Unit - 3
Contouring
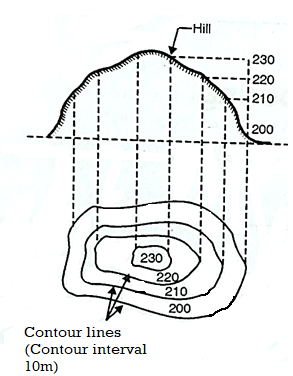
Fig.3.1: Plan (Contour lines indicate hill)
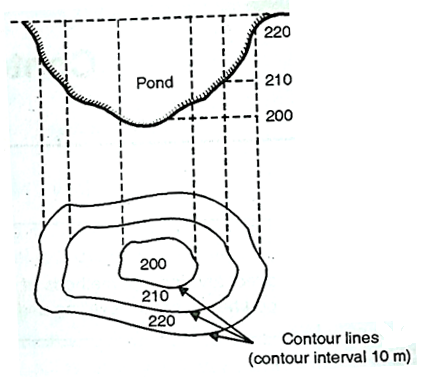
Fig.3.2: Plan (Contour lines indicate pond)
Contour interval:
Choice of contour interval:
Horizontal equivalents:
Key Takeaways:

Fig.3.3: Contour lines of same elevation
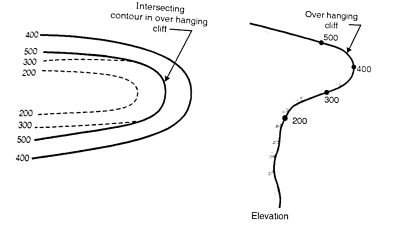
Fig.3.4: Intersecting contours in overhanging cliff
(i) When contour lines come close together then it indicates steep slope. Fig. shows steep slope along X-X.
(ii) Uniform slope: if contour lines are equally spaced, uniform slope is indicated.
(iii) A series of straight, parallel and equally spaced contours represent a plane surface.
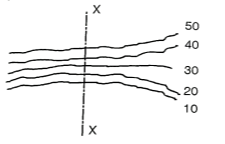
Fig.3.5: Steep slope along X-X
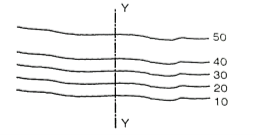
Fig.3.6: A gentle slope along Y-Y
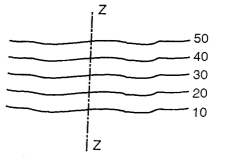
Fig.3.7: Uniform slope along Z-Z
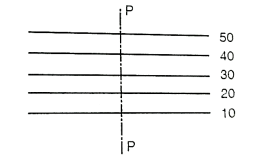
Fig.3.8: Plane surface slope along P-P
Depression: Closed contour lines with lower values inside indicate a depression.
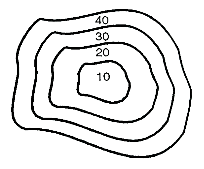
Fig.3.9: shows depression
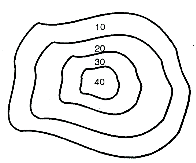
Fig.3.10: Shows a hill
Fig. indicates a ridge line. Contour lines cross ridge at right angles. For ridge line the higher elevation contour is inside the loop or band.
Valley line
Fig. indicates a valley line. Contour lines also cross the valley lines at right angles. Valley line is indicated by higher elevation contours outside the loop.
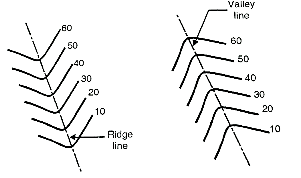
Fig.3.11: Ridge and valley line
Direct method:
Procedure:
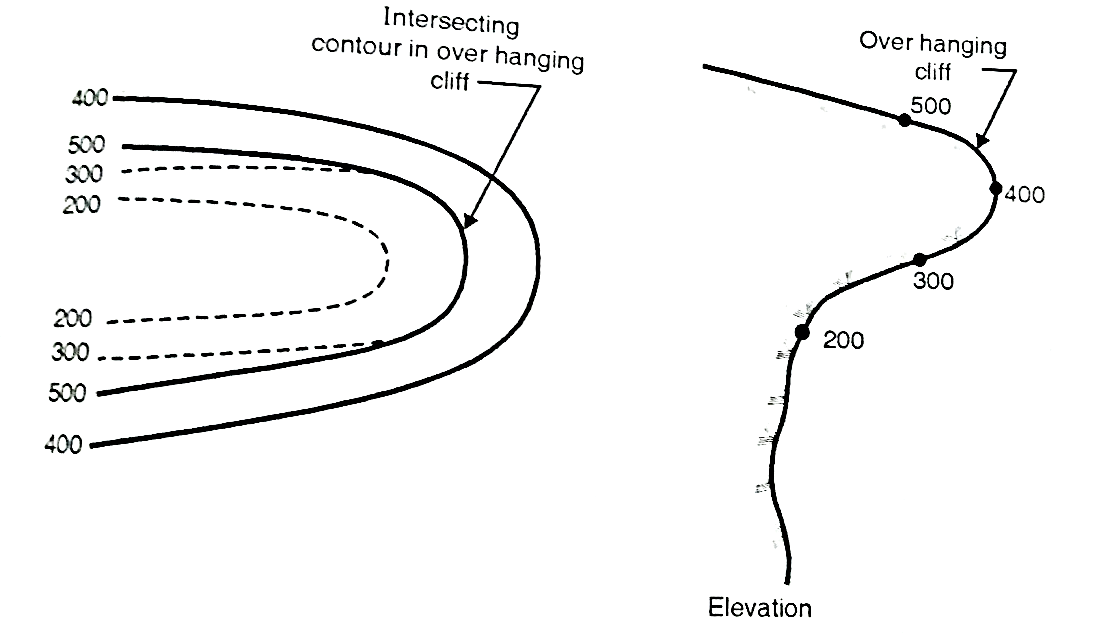
Fig.3.12: Direct method
(a)The work is started from B.M. and level is setup at the centre of the area.
(b) Suppose it is required to find out the contour of 90.000 m then the staff should be moved to various positions on plot where the reading on staff should give R.L. of 90.000 m. on ground. When all the points are located, they are marked on ground directly.
(c) Similar process is followed for locating the contour of 95.000 m and other contours.
Indirect method:
(a) By cross-section:
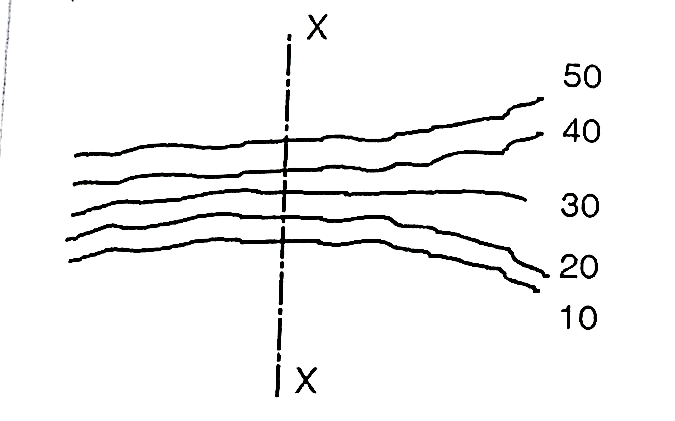
Fig.3.13: Method of cross-sections
(b) By squares:

Fig.3.14: Method of square
(c) By tacheometric method:
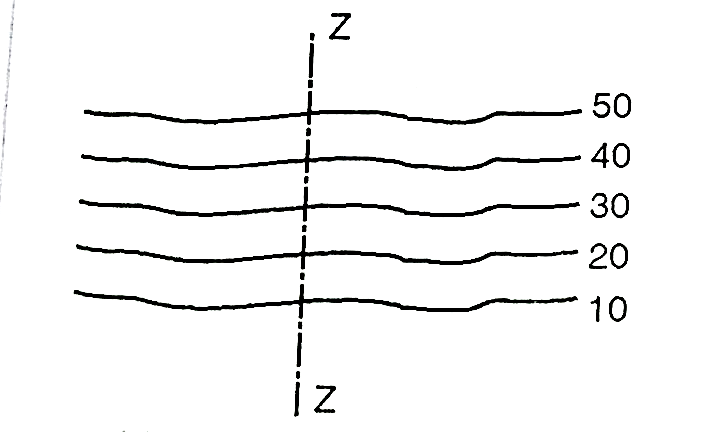
Fig.3.15: Tacheometric method
Key Takeaways:
Direct method: In the direct method, the contour to be plotted is actually traced on the ground.
Indirect method: In this method spot levels are taken at regular interval along predetermined lines on the ground. The work is then plotted on plan and then the required contour lines are drawn by the process of interpolation.
Let the RL of the straight point 100.00 m and
Let the distance of the next point 60 m.
B.S on known point is 0.50
HI =100+ 0.50 =100.05 m
Then R1 of the next point =100-(60/30)
=100-2
=98 m
Hence the staff reading =100.50-98
=2.5 m
References: