UNIT II
Budgetary Control

Meaning of Budget
Preface:
The budget is an accounting plan. This is a formal monetary action plan. You can think of this as a statement of expected income and expenses under certain expected operating conditions. This is a quantified plan for future activities and a quantitative blueprint for action. All organizations achieve their goals by coordinating various activities.
For Goal Execution Efficient planning of these activities is so important that management plays an important role in planning the business. Various activities within the company need to be synchronized by creating a future action plan. These comprehensive plans are commonly referred to as budgets. Budgeting is a management device used for short-term planning and management. It's more than just accounting practice.
Meaning and definition: Budget:
According to the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) UK, budgets are "plans quantified on financial terms prepared and approved prior to a defined period of time, usually with planned income generated and during the period. Shows the expenditure incurred in. The capital employed to achieve a given purpose. "
In Keller & Ferrara's view, "Budget is an action plan to achieve a defined purpose, based on a set of pre-determined related assumptions."
"A budget is a plan that covers the expected activity of a company over a period of time," said G.A. Wales.
After observing the above definition, you can draw out the clear characteristics of your budget. They are…
Budgeting:
Budgeting is the process of planning to spend your money. This spending plan is called a budget. Creating this spending plan allows you to decide in advance if you have enough money to do what you need or what you want to do.
What is a budgeting?
It's an important planning and forecasting process to help you manage your money by balancing your expenses with your income. Budgeting is simply balancing expenses and income. If they are unbalanced and you spend
You will have more problems than you make. Many people are unaware that they will use more. They sink deeper into debt more slowly each year than they earn.
If you don't have enough money to do everything you want to do, you can use this planning process to prioritize your spending and focus your money on what matters most to you.
Why is budgeting so important?
Budgeting allows you to create a spending plan for your money, so it means that you always have enough money for what you need and what is important to you. I guarantee. Adhering to your budget and spending plans can also help you get rid of debt and get out of debt if you are currently in debt.
Key points of effective budgeting:
1) Support from top management: In order for a successful budget structure, not only the consideration of all management teams is fully supported, but also the impulses and directions of management teams are required. Control systems are not effective unless the organization is convinced that management considers the system important.
2) Teamwork: This is an essential requirement if the budget is prepared "bottom-up" in a grassroots way. Top management needs to understand the system and provide enthusiastic support. You need to market the benefits of budgeting to everyone.
3) Realistic Goals: Budget figures should be realistic and represent logically achievable goals. Responsible executives must agree that budget goals are reasonable and achievable.
4) Good reporting system: You need to quickly create a report that compares your budget with actual results, and pay particular attention to important exceptions: numbers that are significantly different from your expectations. An effective budgeting system also requires the existence of an appropriate feedback system.
5) Budget Team Composition: This team receives forecasts and goals for each department, as well as regular reports, and reviews the final acceptable goals in the form of a master budget. The team also approves the department's budget.
6) Well-defined business policy: All budgets reveal business policies developed by higher level managers. In other words, the budget should always be after considering the policies set for a particular department or feature. However, for this purpose, the policy must be accurately and clearly defined and unambiguous.
7) Integration with standard costing system: If a standard costing system is also used, it should be fully integrated with the budgeting program from both budgetary readiness and variance analysis perspectives.
8) Inspirational approach: All non-executive employees or staffs needs to be strongly and appropriately inspired by the budgeting system. Humans essentially hate pressure; they hate what they are forced to do, or even rebel.
Budgetary control
Meaning and definition:
Budgetary management is the process of preparing budgets for various activities, comparing budget figures, and achieving any deviations that will be eliminated in the future. Therefore, budget is a means and budget management is the end result. Budget management is an ongoing process that helps you plan and coordinate. It also provides a control method.
Budget management is a cost that includes budget preparation, coordination of departmental work, establishment of responsibilities, comparison of actual performance with budget, and results-based actions to achieve maximum profitability. It's a system of coordination. Brown and Howard~
Weldon characterizes budget management as planning ahead of various functions of the business so that the entire business is managed.
ICMA defines budget control as follows: “Continuing actual and budget results to set budgets, associate executive responsibilities with policy requirements, and ensure the objectives of the policy through individual actions, or provide the basis for the policy. Its revision to compare with. "
The budget management features as defined above are:
1. A prerequisite for budget management is to set different types of budgets and modify the responsibility of the person responsible for the successful implementation of the policy.
