Unit - 1
Basics of construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations.
Construction management is the process of planning, coordinating and providing monitoring and controlling of a construction project. This style of project management is designed for the, as the name implies, construction industry. There are few types of construction that use construction management, they are industrial, civil, commercial, environmental and residential. Each category has its own way of running projects, but all will follow the construction management methodology.
- Each structure is unique: Even if the structures are similar, there is possibility of variation due to the influence of:
1.2.2 Each structure is commissioned: Civil engineering works are not like factory products which may be available in a stock at the required time. Each civil engineering work is commissioned i.e. order is placed for each structure before construction works commences. However now-a-days construction components are prefabricated which can be kept in start.
Construction engineering companies never initiate themselves. Thus decisions of construction of various projects are taken by taking into consideration their requirements etc. Hence the civil engineering industries are the masters of its own.
1.2.3 Each structure is built in situ: The civil engineering structure is built at a place of its final use. Sometimes components may be fabricated or built elsewhere. However structure has to suit the particular requirements of the site where it is built.
1.3.1. Private Construction Projects
The first type of construction project is the Private Construction Project. Put simply, private projects are projects of every type that are owned, controlled or commissioned by a private party. Private parties include individuals, homeowners, corporations, other business entities, non-profit associations, privately funded schools, hospitals, publicly traded companies, etc. Anything, in other words, that is not the government.
Private construction projects come in all different shapes and sizes, and this is when it’s useful to look at the character of the work performed to segment private construction into different subcategories. These subcategories would include:
1. Residential Construction
Whenever construction work is being performed to a single-family residence or a residential facility with (usually) less than 3 or 4 units. If you are working on an apartment complex this would more likely be considered a commercial project instead of a residential project. Similarly, if you are working at a condominium, the work would be residential if upon a single unit, but if on the entire complex or the 2 common elements, the work would more likely be considered commercial.
2. Commercial Construction
Commercial construction is the construction of any buildings or similar structures for commercial purposes. Commercial construction includes a huge variety of projects including building restaurants, grocery stores, skyscrapers, shopping centers, sports facilities, hospitals, private schools and universities, etc.
3. Industrial Construction
This is a relatively small segment of the construction industry. These projects include power plants, manufacturing plants, solar wind farms, refineries, etc. While termed “industrial construction,” it is pretty interchangeable with “commercial construction.”
4. Infrastructure and Heavy Construction
The last type of construction is infrastructure and heavy construction which encompasses building and upgrading of railways, communications, and roads, railways to the surroundings of a city or existing building construction. This type of construction usually done due to the public interest and is often executed by government agencies and large private corporations.
Some other projects that fall under this type of construction include tunnels, bridges, highways, transit systems, drainage systems, and pipeline.
1.3.2. State Construction Projects
Some people get confused by the term “state” when talking about state construction projects because the term “state” can refer to projects commissioned by a county, city, municipality, government board, public school board or any other state-funded entity. The term “state construction” means, therefore, any government-funded construction that is not “federal” – which is discussed in the next section.
State construction projects can take a variety of forms.
They can be pretty traditional projects like the construction of a public school or government building (like a court room). These projects can also be pretty sophisticated, such as the construction of a bridge, sewer line, highways, etc.
1.3.3 Federal Construction Projects
Federal construction projects are very similar to state projects. Just like state projects they can take on a variety of forms: very simple and traditional, and very complex. And the stuff being constructed can be pretty similar to the stuff constructed by state authority: courthouses, government buildings, flood control projects, etc.
The difference between state and federal projects simply depends on who owns or controls the underlying project site. The difference is not which entity funds the project, because federal funds are all over state (and even private) projects. The difference is in who owns and controls the project.
If work is done on a state courthouse using federally provided funds, it is a state project. If work is done on a federal courthouse, however, it’s a federal project. Work done on a federally funded interstate is usually a state project because the states control the highways. Work done through the US Army Corps of Engineers, however, even on state land such as They can be pretty traditional projects like the construction of a public school or government building (like a court room). These projects can also be pretty sophisticated, such as the construction of a bridge, sewer line, highways, etc.
