Unit – 1
Introduction to Entrepreneurship
The word “entrepreneur” is derived from the French verb enterprendre, which means ‘to undertake’. This refers to those who “undertake” the risk of new enterprises. An enterprise is created by an entrepreneur. The process of creation is called “entrepreneurship”.
Entrepreneurship refers to the process of creating a new enterprise and bearing any of its risks, with the view of making the profit. It is an act of seeking investment and production opportunity, developing and managing a business venture, so as to undertake production function, arranging inputs like land, labour, material and capital, introducing new techniques and products, identifying new sources for the enterprise.
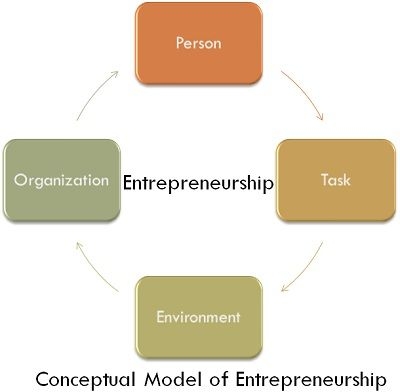
The person who creates a new enterprise and embraces every challenge for its development and operation is known as an entrepreneur. And the undertaking or organisation, typically a startup company, set up by the entrepreneur is called enterprise.
Entrepreneurship is a process of actions of an entrepreneur who is a person always in search of something new and exploits such ideas into gainful opportunities by accepting the risk and uncertainty with the enterprise. Entrepreneurship is a process, a journey, not the destination; a means, not an end. All the successful entrepreneurs like Bill Gates (Microsoft), Warren Buffet (Hathaway), Gordon Moore (Intel) Steve Jobs (Apple Computers), Jack Welch (GE) GD Birla, Jamshedji Tata and others all went through this process.
To establish and run an enterprise it is divided into three parts – the entrepreneurial job, the promotion, and the operation. Entrepreneurial job is restricted to two steps, i.e., generation of an idea and preparation of feasibility report. Here, we shall restrict ourselves to only these two aspects of entrepreneurial process.
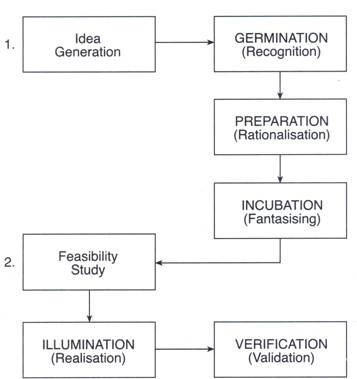
1. Idea Generation: To generate an idea, the entrepreneurial process has to pass through three stages:
a. Germination: This is like seeding process, not like planting seed. It is more like the natural seeding. Most creative ideas can be linked to an individual’s interest or curiosity about a specific problem or area of study.
b. Preparation: Once the seed of interest curiosity has taken the shape of a focused idea, creative people start a search for answers to the problems. Inventors will go on for setting up laboratories; designers will think of engineering new product ideas and marketers will study consumer buying habits.
c. Incubation: This is a stage where the entrepreneurial process enters the subconscious intellectualization. The sub-conscious mind joins the unrelated ideas so as to find a resolution.
2. Feasibility study: Feasibility study is done to see if the idea can be commercially viable. It passes through two steps:
a. Illumination: After the generation of idea, this is the stage when the idea is thought of as a realistic creation. The stage of idea blossoming is critical because ideas by themselves have no meaning.
b. Verification: This is the last thing to verify the idea as realistic and useful for application. Verification is concerned about practicality to implement an idea and explore its usefulness to the society and the entrepreneur.
KEY TAKEAWAY
To trace the genesis of the word entrepreneur it would be prudent to look at word ‘entrepredre’ in French which literally means “between-taker” or “go- between.” The theoretical growth of the concept of entrepreneurship has taken place side by side with growth of term itself.
Entrepreneur refers to individuals who were ‘undertakers’, meaning those who “undertook” the risk of new enterprise. In several literature reviews, it has been observed that as early as in the sixteenth century the Frenchmen who use to organize and lead military expeditions were referred to as entrepreneurs.
In the early 18th century French economist Richard Cantillon used the term entrepreneur to business. Entrepreneur was a dealer who purchases the means of production for combining them into marketable products. Since then the word entrepreneur refers to one who takes the risk of starting a new organization or introducing a new idea, product or service.
Entrepreneur is the most important factor in the process of economic development. He occupies the central place in the growth process because he initiates development in a society and carries it forward. As a change agent, the entrepreneur is the first and foremost a catalyst for change.
The function that is specific to entrepreneur is the ability to take the factors of production—land, labour and capital and use them to produce new goods or services. The entrepreneur perceives opportunities. He works as an originator of a new business venture and also tries to improve an organisation unit by initiating productive changes.
