UNIT 7
The Network Layer
Introduction
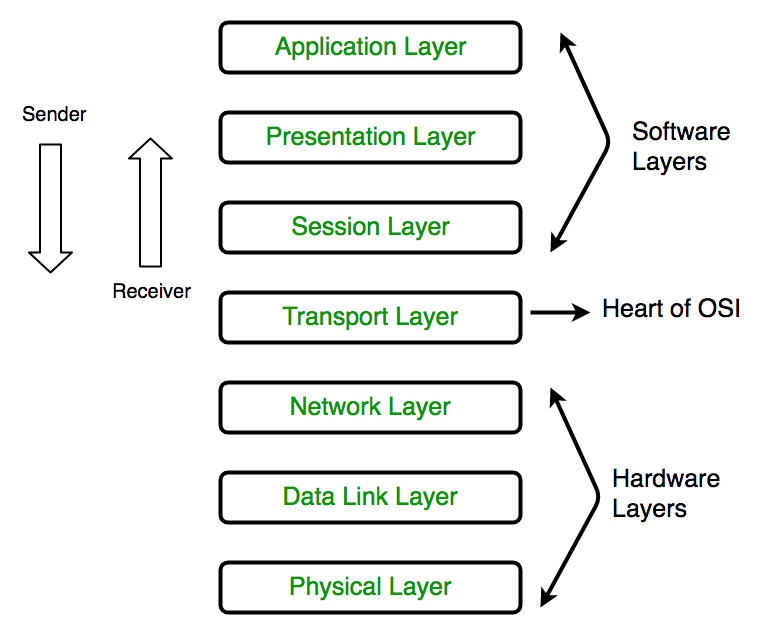
- The Network Layer that is the third layer of the OSI model.
- Network layer handles the service requests from the transport layer and further forwards service request to the data link layer.
- The network layer translates the logical addresses into the physical addresses
- Network layer determines the route from the source to the destination and also it manages the traffic problems for example switching, routing and controls the congestion of data packets.
- The main role of the network layer is to move the packets from the sending host to receiving host.
Network Layer: The layer that is responsible for source to destination delivery of packets.
Characteristics:
i) Logical addressing
Ii) Routing
Iii) Different network is connected.
The network layer design issues:
1) Store and formed packet switching.
2) Service provided to the transport layer.
3) Implementation of connectionless serviceare one of the design issue.
4) Implementation of connection-oriented source.
5) Comparison of virtual circuit and datagram submits.
Store and formed packet switching:
Store and forward operation : -
i) Host transmits packet to router across the LAN or it is oval point to point link.
ii) Packet is stored on that of the router until it is fully arrived and processed.
iii) Packet is forward to next router.
Service provides to transport layer:
The network layer services have been designed with the goals : -
i) the advice should independent of router telnet
ii)the transport layer should be shielded from the number type and topology of the router present.
iii) The network addresses maid available to transport
Implementation of connectionless service:
Connectionless service offer packets are injected into the subnet individually and routed independently of each other. Each packet is transmitted independently.
Connectionless service used in that of the network layer ID and the transport layer.
Packet is frequently called datagram connectionless service is largely for data communication the internet.
Implementation of connection-oriented service is as follows: -
Connection-oriented service is used for a path from that of the source router to that of the destination router which must be established before any data packet can be sent.
Connection oriented service also known as virtual circuit service. This service used the network layer for ATM. It is also used in the transport layer for TCP.
Connections have tobe established before any of the sent packets order preserved logical connection is also established over here.
- Quality of service management is provided
- Load balancing and link management is done
- Security is provided
- Interrelation of different protocols and subnets with different schema are there
- Different logical network design over the physical network design is done
- L3 VPN and tunnels which is to be used to provide end to end dedicated connectivity
Internet protocol is widely respected and then deployed the Network Layer protocol which helps us to communicate end to end devices over the entire internet. It comes in two ways. IPv4 which has ruled the world for many years but now is running out of address space. IPv6 is created to replace IPv4 and hopefully mitigates limitations of IPv4 too.
- Routing: When a packet reaches the router's input link, the router will move the packets to the router's output link. Example, a packet from S1 to R1 must be forwarded to the next router on the path to S2.
- Logical Addressing: The data link layer which implements the physical addressing and network layer which implements the logical addressing. Logical addressing is also used to distinguish between the source and the destination system. The network layer adds a header to the packet which includes the logical addresses of both sender and receiver.
- Internetworking: The main role of the network layer is that it provides the logical connection between different types of networks.
- Fragmentation: The fragmentation is a process of breaking the packets into the smallest individual data units that travel through different networks.
Gateway is a network node which connects two networks using different protocols together.
