lucky enough to survive them. However the impact of natural disasters will be felt at the community, town and state level, or persistently will impact a whole country.
1.2.8 Prevention:
- Prevention is to make sure that human activity or natural phenomena don't end in disaster or emergency. Primary interference is to scale back -avert- avoid the danger of the event occurring, by obtaining obviate the hazard or vulnerability, e.g. To avoid overcrowding, deforestation and to produce services.
- Disaster interference is that the outright dodging of adverse impacts of hazards and connected disasters interference (i.e. disaster prevention) expresses the construct and intention to fully avoid potential adverse impacts through action taken ahead.
- Examples embody dams or embankments that eliminate flood risks, land-use rules that don't allow any settlement in high risk zones, and seismal engineering styles that make sure the survival and performance of a crucial building in any doubtless earthquake. Fairly often the whole dodging of losses isn't possible and also the task transforms to it of mitigation. Partially for this reason, the terms interference and mitigation area unit generally used interchangeably in casual use.
- In jurisprudence, the interference of Disasters Principle, as 1st elaborate within the Agenda arising from the UN surround II conference, permits states to require pre-emptive or restraining actions once a accord of scientific opinion is that failing to try and do thus can cause some disaster to occur. See the preventative Principle.
- Investment in disaster risk interference and reduction enhances the economic, social, health and cultural resilience of individuals, communities, countries and their assets, moreover because the surroundings. ... All mitigation measures area unit vital as they save lives and cut back the price of response to and recovery of the community.
- Prevention and mitigation ways ought to work towards reducing the money and social prices to communities over time, up the engineered surroundings, and reducing the impact on, and injury to, the surroundings.
- Investment in disaster risk interference and reduction enhances the economic, social, health and cultural resilience of individuals, communities, countries and their assets, moreover because the surroundings.
- The effective interference of disaster events includes multiple ways to scale back or take away the impact of hazards and increase the resilience of the community. Disaster managers in any respect levels of Queensland's disaster management arrangements area unit accountable for employing a tested risk management method to spot interference and mitigation choices.
- All mitigation measures area unit vital as they save lives and cut back the price of response to and recovery of the community.
- In Queensland, multiple publications ready by regime agencies for native governments, businesses and people assist and enhance coming up with and also the development of interference and mitigation ways to scale back disaster risk.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Prevention is to make sure that human activity or natural phenomena don't end in disaster or emergency. Primary interference is to scale back -avert- avoid the danger of the event occurring, by obtaining obviate the hazard or vulnerability, e.g. To avoid overcrowding, deforestation and to produce services.
1.2.9 Mitigation:
- Disaster mitigation measures area unit people who eliminate or cut back the impacts and risks of hazards through proactive measures taken before associate emergency or disaster happens. One in every of the simplest known samples of investment in disaster mitigation is that the Red River Floodway.
- One of the simplest known samples of investment in disaster mitigation is that the Red River Floodway. The building of the Floodway was a joint provincial/federal enterprise to safeguard the town of Winnipeg and scale back the impact of flooding within the Red River Basin. It value $60 million to make within the Nineteen Sixties.
- Since then, the floodway has been used over twenty times. Its use throughout the 1997 Red River Flood alone saved associate calculable $6 billion. The Floodway was swollen in 2006 as a joint provincial/federal initiative.
Types of disaster mitigation
- Disaster mitigation measures could also be structural (e.g. Flood dikes) or non-structural (e.g. Land use zoning). Mitigation activities ought to incorporate the activity and assessment of the evolving risk setting. Activities might embody the creation of comprehensive, pro-active tools that facilitate decide wherever to focus funding and efforts in risk reduction.
- Other samples of mitigation measures include:
- Hazard mapping
- Adoption and social control of land use and sectionalisation practices
- Implementing and implementing building codes
- Flood plain mapping
- Reinforced tornado safe rooms
- Burying of electrical cables to stop ice build-up
- Raising of homes in flood-prone areas
- Disaster mitigation public awareness programs
- Insurance programs
- An all-hazards approach to disaster management considers all known hazards and their natural and phylogenesis potential risks and impacts, with the intention of guaranteeing that measures taken to mitigate against one sort of risk don't increase vulnerability to alternative sorts of risks.
- Proactive disaster mitigation measures area unit usually simpler than reactive measures in eliminating or reducing the impacts, however not all disasters area unit fairly predictable, associated once an unforeseen disaster happens, mitigation is essentially when the actual fact.
- Proactive disaster mitigation measures could also be structural or non-structural, and can usually be supported activity and assessment of the danger and also the value of putting in the measures, and probably the price of maintenance.
- Mitigation designing identifies policies and actions that may be confiscated the long run to scale back risk, and within the event of a disaster occurring, minimise loss. Such policies and actions area unit supported a risk assessment, exploitation the known hazards, vulnerabilities and chances of incidence and estimates of impact to calculate risks, and area unit usually planned in cooperation with the neutral teams.
- The principles area unit applicable to mitigation of risk generally.
- Planning processes might include:
- Stakeholder agreement on actions for risk reduction
- Assessment of relative risk and vulnerability
- Building partnerships among stakeholders
- Increasing awareness of hazards, vulnerabilities and risk
- Establishing priorities
- Aligning risk reduction and mitigation methods with alternative objectives
- Risk assessment and mitigation measures might include:
- Hazard mapping
- Flood plain mapping
- Land use and sectionalisation practices
- Implementing and implementing applicable building codes
- Reinforced tornado safe rooms
- Burying of electrical cables to stop ice build-up
- Raising of buildings in flood-prone areas
- Public awareness programs
- Insurance programs
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Disaster mitigation measures area unit people who eliminate or cut back the impacts and risks of hazards through proactive measures taken before associate emergency or disaster happens. One in every of the simplest known samples of investment in disaster mitigation is that the Red River Floodway.
References:
- Tech-max.
- Ghosh G. K.
- Pradeep Sahni.