UNIT 5
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
Contention may refer to the below any of the following:
1. A contention is meant to be a conflict when two or more programs will try to use the same resource or setting at the same time.
2. When referring to a network, a contention is when more than one computer try to access the same file at the same time.
3. With wireless networking, a contention is when more than one data stations attempt to transmit at the very same time over the shared channel.
Short for carrier sense multiple access/collision detection, CSMA/CD is a MAC It defines how network devices will respond when two of the devices attempt to use a data channel simultaneously and then encounter a data collision. The CSMA/CD rules define how long the device will wait if a collision occurs. The medium is often used for multiple data nodes, so that each data node receives transmissions from each of the other nodes on the same medium.
There are several CSMA access modes such as: 1-persistent, P-persistent, and O-persistent. 1-persistent is used in CSMA/CD systems, like Ethernet. This mode waits for the medium to become idle, and then transmits data. P-persistent is used in CSMA/CA systems, like Wi-Fi network. This mode waits for the medium to become idle, and then transmits data with a probability p. If the data node does not transmit the data (a probability of 1-p), the sender waits for the medium to become idle again and then transmit the data with the same probability p. O-persistent is used by Cobra Net, Lon Works, and the controller area network. This mode assigns a transmission order to each of the data node. When the medium becomes idle, the data node will next in line can transmit the data. The data node next in line waits for the medium to become idle again and then transmits its data. After each data node transmits data, the transmission order is then updated to reflect what the data nodes have already transmitted, moving each data node through the queue or line form.
There are many network topologies that can be used for Ethernet communications. The actual form used will depend upon the requirements of work to be done.
- Point to point: This is the simplest configuration as only two of the network units are used. In this simple structure the cable is called the network link. Links of this nature are used to transport data from one place to the other place and where it is convenient to use Ethernet as transport mechanism.
- Coaxial bus: This type of Ethernet network is not commonly used these days. The systems used a coaxial cable where the units of the network were located along the length of the cable. The segment lengths were limited to 500 metres, and it was possible to place up to 1024 DTEs along the length. Although this form of network topology is not installed these days, a very few legacy systems might just still be using it. In view of the way in which it operates, with several nodes on the same leg, the CSMA/CD anti-collision scheme is used.
- Star network: This type of Ethernet network has been the very dominant topology since the early 1990s. It comprises of a central network unit, which may be what is termed to be a multi-port repeater or hub, or a network switch.
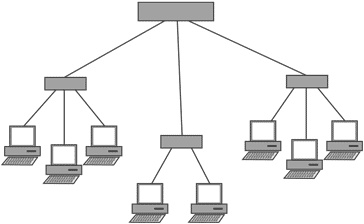
Typical Ethernet data networking topology where all the connections to other nodes radiate out from this and are point to point links. It is this type of network topology that is used and then extended. Connections tend to extend out from a central hub using a series of routers or switches to divert the data to the required end node.
Network repeaters can receive and can retransmit incoming electrical wireless or optical signals with the help of physical media like Ethernet or WIFI. Data transmission only span a limited distance before the quality of the signal gets degrades. Repeaters can attempt to preserve signal integrity and extend the distance over which data can safely travel. A repeater is a small device that plugs directly into a power outlet. Positioning the repeater in the right direction is important Locate the repeater where the Wi-Fi signal is strong. The repeater connects to the Wi-Fi network and boosts the signal strength from its location outward.
Classification of Repeaters
Repeaters can be classified into two categories.
- Local Repeaters
- Remote Repeaters.
Local repeaters are used to connect local area network segments separated by a very small distance.
Remote repeaters are used to connect local area network segments that are far from each other. A transmission line known as a link segment is provided between two remote repeaters. No nodes can be connected to this line.
Introduction
Ethernet is very popular physical layer LAN technology which is in use today. It defines that how many conductors that are required for a connection, the performance thresholds that can be expected, and most importantly provides the framework for data transmission. A standard Ethernet network can transmit the data at a rate up to 10 Megabits per second (10 Mbps). Other LAN types include Token Ring, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Local Talk.
Ethernet is popular because it strikes a very good balance between speed, cost and ease of installation. These benefits, combined with wide acceptability in the computer marketplace and the ability to support virtually all the popular network protocols, which make Ethernet an ideal networking technology for most of the computer users today.
The Institute for Electrical and Electronic Engineers developed an Ethernet standard that is known as IEEE Standard 802.3. This standard defines the rules for configuring an Ethernet network and then also specifies how the elements in an Ethernet network interact with one another and work. By adhering to the IEEE standard, network equipment and network protocols can communicate very efficiently.
Ethernet
It is a standard communication protocol which is embedded in software and hardware devices. Ethernet is used for building a LAN. The local area network is a computer network that interconnects a group of computers and shares the information through cables or wires.
Wired Ethernet Network
A wired network is when there is an Ethernet cable connected from each port linking one device to another, therefore establishing a network connection. Even when there are multiple devices in different areas of a property a cable connects to each component separately. Generally a hub router or switch is required to operate numerous PCs. CAT6 cable is the standard wire used and many new homes are being pre wired during construction to save time at the same time as future proofing there house for year to come.
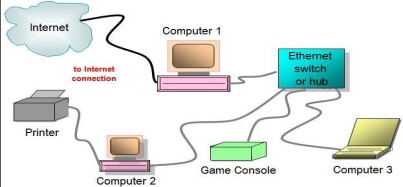
Wireless Ethernet
As the name suggests wireless networks operate wirelessly. To use a wireless network a modem preferably with more than one Ethernet connection is required. A cable runs from the internet access point to the modem. Then a system transmitting radio waves enables components to connect without running a cable between each device.
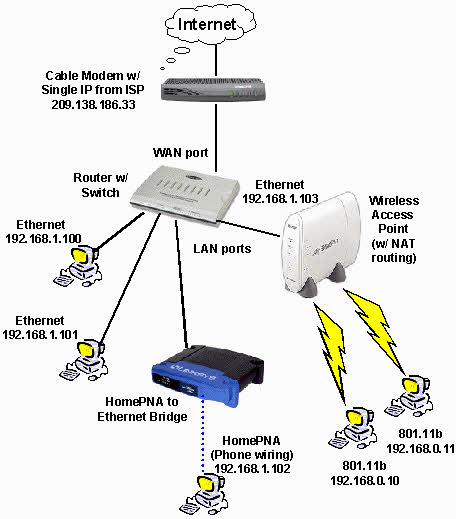
There are 3 types of Ethernet networks
1. Fast Ethernet
2. Giga Ethernet
3. Switch Ethernet
Ethernet types are as follows:
Fast Ethernet
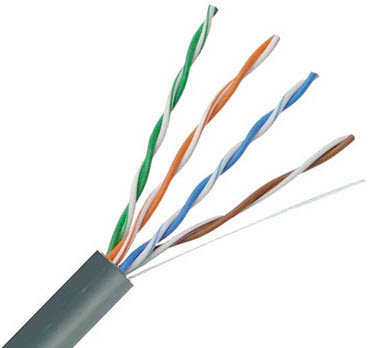 Twisted pair cable
Twisted pair cable
The fast Ethernet is a type of Ethernet network that can be transfer the data at a speed of 100 Mbps using a twisted-pair cable or a fibre-optic cable. The older 10 Mbps Ethernet is still used, but such kind of networks does not provide necessary bandwidth for some network-based video applications.
Fast Ethernet is based on CSMA/CD Media Access Control (MAC) protocol, and use10BaseT cabling. Data can move from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps without any protocol translation or changes done to the application and networking software.
Gigabit Ethernet
 Optic fibre cable
Optic fibre cable
The Gigabit Ethernet is a type of Ethernet network that is capable of transferring data at a speed of 1000 Mbps based on a twisted-pair or fibre optic cable, and it is very commonly used. The type of twisted-pair cables that support Gigabit Ethernet is the Cat 5e cable, where all the four pairs of twisted wires of the cable are used to achieve the very high data transfer rates. The 10 Gigabit Ethernet is a very latest generation Ethernet capable of transferring data at a speed of 10 GBPS using twisted-pair or fibre optic cable.
Switch Ethernet
Multiple network devices in a LAN require network equipment’s for instance a network switch or hub. When using a network switch, a regular network cable which is used instead of a crossover cable. The crossover cable consists of a transmission pair at one of the end and a receiving pair at the other end.
The main function of a network switch is to forward the same data from one device to another device on the same network. Thus a network switch performs this task efficiently as the data which is transferred from one device to another without affecting other devices on the same network.
 Switch Ethernet
Switch Ethernet
The network switch normally gets supports different data transfer rates. The most commonly data transfer rates which include 10 Mbps – 100 Mbps for fast Ethernet, and 1000 Mbps – 10 GBPS for the latest Ethernet.
Switch Ethernet uses the star topology, which is organized around switch. The switch in a network uses a mechanism which is filtering and switching mechanism similar to the one used by the gateways, in which these techniques have been in use for a very long time.
References:
- Data Communication & Networking by Forouzan, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Network, 4e, by Andrew S. Tenenbaum, Pearson Education/ PHI.
- Data Communication and Computer Networks, by Prakash C.Gupta, PHI.
- Networking Ali-in-one Desk Reference by Doug Lowe, Wiley Dreamtech
- Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach featuring the Internet, 3e by James F.Kurose.