Definition of Entrepreneur from 10 Successful Business Owners (2020)
What is the definition of an entrepreneur?
Manoush Zomorodi Author,MediaConsultant |
Someone who envisions, creates, and evangelizes an idea that they are absolutely crazy about. That idea (it could be a product, book, and consultancy) makes it easier for them to get up in the morning, work ridiculous hours, and keep their brain buzzing. The entrepreneur can work alone, within a company, or in a group, but he/she gets itchy at the thought of working a 9-5 job and following the orders of anyone who isn't efficient and imaginative. |
Mark Cuban Shark Tank Investor |
An entrepreneur someone who can define the business they want to create, see where it is going, and do the work to get there.
|
Jeet Banerjee Founder of Statfuse.com |
To me, an entrepreneur is someone who mixes passion, innovation, and drive to turn a vision into a working business.
|
Matt Mickiewicz Owner of 99Designs, Flippa, Sitepoint |
An entrepreneur is someone who has a bias towards action. Someone who views the world through a different lens. Someone who takes “no” for a challenge, not an answer.
|
Jamie Tardy Eventual Millionaire |
An entrepreneur is someone that goes out and does the work to create something that didn't exist before.
|
Michael Fitzgerald Submittable.com |
An entrepreneur someone who makes something useful or pleasurable out of nothing.
|
Matthew Toren Blogger, Mentor, Investor, Small Business BIG Vision |
An entrepreneur is someone who conceives an idea, creates a path to success, does whatever it takes to succeed and tries to dominate their market!
|
Andrew Schrage MoneyCrashers.com |
An entrepreneur is an innovative, risk-taking individual who identifies a need in a market and finds a way to fill it, whether by using his or her own expertise and passion, the knowledge of others, or a combination of the three. More simply stated, an entrepreneur is someone who sees an opportunity and invests in it in order to turn a profit or provide a solution to some larger issue in the world.
|
Caleb Wojcik ThinkTraffic.net |
An entrepreneur is a starter, not just a dreamer. Anybody can think up an idea for a business, but not everyone can put rubber to the road and actually grow something that both matters and earns money. Taking action is the difference between entrepreneurs and non-entrepreneurs.
|
Barbara Corcoran
| The single most defining characteristic of an entrepreneur is passion. It helps to be pushy – pushy people deliver. It helps to have a gimmick – a unique gimmick will give you a great leap over your competitors. It helps to be willing to fail – all my best business successes came on the heels of what first appeared to be a big flop. But great passion is what it really takes to build a successful business. |
KEY TAKEAWAYS-
Ancient India was known across the world for its affluence and wealth. Traders from all over the world travelled to India to take part in this affluence. Be it the Mughals, the Portuguese, the Turks or the British – all of them ventured into Indian boundaries for various financial reasons. While over a long period of time, the entrepreneurial drive among Indians was notably absent, modern India has risen up to the task again. Even those who have little or no entrepreneurial experience are choosing to take part in an entrepreneurship management course to gain theoretical knowledge as well as practical experience before starting their entrepreneurial journey.
It is notable how Indian entrepreneurship is seeing a rise these days. The country stands third in the list of countries with the fastest-growing list of start-ups. The first two countries are the USA and the UK. The digitization of India has led to an ever-increasing interest in the online market. Both urban and rural India is seeing a boom in the way internet-based apps and products are interacting with the people.
FACTORS LEADING TO INCREASE IN ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Government of India is also encouraging the interest in entrepreneurship. It has launched a ‘start-up India’ campaign that provides support to entrepreneurial initiatives. Schemes have been floated to promote world-class innovation hubs and self-employment opportunities for the youngsters. The focus is especially high in technology-driven areas. The government of India realises the potential that entrepreneurship holds in giving a boost to the economy and uplifting the financial status of the people of the country. Such faith in entrepreneurship from the highest body in India leads to the development of interest in this field among the youth of the country.
2. The Rise of Technology:
Technology has led to India becoming a software power. It has the second-highest number of internet users in the world. In addition to this, the uncertainty regarding jobs is fuelling people’s interest in having their own business. Industries are in constant need for innovation to move forward and start-ups are coming up in fields like artificial intelligence and machine learning to help businesses solve their inherent issues or to bring in more efficiency.
3. Female Entrepreneurs:
The entrepreneurial wave is also being driven by women entrepreneurs who are carving a niche for themselves. Start-ups like Zivame, Kaaryah, Your Story and POPxo have become successful ventures. Led by women founders, they are answering the market needs in their respective segments.
CHALLENGES FOR INDIAN ENTREPRENEURS-
1. Raising Funds for the Business:
The challenge for any start-up lies in raising funds for the business. To do so, they need to have a dependable business plan and a strategy on how they want to enter the market. Start-ups get funds from venture capitalists once they have convinced them about the venture’s potential for success.
2. Knowledge on How to Run a Business:
As simple as it may seem, any venture needs to have a good plan, to begin with. Various business schools have started entrepreneurship courses to answer the requirements of interested students who seek to become an entrepreneur. These courses help the students get their expectations right and prepare themselves for a career in entrepreneurship.
3. Keeping Up with Technology:
This point is important for start-ups in the technology sector. It is important for them to keep track of the latest technology and stay ahead of the curve. These days, technological innovations are happening every day leading to technology getting obsolete quickly. They need to keep on improving their products and give new and innovative products to their customers. Innovations need to be useful for customers. They need to have good research backing their product launches. If the product does not answer any need gap in the market, then it will not be successful in the market even if there is cutting edge technology behind it.
4. Quality of Human Resources:
Any business’ success is dependent on the people who work for it. It is critical to have the right mix of people. These people should be trained for their job profiles. For example, a marketing manager should understand the industry and its customers and accordingly plan marketing campaigns. They should also have practical experience in performing their jobs properly. Additionally, they should have the right attitude and keen interest in doing their work to the best of their abilities.
Entrepreneurship thrives in a conducive environment that facilitates the growth of a business. It is crucial for a booming economy to have entrepreneurs since they do not seek jobs but are the job creators for the rest of the people. With the right support, India’s entrepreneurship story can lead to its economic growth as well as the prosperity of its people.
Key Takeaways-
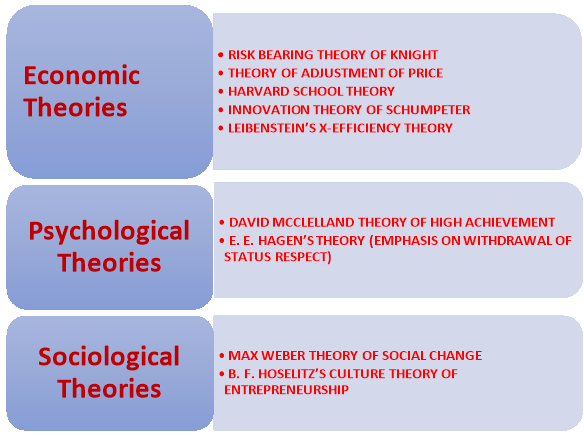
The various theories of entrepreneurship may be broadly divided into three groups-
A) Economic Theory
B) Psychological Theory
C) Sociological Theory
A) ECONOMIC THEORIES
G.F. Papanek and J.R Harris are two economists who advocated economic theory. According to them, economic incentives are the main drive for entrepreneurial activates. A few important economic theories of entrepreneurship are discussed below
1) RISK BEARING THEORY OF KNIGHT
There are certain risks that are measurable and the probability of such risk can be statistically estimated and hence such risks can be insured. Example of insurable risks include theft of commodities, fire in the enterprise, accidental death etc. On the other hand, there are certain risks which cannot be calculated.
The probability of their occurrence cannot be statistically ascertained. Such risks include risks associated to changes in prices, demand and supply. These risks are non-insurable. Prof. Knight opined that the profit is the reward for bearing the non-insurable risks and uncertainties. Uncertainty-bearing is one of the most vital functions in a dynamic economy. The entrepreneur bears the uncertainty involved in the enterprise.
The salient points of Knight’s theory include:
i. According to the theory, the entrepreneur earns pure profits for bearing the uncertainty.
ii. The probability of uncertainty or non-insurable risks cannot be statistically estimated.
Entrepreneurs undertake risks of varying degrees according to their ability ad inclination. The theory suggests that the more risky the nature of enterprise, the higher level of profit earned by the entrepreneurs.
iv. Profit is the reward of the entrepreneur for bearing uncertainties and risks. Hence, it should be a part of the normal cost.
v. The reward of the entrepreneur is uncertain. Entrepreneur guarantees interest to lender of capital, wages to workers and rent to the landlord.
vi. The level of uncertainty in business can be reduced by applying the technique of consolidation. The total level of uncertainty can be reduced by pooling individual instances.
F.H. Knight’s theory is one of the most sophisticated theories to explain supply of entrepreneurship based on profit. But, the theory suffers from certain drawbacks as pointed by the critics.
i. The role of an entrepreneur has not been elaborately provided by the theory. The entrepreneur’s activity has been restricted to uncertainty bearing. Modern business activities are different. Often, there is a dichotomy between ownership and management. These factors have not been taken into consideration.
ii. The uncertainty-bearing theory discussed the concept of profit in a vague way. The exact estimation of profit for the entrepreneur has not been provided in the theory
iii. Profit as a residual income of the entrepreneur has been criticized.
iv. Critics feel that uncertainty-bearing should not be treated like other factors of production like land, labour and capital. It is a psychological concept and should be treated in a different manner.
2) THEORY OF ADJUSTMENT OF PRICE- The adjustment of prices is the main role of the entrepreneur. According to Kirzner, alertness to disequilibrium is the distinguishing characteristics of an entrepreneur. Alertness enables some individuals to intervene in the market by changing the price while other individuals simply respond to market by changing their buying and selling plan in lieu of the new price.
Kirzner further maintains that the primary role of economic theory is to explain behaviour in terms of purposeful human action and consider to that extent purposeful human actions can interact to produce unexpected income.
3) HARVARD SCHOOL THEORY- According to this school theory, entrepreneurship takes a purposeful activity which initiate, maintain or develop an profit earning enterprise in interaction with the internal situation of the business or with the economic, political and social circumstances surrounding the business. This theory emphasized two types of activities.
a) The organization or co-ordination activity and
b) The sensitivity to the environmental characteristics that affect decision making.
4) INNOVATION THEORY OF SCHUMPETER- Joseph Schumpeter propounded the well-known innovative theory of entrepreneurship. Schumpeter takes the case of a capitalist closed economy which is in stationary equilibrium. He believed that entrepreneurs disturb the stationary circular flow of the economy by introducing an innovation and takes the economy to a new level of development. The activities of the entrepreneurs represent a situation of disequilibrium as their activities break the routine circular flow.
Innovation could involve any of the following:
i. Innovation of new products.
ii. Innovation in novel methods or processes of production.
iii. The opening up of a new market.
iv. Entrepreneurs might find new source of supply of raw materials
v. Innovation in management. This means reorganization of an industry
Criticisms:
Schumpeter’s theory has been subjected to the following criticisms:
i. Critics feel that the theory over emphasized on innovative functions of the entrepreneur. It ignored the organizing aspects of entrepreneurship.
ii. Schumpeter had completely ignored the risk-taking function of the entrepreneur, which cannot be ignored. Whenever an entrepreneur develops a new combination of factors of production, there is enough risk involved.
iii. The theory is more applicable in developed countries only. In developing countries there is a paucity of innovative entrepreneurs.
iv. The theory does not provide the explanation as to why few countries have more entrepreneurship talent than others.
Despite of all the above criticisms Schumpeter’s theory is considered as a landmark in the expansion of entrepreneurship theories.
5) LEIBENSTEIN’S X-EFFICIENCY THEORY- The concept of X-efficiency was introduced by Harvey Leibenstein a noted economist in1966 in his article titled “Allocative efficiency vs. X-efficiency”. This is also referred to as X-inefficiency. In general X-inefficiency refers to the difference between the optimal efficient behaviour of business in theory and the observed behaviour is practice which occurs owing to different factors.
X-efficiency refers to the effectiveness with which a given set of inputs are used to produce outputs. If a particular firm is producing the maximum output it can, given the resources it employs with the best available technology, it is said to be technical-efficient. X-inefficiency occurs when technical-efficiency is not achieved. Whenever an input is not used effectively the difference between the actual output and the maximum output attributable to that input is a measure of the degree of X-efficiency.
Harvey Leibenstein had mentioned that for allocative efficiency the whole economy was considered whereas in case of X-efficiency just specific companies and industries are to be considered.
X-efficiency arises either because the firm’s resources are used in the wrong way or because they are wasted, that is, not used at all.
The entrepreneur has been entrusted two roles; first the role of a gap filler and second an input completer. The production function usually has certain deficiencies. These deficiencies and gap arise because all the factors of production function cannot be marketed. The entrepreneur has been entrusted the job to fill the gaps in the market. The second role of the entrepreneur is input completion. The entrepreneur has to mobilize all the available inputs in order to improve the efficiency of existing production methods.
Leibenstein advocated two types of entrepreneurship. First type is the ‘Routine entrepreneurship’ which involves the important functions of management of business. Second type is that of the ‘New entrepreneurship’ which involves innovative entrepreneurship.
The theory has many novel contributions but has been criticized on following counts:
I. The exact influence which the X-efficiency has on output of an organisation cannot be determined.
II. The theory is less predictable as compared to normal theories.
(B) PSYCHOLOGICAL THEORIESAccording to the psychologists, entrepreneurship is most likely to emerge when a society has sufficient supply of individual possessing particular psychological characteristics. The theories proposed by McClelland and Hagen fall under important psychological theories. They are explained below-
1) DAVID MCCLELLAND THEORY OF HIGH ACHIEVEMENT - This theory was developed by David. McClelland. McClelland concerned himself with economic growth and the factors that influence it. In this context, he tries to find the internal factors i.e. “human values and motives that lead man to exploit opportunities, to take advantage of favourable trade conditions.” That is why he gives importance to the innovative characteristics of entrepreneurial role. The entrepreneur is concerned with need for achievement (n-achievement).
The n-achievement is called as “a desire to do well, not so much for the sake of social recognition or prestige, but for the sake of an inner feeling of personal accomplishment.”