2 Compare actual performance to budget and reveal deviations for cost control purposes.
3. Corrective action will be initiated to correctly set the unwanted deviations.
The budget management process includes:
You need a flexible personal initiative and a good range of momentum. Budgetary control is an important tool for making an organization an important tool for cost control and achieving overall goals.
Key takeaways:

What is Budget Control?
Budgeting is the process in which budgets are prepared for future periods and, if there are differences, are compared with actual performance to find differences. Comparison of budget figures with actual figures will help management to find out the differences and take corrective actions without delay. Objectives of Budget Control
The main objectives of Budget Control are:
Benefits of budgeting
Budget Control has become an important tool for organizations to manage costs and maximize profits. Some of the benefits of Budget Control include:
Disadvantages or limitations of Budget Control
The limits of Budget Control are as follows:
1. It is really difficult to accurately prepare the budget under inflation.
2. The budget involves heavy spending that small business care cannot afford.
3. The budget is always prepared for future periods that are uncertain. In the future, the conditions that disrupt the budget may change. Therefore, uncertainty in the future minimizes the usefulness of the Budget Control System.
4. Budget Control is just an administrative tool. Management cannot be replaced in decision-making because it is not a substitute for management.
5. The success of Budget Control depends on the support of top management. This will fail if there is insufficient support from top management.
Key takeaways:
Fixed budget:
This budget is employed for one level of activity and one set of conditions. It’s defined as a budget designed to stay unchanged no matter the quantity of production or sales achieved. This is often a decent budget and is drawn on the idea that the budgeted activity level won't change. Changes in spending thanks to changes in activity levels aren't taken under consideration.
Therefore, changes in spending resulting from changes in expected conditions and activities aren't specified. Therefore, a hard and fast budget is merely useful if the particular activity level corresponds to the budget activity level.
A typical example of a hard and fast budget may be a master budget tailored to one output level of (for example) 20,000 sales units. However, actually, the extent of activity and set conditions change as a result of internal and external factors like changes in supply and demand, shortages of materials and electricity, and fierce competition.
It is almost useless as a budget management mechanism because it doesn't distinguish between fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs, and there's no adjustment of the budget amount thanks to changes in costs thanks to changes in levels activity. It doesn't provide a meaningful basis for comparison and control. It also does nothing to repair prices or violate submissions.
Flexible budget:
The UK Association of Certified Management Accountants recognizes flexible budgets (also referred to as sliding-scale budgets), the difference in fixed and variable cost behaviour related to fluctuations in production, sales, or other variable factors. It’s defined as a budget. The amount of employees is meant to vary appropriately in response to such fluctuations. Therefore, flexible budgets offer different budget costs for various levels of activity.
Flexible budgets are created after intelligently classifying all fixed, semi-variable and variable costs. The usefulness of such a budget depends on the accuracy with which costs are often classified.
Such budgets are begun within the following cases:
1) The annual activity level varies from period to period, either thanks to the seasonal nature of the industry or fluctuations in demand.
2) When the business is new and it's difficult to forecast demand.
3) The business suffers from a shortage of production factors like materials, labor and plant capacity. The extent of activity depends on the supply of such factors of production.
4) When the industry is suffering from changes in fashion.
5) When there's a general change in sales.
6) When a business unit continues to introduce new products or changes product design frequently.
7) When the industry is engaged during a make-to-order business like shipbuilding.
Flexible Budget Utility (or Importance):
In conclusion, a versatile budget is more useful, elastic and practical.
Example:
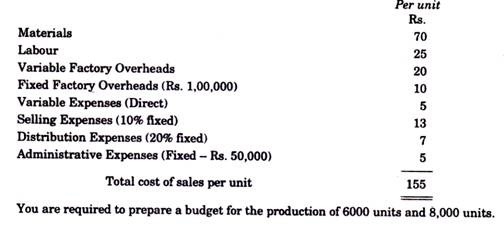
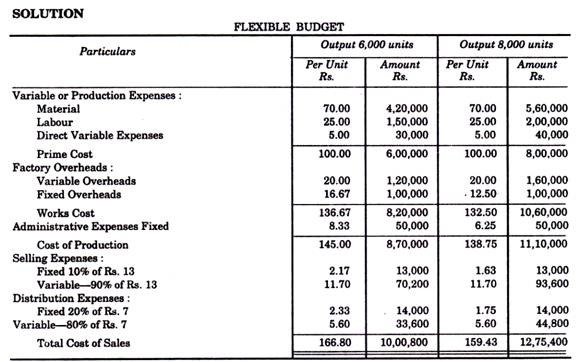
The expenses budget for production of 10,000 units in a factory is furnished below:
Key takeaways:

Zero-based budgeting (ZBB) is an approach that allocates funds supported program efficiency and wishes instead of budget history, as companies struggle to scale back costs and compete in an increasingly complex environment. It’s slowly gaining attention again. ZBB isn't a budgeting methodology, but a philosophy of cost justification and frequent monitoring that gives fine-grained support for spending transparency and allows companies to adapt to changing markets.
Overall adoption of ZBB remains low (a recent Deloitte LLP survey shows that only 16% of Fortune 1000 companies have used it within the last 24 months), but consumer packaged product (CPG) companies We use ZBB at a better rate (22%). They face industry turmoil with evolving consumer preferences, volatile commodity prices, the increase of their own brands, and competition within the digital market.
For CMOs of CPG companies, one area where ZBB are often applied is commercial spending. this is often the value owned by the sales and marketing features. samples of commercial spending include costs related to advertising, trade promotions, and discounts. Commercial spending may be a good candidate for ZBB for the subsequent reasons:
a) It's pretty big- Commercial spending typically accounts for 15% to twenty of total sales within the commodity industry.
b) Can be measured -The ROI of a performance trade (expenditure linked to a private promotion or promotion calendar) are often calculated with acceptable accuracy.
c) Fragmentation -Most commercial spending is fragmented by trade class, customer, and other categories, producing different levels of revenue.
d) Advances in data and analytics allow marketers to ascertain which programs are successful and shift resources accordingly. ZBB can provide easy and repeatable thanks to manage your commercial spending.
How does ZBB work?
Responding to ZBB issues
a) While ZBB are often a strong tool, it also comes with some notable challenges. Organizations can use a spread of methods to effectively address these.
b) ZBBs typically consume more resources than traditional budgeting and need regular reviews, analysis, and reporting. Leaders can leverage advances in analytics and digital technology to accelerate processes, automate analytics, and focus conversations on the foremost important spending factors.
c) ZBB must start the budgeting process from scratch and justify all spending, which may generate short-term thinking. To counter this, organizations can adopt long-term performance measurements as required, but with frequent measurement windows and detailed data (such as social sentiment), long-term initiatives work. Show early that you simply are.
d) Moving a corporation from traditionally targeted cost savings to ZBB requires a serious cultural change. to deal with this challenge, senior executives can involve business leaders, especially those that manage brand teams and key customers, in conversations about ZBB. Showing your commitment to ZBB and providing a rationale for it'll help ensure success.
e) Changes in commercial spending have an immediate impact on retailers. Within the commercial arena, it's more important than other features to determine ROI metrics that are well-tuned for retailers, channels, and segments. Organizations can enjoy a comprehensive view of the speed of return on investment and therefore the use of metrics like volume, growth and share as required.
Channel partners and retailers are often sceptical of ZBB due to the trouble required and therefore the impact it's on their business. You’ll get approval by being as transparent as possible and participating within the decision-making process for these groups.
With the digitization of consumer purchasing channels, the road between marketing and promotional spending is becoming increasingly blurry. It’s important for sales and marketing teams to urge obviate silos that separate various commercial spending program.
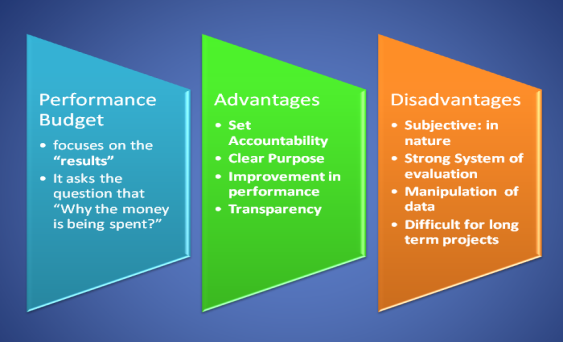
Performance budgeting:

What is a performance budget?
Performance budgeting, also known as performance-based budgeting, is a way to prepare your budget based on an assessment of the productivity of various operations within your organization. The businesses that contribute the most to profitability are allocated a larger share of the budget to that department. It leads to optimal use of resources such as finance, staff skills, and productive use of time.
Basically, a performance budget requires an assessment of performance and productivity from one budget period to another. Therefore, it is the process of identifying the results achieved by each department of the organization.
In addition, the performance budget does not focus on the individual activities required to develop the strategy. Instead, the central focus is on achieving the department's overall goals. This helps managers formulate departmental strategies. Therefore, performance budgeting is based on the concept of zero-based budgeting.
In general, government departments, not commercial organizations, use performance budgets. It is used to justify the application of money. A non-profit organization that the government earns through taxes levied on its citizens and lacks the right information can result in ineffective performance budgets that affect the entire project.
Approach
Performance budgets focus on "results." The final result will be analysed. Performance budgeting is a motivational tool for staff.
Performance-based budgeting process
The organization shall create a list of goals. The goal here shows the final result. Goals need to be clear to each employee in the organization. By communicating the same results as your clear goals, you can successfully implement a performance-based budget.
Therefore, this step is planning and budgeting.
2. Regular evaluation
The next step is a regular assessment of performance to achieve your organization's desired goals. The organization shall develop a systematic, step-by-step approach to evaluation. Performance measurements are subjective and vary from person to person. Therefore, organizations try to quantify results based on them.
Therefore, this step is a measurement of the result.
3. Performance indicators
Performance indicators help you assess the effectiveness and efficiency of your program. Performance indicators are the standard of measurement. The selection is based on the following range:
a) It's relevance
b) Cost-effectiveness
c) Comparability
d) Representative
e) Accountability
The organization is accountable for one or more results. The main focus of a performance budget is results, not inputs. Similarly, staffs are responsible for the goals of the organization. In addition, performance-based budgeting is expected to achieve a certain level of results based on a particular level of resources.
Therefore, this step is called result evaluation and communication.
Performance-based budget and traditional budget
Amounts spent for specific purposes, such as staff salaries, office supplies, and equipment, are included in the traditional budget. However, what you can achieve with a $ 1 spending is indicated by your performance budget. Previously, organizations did not follow a performance-based approach. However, organizations are now following a performance-based approach.
Performance budget example
a) By the end of 2020, the mortality rate of HIV-positive patients will be reduced by 30%.
b) Monthly staff training increased production in 2018 by 20%.
c) By 2022, we will reduce infant mortality by 50% by introducing strong immunization centers in all different parts of the country.
Performance budget benefits-
In developed countries, money management is one of the key factors for any organization. Performance budgets play an important role in achieving efficiency.
For public sector organizations rather than commercial organizations, performance budgets can help increase accountability. Employees need to quantify specific goals based on priorities and taxpayer money. Undoubtedly, taxpayers and donors are interested in knowing where the money is spent. Evaluate the benefits to citizens and society.
2. Clear purpose
The performance budget clearly shows the purpose for which the money is spent. Clarifying the purpose makes it easier to evaluate performance and correct deviations.
Performance Improvements Performance budgets continuously improve the performance of your programs. In addition, it leads to the overall operational efficiency of the organization. It also overcomes traditional budgeting limitations.
3. Transparency
Performance-based budgeting helps provide transparency in budget preparation. Performance budgets help you get better finances financial decisions regarding resource allocation. Check the operational efficiency of the project. Therefore, it links the entire process of planning, porting, and evaluating results.
Performance budget disadvantages
Subjective
Performance budgets are subjective in nature, causing disagreements among management. Social projects also have a long-term vision. It is difficult to quantify with money. Costs may vary from government agency to agency. Therefore, using more of the results-based approach helps improve budgeting processes, accountability, and organizational control.
Powerful evaluation system
Performance budgets require a strong accounting system. Therefore, the reporting system must be powerful for its successful implementation.
Manipulating data
Staff may work with the data. In addition, the calculation of financial information is unreliable due to mispreparation. Therefore, a proper internal control system can help maintain the accuracy of your data.
Long-term difficulty
The time between resource allocation to a project and results can be more than a year. Without a doubt, it is difficult to measure project results in the long run.
Therefore, dividing your project into smaller pieces can help simplify the evaluation process. Undoubtedly, over a period of time, performance budgets have become popular throughout the industry.
Key takeaways:
 References:
References: