UNIT 4
Computers and Communication
TABLE OF CONTENTS
4.1 | WWW and Web Browsers |
4.2 | Basic of Computer networks; LAN, WAN |
4.3 | Networking Devices |
4.4 | Topologies |
4.5 | Cables and connectors |
4.6 | Connecting to internet: ISP |
4.7 | Basics of internet connectivity related troubleshooting |
4.8 | Web Browsing software, Search Engines, URL |
4.9 | Domain Names |
4.10 | IP Addressing |
4.11 | Wi-Fi and Bluetooth technology overview |
4.12 | Internet and Intranet: architecture, various file formats |
4.13 | Applications of INTERNET: Electronic mailing systems (Google Mail features): Creating and Managing mailing accounts, folders, Document collaboration, Instant Messaging, Netiquettes |
4.14 | Skype calling and Messenger services |
4.15 | Functioning and features of smart gadgets |
4.16 | Smart phones |
4.17 | 4K smart television gadgets, kindle, gaming-gadgets, fitness gadgets and alike |
Internet is a global communication system that links together thousands of individual networks. It allows exchange of information between two or more computers on a network. Thus internet helps in transfer of messages through mail, chat, video & audio conference, etc. It has become mandatory for day-to-day activities: bills payment, online shopping and surfing, tutoring, working, communicating with peers, etc.
In this topic, we are going to discuss in detail about concepts like basics of computer networks, Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), concept of internet, basics of internet architecture, services on internet, World Wide Web and websites, communication on internet, internet services, preparing computer for internet access, ISPs and examples (Broadband/Dialup/Wi-Fi), internet access techniques, web browsing software, popular web browsing software, configuring web browser, search engines, popular search engines/search for content, accessing web browser, using favorites folder, downloading web pages and printing web pages.
Sr.No. | Internet, WWW, Web Browsers Concepts & Description |
1 | Basics of computer network Computer network is an interconnection between two or more hosts/computers. Different types of networks include LAN, WAN, MAN, etc. |
2 | Internet Architecture Internet is called the network of networks. It is a global communication system that links together thousands of individual networks. Internet architecture is a meta-network, which refers to a congregation of thousands of distinct networks interacting with a common protocol |
3 | Services on Internet Internet acts as a carrier for numerous diverse services, each with its own distinctive features and purposes. |
4 | Communication on Internet Communication can happens through the the Internet by using Email, Internet Relay Chat, Video Conference etc. |
5 | Preparing Computer for Internet Access We shall learn how to use functions and charts in Microsoft Excel Using Formulas like Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division |
6 | Internet Access Techniques A chart is a graphical representation of worksheet data. Charts can make data interesting, attractive and easy to read and evaluate. They can also help you to analyze and compare data. |
7 | Web Browsing Software "World Wide Web" or simple "Web" is the name given to all the resources of internet. The special software or application program with which you can access web is called "Web Browser". |
8 | Configuring Web Browser Search Engine is an application that allows you to search for content on the web. It displays multiple web pages based on the content or a word you have typed. |
9 | Search Engines Search Engine is an application that allows you to search for content on the web. It displays multiple web pages based on the content or a word you have typed. |
10 | Search for the content Search Engine helps to search for content on web using the different stages |
11 | Accessing Web Browser There are several ways to access a web page like using URLs, hyperlinks, using navigating tools, search engine, etc. |
Summary
This topic summarized the concepts of internet like LAN, WAN, internet architecture, internet services, WWW, communications on the internet, internet service providers, internet access techniques, web browsers, search engines, favourite’s folder, configuration of web browsers, and downloading & printing web pages.
A computer network is a group of computers linked to each other that enables the computer to communicate with another computer and share their resources, data, and applications.
A computer network can be categorized by their size. A computer network is mainly of four types:
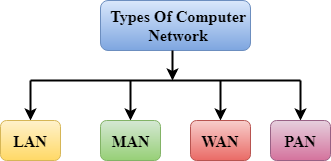
- LAN(Local Area Network)
- PAN(Personal Area Network)
- MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN(Wide Area Network)
LAN(Local Area Network)
- Local Area Network is a group of computers connected to each other in a small area such as building, office.
- LAN is used for connecting two or more personal computers through a communication medium such as twisted pair, coaxial cable, etc.
- It is less costly as it is built with inexpensive hardware such as hubs, network adapters, and ethernet cables.
- The data is transferred at an extremely faster rate in Local Area Network.
- Local Area Network provides higher security.
PAN(Personal Area Network)
- Personal Area Network is a network arranged within an individual person, typically within a range of 10 meters.
- Personal Area Network is used for connecting the computer devices of personal use is known as Personal Area Network.
- Thomas Zimmerman was the first research scientist to bring the idea of the Personal Area Network.
- Personal Area Network covers an area of 30 feet.
- Personal computer devices that are used to develop the personal area network are the laptop, mobile phones, media player and play stations.
There are two types of Personal Area Network:
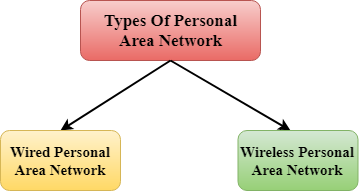
- Wired Personal Area Network
- Wireless Personal Area Network
Wireless Personal Area Network: Wireless Personal Area Network is developed by simply using wireless technologies such as WiFi, Bluetooth. It is a low range network.
Wired Personal Area Network: Wired Personal Area Network is created by using the USB.
Examples Of Personal Area Network:
- Body Area Network: Body Area Network is a network that moves with a person. For example, a mobile network moves with a person. Suppose a person establishes a network connection and then creates a connection with another device to share the information.
- Offline Network: An offline network can be created inside the home, so it is also known as a home network. A home network is designed to integrate the devices such as printers, computer, television but they are not connected to the internet.
- Small Home Office: It is used to connect a variety of devices to the internet and to a corporate network using a VPN
MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)
- A metropolitan area network is a network that covers a larger geographic area by interconnecting a different LAN to form a larger network.
- Government agencies use MAN to connect to the citizens and private industries.
- In MAN, various LANs are connected to each other through a telephone exchange line.
- The most widely used protocols in MAN are RS-232, Frame Relay, ATM, ISDN, OC-3, ADSL, etc.
- It has a higher range than Local Area Network(LAN).
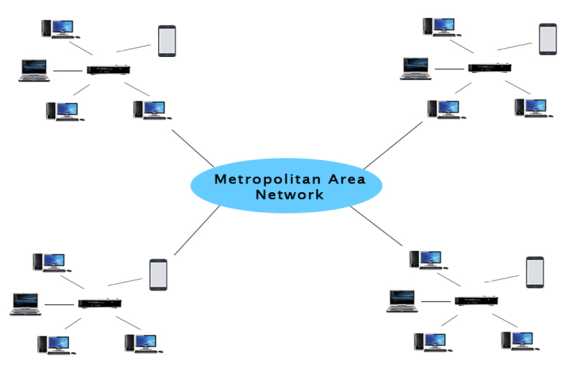
Uses Of Metropolitan Area Network:
- MAN is used in communication between the banks in a city.
- It can be used in an Airline Reservation.
- It can be used in a college within a city.
- It can also be used for communication in the military.
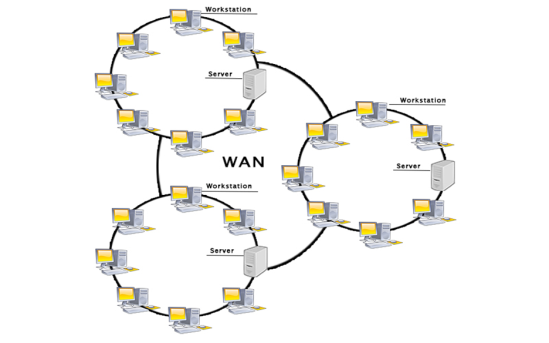
WAN(Wide Area Network)
- A Wide Area Network is a network that extends over a large geographical area such as states or countries.
- A Wide Area Network is quite bigger network than the LAN.
- A Wide Area Network is not limited to a single location, but it spans over a large geographical area through a telephone line, fibre optic cable or satellite links.
- The internet is one of the biggest WAN in the world.
- A Wide Area Network is widely used in the field of Business, government, and education.
Examples Of Wide Area Network:
- Mobile Broadband: A 4G network is widely used across a region or country.
- Last mile: A telecom company is used to provide the internet services to the customers in hundreds of cities by connecting their home with fiber.
- Private network: A bank provides a private network that connects the 44 offices. This network is made by using the telephone leased line provided by the telecom company.
Advantages Of Wide Area Network:
Following are the advantages of the Wide Area Network:
- Geographical area: A Wide Area Network provides a large geographical area. Suppose if the branch of our office is in a different city then we can connect with them through WAN. The internet provides a leased line through which we can connect with another branch.
- Centralized data: In case of WAN network, data is centralized. Therefore, we do not need to buy the emails, files or back up servers.
- Get updated files: Software companies work on the live server. Therefore, the programmers get the updated files within seconds.
- Exchange messages: In a WAN network, messages are transmitted fast. The web application like Facebook, Whatsapp, Skype allows you to communicate with friends.
- Sharing of software and resources: In WAN network, we can share the software and other resources like a hard drive, RAM.
- Global business: We can do the business over the internet globally.
- High bandwidth: If we use the leased lines for our company then this gives the high bandwidth. The high bandwidth increases the data transfer rate which in turn increases the productivity of our company.
