Unit - 4
Bearings
Bearing:
A bearing is a system detail that constrains relative movement to best the favored movement, and decreases friction among shifting parts.
The layout of the bearing may, for example, offer free of charge linear motion of the shifting element or free of charge rotation round a set axis; or, it could save you a movement via way of means of controlling the vectors of everyday forces that endure at the shifting Most bearings facilitate the favored movement via way of means of minimizing friction.
Bearings are categorized extensively in keeping with the kind of operation, the motions allowed, or to the instructions of the hundreds (forces) carried out to the parts. Rotary bearings keep rotating additives which include shafts or axles inside mechanical systems, and switch axial and radial hundreds from the supply of the weight to the shape helping it.
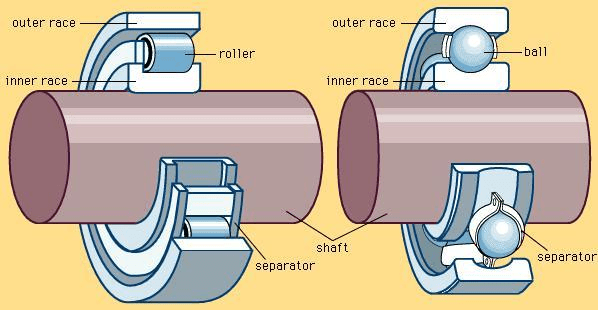
The only shape of bearing, the obvious bearing, includes a shaft rotating in a hole. Lubrication is used to lessen friction. In the ball bearing and curler bearing, to lessen sliding friction, rolling factors which include rollers or balls with a round cross-segment are positioned among the races or journals of the bearing assembly.
A huge form of bearing designs exists to permit the needs of the software to be efficaciously met for optimum efficiency, reliability, sturdiness and performance.
Bearings commonly encompass the subsequent components:
Two jewelry or discs with raceways Rolling factors with inside the shape of rollers or balls a cage which maintains the rolling factors aside and courses them
Inner Ring / Outer Ring The internal and outer ring are commonly crafted from a unique excessive-purity, chrome alloy steel.
This cloth has the essential hardness and purity – each essential elements for an excessive load score and an extended provider life. The raceways are hardened, floor and honed. Special substances which includes ceramic and plastics also are used.
Although plastics can't face up to extraordinarily excessive temperatures, they're extensively lighter than steel. This makes them helpful in sectors which includes the car industry, in which each gram matters.
Ball Bearings: Selection and Types:
Ball bearings are used to offer smooth, low friction movement in rotary applications. Ball bearings are capable of offer excessive overall performance and lengthy lifetime so that you can switch the weight from the balls to the internal races.
The balls have minimum touch with the internal and outer races because of their round form and this lets in them to spin smoothly. A drawback of ball bearings is that the balls can become "flattened" through the years with an excessive amount of strain at the outer races main to eventual failure.
Therefore it's far very essential that the weight rankings and different parameters are monitored regularly.
Construction
- Ball bearings are composed of 4 primary parts: jewelry (or races) the rolling factors (the balls), and the ball separator (retainer).
- Radial ball bearings and angular touch bearings have an internal and outer ring.
- Radial ball bearings and angular touch bearings are designed to guide hundreds perpendicular to the axis of rotation, known as radial hundreds.
- The outer race mounts right into a housing and is stationary. This element additionally aids with inside the switch of the radial load from the bearing to the housing.
- The internal race mounts onto a rotating shaft and helps and courses the shaft at some stage in rotation. The rolling factors deliver the weight and distribute it at some point of the raceways.
- The rolling factors rotate across the internal race, however now no longer on the equal pace because the rotation of the internal race.
- The separator acts as a barrier among the balls stopping them from bumping into every different.
- Thrust bearings are designed to guide hundreds parallel to the axis of rotation, known as axial hundreds. Thrust ball bearings have jewelry of identical size.

