MODULE – 1
Concept of Energy principles
Energy principles in structural mechanics express the relationships between stresses, strains or deformations, displacements, material properties, and external effects in the form of energy or work done by internal and external forces. Since energy is a scalar quantity, these relationships provide convenient and alternative means for formulating the governing equations of deformable bodies in solid mechanics. They can also be used for obtaining approximate solutions of fairly complex systems, bypassing the difficult task of solving the set of governing partial differential equations.
- Virtual work principle
- Principle of virtual displacements
- Principle of virtual forces
- Unit dummy force method
Castigliano’s Theorem:. The Theorem allows for the determining of deflections for objects with changing cross sectional areas. Determining the deflection of beams typically requires repeated integration of singularity functions. Lets us use strain energies at the locations of forces to determine the deflections
For any kind of engineering design to take place the most important aspect that must be taken care of is the safety of the the whole design. Engineering design safety is the discipline that gives complete assurance of the safety of the engineered system. Safety engineers have to analyze what faults can occur in the system and then propose safety requirements in design to make the system safer. Faults should be detected in the early design process as correcting the safety faults later in the design process can turn out to be very expensive and time consuming.
The field of sustainability measurement and reporting has matured as a result of adaptations and innovations that have sought to clarify principles; enhance data reliability, comparability and relevance; and fill gaps related to particular issue areas such as human rights, women’s economic empowerment, climate change and responsible finance and investment. The research aims to assess the extent to which such developments have addressed concerns related to the complexity and cost of measurement and reporting, not least for smaller enterprises; as well as the materiality or usefulness of data and indicators for decision-making by different stakeholders.
A structure is defined as a system of interconnected members assembled in a stable configuration and used to support a load or combination of loads under the equilibrium of various external forces and internal reactions. The load can have vertical or lateral effects on the structural components.
The structural members are connected together by providing different types of joints or supports. Most common types of supports are pin-jointed or hinged, roller support and fixed support.
A structure is in equilibrium when all forces or moments acting upon it are balanced. This means that each and every force acting upon a body, or part of the body, is resisted by either another equal and opposite force or set of forces whose net result is zero. Sir Issac Newton addressed this issue when he noted that a body at rest will remain at rest until acted upon by an external force. Every structure that can be seen to remain standing on a daily basis is in equilibrium; it is at rest and each of its members, combination of its members or any part of a member that is supporting a load, are also at rest. There is a net result of zero in all directions for all of the applied loads and reactions.
The split bamboo beam remains in a state of equilibrium. The scissors rests at a great distance from the fulcrum in order to balance the heavier weight of the thermos on the opposite side. All of the forces and moments must be balanced so that the system is in a stable equilibrium.
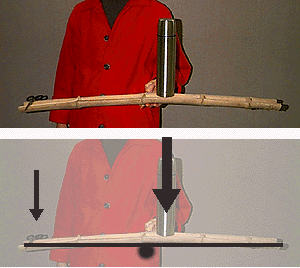
There are two types of equilibrium; External and Internal. External equilibrium encompasses the loads upon, and reactions of, a structural system as a whole. Internal equilibrium describes the various forces are acting within every member of the system. There are conditions of equilibrium that must be satisfied for both types. These are:
Sum of All Vertical Forces (Fy) = 0
Sum of All Horizontal Forces (Fx) = 0
Sum of All Moments (Mz) = 0
(Sum of All Forces (Fz) = 0)
(Sum of All Moments (My) = 0)
(Sum of All Moments (Mx) = 0)
These six equations are all that can be used to determine every one of the forces that are acting with a structure. They are few, but very powerful. The first three are the most common equations and will be utilized in all of the problems associated with this course. The other three are only necessary when considering three-dimensional force systems.
Structural engineers are highly skilled, creative professionals who design the strength and stability of our buildings and bridges.
Structural engineers help create record-breaking structures, beautiful structures, useful structures and sometimes just cool structures - anything from bridges, rollercoasters and skyscrapers to hospitals, homes and public artworks.
They work as part of a team alongside architects, builders and other engineers.
They make sure the building works well in practice, depending on what it is used for: for example, a dance floor shouldn’t vibrate too much when people jump up and down on it.
- To carry out design of structures as per the principles of structural analysis and design. He should also ensure that the design is safe, durable, and economical.
- To prepare the estimates to know the probable cost of completion of work. • To invite tenders & to select contractors for the works.
- To carry out valuation of land or building for the purpose of finding its sale or purchase price or taxation.
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyse, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfil functional objectives and requirements while considering the limitations imposed by practicality, regulation, safety and cost.
Architect:
The term 'architect' has been in existence for many centuries, however, the architect as its own recognised profession is a relatively modern concept dating back only to the mid-16th century. The term and what it represents has evolved through history to its current form in which architects are seen as highly-qualified and educated professionals. See The History of the architect as a profession for more information.
User:
- Providing financing for the project.
- Providing site surveys.
- Securing and paying for easements.
- Warranting the plans and specifications.
- Warranting owner furnished materials.
Builder:
Builders build homes, as well as commercial and industrial buildings. They also do renovations, excavations and demolitions. More specifically, builders do particular tasks in construction, including manual labour and operating machinery. A builder’s job varies from month to month. You could be working on a small residential unit one day and a multi-level office building the next.
Many builders are self-employed. Instead of receiving a wage for their labour, they invoice for their work and operate under an ABN. Being self-employed means that builders must source their own materials. They are also responsible for clean-up onsite and for the safety of their team.
A designer
Structural engineers design buildings so they’re strong enough to support the loads on them (like people and equipment) and stable against elements like wind.
They usually design buildings to last for fifty years, and bridges for over a century, so their structures are used and enjoyed by thousands, or even millions of people.
A safety expert
Structural engineers make sure all our buildings and infrastructure are safe to use. For instance, they study how to stop buildings from falling down during earthquakes, hurricanes, and other natural disasters.
A problem solver
Structural engineers use many skills to solve problems – from basic maths to cutting-edge technology.
Engineers design, build, and maintain various complex systems and structures, from buildings to software. While there are many engineering professions, there is one consistent engineering mind-set: to innovate. To do so, they must think in increasingly cross-disciplinary ways, finding combinations, patterns, and intersections between previously disparate conceptual realms.
Engineers are the architects of the world. While stereotypes paint a picture of engineering as an anti-social hard science that’s primarily conducted behind a computer, engineers are in fact the scientists and artists who created the Palm Islands in Dubai and the Millau Viaduct in France. An engineer’s creativity does not always need to be so grandiose—Nano-engineers work down to a billionth of a meter in scale
The aim of design is the achievement of an acceptable probability that structures being designed will perform satisfactorily during their intended life. With an appropriate degree of safety, they should sustain all the loads and deformations of normal construction and use and have adequate durability and adequate resistance to the effects of misuse and fire. Design, including design for durability, construction and use in service should be considered as a whole. The realization of design objectives requires compliance with clearly defined standards for materials, production, workmanship and also maintenance and use of structure in service.
Reference Books:
- RCC Design and drawing By Neelam Sharma
- Limit state design of reinforced concrete by P.C. Verghese, PHI
- Reinforced concrete: Limit state by A.K. Jain
- Reinforced concrete by B.C. Punamia, A.K. Jain and A.K. Jain