Unit - 5
Wages And Salary Administration
Meaning of wage and salary administration
According to D.S. Beach “Wage and Salary Administration refers to the establishment and implementation of sound policies and practices of employee compensation. It comprises of areas such as job evaluation, surveys of wage and salaries, analysis of relevant organisational problems, development and maintenance of wage structure, establishing rules for administrating wages, wage payment incentives, profit sharing, wage changes and adjustments, supplementary payments, control of compensation costs and other related items.”
Purpose
The purpose for wage and salary administration are as follows:-
- To maintain and establish just wage and salary structure.
- To maintain and establish fair labor-cost structure i.e. ideally balancing the contradicting personnel interests such that the contentment is maximum between the employers and employees and conflicts are minimum.
- The concern of wages and salary administration is to deal with the rewards, motivation and financial aspects. Therefore managers are people who interpret and analyse their employees so they can be rewarded individually according to their needs.
- To make sure that the employees know about the wage and salary policies, practices, procedures and latest amendments.
- To put together a group of people who are dynamic, skilled and talented, so that their productivity increases.
- To institute laws and agreements to ensure proper compensation to employees.
Principle
Following principles are needed to be followed in the wage and salary administration:
- Protection of Interests: The salary policy should be made in such a way that the interests of employees, employers and consumers are kept in view so that the interests of all these people are protected.
- Maintain uniformity: The policy should be developed with the idea of ensuring uniformity among the employees.
- Planning consistency: The administration must maintain their consistency with various organisational programmes and plans.
- Participation of employees: The management must make sure that the employees know and understand about the wage and salary policy of the organization.
- Periodical revision: Wage and salary policies should be revised and reviewed from time to time to adapt with the changing needs of the employees. For revision of salaries, a wage or salary committee should be formed against an individual judgment, in order to prevent the biased nature of a manager.
- Adaptable and flexible: The administration needs to be adaptable and flexible towards the external and internal conditions of the organization.
Factors influencing wage & salary administration
The salary payment is a major factor that affect the labor - management relations. Employees are always concerned about their wages as their wages are directly linked to their standard of living. Higher the pay higher the standard of living. But management do not tend to pay high wages as because of it the production cost goes up and there is decrease in profits as well.
A number of factors influence the wages or salary paid to the employees. Those factors are listed as follows:
- Supply and Demand: The labour market and supply forces determine the organisational wage structure. If the demand for a particular type of labour is more than the supply then the wages will be more. On the other hand, if supply of labour is more and demand is less then the wages will be lower.
2. Living cost: The rates of salary are directly influenced by living cost of a certain place. The workers only accept a wage which ensures their minimum standard of living. Wages also needs to be adjusted according to price index number. The increase in price index will enhance the purchasing power of workers and hence they will demand a higher salary.
3. Bargaining Power of Trade Unions: The wages are also influenced by the trade unions bargaining power. Stronger the trade union higher will be the wages. The strength of a trade union is determined by its financial position, membership and leadership type. Union’s sometimes goes on strike to increase their wages. If the workers are not united then employers will offer low wages.
4. Economy: Economy also influences the wage and salary fixation. Even if some organisations may thrive during recession, there is no doubt that economy affects reimbursement decisions. In a depressed economy their might be increase in the labour supply, which in turn lowers the wage rate.
5. Enterprises ability to Pay: The enterprise’s ability to pay will always influence the wage rates. If the company is in loss then it may not be able to pay high wage. A profitable company may pay more to attract good employees. During the period of profitability, workers are generally paid higher wages because management wants to share the profits with employees.
6. Job Requirements: Job requirements or demands are one of the major factors which influences the wages. It largely depends on the physical, mental and difficulty level in a particular job. The worth of a job can be estimated through job evaluation. Simple, routine tasks that can be completed by people with minimum skills and hence receive relatively low pay. On the other hand, complex, challenging tasks that can be done by people with high skill levels generally receiving a high salary.
Wage is the money paid to the employees by their employers. It is a reimbursement which is paid to the worker for the work he performs that helps the corporate achieve their objectives. But wages do not include travelling allowances, housing accommodation, provident funds contributed by the employees and welfare allowances.
Wages are usually paid only after the completion of a certain amount of work in a certain time. It can be paid for a day, a week or a month.
Salary is a repayment to the professionals for the services they provide on weekly, monthly or annual basis. Salary is usually given to office employees or professionals. Salary generally includes the travelling allowances, provident funds, housing accommodation and welfare allowances. Some other benefits enjoyed by salaried employees are overtime pay, holiday pay, social security benefits and bonuses.
Minimum wage
Minimum wages refer to the minimum amount of reimbursement that the employer needs to pay the workers for the work they completed during a certain period of time and which cannot be reduced by a contract or mutual agreement. Minimum wages can be set by a competent authority, a wage council or a wage board. Minimum wages can also be set with a group of rules and laws.
The purpose of minimum pay is to guard employees against unduly low pay. They help guarantee a just share of the profits to all or any, and a minimum living wage to all or any those who are employed and are in need for such protection. Minimum wages can also be one element of a policy that can overcome impoverishment and reduce difference, in between men and women, by promoting the right to equal remuneration for work of equal worth.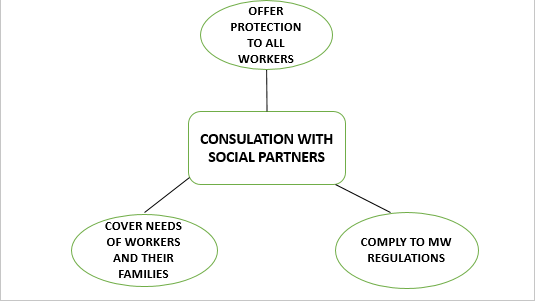
Fig- Main dimensions of effective minimum wages
Fair wage
Fair wages are the minimum wages that has to be paid for specific occupations just like the wages paid by the contractors operating for governments with fair wage policies. These policies usually apply to trades, construction and sometimes cleaning and security workers, and are often tied to union wage rates. They are made to ensure that the contractors pay decent wages on government contracts instead of slashing wages and benefits.
Living wage
Living wage is the minimum wage which should be provided so that an individual can pay for basic needs according to the cost of living in a specific community. Living wages are mostly calculated on an hourly basis and vary from city to city according to the standard of living of the people.
Money wage
Money wage also known as nominal wage is the payment done to the workers in the form of money and does not accounts for inflation rates or any other market condition. For example, if a worker receives $15 per hour from their organization in exchange of the services provided, then that is the nominal wage. Nominal wages do not have a calculation or formula. The basic determinants of the nominal wages is the government regulations and the organization’s compensation policy within its capacity.
Real wage
Real wages are the wages that take inflation rates into consideration. These wages determine the purchasing power of the individual and the amount of goods or services the individual can purchase in the current market conditions. In other words, it can also be defined as the actual amount of goods and services the employee can purchase with the payments given after inflation has been considered.
Time rate
According to this method the workers are paid the wages on the basis of time as, per hour, per day, per week, per fortnight or per month etc. The system do not take account of the production of the employees during this time.
The amount of wages under this system is calculated as under:
Wages = Time spent by the worker × Rate of wages according to time.
Merits of Time Rate System:
1. Simple to calculate: It is easy to calculate the amount of wage according to this system.
2. Certainty of the Amount of the reimbursement: The system provides certainty to the amount of wages to the worker. It develops the feeling of certainty and confidence among them.
3. High Quality of Production: As in this system the wage payment is not concerned with quantity of production hence the quality of production under this system is usually high.
4. Utilisation of Production factors: This system is not related to speed thus the workers perform their work confidently which results in proper utilisation of the factors of production.