Disadvantages of Wide Area Network:
The following are the disadvantages of the Wide Area Network:
- Security issue: A WAN network has more security issues as compared to LAN and MAN network as all the technologies are combined together that creates the security problem.
- Needs Firewall & antivirus software: The data is transferred on the internet which can be changed or hacked by the hackers, so the firewall needs to be used. Some people can inject the virus in our system so antivirus is needed to protect from such a virus.
- High Setup cost: An installation cost of the WAN network is high as it involves the purchasing of routers, switches.
- Troubleshooting problems: It covers a large area so fixing the problem is difficult.
Internetwork
- An internetwork is defined as two or more computer network LANs or WAN or computer network segments are connected using devices, and they are configured by a local addressing scheme. This process is known as internetworking.
- An interconnection between public, private, commercial, industrial, or government computer networks can also be defined as internetworking.
- An internetworking uses the internet protocol.
- The reference model used for internetworking is Open System Interconnection(OSI).
Types Of Internetwork:
1. Extranet: An extranet is a communication network based on the internet protocol such as Transmission Control protocol and internet protocol. It is used for information sharing. The access to the extranet is restricted to only those users who have login credentials. An extranet is the lowest level of internetworking. It can be categorized as MAN, WAN or other computer networks. An extranet cannot have a single LAN, atleast it must have one connection to the external network.
2. Intranet: An intranet is a private network based on the internet protocol such as Transmission Control protocol and internet protocol. An intranet belongs to an organization which is only accessible by the organization's employee or members. The main aim of the intranet is to share the information and resources among the organization employees. An intranet provides the facility to work in groups and for teleconferences.
Intranet advantages:
- Communication: It provides a cheap and easy communication. An employee of the organization can communicate with another employee through email, chat.
- Time-saving: Information on the intranet is shared in real time, so it is time-saving.
- Collaboration: Collaboration is one of the most important advantage of the intranet. The information is distributed among the employees of the organization and can only be accessed by the authorized user.
- Platform independency: It is a neutral architecture as the computer can be connected to another device with different architecture.
- Cost effective: People can see the data and documents by using the browser and distributes the duplicate copies over the intranet. This leads to a reduction in the cost.
Hardware devices that are used to connect computers, printers, fax machines and other electronic devices to a network are called network devices. These devices transfer data in a fast, secure and correct way over same or different networks. Network devices may be inter-network or intra-network. Some devices are installed on the device, like NIC card or RJ45 connector, whereas some are part of the network, like router, switch, etc. Let us explore some of these devices in greater detail.
Modem
Modem is a device that enables a computer to send or receive data over telephone or cable lines. The data stored on the computer is digital whereas a telephone line or cable wire can transmit only analog data.
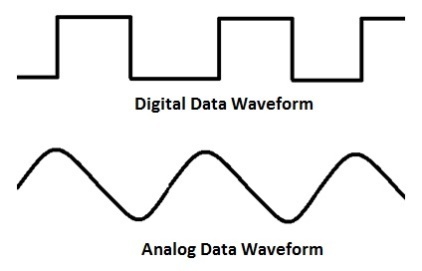
The main function of the modem is to convert digital signal into analog and vice versa. Modem is a combination of two devices −modulator and demodulator. The modulator converts digital data into analog data when the data is being sent by the computer. The demodulator converts analog data signals into digital data when it is being received by the computer.
Types of Modem
Modem can be categorized in several ways like direction in which it can transmit data, type of connection to the transmission line, transmission mode, etc.
Depending on direction of data transmission, modem can be of these types −
- Simplex− A simplex modem can transfer data in only one direction, from digital device to network (modulator) or network to digital device (demodulator).
- Half duplex− A half-duplex modem has the capacity to transfer data in both the directions but only one at a time.
- Full duplex− A full duplex modem can transmit data in both the directions simultaneously.
RJ45 Connector
RJ45 is the acronym for Registered Jack 45. RJ45 connector is an 8-pin jack used by devices to physically connect to Ethernet based local area networks (LANs). Ethernet is a technology that defines protocols for establishing a LAN. The cable used for Ethernet LANs are twisted pair ones and have RJ45 connector pins at both ends. These pins go into the corresponding socket on devices and connect the device to the network.

Ethernet Card
Ethernet card, also known as network interface card (NIC), is a hardware component used by computers to connect to Ethernet LAN and communicate with other devices on the LAN. The earliest Ethernet cards were external to the system and needed to be installed manually. In modern computer systems, it is an internal hardware component. The NIC has RJ45 socket where network cable is physically plugged in.

Ethernet card speeds may vary depending upon the protocols it supports. Old Ethernet cards had maximum speed of 10 Mbps. However, modern cards support fast Ethernets up to a speed of 100 Mbps. Some cards even have capacity of 1 Gbps.
Router
A router is a network layer hardware device that transmits data from one LAN to another if both networks support the same set of protocols. So a router is typically connected to at least two LANs and the internet service provider (ISP). It receives its data in the form of packets, which are data frames with their destination address added. Router also strengthens the signals before transmitting them. That is why it is also called repeater.

Routing Table
A router reads its routing table to decide the best available route the packet can take to reach its destination quickly and accurately. The routing table may be of these two types −
- Static−In a static routing table the routes are fed manually. So it is suitable only for very small networks that have maximum two to three routers.
- Dynamic−In a dynamic routing table, the router communicates with other routers through protocols to determine which routes are free. This is suited for larger networks where manual feeding may not be feasible due to large number of routers.
Switch
Switch is a network device that connects other devices to Ethernet networks through twisted pair cables. It uses packet switching technique to receive, store and forward data packets on the network. The switch maintains a list of network addresses of all the devices connected to it.
On receiving a packet, it checks the destination address and transmits the packet to the correct port. Before forwarding, the packets are checked for collision and other network errors. The data is transmitted in full duplex mode

Data transmission speed in switches can be double that of other network devices like hubs used for networking. This is because switch shares its maximum speed with all the devices connected to it. This helps in maintaining network speed even during high traffic. In fact, higher data speeds are achieved on networks through use of multiple switches.
Gateway
Gateway is a network device used to connect two or more dissimilar networks. In networking parlance, networks that use different protocols are dissimilar networks. A gateway usually is a computer with multiple NICs connected to different networks. A gateway can also be configured completely using software. As networks connect to a different network through gateways, these gateways are usually hosts or end points of the network.

Gateway uses packet switching technique to transmit data from one network to another. In this way it is similar to a router, the only difference being router can transmit data only over networks that use same protocols.
Wi-Fi Card
Wi-Fi is the acronym for wireless fidelity. Wi-Fi technology is used to achieve wireless connection to any network. Wi-Fi card is a card used to connect any device to the local network wirelessly. The physical area of the network which provides internet access through Wi-Fi is called Wi-Fi hotspot. Hotspots can be set up at home, office or any public space. Hotspots themselves are connected to the network through wires.

A Wi-Fi card is used to add capabilities like teleconferencing, downloading digital camera images, video chat, etc. to old devices. Modern devices come with their in-built wireless network adapter.
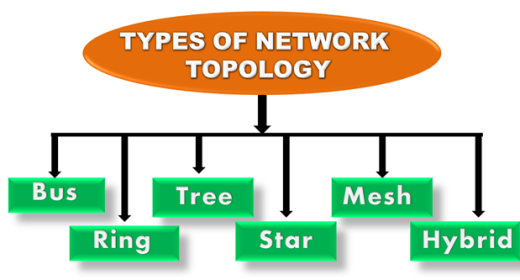
What is Topology?
Topology defines the structure of the network of how all the components are interconnected to each other. There are two types of topology: physical and logical topology.
Physical topology is the geometric representation of all the nodes in a network.
Bus Topology
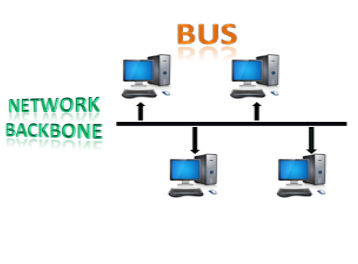
- The bus topology is designed in such a way that all the stations are connected through a single cable known as a backbone cable.
- Each node is either connected to the backbone cable by drop cable or directly connected to the backbone cable.
- When a node wants to send a message over the network, it puts a message over the network. All the stations available in the network will receive the message whether it has been addressed or not.
- The bus topology is mainly used in 802.3 (ethernet) and 802.4 standard networks.
- The configuration of a bus topology is quite simpler as compared to other topologies.
- The backbone cable is considered as a "single lane" through which the message is broadcast to all the stations.
- The most common access method of the bus topologies is CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access).
CSMA: It is a media access control used to control the data flow so that data integrity is maintained, i.e., the packets do not get lost. There are two alternative ways of handling the problems that occur when two nodes send the messages simultaneously.
- CSMA CD: CSMA CD (Collision detection) is an access method used to detect the collision. Once the collision is detected, the sender will stop transmitting the data. Therefore, it works on "recovery after the collision".
- CSMA CA:CSMA CA (Collision Avoidance) is an access method used to avoid the collision by checking whether the transmission media is busy or not. If busy, then the sender waits until the media becomes idle. This technique effectively reduces the possibility of the collision. It does not work on "recovery after the collision".
Advantages of Bus topology:
- Low-cost cable: In bus topology, nodes are directly connected to the cable without passing through a hub. Therefore, the initial cost of installation is low.
