MODULE 6
WATER WITHDRAWLS AND USES
- Hydroelectric electricity generates regarding 10% of the countries energy. Credit: USA Corps of Engineers
- Flowing water creates power that may be captured and have become into electricity. This is often mentioned as electricity power or hydropower.
- The most frequent reasonably hydroelectric power station makes use of a dam on a stream to avoid wasting water in an exceedingly reservoir. Water launched from the reservoir flows via a turbine, spinning it, that successively activates a generator to supply electricity. However hydroelectric energy does not essentially need an enormous dam. Some hydroelectric power plants merely use a tiny low canal to channel the river water through a turbine.
- Another reasonably electricity power station called a tense storage plant will even store power. The facility is distributed from a electricity grid into the electrical high-powered generators. The mills then spin the turbines backward, that motives the generators to pump water from a stream or decrease reservoir to an higher reservoir, wherever the electricity is stored. To use the power, the water is free from the upper reservoir backpedal into the river or decrease reservoir. This spins the mills forward, activating the turbines to supply electricity.
- A tiny or micro-hydroelectric energy gizmo can produce sufficient current for a home, farm, or ranch.
- Agricultural water is water that's accustomed develop sparkling manufacture and maintain livestock.
- The use of agricultural water makes it possible to grow fruits and greens and elevate livestock, that may be a vital part of our diet.
- Agricultural water is employed for irrigation, chemical External and chemical functions External, crop cooling (for example, gentle irrigation), and frost control.
- According to the us geologic Survey (USGS), water used for irrigation cash owed for nearly sixty 5 proportion of the worlds fresh withdrawals excluding thermoelectrical power.
- There are 330 million acres of land used for agricultural functions within the us that manufacture associate degree abundance of food and different products.
- Population and irrigation rose at identical time as till irrigation amounts reached a peak in 1980, when that population keep rising but irrigation born and command steady around a hundred and forty million gallons from 1985 to 2000.
- When agricultural water is employed effectively and safely, producing and crop yield are absolutely affected.
- A cut back in utilised water will cause manufacturing and yield to decrease. Management techniques are the foremost very important thanks to improve agricultural water use and keep gold commonplace production and yield.
- The key's to place into effect administration ways that enhance water use impactivity except lowering yield.
- Some examples include extended irrigation planning and crop specific irrigation management. These techniques alter for the conservation of water and energy, and minimize growers cost. Agricultural water comes from a spread of sources. Typical sources of agricultural water include:
- Surface water
- Rivers, streams, and irrigation ditches
- Open canals
- Impounded water adore ponds, reservoirs, and lakes
- Groundwater from wells
- Rainwater
- Locally accumulated water such as cisterns and rain barrels
- Municipal water structures such as city and rural water may also be used for agricultural purposes.
- The purpose of Hydro-Electric Plant is to harness power from water following under pressure. Water following beneath strain has two varieties of power - Kinetic and Potential. This kinetic and viable electricity possessed by using water is transformed into mechanical electricity through Hydraulic Turbine.
- The hydraulic turbine is, thus, a high mover which when coupled to a generator produces electric power. Hydro-Electric Projects may additionally no longer be used exclusively for energy generation. Sometimes, they are of the shoot of flood manipulate and irrigation initiatives and are regarded as "Multipurpose Projects.
HEAD
- Head is the difference in elevation between two ranges of water. It can be characterized as –
- Gross Head and
- Net or Effective head.
Gross Head : is outlined because the distinction in elevation between the top race level at the intake and therefore the tail race stage at the discharge side, naturally, every the elevations ought to be measured simultaneously. The gross head may additionally fluctuate as each the elevation of water will now not keep the same.
Net or Effective Head: is that the head noninheritable by victimisation subtracting all the losses from gross head in carrying water from the head race to the doorway of the turbine. These losses are because of friction occurring in tunnels, canals and penstocks that lead the water into the turbine.
ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF HYDRO POWER PLANT:
- The variety of components encountered within the course of the ability production the employment of storage reservoir are as proved at a lower place in sequence.
Reservoir. -----> Gated gap like sluice gate.-------> Canal (or tunnel)----|
Power house<----penstock <------ Intake structure <------ surge tank <------|
|-----------> tail race ----------> River.
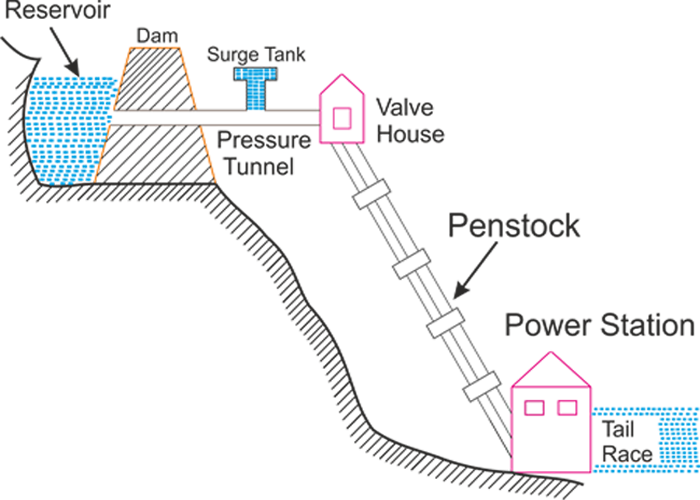
(1)Storage Reservoir : The storage reservoir may be flavouring or artifical.
