UNIT 4
Modulation
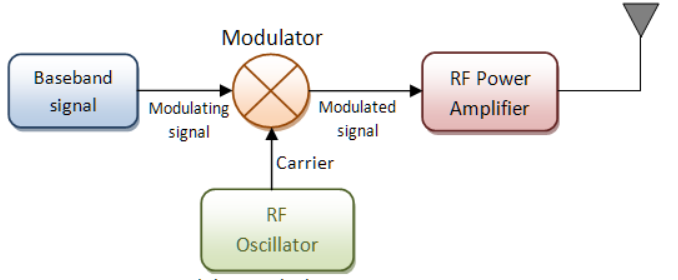
It is a process through which audio, video, image or text information is added to an electrical or optical carrier signal that is to be transmitted over a telecommunication or electronic medium.
It enables the transfer of information on an electrical signal to a receiver that is capable of demodulating the signal to extract the blended information.
It is primarily used in telecommunication technologies that require the transmission of data via electrical signals.
It is considered the backbone of data communication as it enables the use of electrical and optical signals as information carriers.
This is done by altering the periodic waveform or the carrier.
This comprises of its amplitude, frequency and phase.
Modulation has three different types:
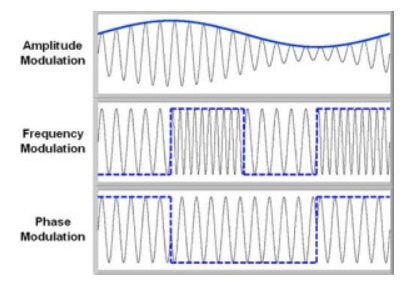
- Amplitude Modulation (AM): Amplitude of the carrier is modulated.
- Frequency Modulation (FM): Frequency of the carrier is modulated.
- Phase Modulation (PM): Phase of the carrier is modulated.
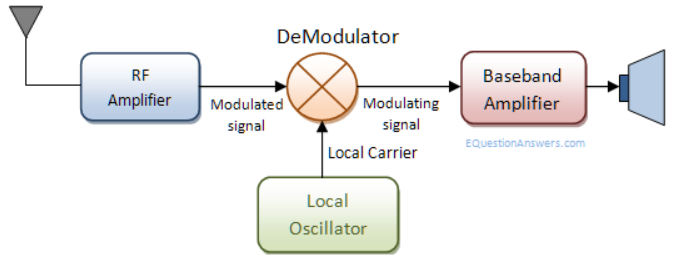
It is the process of extracting the original information-carrying signal from a modulated carrier wave.
A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is mainly used to recover the information from the modulated carrier wave.
There are different types of demodulators.
The output signal via demodulator may be sound, images or binary data.
Problem:
- Voice, Video, bit streams from computer are have lower frequency.
- They can travel few distance with wires but cannot propagate through space.
- Antenna size is half of wavelength hence antenna length for Voice, Video, bit streams would be impractical.
- Voice, Video, bit streams transmit in the same frequency range hence, all channels overlap.
Solution:
- Carrier signal are used to carry message signal to long distance.
- Modulation is used with a selected carrier frequency signal to mix baseband with carrier.
- Carrier frequency is for higher frequency radio wave length and thus antenna height would be smaller.
- Radio waves can travel longer distance with very less altitude.
- Radio wave has a wide range of frequencies to select individual non-overlapping channels.
There are mainly two types of modulations: analog and digital. They are further classified as:
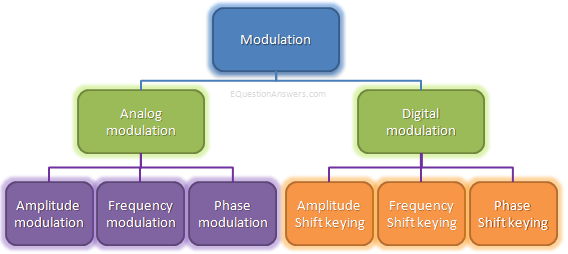
Analog Modulation:
It refers to the process of transferring analog low frequency baseband signal over a higher frequency carrier signal. Baseband signal is always analog for this type of modulation.
There are three properties of a carrier signal amplitute, frequency and phase thus there are three basic types of analog modulations.
- Amplitude Modulation (AM)
- Frequency Modulation (FM)
- Phase modulation (PM)
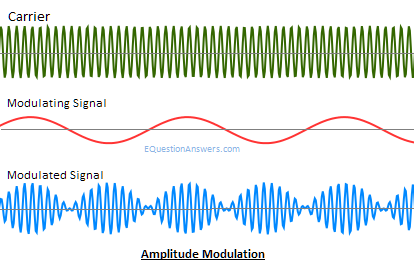
Amplitute Modulation
AM is the process of varying the instantaneous amplitude of carrier signal in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of message signal.
Thus, if m(t) is the message signal and c(t)=Acoswct then AM signal F(t) is written as
F(t)= Acoswct+m(t) coswct
F(t)=[A+m(t)] coswct
AM Advantage
- It is the simplest type of modulation.