- Moderate data speeds: Coaxial or twisted pair cables are mainly used in bus-based networks that support upto 10 Mbps.
- Familiar technology: Bus topology is a familiar technology as the installation and troubleshooting techniques are well known, and hardware components are easily available.
- Limited failure: A failure in one node will not have any effect on other nodes.
Disadvantages of Bus topology:
- Extensive cabling: A bus topology is quite simpler, but still it requires a lot of cabling.
- Difficult troubleshooting: It requires specialized test equipment to determine the cable faults. If any fault occurs in the cable, then it would disrupt the communication for all the nodes.
- Signal interference: If two nodes send the messages simultaneously, then the signals of both the nodes collide with each other.
- Reconfiguration difficult: Adding new devices to the network would slow down the network.
- Attenuation: Attenuation is a loss of signal leads to communication issues. Repeaters are used to regenerate the signal.
Ring Topology
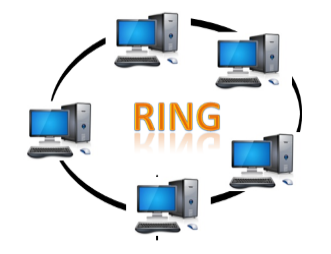
- Ring topology is like a bus topology, but with connected ends.
- The node that receives the message from the previous computer will retransmit to the next node.
- The data flows in one direction, i.e., it is unidirectional.
- The data flows in a single loop continuously known as an endless loop.
- It has no terminated ends, i.e., each node is connected to other node and having no termination point.
- The data in a ring topology flow in a clockwise direction.
- The most common access method of the ring topology is token passing.
- Token passing: It is a network access method in which token is passed from one node to another node.
- Token: It is a frame that circulates around the network.
Working of Token passing
- A token moves around the network, and it is passed from computer to computer until it reaches the destination.
- The sender modifies the token by putting the address along with the data.
- The data is passed from one device to another device until the destination address matches. Once the token received by the destination device, then it sends the acknowledgment to the sender.
- In a ring topology, a token is used as a carrier.
Advantages of Ring topology:
- Network Management: Faulty devices can be removed from the network without bringing the network down.
- Product availability: Many hardware and software tools for network operation and monitoring are available.
- Cost: Twisted pair cabling is inexpensive and easily available. Therefore, the installation cost is very low.
- Reliable: It is a more reliable network because the communication system is not dependent on the single host computer.
Disadvantages of Ring topology:
- Difficult troubleshooting: It requires specialized test equipment to determine the cable faults. If any fault occurs in the cable, then it would disrupt the communication for all the nodes.
- Failure: The breakdown in one station leads to the failure of the overall network.
- Reconfiguration difficult: Adding new devices to the network would slow down the network.
- Delay: Communication delay is directly proportional to the number of nodes. Adding new devices increases the communication delay.
Star Topology
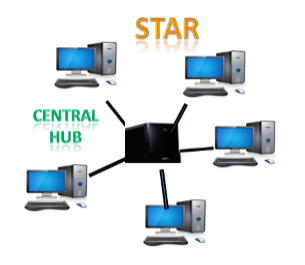
- Star topology is an arrangement of the network in which every node is connected to the central hub, switch or a central computer.
- The central computer is known as a server, and the peripheral devices attached to the server are known as clients.
- Coaxial cable or RJ-45 cables are used to connect the computers.
- Hubs or Switches are mainly used as connection devices in a physical star topology.
- Star topology is the most popular topology in network implementation.
Advantages of Star topology
- Efficient troubleshooting: Troubleshooting is quite efficient in a star topology as compared to bus topology. In a bus topology, the manager has to inspect the kilometers of cable. In a star topology, all the stations are connected to the centralized network. Therefore, the network administrator has to go to the single station to troubleshoot the problem.
- Network control: Complex network control features can be easily implemented in the star topology. Any changes made in the star topology are automatically accommodated.
- Limited failure: As each station is connected to the central hub with its own cable, therefore failure in one cable will not affect the entire network.
- Familiar technology: Star topology is a familiar technology as its tools are cost-effective.
- Easily expandable: It is easily expandable as new stations can be added to the open ports on the hub.
- Cost effective: Star topology networks are cost-effective as it uses inexpensive coaxial cable.
- High data speeds: It supports a bandwidth of approx 100Mbps. Ethernet 100BaseT is one of the most popular Star topology networks.
Disadvantages of Star topology
- A Central point of failure: If the central hub or switch goes down, then all the connected nodes will not be able to communicate with each other.
- Cable: Sometimes cable routing becomes difficult when a significant amount of routing is required.
Tree topology
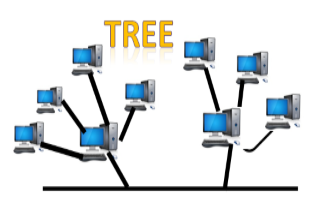
- Tree topology combines the characteristics of bus topology and star topology.
- A tree topology is a type of structure in which all the computers are connected with each other in hierarchical fashion.
- The top-most node in tree topology is known as a root node, and all other nodes are the descendants of the root node.
- There is only one path exists between two nodes for the data transmission. Thus, it forms a parent-child hierarchy.
Advantages of Tree topology
- Support for broadband transmission: Tree topology is mainly used to provide broadband transmission, i.e., signals are sent over long distances without being attenuated.
- Easily expandable: We can add the new device to the existing network. Therefore, we can say that tree topology is easily expandable.
- Easily manageable: In tree topology, the whole network is divided into segments known as star networks which can be easily managed and maintained.
- Error detection: Error detection and error correction are very easy in a tree topology.
- Limited failure: The breakdown in one station does not affect the entire network.
- Point-to-point wiring: It has point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
Disadvantages of Tree topology
- Difficult troubleshooting: If any fault occurs in the node, then it becomes difficult to troubleshoot the problem.
- High cost: Devices required for broadband transmission are very costly.
- Failure: A tree topology mainly relies on main bus cable and failure in main bus cable will damage the overall network.
- Reconfiguration difficult: If new devices are added, then it becomes difficult to reconfigure.
Mesh topology
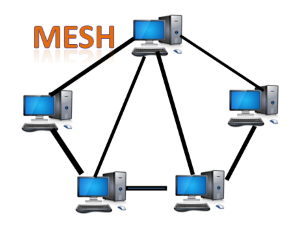
- Mesh technology is an arrangement of the network in which computers are interconnected with each other through various redundant connections.
- There are multiple paths from one computer to another computer.
- It does not contain the switch, hub or any central computer which acts as a central point of communication.
- The Internet is an example of the mesh topology.
- Mesh topology is mainly used for WAN implementations where communication failures are a critical concern.
- Mesh topology is mainly used for wireless networks.
- Mesh topology can be formed by using the formula:
Number of cables = (n*(n-1))/2;
Where n is the number of nodes that represents the network.
Mesh topology is divided into two categories:
- Fully connected mesh topology
- Partially connected mesh topology
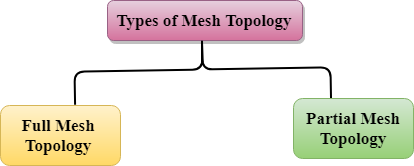
- Full Mesh Topology: In a full mesh topology, each computer is connected to all the computers available in the network.
- Partial Mesh Topology: In a partial mesh topology, not all but certain computers are connected to those computers with which they communicate frequently.
Advantages of Mesh topology:
Reliable: The mesh topology networks are very reliable as if any link breakdown will not affect the communication between connected computers.
Fast Communication: Communication is very fast between the nodes.
Easier Reconfiguration: Adding new devices would not disrupt the communication between other devices.
Disadvantages of Mesh topology
- Cost: A mesh topology contains a large number of connected devices such as a router and more transmission media than other topologies.
- Management: Mesh topology networks are very large and very difficult to maintain and manage. If the network is not monitored carefully, then the communication link failure goes undetected.
- Efficiency: In this topology, redundant connections are high that reduces the efficiency of the network.
Hybrid Topology
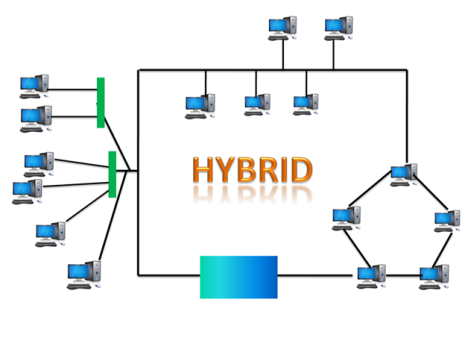
- The combination of various different topologies is known as Hybrid topology.
- A Hybrid topology is a connection between different links and nodes to transfer the data.
- When two or more different topologies are combined together is termed as Hybrid topology and if similar topologies are connected with each other will not result in Hybrid topology. For example, if there exist a ring topology in one branch of ICICI bank and bus topology in another branch of ICICI bank, connecting these two topologies will result in Hybrid topology.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
- Reliable: If a fault occurs in any part of the network will not affect the functioning of the rest of the network.
- Scalable: Size of the network can be easily expanded by adding new devices without affecting the functionality of the existing network.
- Flexible: This topology is very flexible as it can be designed according to the requirements of the organization.
- Effective: Hybrid topology is very effective as it can be designed in such a way that the strength of the network is maximized and weakness of the network is minimized.
