Unit 1
Concept of organization
Organizational Behavior (OB) is the study of human behavior in organizational settings, the interface between human behavior and the organization, and the organization itself.
It is dynamic and changes as per the needs of society, its members, business objectives and environmental changes.
It is defined in different ways by different theorists.
The definitions given by some well know theorists are as given below:
According to L. M. Prasad, “Organizational Behavior can be defined as the study and application of knowledge about human behavior related to other elements of an organization such as structure, technology and social systems”.
According to Davis and Newstram, “Organizational Behavior is the study and application of knowledge about how people act within organizations”.
Scope of Organizational Behavior
The scope of Organizational Behavior includes People, Technology, Structure and Social Systems which may be briefly discussed as under:
People: People refer to the individuals and groups which are evident in an organization. The study of individual behavior, the behavior exhibited by the different groups present in an organization comprises an important element in organizational behavior studies.
Technology: Technology means the equipment’s, machines, technology used by the people who are working in the organization.
Structure: Structure represents the relationships between the people working in the organization. The relationship may be hierarchical like boss subordinate or between same positions or between different departments.
Social Systems: Organization doesn’t operate alone; it does exist in a society which the organization needs to take care of the values and beliefs of the society. The organization also needs to interact with the society where it does business. Organization is just a part of the large supra system consisting of many elements.
Features of Organizational Behavior
- It is a Separate Field of Study: Organizational behavior has evolved as a separate field of study due to the relevance of human behavior in an organization. OB has a multi-disciplinary orientation and thus not based on a specific theoretical background. There are many issues as regards human behavior which needs to be studied separately.
- It has an Interdisciplinary Approach: Organization behavior has drawn concepts from different disciplines like psychology, anthropology and sociology.
- It is a part of Applied Science: The very nature of OB is applied. OB applies various researches to solve the organizational problems related to human behavior.
- It has a Humanistic and Optimistic Approach: OB applies humanistic approach towards the employees in an organization. It deals with the thinking and feeling of human beings. It also realizes that employees actually possess innate capabilities which can be actualized if they are given proper conditions and environment.
- It is a Total System Approach: The system approach is one which integrates all the variables affecting organizational functioning. OB studies all those variables to study the complexity man possess.
The evolution of organizational behavior can be traced back to the era where Max Weber propounded his theories and other organizational studies. The Industrial revolution during the period of 1970 boosted the development of organizational behavior theories development. The industrial revolution brought into mechanization, adopting new production techniques and other industrial developments. This also led to formation of new forms of organizations. At this time, Max Weber propounded his theory of bureaucracy where he emphasized bureaucracy as the ideal form of organization that rested on rational legal principles and maximized technical efficiency.
In 1890, Scientific management formulated by Frederick Winslow Taylor gained popularity where scientific methods were used in production, selection and training of employees. But the failure of scientific management gave birth to the human relations movement which heavily focused on employee cooperation and morale.
The period between 1930 and 1950 was witnessed as the human relations movement period which further contributed in the development of organizational behavior studies. Scholars like Elton May, Chester Barnard, Henry Fayol, Mary Parker Follet, and many others contributed to the development and growth of organizational behavior as a discipline. However, Herbert Sinon’s Administrative Behavior introduced a number of important concepts such as decision making into the field of organizational behavior.
In 1960’s and 1970’s the field of organizational behavior started gaining more importance by the new introduction of concepts like informal organization, resource dependence, Contingency theory, Institutional theory and organizational ecology.
In the starting of 1980’s, organizational change and organizational culture become another area of study under organizational behavior.
Organizational behavior is the study of human behavior and their interrelations in organizations. It does this by a systematic approach where people-organization-relationships are interpreted. Its purpose is to build better relationships between groups, within groups so that the organizational objectives can be achieved smoothly.
A systematic approach to the study of human behavior will help in identifying why a person behaves in a particular way and how a person perceives a situation. There are differences as well as similarities that can be seen in people’s behavior. An overall model of organizational behavior can be developed on the basis of three theoretical frameworks viz., Cognitive, Behavioristic and Social Learning frameworks.
The Cognitive approach gives more credit to the people and is based on the expectancy, demand and incentive concepts. Edward Tolman was the contributor to this approach.
Ivan Pavlov and John B. Watson made significant contributions to the Behavioristic framework which primarily focuses on observable behaviors. They explained human behavior on the basis of the connection that can be created between stimulus and response.
The Social Learning framework incorporates concepts from both Cognitive and Behavioristic concepts. In this behavior is explained as continuous reciprocal relationships between cognitive, behavioral and environmental determinants. The Organization behavior model is represented by S-O-B-C which represents Situation, Organism, Behavior and Consequences respectively.
