Unit II
Writing Skills
2.1.1 Enquiry Letters:
A Business Inquiry letter is a letter written for communication between two organizations or persons belonging to 2 different organizations inquiring regarding some business they're doing together or hoping to try to in future. It's a proper letter and hence one has got to be polite and humble. In some cases, the sender might not have ever met the receiver. One has got to be precise and to the purpose and not drag the letter.
A business letter is a letter where two concerned parties discuss business. Business inquiry letter are often of the many types. The letter of enquiry is often about certain products or services of the receiving company. It can ask the status of the ongoing work being done by the company receiving the letter.
A letter also is a proof for the business being done between 2 organizations and as a history for future references. This sort of letter is brief and to the purpose. Just in case the sender doesn’t have the expertise regarding the inquiry being made he/ she will also ask the receiver to help them.
What is Inquiry Letter -Letter of inquiry is one among the most important sorts of business letters. When a buyer wishes to urge some information about the quantity, price, availability etc. of products to be bought or about the terms of sale, payment etc he writes a letter of inquiry to the seller.
Inquiry Letter –
ACCORDING TO MORRIS PHILIP AND OTHERS, “THE LETTER THAT SEEKS INFORMATION CONCERNING THE GOODS AND SERVICES FROM A BUSINESS CONCERN IS TERMED AN INQUIRY LETTER.”
QUIBLE AND OTHERS SAID, “LETTER OF INQUIRY MAY BE A SORT OF BUSINESS MESSAGE THAT ASKS THE RECIPIENT FOR INFORMATION OR ASSISTANCE.”
IN THE OPINION OF R. V. LESIKAR ET AL., “LETTERS THAT ASKS QUESTIONS OR INFORMATION ABOUT ANYTHING IS CALLED INQUIRY LETTER.” BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
ACCORDING TO GARTSIDE, “AN INQUIRY LETTER ASKS INFORMATION LIKE CATALOGUE, QUOTATION, SAMPLE AND PRICE OF A PRODUCT FORM A SELLER DURING A CONCISE AND CLEAR WAY.”
Objectives of Inquiry Letter in Business Communication –
Every letter has some certain objectives or motives and inquiry letter isn't an exception. It's written on different occasions for various reason. Inquiry letter is written so as to hold out one among the subsequent objectives bellow-
• To get the price quotation of specific commodities
• To ask for catalogue
• To know payment terms
• To know the past records of job applicant
• To know the credit worthiness of a firm or an individual
• To ask for folders
• To get recommendation from former employer
• To know the financial strength of a firm or an individual
• To know the business reputation of a firm
• To know the transportation facility provided by the firm
• To obtain information about social status of an individual or a firm
• To evaluate the performance of an individual or a firm
• To find out about the quality of a product
• To know the availability of an item
• To make request for sample etc.
Types of Inquiries Letter in Business Communication –
Inquiries could also be of various types supported the target, information sought and therefore the initiatives taken. There are generally four sorts of inquires letter-solicited inquiry, unsolicited inquiry, inquiry for a few favour and routine inquiry letter. These are discussed below-
• Solicited Inquiry: An inquiry made in response to the seller’s advertisement and publicity is named a solicited inquiry. Actually, it's a response by the customer to the advertisement or publicity of a seller.
• Unsolicited Inquiry: An inquiry made at the buyer’s own initiative is named unsolicited inquiry. This kind of inquiry is formed when a buyer wants to understand anything from the vendor.
• Inquiry for some Favour: An inquiry made not about goods but information like special price or favourable terms is named inquiry for a few favours.
• Routine Inquiry: An inquiry made by an old or regular buyer within the usual course of action is named routine inquiry. Most of the business inquires fall during this category.
So, we discover that there are differing types of inquiries, regardless of the type is that the bottom line of success of an inquiry depends upon how it's written.
2.1.2 Order Letters:
An order letter is typically written once you got to assign orders for goods. it's quite common and is written almost on a day to day. The language of the letter, however, must be formal and therefore the letter follows a typical format, since the knowledge is extremely specific.
An order letter must pen down the terms and conditions of the acquisition. These benefits both the involved parties. It generally contains details like product specifications, their quantities, a price that the parties have prescribed, the date of delivery, what to try to just in case there occurs a late delivery, etc.
Tips before Writing an Order Letter –
Before writing the order letter, here are some tips for you:
1. The letter should be very precise, there's no exhortation or casual talking required here.
2. The language should be easy while also being formal.
3. don't make any mistakes within the specifications and quantities.
4. Avoid spelling and grammatical errors.
5. Stick with the subject
6. Be polite. you're ordering for goods; you are not ordering the person.
7. Avoid using too many adjectives.
8. Don't use jargons.
9. Don't hesitate to put the order, but do not forget to plan before writing.
Now I can tell you ways to write down an order letter, since you now know all that you simply needed to understand before writing one.
Elements of the Order Letter –
An order letter needs the subsequent things to be in check:
o Contact information about yourself, the person/company which will supply to you and therefore the date.
o A subject line that helps the recipient to know your purpose directly.
o A salutation, like, if you recognize the name of the vendor, write, “Dear ……………”. If you do not know the name of your seller, simply write “Dear Seller”
o Information about your company; but this is often totally optional. However, this will ensure a long-term relationship. you'll also say a couple of words about your future plans associated with the sale.
o Order details, and by details, I mean everything. The model number, colour, size, number, etc. Be attentive since they'll send whatever you'll write. If possible, use bullet points or tables. If you're buying different items of various types, describe them in separate paragraphs.
o Mention your payment mode or if you've paid already, mention that next.
o Indicate your preferred delivery method and date.
o Include any special instructions as a neighbourhood of the terms and conditions agreed between the parties.
o Tell them that you're going to enjoy future cooperation with them and encourage them to contact if needed.
o Close with “Sincerely”, your signature and name.
The quality of the delivered goods will depend upon your instructions. Not just that, it's literally a legal instrument between yourself and therefore the seller. So, watch out for what goes in your order letter and pay an honest deal of attention while drafting one.
2.1.3 Credit Letters:
When you hear the phrase 'letter of credit,' it'd be natural to think it refers to a document verifying that you simply are creditworthy, but that may not the case. A letter of credit may be a document issued by a 3rd party that guarantees payment for goods or services when the vendor provides acceptable documentation. Letters of credit are usually issued by banks or other financial institutions, but some creditworthy financial services companies, like insurance companies or mutual funds, might issue letters of credit under certain circumstances.
A letter of credit generally has three participants. First, there's the beneficiary, the person or company who are going to be paid. Next, there's the customer or applicant of the products or services. this is often the one who needs the letter of credit. Finally, there's the issuing bank, the institution issuing the letter of credit. additionally, the beneficiary may request payment to an advising bank, which may be a bank where the beneficiary may be a client, instead of on to the beneficiary. This could be done, for instance, if the advising bank financed the transaction for the beneficiary until payment was received.
Letters of credit are most frequently utilized in international trade, where they're governed by the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (or UCP), the principles of the International Chamber of Commerce. However, they will be utilized in other situations, as we shall see.
Types and Features of Letters of Credit –
Most letters of credit are import/export letters of credit, which, because the name implies, are letters of credit that are utilized in international trade. an equivalent letter of credit would be termed an import letter of credit by the importer and an export letter of credit by the exporter. In most cases, the importer is that the buyer and therefore the exporter is that the beneficiary.
There also are other sorts of letters of credit. The revocable letter of credit is often changed at any time by either the customer or the issuing bank with no notification to the beneficiary. the foremost recent version of the UCP, UCP 600, did away with this type of letter of credit for any transaction under their jurisdiction. Conversely, the irrevocable letter of credit only allows change or cancellation of the letter of credit by the issuing bank after application by the customer and approval by the beneficiary. All letters of credit governed by the present UCP are irrevocable letters of credit.
A confirmed letter of credit is one where a second bank agrees to pay the letter of credit at the request of the issuing bank. While not usually required by law, an issuing bank could be required by writ to only issue confirmed letters of credit if they're in receivership. As you would possibly guess, an unconfirmed letter of credit is guaranteed only by the issuing bank. this is often the foremost common form with reference to confirmation.
A letter of credit can also be a transferrable letter of credit. These are commonly used when the beneficiary is just an intermediary for the important supplier of the products and services or is one among a gaggle of suppliers. It allows the named beneficiary to present its own documentation but transfer all or a part of the payment to the particular suppliers. As you would possibly guess, an un-transferrable letter of credit doesn't allow transfer of payments to 3rd parties.
A letter of credit can also be at sight, which is payable as soon because the documentation has been presented and verified, or payment could also be deferred. Deferred letters of credit also are called a usance letter of credit and should be postpone until a particular period of time has passed or the customer has had the chance to examine or maybe sell the related goods.
A red clause letter of credit allows the beneficiary to receive partial payment before shipping the products or performing the services. Originally, these terms were written in loss, hence the name. In practical use, issuing banks will rarely offer these terms unless the beneficiary is extremely creditworthy or an advising bank agrees to refund the cash if the shipment isn't made.
Finally, a back-to-back letter of credit is employed during a trade involving an intermediary, like a trading house. it's actually made from two letters of credit, one issued by the buyer's bank to the intermediary and therefore the other issued by the intermediary's bank to the vendor.
Documentation Requirements –
In order to receive payment, the beneficiary must present documentation of completion of their part within the transaction to the issuing bank. The documents that the issuing bank will accept are laid out in the letter of credit, but may often include:
• Bills of exchange
• Invoices
• Government documents, like licenses, certificates of origin, inspection certificates, embassy legalizations, and phytosanitary certificates
• Shipping and transport documents, like bills of lading and airway bills
• Insurance policies or certificates, except cover notes
2.1.4 Status Enquiry Letters:
The letter that's written for obtaining information about a commercial enterprise is termed as business status inquiry letter. Generally, one commercial enterprise writes this letter to another commercial enterprise for collecting information a few prospective customers.
When a firm wants to buy goods on credit, it gives one or more references to which the vendor can invite some information about the credit seekers. Usually, banks, trade associations or competing business firms are mentioned as references. The vendor then writes the inquiry letter to the referees requesting them to supply some information about the customer.
The purpose of scripting this letter is to get information related to:
• Financial capability or creditworthiness
• Goodwill
• Nature of business dealings
• Honesty
• Relationship with business association, etc
In light of the above discussion, we will conclude that when a commercial enterprise writes an inquiry letter to another commercial enterprise, financial organization or trade association to get information about creditworthiness or financial capability of a customer who has applied for credit purchase, it's called business status inquiry letter. Basing on the information supplied by the referees, the seller decides whether to establish business transactions with the firm.
Objectives or importance of business status inquiry letter –
Business status inquiry letter plays a crucial role in modern business. The subsequent are the main objectives of writing this letter:
• Obtaining information about the financial capability of prospective customers.
• Determining the risk of credit sales.
• Deciding whether to enter into credit transactions.
• Getting information about honesty, goodwill and business morality of the probable buyer.
• Knowing about the connection of the potential buyers with other business community and associations.
• Enhancing sales with various parties by evaluating their financial and business viability.
Status Inquiry letter -
|
2.1.5 Claim Letters:
The letter of the announcement is going to be mentioned the upcoming customers, client contacts, existing customers to form them conscious of some offers and schemes which will help them to form big savings. this is able to entitle the aim of offering exciting offers during a money-spinning sense.
These letters are written to the purchasers in order that they will observe profits. It is often written to the prevailing customers to tell changes in rates, supplies, and new offers, etc. It is often associated with introducing a replacement product of the corporate to follow up together with your existing customers or new customers to take care of an honest account.
Your product or service could be top of the road. Your customer service could also be the simplest in school. you're still getting to get complaints. Client complaints or claim letters are often an enormous asset for your business then show you ways to harness those assets. When customers complain, they're actively teaching you ways to enhance your product. this sort of warm, helpful letter to take care of the business scent during the amount you're gathering all the specified information for the prospect.
Claim Letter Writing Tips –
Write briefly about the offers and therefore the schemes; write what benefit the reader goes to urge from the schemes.
Write the amount during which the offer is valid. this may help the customer to avail the offer.
Use a positive tone. invite a positive reply. Use attractive language in order that it can grab the eye of the readers towards the offers and discounts.
Write that the reader may be a very valued customer and hence you're scripting this letter.
State the precise name of the person or company you're pertaining to.
Be clear and concise about the knowledge you would like to supply
Propose how you'll improve the customer’s experience within the future.
If there are any necessary forms, etc., that you simply got to fill out or send, include them together with your letter for faster approval.