Disadvantages of Hybrid topology
- Complex design: The major drawback of the Hybrid topology is the design of the Hybrid network. It is very difficult to design the architecture of the Hybrid network.
- Costly Hub: The Hubs used in the Hybrid topology are very expensive as these hubs are different from usual Hubs used in other topologies.
- Costly infrastructure: The infrastructure cost is very high as a hybrid network requires a lot of cabling, network devices, etc.
Cables-
Thick Coaxial Cable
This type cable is usually yellow in color and used in what is called thicknets, and has two conductors. This coax can be used in 500-meter lengths. The cable itself is made up of a solid center wire with a braided metal shield and plastic sheathing protecting the rest of the wire.
Thin Coaxial Cable
As with the thick coaxial cable is used in thicknets the thin version is used in thinnets. This type cable is also used called or referred to as RG-58. The cable is really just a cheaper version of the thick cable.
Fiber Optic Cable
As we all know fiber optics are pretty darn cool and not cheap. This cable is smaller and can carry a vast amount of information fast and over long distances.
Fiber optic cabling consists of a center glass core surrounded by several layers of protective materials. It transmits light rather than electronic signals eliminating the problem of electrical interference. This makes it ideal for certain environments that contain a large amount of electrical interference. It has also made it the standard for connecting networks between buildings, due to its immunity to the effects of moisture and lighting.
Fiber optic cable has the ability to transmit signals over much longer distances than coaxial and twisted pair. It also has the capability to carry information at vastly greater speeds. This capacity broadens communication possibilities to include services such as video conferencing and interactive services. The cost of fiber optic cabling is comparable to copper cabling; however, it is more difficult to install and modify. 10BaseF refers to the specifications for fibre optic cable carrying Ethernet signals.
The center core of fibre cables is made from glass or plastic fibres. A plastic coating then cushions the fibercenter, and Kevlar fibres help to strengthen the cables and prevent breakage. The outer insulating jacket made of Teflon or PVC.
There are two common types of fibre cables — single mode and multimode. Multimode cable has a larger diameter; however, both cables provide high bandwidth at high speeds. Single mode can provide more distance, but it is more expensive.
Specification | Cable Type |
10BaseT | Unshielded Twisted Pair |
10Base2 | Thin Coaxial |
10Base5 | Thick Coaxial |
100BaseT | Unshielded Twisted Pair |
100BaseFX | Fiber Optic |
100BaseBX | Single mode Fiber |
100BaseSX | Multimode Fiber |
1000BaseT | Unshielded Twisted Pair |
1000BaseFX | Fiber Optic |
1000BaseBX | Single mode Fiber |
1000BaseSX | Multimode Fiber |
Twisted Pair Cables
These come in two flavours of unshielded and shielded.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
Is more common in high-speed networks. The biggest difference you will see in the UTP and STP is that the STP use’s metallic shield wrapping to protect the wire from interference.
-Something else to note about these cables is that they are defined in numbers also. The bigger the number the better the protection from interference. Most networks should go with no less than a CAT 3 and CAT 5 is most recommended.
-Now you know about cables we need to know about connectors. This is pretty important and you will most likely need the RJ-45 connector. This is the cousin of the phone jack connector and looks real similar with the exception that the RJ-45 is bigger. Most commonly your connector are in two flavors and this is BNC (Bayonet Naur Connector) used in thicknets and the RJ-45 used in smaller networks using UTP/STP.
An image of STP –

Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
This is the most popular form of cables in the network and the cheapest form that you can go with. The UTP has four pairs of wires and all inside plastic sheathing. The biggest reason that we call it Twisted Pair is to protect the wires from interference from themselves. Each wire is only protected with a thin plastic sheath.
An image of UTP –
Ethernet Cabling
Now to familiarize you with more on the Ethernet and it’s cabling we need to look at the 10’s. 10Base2, is considered the thin Ethernet, thinnet, and thinwire which uses light coaxial cable to create a 10 Mbps network. The cable segments in this network can’t be over 185 meters in length. These cables connect with the BNC connector. Also as a note these unused connection must have a terminator, which will be a 50-ohm terminator.
10Base5, this is considered a thicknet and is used with coaxial cable arrangement such as the BNC connector. The good side to the coaxial cable is the high-speed transfer and cable segments can be up to 500 meters between nodes/workstations. You will typically see the same speed as the 10Base2 but larger cable lengths for more versatility.
10BaseT, the “T” stands for twisted as in UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) and uses this for 10Mbps of transfer. The down side to this is you can only have cable lengths of 100 meters between nodes/workstations. The good side to this network is they are easy to set up and cheap! This is why they are so common an ideal for small offices or homes.
100BaseT, is considered Fast Ethernet uses STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) reaching data transfer of 100Mbps. This system is a little more expensive but still remains popular as the 10BaseT and cheaper than most other type networks. This on of course would be the cheap fast version.
10BaseF, this little guy has the advantage of fiber optics and the F stands for just that. This arrangement is a little more complicated and uses special connectors and NIC’s along with hubs to create its network. Pretty darn neat and not to cheap on the wallet.
An important part of designing and installing an Ethernet is selecting the appropriate Ethernet medium. There are four major types of media in use today: Thickwire for 10BASE5 networks, thin coax for 10BASE2 networks, unshielded twisted pair (UTP) for 10BASE-T networks and fiber optic for 10BASE-FL or Fiber-Optic Inter-Repeater Link (FOIRL) networks. This wide variety of media reflects the evolution of Ethernet and also points to the technology’s flexibility. Thickwire was one of the first cabling systems used in Ethernet but was expensive and difficult to use. This evolved to thin coax, which is easier to work with and less expensive.
The quality of UTP may vary from telephone-grade wire to extremely high-speed cable. The cable has four pairs of wires inside the jacket. Each pair is twisted with a different number of twists per inch to help eliminate interference from adjacent pairs and other electrical devices. The tighter the twisting, the higher the supported transmission rate and the greater the cost per foot. The EIA/TIA (Electronic Industry Association/Telecommunication Industry Association) has established standards of UTP and rated six categories of wire (additional categories are emerging).
Category | Speed | Use |
1 | 1 Mbps | Voice Only (Telephone Wire) |
2 | 4 Mbps | LocalTalk& Telephone (Rarely used) |
3 | 16 Mbps | 10BaseT Ethernet |
4 | 20 Mbps | Token Ring (Rarely used) |
5 | 100 Mbps (2 pair) | 100BaseT Ethernet |
1000 Mbps (4 pair) | Gigabit Ethernet | |
5e | 1,000 Mbps | Gigabit Ethernet |
6 | 10,000 Mbps | Gigabit Ethernet |
Cat 5 cable-

Connectors –
Unshielded Twisted Pair Connector
The standard connector for unshielded twisted pair cabling is an RJ-45 connector. This is a plastic connector that looks like a large telephone-style connector . A slot allows the RJ-45 to be inserted only one way. RJ stands for Registered Jack, implying that the connector follows a standard borrowed from the telephone industry. This standard designates which wire goes with each pin inside the connector.
An image of RJ45

Coaxial Cable Connectors
The most common type of connector used with coaxial cables is the Bayone-Neill-Concelman (BNC) connector. Different types of adapters are available for BNC connectors, including a T-connector, barrel connector, and terminator. Connectors on the cable are the weakest points in any network. To help avoid problems with your network, always use the BNC connectors that crimp, rather screw, onto the cable.
An image of LAN card –
Internet Service Providers (ISP)
Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a company offering access to internet. They offer various services:
- Internet Access
- Domain name registration
- Dial-up access
- Leased line access
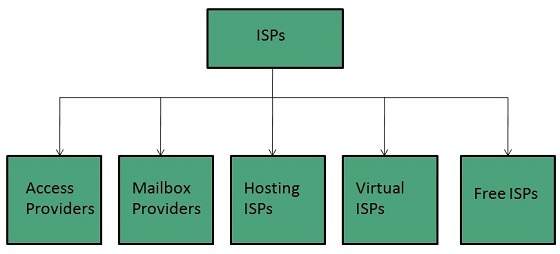
ISP Types
ISPs can broadly be classified into six categories as shown in the following diagram:
Access providers
They provide access to internet through telephone lines, cable wi-fi or fiber optics.
Mailbox Provider
Such providers offer mailbox hosting services.
Hosting ISPs
Hosting ISPs offers e-mail, and other web hosting services such as virtual machines, clouds etc.
Virtual ISPs
Such ISPs offer internet access via other ISP services.
Free ISPs
Free ISPs do not charge for internet services.
Connection Types
There exist several ways to connect to the internet. Following are these connection types available:
- Dial-up Connection
- ISDN
- DSL
- Cable TV Internet connections
- Satellite Internet connections
- Wireless Internet Connections
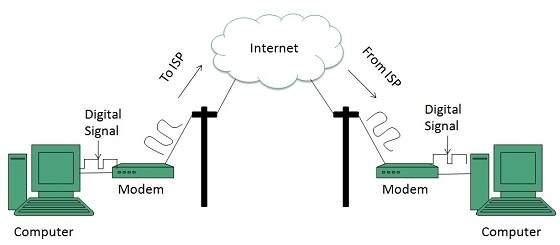
Dial-up Connection
Dial-up connection uses telephone line to connect PC to the internet. It requires a modem to setup dial-up connection. This modem works as an interface between PC and the telephone line.
There is also a communication program that instructs the modem to make a call to specific number provided by an ISP.