Natural-Lakes, Mountains.
Artificial- Dam engineered across stream valley.
(2) Waterways and their manage works: Waterway may be a passage through that water is carried from storage reservoir to the energy house. It consists of tunnel, canal, fumes, fore bays, penstocks etc.
(A) Forebays-
- It may be an enlarged section of a canal detached to accommodate the specified dimension of intake.
- It is furnished intake structure, to direct water into the penstock
- Intake got to be furnished with trash racks thus on stop the entry of dust into the penstock and consequently avoid the viable injury to rotary engine runes
- Its perform is save briefly the water rejected by method of the plant once tube electrical load is reduced and additionally to fulfill the instantly increased demand of water because of shocking expand in load.
B) Surge Tank -
- It is a reservoir outfitted at some gap created on aboard pipe line to receive the rejected go together with the flow once the pipeline is fastly closed
- It in addition helps in fascinating the sudden strain zees because of closing of valve when load on rotary engine is reduced as a consequence eliminating blast effect.
- When it's impractical to grant forebay we tend to furnish surge tank to absorb pressure fluctuation.
- It reduces the gap between the turbine and free surface.
(C) Penstock:
- It is pressure pipe carrying water from the storage neighbourhood to the turbine.
- Long penstock got to be equipped surge tank so water hammer pressure may be dissipated.
(3) Hydraulic Turbines: Turbines are machines that convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy.
(4) the ability House: A energy residence may be a building consisting of a sub form to assist the hydraulic and electrical instrumentality and a high-quality shape to accommodate and protect this equipment.
(5)The Draft Tube: it's a passage which connects the outlet of a turbine runner to the tailrace.
(6) The Tailrace: it's a waterway to behavior water discharged from turbine to an acceptable purpose the place it will be safely disposed of or saved to be pumped up lower into distinctive reservoir.
CLASSIFICATION OF WATER POWER PLANT
- Hydro-Electric flora might in addition be classified per the subsequent basis.
(A) Classification supported Head.
(1)High Head Plant- 100m and higher than.
(2) Medium Head Plant- thirty to five hundred m.
(3) Low Head Plant - twenty five to eighty ml.
E.g. Canal water Power Plant.
It is to be mentioned that the figures given above overlap each other. Therefore, it's troublesome to classify the plants directly on the premise of head alone. The basis, therefore, technically adopted is exclusive rate of the rotary engine used.
(B) Classification on the inspiration of their function
(1)Run-off stream Plants: This plant is one that doesn't store any water and makes use of the water as it flows. So water is not any longer hold on at some stage overflowing intervals and in addition once the generators use less water because of low hundreds with the tip result the water is wasted.
However, Run-off stream plant having terribly restricted storage capacity, referred to as pondage is given a weir or barrage to fulfill fluctuations of load or of movement flow.
Such a theme is admittedly an occasional head scheme and applicable on a perennial river.
Note: The strength station developed on diversion canals (Irrigation )
Detention Reservoirs
- A detention reservoir consents of an obstruction to a stream with an uncontrolled outlet. These are primarily tiny structures and operate to scale back the food peak by providing temporary storage and by restriction of the outflow rate.
Levees
- Levees, conjointly called dikes or flood embankments are stuff banks created parallel to the course of the river to confine it to a set course and restricted cross-sectional width. The bights of levees are going to be beyond the move flood pretty with economical free board. The confinement of the river to fixed path free giant tracts of land from inundation and subsequent damage.
- Masonry structures accustomed confine the stream in a very manner almost like levees are called flood walls.
Floodways
- Floodways are natural or manmade channels into that an area of the foggily be entertained throughout high stages.
Channel Improvement
- The works underneath this class involve:
- Widening or deepening of the channel to extend the cross
- Reduction of the channel roughness, by clearing of vegetation from e channel perimeter,
- Short circuiting of meander loops by cutoff channels, leering to in excited slopes.
- In general surface water is most well-liked as a supply of drinkable thanks to its convenient convenience and its constant and sensible quality. However, the supply is contaminated by many substances
- Substances that colly the surface water are often divided as substances that occur naturally and substances created or introduced by human activities
- Naturally occurring substances inflicting pollution of surface water embody to Illustrate the deposition of dust, part method of evapotranspiration, by the natural action of organic matter and nutrients from soil, by hydrological factors that result in runoff and by biological processes inside the aquatic setting that may alter the physical and chemical composition of water.
- As a result water in natural environment contains several dissolved substances and non-dissolved particulate matter.
- The natural quality of surface water depends upon the physical setting the origin and movement of the water. Pollution is one in all the foremost serious environmental issues in Tindivanam Toluca.
- The surface water qualities are tormented by numerous evolution activities. The surface water contains various contaminants love turbidity, Dissolved oxygen, organic and inorganic impurities and pesticides.
- These substances embody menage chemicals, agricultural chemicals some inorganic and organic contaminants.