Types
Ball bearing sorts include:
Radial ball bearings –
Radial ball bearings are designed to hold each radial and (light) axial (thrust) hundreds, even as thrust ball bearings are designed for natural thrust hundreds only.
Deep groove –
Radial, or deep groove bearings, can take radial and axial hundreds to various levels however are used whilst the number one load is with inside the radial direction. They include an internal ring, an outer ring, balls and every now and then a cage to comprise and separate the balls.
Angular touch –
Angular touch ball bearings are designed such that a touch perspective among the races and the balls is shaped whilst the bearing is in use. The main layout function of this kind of ball bearing is that one or each or the hoop races have one shoulder better than the different.
In order for those bearings to characteristic properly, they should be assembled with a thrust load. This loading (or preload) creates a line of touch (or touch perspective) among the internal race, the ball and the outer race.
The preload may be constructed into the bearing or created whilst the bearing is inserted into an assembly.
The touch perspective varies from 15° to 40° and is measured relative to a line going for walks perpendicular to the bearing axis. Angular touch bearings are one-directional thrust bearings that could face up to heavy thrust hundreds and slight radial hundreds.
Thrust ball bearings –
Thrust ball bearings are designed for natural thrust hundreds. These bearings can deal with very little radial hundreds. The rolling detail may be a ball, needle, or roller. Slewing ring or turntable bearings can accommodate axial, radial and second hundreds.
They aren't established in a housing or on a shaft, however as a substitute are established immediately to a seating surface. The internal and outer jewelry are furnished with mounting holes.
The internal ring, outer ring, or each may also have critical gears. These bearings are known as tabletop bearings, turntable bearings, and slewing jewelry.
Roller Bearing selection and types:
Roller bearings are used to update sliding motion with low friction, rolling movement in rotary programs. The main kinds of curler bearings are cylindrical, round, and tapered. In general, curler bearings provide better load capacities than ball bearings of the identical size.
Types
There are 5 major kinds of curler bearings:
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Have excessive radial-load ability and mild thrust masses. They incorporate rollers which can be cylindrically-shaped, however topped or end-relieved to lessen strain concentrations.
Cylindrical curler bearings
Are comparable in layout to needle curler bearings however the dimensions of diameter and curler period are nearer in magnitude.
Spherical Roller Bearings
Are self-aligning, double row, and mixture radial and thrust bearings. They use a round or topped curler because the rolling element a way to pick curler bearings
Tapered Roller Bearings
Include an internal ring (cone), an outer ring (cup), a cage and rollers, which can be profiled to distribute the burden flippantly throughout the curler.
During operation, tapered curler bearings create a line touch among the raceway and rolling element, dispensing masses throughout a bigger area.
Needle Roller Bearings
Are a form of cylindrical curler bearing wherein the period of the curler is a good deal large than then the diameter. Needle curler bearings are designed for radial load programs wherein a low profile is desired.
Thrust Bearings
Are designed for natural thrust masses, and may manage very little radial load. Roller thrust bearings use rollers just like different kinds of curler bearings
Components
Radial kind curler bearings (cylindrical, tapered, round, and needle) include 4 simple components, an internal ring, an outer ring, rollers, and a cage (curler retainer).
Under regular working conditions, bearing earrings and rollers deliver the burden at the same time as the cage areas and keeps the rollers at the cone.
A way to pick curler bearings Comparison of Cylindrical Roller Bearing and Ball Bearing Components Image Credit: Bridget Roller thrust bearings are designed to hold natural thrust masses. Like radial curler bearings, curler thrust bearings additionally include earrings, rollers, and a cage (curler retainer).
However, rather than an internal and outer ring concentric to the axis of rotation, they have got earrings or thrust washers on both aspect of the curler.
Bearing choice is a technique of matching of a specific bearing and the software requirements, inclusive of load, misalignment, speed, and torque.
Rolling-detail bearings help the weight thru the touch present among the rolling factors and the raceways. During the rotation, a movement of 1 raceway relative to any other raceway occurs. In general, a bearing includes an internal raceway, outer raceway, rolling factors and commonly a cage, as proven with inside the discern below.
The cage is needed to preserve suitable spacing among the rolling factors in order that they do now no longer come into touch with every different.
Rolling-detail bearings exist in lots of distinct bureaucracy with every one having a completely unique set of capabilities.
The suitability of a rolling-detail bearing to a specific software is primarily based totally at the fit among those capabilities and the software requirements. In this type of context, it turns into critical to bear in mind sure elements while choosing the maximum appropriate sort of bearing.
- Available space
- Loading conditions (importance and direction)
- Misalignment Speed
- Operating temperature
- Precision requirement
- Stiffness
- Vibration level
- Contamination level
- Lubrication conditions
In addition to those elements, it's far critical to bear in mind now no longer handiest the bearing itself, however the complete assembly, like shafts and housing.
Thus, for a most suitable bearing choice, one need to additionally bear in mind the subsequent elements:
- Proper layout of different components
- Suitable clearances and preload
- Proper sealing
- Type and amount of lubricant
- Appropriate set up and elimination methods
Applications
- The capabilities possessed with the aid of using the rolling-detail bearings lead them to appropriate for sure applications.
- For instance, cylindrical curler bearings are famous in rolling mills, system device spindles, and mid- to heavy-obligation electric powered automobiles.
- High radial load-wearing potential, precision, excessive aid stiffness, excessive-velocity functionality amongst others makes them appropriate for such applications.
- The ball bearings are utilized in electric powered cars automobiles in which the weight is typically blended or radial and comparatively low, whilst the velocity variety is as a substitute broad, accomplishing pretty excessive levels.
- The bearings also are discovered in mild-obligation gearboxes, conveyor rollers, and small cars. The critical components for the choice encompass mild load, twin load-wearing potential, and coffee cost.
- The tapered curler bearings constitute a higher desire while seeking out a bearing that helps blended axial and radial masses in addition to excessive load.
- As a result, they're used with inside the wheels of off-avenue cars, passenger cars, gearboxes of marine drives, touchdown wheels of aircrafts, printing presses, different transmission systems, and system device spindles.
- Particular elements which include heavy load wearing potential and adjustment capacity that facilitate precision and stiffness must be taken into consideration all through the choice process.
- The round curler bearings are applied in windmills, rolling mills, paper mills, massive business gearboxes and others. They have green misalignment capacity and heavy radial load wearing potential.
Dynamic and static load rating:
Rolling detail linear bearings, along with spherical shafts and bushings, profiled rail guides, crossed curler slides, or even ball screws, have load ability specifications — dynamic load ability and static load ability — that are primarily based totally on exclusive working parameters and overall performance standards and are impartial of every other.
To appropriately length and pick out a rolling detail linear bearing or ball screw, it’s important to recognize the variations among them and whilst everyone is used.
Dynamic load ability, C, is primarily based totally on empirical trying out wherein a load this is steady in significance and regular to the load-bearing surfaces permits the bearing to attain a described journey distance (linear guide) or quantity of revolutions (ball screw) without fatigue.
Fatigue is described because the presence of flaking at the floor of the rolling factors or the raceways. The dynamic load ability is used to decide the rated lifestyles of a rolling detail bearing.
This lifestyles is generally called the L10 lifestyles, due to the fact it's far the lifestyles that ninety percentage of a collection of same bearings is anticipated to attain beneath set situations of load and speed.
For linear bearings that use balls:
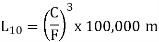
For linear bearings that use rollers:
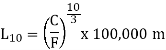
L10 = calculated (rated) life of the bearing
C = basic dynamic load capacity
F = applied load
The ball screw well-known specifies that dynamic load ability is primarily based totally on an L10 existence of one million revolutions.
However, the linear bearing well-known lets in the dynamic load ability to be particular for an L10 existence of both 50,000 m and 100,000 m.
The foundation of the L10 existence for linear bearings is vital to note — especially while evaluating linear publications from distinctive producers, or maybe of various collection from the identical manufacturer. If a linear manual whose dynamic load ability is primarily based totally on 100,000 m is being as compared to a linear manual whose dynamic load ability is primarily based totally on 50,000 m, one of the following conversions have to be carried out:
Divide the 50,000 m load ability through 1. 26 OR multiply the 100,000 m load ability through 1.26. (This article explains how the 1.26 conversion issue is derived.)
Static load ability, C0, is the quantity of load a bearing can resist earlier than the sum of the ball and raceway deformation equals 0.01 percentage of (0.0001 times) the ball diameter, as described through ISO 14728-2. Static load ability is sort of constantly better than dynamic load ability due to the fact its trouble is plastic deformation of the ball and raceway material, which takes place while the burden is carried out to the bearing in a static (non-transferring) or slow-transferring state.
Static hundreds are regularly the end result of shocks to the bearing which can be unplanned and hard to quantify. Therefore, linear bearing and ball screw producers endorse making use of a static protection issue, relying at the kind of utility and the running situations. The static protection issue is the ratio among the primary static load score and the most blended static load carried out to the bearing. It can variety from 2 for easy running situations with a low threat of vibrations, to as excessive as five or 6 for programs that can be subjected to excessive surprise hundreds.
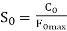
S0 = static load safety factor
C0 = static load capacity
F0max = maximum combined static load
Bearing Life:
Size of the bearing with a view to be utilized in a selected answer is at the beginning decided on basing on: bearing’s load score with regards to masses which are going on, necessities on carrier existence and reliability.
In bearing era each static and dynamic load situations needs to be independently checked. In bearing era each static and dyna- mic load situations needs to be independently checked (n < 10 rev/min).
For such masses the protection concerning plastic deformations (because of touch stresses) at raceways and rolling factors touch factor is checked. In dynamically loaded bearings earrings are rotating with relation to every other.
In that example the protection elements concerning fatigue of raceway and rolling factors cloth is likewise considered beside plastic deformation. Fatigue going on rolling surfaces is the primary purpose of bearings failure.
For calculations of dynamically loaded bearings i.e. bearings which are rotating beneath load, the simple dynamic load score Cis used.
This amount is a constant (as for fee and bearing load direction) at which bearing will gain nominal carrier existence of a million revolutions acc. To ISO 281 standard, presenting that for radial bearing the burden is solely radial – simple dynamic radial load score, and for thrust bearings the burden is solely axial – simple dynamic axial load score.
Values of load score offered on this e-book are concerning to bearings made of bearing steel, hardened until at the least fifty eight HRC. Bearing carrier existence may be described as unique quantity of revolutions or as quantity of labored hours which bearing is successful to gain until first symptoms and symptoms of fatigue wear (scoring, spelling) on one of the earrings or on rolling factors.
Life adjustment factors allow the original equipment manufacturer to better predict the actual service lives and reliability of bearings that you select and install in your equipment. An adjusted calculated L10 rating life is calculated by using the following formula:
Lna = a1 x a2 x a3 x L10
Where:
- Lna = adjusted rating life
- a1 = life adjustment factor for reliability
- a2 = life adjustment factor for special bearing properties, such as material
- a3 = life adjustment factor for operating conditions, lubrication, cleanliness, etc.
- Life adjustment factors, a1, a2 and a3, can theoretically be greater or less than 1.0, depending on their evaluation.
Life Adjustment for Reliability - a1
In the OEM’s process of predicting the service reliability of his/her equipment, it is sometimes necessary to increase the reliability of the selected bearings to predict a longer mean time between failures. The a1 factors shown below are for increased values of reliability. If a lower value for L10 is calculated with an a1 factor, and it is not acceptable, then a bearing with greater Dynamic Capacity needs to be chosen.
Reliability - % Ln a1 factor |
90 L10 1.00 |
95 L5 0.64 |
96L4 0.55 |
97 L6 0.47 |
98 L2 0.37 |
99 L1 0.25 |
Key Takeaways:
- During the rotation, a movement of 1 raceway relative to any other raceway occurs. In general, a bearing includes an internal raceway, outer raceway, rolling factors and commonly a cage, as proven with inside the discern below.
- High radial load-wearing potential, precision, excessive aid stiffness, excessive-velocity functionality amongst others makes them appropriate for such applications.
- It can variety from 2 for easy running situations with a low threat of vibrations, to as excessive as five or 6 for programs that can be subjected to excessive surprise hundreds.
Design of Sliding contact bearing:
A bearing is a gadget detail which help some other transferring gadget detail (called magazine). It lets in a relative movement among the touch surfaces of the members, even as sporting the load.
A little attention will display that because of the relative movement among the touch surfaces, a positive quantity of energy is wasted in overcoming frictional resistance and if the rubbing surfaces are in direct touch, there might be speedy put on.
In order to lessen frictional resistance and put on and in a few instances to hold away the warmth generated, a layer of fluid (called lubricant) can be provided. The lubricant used to split the magazine and bearing is mostly a mineral oil delicate from petroleum, however vegetable oils, silicon oils, greases etc., can be used.
Following techniques are utilized in designing the sliding touch bearing design.
1. PETROFF’S EQUATION
Petroff’s equation is used to decide the coefficient of friction in magazine bearings. It is primarily based totally on the subsequent assumptions:
(i) The shaft is concentric with the bearing
(ii) The bearing is subjected to a mild load in practice, such situations do now no longer exist.
However, Petroff’s equation is vital as it defines the organization of dimensionless parameters that govern the frictional homes of the bearing. It is given by,
f=2π2(r/c)(μns/p)
Petroff’s equation suggests that there are critical dimensionless parameters, rc and μnsp that govern the coefficient of friction and different frictional houses like frictional torque, frictional energy loss and temperature upward thrust with inside the bearing.
2. MCKEE's EQUATION
Bearing Modulus is a dimensionless parameter on which the coefficient friction in a bearing relies upon fig. In the location to the left of Point C, running situations are excessive and combined lubrication takes place as proven with inside the fig below.
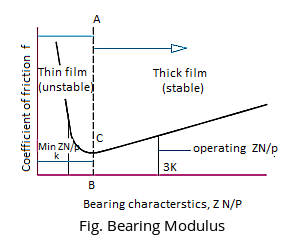
A small change in speed or increase in load can reduce ZN′/p and a small education in ZN′/p can increase the coefficient of friction drastically. This increases heat which reduces the viscosity of the lubricant. This further reduces ZN′/p leading to further increase in friction.
3. REYNOLD'S EQUATION
The idea of hydrodynamic lubrication is primarily based totally on a differential equation derived with the aid of using Osborne Reynolds.
This equation is primarily based totally on the subsequent assumptions:
(i) The lubricant obeys Newton’s regulation of viscosity
(ii) The lubricant is incompressible
(iii) The inertia forces with inside the oil movie are negligible
(iv) The viscosity of the lubricant is consistent
(v) The impact of the curvature of the movie with appreciate to movie thickness is neglected. It is believed that the movie is so skinny that the stress is consistent throughout the movie thickness
(vi) The shaft and the bearing are rigid
(vii) There is a non-stop deliver of lubricant
The Reynold's equation is as follows,
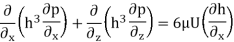
There is no exact analytical solution for this equation for bearings with finite length. Theoretically, exact solutions can be obtained if the bearing is assumed to be either infinitely long or very short. These two solutions are called Somerfield’s solutions. Approximate solutions using numerical methods are available for bearings with finite length.