Due to the advent of globalization, the managers’ today face, many challenges due to the different backgrounds of the employees in an organization. The managers need to understand, study, analyses and act accordingly while dealing with such employees. This is basically a challenge in front of the managers which can be tackled by studying the organizational behavior model.
The Custodian Model of Organizational Behavior gives priority to the security needs of the employees where the model gives psychological reassurance of economic rewards and benefits.
The Supportive Model of organizational behavior focuses on providing a supportive work environment and motivates employees to give their best efforts.
The Collegial model focuses on making the employees feel as asset for the organization. Employees are considered partners in the organization.
A manager needs to perform various roles in an organization. A manager is flooded with many responsibilities which he needs to pursue altogether. In an organization, the role of manager can be segregated into 10 different roles which are diagrammed below in a chart:
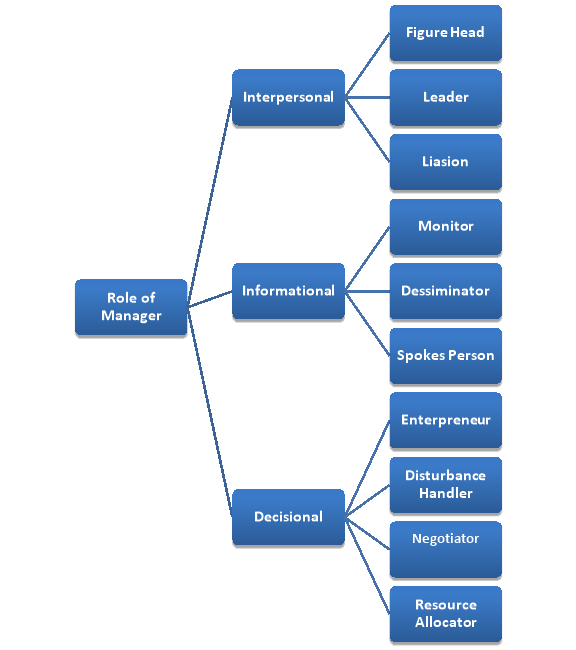
As a figure head, a manager has to sign some legal documents, receive guest from outside, take decisions and sort out activities of subordinates. He is also responsible to motivate employees for an enhanced performance. In case the employees don’t perform well, he needs to understand the employee and act accordingly to bring out the best from the employee.
(a) Informational Roles
A manager needs to stay updated as regards the information from outside and also from inside. The information collected from outside sources by the manager needs to be communicated or disseminated to the subordinates in the organization. The manager might also require becoming the spokesperson in many events or meetings representing the organization.
(b) Decision Roles
A manager performs four different decisional roles. As an entrepreneur, the manger needs to initiate and oversee projects for the development of the organization. As a disturbance handler, the manager needs to provide solutions as regards any differences or grievances cropping up within the organizational atmosphere. The manager also acts as an allocator when he assigns and monitors the allocation of human, physical and monetary resources. A manager also acts as a negotiator when he needs to bargain with outsiders for acquiring benefit for the organization.
The challenges and opportunities for the managers are increasing due to the thrust for excellence in productivity of an organization. The need to fight competition due to globalization and new companies has prioritized the study of organizational behavior which can contribute towards the study of human behavior and hence enhance organizational efficiency. However, certain points as regards challenges have been identified:
- Improving people’s skills: The skills of the people should always be in the mode of improving if increased organizational performance is expected. Hence the managers need to strive towards continuous skill development of employees in the organization.
- Improving quality and productivity: The quality of performance as well as productivity of employees should be given emphasis which will further contribute towards the achievement of organizational goal.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Due to globalization, stiff competition is evident in the market which needs to be tackled at every step of business. Hence TQM should be adopted by organizations which will help in giving a competitive edge to the organization. TQM refers to reducing errors in the managing process, reducing customer complaints by continuously enhancing employee skills.
- Managing Workforce Diversity: Globalization has brought forward employees from different parts of the world. This means employees dwell from different cultural background with different social nurturing. The challenge of OB here is to deal with such workforce diversity.
- Responding to Globalization: Globalization has led to the introduction of new companies from other countries into our home country. More companies with better technology poses challenges to the companies of home countries. To survive, the best option is to upgrade up to the level of foreign companies.
- Empowering people: The employees needs to be given autonomy as regards decision making and allow them to bring in creativity and innovation in the thinking process.
References:
- Organizational behavior by Stephen P. Robbin & Seema Sanghi- pearson
2. Organizational behavior by L.M. Prasad-S Chand & sons
3. Organization behavior: managing people and organization by Gregory moorehead – Biztantra