Dial-up connection uses either of the following protocols:
- Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP)
- Point to Point Protocol (PPP)
The following diagram shows the accessing internet using modem:
ISDN
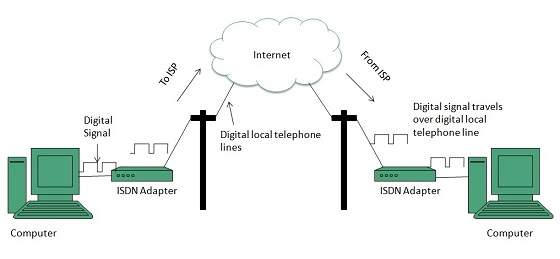
ISDN is acronym of Integrated Services Digital Network. It establishes the connection using the phone lines which carry digital signals instead of analog signals.
There are two techniques to deliver ISDN services:
- Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
- Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
Key points:
- The BRI ISDN consists of three distinct channels on a single ISDN line: t1o 64kbps B (Bearer) channel and one 16kbps D (Delta or Data) channels.
- The PRI ISDN consists of 23 B channels and one D channels with both have operating capacity of 64kbps individually making a total transmission rate of 1.54Mbps.
The following diagram shows accessing internet using ISDN connection:
DSL
DSL is acronym of Digital Subscriber Line. It is a form of broadband connection as it provides connection over ordinary telephone lines.
Following are the several versions of DSL technique available today:
- Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
- Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
- High bit-rate DSL (HDSL)
- Rate adaptive DSL (RDSL)
- Very high bit-rate DSL (VDSL)
- ISDN DSL (IDSL)
All of the above mentioned technologies differ in their upload and download speed, bit transfer rate and level of service.
The following diagram shows that how we can connect to internet using DSL technology:
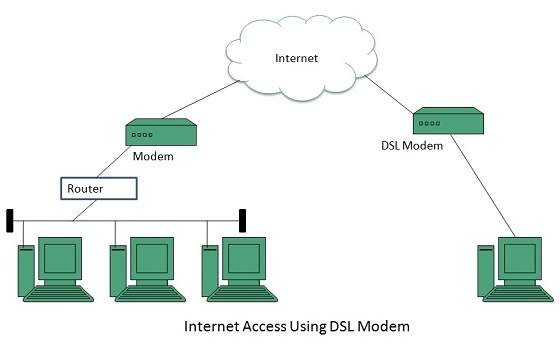
Cable TV Internet Connection
Cable TV Internet connection is provided through Cable TV lines. It uses coaxial cable which is capable of transferring data at much higher speed than common telephone line.
Key Points:
- A cable modem is used to access this service, provided by the cable operator.
- The Cable modem comprises of two connections: one for internet service and other for Cable TV signals.
- Since Cable TV internet connections share a set amount of bandwidth with a group of customers, therefore, data transfer rate also depends on number of customers using the internet at the same time.
The following diagram shows that how internet is accessed using Cable TV connection:
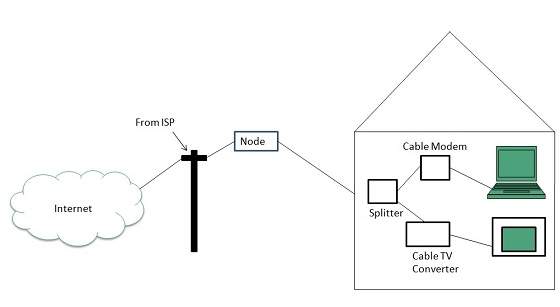
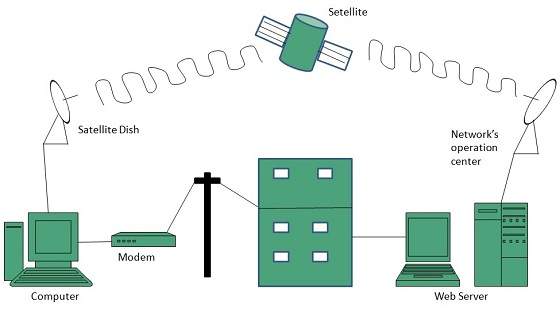
Satellite Internet Connection
Satellite Internet connection offers high speed connection to the internet. There are two types of satellite internet connection: one way connection or two way connection.
In one way connection, we can only download data but if we want to upload, we need a dialup access through ISP over telephone line.
In two way connection, we can download and upload the data by the satellite. It does not require any dialup connection.
The following diagram shows how internet is accessed using satellite internet connection:
Wireless Internet Connection
Wireless Internet Connection makes use of radio frequency bands to connect to the internet and offers a very high speed. The wireless internet connection can be obtained by either WiFi or Bluetooth.
Key Points:
- Wi Fi wireless technology is based on IEEE 802.11 standards which allow the electronic device to connect to the internet.
- Bluetooth wireless technology makes use of short-wavelength radio waves and helps to create personal area network (PAN).
If You Can't Access the Web
We'll assume that your Internet was working at an earlier point. If you are setting it up for the first time, the steps listed below were not designed with that purpose in mind. You need to follow the instructions that came with your router or modem.
I've included a series of definitions for the terminology used on this page.
Reboot the Computer
The first step should be rebooting your computer or device to see if that fixes the problem. You'd be surprised how often that simple step resolves issues.
If restarting your computer or device doesn't work, you'll have to check out each potential problem area to see if it restores access.
Check These Areas
The most likely problem areas related to a loss of Internet assess are one or more of the following:
- Your computer is disconnected from the network (check the network settings;
- a proxy has been added to your browser or operating system;
- Your high-speed modem and/or router needs resetting or is disconnected;
- a disconnected network cable (if your computer is wired);
- Your computer needs to reboot;
- Your firewall or security software is misconfigured; or
- Your software is misconfigured for access to the Internet.
Progress through the suggestions on this page to test alternative solutions. I've presented them in the order I'd likely progress if I were to be assessing the problem and looking for solutions.
ISP Issues
If the issue is with your ISP or (rarely) a regional access issue, the resolution is beyond your control. You'll just have to wait for your ISP or the Internet structure to repair the problem.
Everything Connects via a Network
Everything about Internet connection issues relates to how the various networks are operating. Unless the problem is directly related to your computer or device (tablet, smartphone, virtual assistant, Smart Home appliance) then it will involve either your own network or one that is further along the chain.
I'm going to use the terms computer and device interchangeably, because all that differs is how they are configured to connect to the Internet.
A network is a collection of computers and other devices connected and talking to each other.
- The most immediate network is the one inside your home or business (your home network).
- The next is your connection to your ISP (another network).
- Your ISP connects to the Internet (a world-wide network) through a regional collection of related networks.
Let's have a look at how each of these may be involved in the chain of connections from your computer to the website or service you're trying to reach.
Your Home Network
Your most basic home network is your computer connected directly to a modem provided by your ISP (usually via either a router or a router/modem combination).
The router provides access to all other connected devices connected to your network as well as to the Internet. Whether these devices can talk to each other (i.e. share information) depends upon how the network and the devices are configured.
Your network should be secured using secure passwords for both your router and your WiFi.
Your ISP
Your ISP (Shaw, Telus, Rogers, etc.) provide you with your connection to the Internet via their own network (which includes all their customers' networks).
Your ISP then connects through a network of additional connections to the Internet (designed originally to withstand a nuclear attack by switching automatically to whatever routing is available).
Public Networks
Public networks include free community WiFi networks, coffeeshopWiFi, public library networks and other similar Internet connection that you don't control.
You may be connected using your own laptop, tablet or smartphone or you may be using a public computer (such as those provided by a library or school).
If you're having difficulty connecting on a public network, you'll need to talk to the staff to determine how to resolve the issue. Sometimes the staff have no control.
You Can't Trust Public Networks
If you are using public access from a connection that you don't control (something other than your home network) or one that isn't secured properly (you haven't changed the default passwords or enabled security) then you are placing your computer and data at risk.
Everyone on an insecure (public) network such as a coffee shop can potentially “see” the information you are sending and received on that WiFi service. All it takes is some software that is easily obtained on the Internet.
Even if you're using a gated network (one that requires you to sign on), unless you control that network, you can't trust it.
NEVER do Internet banking or similar risky activity on a public network.
Cellular Networks
Cellular networks are those provided by cellular ISPs. These networks are separate from the typical home or business network and usually have relatively small data caps. Cellular networks are fairly reliable (the number of cell towers and their location determines the strength of your signal) but do sometimes go down.
Cellular service is more secure than free WiFi. However, just like your home network, everything you do on your cell is visible to your cellular provider unless you use a VPN.
Other than ensuring your cellular service is turned on for your device, there is little you can do to resolve connection issues other than to move to an area with better reception or call your cellular provider for assistance.
Securing Your Network
It is important that you secure your own network. It is beyond the scope of connection issues, but there are resources on this site that will help you to do that.
At the very least, you should change the default passwords used to configure your router and connect to your Wi-Fi.
Basic Internet Terminology
You might wish to review basic computer terminology (including additional Internet terminology) and Windows terminology to better understand how they are involved in connecting to the Internet.
Networks
A network is a collection of computers and devices that are connected together, allowing them to share information.
- A local network refers to the network served by a single router in a specific location.
- The Internet is a world-wide network.
The Internet is a network that spans the globe. Most people connect to the Internet either via their home or work network (router) or via a free wireless service provide by a coffee shop or community broadband service or via their cellular provider.