Claim Letter Template -
From,
_____________
_______________
Date: ______________ (date on which the letter is written)
To,
____________
_________
Subject: Claim letter
Dear Sir/ Madam,
I am ___________ (name) scripting this letter to you to declare the schemes and offers on behalf of our company that's ____________ (name of the company). On this Diwali, we've declared festive season offers. We are delighted to satisfy your needs and consider it a compliment whenever you place an order.
In appreciation for your business, we've included a coupon for 10 percent off any service for each product in your fleet. If you place an order between 01.11.2013 to 15.11.2013 then you'll avail these offers.
We will also sell regular products prices during this period. So, if you would like to realize huge profits, then you'll place big orders during this period. you'll also buy larger quantities. These offers are for all our important customers, and you're one among them.
We encourage you to contact us regarding this special offer and to think about us your one-stop service centre. At eBay, we are committed to providing superior care. Again, it's a privilege of servicing you. Hence, you're requested to be benefited by these offers.
Hope to listen to soon from you.
Thanking You.
Yours Sincerely,
____________
2.1.6 Complaint Letters:
Letters which are written by the purchasers to the sellers about their inconveniences created by some unexpected situations are referred to as complaint letters. However efficient a corporation could also be in running a business, everything doesn't go all the time consistent with plan. there'll be some mistake and a few accidents. Important service is sometimes rendered unsatisfactorily; goods are consigned to wrong destinations, sometimes too late, sometimes in but the specified quantities, sometimes in damaged condition.
Complaint letter is –
Letter written to bring these mistakes to the notice of these who must own the responsibilities for them are called claim or complaint letters. So, when a letter is written to the vendor by the customer raising complaints or claims regarding mistakes taken place during the order to payment period is named a claim or complaint letter.
Business complaint letter is written by customers who aren't satisfied by the amount of consumer services provided. If you are feeling that your supplier is dishonest about the products, they deliver to you, whether in terms of content or pricing, you'll write them a customer complaint letter to precise your grievances.
Don't forget to say that there'll be consequences should they fail to deal with the difficulty in question.

2.1.7 Adjustment Letters:
Adjustment Letter is response letter to customer complaint or claim. it's official in nature and explains the relevancy of the complaint or claim and the way it is often resolved.
Adjustment Letter Definition -
A sort of letter addressed in response to a customer's claim or complaint letter, written by a representative of an organisation or a gaggle because of the client-vendor relation, a letter of adjustment also acts as a legal instrument demonstrating the small print of the correspondence and therefore the resolution or dissolution the between the 2 parties.
A letter of adjustment doesn’t mean that your complaint or claim are going to be accepted. It notifies the sender that their claim or complaint letter has been received. It depends upon the validity of your claim that a letter of adjustment will contain conformity of its mistake and its rectification. Adjustment letters are meant to resolve a conflict that's why they're referred to as such. Letters of adjustment also are referred as Claim Adjustment Letters, Complaint Response Letters, Customer Complaint Reply, Letter of Complaint Response, Letter of response to Complaint and similar other terms. A letter of adjustment deals with all kinds of claims and complaints; defective product, poor service, goods not delivered, shipment arriving late, salary not received et al.
Bangladesh Textiles Mills Ltd. 10th Feb. 04 Marketing Manager Ref: Your letter dated 5th Feb. 04. Dear Sir, We thank you .for your letter of 5th Feb. 04 along with/ sample of cloth for examination. The report that we have received just today shows that the consignment forwarded to you was the wrong one full of defective clothes. It was a mistake because of our despatch section and we regret this mistake which has caused you both embarrassment and inconvenience. We have already sent the replacement by passenger train. You can be sure of the quality of cloth now sent. You can, of course, return the clothes to us and debit our account for the loss caused to you. We again regret the inconvenience to you and assure you that such mistakes will be avoided in future. Yours faithfully
M. Ashraf |
2.1.8 Collection Letters:
Letters written for realizing payments from the debtors are referred to as collection letters. the necessity for writing collection letters arises from credit sales. Selling on credit may be a traditional business policy that enhances volume of sales. Under the credit sales policy, the sellers allow the purchasers a particular period for payment of dues. However, sometimes the buyers make unexpected delay in paying their dues. Even, some custom stances, the sellers write letters reminding and requesting the purchasers to pay the due bills. rather than sending one letter or repeated copies of an equivalent letter, credit departments send a series of letters.
In the opinion of Kitty O. Locker, “Collection letters ask customers to buy the products and services they need already received.”
Quibble et al. defined, “Collection letters are employed by a corporation to entice its charge customers to pay an impressive charge-account balance.”
Collection letters are written during a series. When collection letters are written during a series beginning with an easy reminder and end with a warning letter indication action the dues promptly by retaining the purchasers with the corporate.
2.1.9 Circular Letters:
Circular letter is one of the oldest sorts of letters. This type of letter originated in ancient time when people felt the need of circulating any message to a large number of individuals at a time in the same way.
Generally, the letter that's won’t to circulate any special message to a large member of audiences at the same time is known as circular letter. It's one of the cost-effective means of circulating information or introducing new products to mass people. However, circular letters aren't only used in business, but also in social, political and personal affairs.
Prof. W. J. Weston said, “A circular letter is one which is meant to be read by variety of correspondents. It's of the nature of an advertisement and is typically a business announcement or an effort to advance business.”
From the above discussion we can say that circular letter may be a quite written announcement that's distributed to a large number of people to convey any commercial or non-commercial message at minimum time, costs and efforts. Drafting circular letter is only an art. It should be drafted in such how that can attract readers’ attention and may serve its purpose.

Importance or advantages of circular letter –
Circular letter circulates information relating to a company, its products and services etc. to a large number of individuals at a time. It plays a crucial role within the growth and development of business. Its importance is briefly discussed below:
1. Easy method of conveying information: Circular letter is that the most easy, simple and effective thanks to convey any information to a large number of individuals.
2. Achieving economy: Circular letter are often used for wide publicity of products. As a result, organizations can save cost of sending letters to different parties separately and may gain economy.
3. Saving time: Circular letter transmits information to a large number of individuals at a time. It doesn't require reaching each individual separately. Thus, it saves time.
4. Less effort: Circulating information to every individual separately is a time consuming and laborious job. Circular letter helps to overcome this problem. Through circular letter, we will communicate with large number of individuals at a minimum effort.
5. Creating market: Through circular letter, a company can inform potential customers about its products and services. During this way, new markets are often created.
6. Increasing consumer’s confidence: Convincing and attractive circular letter can easily touch the reader’s heart and thus helps to boost consumer’s confidence on the company’s products.
7. Creating public consciousness: In circular letter, information like price, quality, utility, place of availability, etc. are mentioned in detail that creates people more conscious about the product.
A tender is a formal, transactional document used by large organizations, companies, government bodies and NGOs find suppliers and contractors for particular projects or procurements. Hence, it can be said that tenders are the foundational pillars of bidding process used by both public and private institutions. Invitations to Tender or Requests for Tender (RTF) are documents used by an organization or government institution to invite bids from interested contractors for a large project or the procurement of goods and services.
Important Elements in a Tender Document:
Conditions for participation: This section outlines the important conditions that a supplier or contractor must meet in order to be considered by the organizer. All the important required documents and records proving the supplier’s eligibility for the project are to be enclosed in this section. Financial records, licenses, insurance documents and data related to past projects may be some of the conditions required to be met for participation in the bidding process.
Accreditation and quality standard: Under this section, the potential contractor or provider must demonstrate that they can satisfy all the requirements stated by the organizer in the previous section. The bidder has to present the organizer with certifications of quality and authority accreditations such as ISO, ISI, etc. This section may also outline certain processes or procedures followed by the firm that will ensure superior quality for your product or service.
Specifications: Included in this section is the specific information the potential contractor must outline about the project that the client might be interested in. These specifications may include the goods and services required for the project, the expected time-frame for project completion and also any associated requirements related to pricing, delivery and performance. This information will play an important role in the final evaluation made by the organizer.
Conditions of contract: Under this section, the tender document has to provide all the significant information regarding the rights and responsibilities of the client as well as the potential contractor. All the terms and conditions of the project must also be clearly outlined in this section. This section must ensure clarity, comprehension and transparency in the transactional process.
The condition of offer: While the bidder or contractor is submitting their offer, they must provide the client with their official agreement to the proposed terms and conditions of the contract. The estimated timeline of the entire tendering process as well as the location wherein the submission must be made are to be indicated in this section. Other relevant information that might be included in this section are the submission process, the evaluation process, etc.
Techniques and Elements of a Good Tender Response
Below are the techniques involved in writing a good tender response:
1. Use the templates or formats provided
All tender specification documents adhere to a specific format which is provided by the organization that has required you to fill the tender consisting of multiple sections and sub-sections. These sections may contain certain word limits and require specific file formats.
By accurately following all of the requirements in the tender, your tender response will become clearer and it will be easier for the tender review panel to consider your offer.
2. Structure your tender document clearly
Many a times, organizations do not ask for a particular format or structure, in those cases, be sure to keep your tender document clear, logical and well organized. Begin with a clear and persuasive introduction that states the purpose, rationale and central proposition of your bid for the project.
Diagrams, charts and statistical data also help in convincing the panel to consider your bid. It can be used as an effective way to break up blocks of text and communicate to the reader complex propositions.
3. Provide all relevant details
As with quotes, tenders must include certain information in order to be considered, including:
- Your ABN
- a company profile and capability statement
- Whether you propose to subcontract
- The price for each product or service you propose, and an indication of whether these are fixed or variable (e.g. Based on exchange rates or consumer price index variations)
- Any conditions affecting the price
- Delivery details and charges
- a proposed schedule indicating milestones or delivery dates
- Whether goods or services are periodic or recurrent
- GST and other taxes
- Applicable insurances
- Intellectual property rights where relevant
- a description of any variations you propose in meeting the conditions of the contract.
- Address the selection criteria
Closely follow the criteria in the tender request. Make sure your proposed offer precisely meets the buyer's needs. Describe the advantages the buyer will receive from your organization's products or services.
Provide specific examples of how you meet the selection criteria rather than simply stating that you do. It is important to highlight your credentials and provide verifiable experience, as well as explaining how your approach to delivering the tender will meet the buyer's needs. Identify the requirements that are most important to the buyer and cater for this in your tender response.
4. Choose the right referees
Another key part of delivering a successful tender response is choosing the right referees.
Use referees that know your products or services. Make sure you get permission to use referees before including them in your response. Brief them on the highlights of the request so they can target their comments to the job specifications.
5. Proofread your tender
Use spell check and, if possible, ask someone outside of the tender development process to read your tender response and give feedback. Ideally, get a professional copy editor or proof-reader to carry out this task. If several authors have contributed to different parts of the tender response, ensure that one person reads the entire tender response document for consistency.
6. Submit your tender in time
Late or incomplete tender responses are usually excluded from consideration barring exceptional, pre-agreed circumstances.
If you are submitting online, do not leave your tender submission until the last minute in case you have computer, internet or network issues. If your tender response is to be posted, make sure you allow time for delays. Consider using ‘same day delivery' for courier services or hand-delivering your tender response (if allowed).
An auction is a sales process wherein potential buyers place competitive bids on assets or services either in an open or closed format. Auctions are popular because buyers and sellers believe they can get a decent deal buying or selling assets.
In an open format, all bidders are aware of the bids submitted. In a closed format, bidders aren't conscious of other bids. Auctions may be live, or can be conducted on an internet platform. The asset or service in question is sold to the party that places the highest bid during an open auction and typically to the highest bidder in a closed auction.
In an open auction, parties gather at a physical venue or online exchange to bid on assets. An interested party is conscious of the competing bid amounts and continues to boost their bid until they're either declared the winner of the auction (i.e., they submitted the last highest bid within the auction time limit) or until they concede and drop out of the bidding.
Examples of auctions include car auctions, or an auction room where collectors bid on works of art, auctions for leftover material, auctions for personal assets such as houses etc. Leading online marketplace eBay and many others are a host of online auctions.
Price isn't always the deciding factor when assets are sold by auction; a corporation that's purchasable might choose a buyer who will provide the most effective terms for its employees.
Auctions are conducted in a closed format in many business transactions (including the sale of company assets or an entire company) whereby interested parties submit sealed bids to the seller. These bid amounts are only known by the seller. The seller may prefer to hold only one round of bidding, or the seller may select two or more bidders for an extra auction round.
In a situation wherein, a division of an organization or the entire company is up for sale, price isn't the sole consideration. The seller, for example, may want to preserve as many jobs as possible for its employees. If a bidder doesn't submit the highest price but offers the most effective terms for continuity for workers, the seller may select that bidder.
