UNIT 2
Public Expenditure
German political economist Adolf Wagner propounded a principle Wagner’s law known as law of increasing state spending. The theory states that economic development of a nation will result in the increase in the activity of public sector.
Definition
Wagnar's law states that "as the economy develops over time, the activities and functions of the government increase".
According to Adolph Wagner, "Comprehensive comparisons of different countries and different times show that among progressive peoples (societies),with which alone we are concerned; an increase regularly takes place in the activity of both the Central Government and Local Governments, constantly undertake new functions, while they perform both old and new functions more efficiently and more completely. In this way economic needs of the people to an increasing extent and in a more satisfactory fashion, are satisfied by the Central and Local Governments."
A Wagner law is applicable to modern government in which the state is interested in expanding public sector of the economy. Wagner states that function of the state increases extensively and intensively.
Intensive means expansion of traditional function of the state. Extensive increase the welfare function.
According to Wagner, the following reason increases the expenditure of public.
Traditional function includes defense, justice, law and order and provision of social overheads. The traditional functions have increased gradually. In modern times defense expenditure has expanded and became sophisticated. The maintenance of sophisticated weapons, men and material has increased in modern times. Similarly areas of administration and government machinery have become more expensive.
2. Coverage of new functions:
New function included expanding in various fields of welfare to enrich the cultural life of the society. The government increases expenditure on education, public health, low-cost housing, subsidized provision of food, agricultural inputs, etc
3. Expanding sphere of public goods:
Government is focusing on expanding the public goods. Government stated investing to areas like irrigation and flood control projects, construction and maintenance of public parks, provision of education and health care facilities, creation of economic overhead capital etc.,. This leads to heavy investment in public enterprises.
Graphic Presentation of the Wagner Hypothesis
The modern formulation of Wagner’s law is that “as per capita income rises in industrializing nations, their public sector will grow in relative importance”
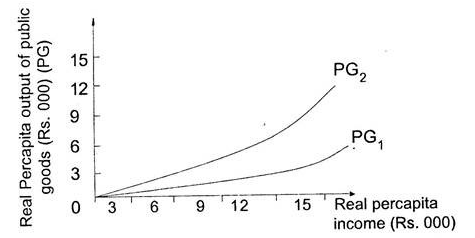
In the above figure, x axis shows real per capita income and Y axis shows real per capital output of public goods.
Line PG1 represents a circumstance where real income increases due to economic development of the society. While public sector remains constant of the economic production. Line PG2 depicts Wagner hypothesis which states that increase in the income due to economic development in the society. Similarly, real per capita output of public goods is expanding overtime. The income elasticity of expenditure for public goods is elastic.
The Peacock-Wiseman Hypothesis
Based on Wagner's Law Peacock and Wiseman conducted a new study. From 1891 to 1955 they studied the public expenditure in U.K. They found out that Wagner's Law is still valid.
Peacock and Wiseman further stated that :-
"The rise in public expenditure greatly depends on revenue collection. Over the years, economic development results in substantial revenue to the governments, this enabled to increase public expenditure".
The government cannot ignore the demands made by the people as there exists a big gap between the expectations of the people about public expenditure and the tolerance level of taxation. Especially, when the revenue collection is increasing at constant rate of taxation.
During the times of war they further stated that, the government increases the tax rates to generate more funds to meet the increase in defense expenditure. While after the war, the new tax rates and tax structures will remain the same, as people get used to them. Thus, the increase in revenue results in rise in government expenditure.
2. Inspection effect - War and other social disturbances frequently force people and their govt to find out solution of problems which previously neglected.
3. Concentration effect - When an economy is experiences economic growth there is a tendency Central govt economic activities to grow faster rate than the state or local govt. activities. There is constant and systematic expansion in the public expenditure.
Key takeaways –
Public expenditure is the spending made by the government of a country on the collective needs and wants such as infrastructure, pension, provision, etc. In the 19th century the expenditure of the government was very small and thus public expenditure was neglected. But now, the expenditure of the government has increased significantly.
Definition
“ Public expenditure refers to the expenditure incurred by the central, state, or local government of a country for its own administration, social welfare, economic development and for providing help to other countries”
Canons of public expenditure:
2. Canon of economy – It states that public money should not be misused and not result in any wastages. It implies that public expenditure should bring maximum benefit and should not produce unfavorable effect on production.
3. Canon of sanction – No money should be spent without sanction of the public authority. In the same way the money must be spent for the purpose it is sanctioned. There may be misuse and misappropriation of public funds in the absence of proper sanction.
4. Canon of elasticity – This implies according to the needs or circumstances there should be scope for varying the expenditure. There should not be any rigidity in public expenditure.
5. Canon of surplus – The aim of the government is at the surplus of income over expenditure. The surplus can be used to meet unavoidable deficit. Surplus can be generated by controlling public expenditure or by increasing current revenue.
6. Canon of neutrality - Canon of neutrality states that public expenditure should have no adverse effect on production and distribution activities of the economy. The result of public expenditure should be in increased production, reduced inequality of income and wealth and increased economic activity.
7. Canon of productivity - This canon states that, public expenditure of the government should encourage production and productive efficiency of the economy. Public expenditure should be always focusing towards enhancing the productive capacity of the economy.
8. Canon of equitable distribution - According to this canon, public expenditure should be distributed in such a way that it minimizes the inequalities in the distribution of income and Wealth. The expenditure pattern of the government should be so incurred to benefit the poorer sections of the community.
Classification of public expenditure effects on production, Distribution and economic stability
Since public expenditure influences the economy in many directions so it is beneficial. The public expenditure effects are always beneficial. It increases the capacity of the people to produce output efficiently. It helps in promoting social and economic equality and finally increases income, employment and welfare.
2. Effects on distribution- Public expenditure are an ideal way to remove economic inequalities in society. The government should impose more tax to the rich. The amount collected from the tax should be spent on free education, medical aid, cheap food, subsidized houses, old age pension, etc. This process of public expenditure will bring about redistribution of national income in favour of the poor.
3. Effects on income and employment - The level of income and employment in the country are affected by the public expenditure by removing the widespread unemployment. Investing more on public works like roads, hydro-electric generating works, etc. will create a good effect on the economy and result in increasing the income and employment. This results in increased consumption which leads to develop the consumption goods industries and capital goods industries.
Thus, public expenditure plays an important role in the economic development of a country. Public expenditure also provide environment for the expansion of private enterprise and initiative.
Key takeaways –
Sources-
1. Public finance in theory Baltic – Musgrave.
2. Public Finance Department and Developing countries - Dr. S.K. SINGH.