- Due to the current environmental persistence, these pollutants will cause contamination of surface water that is that the main water resources of production of drinkable in Tindivanam Taluk; this space surface water becomes a lot of and more seriously contaminated due to disposal of domestic and agricultural runoff.
- At gift study to research the water quality particularly the presence of rising contaminants from surface water that's used as a supply of drinking and even for domestic and irrigation purpose in Tindivanam Toluca, Tamil Nadu, India.
Method of Sampling:
- Water samples were collected directly from ponds in Thenkalavoy oorani, Tindivanam Taluca, Tamil Nadu. Exploitation clean stopper synthetic resin bottles and labeled, it absolutely was preserved in a very refrigerator. The analysis was meted out consistent with Water and sewer water standards [APHA-2012] methodology for numerous physico-chemical parameters.
- Water is one in all the foremost vital inputs essential for the assembly of crops. Usually a crop must be irrigated before soil wetness is depleted below 50% of its convenience within the root-zone. Thence water management is arrange for the utilization of water for higher utilization in agricultural. Thence crop coming up with ought to be done considering 1. Water demand and 2. Convenience of water.
WATER REQUIREMENT
- Water requirement is disagree consistent with crops and soil type. The water requirement of crops is that amount of water needed by the crops inside a given amount of your time for his or her maturity and it includes losses because of evapotranspiration and the ineluctable losses during the appliance of water and water needed for special operations love land preparation, paddling and leaching.
- The amount of water required for irrigation on different soil sorts per meter depth of profile at 50% of soil wetness convenience is as follows. Sandy soils (25-50 mm), Sandy-loam (45-80 mm), soil (70-110 mm), Clay-loam (80-120 mm) and significant clay (100-140 mm). The water demand of various crops is given below-
Rice
- The quantity of water required for growing rice is varies wide underneath different conditions: - 1000-1500 mm- heavy soils high water table, short length variety, Kharif season. 1500-2000 mm- medium soils Kharif or early spring season. 2000-2500 mm- light-weight soils, long length varieties throughout Kharif, medium duration varieties during summer. For low land rice, the apply of keeping the soil saturated of submerges of regarding five cm throughout the growing period is beneficial.
Wheat
- It needs regarding 4-5 irrigation. The dwarf wheat wants a lot of condition and also the optimum wetness vary is from 100-60% of convenience. For tall wheat the optimum-moisture range is from the sphere capability to 50% of availability.
Barley
- About 2-3 irrigation are adequate and the optimum soil moisture ranges from the field capacity to 40% of availability.
Maize
- The optimum soil moisture range is from 100-60% of availability within the most root-zone, that extends from 40-60 cm on totally different soil types. Within the northern elements 2-3 irrigation are needed before the onset of the monsoon. In state 2,5 irrigation are necessary throughout Kharif and Rabi respectively. At Rajasthan four irrigation (500 millimetre of water) are needed throughout Kharif.
Sorghum and alternative Millets
- The optimum wetness vary is from the sphere capability to 40% of the availability. At boot stage and grain development, the water demand is extremely important.
Pluses or Grain Legumes
- When big alone, one or two irrigation would be beneficial. The grain legumes (gram, lentil, pea and Indian bean) are irrigated 2 or three times during their growth.
Oilseeds
- The crops are usually grown underneath rained conditions. Groundnut eight to ten irrigation of regarding fifty mm every are applied at 10-15 days interval during its growth period. Safflower, Mustard and Linseeds are big alone are mixed with cereals ought to receive three or four irrigation throughout their growth.
Cotton
- The optimum wetness vary of soil moisture for the crop is from the sphere capability to 20% of convenience in 0-75 cm of the root-zone. Water needs varied from 400-800 millimetre underneath totally different conditions and regarding 4-7 irrigation are needed for cotton.
Jute
- The optimum moisture regime is from the field capacity to 70% of availability within the most root-zone of the crop which may reach about forty five cm of soil depth.
Sugarcane
- The optimum soil moisture for sugarcane has been found to be 100-50% range of availability within the most root-zone, extending up to 50-75 cm in depth. Within the north, the crop is planted throughout February-March and irrigated until the commencement of the monsoon. In geographical area irrigation is needed throughout the year (2800-3000 millimetre per year).
Tobacco
- For cigar, water pipe and bidi tobacco the optimum wetness regimes are from the sphere capacity to 70, sixty and 50% of the provision respectively. Smoke tobacco wants light-weight and frequent irrigation during four months. For hookah tobacco, 12-13 irrigation of fifty mm of water is required.
Forage Crops
- The optimum moisture vary is from capacity measure to regarding 75% of availability. Berseem needs regarding twenty irrigation throughout its growth at intervals of about 20 days- December-January, fifteen days-November-February-March. And ten days-September-October-April. For medick 1800 to 2000 millimetre of water need during the primary year of growth.
Vegetables
- The soil wetness ought to vary between 70-80% of convenience within the most root-zone. Potato wants water at intervals of 10-12 days. Onion and Garlic would like terribly frequent irrigation about three weeks before maturity the irrigation is delayed to reinforce the keeping quality of the bulb. Tomato needs irrigation at intervals of 10-12 days during summer and 15-20 days during winter.