- ISP refers to the company that provides you with access to the Internet (Shaw, Telus, Bell, etc.).
- An IP address is usually represented with a numeric series of numbers separated with dots (e.g. 192.168.1.1). Every device on your local network (and on the Internet) has an IP address. For most users an IP address is leased (i.e. not permanent).
- A domain is the main address of a website (e.g. Google.ca). There are also subsets of domains such as sites hosted on WordPress or Blogger (e.g. Russ-rants.blogspot.com). A Domain Name Service (DNS) converts the domain name into the IP address that is the actual physical address on the Internet.
Connection Protocols
The following describes the common methods used in connecting to a network, including the Internet.
- A Local Area Network (LAN)is wired connection to a common router.
- A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a wireless connection to a router.
- A cellular network is a wireless connection to a cellular service (Rogers, Bell, Telus, Fido, etc.) rather than via an ISP.
Hardware
The following describes the hardware involved in connecting to a network.
- A router combines the splitting power of a network hub with the ability to protect you with a hardware firewall. Most current routers include both wired (LAN) and wireless (WLAN) connections.
- A network adapter connects your computer to the network and can be LAN or WLAN adapters (laptops often have both).
- A modem can generally refer to either cable or ADSL modems that connect you to the Internet. Most current modems provided by your ISP are combined with a built-in router.
- Dial-up modems are mostly obsolete but were once the primary method of connecting to the Internet.
Software
These are the basic programs used to view content on the Internet:
- A (web) browser is a program used to view web pages on the Internet. Examples are Firefox and Google Chrome. Choose your browser carefully.
- A email client is a program used to send and receive emails and to display them. Examples are Thunderbird and Outlook.
- Webmail is an online service that allows your to view your emails via a web browser. Examples are Gmail and Shaw Webmail.
- A FTP client is a program used to upload websites to the server where they can be viewed on the Internet. Examples are WS-FTP and FileZilla.
- An app is a specialized program used to view content from a specific source. Apple, Microsoft and Google have app stores that provide applications for their various operating systems.
Issues with Slow Internet Access
If you have Internet access but it seems that your service is slow:
- Speed Check can test how fast your Internet access is and provide some solutions for resolving issues.
- In some cases, an ISP like Shaw may be delivering full speed Internet into your neighbourhood, but high-volume users may be sapping the bulk of the available bandwidth.
The problem may also be with your computer or device. Older computers contain older, less capable hardware and software. If the device's storage capacity is maxed out it can create issues with how well you can connect with the Internet.
No Internet Access?
If you have no Internet access a series of troubleshooting steps will help to determine where the breakdown is and how to resolve the problem.
Basic Troubleshooting
When your Internet service is disrupted, there can be many things that have gone wrong. The best way to start is to determine if everything is broken (i.e. you can't access any websites or Internet services) or if the difficulty is only with a certain program or a specific website is not responding.
If Access is Limited
If you are able to view certain sites, but not others, it is possible that one or more specific sites are down. Sites go dead for a variety of reasons and the issue may be temporary or permanent.
If you see a 404 error (“page not found”), it means that the site is up but the page you requested is not available. This is not an issue with your Internet connection.
- Go to Is it UP?and enter the domain of the site you're looking for.
- Is It Up?will check to see if they can connect.
- If Is It Up?can connect to the site and you still can't, the issue is either with you or your ISP's connection.
Regional Outages
If you are able to view local content but cannot see sites hosted across the country or elsewhere, there could be a blockage in the Internet grid (a regional outage).
- Have a look at The Internet Traffic Report which monitors the flow of data around the world. You can view data for specific cities, helping to pinpoint potential problems.
- These are issues with the Internet itself and there is little you can do but wait it out.
Issues with Specific Programs
If only some of your programs are working, try the following:
- If your email works fine but your problem appears to be related only to your web browser, have a look at Browser Problems.
- If you can surf the Web okay, but you have difficulty sending or receiving email, have a look at Email Problems.
Check to See if the Problem is the Computer
If you have more than one computer, see if both computers are experiencing difficulties accessing the Internet. If the second computer has full access then your problem is localized to the first computer (you can skip any tests that don't deal with the computer itself).
Troubleshooting Access Problems
Where I refer to your router this may be configured as a separate high-speed modem connected to an external router or as an all-in-one combined modem/router supplied by your ISP (most common).
If the devices are separate then both need to be reset when you are instructed to reset your router in the steps listed on this page.
- Turn off the modem first, then the router;
- Use the reverse sequence when restoring power.
A separate power bar with only the two devices attached simplifies matters.
There is No Internet Access
The following steps assume there is NO Internet access. Specific websites and ISPs can have outages that have nothing to do with your computer or its settings.
Troubleshooting Steps
Try the following series of steps, in order, to see if this fixes your problem. You can stop when you resolve the issue(s) you are having.
- Check the network icon (or wireless connection settings) to see if you have Internet access. Ensure that your network adapter is not turned off.
- Check for changes to proxy settings.
- Check the network cables if your computer is wired to the router.
- Reset your router.
- Check your firewall or security software. There are specific troubleshooting steps for ZoneAlarm issues.
- Check your browser access issues or email problems.
The next few sections will expand these steps into a series of instructions. Where Linux is indicated, I've based these on Linux Mint, the version I'm currently working with.
Check the Network
Check the network connection on your computer. This connects other computers in your network as well as providing access to the Internet via your ISP.
Depending upon your operating system and your settings, there may be a network icon at the top or bottom of the screen or it may be hidden.
Your Internet connection can include either or both wired and wireless connections Whichever you're using, there is likely a router involved, whether it is your home network or a public network such as at a coffee shop or a business network, or a community wireless network).
If you're not using your own network, you'll need to speak to the person responsible for that network for details on how to fix any issues.
Check the Wireless Settings
If you're connected wirelessly you'll see a listing of available wireless networks. The wireless network you're currently logged into (if any) should be indicated. Most networks are protected by a security protocol and a password.
- You'll need to verify that your connection is strong enough and that the settings don't indicate any problems.
- If you're having difficulties connecting or if there is a problem with the connection, you'll need to diagnose it.
- If you don't control the network, you'll need to ask for the password and may need additional help diagnosing the problems.
- Some public networks are heavily used and can be very slow even when everything is working fine.
Check the Wired Settings
If you're connected via CAT5 or CAT6 network cables, you should check the following:
- Check the cables to ensure that they aren't unplugged or damaged.
- Be sure that the network adapter isn't disabled.
- You may need to reset the router then reboot your computer.
Network Settings by Operating System
The following are specific to each operating system. If you're isn't listed, look for your computer or device documentation.
Windows 10
Windows 10 has changed the way that these settings work over time, so you may see something different than what is indicated here.
Windows 10's network icon is on the right side of the taskbar in its default configuration. The icon changes from a globe to a computer to a WiFi icon depending upon your connection and its status.
Click the network icon to see the status of your Internet connection(s) and to connect to listed WiFi networks. Look for the word “connected” for both LAN and WLAN connections to ensure they are working correctly.
Clicking on Network & Internet settings brings up the Status page. At the top is a diagram of your network status:
There should be solid lines between your computer, the network and the Internet as shown above (a private LAN connection — yours could display different icons).
Through the various settings on this Status page, you can
- Label the network a metered connection if you have a limited data plan.
- You can also change other properties here and troubleshoot problems using the network troubleshooter.
- Enable or disable a network adapter.
- Add a VPN or manage other services.
A VPN may disable your connection to the Internet if it is disconnected (a security measure to protect your privacy). Reconnecting or turning off the VPN should resolve any issues.
Mac
Open the Network Preferences from the WLAN icon or look in the Systems Preferences to see your network connections. You may have active connections for Ethernet (LAN) and/or WiFi (WLAN).
If everything is normal, you should see “connected” indicated in the appropriate location(s).
If not, click on Assist Me at the bottom then Diagnostics on the dialogue box that appears. Follow the instructions for the connection that is having problems.
Linux
There are two areas dealing with your network connections:
- Under Administration (Network: configure network devices and connections); and
- Under Preferences (Network Connections: manage and change your network connection settings).
You'll need to unlock the Network Settings with the Administrator password to make changes.
iOS or Android
Mobile devices can connect via both wireless networks and cellular networks (smart phones and cellular-capable tablets). At least one must be enabled and have access to an available network to use the Internet.
- Look under setting for the Wi-Fi and cellular (where available) settings.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi or cellular is enabled.
- Ensure that airplane mode is NOT on.
- Ensure that Do Not Disturb is NOT enabled.
Check the Proxy Settings
Most users should not touch the proxy settings, leaving them at the default which is System Settings. Changing the proxy settings can disable Internet access and is something that malware and other malicious programs do to maintain control of your computer.
Browser Proxy Settings
Each browser has proxy settings but most users should leave these settings alone.
System Proxy Settings
If you're in an office where your computer is provided by your employer you'll want to verify the settings with whoever is responsible for the network.
It is generally not recommended that users change these, but it is possible your Internet connection isn't working because something else changed the proxy settings such as malware or a program installed by a scammer.
- Windows users will find these in the Network & Internet settings. Click on the Proxy tab. Only Automatically detect settings should be checked. Uncheck Use a proxy server then verify that you have Internet access.
- Mac users will find these in the in the System Preferences. Click on Network then Advanced and choose the Proxies tab. Normally none of the options should be checked other than Use Passive FTP Mode at the bottom. My computer also has *local, 169.254/16 under Bypass proxy settings for these Hosts & Domains.
- Linux users will find these settings in the Network Proxy Preferences (click on Preferences then Network Proxy). The default should be Direct internet connection.
Check the Cables
The troubleshooter may prompt you to check the router settings, but first you'll need to ensure that the network cables are firmly attached and that your modem is connected to either the cable outlet or the phone line (depending upon which ISP's service you're using) and that the cables are not damaged.
- Check the connections at both ends of all the wires. This may sound silly, but things get pulled or simply break.
- Check the connection to the cable jack or phone line as well as the CAT5 or CAT6 network cables between the modem and/or router as well as the computers.
- On most systems there should be a green LED lit if the network cable connection is working.
Try replacing the cables. If the connector retainer (a small, springy plastic that holds the cable firmly in place) is broken or has lost its ability to retain a firm connection then the connection may be weak or intermittent.
Reset the Router
If instructed by the network trouble shooter (or if you've completed the steps above) you'll need to ensure that the problem isn't with your router.
Recycling Power to Your Router
Start by recycling the power to your router (and modem if they are separate):
- Turn off the power to the modem (then the router), and wait for two minutes.
- Turn the modem on and wait for the lights to settle (you should see a steady light on the modem) then turn on the router.
- Wait 30 seconds.
- Turn your computer on.
This process will force a new IP lease from your ISP and everything should now work.
Recycling the power is necessary because your ISP (Shaw, Rogers, Telus, etc.) changes dynamic IP addresses every so often, disabling those that have been running for too long.
I strongly recommend that you purchase a decent power bar to protect your investment in your modem/router if a power surge hits your system.
- This will allow you to turn off the power to both the modem and router with a single switch.
- Don't use the $10 variety — replacing your computer, modem, router and associated gear will cost more than that.
Try Without the Router
If you continue to have problems and you have a separate modem you can try your modem without the router. If the Internet is accessible, try to run it with the router again. If that fails, proceed to the next step in resetting and setting up your router.
It doesn't take more than a couple of minutes for an unprotected computer to become infected. Be careful while accessing the Internet at this stage.
Resetting Your Router
If you continue to have problems, you should try resetting the router.
- Factory settings are the defaults that came with your router. Resetting your router will remove any customized settings.
- Make a note of any existing settings before resetting your router (if possible). Many provide a method of saving settings to your computer.
- Most have a recessed reset button. To restore factory settings, hold down the button for a minute or two with the tip of a ball point pen or paper clip.
Configuring the Router
You will then have to configure your router to set up your network and connect to your ISP.
- Ensure that your computer is connected to the router with a network cable during the setup process.
- Never alter your router settings while connected through a wireless connection — you will lose access to the router when it reboots during the setup process.
You may wish to have some professional help to ensure you retain the maximum security and correct settings for your network.
At the very least you should read the manual provided with your router so you understand the process and what each of the settings will change.
- You can obtain the instructions for your particular router from the manufacturer's website or from the documentation that came with your router.
- Never retain default settings as this compromises your network security.
- Change the default settings (especially the password) to protect your network from malicious attacks.
A browser is a software program that is used to explore, retrieve, and display the information available on the World Wide Web. This information may be in the form of pictures, web pages, videos, and other files that all are connected via hyperlinks and categorized with the help of URLs (Uniform Resource Identifiers). For example, you are viewing this page by using a browser.
A browser is a client program as it runs on a user computer or mobile device and contacts the web server for the information requested by the user. The web server sends the data back to the browser that displays the results on internet supported devices. On behalf of the users, the browser sends requests to web servers all over the internet by using HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). A browser requires a smart phone, computer, or tablet and internet to work.
History of Web Browser
- The World Wide Web was the first web browser. It was created by W3C Director Tim Berners-Lee in 1990. Later, it was renamed Nexus to avoid confusion caused by the actual World Wide Web.
- The Lynx browser was a text-based browser, which was invented in 1992. It was not able to display the graphical content.
- Although, the first graphical user interface browser was NCSA Mosaic. It was the first most popular browser in the world, which was introduced in 1993.
- In 1994, there were some improvements occurred in Mosaic and came to Netscape Navigator.
- In 1995, Microsoft introduced the Internet ExplorerIt was the first web browser developed by Microsoft.
- A research project started on Opera in 1994. Later, it was publicly introduced in 1996.
- Apple's Safari browser was introduced in 2003. It was specifically released for Macintosh computers.
- In 2004, Mozilla introduced Firefox as Netscape Navigator.
- In 2007, a browser Mobile Safari was released as Apple mobile web browser.
- The popular browser Google Chrome was launched in 2008.
- The fast-growing mobile-based browser Opera Mini was released in 2011.
- The Microsoft Edge browser was launched in 2015.
Features of Web Browser
Most Web browsers offer common features such as:
- Refresh button: Refresh button allows the website to reload the contents of the web pages. Most of the web browsers store local copies of visited pages to enhance the performance by using a caching mechanism. Sometimes, it stops you from seeing the updated information; in this case, by clicking on the refresh button, you can see the updated information.
- Stop button: It is used to cancel the communication of the web browser with the server and stops loading the page content. For example, if any malicious site enters the browser accidentally, it helps to save from it by clicking on the stop button.
- Home button: It provides users the option to bring up the predefined home page of the website.
- Web address bar: It allows the users to enter a web address in the address bar and visit the website.
- Tabbed browsing: It provides users the option to open multiple websites on a single window. It helps users to read different websites at the same time. For example, when you search for anything on the browser, it provides you a list of search results for your query. You can open all the results by right-clicking on each link, staying on the same page.
- Bookmarks: It allows the users to select particular website to save it for the later retrieval of information, which is predefined by the users.
What is the URL (Uniform Resource Locator)?
A uniform resource locator is the address of a resource on the internet or the World Wide Web. It is also known as a web address or uniform resource identifier (URI). For example, https: www.javatpoint.com, which is the URL or web address for the javatpoint website. A URL represents the address of a resource, including the protocol used to access it.
A URL includes the following information:
- It uses the protocol to access the resource.
- It defines the location of a server by IP address or the domain name.
- It includes a fragment identifier, which is optional.
- It contains the location of the resource in the directory of the server.
A URL forwards user to a particular online resource, such as a video, webpage, or other resources. For example, when you search information on Google, the search results display the URL of the relevant resources in response to your search query. The title which appears in the search results is a hyperlink of the URL of the webpage. It is a Uniform Resource Identifier, which refers to all kinds of names and addresses of the resources on the webservers. URL's first part is known as a protocol identifier, and it specifies the protocol to use, and the second part, which is known as a resource name, represents the IP address or the domain name of a resource. Both parts are differentiated by a colon and two forward slashes like http://www.javatpoint.com.
Component of a Web browser
The primary components of a browser are shown in the below image:
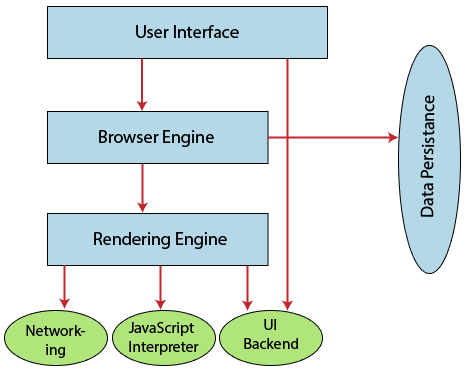
- User Interface: The user interface is an area where the user can use several options like address bar, back and forward button, menu, bookmarking, and many other options to interact with the browser.
- Browser Engine: It connects the UI (User Interface) and the rendering engine as a bridge. It queries and manipulates the rendering engine based on inputs from several user interfaces.
- Rendering Engine: It is responsible for displaying the requested content on the browser screen. It translates the HTML, XML files, and images, which are formatted by using the CSS. It generates the layout of the content and displays it on the browser screen. Although it can also display the other types of content by using different types of plugins or extensions. Such as:
- Internet Explorer uses Trident
- Chrome & Opera 15+ use Blink
- Chrome (iPhone) & Safari use Web kit
- Firefox & other Mozilla browsers use Gecko
- Networking: It retrieves the URLs by using internet protocols like HTTP or FTP. It is responsible for maintaining all aspects of Internet communication and security. Furthermore, it may be used to cache a retrieved document to reduce network traffic.
- JavaScript Interpreter: As the name suggests, JavaScript Interpreter translates and executes the JavaScript code, which is included in a website. The translated results are sent to the rendering engine to display results on the device screen.
- UI Backend: It is used to draw basic combo boxes and Windows (widgets). It specifies a generic interface, which is not platform-specific.
- Data Storage: The data storage is a persistence layer that is used by the browser to store all sorts of information locally, like cookies. A browser also supports different storage mechanisms such as IndexedDB, WebSQL, localStorage, and FileSystem. It is a database stored on the local drive of your computer where the browser is installed. It handles user data like cache, bookmarks, cookies, and preferences.
How does a browser work?
When a user enters a web address or URL in the search bar like javatpoint.com, the request is passed to a domain name servers (DNS). All of these requests are routed via several routers and switches.
The domain name servers hold a list of system names and their corresponding IP addresses. Thus, when you type something in the browser search bar, it gets converted into a number that determines the computers to which the search results are to be displayed.
