UNIT 3
IMAGE AND VIDEO
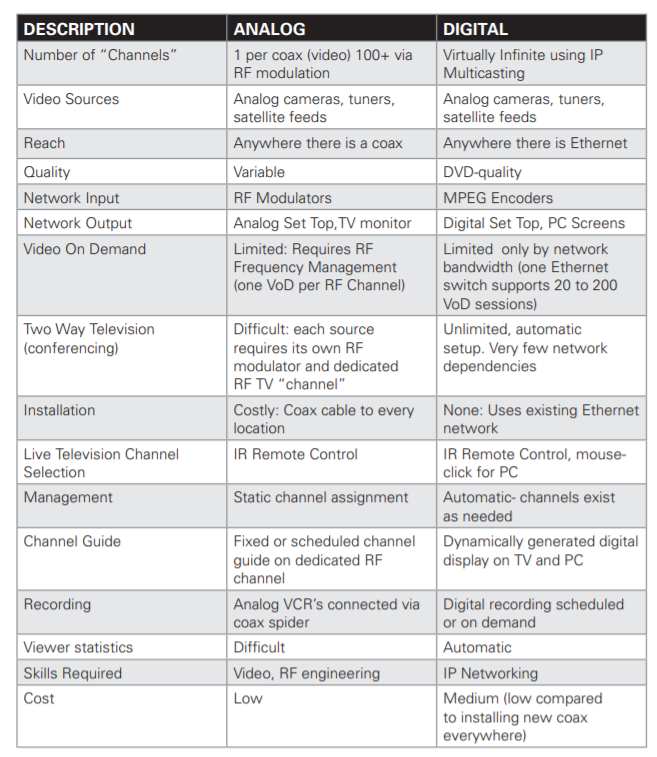
There are 5 main formats in which to store images.
1. TIFF (also known as TIF), extension: .tif
- TIFF stands for Tagged Image File Format.
- It create very large file sizes.
- TIFF images are uncompressed and thus contain a lot of detailed image data and are also extremely flexible in terms of color and content.
- TIFF is the most common file type used in photo software.
2. JPEG (also known as JPG), extension: .jpg
- JPEG stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group.
- It is used for image formatting.
- These are images that have been compressed to store a lot of information in a small-size file.
- Most digital cameras store photos in JPEG format, because then you can take more photos on one camera card than you can with other formats.
- It is compressed in a way that loses some of the image detail during the compression in order to make the file small hence known as “lossy” compression.
3. GIF, extension: .gif
- GIF stands for Graphic Interchange Format.
- This format compresses images and the compression is lossless.
- It has an extremely limited color range suitable for the web but not for printing.
- This format is never used for photography, because of the limited number of colors.
- GIFs can also be used for animations.
4. PNG, extension: .png
- PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics.
- It was created as an open format to replace GIF.
- It also allows for a full range of color and better compression.
- It’s used almost exclusively for web images, never for print images.
- For eg : When you take a screenshot on your Mac, the resulting image is a PNG–probably because most screenshots are a mix of images and text.
5. Raw image files
- Raw image files contain data from a digital camera.
- The files are called raw because they haven’t been processed and therefore can’t be edited or printed yet.
- Raw files usually contain a vast amount of data that is uncompressed. Because of this, the size of a raw file is extremely large.

- Image enhancement is the procedure of improving the quality and the information content of original data before processing.
- The common practices include contrast enhancement, spatial filtering, density slicing and FCC.
- Contrast enhancement or stretching is performed by linear transformation expanding the original range of gray level.
- Spatial filtering improves the naturally occurring linear features like fault, shear zones and lineaments.
- Density slicing converts the continuous gray tone range into a series of density intervals marked by separate color or symbol to represent different features.
JPEG
- It Stands for "Joint Photographic Experts Group."
- It is a popular image file format and commonly used by digital cameras to store photos since it supports 224 or 16,777,216 colors.
- The format also supports varying levels of compression, which makes it ideal for web graphics.
- The 16 million possible colors in a JPEG image are produced by using 8 bits for each color (red, green, and blue) in the RGB color space.
- This provides 28 or 256 values for each of the three colors, which combined allow for 256 x 256 x 256 or 16,777,216 colors.
- The JPEG compression algorithm may reduce the file size of a bitmap (BMP) image by ten times with almost no degradation in quality.
- Hence, professional digital photographers often choose to capture images in a raw format so they can edit their photos in the highest quality possible.
File extensions: .jpg
MPEG
- It stands for "Moving Picture Experts Group."
- It is an organization that develops standards for encoding digital audio and video. It works with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electro technical Commission (IEC) to ensure media compression standards are widely adopted and universally available.
- The MPEG organization has produced a number of digital media standards since its inception in 1998.
- Using MPEG compression, the file size of a multimedia file can be significantly reduced with little noticeable loss in quality. This makes transferring files over the Internet more efficient, which helps conserve Internet bandwidth.
File extensions: .MP3, .MP4, .M4V, .MPG, .MPE, .MPEG
H.261
- The H.261 standard was developed in 1988-90 for video conferencing applications over ISDN telephone lines.
- The baseline ISDN has a bit-rate of 64 Kbits/ sec and at the higher end, ISDN supports bit-rates having integral multiples (p) of 64 Kbits/sec.
- For this reason, the standard is also referred to as the p x 64 Kbits/sec standard.
- The H.261 standard supports two picture formats:
- Common Intermediate Format (CIF), having 352 x 288 pixels and are used when p ≥ 6, that is for video conferencing applications.
- Quarter of Common Intermediate Format (QCIF) having 176 x 144 pixels for the Y and 88 x 72 pixels each for U and V.
- H.261 frames are of two types
- I-frames: These are coded without any reference to previously coded frames.
- P-frames: They are coded by a forward predictive coding method in which current macro blocks are predicted from similar macro blocks in the preceding J or P-frame.
By Wireless Transmitters and Receivers
When it is difficult to run a cable to transmit video signals of the camera to the monitor, wireless transmission is needed. The wireless signals can be blocked by heavy metal walls, high voltage power lines, microwave equipment and others.
At present, the most commercialized wireless systems are;
a) 900Mhz Frequency with 300ft maximum transmission,
b) 2.4Ghz Frequency with 300ft maximum transmission, and c) 2.4Ghz Frequency with 700ft maximum transmission.
The wireless system is strictly controlled by the FCC. Most commercialized wireless systems have 4 channels; one can not use more than 4 transmitters in one area due to conflicts of the overlapped channel(s). But many additional wireless receivers can be there as needed.
Some transmitters have a built-in camera to transmit the video signals. Wireless receivers are to be connected to CCTV monitor, VCR or standard TV by RCA connectors.
Animation means giving life to any object in computer graphics. It has the power of injecting energy and emotions into the most seemingly inanimate objects. Computer-assisted animation and computer-generated animation are two categories of computer animation. It can be presented via film or video.
Animation can be used in many areas like entertainment, computer aided-design, scientific visualization, training, education, e-commerce, and computer art.
Animation Techniques
Traditional Animation frame by frame
Traditionally most of the animation was done by hand. All the frames in an animation had to be drawn by hand. Since each second of animation requires 24 frames film, the amount of efforts required to create even the shortest of movies can be tremendous.
Procedural
In a procedural animation, the objects are animated by a procedure which is a set of rules. The animator specifies rules and initial conditions and runs simulation. Rules are often based on physical rules of the real world expressed by mathematical equations.
Behavioral
In behavioral animation, an autonomous character determines its own actions, at least to a certain extent. This gives the character some ability to improvise, and frees the animator from the need to specify each detail of every character's motion.
Performance Based Motion Capture
In this the magnetic or vision-based sensors record the actions of a human or animal object in three dimensions. A computer then uses these data to animate the object.
This technology has enabled a number of famous athletes to supply the actions for characters in sports video games.
Physically Based Dynamics
Simulation uses the laws of physics to generate motion of pictures and other objects. It can be easily used to produce slightly different sequences while maintaining physical realism. It allows a higher degree of interactivity where the real person can maneuver the actions of the simulated character.
Key Framing
A key frame is a frame where we define changes in animation. Every frame is a key frame when we create frame by frame animation. When someone creates a 3D animation on a computer, they usually don’t specify the exact position of any given object on every single frame. They create key frames.
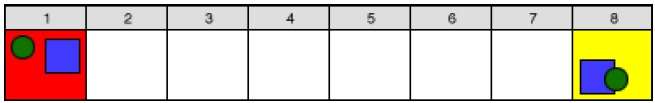
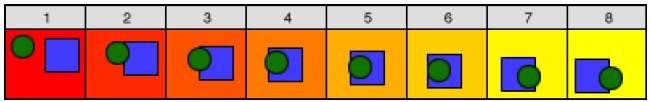
Morphing
The transformation of object shapes from one form to another form is called morphing. It is one of the most complicated transformations.
References:
- Multimedia : Computing, Communications & Applications by Ralf Steinmetz and Klara Nahrstedt, Pearson Ed.
2. Multimedia Systems Design by Prabhat K. Andleigh & Kiran Thakrar, PHI.
3. Principles of Multimedia by Parekh, TMH.