Unit - 3
Market
Introduction
There are pretty few exclusive marketplace systems so that you can represent the economy. However, in case you are simply beginning out in this subject, it is a sincere concept to first test out the 4 primary forms of marketplace systems: ideal opposition, monopoly opposition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Each has its personal traits and assumptions that impact company selection making and company profits.
It is vital to observe that now no longer all of these marketplace systems virtually exist. Some of them are simply theoretical constructs. Still, those are vital due to the fact they assist you apprehend how your competition make decisions. Let's take a higher test out the 4 marketplace systems.
Concept of Perfect Competition
Perfect competition refers to ‘A market structure in which there are large number of buyers and sellers with a single uniforms price for the product which is determined by the forces of demand & supply.’ The price prevailing in perfect competition market is equilibrium price.
Definition:
It is diagnosed via way of means of the lifestyles of the various company; all of them promote an equal merchandise an equal way. The provider is the only who accepts the rate."- Vilas
Such marketplace profits while the request for product of each manufacturer is absolutely elastic. Mrs Joan Robinson.
It is a marketplace circumstance with an oversized wide variety of dealers and shoppers, comparable merchandise, loose access of companies into the enterprise is good understanding among shoppers and dealers of current marketplace situations and loose mobility of manufacturing elements among opportunity uses.
Characteristic of perfect competition:
1)Large number of seller / sellers are price takers: There are many capability dealers promoting their commodity withinside the marketplace. Their wide variety is so massive that an unmarried supplier can't impact the marketplace rate due to the fact every supplier sells a small fraction of general marketplace deliver. The rate of the product is decided on the idea of marketplace call for and marketplace deliver of the commodity that is established via way of means of the corporations, hence supplier is a rate taker and now no longer a rate maker.
2)Large number of buyers: There are many shoppers withinside the marketplace. An unmarried customer can't impact the rate of the commodity due to the fact character call for is a small fraction of general marketplace call for.
3)Homogeneous product: The product offered withinside the marketplace is homogeneous, i.e., equal in best and size. There isn't any distinction among the merchandise. The merchandise are ideal substitutes for every different.
4)Free entry and exit: There is freedom for brand new corporations or dealers to go into the marketplace or enterprise. There isn't any legal, monetary or any form of regulations. Similarly, the vendor is loose to go away the marketplace on enterprise.
5) Perfect knowledge: The supplier and shoppers have ideal understanding approximately the marketplace together with rate, call for and deliver. This will save you the customer from paying better rate than the marketplace rate. Similarly, dealers can't alternate an exclusive rate than the triumphing marketplace rate.
6)Perfect mobility of factors of production: Factors of manufacturing are freely cell from one company to any other or from one location to any other. This guarantees freedom of access and go out corporations. This additionally make certain that the elements price is the identical for all corporations.
7)No transport cost: It is believed that there aren't any shipping costs. As an end result, there may be no opportunity of converting a better rate at the behalf of shipping costs.
8)Non-intervention by the government: It is believed that authorities do now no longer intrude withinside the operating of the marketplace economy. Price is decided freely in line with call for and deliver situations of the marketplace.
9)Single Price: In Perfect Competition all gadgets of a commodity have uniforms or an unmarried rate. It is decided via way of means of the forces of call for and deliver.
In Perfect Competition all units of a commodity have uniforms or a single price. It is determined by the forces of demand and supply.
Monopoly
The phrase monopoly has been derived from the mixture of phrases i.e., ‘Mono’ and ‘Poly’. Mono refers to an unmarried and poly to manipulate.
Thus, monopoly refers to a marketplace scenario wherein there may be simplest one supplier of a commodity.
In monopoly marketplace, single company or one supplier controls the complete marketplace. The company has all of the marketplace strength, so he can set the charges to earn extra earnings because the clients do now no longer have any opportunity.
Definition:
“Pure monopoly is represented via way of means of a marketplace scenario wherein there may be an unmarried supplier of a product for which there aren’t any substitutes; this unmarried supplier is unaffected via way of means of and does now no longer have an effect on the charges and outputs of different merchandise offered with inside the economy.”- Bilas
“Monopoly is a marketplace scenario wherein there may be an unmarried supplier. There aren’t any near substitutes of the commodity it produces, there are boundaries to access”. –Koutsoyiannis
“A natural monopoly exists while there may be simplest one manufacturer with inside the marketplace. There aren’t any dire competitions.” – Ferguson
Features:
- One seller and large number of buyers – - In a monopoly one supplier produces all the output for an excellent or service. The complete marketplace is served via way of means of an unmarried company. For realistic functions the company is similar to the enterprise. But the wide variety of shoppers is believed to be massive.