It is this motive of n-achievement that guides the actions of entrepreneur. People with high n-achievement behave in an entrepreneurial way. So it is better to develop n-achievement among individuals to ensure high scale of economic development. In practice, n-achievement motive is inculcated through child rearing practices, which stress standards of excellence, material warmth, self-reliance, training and low father dominance.
McClelland identified two characteristics of entrepreneurship. First doing things in a new and better way. Secondly, decision making under uncertainty.
This motive is called as the tendency to strive for success in situations involving an evaluation of one’s performance in relation to some standard of excellence. People having high need for achievement are more likely to succeed as entrepreneurs.
According to McClelland, individuals with high need achievement will not be motivated by monetary incentives but that monetary rewards will constitute a symbol of achievement for them. Similarly, they are also not interested much for social recognition or prestige but their ultimate goal is personal accomplishment. That is why McClelland suggests that in order to raise the level of achievement motivation, parents should set high standards for their children
Critical Evaluation:
Research studies on the psychological roots of entrepreneurship reveal that high achievement orientation ensures the success of entrepreneurs. But the empirical tools of concept used by McClelland are found to be highly suspect and one wonders how many of the individuals who are judged to have high n-achievement could succeed in utilising it in practice in the present day developing countries unless strengthened by other reinforcing circumstances.
2) E. E. HAGEN’S THEORY (EMPHASIS ON WITHDRAWAL OF STATUS RESPECT): E. Hagen attempted to formulate a theory of social change. The theory of social change explains that when members of some social groups feel that their values and status are not respected by the society, they turn to innovation to get the respect of the society. According to Hagen, entrepreneurship is a function of status withdrawal. This theory provides that a class which lost its previous prestige or a minority group tends to show aggressive entrepreneurial drive.
Hagen postulates four types of events which can produce status withdrawal:
(i) Displacement of a traditional elite group from its previous status by another traditional group by physical force.
(ii) Denigration of values, symbols through some change in the attitude of superior group.
(iii) Inconsistency of static symbol with a changing distribution of economic power and.
(iv) Non-acceptance of expected status on migration to a new society.
Hagen further opined that creative innovation or change is the basic feature of economic growth. He describes an entrepreneur as a creative problem shooter interested in things in the practical and technological realm. Such type of individual feels a sense of increased pleasure when facing a problem and tolerates disorder without discomfort.
In traditional societies, positions of authority are granted on the basis of status, rather than individual ability. That is why, Hagen visualised an innovative personality.
There are four responses which assess the personality-
(i) Retreatist – One who combines to work in the society but remains indifferent to his work and position.
ii) Ritualist – One who adopts a kind of defensive behaviour and acts in the ways accepted and approved in his society but with no hopes of improving his position.
(iii) Reformist- One who foments a rebellion and attempts to establish a new society?
(iv) Innovator- A creative individual who is likely to be an entrepreneur.
Innovation requires creativity and such creative individuals cause economic growth. In practice creative personalities emerge when the members of some social groups experience the withdrawal of status respect. Whenever there is any withdrawal of status respect, it would give rise to innovation—a creative individual who is likely to be an entrepreneur.
Critical Evaluation:
The theory acts to distinguish between entrepreneurship and intra-preneurship. There are different factors within the organisation which motivate the executives and professionals to do some innovative behaviour leading to new products and services. Actually, they are not governed by status withdrawal.
The theory only suggests that the people, who had enjoyed social standing at some stage in their histories fall into a retreatist phase and with an urge to regain that lost status emerge as entrepreneurial personality. The theory also presupposes a long term perspective for entrepreneurial growth about three to five generations for the emergence of entrepreneurship.
But actually it does not happen. In India, first generation entrepreneurs are quite successful in their entrepreneurial behaviour. J.P. Gour of Jai Prakash Industries and Sunil Mittal of Bharti group etc. can be cited in this context.
(C) SOCIOLOGICAL THEORIES
The supporters of sociological theory say that the entrepreneurial activities is affected from social status hierarchy and values. Individuals’ position, tradition, cultural values, mobility and social status etc. are thoroughly effected to entrepreneurship development. The sociological theories depend on this concept.
Two important social and cultural theories are:
1) MAX WEBER THEORY OF SOCIAL CHANGE
According to Weber, “A person who lives in which community, religion and follows the conventions and religious values.”
All these things completely affect by their professional life, energy, livelihood and enthusiasm.
In other words, Max Weber is connected with the emergence and success of entrepreneurs with social ethical values systems. He also associated the entrepreneurship development with protestants and other non-convents.
According to him, non-convents groups are those groups who gives pressure on capitalism, money rationality and thinking. They were almost successful in creating entrepreneurs, wealth collection, technology, capital formation and economic development.