- Hardware design of both transmitter and receiver is very simple and less cost effective.
AM Disadvange:
AM is very susceptible to noise.
Application:
1) AM radio broad cast is an example
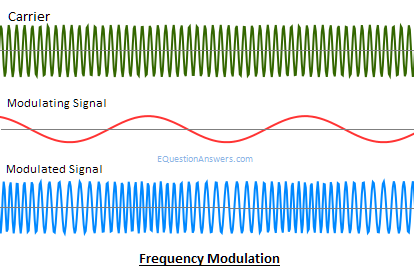
Frequency modulation
FM is the process of varying the in instantaneous frequency of Carrier signal in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of message signal.
Thus, if m(t) is the message signal and c(t)=Acoswct then FM signal will be
F(t)= Acos(wc t+kf ∫m(α)dα)
FM Advantage
Modulation and demodulation does not catch any channel noise.
FM Disadvange:
Circuit needed for FM modulation and demodulation is bit complicated than AM
Application:
1) FM radio broad cast is an example
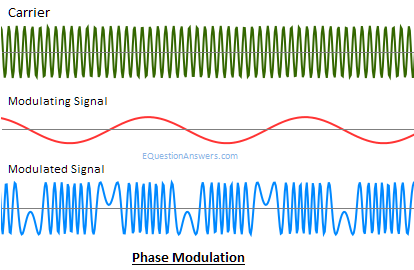
Phase modulation (PM)
It is the process of varying the instantaneous phase of Carrier signal in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of message signal.
Thus if m(t) is the message signal and c(t)=Acoswct then PM signal will be
F(t)= Acos(wct+kpm(t))
PM Advantage
Modulation and demodulation does not catch any channel noise.
PM Disadvange:
Circuit needed for PM modulation and demodulation is bit complicated than AM and FM
Application:
1) Satellite communication.
Digital modulation:
Here, base band signal is of discrete amplitude level.
For binary signal it has only two level, either high or logic 1 or low or logic 0.
The modulation scheme is mainly three types.
- ASK or Amplitude shift Key
- FSK or Frequency shift key
- PSK or Phase shift key
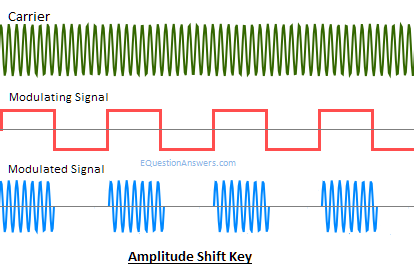
ASK or Amplitude shift Key:
In this, the carrier signal's instantaneous amplitude is varied in proportion to message signal m(t).
We have the modulated carrier m(t)coswct where coswct is the carrier signal.
As the information is an on-off signal the output is also an on-off signal where the carrier is present when information is 1 and carrier is absent when information is 0.
Thus this modulation scheme is known as on-off keying (OOK) or amplitude shift key.
Application:
- Used in our infrared remote controls
- Used in fibre optical tranmitter and receiver.
FSK or Frequency shift key:
Here, Data is transmitted by varying instantaneous frequency of the carrier.
In this modulation carrier has two predefined frequency wc1 and wc2.
When information bit is 1 carrier with wc1 is transmitted i.e. coswc1 and When information bit is 0 carrier with wc0 is transmitted i.e. coswc0
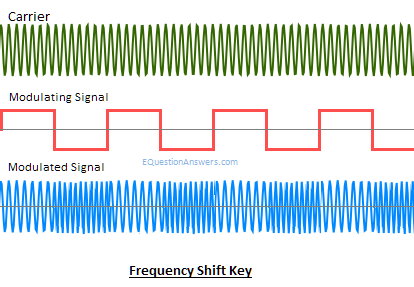
Application:
- Many modems used FSK in telemetry systems
PSK or Phase shift key:
Here, the instantaneous phase of the carrier is shifted for this modulation.
If the base band signal m(t) =1 carrier in phase is transmitted.
If m(t)=0 carrier with out of phase is transmitted i.e. cos(wct+П).
If phase shift is done in 4 different quadrants then 2bit of information can be sent at a time.
This scheme is a special case of PSK modulation known as QPSK or Quadrature Phase Shift Key.
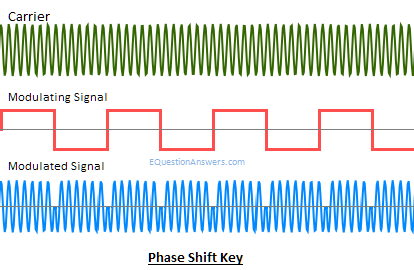
Application:
- Used in our ADSL broadband modem
- Used in satellite communication
- Used in our mobile phones
References:
- Communication system by Bruce carison . TMH.
- Electronic Communication system by Kennedy IV Edition. TMH.
- Electronic Communication system by Roddey & Coolen, Pearson.
- Telecommunication system Engg. By Freeman John Wiley
- Communication system by Haykin,Wiley