1.4.1 Estimating
In most cases, an estimating tool is the number-one feature sought by buyers of construction project management software. That makes sense, considering that operating within a budget is one of the most important success factors of a construction project. At the same time, you want to make money and stay profitable. Look for a platform that helps you deliver higher price bids and back them up with benchmarking and integrated scheduling. Some of these may even integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, to provide more accurate estimates based on your outfit’s capabilities and timeline.
1.4.2 Project Information Modeling
Most projects in the construction industry are highly complex, involve numerous stakeholders, and span long periods of time. Over time, the data models and drawings associated with the project pile up. It’s important to have the ability to draw from this expanding repository of data at any point during the project lifecycle and find the insight you need. That’s where project information modeling comes in handy. Some vendors may also refer to this as “design data management.” Look for features that help you easily share models and business information between operations, finance, and leadership, with built-in analytics and reporting.
1.4.3 Cost Management and Accounting
Nearly every construction PM system will offer basic budgeting and benchmarking capabilities. However, a more robust cost management solution will include estimating and forecasting to give you an overall picture of each project’s financials. When you can effectively track and manage these details, you minimize the chance of surprises. This is also a must-have feature if your company handles accounting in-house. Excel spreadsheets are great for tracking costs and payroll, but it’s not always easy to access important data from the field or share up-to-date files with other key decision makers. Many construction PM tools include accounting capabilities that let you track budgets, payroll, invoicing, and billing so you can see your cash flow at a glance. Ideally, you’ll be able to select different forecast methods based on the type of item, using performance trends and goals stored in the same system.
1.4.4 Field Management
As job sites start to add up, it can be difficult for a project manager to oversee field work at every location. Look for software that offers field management and execution features to help create and communicate daily work plans, keep in touch with crew members, and capture the results of the workday at the end of each shift. Some software can even help you stay compliant by managing inspection forms, and streamlining the process for equipment, safety, and quality inspections.
1.4.5 Actionable Data Analytics
Most construction PM tools will help you organize your workflow, keep track of client communications, and manage projects. But if you want the most bang for your buck, find a tool that will make it easy to review data in order to improve your processes. Some tools offer reporting features that will give you insight into your productivity and utilization of assets. You may be able to monitor resources and measure earned value by tracking processes on a cost and schedule basis. This can help you increase productivity, improve performance, and enable strategic insight. If you have a labor shortage (a serious problem for most construction projects), you can spot it faster and take action immediately. If you are searching for the best construction project management software, check out our Product Selection Tool or contact one of our trusted Technology Advisors for free.
A standard construction project, in general, has following five major life cycle phases:
This has been shown in following figure in sequence:
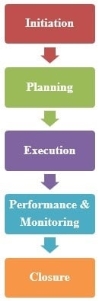
A brief description specifically about each stage are explained below.
1.5.1 Initiation Phase of Construction Project
We have to create and evaluate the project in order to determine if it is feasible and if it should be undertaken, at the beginning of the project. Here the project objective or need is identified; this can be a business problem or opportunity.
A suitable response to the need is documented in a business case with recommended solution options. A feasibility study is conducted to examine whether each option clearly identifies the project objective and a final recommended solution is determined.
Many questions related to the issues of feasibility i.e. “can we do the project?” and justification like “should we do the project?” are mentioned and faced.
When a solution is approved, a project is initiated to implement the approved solution. For this, a project manager is appointed. At this stage, the major deliverables and the participating work groups are identified. This is the time when the project team begins to take shape. Approval is then required by the project manager to move onto the detailed planning phase.
1.5.2 Planning Phase of Construction Project
The planning phase involves further development of the project in detail to meet the project’s objective. The team identifies all of the work to be done. The project’s tasks and resource requirements are identified, along with the strategy for producing them.
In a broader sense identification of each activity as well as their resource allocation is also carried out. A project plan outlining the activities, tasks, dependencies, and timeframes is created.
The project manager is the one who coordinates the preparation of a project budget by providing cost estimates for the labor, equipment, and materials costs. This is mainly carried out by project scheduling software like MS project or PRIMAVERA. This scheduling charts would help us to track the stages of our project as time passes. This is also referred to as “scope management.”
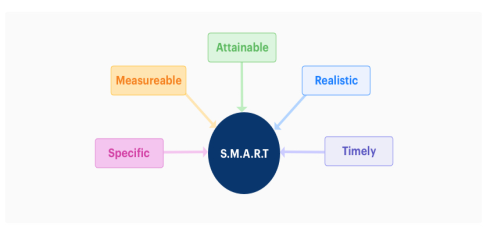
S.M.A.R.T Goals:
The ‘SMART’ criteria ensure that the goals you set for your project are critically analyzed. It is an established method that reduces risk and allows managers to make clearly defined and achievable goals.
The acronym SMART stands for
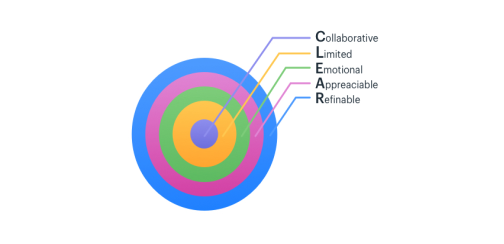
C.L.E.A.R. Goals:
The ‘CLEAR’ method of setting up goals is designed to cater to the dynamic nature of a modern workplace. Today’s fast-paced businesses require flexibility and immediate results and CLEAR can help you with that.
The acronym for CLEAR stands for
During the planning stage, the scope of the project is defined. There is a possibility of changing the scope of the project demands it but the project manager must approve the change. Project managers also develop a work breakdown structure (WBS), which clearly visualizes the entire project in different sections for the team.
The budget of the project already estimated is used to monitor and control cost expenditures during project implementation.
Finally, we require a document to show the quality plan, providing quality targets, assurance, and control measures, along with an acceptance plan, listing the criteria to be met to gain customer acceptance. At this point, the project would have been planned in detail and is ready to be executed.
1.5.3 Execution Phase of Construction Project
This is the implementation phase, where the project plan is put into motion and the work of the project is performed practically on site. It is essential to maintain control and communicate as needed during each implementation stages.
Progress should be continuously monitored and appropriate adjustments are made and recorded as variances from the original plan. A project manager is the one who spends most of the time in this step. Throughout the project implementation, people carry out the tasks, and progress information is being reported through regular project team meetings.
The project manager uses this information to preserve control over the direction of the project by comparing the progress reports with the project plan to measure the performance of the project activities. If any deviation is found from the already defined plan corrective measures are made.
The first option of action should always be to bring the project back to the original plan. If that cannot happen, the team should record variations from the original plan and record and publish modifications to the plan. all through this step, project sponsors, and other key stakeholders are kept informed about the project’s status as per the agreed rate and format of communication. The plan should be updated and available on a regular basis.
Status reports should always highlight the probable end point in terms of cost, schedule, and quality of deliverables. Each project deliverable produced should be reviewed for quality and measured against the acceptance criteria.
When deliverables have been produced and the customer has agreed on the final solution, the project is said to be ready for closure.
1.5.4 Performance and Monitoring Phase of Construction Project
This stage is all related to the measurement of progress and performance to make sure that items are tracking with the project management scheduling. This phase regularly happens at the same time as the execution phase.
1.5.5 Closure Phase of Construction Project
During the final closure, the importance is on providing the final deliverables to the customer, that is:
This type of analysis would make the knowledge of experience to be transferred back to the project organization, which will help future project teams.
Project Execution Process Flow Chart
The project execution process consists of the following activities.
1.6.1 Conduct Procurements
The objective of this activity is to analyze different sellers in order to identify the most suitable vendor. Timely execution of the project requires timely delivery of different raw materials. This implies that the project manager needs to select vendors carefully to avoid working with individuals or companies that will not deliver materials on time.
To achieve this, the project manager organizes bidder conferences, issues out the bid packages to suppliers, and leads in the evaluation of the potential suppliers. Besides, he heads the team that conducts the selection of the most suitable bidder. The project manager documents the final results and informs the selected supplier about what they need to do. The project manager communicates with the vendor about the need for cooperation to facilitate the execution of the project based on the set plan. The Project Management Plan is reference to undertake this activity effectively and appropriately.
1.6.2 Validate Procurements
This activity involves the validation of the procurement process. The purpose of validating the procurements is to provide the assurance that the equipment and resources needed for the completion of the project will be provided.
This is essential because the projects sponsor gets to approve the chosen bidder and the items to be purchased.in relation to the project. Validation also guarantees that the bidder will be paid for delivering his or her supplies.
1.6.3 Acquire Project Team
The objective of this activity is to select individuals who will constitute the project team. Members of the project team perform different project tasks with some requiring specialized skills. This requires determining the skills of different individuals to allocate each task to the most qualified individual.
This activity also seeks to ascertain availability of individuals who can perform various project activities. Thus, the project manager gathers information pertaining to the experience and competence of all team members. The skills of the project team members are evaluated in consideration of the level of experience required and how project execution will be performed.
1.6.4 Execute Project Activates According to Plan
The objective of this activity is to make sure that actual work on the project has started. Members of the project team implement the tasks and activities they have been assigned. In other words, the project plan is translated into action. The project manager oversees project works and ensures that all activities are executed according to plan to guarantee project success.
The activities detailed in the project plan are initiated and the project manager ensures that they are executed as planned. During this activity, the project manager references the Project Management Plan to ensure that all activities, operations, processes, and tasks are executed as planned.
1.6.5 Manage Project Team
The objective of this activity is to follow up on the performance of project team members to ensure the project performance is optimized. Besides, this activity concerns resolving issues, providing feedback, and managing team changes. This activity is vital to the project because it helps to appraise the performance of team members, resolve issues, manage conflict, and influence team behavior.
As such, the project manager makes sure that team members are performing their roles correctly and as expected. The project manager intervenes whenever issues arise to help resolve them early on. In order to perform effectively, all the necessary resources are provided to the team members. Besides, the project manager makes sure that optimal work is allocated to the team members.
1.6.6 Manage Communication
This activity is concerned with facilitating effective and efficient communication between the stakeholders. The activity is vital because it facilitates communication between stakeholders who communicate often on project implementation matters. Different communication tools, measures, and techniques are utilized to suit the intended purpose. The output documents in this activity are Meeting Minutes and Emails.
1.6.7 Manage Stakeholder Engagement
This activity is absolutely necessary for every project because it boosts the support of the project by stakeholders and significantly reduces their resistance to the project. A great way to raise the possibility of achieving project success is to ensure that stakeholders are engaged and managed effectively.
To effectively manage stakeholders’ engagement, the project manager should consult the stakeholder management strategy to familiarize himself with approaches for enhancing support from stakeholders and minimize their resistance. Communicating and working with stakeholders at every stage of the project is vital to make sure that their needs and expected outcomes are considered and satisfied.
This involves providing updates on the project to the stakeholders and getting their input whenever it’s needed. The issues that happen from time to time during project execution should be notified to the stakeholders and it is wise to seek their input when coming up with the most appropriate solution for the same. Thus, the document that is referenced at this stage is the Stakeholder Management Strategy.
1.6.8 Perform Quality Assurance
This activity is carried out as the project work is being carried out. The purpose of performing quality assurance is to enhance quality processes in the project. It involves performing an audit on the quality requirements and findings of quality control assessment to make sure that appropriate operational definitions and quality standards are used. A key benefit of conducting quality assurance is that it helps to improve quality processes. Some of the tools and techniques used to achieve the objectives of this activity are process analysis, quality audits, tree diagrams, and matrix diagrams. Thus, when undertaking this activity, the project manager establishes and plans those processes that are related to the objectives of the project. The identification of processes that are required to deliver quality is also performed. Another activity that is performed here is process testing, which aims to determine whether they meet the set quality level. The inputs utilized in the quality assurance activity include project management plan, quality management plan, and quality control measurements.
At the end of this activity, the project manager prepares a Quality Audit Report that documents the quality assessment findings. Although corrective actions for issues identified may not be suggested in this report, areas in the organization that are non-compliant with the set quality systems and standards are recorded. Using this information, appropriate corrective actions and strategies can be developed.
Key takeaways-
Reference-
1. Punmia ,B.C khandewala k.k. project planning with PERT and CPM,laxmi publication,2016.
2. National building code ,bureau of Indian standards ,new delhi,2017.