UNIT- 2
THE INDIVIDUAL
No organization can exist without individuals. Organization behavior includes the study of individual performance as well as group performance in an enterprise. Individual behavior means how an employee or individual behaves, reacts or responds in a given environment. It the way in which a person reacts in different situations and the way an individual expresses different emotions like anger, happiness, love etc. The study of OB relates to the expected behavior of an individual in the organization. No two individuals behave in the same manner in a particular work situation. The value system, emotional intelligence, organizational culture, job design and the work environment are important casual agents in determining human behavior.
Kurt Lewis, a popular psychologist, stated the Field theory and outlined the behavior framework. This theory studies the patterns of interaction between an individual and the environment. Individual behavior can be understood the help of the following formula:
B = ƒ (P, E, O)
Where, B = Individual Behavior
P = Person
E = Environment
O = Organization
Thus, it can be said that individual behavior is a function of person, environment and the organization.
Individual differences are the traits and facts about an individual that differentiate him/her from others. Individuals differ from each other owing to their varying characteristics that form an individual’s individuality. Each individual can be considered as an island. We all are different from one another in some way or the other. There are many factors which are unique to each individual in this world. From organization point of view we can say that every individual in an organization is different from one another and should be handled differently for the smooth functioning of the organization. The manager must know the different traits of different employee and find ways to tackle each of them. If there would not be any individual difference, there would be no question of quarrels or dispute.
Individuals may differ in likes, dislikes, interests, values, attitude, psychological set-up etc. i.e., the whole personality.
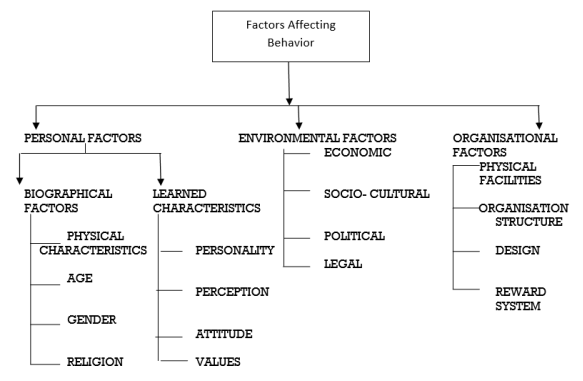
The following factors affect the individual behavior. These help in identifying individual differences.
|
The personal factors which influence the individual behavior can be biographic characteristics and learned characteristics. Biographical characteristics are genetic in nature and are inherited, that is why these are difficult to change or modify. Learning is a relatively permanent change in an individual’s behavior which results from interactions with the environment. Learned characteristics are acquired from the environment the individual is in. Such characteristics are personality, perception, attitude and values. The manager must emphasize on studying, learning and predicting the learned characteristics.
The external environment also influences an individual’s behavior. It includes economic factors like employment level/opportunities, wage rates, general economic environment of the nation, technological developments etc.; socio-cultural factors, political factors and the legal environment.
Individual behavior is influenced by a wide variety of organizational systems and resources. These organizational factors are physical facilities at the work place, organization structure and design, leadership skills of superiors and the reward system of the organization.
Abilities are the traits a person learns from the environment around himself, and also from the traits he is gifted with by birth. These traits may be broadly classified as:
a) Intellectual Abilities: It implies a person’s intelligence, reasoning abilities, memory power and verbal comprehension.
b) Physical Abilities: It implies a person’s physical strength, stamina, co-ordination, motor skills etc.
c) Self-awareness Abilities: It symbolizes how a person feels about the task allotted to him, based on the manager’s perception of his ability.
Thus, the psychological or intellectual, physical and self-awareness ability of a person defines his/her behavior in personal as well as social life.
Attitude is a functional state of readiness which determines the organism to react in a particular way to certain stimuli or stimulus situations.
According to Murphy and Murphy, attitude is primarily a way of being set towards or against certain things.
Baldwin views that attitude is a readiness for attention or action of a definite pattern.
“The concept of attitude is probably the most distinctive and indispensable concept in contemporary social psychology.”
The factors which lead to development of attitudes are:
a. Family
b. Peers
c. Conditioning
d. Social adjustment functions
e. Direct instruction
f. Modeling
g. Satisfaction of wants
h. Prejudices
Method of finding Employee’s attitude
It is a purposeful conversation in which the interviewer tries to obtain honest and complete answers to a specific number of questions. It has the advantage of face-to-face contact. This type of interview is used most frequently in industry when considering an applicant for a job. It can be used in handling group complaints of workers. However, it has not been used very often in determining employee attitudes.
3. Unguided Interview (Non-directive):
It is characterized by the free nature of the discussion and by the fact that it is the person interviewed who really defines its limits. There are no specific questions that the interviewer asks and his main concern is to probe and establish the emotional content of the interview.
It lends to the mass-production techniques of determining employee attitudes. It is similar to guided interview. The fact that eight minutes are reported as the length of the interview means that they went at a very rapid pace.
It is intended to provide a more free rein of expression. The objective is to explore the “deeper levels rather than to deal only with the manifest verbal content.” This method deliberately attempts to conceal the intent of the measurement and allows the experimenter to observe and measure without producing an effect on the attitude itself. Varieties of techniques have been included within this category: word associations, sentence completions, or picture and story theme completion.
Aptitude is an innate, learned or acquired ability. It is one’s ability to learn or excel in a certain area. Bingham refers aptitude to those qualities characterizing a person’s way of behavior which serve to indicate how well he can learn to meet and solve certain specified kinds of problems. Specific aptitude is potential in a particular area while general aptitude is potential in several fields. Aptitude is different from ability as ability is an existing competence and aptitude is acquired.
Value is defined as the collective conceptions of what is considered good, desirable, and proper or bad, undesirable, and improper in a culture. A value is a shared idea about how something is ranked in terms of desirability, worth or goodness.
There are two types of values:
It deals with views on acceptable modes of conductor means of achieving the terminal values. These include being honest, sincere, ethical, and being ambitious. These values are more focused on personality traits and character.
Differences between Values and Attitudes
Values | Attitude |
Values are built upon one’s moral attributes. | Attitudes are the standpoints one has regarding various issues. |
Values guide our behavior. | Attitudes are the response that is a result of our values. |
Values decide what we think as for right, wrong, good or unjust. | Attitudes are our likes and dislikes of things, people and objects. |
Values are more or less permanent in nature. | Attitudes are changeable with favorable experiences. |
They represent a single belief that guides actions and judgement across objects and situations. | They represent several beliefs focused on a specific object or situation. |
Key Takeaways
- Organizations are made by individuals. The need for understanding individual behavior and their differences is essential for smooth functioning of the enterprise.
- Individuals differ in various aspects such as perception, personality, likes, dislikes, attitude, ability, values, emotions etc.
- Abilities are the traits a person learns from the environment around himself, and also from the traits he is gifted with by birth.
- Attitude is a functional state of readiness which determines the organism to react in a particular way to certain stimuli or stimulus situations.
- Aptitude is an innate, learned or acquired ability. It is one’s ability to learn or excel in a certain area.
- A value is a shared idea about how something is ranked in terms of desirability, worth or goodness.
References
- Gupta, S.K. & Joshi, R. Human Resource Management. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi (2002).
- Khanka, S.S. Organizational Behavior. S. Chand & Company Pvt. New Delhi (2000), pp. 560.
- www.theintactone.com
- www.iedunote.com