5. Co-Operation between Labour and Capital: As this system of wage payment is dependent on the time the workers spend it brings peace between the workers and the industrialists. Thus, it develops harmony and cooperation between labour and capitalists.
Demerits of Time Rate System:
1. Need of Intensive Supervision: The system requires intensive supervision over workers which results in increase in the cost of supervision.
2. Lack of Incentive: As this system of wage payment depend on time it provide equal payment to both the efficient and inefficient workers. Thus, efficient workers do not get any incentive for more production.
3. Encouragement of Labour Unions: This system encourages labour unions. Sometimes, these labour unions misuse their powers.
4. Misuse of Time by Workers: The workers do not make proper utilisation of their time, under this system of wage payment.
5. Fall in the Quantity of Production: Under this system of wage payment, the quantity of production decreases because the workers do not get any incentive for increase in the production.
Piece Rate System
The workers are paid the wages on the basis of quantity and quality of work performed by them, under this system of wage payment. The rates of wages are determined according to quantity and quality of work and the workers are paid according to these rates.
The amount of wages to be paid to a worker under this system is calculated as under:
Wages = Units of production × Rate per unit.
Merits of Piece Rate System:
1. Incentive to More Work: The system encourages the workers to do more work as they get their wages according to their work.
2. Proper Utilisation of Machines: The workers use their machines and equipment with proper care because they feel that if their machine is out of order, their work would caught up and in turn their wages will be low.
3. Increase in the Quantity of Production: The workers get more payment with more production thus they make their best efforts to increase the production.
4. Best Utilisation of Time: As the workers are paid according to their work, they make the best utilisation of their time. They do not waste their time.
5. Improvement in the Standard of Living of Workers: Workers get more wages because they produce more. It increases their efficiency and productivity. It increases their remuneration also which improves their standard of living.
Demerits of Piece Rate System:
1. Lack of Unity among Workers: This system creates a lack of unity among workers. They feel that they are competitors.
2. Loss to Workers on the Failure of Machines: If for some reason, the machines fail or the power fails, the workers cannot do their jobs and they lose their wages.
3. Quality of Production: The workers do not pay proper attention towards the quality of production. They just want to increase the speed of production and thus the quality of the product deteriorates.
4. Adverse Effect on the Health of Workers: The system motivates the workers to do more and more work which in turn affects their health of adversely.
5. Unsuitable for Artistic Work: This system is not suitable for artistic work because the artistic works is not paid on the basis of quantity of production.
Financial and non-financial incentive
Incentives act as a positive influence on a worker that helps to improve his performance. Thus, it can be stated that the measures taken by the management to improve the performance of its employees are known as incentives. The incentives are broadly classified as financial incentives and non-financial incentives.
Financial incentive
In today’s socio-economic condition cash has become a really necessary a part of our lives. We need cash to satisfy most our desires because it has purchasing power. Thus, money incentives are those incentives that are in direct monetary type i.e. cash or are often measured in financial terms.
Financial incentives are often provided on a private or cluster basis and satisfy the financial and future security desires of people. The foremost ordinarily used money incentives are:
(a) Pay and Allowances
Salary is that the basic incentive for each worker to work expeditiously for a corporation. Earnings includes basic pay, inflation allowance, house rent allowance, and similar alternative allowances. Workers are also given increments in basic pay each year and additionally a rise in their allowances from time-to-time. Typically these increments are given to support the performance of the worker throughout the year.
(b) Bonus
It is a total of cash offered to associate degree worker on top of the earnings or wages as a bequest for his good performance.
(c) Productivity connected Wage Incentives
Many wage incentives are connected with the rise in productivity at an individual or cluster level. For example, an employee is paid fifty rupees per piece if he produces 50 items every day however if he produces more than 50 pieces a day, he's paid five rupees more per piece. Thus, on the 51st piece, he is going to be paid fifty five rupees.
(d) Profit-Sharing
Sometimes the staff are given a share within the profits of the organization. This motivates them to perform expeditiously and provide their best to increase the profits of the organization.
(e) Stock choices or Co-partnership
Under the staff stock option plan, the worker is offered the normal shares of the corporate at a price under its market value for a specified amount of your time. These are non-standardized offers and shares are issued as a personal contract between the leader and worker. These are typically offered to management as a vicinity of their social control compensation package.
Non-Financial Incentives
Apart from the financial and future security desires, a person additionally has psychological, social and emotional desires. Satisfying these desires additionally plays a very important role in their motivation. Non-financial incentives focus chiefly on the fulfillment of these desires and so can't be measured in terms of cash.
However, there are possibilities that a specific non-financial incentive may involve the financial incentive. For example, once an individual is promoted his psychological desires are fulfilled as he gets a lot of authority, his status will increase and at the similar time, he is benefitted with an increase in earnings. The foremost common non-financial incentives are:
(a) Status
With regard to a corporation, status refers to the position within the hierarchy of the structure chart. The amount of authority, responsibility, recognition, salary, perks, etc. verify the status of associate degree worker within the organization.
A person at the highest level management has a lot of authority, responsibility, recognition and earnings and vice-versa. Status satisfies the conceit and psychological desires of a person and successively, motivates him to work harder.
(b) Organizational Climate
Organizational climate refers to the environmental characteristics of a corporation that are perceived by its workers concerning the organization and it has a significant influence on their behavior. Every organization features a completely different organizational climate that distinguishes it from alternative organizations..
(c) Career Advancement chance
It is important for a corporation to possess an appropriate talent development program and a sound promotion policy for its workers. It works as a booster for them to perform well and get promoted.
(d) Job Enrichment
It refers to the coming up with jobs in a simple way that it involves the next level of information and talent, a range of work content, a lot of authority and responsibility among the workers.
(e) Job Security
Job security provides future stability and a way of security among the staff. The staff are not concerned about the future and so work with a lot of enthusiasm. Due to the state unemployment in our country, job security works as an excellent incentive for the staff.
Method of wage payment based on result
The workers are paid the wages on the basis of quantity and quality of work performed by them, under this system of wage payment. The rates of wages are determined according to quantity and quality of work and the workers are paid according to these rates.
The amount of wages to be paid to a worker under this system is calculated as under:
Wages = Units of production × Rate per unit.
Merits of Result Based System:
1. Incentive to More Work: The system encourages the workers to do more work as they get their wages according to their work.
2. Proper Utilisation of Machines: The workers use their machines and equipment with proper care because they feel that if their machine is out of order, their work would caught up and in turn their wages will be low.
3. Increase in the Quantity of Production: The workers get more payment with more production thus they make their best efforts to increase the production.
4. Best Utilisation of Time: As the workers are paid according to their work, they make the best utilisation of their time. They do not waste their time.
5. Improvement in the Standard of Living of Workers: Workers get more wages because they produce more. It increases their efficiency and productivity. It increases their remuneration also which improves their standard of living.
Demerits of Result Based System:
1. Lack of Unity among Workers: This system creates a lack of unity among workers. They feel that they are competitors.
2. Loss to Workers on the Failure of Machines: If for some reason, the machines fail or the power fails, the workers cannot do their jobs and they lose their wages.
3. Quality of Production: The workers do not pay proper attention towards the quality of production. They just want to increase the speed of production and thus the quality of the product deteriorates.
4. Adverse Effect on the Health of Workers: The system motivates the workers to do more and more work which in turn affects their health of adversely.
5. Unsuitable for Artistic Work: This system is not suitable for artistic work because the artistic works is not paid on the basis of quantity of production.
References:
1. Personal management by C.B.Memoria& G.V. Gankar- Himalaya
2. Personal management & industrial relation by P.C.Tripathi-S.chand
3. Industrial relation, Trade Union &Labour Relation by G.P.Sinha& PRN Sinha, Pearson.