Gateway also acts as a gate between two networks. It can be a router or a firewall or a server or any other device that enables traffic to flow in and out of the network.
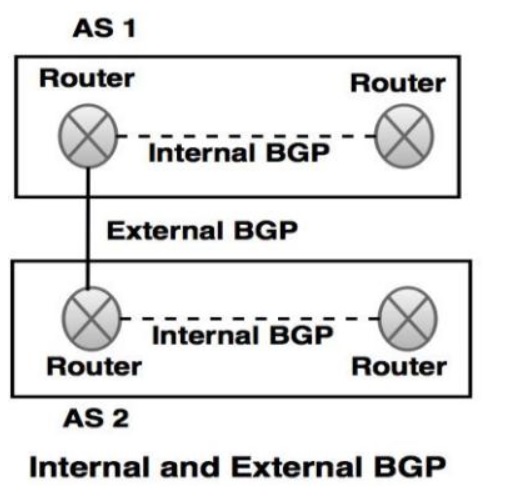
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a routing protocol which is used to transfer data and the information between different host gateways, the Internet or the autonomous systems. It is a Path Vector Protocol (PVP), which maintains paths to different hosts, networks and gateway routers which determines the routing decision based on that.
- BGP is an inter-domain protocol which is used to exchange network reachability information between two or more BGP routers (also known as BGP speakers).
- BGP is used to enable two different autonomous systems to exchange the routing information in such a way so that IP traffic can flow across the autonomous system border.
- Each BGP router that can establish a TCP connection with one or more BGP routers.
- If two of the routers are connected in the same subnetwork, they are considered as neighbours.
- If two of the routers are connected in different autonomous systems, they are allowed to exchange the routing information. BGP uses TCP/IP protocol to create reliable connection in sessions.
- BGP connections inside an autonomous system are known as internal BGP and connection between two different autonomous systems are known as external BGP.
References:
- Data Communication & Networking by Forouzan, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Network, 4e, by Andrew S. Tenenbaum, Pearson Education/ PHI.
- Data Communication and Computer Networks, by Prakash C.Gupta, PHI.
- Networking Ali-in-one Desk Reference by Doug Lowe, Wiley Dreamtech
- Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach featuring the Internet, 3e by James F.Kurose.
- Computer Network by Godbole, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Networking, by Stanford H. Rowe, Marsha L. Schuh
UNIT 7
The Network Layer
Introduction
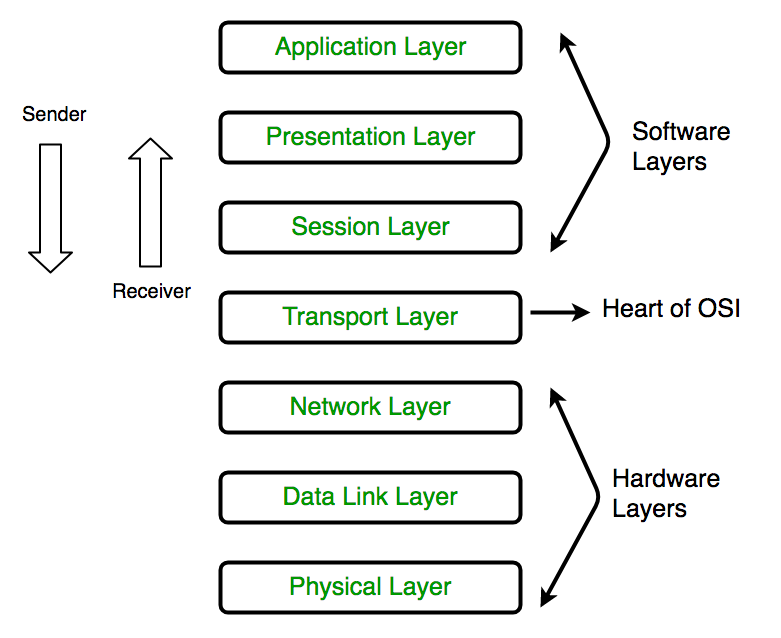
- The Network Layer that is the third layer of the OSI model.
- Network layer handles the service requests from the transport layer and further forwards service request to the data link layer.
- The network layer translates the logical addresses into the physical addresses
- Network layer determines the route from the source to the destination and also it manages the traffic problems for example switching, routing and controls the congestion of data packets.
- The main role of the network layer is to move the packets from the sending host to receiving host.
Network Layer: The layer that is responsible for source to destination delivery of packets.
Characteristics:
i) Logical addressing
Ii) Routing
Iii) Different network is connected.
The network layer design issues:
1) Store and formed packet switching.
2) Service provided to the transport layer.
3) Implementation of connectionless serviceare one of the design issue.
4) Implementation of connection-oriented source.
5) Comparison of virtual circuit and datagram submits.
Store and formed packet switching:
Store and forward operation : -
i) Host transmits packet to router across the LAN or it is oval point to point link.
ii) Packet is stored on that of the router until it is fully arrived and processed.
iii) Packet is forward to next router.
Service provides to transport layer:
The network layer services have been designed with the goals : -
i) the advice should independent of router telnet
ii)the transport layer should be shielded from the number type and topology of the router present.
iii) The network addresses maid available to transport
Implementation of connectionless service:
Connectionless service offer packets are injected into the subnet individually and routed independently of each other. Each packet is transmitted independently.
Connectionless service used in that of the network layer ID and the transport layer.
Packet is frequently called datagram connectionless service is largely for data communication the internet.
Implementation of connection-oriented service is as follows: -
Connection-oriented service is used for a path from that of the source router to that of the destination router which must be established before any data packet can be sent.
Connection oriented service also known as virtual circuit service. This service used the network layer for ATM. It is also used in the transport layer for TCP.
Connections have tobe established before any of the sent packets order preserved logical connection is also established over here.
- Quality of service management is provided
- Load balancing and link management is done
- Security is provided
- Interrelation of different protocols and subnets with different schema are there
- Different logical network design over the physical network design is done
- L3 VPN and tunnels which is to be used to provide end to end dedicated connectivity
Internet protocol is widely respected and then deployed the Network Layer protocol which helps us to communicate end to end devices over the entire internet. It comes in two ways. IPv4 which has ruled the world for many years but now is running out of address space. IPv6 is created to replace IPv4 and hopefully mitigates limitations of IPv4 too.
- Routing: When a packet reaches the router's input link, the router will move the packets to the router's output link. Example, a packet from S1 to R1 must be forwarded to the next router on the path to S2.
- Logical Addressing: The data link layer which implements the physical addressing and network layer which implements the logical addressing. Logical addressing is also used to distinguish between the source and the destination system. The network layer adds a header to the packet which includes the logical addresses of both sender and receiver.
- Internetworking: The main role of the network layer is that it provides the logical connection between different types of networks.
- Fragmentation: The fragmentation is a process of breaking the packets into the smallest individual data units that travel through different networks.
Gateway is a network node which connects two networks using different protocols together.
Gateway also acts as a gate between two networks. It can be a router or a firewall or a server or any other device that enables traffic to flow in and out of the network.
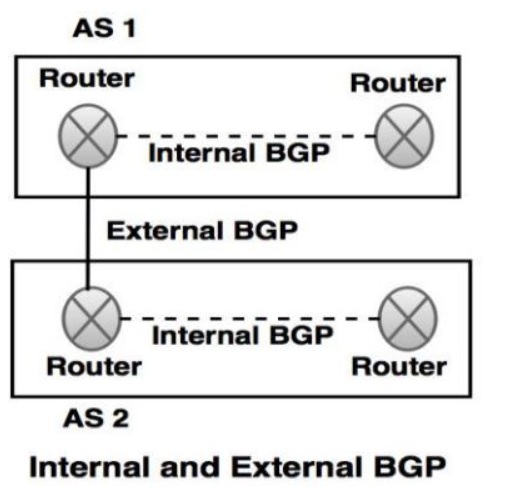
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a routing protocol which is used to transfer data and the information between different host gateways, the Internet or the autonomous systems. It is a Path Vector Protocol (PVP), which maintains paths to different hosts, networks and gateway routers which determines the routing decision based on that.
- BGP is an inter-domain protocol which is used to exchange network reachability information between two or more BGP routers (also known as BGP speakers).
- BGP is used to enable two different autonomous systems to exchange the routing information in such a way so that IP traffic can flow across the autonomous system border.
- Each BGP router that can establish a TCP connection with one or more BGP routers.
- If two of the routers are connected in the same subnetwork, they are considered as neighbours.
- If two of the routers are connected in different autonomous systems, they are allowed to exchange the routing information. BGP uses TCP/IP protocol to create reliable connection in sessions.
- BGP connections inside an autonomous system are known as internal BGP and connection between two different autonomous systems are known as external BGP.
References:
- Data Communication & Networking by Forouzan, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Network, 4e, by Andrew S. Tenenbaum, Pearson Education/ PHI.
- Data Communication and Computer Networks, by Prakash C.Gupta, PHI.
- Networking Ali-in-one Desk Reference by Doug Lowe, Wiley Dreamtech
- Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach featuring the Internet, 3e by James F.Kurose.
- Computer Network by Godbole, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Computer Networking, by Stanford H. Rowe, Marsha L. Schuh