“The modern economic development is explained to a greater extent, by the social factors as discussed in the foregoing lines. This becomes more prominently evident when we contrast the Indian culture with that of the western of particularly of the American culture. Even if we contrast the different sub cultures within the same larger society, the story of economic development is explained.”
Weber says that the religious beliefs and moral values are basically affected to people’s attitude, view trust and thinking pattern and people’s selected occupational pursuits as per earlier things.
i. Entrepreneurship development is based on Protestants.
ii. Selection of occupation pursuits is effected from religious and social values.
iii. Religious and moral values are effected to people’s attitude, thinking power.
2)B. F. HOSELITZ’S CULTURE THEORY OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP
According to Hoselitz, “The development of industrial entrepreneur is based on only which type of society are there.”
a. Social process is not static.
b. Sufficient employment pattern is available.
c. Encourage to entrepreneurs for personality development.
Hoeslitz says, “Culturally marginal groups plays an important role in encouraging the economic development of any nation.”
He think that the marginal persons are more able in making creative adjustment in changed situations and during the adjustment process they make efforts in bringing real innovations in social behaviour. In addition to this, he emphasised on development of personal qualities for entrepreneurial development.
According to Hoselitz, “Managerial skill and leadership qualities are important factors for entrepreneurship. Besides this, education, training, social values, behaviour and social behaviour/institutions play a crucial role in personality development.”
Highlighted Points:
i. Entrepreneurship development is based on social progress and employment patterns.
ii. Personality development is an essential quality for entrepreneurship development.
iii. Culturally marginal groups are important characters for development process.
iv. Marginal groups are having the ability of innovation.
v. Managerial ability and leadership quality is must for entrepreneurship development.
Key takeaways-
A) Economic Theory- Risk Bearing Theory Of Knight,Theory Of Adjustment Of Price ,Harvard School Theory , Innovation Theory Of Schumpeter
Leibenstein’s X-Efficiency Theory .
B) Psychological Theory- David Mcclelland Theory Of High Achievement and
E. E. Hagen’s Theory (Emphasis On Withdrawal Of Status Respect)
C) Sociological Theory- Max Weber Theory Of Social Change and
B. F. Hoselitz’s Culture Theory Of Entrepreneurship .
The entrepreneurial activity depends upon a complex and varying combination of socio-economic, political, psychological and other factors. Entrepreneurship is not an inborn quality; it is a product of environment. To be successful, an entrepreneur has to remain dynamic and responsible to the whole environment. Environment is a combination of various dynamic, complex and uncontrollable external influences within which an entrepreneur has to function. In case of favorable business environment, entrepreneurship developed rapidly. Environment creates challenges, pressures, risks, opportunities, gains and threats for the entrepreneur. Entrepreneur needs a rational vision on his part to take advantages of these changing conditions.
The economic environment exercises perhaps the most direct and immediate influence of business environment. They include capital, raw materials and markets etc. Further, type of economy whether developed, developing, or underdeveloped, rates of savings and investment, growth rate of G.N.P per capita income, volume of exports and imports balance of payments position, price level, rates of inflation, deflation and reflection means of transport and communication also affect the economy of the country.
The important elements of economic environment and their influences may be discussed as follows:
(1) Economic System: Economic System of a country may be capitalist, socialist, democratic or mixed. Economic system determines the nature and scope of entrepreneurship. It also affects mobilization of resources. In the capitalist system, entrepreneur-ship developed rapidly while socialist economy creates hindrance in the way of entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurs can work independently in the capitalist economy which is not so in the socialist economy.
(2) Economic Conditions: Economic condition of a country may be of developed, developing and underdeveloped. The nature of Entrepreneurship is determined by the level of development of economy. ‘In developed economy, entrepreneurs have to undertake innovative activities for survival and growth but in the developing and underdeveloped countries, entrepreneurs do not take much interest in the innovative activities. In these countries, entrepreneurs have to face many problems and challenges for their development,
(3) Structure of Economy: The factors like national income, rate of capital formation, development of capital market, rate of investment, saving and foreign trade etc., is the structure of the economy. The favorable growth of these factors may promote entrepreneurship.
(4) Trade Cycles: Cycle of inflation and deflation, create many challenges and problems in the development and expansion of entrepreneurship. Changes in major economic variables like money income, cost of living, interest rates, savings, credit availability etc. have an immediate impact on the working an enterprise.
(5) Economic Policies and Laws: The government enacts various laws to regulate the business environment. Industrial policy, Licensing policy, monetary policy, import-export policy are considered economic policies which produce a great effect on the entrepreneurship activities. Favorable economic policies and laws promote the development of entrepreneurship.
(6) Financial Resources: Adequate Funds are required for bringing together other factors of production. It also encourages innovations and introduction of new things. Lack of required capital for industrial activities may impede and discourage entrepreneurs.
Social external environmental factors in a country also exercise a significant impact on the emergence of entrepreneurship in a country. Social factors in a country determine the extent and level of industrialization, as they influence, the demand of a product or service at a given point of time. Social factors are bound to have deep influence on consumer’s taste, preference, life and living. They include -
(i) Customs and Religious Traditions: Customs, religious faith and ideology also affect entrepreneurial growth. In a developing country like India, there are such religious traditions which are not conductive to entrepreneurship. People are fatalists and they do not like to work hard or do something new. They remain satisfied with old.
(ii) Family Background: The environment of family affects entrepreneurship. Joint family can provide family resources to invest and expand family business. If the father is a professional, entrepreneur or businessman, the son is more likely to enter the same line because of certain inherent advantages. Mobility of the entrepreneur is influenced by the occupational and social status of the family.
(iii) Desire for improvement and protection of status: The desire for improvement and protection of status forces people to behave responsibly. People work hard to maintain and improve their status and it contributes to entrepreneurial growth.
(iv) Social Mobility and Social Marginality: There are some persons of the view point that high degree of mobility is conductive for the emergence of entrepreneurship. Social marginality also positively influences entrepreneurship.
(v) Values: Values are enduring beliefs that people hold about morals, equality, freedom, work ethic, and so on. When values change, the impact is felt in the ways in which entrepreneurs, government and society operate.
(vi) Attitude towards changes and Risk-taking: People’s attitude towards changes, capacity and feelings of risk-taking etc. also affects the entrepreneurial environment. Positive attitude to adopt changes and risk-taken, influence the development of entrepreneurship.
(vii) Work Ethics: It is dedication or preoccupation with work. It is a sense of duty and work which is needed for entrepreneurial progress. The Japanese have achieved tremendous progress because of their commitment of work.
 (viii) Educational and Technical Know How: Education, entrepreneurship and development are very closely related, rather say they are interrelated. Education is the best means of developing man’s resourcefulness, which encompass different dimensions of entrepreneurship. It is further expected that the high level of education may enable the entrepreneurs to exercise their entrepreneurial talent more effectively and efficiently.
(viii) Educational and Technical Know How: Education, entrepreneurship and development are very closely related, rather say they are interrelated. Education is the best means of developing man’s resourcefulness, which encompass different dimensions of entrepreneurship. It is further expected that the high level of education may enable the entrepreneurs to exercise their entrepreneurial talent more effectively and efficiently.
Key takeaways-
If we go through the business history of India, we come across the names of some persons who have emerged as successful entrepreneurs like (late) Dhiru Bhai Ambani of Reliance Industries Ltd, Azim Premji of Wipro, Narayan Murthy of Infosys Technologies Ltd., Kiran Mazumdar- Shaw of The Biocon India Group, Verghese Kurien of Gujrat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federations popularly known for utterly butterly delicious “Amul” and many more. The entrepreneurial profiles of these business/industry men are found quiet fascinating. Some are highly educated, others are high school/college dropouts. Some are inheritors, others are self made. Some topped their chosen field in their thirties, others did not approach the starting line until their fifties. Thus, there is no typical entrepreneur as such.
Then, the question arises is : What makes an entrepreneur successful? The scanning of their personalities shows that there are certain commanalities called charecteristics found in them. An entrepreneur is highly achievement oriented, enthusiastic and energetic individual, who has following characteristics:
2. Secrecy – An entrepreneur must be able to guard business secrets. Leakage of business secrets to trade competitions is a serious matter which should be carefully guarded against by an entrepreneur.
3. Technical Knowledge – An entrepreneur should have a minimum technical knowledge in their respective field.
4. Creativity and innovation – It involves discovering new ideas and implementing it in business. The entrepreneur continuously evaluates current modes of running a business and identifies new methods and techniques for operating the business more efficiently and effectively.
5. Realism - Entrepreneurs accept things as they are and deal with them accordingly. They may or may not be idealistic, but they are seldom unrealistic. They will change their direction when they see that change will improve their prospects for achieving their goals.
6. Self Confidence- Entrepreneurs should have confidence in their abilities to make both strategic and day-to-day decisions regarding technical matters, marketing and overall business strategy. They should also feel capable of overcoming any future unanticipated problem.
7. Hard Work – Willingness to work hard is the key of success of an entrepreneur. The entrepreneur with tedious efforts, sweat filled hours and perseverance can revive the business even if it has reached to a point of no return of failure. A successful entrepreneur should work hard endlessly.
8. Optimistic – They should be always optimistic for future. It may help them to bear the shock and provide more energy to face the future challenges.
9. Desire for high achievement –The entrepreneurs have a strong desire to achieve high goals in business. This high achievement motive strengthens them to surmount the obstacles, suppress anxieties, repair misfortunes, and devise expedients and set up and run a successful business.