2. No Close Substitutes – There isn't any near substitutes for the product offered via way of means of the monopolist. The go elasticity of call for among the fabricated from the monopolist and others should be negligible or zero.
3. Difficulty of Entry of New Firms – There are regulations at the access of corporations into the enterprise, even if the company is making odd profits. Other dealers are not able to go into the marketplace of the monopoly
4. Profit maximize- A monopoly maximizes profits. Due to the shortage of opposition a company can rate a hard and fast rate above what could be charged in an aggressive marketplace, thereby maximizing its revenue.
5. Price Maker – Under monopoly, monopolist has completed manipulate over the delivery of the commodity. The rate is ready via way of means of figuring out the amount for you to call for the rate preferred via way of means of the company. Therefore, shoppers need to pay the rate constant via way of means of the monopolist.
Monopolistic competition
In Monopolistic competition there are large numbers of buyers and sellers which do not sell homogenous product unlike perfect competition. This is more realistic in the real world. Monopolistic competition occurs when an industry in which many firms selling products that are similar but not identical.
Monopolistic competitions try to differentiate its product. Thus, it is closely related to business strategy of brand differentiation. In monopolistic competition heavy advertising and marketing is common among firms.
Monopolistic competition combines element of both monopoly and perfect competition. All firms in monopolistic competition relatively have low market power and they are all market makers.
Monopolistic competitive market -
- The firm offer highly differentiated product.
- Free entry and exit in the market i.e.- no barriers.
- Firm can make decision independently.
- Customers have the preference of choosing products.
- Seller becomes price setter.
- Seller can charge marginally high price to enjoy some degree of market power
Features:
- Product differentiation – monopolistic opposition consists of corporations that provide comparable product however aren't equal. The merchandise is differentiated now no longer on the idea of rate however the distinction consists of bodily components of the product, vicinity from wherein it sells and intangible components of the product. The product and offerings play the primary characteristic however have distinction ion best together with type, colour, appearance, reputation, vicinity that distinguish the product from every different. For ex, motor cars are identical to transport humans from one factor to any other. But there are numerous sorts of motor cars together with car, bike, scooter.
2. Many firms – there are numerous corporations in every product organization. A product organization is a "series of comparable merchandise". Under monopolistic marketplace, every corporation has a small marketplace share. This offers every company a freedom to set rate and every company motion have negligible effect at the marketplace. A company can reduce the rate to boom sale with none fear. As its motion will now no longer set off retaliatory responses from competition.
3. Freedom of entry and exit Like ideal opposition, beneath neath monopolistic opposition the corporations can freely input or go out. When the prevailing corporations makes super-ordinary profits, then new corporations will input. The access of recent corporations’ results in boom the delivery of products and offerings and this will lessen the rate and hence the prevailing corporations might be left simplest with ordinary profits. Similarly, if the prevailing corporations are incurring losses, a number of the corporations will go out. This will lessen the deliver which end result lower in rate and the prevailing corporations might be left simplest with ordinary earnings.
4. Independent decision making – beneath neath monopolistic marketplace, every company can independently units the phrases and situations of alternate for its product. The company does now no longer take into account how their selection may have effect on competition. In different phrases, every company feels loose to set charges and prompting heightened opposition.
5. Market power - below monopolistic opposition, the companies have low diploma of marketplace strength. Market strength method that the corporation has manage over the phrases and situations of trade for its product. All companies below monopolistic opposition are fee makers. A corporation can enhance the costs of services and products without dropping all its client’s base. The corporation also can decrease costs with none impact at the competitors. Since the corporation have pretty low marketplace strength, there's no barrier to entry.
Concept of Oligopoly
In oligopoly there are small numbers of companies with inside the marketplace. As in line with the norms, oligopoly include 3 -five dominant companies. The companies can compete with every different or collaborate to earn extra earnings. Here the customers are extra than the dealers.