- Computer Network by Godbole, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Networking, by Stanford H. Rowe, Marsha L. Schuh
UNIT 5
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
Contention may refer to the below any of the following:
1. A contention is meant to be a conflict when two or more programs will try to use the same resource or setting at the same time.
2. When referring to a network, a contention is when more than one computer try to access the same file at the same time.
3. With wireless networking, a contention is when more than one data stations attempt to transmit at the very same time over the shared channel.
Short for carrier sense multiple access/collision detection, CSMA/CD is a MAC It defines how network devices will respond when two of the devices attempt to use a data channel simultaneously and then encounter a data collision. The CSMA/CD rules define how long the device will wait if a collision occurs. The medium is often used for multiple data nodes, so that each data node receives transmissions from each of the other nodes on the same medium.
There are several CSMA access modes such as: 1-persistent, P-persistent, and O-persistent. 1-persistent is used in CSMA/CD systems, like Ethernet. This mode waits for the medium to become idle, and then transmits data. P-persistent is used in CSMA/CA systems, like Wi-Fi network. This mode waits for the medium to become idle, and then transmits data with a probability p. If the data node does not transmit the data (a probability of 1-p), the sender waits for the medium to become idle again and then transmit the data with the same probability p. O-persistent is used by Cobra Net, Lon Works, and the controller area network. This mode assigns a transmission order to each of the data node. When the medium becomes idle, the data node will next in line can transmit the data. The data node next in line waits for the medium to become idle again and then transmits its data. After each data node transmits data, the transmission order is then updated to reflect what the data nodes have already transmitted, moving each data node through the queue or line form.
There are many network topologies that can be used for Ethernet communications. The actual form used will depend upon the requirements of work to be done.
- Point to point: This is the simplest configuration as only two of the network units are used. In this simple structure the cable is called the network link. Links of this nature are used to transport data from one place to the other place and where it is convenient to use Ethernet as transport mechanism.
- Coaxial bus: This type of Ethernet network is not commonly used these days. The systems used a coaxial cable where the units of the network were located along the length of the cable. The segment lengths were limited to 500 metres, and it was possible to place up to 1024 DTEs along the length. Although this form of network topology is not installed these days, a very few legacy systems might just still be using it. In view of the way in which it operates, with several nodes on the same leg, the CSMA/CD anti-collision scheme is used.
- Star network: This type of Ethernet network has been the very dominant topology since the early 1990s. It comprises of a central network unit, which may be what is termed to be a multi-port repeater or hub, or a network switch.
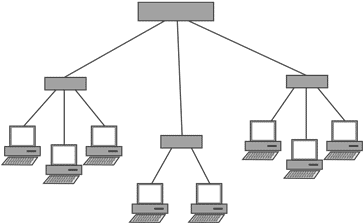
Typical Ethernet data networking topology where all the connections to other nodes radiate out from this and are point to point links. It is this type of network topology that is used and then extended. Connections tend to extend out from a central hub using a series of routers or switches to divert the data to the required end node.
Network repeaters can receive and can retransmit incoming electrical wireless or optical signals with the help of physical media like Ethernet or WIFI. Data transmission only span a limited distance before the quality of the signal gets degrades. Repeaters can attempt to preserve signal integrity and extend the distance over which data can safely travel. A repeater is a small device that plugs directly into a power outlet. Positioning the repeater in the right direction is important Locate the repeater where the Wi-Fi signal is strong. The repeater connects to the Wi-Fi network and boosts the signal strength from its location outward.
Classification of Repeaters
Repeaters can be classified into two categories.
- Local Repeaters
- Remote Repeaters.
Local repeaters are used to connect local area network segments separated by a very small distance.
Remote repeaters are used to connect local area network segments that are far from each other. A transmission line known as a link segment is provided between two remote repeaters. No nodes can be connected to this line.
Introduction
Ethernet is very popular physical layer LAN technology which is in use today. It defines that how many conductors that are required for a connection, the performance thresholds that can be expected, and most importantly provides the framework for data transmission. A standard Ethernet network can transmit the data at a rate up to 10 Megabits per second (10 Mbps). Other LAN types include Token Ring, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Local Talk.
Ethernet is popular because it strikes a very good balance between speed, cost and ease of installation. These benefits, combined with wide acceptability in the computer marketplace and the ability to support virtually all the popular network protocols, which make Ethernet an ideal networking technology for most of the computer users today.
The Institute for Electrical and Electronic Engineers developed an Ethernet standard that is known as IEEE Standard 802.3. This standard defines the rules for configuring an Ethernet network and then also specifies how the elements in an Ethernet network interact with one another and work. By adhering to the IEEE standard, network equipment and network protocols can communicate very efficiently.
Ethernet
It is a standard communication protocol which is embedded in software and hardware devices. Ethernet is used for building a LAN. The local area network is a computer network that interconnects a group of computers and shares the information through cables or wires.