10. Human Relation Approach – It is not possible for an entrepreneur to achieve its goal alone without the help of concerned people such as employers, suppliers, creditors, consumers, middlemen etc. To get the required co-operation and co- ordination for all the round development, he must maintain good relationship with all the concerned people in his venture.
“To sum up the various characteristics of an entrepreneur may be classified into four characteristics namely – Leadership, Risk- Taking, Decision Making and Business Planning”.
According to B.F. Hostellitz, an entrepreneur must have the ability to lead and manage. He identifies three types of business leadership, namely- merchant money leaders manager and entrepreneurs. The function of the first first group is market oriented, the second group authority oriented while the third group in addition to these a better and improved result oriented. An entrepreneurship is a creative activity. He is basically an innovator who introduces something new into the economy. He therefore, must have the leadership quality to make the innovation popular among the concerning people such as consumers, middlemen, employees and associates.
Chris Roebuck defined entrepreneurial leadership as “organizing a group of people to achieve a common goal using proactive entrepreneurial behavior by optimising risk, innovating to take advantage of opportunities, taking personal responsibility and managing change within a dynamic environment for the benefit of [an] organisation”.
Entrepreneurial leaders may work within a formalised organisation structure. But they use the skills and approaches associated with successful entrepreneurs. An entrepreneur takes lead to co-ordinate, assemble and supervise land, labour and capital during the promotion stage and at the performance stage for optimum utilization of the resources.
2. Risk Bearing is another element – of entrepreneurship. Every entrepreneur has to bear the risk of the business. He should have the courage to take the risk rather than avoid it. A new business always involves risk because one invests money to get profits in the future. It is quite risky to try out something new. It could be possible that a new project may not bring expected returns and may run into losses.
A business fails due to many reasons like increasing competition, shortage of raw material supply, a change in customer preferences or sudden unexpected calamities. He should be bold and courageous to assume the risks. Reward of risk is sometimes profit. That is why in order to get reward, he should be prepared to take risks. An entrepreneur can succeed if he persists, when he fails in one venture or project. This particular element should be present in entrepreneurs so that the business runs smoothly, effectively and efficient.
The entrepreneur is a person who bears risk in uncertainty period of business and takes all positive decision about risk. According to Laurence Lamond, “Propensity for risk taking is the realistic character of entrepreneur.”Mereditch and Nelson also say that, “Entrepreneurs are calculated as risk takers.”
Often, the entrepreneur is typically described as a risk taker. Some of the most successful business people took huge risks in the early days of their businesses. They are open to taking a level of risk that is most likely to possess a level of entrepreneurial attitude.The risk taking capability is one of the most important factors in the life of the entrepreneurs. They take the risk because they are very much confident about the outcome. They apply all the tools to know about the results. They do through R & D to reach near to the success.
3. Decision making - One of the most important characteristics of an entrepreneur is being able to take quick decisions that more often than not, decide the fate of his/her company. At the helm of the company, entrepreneurs often have to take that one decision at the right time which can define the future of their company. As an entrepreneur, he/she has to make difficult decisions on a daily basis. Those decisions can make or break the future of his/her business – so, if he/she don't have the right decision-making process, they might put their business at risk. So, it's important to get a good decision-making process down.
An entrepreneur as a decision maker has to take various decisions regarding the following matters-
(a) Determination of the business objectives of the enterprise.
(b) Decision regarding procurement of machines, material, men, money and market.
(c) Decision regarding requisition of efficient technology and new equipments.
(d) Decision regarding development of a marker for the product.
(e) Maintenance of good relations with public authorities and with society at large.
Business planning is an important precursor to action in new ventures.. Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. The most common external purpose for a business plan is to raise capital. Ventures that are thoughtfully planned are more likely to succeed than those based primarily on guesswork and hope. The planning process helps an entrepreneur identify exactly what needs to be accomplished to build the venture, and what human and financial resources are required to implement the plan. The forecast profit and loss statement provides a means to compare actual results to what had been forecast, and make corrections to business strategy if shortfalls in revenue occur.
Business Planning of an entrepreneur involves the following steps-
a) Scanning of the best suitable idea
b) Selection of product line.
c) Determination of the form of business organization
d) Estimation of the capital needed.
e) Selection of capital resources.
f) Selection of location.
g) Studying the government, rules, regulations and policies.
h) Selection of process to fulfill to government formalities.
i) Study of availability of labour force.
j) Study of market and market strategy tobe adopted etc.
Key takeaway –
 REFERENCES:
REFERENCES:
1) Dr. R.K Pathak, M.C Kalwar, Business Organisation and Entrepreneurship Development, Ashok Publication.
2) Dr. S.S Khanka, Entrepreneurship, Entrepreneurship Development, S. Chand Publication.
3) Vasant Desai, Appannaiah, Reddy, Gopalakrishna, Entrepreneurship Development, Himalaya Publishing House
4) R.K Pathak, M.C Kalwar, Entrepreneurship, Ashok Publication.