Features:
- Existence of few sellers: The number one functions of oligopoly is the life of some dealers who dominate the complete enterprise and have an impact on the costs of every different. Also, there are massive range of customers below oligopoly
- Identical or differentiated products: An essential feature of oligopoly is the manufacturing of same merchandise or differentiated merchandise.
- Barriers in entry: Another essential feature of oligopolistic opposition is that agencies can't without problems input the marketplace; nor can they make a go out from the marketplace.
- Enhanced role of government: Under oligopolistic marketplace structure, the authorities have an extra function because it acts as a shield because its miles located that oligopolists may also interact withinside the unlawful exercise of collusion, in which they collectively make manufacturing and pricing decisions.
- Oligopolists may also begin appearing as an unmarried employer and in addition boom costs and earnings. Thus, the authorities call for to preserve an eye on such sports to diminish the unlawful practices.
- Mutual interdependence: Under oligopoly marketplace structure, some numbers of dealers compete with every different. Thus, mutual interdependence refers back to the have an impact on that agency create on every different decision, which includes pricing and output decisions.
- Existence of price rigidity: Under oligopolistic marketplace, agencies do now no longer opt to extrude the costs in their merchandise as this could adversely have an effect on the earnings of the employer.
Key takeaways:
- A perfectly competitive market is characterized by many buyers and sellers, undifferentiated products, no transaction costs, no barriers to entry and exit, and perfect information about the price of a good.
- Monopolistic competition combines element of both monopoly and perfect competition.
- A monopolistic competitor creates output at which the marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue. The price is greater than marginal cost.
- Oligopoly is a market structure with a small number of firms, none of which can keep the others from having significant influence.
Under perfect competition, many factors influence the pricing of goods. In this article, we will look at industry equilibrium and corporate equilibrium as key factors behind perfect competition pricing.
Industrial equilibrium under perfect competition
Economically, the industry is made up of many independent companies. Each company has several factories, farms, or mines as needed. Each such company in the industry produces homogeneous products. Industrial equilibrium occurs when the total production of an industry is equal to the aggregate demand. In such a scenario, the prevailing price of the item is its equilibrium price.
We know that in a highly competitive situation, the interaction between supply and demand determines the equilibrium price as shown below.
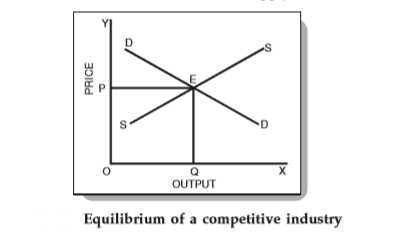
In Figure above, OP is the equilibrium price. In addition, OQ is the equilibrium quantity sold at that price. Now, the equilibrium price is the price at which both supply and demand are equal. In other words, the buyer who wants to buy at that price will not be dissatisfied, and the seller who wants to sell the item at that price will not be dissatisfied.
Note that the market is not in equilibrium if the demand remains the same and the price is higher or lower than the OP. Also, if the goods are less or more than the demand, the equilibrium will not be achieved.
Equilibrium of companies under perfect competition
Enterprises are in equilibrium when maximizing profits. Therefore, the output that gives the company the greatest profit is the equilibrium output. When a company is in equilibrium, there is no reason to increase or decrease production.
In a highly competitive market, companies are price takers. The reason is that there are many companies that manufacture homogeneous products. Therefore, companies cannot influence prices with their individual capabilities. They must follow prices determined by the industry.
The following figure shows the demand curve of a company under perfect competition.
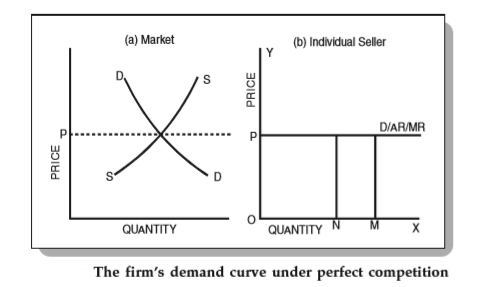
From Figure above, we can see that the industry price OP is fixed through the interaction of industry supply and demand. Companies must accept this price. Therefore, they are price takers, not price makers. Therefore, the price OP cannot be increased or decreased.
Therefore, the line P serves as the demand curve for such an enterprise. Therefore, in perfect competition, the demand curve of an individual company is a horizon at the level of market prices set by the industry. Companies need to choose the level of production that produces the most profit.