An auction notice is a formal document issued in the interest of the general public which informs them regarding the auction of a product. Interested parties follow the instructions on the notice and place their bids on the required goods accordingly. The format of an auction notice consists of the following elements:
- Issuing Authority: This included the name of the company, individual or the government organization that has issued the notice.
- Memo No.: This covers the specific number issued to that auction notice. This is an optional section and is not included in all notices.
- Date: The date when the auction notice is written.
- Subject: Contains the main reason why the notice is written i.e. the selling of a particular product or service.
- The Body: This section includes the details regarding the auctioned goods or services; the date, time and place of the auction; contact information of the issuing authority if required.
- Signature: This section contains the signature of the issuing authority.
Sample Notice
Given below is a sample auction notice issued by the West Bengal Information and Cultural Centre for disposal of scrap material:

Public notice writing is a formal written document. It is one of the common methods of communication. It gives important information regarding something that is about to take place or has taken place.
It is usually meant for a wider audience. It is usually put up in a public place for easy accessibility.
A notice must include:
What is going to happen.
Where it will take place.
When it will take place.
Who can apply or is eligible for it?
Who to contact?
Points to remember while writing notices:
Only include the most important points.
The sentences must be short and grammatically correct.
Notices must be presented in the passive voice as much as possible.
Present the notice in a box.
The word limit for the body of a notice is 40–50 words
The information must be clear. It should not cause any confusion.
A notice must attract the reader’s attention immediately.
Increase its visual appeal by using bold letters and catchy slogans.
You can use standard abbreviations.
Types of Notices
Before one can fully understand the dynamics of making notices, understanding the basic principles and types of notices must be considered.
- Public Notice – These types of notices are made and disseminated by government offices and departments. They are for the benefit of the general public in order for them to know the government-related updates such as the passage of new law, details about certain legal proceedings, and many more.
- Private Notices – In contrast to public notices which are used to raise public awareness, private notices are given and address to particular parties. These types of notices spring from contractual obligations such as in the case of job notice templates, two weeks’ notice letter sent by a landlord to his or her tenants, and many more. These are also used by companies and organization in terms of disseminating significant information. If there will be company meetings, secretaries can refer to notice of meeting templates
in drafting the notice for an upcoming meeting or company conference.
Format of a public Notice
The structure of a formal notice consists of the following elements:
- Name of the organization
The name of the organisation or faculty should be written at the very top of the notice.
This is important as it makes it easier for the reader to decide whether the given information concerns them or not.
2. Title
The title “NOTICE” should always be written on top and must be underlined. Since notices are usually put in public places, they must be easily discernible.
Because public places generally have a lot of posters, pamphlets, etc. a bold title is important for the notice to be conspicuous.
3. Date
The date on which notice was published is to be mentioned on the left-hand side of the document.
This is a formal document; hence, it is important to mention the date as it stays on record.
4. Heading
Heading must always precise and clear as it gives a clear idea about the purpose of the notice.
5. Body
Here one should write the relevant information as briefly as possible. Since a notice is a very short written document,
One should provide all the significant and pertinent information in a precise manner.
The body should cover all the five W’s, i.e., what, where, when, who and whom.
6. Writer’s name
The name and designation of the writer of the notice should be mentioned in the end.
Sample Notice

A memorandum is an internal and informal form of communication which is written to inform and to call to action. It is normally used for communicating policies, procedures or other information within the organisation.
Unlike Interpersonal communication a memorandum is presented to a large number of people. A memo has to be concise and concrete in terms of providing information.
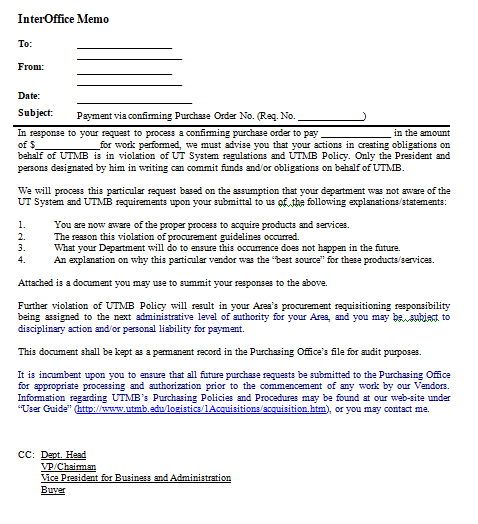
Interoffice memorandums (memos) are used by employees within an organization to communicate with one another.
A memo heading consists of four standard parts: TO, FROM, DATE, and SUBJECT. (See illustration of an interoffice memo.) The memo is usually keyed on a pre-printed form with the organization’s name printed at the top of the page. If the headings TO, FROM, DATE, and SUBJECT need to be keyed, use the format guides presented below.
The heading part follows the format given below:
TO: (The name of the receiver and their designation)
FROM: (Your name and designation or title)
DATE: (Current Date)
SUBJECT: (The purpose of writing the report)
The Body
The body of a memo report, like any technical report, should be concise and to the point. It needs to be properly structured and organised. It should consist of the following elements:
Opening:
This section should consist of 2 to 3 sentences and should state the main purpose of the memo. It should include the main problem with which the memo is concerned with and how it is going to be addressed. A good way to start the opening statement would be “The purpose of this circular is to inform you regarding the recent changes….”
Discussion:
This is the longest section in the memo which deals with all the information and evidences you have collected to support your arguments. This section can be subdivided into four subsections namely,
Conclusion:
After discussing your research, you should summarize the main elements of your finding in 2 or 3 sentences that should reiterate all the implications in the circular.
Attachment/Enclosure notation
If another document is attached to a memo, the word Attachment is keyed at the left margin one line below the reference initials. If a document is included but not attached, the word Enclosure is used. If no reference initials are used, the notation is keyed one line below the last line of the body.
Sample Inter-Office Memo
The term precis comes from a French word “précis”, which can be translated as "precise, clear, up to the point”. Therefore, the word precis in the context of writing means a summary of any writing piece, be it a book, an article, or a novel. What is typical while writing a precis is the outline of the main points and arguments presented in the given text. A precis does not contain a deep or critical analysis of the text, but it nevertheless objectively explains the situation narrated in a text.
Precis vs. Summary
A precis and a summary are quite similar to each other but they do contain certain major differences which set them apart. Below are the two main differences between a precis and a summary:
- A summary consists of a number of brief statements which covers the main points of the text. It has no pre-defined word limit. A precis on the other hand, has its own title and should be 1/3 of the total words of the original passage.
- A summary is a sort of general overview of the contents of a passage. Here only the main events in the passage are discussed. A precis, however, focuses on every detail and analyses a particular situation.
Rules
Below are the fundamental rules to be followed while writing a precis:
- Understand the theme of the passage
The first and the most important thing is to thoroughly read and comprehend the purpose of the passage. Once you understand the theme, it is easier to grasp the key ideas in the passage, which will help you remember them while writing the precis.
b. No copying from the passage
It is important in precis writing to use your own words and not copy from the passage. If you find certain sentences in the passage that you would like to incorporate in your precis, you need to understand them and then craft that sentence in your own words. Key words can be used but entire sentences should always be avoided.
c. Carry clarity and conciseness
One of the most fundamental rules of writing a precis is clarity. The sentences should be clear, concise, meaningful and to the point. They should reflect the central ideas from the passage.
d. A reflection of your intelligence
The precis should be written in such a way that it flaunts your writing skills. The use of language, vocabulary and structure of sentences should be perfect. A good precis will provide the readers a good impression of your writing skills and it will also make the precis comprehensible to the readers.
e. Be original
Each and every sentence in the precis should be one's own creation with no plagiarism whatsoever. If you find a significant idea or motif from the passage that you want to include in your precis, read the passage again and again and try to re-construct the idea from your memory using your own words.
f. Use of indirect speech
A precis must always be written in indirect speech since it employs the perspective of a third person. Direct speech leaves a personal impact and should be avoided while writing a precis.
g. Use facts and statistics
To maintain the credibility of the text, try to include all the numbers and facts you read in the text. It will also help you enhance the quality of your writing and will build the interest of the reader in your precis. Therefore, any of the facts and numbers should not be missed while writing the Precis.
h. An analysis of the various sections
Divide the text into sections and try to analyse each section carefully. A careful analysis of each section will let you draw in closer to the main themes and concepts in the text. Further, you can only mention the crucial content of the passage, if you have read it thoroughly and have identified the areas which carry high proportional value.
i. An interpretation of the original passage
Always conclude the passage by providing your own understand instead of the writer's perspective. The conclusion has to be from your own point of view but should still be in the third person as if spoken by a third party. It is your interpretation of the text that gives meaning to the precis.
j. The size of the precis
The size of a precis should always be one third of the original passage. While writing the precis one should always be aware of the word count but one should also be able to retain the individuality of the passage in the prescribed word limit.
Precis Format
A precis should be short and concise and comprises of three parts: The introduction, the main body and the conclusion.
The Introduction
- The introductory sentence of a precis should mention the author’s name along with the article/book title. It should also include the date of publishing in parenthesis. After that, the topic that you want to discuss in your precis has to be elaborated using a few key words. Extravagant detailing of the topic should be avoided.
- In the introduction, try to include a rhetorical verb outlining the author’s primary purpose (e.g., “assert,” “argue,” “deny,” “refute,” “prove,” disprove,” “explain”). This will give a strong definition to the facts and concepts you are about to present in the main body of your precis.
- It is important to include the thesis statement of the text in the introduction. A thesis statement is the main idea or crux of a particular text. This thesis statement will be elaborated in the main body by providing facts and evidences in its favour.
The Main Body
- The main body should include clarification of how the author formulates and further explains the main themes in the text. It should be informative enough to incite the reader's interest and short enough to retain that interest.
- It should include a sentence that states the purpose of the author in writing the text. Phrases such as “in order” are helpful in developing this sentence.
- Describe how the author establishes his connection with the readers. Always keep the audience for whom you are writing in mind while writing a precis. This includes the using vocabulary and structuring sentences according to the needs of your audience.
- All key points and arguments must be contained in this section.
The Conclusion
- Present a finishing remark of 2-3 sentences to shed light on the author’s intended idea for the book or passage.
- Give a 1-sentence restatement of the major claim which the author used to develop their evidence in the reading.
Steps for Writing a Precis
Below are the steps involved in writing a precis
Step 1: As discussed, the very first step of Precis writing is to form a clear understanding of the passage. You should fully acquaint yourself with the subject first in order to get the meaning behind a passage before starting to write a precis.
Step 2: While reading the content, make sure you highlight the important points of the passage. It will help you in keeping track of the important information that needs to be written in your Precis. Also, you should omit the information, which you feel is not important for your Precis.
Step 3: Further, you need to remember that logical ordering is highly important when it comes to precis writing. Additionally, a logically organised text helps in making things much clearer to your audience and they tend to understand your take in a processed way.
Step 4: If you have some names to be mentioned in your Precis, remember, they should be with the designations, as it helps to increase the credibility of the content. In case, the designations are not mentioned in the passage, you can write the first name.
Step 5: Moving on, the word count of the passage should be taken into account, because one- third of the same has to be written in Precis. Therefore, conducting a word count before beginning the precis could be beneficial.
Step 6: Now, prepare the draft of your Precis by jotting all the important points together. While writing always remember to maintain the flow of your concepts and you should not miss any important information you have gathered while reading the passage.
Step 7: Before finally submitting your Precis, make sure you review all the details carefully. Also, you must do a thorough check of your grammatical and structural errors. Furthermore, one thing not to miss is to mention the total count in a bracket after the end point of your Precis.
The resume or bio-data may be a brief record of the applicant’s personal details, educational qualifications, specialized training, experiences, references and the other relevant information. It's a summary of one’s personal and academic accounts. A resume is considered as a formal advertisement of a person’s qualifications.
ACCORDING TO BOVEE, THILL AND SCHATZMAN, “A RESUME may be a STRUCTURED, WRITTEN SUMMARY OF A PERSON’S EDUCATION, EMPLOYMENT BACKGROUND AND JOB QUALIFICATIONS.”
MURPHY AND HILDEBRANDT SAID, “CURRICULUM VITAE IS A DOCUMENT LABELING ONE’S QUALIFICATIONS AND CAREER PATH.”
LOCKER DEFINED, “A RESUME may be a PERSUASIVE SUMMARY OF ONE’S QUALIFICATIONS FOR EMPLOYMENT.”
So, a resume is brief description of one’s personal, educational and employment qualifications. The aim of the resume is to get an interview, not to tell readers everything about you. In fact, it's a sort of advertising. Now-a-days, it becomes almost traditional to send a resume with the job application letter.
Contents of a CV –
The bio-data must be properly arranged under some heading or sub-headings. It includes information about a few persons in various areas. Usually the knowledge is presented during a bio-data under the subsequent heading-
• Personal Information: This section includes complete name, address both temporary and permanent, telephone number, date-of-birth, parent’s names, marital status, nationality, religion and cast in some cases etc.
• Career Objectives: Clearly state your objective or future plan in your career. Tell what you're interested to try to and what level of responsibility you want to hold. So, short term and future target of your career must be mentioned here.
• Educational Qualifications: an entire record of the academic qualifications should be given during this section. It includes the name of degrees obtained, the name of the institution attended, year of passing, board or university form where degree is obtained and the division or grade or class obtained etc.
• Experience: This section includes the applicant’s previous experience relevant to the work applied for. Details to be included here are- the period of time or length of previous or current job the joining and therefore the levelling dates, the name of the organization, position held and a quick description of the duties or nature of work or tasks done on the job.
• Honours and Awards: Honours and awards are given for outstanding work. This section includes fellowships and scholarship or honorary scholarship, awards given by professional associations and civic groups.
• Extra-Curricular Activities: The applicant’s extra-curricular activities like membership in various organizations, participation in several seminar and workshops, prizes won in cultural functions etc. are to be mentioned here.
• References: Names and addresses of the persons who known the applicant and may express a private opinion about his abilities and qualities must tend in this section. It customary to offer three references sort of a teacher, an employer and a friend of the family with high social or professional status. But if the number of referees isn't dictated by the prospective employer, it's better to mention the names and addresses of at least two references. The name, title, complete address and phone number of the referees must tend and it's preferable to point their social relationship to the applicant. The applicant should take permission from the referees to give their names or a minimum of inform them immediately after, with details of the job applied for.
• Signature of the Applicant: At the end of the resume, the applicant should put his signature and date with the left margin. Below the signature, there must be enough space for typing the complete name of the applicant.
In concluding note, we will say that a resume must include everything relevant to the post or job applied for and must exclude irrelevant things. If the employer invites only resume, sometimes it's better to attach a recent photograph with it.
Types of a CV –
Type | Function | Advantage | Disadvantage |
Reverse Chronological | Reverse chronological CV (also called reverse time order) focus on work history. | Demonstrates a consistent work history | It may be difficult to highlight |
Functional | Functional CV (also called competency-based rEsumEs) focus on skills. | Demonstrates skills that can clearly link to job functions or duties | It is often associated with people who have gaps in their employment history |
Combination | A combination CV lists your skills and experience first, then employment history and education | Highlights the skills you have that are relevant to the job and provides a reverse chronological work history | Some employers prefer a reverse |
Targeted | A targeted CV is a custom document that specifically highlights the experience and skills that are relevant to the job. | Points out to the reader how your qualifications and experience clearly match the job duties | Custom documents take additional time, preparation, analysis of the job announcement, and may not fit the established guidelines |
Scannable | A scannable CV is specifically formatted to be read by a scanner and converted to digital information. | Increasingly used to facilitate search and retrieval, and to reduce physical storage costs | Scanners may not read the CV |
Business Reports
The success of a business or industrial organization lies in doing its job for this purpose, gathering information and passing it on to those who need it is important. In the broader collection and transfer of information is happening all the time in every area of formal life. So, scientists, working brokers, testers, journalists, and various professionals, government and private organizations are asked to write and report to their management on important topics at the institution or the person involved.
Reports can be as short as a few sentences and as long as a few large pages. Although reports can be verbal and informal, here we are concerned with written and formal reports.
Types of Reports
Reports are available all sizes, but are typically longer than a page and somewhat shorter than a book. the sort of report depends on its function. The function of the report is its essential purpose, often indicated within the thesis or purpose statement.
The function also will influence the kinds of visual content or visual aids, representing words, numbers, and their relationships to the central purpose in graphic, representational ways in which are easy for the reader to know. The function can also contribute to parameters like report length (page or word count) or word choice and readability. “Focusing on the content of your longer business documents isn't only natural but necessary because doing so helps ensure complete, correct information”.
Reports vary by function, and that they also vary by style and tradition. Within your organization, there could also be employer-specific expectations that require to be addressed to satisfy audience expectations.
There are two main categories for reports, no matter their specific function or type:
Informational Report
An informational report informs or instructs and presents details of events, activities, individuals, or conditions without analysis. An example of this sort of “just the facts” report may be a police accident report. The report will note the time, date, place, contributing factors like weather, and identification information for the drivers involved in an automobile accident. It doesn't establish fault or include judgmental statements. you ought to not see “Driver was falling down drunk” during a police accident report.
Instead, you'd see “Driver failed sobriety tests and Breathalyzer test and was transported to the station for a blood sample.” The policeman isn't a trained medical doctor and is therefore not licensed to form definitive diagnoses, but can collect and present relevant information which will contribute thereto diagnosis.
Analytical Report
The second sort of report is named an analytical report.
An analytical report presents information with a comprehensive analysis to unravel problems, demonstrate relationships, or make recommendations.
An example of this report could also be a field report by a middle for Disease Control (CDC) physician from the location of an epidemic of the H1N1 virus, noting symptoms, disease progression, steps taken to arrest the spread of the disease, and to form recommendations on the treatment and quarantine of subjects.
Types of Reports and Their Functions
Types of Reports and their functions include common reports that, counting on the audience needs, could also be informational or analytical.
1. Laboratory Report Communicate the procedures and results of laboratory activities.
2. Research Report Study problems scientifically by developing hypotheses, collecting data, analysing data, and indicating findings or conclusions.
3. Field Study Report Describe one-time events, like trips, conferences, seminars, also as reports from branch offices, industrial and manufacturing plants.
4. Progress Report Monitor and control production, sales, shipping, service, or related business process.
5. Technical Report Communication process and merchandise from a technical perspective.
6. Financial Report Communication status and trends from a finance perspective.
7. Case Study Represent, analyse, and present lessons learned from a selected case or example.
8. Needs Assessment Report Assess the necessity for a service or product.
9. Comparative Advantage Report Discuss competing products or services with an analysis of relative advantages and drawbacks.
10. Feasibility Study Analyse problems and predict whether current solutions or alternatives are going to be practical, advisable, or produced the specified outcome(s).
11. Instruction Manuals Communicate step-by-step instructions on the utilization of a product or service.
12. Compliance Report Document and indicate the extent to which a product or service is within established compliance parameters or standards.
13. analysis Report Communicate costs and benefits of products or services.
14. Decision Report Make recommendations to management and become tools to unravel problems and make decisions.
15. Benchmark Report Establish criteria and evaluate alternatives by measuring against the establish benchmark criteria.
16. Examination Report or record data obtained from an examination of an item or conditions, including accidents and natural disasters.
17. Physical Description report Describe the physical characteristics of a machine, a device, or object.
18. Literature Review Present summaries of the knowledge available on a given subject.
Characteristics
Below are the fundamental Characteristics of a business report:
- The Audience:
When organizing and preparing your reports you need to know who your audience is and whether or not your content meets their interests and needs.
- Conciseness:
Legitimacy has to do with how easy or readable it is. As most reports in normal cases type, all meetings with good typing should be followed. If there are handwritten reports, special attention should be given to writing clearly and clearly. Any departure from the above requirement will prove displeasing to your audience.
- Readability:
Clarity, durability and systematic presentation of readable content. The concept is summarized better than the following:
The author does a lot by giving his reader a lot of information and taking away from him a little time.
In this regard the following five goals are met:
a) Use short sentences.
b) You prefer convenience to the building.
c) Choose a common name.
d) Use the economy and avoid unnecessary words.
e) Act actions as far as possible
- Clarity:
Just like unwanted fat in the body, padding, prolixity and repetition violates the respect of good writing, not to mention the respect they wrote for you. So 'agree' and 'prefer' will be more acceptable than pompous 'agree with' and 'prefer'. As such, why use 'at that point in time' and at a time when we have the best and most economical holdings at that time 'and' when '. Viewed from the point of view of the report, or requested for the report, a good report will contain four important details, an analysis of the information, conclusions and recommendations. It should always be remembered that effective reporting requires special attention to the needs and expectations of the reader. It means that the author of the report has to 'snap a picture', he must think and understand himself.
Importance
Reports are documents designed to record and convey information to the reader. Reports are a part of any business or organization; from credit reports to police reports, they serve to document specific information for specific audiences, goals, or functions. the sort of report is usually identified by its primary purpose or function, as in an accident report, a laboratory report, a sales report, or maybe a book report. Reports are often analytical, or involve the rational analysis of data. Sometimes they simply “report the facts” with no analysis in the least, but still got to communicate the knowledge during a clear and concise format. Other reports summarize past events, present current data, and forecast future trends. While a report may have conclusions, propositions, or maybe a call to action, the demonstration of the analysis is that the primary function.
A sales report, for instance, isn't designed to form a private sale. It is, however, alleged to report sales so far, and should forecast future sales supported previous trends.
Writing good business reports can save time and money, and play a dramatic role in the future of a company. Below are some reasons why business reports are important:
Tracks Development Over Time
Business reports document progress and provide a means of comparing periods of time, project details, and history of growth. While one may rely on a superior memory or the amount of profits, they make each year to gauge progress, the data collected in reports can serve a number of important purposes. It can help in the formulation of budget and marketing plans for the upcoming year. It may also help in realizing which products or services are the most successful, and which markets have been overlooked.
Provides an Audit Trail
In addition to making decisions about the company and its future, reports help in building a paper trail of the past. Reports that document sales, meetings, plans, initiatives and annual budgets are an integral part of the proprietary materials that make up a business. If one ever approaches a bank for a loan or decides to sell their business, they will be required to produce more than personal tax returns to support their requests or asking price.
Duty to Stakeholders
A corporation has to produce an annual report each year as part of its legal fiduciary obligations to its stockholders and the government agencies that oversee corporate businesses. Through this process, large companies have come to learn about the many benefits they can reap from producing an annual report. Small businesses can tap into those same resources if they create a summary and overview the previous year in business.
The annual report usually is a glossy report with pictures and contact information that doubles nicely as a marketing package. It is useful when making introductions to new clients or trying to build name recognition in a community. An annual report is an effective tool for providing employees, investors and clients with a complete picture of the business.
Supports Purchasing Decisions
Even if one does not report to a corporate board or have to produce documentation for a team of investors, there may come a time when one wants to expand or make a substantial purchase to increase business, and they may be required to produce a financial history of the company. A sole proprietor may face the time when the best way to grow means taking on a corporate label, and they will be required to create those reports on a regular basis.
Structure
Business reports may be of various types but they follow a similar structure in most cases. The elements contained in a business report may be as follows:
- Executive summary
The executive summary gives the audience a complete understanding of the points being addressed, the report's topic, the type of evidence and sources that compiled the report and the purposed solutions based on the data. The summary can be less than a page or up to four pages depending on the amount of detail required, but you should wait until you gather your findings to write this section, so it can be comprehended by reviewers of your presentation.
B. Title Page
The title page includes the main title of the report, it must be short and concise. You can also include the word counts of your summary and main body.
C. Table of Contents
Help your reader quickly and easily find what they are looking for by using informative headings and careful numbering of your sections and sub-sections.
For example:

D. Introduction
The introductory part of the report comprises of statement of the objectives of the report and how the report should be treated by the readers. It should indicate towards the problem that is going to be addressed in the main body. It should be catchy and interesting to grasp the attention of the reader from the very start.
E. The Body
The main body consists of the central theme or the main idea of the report. It can be divided into a number of sections and subsections to separate your research and subsequent findings in a logical order.
F. Figures, Graphs, Formulae and Tables
This section consists of the statistical representation of the data you have collected. Ideas should be conveyed in the form which is most suitable to the reader and easily understandable by the reader. Excessive use of these tools should be avoided.
G. Conclusion
The conclusion is a kind of summing up of all the points you have stated in the main text. It should be a definite solution to the problem introduced during the introductory part of the report. The conclusion must be short and to the point.
H. Summary
Summarize all the key points stated in the report including your research, your findings and your conclusion. The summary should feel like a brief overview of your investigations and outcomes. The summary should be constructed in such a way that it can be called a stand-alone document on its own.
I. References
References must include detailed information of all your citations and the sources of material quoted in your texts. It can also include bibliography for further reading.
J. Appendices
This is the last element of a report. It refers to any material which can be useful in the detailed understanding of your subject. It is not meant for the casual reader but for readers who are highly interested in the subject.
