MTA
UNIT 5
Storage models and Access Techniques
- Any storage medium that utilizes magnetic patterns to represent information is considered magnetic media.
- Examples: Magnetic media and Magnetic storage is a tape drive, floppy disk and hard drive.
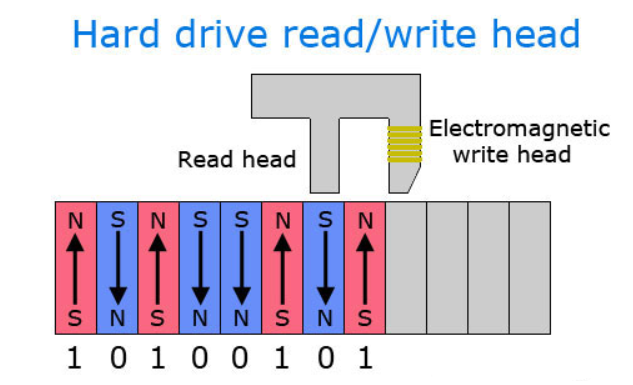
- The electromagnetic hard drive’s write head polarizes tiny sections so they face up or down ("North" or "South") to represent the binary digits 1 or 0.
- Information is read by the read head, which detects the polarization of each section of the drive to understand the data that was written.

- The compact disk (CD) are storage media that hold content in digital form and that are written and read by a laser.
- It includes all CD and DVD variations, as well as optical jukeboxes and autochangers.
- Optical media have various advantages over magnetic media such as the floppy disk.
- Optical disk capacity ranges up to 6 gigabytes.
- One optical disk holds about the equivalent of 500 floppies worth of data.
- Optical media is durable. They last up to seven times as long as traditional storage media.
- The Optical Storage Technology Association (OSTA) is an international trade organization dedicated to the promotion of standardized writable optical technologies and related products.
- Computers use particular kinds of file systems to store and organize data on media, such as a hard drive, the CDs, DVDs, and BDs in an optical drive or on a flash drive.
- A file system is an index or database containing the physical location of every piece of data on the hard drive or another storage device. This data is organized in folders called directories, which contains other folders and files.
- Any device that stores data employs some type of file system.
- Example: your Windows computer, your Mac, your smart phone, your bank's ATM etc.
- The Microsoft Windows operating systems have always supported various versions of the FAT file system.
- FAT stands for File Allocation Table. It maintains a table of each file's space allocation.
- Files on a storage device are kept in sectors. Sectors marked as unused can store data, typically in groups of sectors called blocks. It's the file system that identifies the size and position of the files as well as which sectors are ready to be used.
- Without a structure for organizing files, it not only would be next to impossible to remove installed programs and retrieve specific files, but no two files could exist with the same name because everything might be in the same folder.
References:
- Multimedia : Computing, Communications & Applications by Ralf Steinmetz and Klara Nahrstedt, Pearson Ed.
2. Multimedia Systems Design by Prabhat K. Andleigh & Kiran Thakrar, PHI.
3. Principles of Multimedia by Parekh, TMH.
0 matching results found
Browse by Topics