Conditions of corporate equilibrium
To reach equilibrium, a company must meet two conditions:
They must ensure that the marginal revenue is equal to the marginal cost (MR = MC).
If MR> MC, the company has an incentive to expand production and sell additional units.
For MR <MC, companies need to reduce production because adding unit’s costs more than revenue.
Only when MR = MC does the company get the most profit.
The MC curve has a positive gradient and the MR curve should be cut from below.
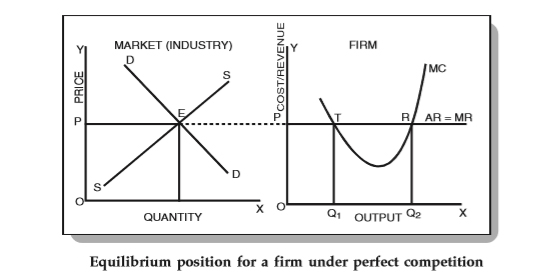
In Figure above, DD is the demand curve and SS is the supply curve. They equilibrate at point E and set the market price as OP. Under perfect competition, companies adopt OP as the industry price and consider the P line as the demand curve or the AR-average return curve (fully elastic at P).
The MR curve is a horizontal line, which is the same as the AR line, because the prices of all units are the same. Make sure that the curve MC cuts the MR curve at two points (T and R). At point T, the MC curve cuts the MR curve from above, and at point R, the MR curve cuts from below. Therefore, according to the equilibrium conditions of a company, point R is the equilibrium point and OQ2 is the equilibrium level of output.
Key takeaways:
- Under perfect competition, many factors influence the pricing of goods.
- Economically, the industry is made up of many independent companies.
- Industrial equilibrium occurs when the total production of an industry is equal to the aggregate demand
- Enterprises are in equilibrium when maximizing profits.
- In a highly competitive market, companies are price takers.
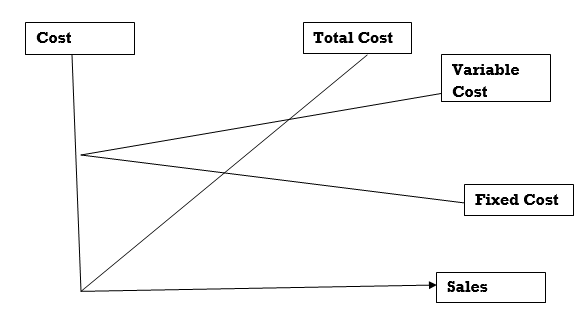
Break-even analysis is additionally referred to as cost-volume profit analysis. Break-even point analysis is a relationship between asking price, sales volume, fixed costs, variable costs, and profits at various level activity. Break-even analysis may be a widely used technique for studying the cost-volume-profit relationship narrow
Here, the entire cost is adequate to the entire asking price. The broader interpretation refers to the analytical system. Determines expected profits for all levels of activity. It describes the connection between production costs, Production volume and sales value.
Here, CVP analysis is additionally commonly performed, but it's not accurate, but it's called "break-even point analysis". The difference between the 2 terms is extremely narrow. CVP analysis includes full range Break-even analysis is one among the techniques utilized in this process. But as mentioned the above break-even point analysis techniques are so popular in CVP analysis research that the 2 terms are used as a synonym. For the needs of this investigation, we also these two terms to know the concept of break-even analysis, it's helpful to understand the following specific basic terms listed below application
- You’ll use break-even analysis to work out your company's break-even point (BEP).
- The break-even point is that the level of activity where total revenue is adequate to total cost. At this level, the corporate doesn't make a profit
1. Contribution
This is a more than the asking price that exceeds the variable cost also called "gross profit". The amount of profit (loss) is often confirmed by deducting fixed costs from contributions. In other words, it had been fixed Costs and benefits correspond to contributions. It is often expressed by the subsequent formula.
Contribution = Selling Price – Variable Cost or Contribution = Fixed Cost + Profit = Contribution – Fixed Cost
Profit / Volume ratio (P / V ratio)
This term is important for studying the profitability and profit ratio of operating a business.
Establish a relationship between contribution and sales. The ratio can be displayed in the following format Percentage too. The expression can be expressed as:
This ratio can also be found by comparing changes Contribution to changes in sales or changes in profits due to changes in sales. Increased contribution. Fixed costs are assumed to be constant at all production levels, which mean increased profits.
Therefore,
P/V Ratio (or, C/S ratio) = Contribution S𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 = C S or, P/V Ratio = Sales−Variable Cost S𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 = S−V S or, 1- Variable Cost S𝑎𝑙𝑒
This ratio is also known as the "contribution / sales" ratio. This ratio can also be found by comparing changes Contribution to changes in sales or changes in profits due to changes in sales increased contribution. Fixed costs are assumed to be constant at all production levels, which mean increased profits.
Therefore, thus, P/V Ratio = Change in Contribution by Change in S𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 or, P/V Ratio = Change in Profit (or Loss) Change in S𝑎𝑙𝑒
The characteristics of the P / V ratio are as follows.
(I) Helps administrators see the total amount of contribution to a particular sale.
(II) The selling price and the variable cost per unit are constant or constant as long as they are constant. It fluctuates at the same rate.
(III) Not affected by changes in activity level. In other words, the PV ratio of the product. The amount of activity is the same whether it is 1,000 units or 10,000 units.
(IV) Fixed costs are not considered at all, so the ratio is also unaffected by fluctuations in fixed costs while calculating the PV ratio. For multi-product organizations, PV ratios are very important for management to decide which one to find. The product is more profitable. Management is trying to increase the value of this ratio by reducing variable costs or by raising the selling price.
3. Break-even point: A point that indicates the level of output or sales by dividing the total cost and sales price evenly. There is no profit or loss, it is considered a break-even point. At this point, business income exactly equal to that spending. If production is boosted beyond this level, profits will be generated in the business. And if it decreases from this level, the loss will be incurred by the business. Here it is appropriate to understand the different concepts of marginal costs and break-even points. Go further. This is explained below.
It's neither a profit nor a loss. Therefore, at the break-even point, the contribution is equal to the fixed cost.
Contribution = Fixed cost (1) Break-even point (in units) = Fixed Cost Contribution per unit (2) Break-even point (in amount) = Fixed Cost Contribution per unit x Selling Price per unit Or, = Fixed Cost Total Contribution x Total Sales Or, = Fixed Cost 1− Variable Cost per unit Selling price per unit = Fixed Cost P/V Ratio
Sales at break-even point = break-even point x selling price per unit
At the break-even point, the desired profit is zero. When calculating production or sales
You need to add a fixed amount of "desired profit" or "target profit" "desired profit" or "target profit "The cost of the above formula. For example:
(1) No. Of units at Desired Profit = Fixed Cost +Desired Profit Contribution per unit (2) Sales for a Desired Profit = Fixed Cost +Desired Profit P/V Ratio
(2) Sales at break-even point = break-even point x selling price per unit
(3) At the break-even point, the desired profit is zero. When calculating production or sales
(4) You need to add a fixed amount of "desired profit" or "target profit" "desired profit" or "target profit"
(5) The cost of the above formula. For example:
Break-even point analysis: Relationship between selling price, sales volume, fixed costs, variable costs, and profits at various levels activity application.
- You can use break-even analysis to determine your company's break-even point (BEP).
- The break-even point is the level of activity where total revenue is equal to total cost.
- At this level, the company does not make a profit
Break-even point analysis assumptions
- Related range
- The relevant range is the range of activities for which fixed costs remain fixed in total.
- Variable costs per unit remain constant
- Fixed costs
- Total fixed costs are assumed to be constant in total Variable cost
- Total variable costs increase because the number of units produced increases Sales
- Total revenue increases as the number of units produced increases Safety range.
Key takeaways:
- Break-even analysis is additionally referred to as cost-volume profit analysis.
- The broader interpretation refers to the analytical system.
- The selling price and the variable cost per unit are constant or constant as long as they are constant
- A point that indicates the level of output or sales by dividing the total cost and sales price evenly.
- Relationship between selling price, sales volume, fixed costs, variable costs, and profits at various levels activity application.
- Total fixed costs are assumed to be constant in total Variable cost
References:
- Https://www.toppr.com/guides/business-economics/determination-of-prices/price-determination-under-perfect-competition/
- Https://www.toppr.com/guides/business-economics/meaning-and-types-of-markets/types-of-market-structures/
- Https://cleartax.in/s/break-even-analysis