Unit II
Writing Skills
2.1.1 Enquiry Letters:
A Business Inquiry letter is a letter written for communication between two organizations or persons belonging to 2 different organizations inquiring regarding some business they're doing together or hoping to try to in future. It's a proper letter and hence one has got to be polite and humble. In some cases, the sender might not have ever met the receiver. One has got to be precise and to the purpose and not drag the letter.
A business letter is a letter where two concerned parties discuss business. Business inquiry letter are often of the many types. The letter of enquiry is often about certain products or services of the receiving company. It can ask the status of the ongoing work being done by the company receiving the letter.
A letter also is a proof for the business being done between 2 organizations and as a history for future references. This sort of letter is brief and to the purpose. Just in case the sender doesn’t have the expertise regarding the inquiry being made he/ she will also ask the receiver to help them.
What is Inquiry Letter -Letter of inquiry is one among the most important sorts of business letters. When a buyer wishes to urge some information about the quantity, price, availability etc. of products to be bought or about the terms of sale, payment etc he writes a letter of inquiry to the seller.
Inquiry Letter –
ACCORDING TO MORRIS PHILIP AND OTHERS, “THE LETTER THAT SEEKS INFORMATION CONCERNING THE GOODS AND SERVICES FROM A BUSINESS CONCERN IS TERMED AN INQUIRY LETTER.”
QUIBLE AND OTHERS SAID, “LETTER OF INQUIRY MAY BE A SORT OF BUSINESS MESSAGE THAT ASKS THE RECIPIENT FOR INFORMATION OR ASSISTANCE.”
IN THE OPINION OF R. V. LESIKAR ET AL., “LETTERS THAT ASKS QUESTIONS OR INFORMATION ABOUT ANYTHING IS CALLED INQUIRY LETTER.” BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
ACCORDING TO GARTSIDE, “AN INQUIRY LETTER ASKS INFORMATION LIKE CATALOGUE, QUOTATION, SAMPLE AND PRICE OF A PRODUCT FORM A SELLER DURING A CONCISE AND CLEAR WAY.”
Objectives of Inquiry Letter in Business Communication –
Every letter has some certain objectives or motives and inquiry letter isn't an exception. It's written on different occasions for various reason. Inquiry letter is written so as to hold out one among the subsequent objectives bellow-
• To get the price quotation of specific commodities
• To ask for catalogue
• To know payment terms
• To know the past records of job applicant
• To know the credit worthiness of a firm or an individual
• To ask for folders
• To get recommendation from former employer
• To know the financial strength of a firm or an individual
• To know the business reputation of a firm
• To know the transportation facility provided by the firm
• To obtain information about social status of an individual or a firm
• To evaluate the performance of an individual or a firm
• To find out about the quality of a product
• To know the availability of an item
• To make request for sample etc.
Types of Inquiries Letter in Business Communication –
Inquiries could also be of various types supported the target, information sought and therefore the initiatives taken. There are generally four sorts of inquires letter-solicited inquiry, unsolicited inquiry, inquiry for a few favour and routine inquiry letter. These are discussed below-
• Solicited Inquiry: An inquiry made in response to the seller’s advertisement and publicity is named a solicited inquiry. Actually, it's a response by the customer to the advertisement or publicity of a seller.
• Unsolicited Inquiry: An inquiry made at the buyer’s own initiative is named unsolicited inquiry. This kind of inquiry is formed when a buyer wants to understand anything from the vendor.
• Inquiry for some Favour: An inquiry made not about goods but information like special price or favourable terms is named inquiry for a few favours.
• Routine Inquiry: An inquiry made by an old or regular buyer within the usual course of action is named routine inquiry. Most of the business inquires fall during this category.
So, we discover that there are differing types of inquiries, regardless of the type is that the bottom line of success of an inquiry depends upon how it's written.
2.1.2 Order Letters:
An order letter is typically written once you got to assign orders for goods. it's quite common and is written almost on a day to day. The language of the letter, however, must be formal and therefore the letter follows a typical format, since the knowledge is extremely specific.
An order letter must pen down the terms and conditions of the acquisition. These benefits both the involved parties. It generally contains details like product specifications, their quantities, a price that the parties have prescribed, the date of delivery, what to try to just in case there occurs a late delivery, etc.
Tips before Writing an Order Letter –
Before writing the order letter, here are some tips for you:
1. The letter should be very precise, there's no exhortation or casual talking required here.
2. The language should be easy while also being formal.
3. don't make any mistakes within the specifications and quantities.
4. Avoid spelling and grammatical errors.
5. Stick with the subject
6. Be polite. you're ordering for goods; you are not ordering the person.
7. Avoid using too many adjectives.
8. Don't use jargons.
9. Don't hesitate to put the order, but do not forget to plan before writing.
Now I can tell you ways to write down an order letter, since you now know all that you simply needed to understand before writing one.
Elements of the Order Letter –
An order letter needs the subsequent things to be in check:
o Contact information about yourself, the person/company which will supply to you and therefore the date.
o A subject line that helps the recipient to know your purpose directly.
o A salutation, like, if you recognize the name of the vendor, write, “Dear ……………”. If you do not know the name of your seller, simply write “Dear Seller”
o Information about your company; but this is often totally optional. However, this will ensure a long-term relationship. you'll also say a couple of words about your future plans associated with the sale.
o Order details, and by details, I mean everything. The model number, colour, size, number, etc. Be attentive since they'll send whatever you'll write. If possible, use bullet points or tables. If you're buying different items of various types, describe them in separate paragraphs.
o Mention your payment mode or if you've paid already, mention that next.
o Indicate your preferred delivery method and date.
o Include any special instructions as a neighbourhood of the terms and conditions agreed between the parties.
o Tell them that you're going to enjoy future cooperation with them and encourage them to contact if needed.
o Close with “Sincerely”, your signature and name.
The quality of the delivered goods will depend upon your instructions. Not just that, it's literally a legal instrument between yourself and therefore the seller. So, watch out for what goes in your order letter and pay an honest deal of attention while drafting one.
2.1.3 Credit Letters:
When you hear the phrase 'letter of credit,' it'd be natural to think it refers to a document verifying that you simply are creditworthy, but that may not the case. A letter of credit may be a document issued by a 3rd party that guarantees payment for goods or services when the vendor provides acceptable documentation. Letters of credit are usually issued by banks or other financial institutions, but some creditworthy financial services companies, like insurance companies or mutual funds, might issue letters of credit under certain circumstances.
A letter of credit generally has three participants. First, there's the beneficiary, the person or company who are going to be paid. Next, there's the customer or applicant of the products or services. this is often the one who needs the letter of credit. Finally, there's the issuing bank, the institution issuing the letter of credit. additionally, the beneficiary may request payment to an advising bank, which may be a bank where the beneficiary may be a client, instead of on to the beneficiary. This could be done, for instance, if the advising bank financed the transaction for the beneficiary until payment was received.
Letters of credit are most frequently utilized in international trade, where they're governed by the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (or UCP), the principles of the International Chamber of Commerce. However, they will be utilized in other situations, as we shall see.
Types and Features of Letters of Credit –
Most letters of credit are import/export letters of credit, which, because the name implies, are letters of credit that are utilized in international trade. an equivalent letter of credit would be termed an import letter of credit by the importer and an export letter of credit by the exporter. In most cases, the importer is that the buyer and therefore the exporter is that the beneficiary.
There also are other sorts of letters of credit. The revocable letter of credit is often changed at any time by either the customer or the issuing bank with no notification to the beneficiary. the foremost recent version of the UCP, UCP 600, did away with this type of letter of credit for any transaction under their jurisdiction. Conversely, the irrevocable letter of credit only allows change or cancellation of the letter of credit by the issuing bank after application by the customer and approval by the beneficiary. All letters of credit governed by the present UCP are irrevocable letters of credit.
A confirmed letter of credit is one where a second bank agrees to pay the letter of credit at the request of the issuing bank. While not usually required by law, an issuing bank could be required by writ to only issue confirmed letters of credit if they're in receivership. As you would possibly guess, an unconfirmed letter of credit is guaranteed only by the issuing bank. this is often the foremost common form with reference to confirmation.
A letter of credit can also be a transferrable letter of credit. These are commonly used when the beneficiary is just an intermediary for the important supplier of the products and services or is one among a gaggle of suppliers. It allows the named beneficiary to present its own documentation but transfer all or a part of the payment to the particular suppliers. As you would possibly guess, an un-transferrable letter of credit doesn't allow transfer of payments to 3rd parties.
A letter of credit can also be at sight, which is payable as soon because the documentation has been presented and verified, or payment could also be deferred. Deferred letters of credit also are called a usance letter of credit and should be postpone until a particular period of time has passed or the customer has had the chance to examine or maybe sell the related goods.
A red clause letter of credit allows the beneficiary to receive partial payment before shipping the products or performing the services. Originally, these terms were written in loss, hence the name. In practical use, issuing banks will rarely offer these terms unless the beneficiary is extremely creditworthy or an advising bank agrees to refund the cash if the shipment isn't made.
Finally, a back-to-back letter of credit is employed during a trade involving an intermediary, like a trading house. it's actually made from two letters of credit, one issued by the buyer's bank to the intermediary and therefore the other issued by the intermediary's bank to the vendor.
Documentation Requirements –
In order to receive payment, the beneficiary must present documentation of completion of their part within the transaction to the issuing bank. The documents that the issuing bank will accept are laid out in the letter of credit, but may often include:
• Bills of exchange
• Invoices
• Government documents, like licenses, certificates of origin, inspection certificates, embassy legalizations, and phytosanitary certificates
• Shipping and transport documents, like bills of lading and airway bills
• Insurance policies or certificates, except cover notes
2.1.4 Status Enquiry Letters:
The letter that's written for obtaining information about a commercial enterprise is termed as business status inquiry letter. Generally, one commercial enterprise writes this letter to another commercial enterprise for collecting information a few prospective customers.
When a firm wants to buy goods on credit, it gives one or more references to which the vendor can invite some information about the credit seekers. Usually, banks, trade associations or competing business firms are mentioned as references. The vendor then writes the inquiry letter to the referees requesting them to supply some information about the customer.
The purpose of scripting this letter is to get information related to:
• Financial capability or creditworthiness
• Goodwill
• Nature of business dealings
• Honesty
• Relationship with business association, etc
In light of the above discussion, we will conclude that when a commercial enterprise writes an inquiry letter to another commercial enterprise, financial organization or trade association to get information about creditworthiness or financial capability of a customer who has applied for credit purchase, it's called business status inquiry letter. Basing on the information supplied by the referees, the seller decides whether to establish business transactions with the firm.
Objectives or importance of business status inquiry letter –
Business status inquiry letter plays a crucial role in modern business. The subsequent are the main objectives of writing this letter:
• Obtaining information about the financial capability of prospective customers.
• Determining the risk of credit sales.
• Deciding whether to enter into credit transactions.
• Getting information about honesty, goodwill and business morality of the probable buyer.
• Knowing about the connection of the potential buyers with other business community and associations.
• Enhancing sales with various parties by evaluating their financial and business viability.
Status Inquiry letter -
|
2.1.5 Claim Letters:
The letter of the announcement is going to be mentioned the upcoming customers, client contacts, existing customers to form them conscious of some offers and schemes which will help them to form big savings. this is able to entitle the aim of offering exciting offers during a money-spinning sense.
These letters are written to the purchasers in order that they will observe profits. It is often written to the prevailing customers to tell changes in rates, supplies, and new offers, etc. It is often associated with introducing a replacement product of the corporate to follow up together with your existing customers or new customers to take care of an honest account.
Your product or service could be top of the road. Your customer service could also be the simplest in school. you're still getting to get complaints. Client complaints or claim letters are often an enormous asset for your business then show you ways to harness those assets. When customers complain, they're actively teaching you ways to enhance your product. this sort of warm, helpful letter to take care of the business scent during the amount you're gathering all the specified information for the prospect.
Claim Letter Writing Tips –
Write briefly about the offers and therefore the schemes; write what benefit the reader goes to urge from the schemes.
Write the amount during which the offer is valid. this may help the customer to avail the offer.
Use a positive tone. invite a positive reply. Use attractive language in order that it can grab the eye of the readers towards the offers and discounts.
Write that the reader may be a very valued customer and hence you're scripting this letter.
State the precise name of the person or company you're pertaining to.
Be clear and concise about the knowledge you would like to supply
Propose how you'll improve the customer’s experience within the future.
If there are any necessary forms, etc., that you simply got to fill out or send, include them together with your letter for faster approval.
Claim Letter Template -
From,
_____________
_______________
Date: ______________ (date on which the letter is written)
To,
____________
_________
Subject: Claim letter
Dear Sir/ Madam,
I am ___________ (name) scripting this letter to you to declare the schemes and offers on behalf of our company that's ____________ (name of the company). On this Diwali, we've declared festive season offers. We are delighted to satisfy your needs and consider it a compliment whenever you place an order.
In appreciation for your business, we've included a coupon for 10 percent off any service for each product in your fleet. If you place an order between 01.11.2013 to 15.11.2013 then you'll avail these offers.
We will also sell regular products prices during this period. So, if you would like to realize huge profits, then you'll place big orders during this period. you'll also buy larger quantities. These offers are for all our important customers, and you're one among them.
We encourage you to contact us regarding this special offer and to think about us your one-stop service centre. At eBay, we are committed to providing superior care. Again, it's a privilege of servicing you. Hence, you're requested to be benefited by these offers.
Hope to listen to soon from you.
Thanking You.
Yours Sincerely,
____________
2.1.6 Complaint Letters:
Letters which are written by the purchasers to the sellers about their inconveniences created by some unexpected situations are referred to as complaint letters. However efficient a corporation could also be in running a business, everything doesn't go all the time consistent with plan. there'll be some mistake and a few accidents. Important service is sometimes rendered unsatisfactorily; goods are consigned to wrong destinations, sometimes too late, sometimes in but the specified quantities, sometimes in damaged condition.
Complaint letter is –
Letter written to bring these mistakes to the notice of these who must own the responsibilities for them are called claim or complaint letters. So, when a letter is written to the vendor by the customer raising complaints or claims regarding mistakes taken place during the order to payment period is named a claim or complaint letter.
Business complaint letter is written by customers who aren't satisfied by the amount of consumer services provided. If you are feeling that your supplier is dishonest about the products, they deliver to you, whether in terms of content or pricing, you'll write them a customer complaint letter to precise your grievances.
Don't forget to say that there'll be consequences should they fail to deal with the difficulty in question.

2.1.7 Adjustment Letters:
Adjustment Letter is response letter to customer complaint or claim. it's official in nature and explains the relevancy of the complaint or claim and the way it is often resolved.
Adjustment Letter Definition -
A sort of letter addressed in response to a customer's claim or complaint letter, written by a representative of an organisation or a gaggle because of the client-vendor relation, a letter of adjustment also acts as a legal instrument demonstrating the small print of the correspondence and therefore the resolution or dissolution the between the 2 parties.
A letter of adjustment doesn’t mean that your complaint or claim are going to be accepted. It notifies the sender that their claim or complaint letter has been received. It depends upon the validity of your claim that a letter of adjustment will contain conformity of its mistake and its rectification. Adjustment letters are meant to resolve a conflict that's why they're referred to as such. Letters of adjustment also are referred as Claim Adjustment Letters, Complaint Response Letters, Customer Complaint Reply, Letter of Complaint Response, Letter of response to Complaint and similar other terms. A letter of adjustment deals with all kinds of claims and complaints; defective product, poor service, goods not delivered, shipment arriving late, salary not received et al.
Bangladesh Textiles Mills Ltd. 10th Feb. 04 Marketing Manager Ref: Your letter dated 5th Feb. 04. Dear Sir, We thank you .for your letter of 5th Feb. 04 along with/ sample of cloth for examination. The report that we have received just today shows that the consignment forwarded to you was the wrong one full of defective clothes. It was a mistake because of our despatch section and we regret this mistake which has caused you both embarrassment and inconvenience. We have already sent the replacement by passenger train. You can be sure of the quality of cloth now sent. You can, of course, return the clothes to us and debit our account for the loss caused to you. We again regret the inconvenience to you and assure you that such mistakes will be avoided in future. Yours faithfully
M. Ashraf |
2.1.8 Collection Letters:
Letters written for realizing payments from the debtors are referred to as collection letters. the necessity for writing collection letters arises from credit sales. Selling on credit may be a traditional business policy that enhances volume of sales. Under the credit sales policy, the sellers allow the purchasers a particular period for payment of dues. However, sometimes the buyers make unexpected delay in paying their dues. Even, some custom stances, the sellers write letters reminding and requesting the purchasers to pay the due bills. rather than sending one letter or repeated copies of an equivalent letter, credit departments send a series of letters.
In the opinion of Kitty O. Locker, “Collection letters ask customers to buy the products and services they need already received.”
Quibble et al. defined, “Collection letters are employed by a corporation to entice its charge customers to pay an impressive charge-account balance.”
Collection letters are written during a series. When collection letters are written during a series beginning with an easy reminder and end with a warning letter indication action the dues promptly by retaining the purchasers with the corporate.
2.1.9 Circular Letters:
Circular letter is one of the oldest sorts of letters. This type of letter originated in ancient time when people felt the need of circulating any message to a large number of individuals at a time in the same way.
Generally, the letter that's won’t to circulate any special message to a large member of audiences at the same time is known as circular letter. It's one of the cost-effective means of circulating information or introducing new products to mass people. However, circular letters aren't only used in business, but also in social, political and personal affairs.
Prof. W. J. Weston said, “A circular letter is one which is meant to be read by variety of correspondents. It's of the nature of an advertisement and is typically a business announcement or an effort to advance business.”
From the above discussion we can say that circular letter may be a quite written announcement that's distributed to a large number of people to convey any commercial or non-commercial message at minimum time, costs and efforts. Drafting circular letter is only an art. It should be drafted in such how that can attract readers’ attention and may serve its purpose.

Importance or advantages of circular letter –
Circular letter circulates information relating to a company, its products and services etc. to a large number of individuals at a time. It plays a crucial role within the growth and development of business. Its importance is briefly discussed below:
1. Easy method of conveying information: Circular letter is that the most easy, simple and effective thanks to convey any information to a large number of individuals.
2. Achieving economy: Circular letter are often used for wide publicity of products. As a result, organizations can save cost of sending letters to different parties separately and may gain economy.
3. Saving time: Circular letter transmits information to a large number of individuals at a time. It doesn't require reaching each individual separately. Thus, it saves time.
4. Less effort: Circulating information to every individual separately is a time consuming and laborious job. Circular letter helps to overcome this problem. Through circular letter, we will communicate with large number of individuals at a minimum effort.
5. Creating market: Through circular letter, a company can inform potential customers about its products and services. During this way, new markets are often created.
6. Increasing consumer’s confidence: Convincing and attractive circular letter can easily touch the reader’s heart and thus helps to boost consumer’s confidence on the company’s products.
7. Creating public consciousness: In circular letter, information like price, quality, utility, place of availability, etc. are mentioned in detail that creates people more conscious about the product.
A tender is a formal, transactional document used by large organizations, companies, government bodies and NGOs find suppliers and contractors for particular projects or procurements. Hence, it can be said that tenders are the foundational pillars of bidding process used by both public and private institutions. Invitations to Tender or Requests for Tender (RTF) are documents used by an organization or government institution to invite bids from interested contractors for a large project or the procurement of goods and services.
Important Elements in a Tender Document:
Conditions for participation: This section outlines the important conditions that a supplier or contractor must meet in order to be considered by the organizer. All the important required documents and records proving the supplier’s eligibility for the project are to be enclosed in this section. Financial records, licenses, insurance documents and data related to past projects may be some of the conditions required to be met for participation in the bidding process.
Accreditation and quality standard: Under this section, the potential contractor or provider must demonstrate that they can satisfy all the requirements stated by the organizer in the previous section. The bidder has to present the organizer with certifications of quality and authority accreditations such as ISO, ISI, etc. This section may also outline certain processes or procedures followed by the firm that will ensure superior quality for your product or service.
Specifications: Included in this section is the specific information the potential contractor must outline about the project that the client might be interested in. These specifications may include the goods and services required for the project, the expected time-frame for project completion and also any associated requirements related to pricing, delivery and performance. This information will play an important role in the final evaluation made by the organizer.
Conditions of contract: Under this section, the tender document has to provide all the significant information regarding the rights and responsibilities of the client as well as the potential contractor. All the terms and conditions of the project must also be clearly outlined in this section. This section must ensure clarity, comprehension and transparency in the transactional process.
The condition of offer: While the bidder or contractor is submitting their offer, they must provide the client with their official agreement to the proposed terms and conditions of the contract. The estimated timeline of the entire tendering process as well as the location wherein the submission must be made are to be indicated in this section. Other relevant information that might be included in this section are the submission process, the evaluation process, etc.
Techniques and Elements of a Good Tender Response
Below are the techniques involved in writing a good tender response:
1. Use the templates or formats provided
All tender specification documents adhere to a specific format which is provided by the organization that has required you to fill the tender consisting of multiple sections and sub-sections. These sections may contain certain word limits and require specific file formats.
By accurately following all of the requirements in the tender, your tender response will become clearer and it will be easier for the tender review panel to consider your offer.
2. Structure your tender document clearly
Many a times, organizations do not ask for a particular format or structure, in those cases, be sure to keep your tender document clear, logical and well organized. Begin with a clear and persuasive introduction that states the purpose, rationale and central proposition of your bid for the project.
Diagrams, charts and statistical data also help in convincing the panel to consider your bid. It can be used as an effective way to break up blocks of text and communicate to the reader complex propositions.
3. Provide all relevant details
As with quotes, tenders must include certain information in order to be considered, including:
- Your ABN
- a company profile and capability statement
- Whether you propose to subcontract
- The price for each product or service you propose, and an indication of whether these are fixed or variable (e.g. Based on exchange rates or consumer price index variations)
- Any conditions affecting the price
- Delivery details and charges
- a proposed schedule indicating milestones or delivery dates
- Whether goods or services are periodic or recurrent
- GST and other taxes
- Applicable insurances
- Intellectual property rights where relevant
- a description of any variations you propose in meeting the conditions of the contract.
- Address the selection criteria
Closely follow the criteria in the tender request. Make sure your proposed offer precisely meets the buyer's needs. Describe the advantages the buyer will receive from your organization's products or services.
Provide specific examples of how you meet the selection criteria rather than simply stating that you do. It is important to highlight your credentials and provide verifiable experience, as well as explaining how your approach to delivering the tender will meet the buyer's needs. Identify the requirements that are most important to the buyer and cater for this in your tender response.
4. Choose the right referees
Another key part of delivering a successful tender response is choosing the right referees.
Use referees that know your products or services. Make sure you get permission to use referees before including them in your response. Brief them on the highlights of the request so they can target their comments to the job specifications.
5. Proofread your tender
Use spell check and, if possible, ask someone outside of the tender development process to read your tender response and give feedback. Ideally, get a professional copy editor or proof-reader to carry out this task. If several authors have contributed to different parts of the tender response, ensure that one person reads the entire tender response document for consistency.
6. Submit your tender in time
Late or incomplete tender responses are usually excluded from consideration barring exceptional, pre-agreed circumstances.
If you are submitting online, do not leave your tender submission until the last minute in case you have computer, internet or network issues. If your tender response is to be posted, make sure you allow time for delays. Consider using ‘same day delivery' for courier services or hand-delivering your tender response (if allowed).
An auction is a sales process wherein potential buyers place competitive bids on assets or services either in an open or closed format. Auctions are popular because buyers and sellers believe they can get a decent deal buying or selling assets.
In an open format, all bidders are aware of the bids submitted. In a closed format, bidders aren't conscious of other bids. Auctions may be live, or can be conducted on an internet platform. The asset or service in question is sold to the party that places the highest bid during an open auction and typically to the highest bidder in a closed auction.
In an open auction, parties gather at a physical venue or online exchange to bid on assets. An interested party is conscious of the competing bid amounts and continues to boost their bid until they're either declared the winner of the auction (i.e., they submitted the last highest bid within the auction time limit) or until they concede and drop out of the bidding.
Examples of auctions include car auctions, or an auction room where collectors bid on works of art, auctions for leftover material, auctions for personal assets such as houses etc. Leading online marketplace eBay and many others are a host of online auctions.
Price isn't always the deciding factor when assets are sold by auction; a corporation that's purchasable might choose a buyer who will provide the most effective terms for its employees.
Auctions are conducted in a closed format in many business transactions (including the sale of company assets or an entire company) whereby interested parties submit sealed bids to the seller. These bid amounts are only known by the seller. The seller may prefer to hold only one round of bidding, or the seller may select two or more bidders for an extra auction round.
In a situation wherein, a division of an organization or the entire company is up for sale, price isn't the sole consideration. The seller, for example, may want to preserve as many jobs as possible for its employees. If a bidder doesn't submit the highest price but offers the most effective terms for continuity for workers, the seller may select that bidder.