- The optimum moisture regime is from 100-50% of the provision just in case of cabbage, cauliflower and knol-khol. Water-melon and musk-melon would like water at intervals of 8-10 days. Alternative crop of magnoliopsid family family wants irrigation at intervals of 10-12 days throughout summer.
Spices and Condiments
- Important crops are turmeric, ginger, chillis, ajwan, cumin and coriander. Turmeric and ginger ought to be irrigated to take care of 100-60% of the accessible wetness within the most root-zone, the highest fifty cm of the soil. Chillies should be irrigated to maintain 100-50% of the available moisture to regarding sixty cm in the soil. Coriander, cumin and ajwan need irrigation at intervals of 10-12 days on light-weight soil and 15-20 days on serious soils.
Fruit-trees
- For fruit trees soil wetness ought to be maintain within the vary of 100-75% of availability. On the total development of the root-zone right down to 75-90 cm, the crops could also be irrigated once 2/3 of the accessible moisture is depleted throughout blossoming, fruit settings are fruit enlargement. Papaya and banana wants irrigation at intervals of 8-10 days in an exceedingly tropical climate. The Phoenix dactylifera needs regular irrigation during flowering and mature to supply sensible yields.
Coffee
- To irrigate low when the halt of the monsoon rains during flowering to avoid flower shedding is of profitable.
AVAILABILITY OF WATER
- When the land doesn't receive any irrigation, the cultivator takes one crop in Kharif season on the accessible wetness within the soil.
- If the soil is serious, a second crop in Rabi season when a brief length crop in Kharif season, however 2 seasonal or perennial crops isn't beneficial.
- When irrigation becomes available the cropping set up will embody heavy perennials like sugarcane and banana, light-weight perennials like guava or orange, two seasonal crops like long staple cotton, chillies, turmeric and so forth besides Kharif and Rabi seasonal crops and conjointly follow double cropping like groundnut inexperienced gram, black gram etc. followed by wheat or rabbi jowar, kharif jowar or cotton followed by wheat, gram or some vegetable to seasonal crop followed by summer groundnut or some vegetable crop.
- The cropping set up in irrigated space is a lot of intensive.
- Green manuring also can be followed maintain the fertility of the soil and to scale back the expenditure on organic manures and fertilizers. With the chances of double cropping its ought to see that it doesn't become lopsided.
1.Rabi
- Time length - sown: October, December. Harvested: Apr June.
- Crops - wheat barley, peas, gram, mustard etc
- States - Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh.
2.kharif
- Time period- sown: June July harvested: September October
- Crops - rice ,maize, jowar, bajra, moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut, soybean etc.
- States - Assam, West Bengal, coastal place of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra.
3.zaid
- Time period- seeded and harvested: march july
- Crops - seasonal fruits, vegetables, fodder vegetation etc.
- States - most of the northern and northwestern states.
- Cropping pattern refers to the proportion of land below cultivation of various crops at different points of time. This means the time and arrangement of crops during a explicit land area. Any amendment within the cropping pattern would cause:
- Change in the proportion of land under different crops
- Change in area sequence and time of crops
- In India, the cropping pattern is decided by rainfall, temperature, climate, technology and soil type.
- In order to get most yields, different patterns of cropping are practised. The major cropping patterns embrace the following:
Monocropping
- Monocropping reduces soil fertility and destroys the structure of the soil. Chemical fertilizers are needed to upgrade production. This apply permits the unfold of pests and diseases.
Mixed Cropping
- When 2 or a lot of crops are mature on a similar land simultaneously, it's referred to as mixed cropping. For eg., growing wheat and gram on the same land at the same time is mixed cropping. This practice minimizes the danger of failure of 1 of the crops and insures against failure because of abnormal weather conditions.
- The crops to be grown along ought to have a special maturation time and totally different water requirements. One tall and one dwarf crop ought to be mature together. The nutrients needed by one crop should be lower than those required by the other. One crop should have deep roots, others should be shallow. Of these criteria cause a prospering mixed cropping pattern.
Advantages of Mixed Cropping
- The crop yield increases.
- The blighter infestation is minimized.
- Reduction within the risk of crop failure.
- The soil is used properly.
- More than one form of crops are often harvested at a similar time.
Intercropping
- Intercropping is that the apply of growing quite one crop on the same field at the same time in a definite row pattern. When one row of the most crop, 3 rows of intercrops are often mature. This will increase productivity per unit area.
Intercropping can be of various types:
Row Intercropping
- When the part crops are organized in alternate rows it's referred to as row intercropping. It helps in optimum utilization of land area and suppression of weeds throughout the first stages of the main crop.
Strip Intercropping
- When two or a lot of crops are grown in wide strips in order that the 2 crops can be managed separately, it is known as strip cropping. However, the crops are shut enough to interact.
Relay Intercropping
- In this kind of intercropping, a second crop is planted once the existed crop has floral however not harvested. For eg., Rice-Cauliflower-Onion-Summer gourds.
Advantages of Intercropping
- The fertility of the soil is maintained.
- The unfold of diseases and pests is controlled.
- Optimum utilization of resources.
- The area and time of growing quite one crop are saved.
- Maximum utilization of nutrients gift within the soil.
- Maize and soybean, bajra and lobea are a number of the crops mature as intercrops.
Crop Rotation
- In this pattern, totally different crops are grown on a similar land in preplanned succession. The crops are classified as annual rotation, biennial rotation, and three-year rotation, relying upon their duration.
- Legumes are included within the crop rotation programmed to extend soil fertility. The crops that require high fertility level (wheat) are often mature when the legumes. The crops which require low inputs can be grown after the crops that need high inputs.
- How are the crops designated for Rotation?
- While choosing the crops for rotation, the subsequent criteria ought to be adopted:
- Enough wet should be available.
- Availability of fertilizers, man-power, and machine-power.
- Marketing and process facilities.
- Availability of nutrients in the soil.
- The crop duration- short or long.
Advantages of Crop Rotation
- The soil fertility is maintained for a chronic period.
- The growth of weeds and pests is prevented.
- A ton of chemical fertilizers don't seem to be required.
- The physical and chemical nature of the soil remains unaltered.
Factors moving Cropping Patterns
- The cropping patterns verify the amount of agricultural production. This reflects the agricultural economy of any region.
- The cropping patterns are laid low with changes in rural policy, handiness of agricultural inputs, and improvement in technology.
- Thus, the cropping patterns are helpful in rising the fertility of the soil, thereby, increasing the yield of the crops. It ensures crop protection and availability of nutrients to the crops
Duty:
- The term duty suggests that the realm of land that may be irrigated with unit volume of irrigation water. Duty represents the irrigating capability of a unit. It's the relation the between the realm of a crop irrigated and therefore the amount of irrigation water needed throughout the complete amount of the expansion of that crop. For example, if 3 comics of installation is required for a crop seeded in a part of 5100 hectares, the duty of irrigation water are going to be 5100/3 = 1700 hectares/comics, and the discharge of three comics will be required throughout the bottom period.
Delta:
- It is that the total depth of the water needed by a crop throughout the complete amount the crop is within the field ANd is denoted by the image ∆. For example, if a crop needs regarding twelve watering at an interval of ten days, and a water depth of 10 cm. If the world beneath the crop may be a hectares, the whole amount are going to be 1.20 X A = 1.2 A hectare-meters during a period of one hundred twenty days.
- The concentration and composition of soluble salts in water can verify its quality for varied functions (human and eutherian mammal drinking, irrigation of crops, etc.). The standard of water is, thus, a vital part with relation to property use of water for irrigated agriculture, particularly once salinity development {is expected} to be a retardant in an irrigated agricultural area.
- There are four basic criteria for evaluating water quality for irrigation purposes:
- Total content of soluble salts (salinity hazard)
- Relative proportion of atomic number 11 (Na+) to metal (Ca2+) and metal (Mg2+) ions – sodium surface assimilation magnitude relation (sodium hazard)
- Residual sodium carbonates (RSC) – hydrogen carbonate (HCO3−) and carbonate (CO32−) anions concentration, because it relates to Ca 2+ and Mg2+ ions.
- Excessive concentrations of parts that cause an ionic imbalance in plants or plant toxicity.
- In order to attain the primary 3 vital criteria, the subsequent characteristics have to be compelled to be determined within the irrigation waters: electrical conduction (EC), soluble anions (CO32−, HCO3−, Cl− and SO42−) wherever Cl− and SO42− are facultative and soluble captions (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+) where K is optional. Finally, atomic number 5 level should even be measured. The hydrogen ion concentration of the irrigation water isn't a suitable criterion of water quality as a result of the water pH tends to be buffered by the soil, and most crops will tolerate a large pH range. a close description of the techniques normally utilized for the analysis of irrigation water is available (USSL Staff 1954; Bresler et al. 1982).
- Soil moisture limits forage production potential the most in semiarid regions. Estimated water use efficiency for irrigated and dry-land crop production systems is 50 percent, and available soil water has a large impact on management decisions producers make throughout the year. Soil moisture available for plant growth makes up approximately 0.01 percent of the world's stored water.
- By understanding a little about the soil's physical properties and its relationship to soil moisture, you can make better soil-management decisions. Soil texture and structure greatly influence water infiltration, permeability, and water-holding capacity.
- Soil texture refers to the composition of the soil in terms of the proportion of small, medium, and enormous particles (clay, silt, and sand, respectively) during a specific soil mass. For example, a rough soil is sand or loamy sand, a medium soil may be a loam, silt loam, or silt, and a fine soil is a sandy clay, loose clay, or clay.
- Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles (sand, silt, and clay) into stable units known as aggregates, that provide soil its structure. Aggregates are often loose and friable, or they will kind distinct, uniform patterns. For example, granular structure is loose and friable, blockish structure is six-sided and might have angular or rounded sides, and plate like structure is stratified and may indicate compaction problems.
- Soil consistency refers to the house between soil particles, that consists of varied amounts of water and air. Consistency depends on each soil texture and structure. For example, a fine soil has tinyer however a lot of varied pores than a rough soil. a rough soil has larger particles than a fine soil, but it's less porosity, or overall pore space. Water are often command tighter in small pores than in large ones, therefore fine soils will hold a lot of water than coarse soils.
- Water infiltration is that the movement of water from the soil surface into the soil profile. Soil texture, soil structure, and slope have massivest impact on infiltration rate. Water moves by gravity into the open pore areas within the soil, and also the size of the soil particles and their spacing determines what proportion water can flow in. Wide pore spacing at the soil surface will increase the speed of water infiltration, so coarse soils have a better infiltration rate than fine soils.
- Permeability refers to the movement of air and water through the soil, which is important because it affects the supply of root-zone air, moisture, and nutrients available for plant uptake. A soil's permeability is determined by the relative rate of moisture and air movement through the most restrictive layer within the upper 40 inches of the effective root zone. Water and air rapidly permeate coarse soils with granular subsoils, which tend to be loose when moist and don't restrict water or air movement. Slow permeability is characteristic of a moderately fine subsoil with angular to sub angular blocky structure. It is firm when moist and hard when dry.
- Water-holding capacity is controlled primarily by soil texture and organic matter. Soils with smaller particles (silt and clay) have a bigger expanse than those with larger sand particles, and an oversized surface area permits a soil to carry a lot of water. In different words, a soil with a high share of silt and clay particles, that describes fine soil, includes a higher water-holding capability. The table illustrates water-holding-capacity variations as influenced by texture. Organic matter percentage additionally influences water-holding capacity. Because the percentage will increase, the water-holding capacity increases thanks to the affinity organic matter has for water.
- A daily water balance, expressed in terms of depletion at the tip of the day, is
Dr,i = Dr, i-1 - Pi + ROi - Ii - CRi + ETa,i + Dpi
Where
Dr,i = root zone depletion at the end of day i [mm]
Dr, i-1 = depletion within the root zone at the end of the previous day, i-1 [mm]
Pi = effective precipitation on day i [mm], restricted by most daily infiltration rate [mm]
ROi = surface runoff from the soil surface on day i [mm]
Ii = web irrigation depth (averaged over the complete area) on day i that infiltrates the soil [mm]
CRi = capillary rise from the groundwater table on day i [mm]
ETa,i = actual crop evapotranspiration on day i [mm]
DPi = water flux out of the foundation zone by deep percolation on day i [mm]
- The capillary rise, CRi, will commonly be assumed to be zero once the geological formation is over regarding one m below all-time low of the root zone. Following serious rain or irrigation, the soil water content within the root zone might quickly exceed cubature unit or maybe saturation.
- The amount on top of saturation goes to surface runoff, whereas the number between field capacity and saturation goes to deep percolation (limited by most percolation rate -- any excess can stay within the soil) at intervals an equivalent day of a wetting event, and depletion Dr,i becomes zero.
- As long because the soil water content in the foundation zone is below cubature unit (i.e., Dr,i > 0), the soil is assumed to not drain.
- The root zone depletion will step by step increase as a results of ETa. Within the absence of a wetting event, the root zone depletion will reach the worth TAW. At that moment no water is left for ETa, and American state and ETa become zero.
- The DPi term isn't to be confused with the DPe,i term used for the evaporation layer. Each terms are often calculated at an equivalent time, however are freelance of 1 another.
- Infiltration is that the method by that water on the bottom surface enters the soil. It's unremarkably utilized in each geophysical science and soil sciences.
- The infiltration capability is outlined because the most rate of infiltration. It's most frequently measured in meters per day however may be measured in different units of distance over time if necessary.
- The infiltration capacity decreases as the soil wet content of soils surface layers increases.
- If the precipitation rate exceeds the infiltration rate, runoff will usually occur unless there's some physical barrier. Infiltrometers, permeameters and rain simulators are all devices which will be wont to measure infiltration rates.
- Infiltration is caused by multiple factors including; gravity, capillary forces, sorption and osmosis. Several soil characteristics may play a job in deciding the speed at which infiltration occurs.
- There are 2 ways in which within which we will classify our water use. One sort is in-stream use; this includes electricity power, water travel and swimming, for example. Whereas in-stream activities don't deplete the water, they'll degrade the water quality through pollution.
- The different variety of water use is that the withdrawal of water, and this classification includes house use, business use, irrigation, eutherian watering and thermal and nuclear power.
- Most withdrawals are consumptions, that means that the activity uses the water and doesn't come back it to the supply.
- The quantity of water that's taken (or withdrawn) from the source is termed the water intake, and therefore the amount that is came is called the water discharge.
- The distinction between the water intake and the water discharge is that the amount consumed.
Water intake Water discharge = Consumption
- The total amount of water that is used is called the gross water use. The difference between the gross water use and the water intake is up to the quantity of water that's recirculated.
- The recirculated amount is expressed as a employment rate and may be a sensible indicator of water efficiency.
- Gross water use Water intake = quantity recirculated (or recycling rate)
WHAT ARE THE KEY CAUSES OF WATER CONSUMPTION?
- In 1996, atmosphere North American country found that the major withdrawal uses of water were for thermal power generation, manufacturing, municipal use, agriculture and mining.
- The following diagram illustrates the amount of water that was withdrawn for every use, still because the amount that was recirculated, consumed and discharged.
- While thermal power generation withdraws the best amount of water, agriculture consumes way more water than thermal power generation does.
- Also note that there's no indication of recycled water within the home, creating domestic water use terribly inefficient.
- It is additionally necessary to note that the consumption rate for the mining sector is inaccurate, thanks to an absence of data. In fact, the oil sands mining operations in Canadian province consume nice quantities of water.
- To manufacture one barrel of artificial fossil oil needs between a pair of and five barrels of water. Every year, over three hundred million isometric metres of water are entertained from the Athabasca watercourse in Alberta.
- With the planned expansions, the quantity of withdrawn water might increase to over five hundred million isometric metres of water every year! As well, oil mining is sort of inefficient within the space of water recycling, and an excellent deal of the withdrawn water finishes up in tailings ponds. Of the water taken from the Athabasca watercourse for mining in Albertas tar sands, solely ten p.c is came to the river; the rest is consumed or sent to tailings ponds, as a result of it's too contaminated to enter the river. For a lot of data concerning oil mining, see the Oil Fields reality sheet.
FREQUENCY OF IRRIGATION:
1. IRRIGATION SYSTEM
- The variety of irrigation system plays a key role in deciding however oftentimes water is applied. Microirrigation systems are high frequency irrigation systems with irrigations often occurring daily for drip systems operational throughout peak water demand periods. Microsprinkler systems are often operated each three to four days at peak ET periods.
- Sprinkler irrigation systems are operated less frequently than microirrigation systems, with irrigation events being seven to ten days or a lot of apart. Flood irrigation events are usually the smallest amount frequent. The time between irrigations is usually a pair of weeks or more.
Irrigation System Irrigation Frequency During Peak Water demand
Drip Irrigation - Daily
Microsprinklers - Approx. Every 3-4 days
Sprinklers - 10-14 days
Furrow - 14+ days
Border check - 14+ days
2. SOIL CHARACTERISTICS:
- The call of once to irrigate is usually determined by the degree of soil wet depletion. The crop withdraws soil moisture to fulfill its evapotranspiration (ET) demands. It becomes a lot of and harder for the crop to withdraw water because the soil becomes drier, till the plant can now not withdraw soil moisture and dies (permanent weakening point).
- Soils that may store bigger amounts of accessible water (stored soil moisture available to the plant) don't have to be compelled to be irrigated as ofttimes as soils that store less. In general, sandier (light textured) soils need to be irrigated more frequently than soils with a bigger clay content (heavier textured).
Soil Texture Available Water holding capacity
(in. Of water/foot of soil)
Very coarse sands 0.4 - 0.75
Coarse sands, fine sands, loamy sands 0.75 - 1.25
Sandy loams, fine sandy loams 1.25 - 1.75
Very fine sandy loams, loams, silt loams 1.50 - 2.30
Clay loams, silty clay loams, sandy clay loams 1.75 - 2.50
Sandy clays, silty clays, clays 1.60 - 2.50
3. CROP ROUTINE DEPTH :
- While the soil's texture impacts the amount of stored soil moisture, the plant's rooting characteristics determine how much of the soil moisture can be accessed by the plant.
- A deep rooted crop has access to a greater amount of soil moisture than does a shallow-rooted crop, usually allowing it to go longer between irrigations.
- The rooting depths of a number of crops are shown in the table below.
- The rooting depth may be affected by the soil depth, constraining soil layers (hardpan, plowpan, etc.), or even abrupt changes in soil texture.
- When in doubt about the soil profile or rooting depth, use a soil auger or higher nevertheless a backhoe, to see the growth depth and profile textural characteristics.
- Irrigation water is usually applied to crops by:
- Flooding on the sphere surface
- Applying at a lower place the soil surface
- Spraying below pressure
- Applying in drops within the crop root zone
- The application technique should guarantee the same distribution of water on the cropped field moreover as in the root zone of the crop with high application efficiency. The quantitative relation of water hold on in the root zone thereto delivered to the field ought to be maximum. There should be minimum or no wastage of water either through surface run-off or deep percolation below the basis zone of a crop.
- Several water application ways are practiced to suit completely different soil types, water system and its quantity, the topography of the land, crops to be irrigated and costs.
Surface Application Method.
- In this technique, water is applied to the crop by flooding it on the soil surface.
- This method needs correct land grading for the flow of water over the land surface.
- More than 95% of the irrigated space in Republic of India is below surface irrigation.
Merits:
- It is easy in layout and operation.
- The quantity of manual labor needed is minimum.
- It will not impede the employment of machinery for land preparation, cultivation, harvesting, etc.
Demerits:
- The overall irrigation potency is low. The worldwide average irrigation in canal command areas shows associate degree overall efficiency of as low as 28%.
- It could lead to water=logging and soil salinization besides the large quantity of water losses.
- Surface Irrigation ways could also be loosely classified as:
Border Method:
- Borders are fashioned by dividing the sphere into variety of strips that are separated by ridges.
- The strips are usually levelled on the dimension however may or might not have slope along the length.
- An irrigation channel runs along the higher finish of the borders.
- The water is pleased from the channel into the strips. The water flows slowly towards the lower end, wetting the soil because it advances. Additional water is usually off from the strip by suggests that of a assembling drain. It's provided at the opposite end.
- This technique is appropriate within the fields wherever the soil is sufficiently capable of riveting the water.
Furrow Method:
- Furrow irrigation is filmable to an excellent variation in slope, crops and topography.
- When the crops are big and planted in rows this method is that the best suited. During this method, in contrast to flooding, solely a region of the sphere is wetted. The area wetted varies from 1/2 to 1/5 of total space over that crops are grown.
- Close growing crops, on slopes and soils that develop crust when being wet, could also be irrigated with little furrows which are known as corrugations or rills.
- The main style parameters of furrows are
- Longitudinal slope
- Inflow stream design
Furrow spacing:
- Furrow spacing ought to be specified the lateral water movement of the moisture wets the ridges by the time irrigation is complete. The lateral movement from the furrows depends on the soil type.
- Furrow spacing is set by agronomical needs of row-to-row spacing and machinery to be used for planting and cultivation.
- Furrow length: Longer furrows = a lot of percolation and fewer run-off
Benefits of this technique:
- In this method plants in their early tender age don't seem to be broken by the flow of water.
- The land between the rows of plants is used to construct furrows, so helpful irrigable land isn't wasted.
- As the realm wetted is simply 1/2 to 1/5 of the cropped area of the field, puddling and crusting of the soil is minimum.
Check basin:
- It consists of running water into comparatively level plots enclosed by little ridges.
- The length of the plot is usually not up to three times the width.
- The main and lateral channels irrigate the most channel is aligned on the higher finish of the sphere and checks are created on the either facet of the lateral channels.
- The check basins are particularly appropriate for significant soils with low infiltration rate or extremely pervious sandy soils.
- The key to attaining high irrigation potency within the style of the check basin is to unfold water over the complete basin as apace as possible.
- Therefore, the employment of enormous influx stream reduces water spread time over the basin.
SPRINKLER AND MICRO SPRINKLER APPLICATION:
Sprinklers:
- This device sprinkles water in a way just like rainfall in order that run-off and deep percolation losses are prevented and the uniformity of software is pretty excessive.
- The device includes sprinkler heads or nozzles, that are set up on risers in lateral traces taken from the primary line, that's in addition linked to a pumping unit.
- This device of irrigation is appropriate when:
- The soil is just too porous for right distribution with the aid of using floor irrigation.
- The fields have an choppy floor.
- The soil is effortlessly erodable.
- The water deliver is simply enough for crop increase.
Merits:
- Sprinklers may be used on all soil sorts of any topography.
- It includes improved irrigation frequency which has a tremendous impact on crop yield.
- In this technique, a water saving of 30% to 50% is mentioned in evaluation to the floor technique of irrigation
- Thus with the aid of using introducing sprinklers, an extra place as much as 50n be introduced beneath irrigation except improved crop yields
- The general performance of the device is above 80% and no land is wasted on making bunds and channels, and approximately 40-50% of saving in labour compared to floor irrigation.
- Only 2 to 5% water is misplaced thru evaporation.
Demerits:
- Expensive
- Requires non-stop renovation and talent for set up and operation
- The excessive power requirement for operation as sprinklers function at water strain starting from 1 to ten kg/sq cm.
- Wind interferes with the distribution pattern. It reduces the spreading fee and in flip the performance. Under excessive temperatures and sturdy winds heavy evaporation loss takes vicinity thereby offsetting the saving in water.
Micro-sprinklers:
- It sprinkles across the root region with small sprinklers that paintings beneath low strain.
- In this technique, water is carried out most effective to the basis region place not like to the complete subject as withinside the case of sprinkler irrigation technique.
- This technique is relatively appropriate for orchard vegetation and vegetable vegetation.
DRIP APPLICATION:
- In this technique, the software of water is particular however sluggish as discrete drops, non-stop drops, tiny streams or miniature sprays thru mechanical devices, known as emitters or applicators placed at decided on factors alongside water shipping traces.
- This is beneficial in regions with water shortage and salt problems.
- Drip irrigation device includes fundamental pipe, sub-mains, lateral valves, drippers or emitters, a riser valve, vacuum breakers, strain gauges, water metres, filters, fertiliser tanks etc.
- These are designed to deliver water at favored rates (1 to ten litres/hour) immediately to the soil.
- Low pressures starting from 0.35 to kg/sq cm are enough for drip device
Merits:
- Water saving
- Enhanced plant increase and yield
- Saving of labour and power
- More applicable to bad soils
- Controls weed increase
- Easy operations
- Fertilisers or different chemical amendments may be correctly carried out to character or separate vegetation the use of drip irrigation.
- Flexibility in operation
- No soil erosion
- Requires much less land preparation
- Minimum ailment and pest problems
- This technique has been determined to be of terrific price in reclaiming and growing wasteland and arid regions.
Demerits:
- Expensive
- Technical Limitations
- Requirement of excessive capabilities for design, set up and operation