Unit - 2
Manpower Planning
- Manpower Planning is also known as Human Resource Planning.
- It consists of putting right number and right kind of people at the right place, in the right time, doing the right things for which they are best suited for.
- It has an important place in the arena of industrialization.
- It has a systematic approach and is carried out in a set procedure.
Manpower planning not only analyses the current human resources but also makes forecasts and thereby draw employment programmes.
It is advantageous to firm in following manner:
- Shortages and surpluses of human resources can be identified so that quick action can be taken wherever required.
- All the recruitment and selection programs are based on manpower planning.
- It also helps to reduce the labour cost as excess staff can be identified and hence overstaffing can be avoided.
- It also helps to identify the available talents and accordingly training programs can be chalked out to develop those talents.
- It helps in growth and diversification of business.
Macro-level HRP
- Here, HRP focuses on aligning human resources administration with the organization’s mission and overall strategic plan.
- Often called as HR strategic planning or organizational design and development.
- It examines employee management policies and procedures and their effect on human resources management.
- Its objectives may affect performance evaluation, compensation and benefits, employee recruitment, employment law compliance, labor relations and workplace safety.
Micro-level HRP
- Micro-level HRP depends on Macro-level HRP.
- It develops and implements the tactics needed to help the organization achieve its strategic objectives.
- It ensures that the business has the appropriate number of employees with the appropriate mix of knowledge, skills and abilities in the proper areas or departments.
Micro-level Basics
- It uses three basic tools.
- Demand forecasting: It uses historical and current operations data to identify future needs.
- Manpower supply analysis: It involves scanning the current labor market to determine the workforce available and analyzing any gaps between the kind of workforce needed with what is available.
- Manpower planning: It uses this information to set priorities and develop plans for employee recruitment, retention and development, and workforce reductions, if necessary.
Competency-based Management
- The competency-based management model is used to develop micro-level HRP tactics that matches the organization’s mission and strategic objectives to employee skills and knowledge.
- It ensures that employees have the mix of skills, education and experience to increase productivity over time and contain costs.
- It is a systematic and detailed examination of jobs.
- It is the process of collecting information like knowledge, skills, and the experience needed to carry out a job effectively.
- The jobholder is supposed to possess job-related knowledge useful to carry out the job easily.
- It collects and analyzes data related to a job in an organization.
- It is defined as “the process of determining by observing and study the tasks, which comprise the job, the methods and equipments, used, and the skills and attitudes required for successful performance of the job.”
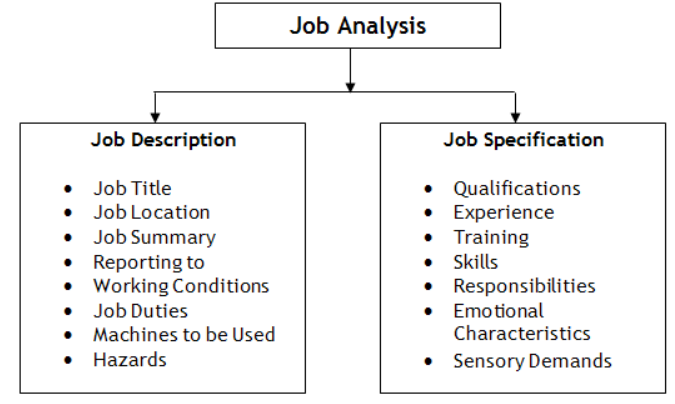
Job Description
It includes basic job-related data that is useful to advertise a specific job and attract a pool of talent including information like job title, job location, reporting to and of employees, job summary, nature and objectives of a job, tasks and duties to be performed, working conditions, machines, tools and equipments to be used by a prospective worker and hazards involved in it.
Purpose
- To collect job-related data in order to advertise for a particular job. This helps in attracting, targeting, recruiting and selecting the right candidate for the right job.
- To determine what needs to be delivered in a particular job. It clarifies what employees are supposed to do if selected for that particular job opening.
- To recruit staff with a clear view of what kind of candidate is required by a particular department or division to perform a specific task or job.
- To clarify who will report to whom.
Job Specification
It is also called as employee specifications. It is a written statement of educational qualifications, specific qualities, level of experience, physical, emotional, technical and communication skills required to perform a job, responsibilities involved in a job and other unusual sensory demands. It also includes general health, mental health, intelligence, aptitude, memory, judgment, leadership skills, emotional ability, adaptability, flexibility, values and ethics, manners and creativity, etc.
Purpose
- To help candidates analyze whether they are eligible to apply for a particular job or not on the basis of job description.
- To understand what level of qualifications, qualities and set of characteristics should be present in a candidate to make him or her eligible for the job opening.
1. Human Resource Planning:
The estimates the quantity and quality of people will be required in future.
2. Recruitment and Selection:
Job analysis serves as basis for recruitment and selection of employees in the organization.
3. Training and Development:
It enables the management to design the training and development programmes to acquire these job requirements.
4. Placement and Orientation:
The management can gear orientation programs towards helping the employees learn the required skills and qualities on the basis of information about what skills and qualities are required to do a job.
5. Job Evaluation:
It is the determination of relative worth of different jobs. It, thus, helps in developing appropriate wage and salary structures.
6. Performance Appraisal:
It involves comparing the actual performance of an employee with the standard one, i.e., what is expected of him/her.
7. Personnel Information:
Increasing number of organizations maintain computerized information about their employees. This is popularly known as Human Resource Information System (HRIS).
8. Health and Safety:
It facilitates management to take corrective measures to minimise and avoid the possibility of accidents causing human injury.
- It involves attracting candidate to fill the positions in the organization structure.
- Before recruiting, the requirement of positions must be cleared identified.
- Enterprises with a favourable public image find it easier to attract qualified candidates.
Definitions –
1. Mc Fariand, “The term recruitment applies to the process of attracting potential employees of the company.”
2. Flippo, “Recruitment is the process of searching prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for the jobs in the organization.”
Need of recruitment
1. Vacancies due to transfer, promotion, retirement, permanent disability or death of worker.
2. Creation of vacancies due to expansion, diversification or growth.
Methods
1) Direct Methods :
It includes travelling visitors to educational and professional institutions, employee’s contacts with public and manned exhibits and waiting lists.
2) Indirect Methods:
It includes advertising in newspaper radio, in trade and professional journals, technical journals, brochures etc.
3) Third Party Methods:
It includes the use of commercial and private employment agencies, state agencies, placement offices of the colleges and universities, and professional association recruiting firms.
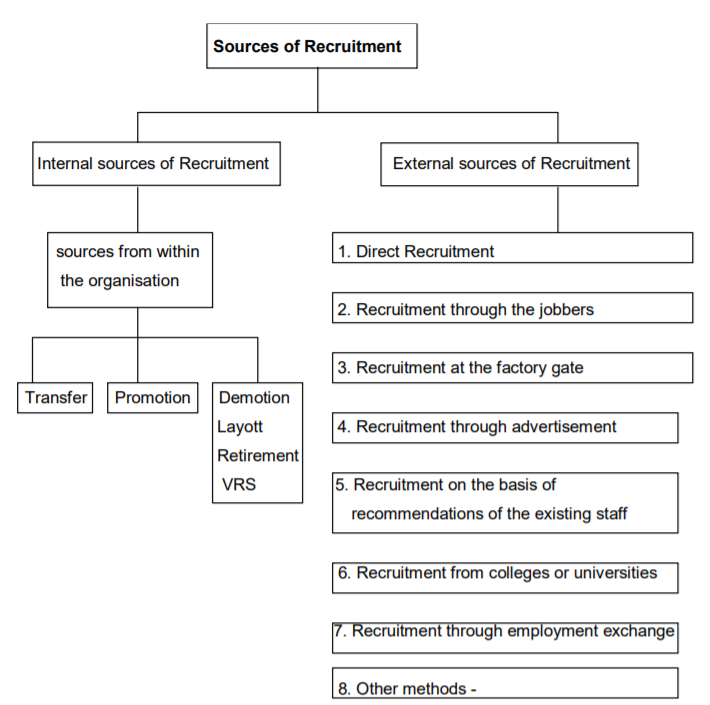
Sources of Recruitment
A. Internal sources – This method is followed mostly in Government organisations. Here, preference is given to people within the company because the best employees can be found from within the organisation itself. Under this policy, if there is any vacancy the persons already working in the organisation are appointed to fill it.
B. External sources or recruitment from outside – If Internal sources do not fulfil the needs of an organisation then they have to look for the external sources for recruitment the required number of employees with the requisite qualifications.
The external sources of recruitment may be.
1. Direct Recruitment – A separate department called personnel department is present in all organizations to select right employees. For this they receive direct applications from the candidate. The technical and clerical staff is appointed in this way.
2. Intermediaries Here the intermediary keeps a vital link between workers and employers. They are always willing to supply the required number of workers.
3. Recruitment at the factory gate –In this, large number of unemployed workers assembles at the factory gate for employment. The factory manager may select the necessary workers as per his choice.
4. Through advertisement –In this, the vacancies are advertised in the popular daily newspapers and applications are invited from the persons having required qualifications. It is most common method for recruiting skilled workers, clerical staff, managerial personnel, technical personnel.
5. Through employee referral – The existing employees recommend the suitable names for the employment.
6. Campus placements – This method is used when the recruitment of persons required for administration and technical personnel.
7. Through employment exchange – The Employment exchanges are the special offices for bringing together those workers who are in need of employment. Here, workers who want jobs make their registration where their details are recorded.
8. Other methods –
i) Badli Control system or Decasualisation of labour
Ii) Contract labour
Selection is the process of choosing the most suitable person for the current position. It is one of the most critical steps in the entire process of managing.
Steps of selection process:
1) Receiving and screening the application : In this, the applications that are received have to be screened. Here, the applications of candidates without the requisite qualification are rejected.
2) Sending the Blank application form : After preparing the list of candidates suitable for job, blank application forms will be sent to the candidates. In this application form information should be given about the name and address of the candidate, educational qualification, experience, salary expected etc.
3) Preliminary Interview : The interviewer has to decide whether the applicant is fit for job or not. By this interview the appearance, attitudes, behaviour of the candidate can be known easily.
4) Administering Tests : Tests are conducted for checking the knowledge, personal behaviour, efficiency of work and interest. Various types of tests are conducted
5) Checking References: Applicants are generally asked to give names of at least two persons to whom the firm may make a reference.
6) Interviewing : In interview, the intimation given in the application form is checked. It helps in finding out the physical appearance and mental alertness of the candidate and whether he possesses the required qualities.
7) Final Selection : On the basic of results of previous interview the candidate is informed whether he/she is selected for the said post or not.
- Induction of Employee is the first step towards gaining an employees' commitment, Induction is aimed at introducing the job and organization to the recruit and him or her to the organization.
- Induction involves orientation and training of the employee in the organizational culture, and showing how he or she is interconnected to (and interdependent on) everyone else in the organization.
References:
1. Personal management by C.B.Memoria& G.V. Gankar- Himalaya
2. Personal management & industrial relation by P.C.Tripathi-S.chand
3. Industrial relation, Trade Union &Labour Relation by G.P.Sinha& PRN Sinha, Pearson.