An auction notice is a formal document issued in the interest of the general public which informs them regarding the auction of a product. Interested parties follow the instructions on the notice and place their bids on the required goods accordingly. The format of an auction notice consists of the following elements:
- Issuing Authority: This included the name of the company, individual or the government organization that has issued the notice.
- Memo No.: This covers the specific number issued to that auction notice. This is an optional section and is not included in all notices.
- Date: The date when the auction notice is written.
- Subject: Contains the main reason why the notice is written i.e. the selling of a particular product or service.
- The Body: This section includes the details regarding the auctioned goods or services; the date, time and place of the auction; contact information of the issuing authority if required.
- Signature: This section contains the signature of the issuing authority.
Sample Notice
Given below is a sample auction notice issued by the West Bengal Information and Cultural Centre for disposal of scrap material:

Public notice writing is a formal written document. It is one of the common methods of communication. It gives important information regarding something that is about to take place or has taken place.
It is usually meant for a wider audience. It is usually put up in a public place for easy accessibility.
A notice must include:
What is going to happen.
Where it will take place.
When it will take place.
Who can apply or is eligible for it?
Who to contact?
Points to remember while writing notices:
Only include the most important points.
The sentences must be short and grammatically correct.
Notices must be presented in the passive voice as much as possible.
Present the notice in a box.
The word limit for the body of a notice is 40–50 words
The information must be clear. It should not cause any confusion.
A notice must attract the reader’s attention immediately.
Increase its visual appeal by using bold letters and catchy slogans.
You can use standard abbreviations.
Types of Notices
Before one can fully understand the dynamics of making notices, understanding the basic principles and types of notices must be considered.
- Public Notice – These types of notices are made and disseminated by government offices and departments. They are for the benefit of the general public in order for them to know the government-related updates such as the passage of new law, details about certain legal proceedings, and many more.
- Private Notices – In contrast to public notices which are used to raise public awareness, private notices are given and address to particular parties. These types of notices spring from contractual obligations such as in the case of job notice templates, two weeks’ notice letter sent by a landlord to his or her tenants, and many more. These are also used by companies and organization in terms of disseminating significant information. If there will be company meetings, secretaries can refer to notice of meeting templates
in drafting the notice for an upcoming meeting or company conference.
Format of a public Notice
The structure of a formal notice consists of the following elements:
- Name of the organization
The name of the organisation or faculty should be written at the very top of the notice.
This is important as it makes it easier for the reader to decide whether the given information concerns them or not.
2. Title
The title “NOTICE” should always be written on top and must be underlined. Since notices are usually put in public places, they must be easily discernible.
Because public places generally have a lot of posters, pamphlets, etc. a bold title is important for the notice to be conspicuous.
3. Date
The date on which notice was published is to be mentioned on the left-hand side of the document.
This is a formal document; hence, it is important to mention the date as it stays on record.
4. Heading
Heading must always precise and clear as it gives a clear idea about the purpose of the notice.
5. Body
Here one should write the relevant information as briefly as possible. Since a notice is a very short written document,
One should provide all the significant and pertinent information in a precise manner.
The body should cover all the five W’s, i.e., what, where, when, who and whom.
6. Writer’s name
The name and designation of the writer of the notice should be mentioned in the end.
Sample Notice

A memorandum is an internal and informal form of communication which is written to inform and to call to action. It is normally used for communicating policies, procedures or other information within the organisation.
Unlike Interpersonal communication a memorandum is presented to a large number of people. A memo has to be concise and concrete in terms of providing information.
Interoffice memorandums (memos) are used by employees within an organization to communicate with one another.
A memo heading consists of four standard parts: TO, FROM, DATE, and SUBJECT. (See illustration of an interoffice memo.) The memo is usually keyed on a pre-printed form with the organization’s name printed at the top of the page. If the headings TO, FROM, DATE, and SUBJECT need to be keyed, use the format guides presented below.
The heading part follows the format given below:
TO: (The name of the receiver and their designation)
FROM: (Your name and designation or title)
DATE: (Current Date)
SUBJECT: (The purpose of writing the report)
The Body
The body of a memo report, like any technical report, should be concise and to the point. It needs to be properly structured and organised. It should consist of the following elements:
Opening:
This section should consist of 2 to 3 sentences and should state the main purpose of the memo. It should include the main problem with which the memo is concerned with and how it is going to be addressed. A good way to start the opening statement would be “The purpose of this circular is to inform you regarding the recent changes….”
Discussion:
This is the longest section in the memo which deals with all the information and evidences you have collected to support your arguments. This section can be subdivided into four subsections namely,
Conclusion:
After discussing your research, you should summarize the main elements of your finding in 2 or 3 sentences that should reiterate all the implications in the circular.
Attachment/Enclosure notation
If another document is attached to a memo, the word Attachment is keyed at the left margin one line below the reference initials. If a document is included but not attached, the word Enclosure is used. If no reference initials are used, the notation is keyed one line below the last line of the body.
Sample Inter-Office Memo
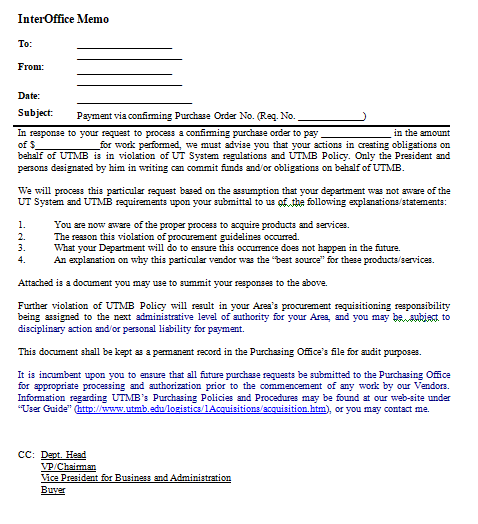
The term precis comes from a French word “précis”, which can be translated as "precise, clear, up to the point”. Therefore, the word precis in the context of writing means a summary of any writing piece, be it a book, an article, or a novel. What is typical while writing a precis is the outline of the main points and arguments presented in the given text. A precis does not contain a deep or critical analysis of the text, but it nevertheless objectively explains the situation narrated in a text.
Precis vs. Summary
A precis and a summary are quite similar to each other but they do contain certain major differences which set them apart. Below are the two main differences between a precis and a summary:
- A summary consists of a number of brief statements which covers the main points of the text. It has no pre-defined word limit. A precis on the other hand, has its own title and should be 1/3 of the total words of the original passage.
- A summary is a sort of general overview of the contents of a passage. Here only the main events in the passage are discussed. A precis, however, focuses on every detail and analyses a particular situation.
Rules
Below are the fundamental rules to be followed while writing a precis:
- Understand the theme of the passage
The first and the most important thing is to thoroughly read and comprehend the purpose of the passage. Once you understand the theme, it is easier to grasp the key ideas in the passage, which will help you remember them while writing the precis.
b. No copying from the passage
It is important in precis writing to use your own words and not copy from the passage. If you find certain sentences in the passage that you would like to incorporate in your precis, you need to understand them and then craft that sentence in your own words. Key words can be used but entire sentences should always be avoided.
c. Carry clarity and conciseness
One of the most fundamental rules of writing a precis is clarity. The sentences should be clear, concise, meaningful and to the point. They should reflect the central ideas from the passage.
d. A reflection of your intelligence
The precis should be written in such a way that it flaunts your writing skills. The use of language, vocabulary and structure of sentences should be perfect. A good precis will provide the readers a good impression of your writing skills and it will also make the precis comprehensible to the readers.
e. Be original
Each and every sentence in the precis should be one's own creation with no plagiarism whatsoever. If you find a significant idea or motif from the passage that you want to include in your precis, read the passage again and again and try to re-construct the idea from your memory using your own words.
f. Use of indirect speech
A precis must always be written in indirect speech since it employs the perspective of a third person. Direct speech leaves a personal impact and should be avoided while writing a precis.
g. Use facts and statistics
To maintain the credibility of the text, try to include all the numbers and facts you read in the text. It will also help you enhance the quality of your writing and will build the interest of the reader in your precis. Therefore, any of the facts and numbers should not be missed while writing the Precis.
h. An analysis of the various sections
Divide the text into sections and try to analyse each section carefully. A careful analysis of each section will let you draw in closer to the main themes and concepts in the text. Further, you can only mention the crucial content of the passage, if you have read it thoroughly and have identified the areas which carry high proportional value.
i. An interpretation of the original passage
Always conclude the passage by providing your own understand instead of the writer's perspective. The conclusion has to be from your own point of view but should still be in the third person as if spoken by a third party. It is your interpretation of the text that gives meaning to the precis.
j. The size of the precis
The size of a precis should always be one third of the original passage. While writing the precis one should always be aware of the word count but one should also be able to retain the individuality of the passage in the prescribed word limit.
Precis Format
A precis should be short and concise and comprises of three parts: The introduction, the main body and the conclusion.
The Introduction
- The introductory sentence of a precis should mention the author’s name along with the article/book title. It should also include the date of publishing in parenthesis. After that, the topic that you want to discuss in your precis has to be elaborated using a few key words. Extravagant detailing of the topic should be avoided.
- In the introduction, try to include a rhetorical verb outlining the author’s primary purpose (e.g., “assert,” “argue,” “deny,” “refute,” “prove,” disprove,” “explain”). This will give a strong definition to the facts and concepts you are about to present in the main body of your precis.
- It is important to include the thesis statement of the text in the introduction. A thesis statement is the main idea or crux of a particular text. This thesis statement will be elaborated in the main body by providing facts and evidences in its favour.
The Main Body
- The main body should include clarification of how the author formulates and further explains the main themes in the text. It should be informative enough to incite the reader's interest and short enough to retain that interest.
- It should include a sentence that states the purpose of the author in writing the text. Phrases such as “in order” are helpful in developing this sentence.
- Describe how the author establishes his connection with the readers. Always keep the audience for whom you are writing in mind while writing a precis. This includes the using vocabulary and structuring sentences according to the needs of your audience.
- All key points and arguments must be contained in this section.
The Conclusion
- Present a finishing remark of 2-3 sentences to shed light on the author’s intended idea for the book or passage.
- Give a 1-sentence restatement of the major claim which the author used to develop their evidence in the reading.
Steps for Writing a Precis
Below are the steps involved in writing a precis
Step 1: As discussed, the very first step of Precis writing is to form a clear understanding of the passage. You should fully acquaint yourself with the subject first in order to get the meaning behind a passage before starting to write a precis.
Step 2: While reading the content, make sure you highlight the important points of the passage. It will help you in keeping track of the important information that needs to be written in your Precis. Also, you should omit the information, which you feel is not important for your Precis.
Step 3: Further, you need to remember that logical ordering is highly important when it comes to precis writing. Additionally, a logically organised text helps in making things much clearer to your audience and they tend to understand your take in a processed way.
Step 4: If you have some names to be mentioned in your Precis, remember, they should be with the designations, as it helps to increase the credibility of the content. In case, the designations are not mentioned in the passage, you can write the first name.
Step 5: Moving on, the word count of the passage should be taken into account, because one- third of the same has to be written in Precis. Therefore, conducting a word count before beginning the precis could be beneficial.
Step 6: Now, prepare the draft of your Precis by jotting all the important points together. While writing always remember to maintain the flow of your concepts and you should not miss any important information you have gathered while reading the passage.
Step 7: Before finally submitting your Precis, make sure you review all the details carefully. Also, you must do a thorough check of your grammatical and structural errors. Furthermore, one thing not to miss is to mention the total count in a bracket after the end point of your Precis.
The resume or bio-data may be a brief record of the applicant’s personal details, educational qualifications, specialized training, experiences, references and the other relevant information. It's a summary of one’s personal and academic accounts. A resume is considered as a formal advertisement of a person’s qualifications.
ACCORDING TO BOVEE, THILL AND SCHATZMAN, “A RESUME may be a STRUCTURED, WRITTEN SUMMARY OF A PERSON’S EDUCATION, EMPLOYMENT BACKGROUND AND JOB QUALIFICATIONS.”
MURPHY AND HILDEBRANDT SAID, “CURRICULUM VITAE IS A DOCUMENT LABELING ONE’S QUALIFICATIONS AND CAREER PATH.”
LOCKER DEFINED, “A RESUME may be a PERSUASIVE SUMMARY OF ONE’S QUALIFICATIONS FOR EMPLOYMENT.”
So, a resume is brief description of one’s personal, educational and employment qualifications. The aim of the resume is to get an interview, not to tell readers everything about you. In fact, it's a sort of advertising. Now-a-days, it becomes almost traditional to send a resume with the job application letter.
Contents of a CV –
The bio-data must be properly arranged under some heading or sub-headings. It includes information about a few persons in various areas. Usually the knowledge is presented during a bio-data under the subsequent heading-
• Personal Information: This section includes complete name, address both temporary and permanent, telephone number, date-of-birth, parent’s names, marital status, nationality, religion and cast in some cases etc.
• Career Objectives: Clearly state your objective or future plan in your career. Tell what you're interested to try to and what level of responsibility you want to hold. So, short term and future target of your career must be mentioned here.
• Educational Qualifications: an entire record of the academic qualifications should be given during this section. It includes the name of degrees obtained, the name of the institution attended, year of passing, board or university form where degree is obtained and the division or grade or class obtained etc.
• Experience: This section includes the applicant’s previous experience relevant to the work applied for. Details to be included here are- the period of time or length of previous or current job the joining and therefore the levelling dates, the name of the organization, position held and a quick description of the duties or nature of work or tasks done on the job.
• Honours and Awards: Honours and awards are given for outstanding work. This section includes fellowships and scholarship or honorary scholarship, awards given by professional associations and civic groups.
• Extra-Curricular Activities: The applicant’s extra-curricular activities like membership in various organizations, participation in several seminar and workshops, prizes won in cultural functions etc. are to be mentioned here.
• References: Names and addresses of the persons who known the applicant and may express a private opinion about his abilities and qualities must tend in this section. It customary to offer three references sort of a teacher, an employer and a friend of the family with high social or professional status. But if the number of referees isn't dictated by the prospective employer, it's better to mention the names and addresses of at least two references. The name, title, complete address and phone number of the referees must tend and it's preferable to point their social relationship to the applicant. The applicant should take permission from the referees to give their names or a minimum of inform them immediately after, with details of the job applied for.
• Signature of the Applicant: At the end of the resume, the applicant should put his signature and date with the left margin. Below the signature, there must be enough space for typing the complete name of the applicant.
In concluding note, we will say that a resume must include everything relevant to the post or job applied for and must exclude irrelevant things. If the employer invites only resume, sometimes it's better to attach a recent photograph with it.
Types of a CV –
Type | Function | Advantage | Disadvantage |
Reverse Chronological | Reverse chronological CV (also called reverse time order) focus on work history. | Demonstrates a consistent work history | It may be difficult to highlight |
Functional | Functional CV (also called competency-based rEsumEs) focus on skills. | Demonstrates skills that can clearly link to job functions or duties | It is often associated with people who have gaps in their employment history |
Combination | A combination CV lists your skills and experience first, then employment history and education | Highlights the skills you have that are relevant to the job and provides a reverse chronological work history | Some employers prefer a reverse |
Targeted | A targeted CV is a custom document that specifically highlights the experience and skills that are relevant to the job. | Points out to the reader how your qualifications and experience clearly match the job duties | Custom documents take additional time, preparation, analysis of the job announcement, and may not fit the established guidelines |
Scannable | A scannable CV is specifically formatted to be read by a scanner and converted to digital information. | Increasingly used to facilitate search and retrieval, and to reduce physical storage costs | Scanners may not read the CV |
Business Reports
The success of a business or industrial organization lies in doing its job for this purpose, gathering information and passing it on to those who need it is important. In the broader collection and transfer of information is happening all the time in every area of formal life. So, scientists, working brokers, testers, journalists, and various professionals, government and private organizations are asked to write and report to their management on important topics at the institution or the person involved.
Reports can be as short as a few sentences and as long as a few large pages. Although reports can be verbal and informal, here we are concerned with written and formal reports.
Types of Reports
Reports are available all sizes, but are typically longer than a page and somewhat shorter than a book. the sort of report depends on its function. The function of the report is its essential purpose, often indicated within the thesis or purpose statement.
The function also will influence the kinds of visual content or visual aids, representing words, numbers, and their relationships to the central purpose in graphic, representational ways in which are easy for the reader to know. The function can also contribute to parameters like report length (page or word count) or word choice and readability. “Focusing on the content of your longer business documents isn't only natural but necessary because doing so helps ensure complete, correct information”.
Reports vary by function, and that they also vary by style and tradition. Within your organization, there could also be employer-specific expectations that require to be addressed to satisfy audience expectations.
There are two main categories for reports, no matter their specific function or type:
Informational Report
An informational report informs or instructs and presents details of events, activities, individuals, or conditions without analysis. An example of this sort of “just the facts” report may be a police accident report. The report will note the time, date, place, contributing factors like weather, and identification information for the drivers involved in an automobile accident. It doesn't establish fault or include judgmental statements. you ought to not see “Driver was falling down drunk” during a police accident report.
Instead, you'd see “Driver failed sobriety tests and Breathalyzer test and was transported to the station for a blood sample.” The policeman isn't a trained medical doctor and is therefore not licensed to form definitive diagnoses, but can collect and present relevant information which will contribute thereto diagnosis.
Analytical Report
The second sort of report is named an analytical report.
An analytical report presents information with a comprehensive analysis to unravel problems, demonstrate relationships, or make recommendations.
An example of this report could also be a field report by a middle for Disease Control (CDC) physician from the location of an epidemic of the H1N1 virus, noting symptoms, disease progression, steps taken to arrest the spread of the disease, and to form recommendations on the treatment and quarantine of subjects.
Types of Reports and Their Functions
Types of Reports and their functions include common reports that, counting on the audience needs, could also be informational or analytical.
1. Laboratory Report Communicate the procedures and results of laboratory activities.
2. Research Report Study problems scientifically by developing hypotheses, collecting data, analysing data, and indicating findings or conclusions.
3. Field Study Report Describe one-time events, like trips, conferences, seminars, also as reports from branch offices, industrial and manufacturing plants.
4. Progress Report Monitor and control production, sales, shipping, service, or related business process.
5. Technical Report Communication process and merchandise from a technical perspective.
6. Financial Report Communication status and trends from a finance perspective.
7. Case Study Represent, analyse, and present lessons learned from a selected case or example.
8. Needs Assessment Report Assess the necessity for a service or product.
9. Comparative Advantage Report Discuss competing products or services with an analysis of relative advantages and drawbacks.
10. Feasibility Study Analyse problems and predict whether current solutions or alternatives are going to be practical, advisable, or produced the specified outcome(s).
11. Instruction Manuals Communicate step-by-step instructions on the utilization of a product or service.
12. Compliance Report Document and indicate the extent to which a product or service is within established compliance parameters or standards.
13. analysis Report Communicate costs and benefits of products or services.
14. Decision Report Make recommendations to management and become tools to unravel problems and make decisions.
15. Benchmark Report Establish criteria and evaluate alternatives by measuring against the establish benchmark criteria.
16. Examination Report or record data obtained from an examination of an item or conditions, including accidents and natural disasters.
17. Physical Description report Describe the physical characteristics of a machine, a device, or object.
18. Literature Review Present summaries of the knowledge available on a given subject.
Characteristics
Below are the fundamental Characteristics of a business report:
- The Audience:
When organizing and preparing your reports you need to know who your audience is and whether or not your content meets their interests and needs.
- Conciseness:
Legitimacy has to do with how easy or readable it is. As most reports in normal cases type, all meetings with good typing should be followed. If there are handwritten reports, special attention should be given to writing clearly and clearly. Any departure from the above requirement will prove displeasing to your audience.
- Readability:
Clarity, durability and systematic presentation of readable content. The concept is summarized better than the following:
The author does a lot by giving his reader a lot of information and taking away from him a little time.
In this regard the following five goals are met:
a) Use short sentences.
b) You prefer convenience to the building.
c) Choose a common name.
d) Use the economy and avoid unnecessary words.
e) Act actions as far as possible
- Clarity:
Just like unwanted fat in the body, padding, prolixity and repetition violates the respect of good writing, not to mention the respect they wrote for you. So 'agree' and 'prefer' will be more acceptable than pompous 'agree with' and 'prefer'. As such, why use 'at that point in time' and at a time when we have the best and most economical holdings at that time 'and' when '. Viewed from the point of view of the report, or requested for the report, a good report will contain four important details, an analysis of the information, conclusions and recommendations. It should always be remembered that effective reporting requires special attention to the needs and expectations of the reader. It means that the author of the report has to 'snap a picture', he must think and understand himself.
Importance
Reports are documents designed to record and convey information to the reader. Reports are a part of any business or organization; from credit reports to police reports, they serve to document specific information for specific audiences, goals, or functions. the sort of report is usually identified by its primary purpose or function, as in an accident report, a laboratory report, a sales report, or maybe a book report. Reports are often analytical, or involve the rational analysis of data. Sometimes they simply “report the facts” with no analysis in the least, but still got to communicate the knowledge during a clear and concise format. Other reports summarize past events, present current data, and forecast future trends. While a report may have conclusions, propositions, or maybe a call to action, the demonstration of the analysis is that the primary function.
A sales report, for instance, isn't designed to form a private sale. It is, however, alleged to report sales so far, and should forecast future sales supported previous trends.
Writing good business reports can save time and money, and play a dramatic role in the future of a company. Below are some reasons why business reports are important:
Tracks Development Over Time
Business reports document progress and provide a means of comparing periods of time, project details, and history of growth. While one may rely on a superior memory or the amount of profits, they make each year to gauge progress, the data collected in reports can serve a number of important purposes. It can help in the formulation of budget and marketing plans for the upcoming year. It may also help in realizing which products or services are the most successful, and which markets have been overlooked.
Provides an Audit Trail
In addition to making decisions about the company and its future, reports help in building a paper trail of the past. Reports that document sales, meetings, plans, initiatives and annual budgets are an integral part of the proprietary materials that make up a business. If one ever approaches a bank for a loan or decides to sell their business, they will be required to produce more than personal tax returns to support their requests or asking price.
Duty to Stakeholders
A corporation has to produce an annual report each year as part of its legal fiduciary obligations to its stockholders and the government agencies that oversee corporate businesses. Through this process, large companies have come to learn about the many benefits they can reap from producing an annual report. Small businesses can tap into those same resources if they create a summary and overview the previous year in business.
The annual report usually is a glossy report with pictures and contact information that doubles nicely as a marketing package. It is useful when making introductions to new clients or trying to build name recognition in a community. An annual report is an effective tool for providing employees, investors and clients with a complete picture of the business.
Supports Purchasing Decisions
Even if one does not report to a corporate board or have to produce documentation for a team of investors, there may come a time when one wants to expand or make a substantial purchase to increase business, and they may be required to produce a financial history of the company. A sole proprietor may face the time when the best way to grow means taking on a corporate label, and they will be required to create those reports on a regular basis.
Structure
Business reports may be of various types but they follow a similar structure in most cases. The elements contained in a business report may be as follows:
- Executive summary
The executive summary gives the audience a complete understanding of the points being addressed, the report's topic, the type of evidence and sources that compiled the report and the purposed solutions based on the data. The summary can be less than a page or up to four pages depending on the amount of detail required, but you should wait until you gather your findings to write this section, so it can be comprehended by reviewers of your presentation.
B. Title Page
The title page includes the main title of the report, it must be short and concise. You can also include the word counts of your summary and main body.
C. Table of Contents
Help your reader quickly and easily find what they are looking for by using informative headings and careful numbering of your sections and sub-sections.
For example:

D. Introduction
The introductory part of the report comprises of statement of the objectives of the report and how the report should be treated by the readers. It should indicate towards the problem that is going to be addressed in the main body. It should be catchy and interesting to grasp the attention of the reader from the very start.
E. The Body
The main body consists of the central theme or the main idea of the report. It can be divided into a number of sections and subsections to separate your research and subsequent findings in a logical order.
F. Figures, Graphs, Formulae and Tables
This section consists of the statistical representation of the data you have collected. Ideas should be conveyed in the form which is most suitable to the reader and easily understandable by the reader. Excessive use of these tools should be avoided.
G. Conclusion
The conclusion is a kind of summing up of all the points you have stated in the main text. It should be a definite solution to the problem introduced during the introductory part of the report. The conclusion must be short and to the point.
H. Summary
Summarize all the key points stated in the report including your research, your findings and your conclusion. The summary should feel like a brief overview of your investigations and outcomes. The summary should be constructed in such a way that it can be called a stand-alone document on its own.
I. References
References must include detailed information of all your citations and the sources of material quoted in your texts. It can also include bibliography for further reading.
J. Appendices
This is the last element of a report. It refers to any material which can be useful in the detailed understanding of your subject. It is not meant for the casual reader but for readers who are highly interested in the subject.