Journal bearing:
Journal or undeniable bearings include a shaft or magazine which rotates freely in an assisting metallic sleeve or shell. There aren't any any rolling factors in those bearings. Their layout and production can be highly simple, however the concept and operation of those bearings may be complex.
This article concentrates on oil and grease-lubricated complete fluid movie magazine bearings; however first a short dialogue of pins and bushings, dry and semi lubricated magazine bearings, and tilting-pad bearings.
Low-pace pins and bushings are a shape of magazine bearing wherein the shaft or shell usually does now no longer make a complete rotation. The partial rotation at low pace, earlier than usually reversing direction, does now no longer permit for the formation of a complete fluid movie and hence metallic-to-metallic touch does arise in the bearing.
Pins and bushings usually function with inside the boundary lubrication regime. These forms of bearings are usually lubricated with an intense stress (EP) grease to resource in assisting the burden.
Solid molybdenum disulfide (moly) is blanketed with inside the grease to beautify the burden-wearing functionality of the lubricant.
Many out of doors production and mining gadget programs contain pins and bushings. Consequently, surprise loading and water and dust infection are frequently predominant elements of their lubrication.
Dry magazine bearings include a shaft rotating in a dry sleeve, normally a polymer, which can be combined with solids which include molybdenum, graphite, PTFE or nylon. These bearings are confined to low-load and low-floor space programs.
Semi lubricated magazine bearings include a shaft rotating in a porous metallic sleeve of sintered bronze or aluminum wherein lubricating oil is contained in the pores of the porous metallic.
These bearings are confined to low hundreds, low-to-medium pace and temperatures as much as one hundred (210°F). Tilting-pad or pivoting-shoe bearings include a shaft rotating inside a shell made from curved pads. Each pad is capable of pivot independently and align with the curvature of the shaft.
The benefit of this layout is the extra correct alignment of the assisting shell to the rotating shaft and the growth in shaft balance that's obtained.
1 Journal bearings are intended to encompass sleeve, undeniable, shell and Babbitt bearings. The time period Babbitt sincerely refers back to the layers of softer metals (lead, tin and copper) which shape the metallic touch floor of the bearing shell.
These softer metals overlay a more potent metallic help shell and are had to cushion the shell from the tougher rotating shaft. Simple shell-kind magazine bearings take delivery of best radial loading, perpendicular to the shaft, usually because of the downward weight or load of the shaft.
Thrust or axial hundreds, alongside the axis of the shaft, also can be accommodated via way of means of magazine bearings designed for this purpose.
Journal bearings function with inside the boundary regime (metallic-to-metallic touch) best for the duration of the startup and shutdown of the gadget whilst the rotational pace of the shaft (magazine) is inadequate to create an oil movie. It is for the duration of startup and shutdown whilst nearly all the harm to the bearing occurs.
2 Hydrostatic lift, created via way of means of an outside pressurized oil feed, can be hired to glide large, heavy journals previous to startup (shaft rotation) to save you this kind of harm.
During regular operation, the shaft rotates at enough pace to pressure oil among the conforming curved surfaces of the shaft and shell, hence developing an oil wedge and a hydrodynamic oil movie.
This complete hydrodynamic fluid movie permits those bearings to help extraordinarily heavy hundreds and function at excessive rotational speeds. Surface speeds of one hundred seventy five to 250 meters/second (30,000 to 50,000 feet/minute) are not unusual place.
Temperatures are frequently confined via way of means of the lubricant used, because the lead and tin Babbitt is able to temperatures attaining 150°C (three hundred).
Normally, the minimal oil movie thickness is likewise the dynamic working clearance of the bearing. Knowledge of the oil movie thickness or dynamic clearances is likewise beneficial in figuring out filtration and metallic floor end requirements.
Typically, minimal oil movie thicknesses with inside the load region for the duration of operation stages from 1.zero to three hundred microns, however values of five to seventy five microns are extra not unusual place in midsized commercial gadget.
The movie thickness could be more in gadget which has a bigger diameter shaft. Persons requiring an extra genuine fee ought to searching for facts at the Somerfield Number and the Reynolds Number.
Foot step bearing:
A footstep bearing is a cylindrical inflexible block with a stable basis. It has a hollow space inner it inside which the shaft is positioned.
The footstep bearing helps a vertical shaft. Many a time vertical shafts overhang, consequently the footstep bearing is used as quit help.
Long shafts in machines, while in use generally tend to bend because of their personal weight and consequently purpose vibration, noise, and inefficient electricity delivery.
A Footstep bearing permits unfastened rotation of the shaft inner it, additionally even as assisting it with minimal resistance.
Construction of Foot step bearing
The footstep bearing is made of the subsequent components:
- The frame
- Disc Pin
- Bush
- The frame
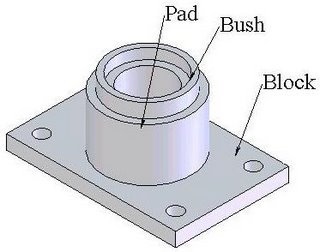
The base additionally referred to as the frame is made of Grey forged iron, spheroidal forged iron, or forged metal and is bolted to a basis or an inflexible structure.
Body of Footstep bearing Body of foot step bearing
The frame has a cylindrical extrusion inner which a small hollow for the pin to match is furnished as proven with inside the discern below.
There is a small cut-out on the pinnacle a part of the cylinder for locking the cushy of the bush.
Disc
The disc is a round component with its pinnacle floor being concave. The disc is positioned at the lowest of the cylinder of the frame, such that the hollow of the disc and the frame align perfectly.
Disc of Footstep bearing
Disc of footstep bearing the fundamental characteristic of the disc is to help the face of the shaft and save you the wear and tear of the frame because of the rotating of the shaft.
The disc is made of softer fabric like gunmetal. The disc receives wiped out because of the rubbing movement and is effortlessly replaceable.
Pin
The pin is made of Fe 410W. The characteristic of the pin is to stable the disc to the frame and save you the disc from rotating because of the rotation of the shaft. Pin of foot step bearing Half a part of the pin is with inside the frame while the opposite 1/2 of is in the disc.
Bush
The bush is a whole cylindrical component inner which the shaft is positioned. The bush is positioned in the cylindrical a part of the frame.
The bush is made of gunmetal or different smooth fabric and serves the identical cause because the disc.
The fundamental characteristic of the bush is to defend the frame from put on prompted because of the rotation of the shaft inner it. The bush has an extruded component on the facet known as the cushy.
The sung suits with inside the cut-out of the frame. This prevents the bush from rotating while the shaft rotates inner it.
Limitations of foot step bearing
- Unlike the pedestal bearing or the Plummer block, the foot step bearing may be positioned at the lowest of the shaft only.
- The foot step bearing cannot be efficaciously lubricated.
- Also the bush and disc ought to get replaced on occasion because of put on.
- That’s a top level view of the Footstep bearing.
- If you want this put up or have any pointers do allow us to realize with inside the remarks we would like to listen from you.
Key Takeaways:
- The idea of hydrodynamic lubrication is primarily based totally on a differential equation derived with the aid of using Osborne Reynolds.
- Thrust or axial hundreds, alongside the axis of the shaft, also can be accommodated via way of means of magazine bearings designed for this purpose.
- Long shafts in machines, while in use generally tend to bend because of their personal weight and consequently purpose vibration, noise, and inefficient electricity delivery.
References:
1. Design of Machine Elements, V.B. Bhandari, Tata McGraw Hill
2. Mechanical Engineering Design, J.E. Shigley, C.R. Mischke, R.G. Budynas and K.J. Nisbett, TMH
3. Machine Design, Pandya and Shah, Charotar Book Stall
4. Fundamentals of Machine Component Design by R.C. Juvinall and K.M. Marshek, John Wiley & Sons.
5. Machine Drawing by N.Sidheswar, McGraw-Hill