Wired Ethernet Network
A wired network is when there is an Ethernet cable connected from each port linking one device to another, therefore establishing a network connection. Even when there are multiple devices in different areas of a property a cable connects to each component separately. Generally a hub router or switch is required to operate numerous PCs. CAT6 cable is the standard wire used and many new homes are being pre wired during construction to save time at the same time as future proofing there house for year to come.
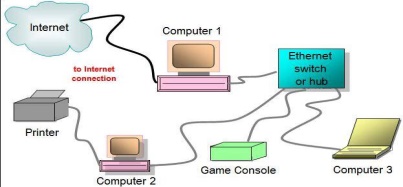
Wireless Ethernet
As the name suggests wireless networks operate wirelessly. To use a wireless network a modem preferably with more than one Ethernet connection is required. A cable runs from the internet access point to the modem. Then a system transmitting radio waves enables components to connect without running a cable between each device.
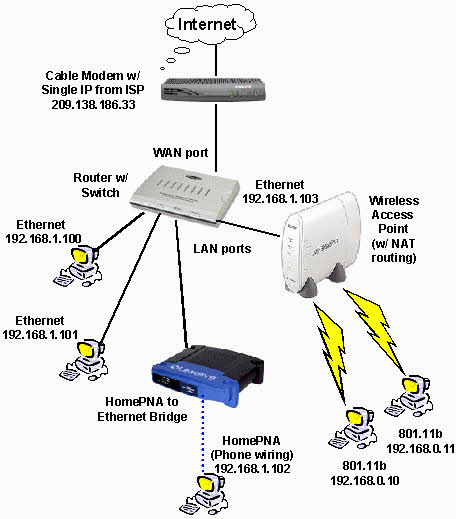
There are 3 types of Ethernet networks
1. Fast Ethernet
2. Giga Ethernet
3. Switch Ethernet
Ethernet types are as follows:
Fast Ethernet
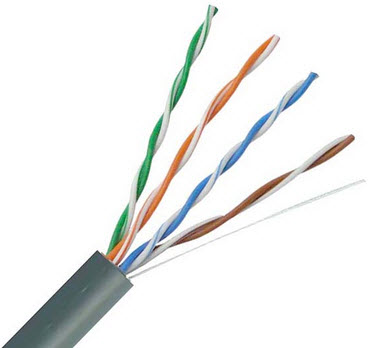 Twisted pair cable
Twisted pair cable
The fast Ethernet is a type of Ethernet network that can be transfer the data at a speed of 100 Mbps using a twisted-pair cable or a fibre-optic cable. The older 10 Mbps Ethernet is still used, but such kind of networks does not provide necessary bandwidth for some network-based video applications.
Fast Ethernet is based on CSMA/CD Media Access Control (MAC) protocol, and use10BaseT cabling. Data can move from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps without any protocol translation or changes done to the application and networking software.
Gigabit Ethernet
 Optic fibre cable
Optic fibre cable
The Gigabit Ethernet is a type of Ethernet network that is capable of transferring data at a speed of 1000 Mbps based on a twisted-pair or fibre optic cable, and it is very commonly used. The type of twisted-pair cables that support Gigabit Ethernet is the Cat 5e cable, where all the four pairs of twisted wires of the cable are used to achieve the very high data transfer rates. The 10 Gigabit Ethernet is a very latest generation Ethernet capable of transferring data at a speed of 10 GBPS using twisted-pair or fibre optic cable.
Switch Ethernet
Multiple network devices in a LAN require network equipment’s for instance a network switch or hub. When using a network switch, a regular network cable which is used instead of a crossover cable. The crossover cable consists of a transmission pair at one of the end and a receiving pair at the other end.
The main function of a network switch is to forward the same data from one device to another device on the same network. Thus a network switch performs this task efficiently as the data which is transferred from one device to another without affecting other devices on the same network.
 Switch Ethernet
Switch Ethernet
The network switch normally gets supports different data transfer rates. The most commonly data transfer rates which include 10 Mbps – 100 Mbps for fast Ethernet, and 1000 Mbps – 10 GBPS for the latest Ethernet.
Switch Ethernet uses the star topology, which is organized around switch. The switch in a network uses a mechanism which is filtering and switching mechanism similar to the one used by the gateways, in which these techniques have been in use for a very long time.
References:
- Data Communication & Networking by Forouzan, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Network, 4e, by Andrew S. Tenenbaum, Pearson Education/ PHI.
- Data Communication and Computer Networks, by Prakash C.Gupta, PHI.
- Networking Ali-in-one Desk Reference by Doug Lowe, Wiley Dreamtech
- Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach featuring the Internet, 3e by James F.Kurose.
- Computer Network by Godbole, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Networking, by Stanford H. Rowe, Marsha L. Schuh