The browser acts as a part of the client-server model. A browser is a client program that sends the request to the server in response to the user search queries by using Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP. When the server receives the request, it collects information about the requested document and forwards the information back to the browser. Thereafter, the browser translates and displays the information on the user device.
In Brief:
- When a user enters something (like javatpoint.com) in the browser. This request goes to a domain name server.
- The browser sends the user request to the server using an IP address, which is described by the domain name server.
- The domain name server sends an IP address to the web server that hosts the website.
- The server sends the information back to the IP address, which is defined by the browser at the time of the request. The requested page may include links to other files on the same server, like images, for which the browser also requests the server.
- The browser gathers all the information requested by the user, and displays on your device screen in the form of web pages.
List of Internet Browsers
There are various types of internet browsers, which are as follows:
- Microsoft Edge: Microsoft Edge is a web browser that comes pre-installed with Windows 10 operating system and Windows Server 2016. It was introduced to replace the Internet Explorer Web browser, and its code name was Spartan. It offers various types of features such as freestyle writing over Web page displays, refined search, and presentations for e-books and other reading resources.
Microsoft Edge was developed under the Spartan codename Project. In April 2015, Microsoft changed the project Spartan name as Microsoft Edge. Although Internet Explorer and Edge are included with Windows 10, Edge act as a default browser. It combines new web technology evaluations and enhances the speed of browsing.
Although, Internet Explorer 11 was available in Microsoft Windows operating system, Microsoft Edge has become the default browser in Windows 10. It needs at least 1 gigabyte of memory. It offers several types of features, such as annotation features, a new rendering engine, and easy-to-use icons, etc. Furthermore, it also provides better security as compared to Internet Explorer, and it can be combined with Cortana, Microsoft's virtual personal assistant.
Features of Microsoft Edge
- It provides support for Firefox and Chrome add-ons.
- It has the ability to fill the form automatically.
- It can be integrated with Cortana.
- It provides faster page rendering.
- It has more security features and also allows private browsing.
- It is modern, lightweight, and reduces resource consumption.
Latest versions of Edge browser
Platform | Versions | Release Date |
Window 10 | 79.0.309.71 | 22-01-2020 |
Window 10 Mobile | 40.15254.603 | 21-01-2020 |
Xbox One | 40.15063.0 | 30-08-2018 |
|
|
|
- Amazon Silk: Amazon silk is a proprietary Internet browser. It was released for Fire OS devices on 15 November 2011. It is based on the open-source Chromium project and derives most of the features from the Google Chrome browser. It divides the task of loading webpages between Amazon's servers and Fire.

Silk is the default browser on most Amazon hardware devices as well as on app-based Kindle devices, TV, Fire, and compatible Echo devices. Furthermore, it is the first new mass-market, client software delivery mechanism, which should be built from the base of the cloud, not only the web.
How does Silk Work?
Silk browser works through Amazon EC2 (Elastic cloud computing). EC2 acts as the middleman between devices and webpages and simplify them for examined mobile consumption. Then, it includes the whole host of processes like page caching, file compression, and local file storage.
It tries to guess your browsing habits. Accordingly, it predicts the pages that you may like to visit, and then pre-loads those pages in advance. These background processes use lower bandwidth and promote speed of page loading. If EC2 is offline, the silk browser switches to a backup mode where it translates all information on the Kindle Fire itself.
Rendering pages on EC2
When the all contents of a page have been fetched on EC2, it renders the pages for display in the client's browser window. It depends on the amount of load and the client's network conditions.
The components that can be handed off to EC2 to speed up browsing are: HTML, CSS, Networking, JavaScript, Block building, Marshalling, Native OM, etc.
- Opera: An Opera web browser was first conceived at Telenor company in 1994, later bought by the Opera Software on 1 April 1995. It was designed for desktop and mobile interfaces, but it is more popular now for mobile phones. It is based on Chromium, and it uses the blink layout engine. An opera mini was released for smart phones on 10 August 2005 that could run standard web browsers. It can be downloaded from the Google play store or Apple play store.
- Apple Safari: Safari is an internet browser available for the Macintosh, and Windows operating systems included the iPhone, iPad, and iPod Touch. It was developed by Apple, Inc. On 30 June 2003. It is the default browser for the operating system in its products, such as OS X for the MacBook and Mac computers and iOS for the iPad and iPhone mobile devices. It is at number four in the browser market after Microsoft Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, and Google Chrome. It uses the WebKit engine, which is used for rendering fonts, displays graphics, determining page layout, and running JavaScript.
- Google Chrome: Google Chrome is an open-source internet browser. It is developed by Google on 11 December 2008 for Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, Android, and iOS operating systems.
- Mozilla Firefox: The Mozilla Firefox web browser is developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subordinate company, Mozilla Corporation. It was first released was beta on 23 September 2002. Although it was released as the Mozilla Browser, it was internally code-named Phoenix. The First version 1.0 of Firefox was introduced on 9 November 2004. Internet Explorer: It is a web browser that is manufactured by Microsoft Corporation, and it is included with the Microsoft Windows operating system. But It was removed in Window 10 in support of Microsoft's new Edge Browser.
Search Engine refers to a huge database of internet resources such as web pages, newsgroups, programs, images etc. It helps to locate information on World Wide Web.
User can search for any information by passing query in form of keywords or phrase. It then searches for relevant information in its database and return to the user.
Search Engine Components
Generally there are three basic components of a search engine as listed below:
- Web Crawler
- Database
- Search Interfaces
Web crawler
It is also known as spider or bots. It is a software component that traverses the web to gather information.
Database
All the information on the web is stored in database. It consists of huge web resources.
Search Interfaces
This component is an interface between user and the database. It helps the user to search through the database.
Search Engine Working
Web crawler, database and the search interface are the major component of a search engine that actually makes search engine to work. Search engines make use of Boolean expression AND, OR, NOT to restrict and widen the results of a search. Following are the steps that are performed by the search engine:
- The search engine looks for the keyword in the index for predefined database instead of going directly to the web to search for the keyword.
- It then uses software to search for the information in the database. This software component is known as web crawler.
- Once web crawler finds the pages, the search engine then shows the relevant web pages as a result. These retrieved web pages generally include title of page, size of text portion, first several sentences etc.
These search criteria may vary from one search engine to the other. The retrieved information is ranked according to various factors such as frequency of keywords, relevancy of information, links etc.
- User can click on any of the search results to open it.
Architecture
The search engine architecture comprises of the three basic layers listed below:
- Content collection and refinement.
- Search core
- User and application interfaces
Search Engine Processing
Indexing Process
Indexing process comprises of the following three tasks:
- Text acquisition
- Text transformation
- Index creation
Text acquisition
It identifies and stores documents for indexing.
Text Transformation
It transforms document into index terms or features.
Index Creation
It takes index terms created by text transformations and create data structures to suport fast searching.
Query Process
Query process comprises of the following three tasks:
- User interaction
- Ranking
- Evaluation
User interaction
It supporst creation and refinement of user query and displays the results.
Ranking
It uses query and indexes to create ranked list of documents.
Evaluation
It monitors and measures the effectiveness and efficiency. It is done offline.
Examples
Following are the several search engines available today:
Search Engine | Description |
It was originally called BackRub. It is the most popular search engine globally. | |
Bing | It was launched in 2009 by Microsoft. It is the latest web-based search engine that also delivers Yahoo’s results. |
Ask | It was launched in 1996 and was originally known as Ask Jeeves. It includes support for match, dictionary, and conversation question. |
AltaVista | It was launched by Digital Equipment Corporation in 1995. Since 2003, it is powered by Yahoo technology. |
AOL.Search | It is powered by Google. |
LYCOS | It is top 5 internet portal and 13th largest online property according to Media Matrix. |
Alexa | It is subsidiary of Amazon and used for providing website traffic information. |
Understanding URL
Every document on the Web has a unique address. This address is known as Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
Several HTML/XHTML tags include a URL attribute value, including hyperlinks, inline images, and forms. All of them use the same syntax to specify the location of a web resource, regardless of the type or content of that resource. That's why it is known a Uniform Resource Locator.
URL Elements
A URL is made of up several parts, each of which offers information to the web browser to help find the page. It is easier to learn the parts of a URL, if you look at the example URL given below, there are three key parts: the scheme, the host address, and the file path. The following section will discuss each of them:
Http://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm
The Scheme
The scheme identifies the type of protocol and URL you are linking to and therefore, how the resource should be retrieved. For example, most web browsers use Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to pass information to communicate with the web servers and this is the reason a URL starts with http://.
There are other schemes available and you can use either of them based on your requirement:
Sr.No | Scheme & Description |
1 | Http:// Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is used to request pages from Web servers and send them back from Web servers to browsers. |
2 | Https:// Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) encrypts the data sent between the browser and the Web server using a digital certificate. |
3 | Ftp:// File Transfer Protocol is another method for transferring files on the Web. While HTTP is a lot more popular for viewing Web sites because of its integration with browsers, FTP is still commonly used protocol to transfer large files across the Web and to upload source files to your Web server. |
4 | File:// Used to indicate that a file is on the local hard disk or a shared directory on a LAN. |
The Host Address
The host address is where a website can be found, either the IP address (four sets of numbers between 0 and 255, for example 68.178.157.132 ) or more commonly the domain name for a site such as www.tutorialspoint.com. Note that "www" is not actually part of the domain name although it is often used in the host address.
The File Path
The file path always begins with a forward slash character, and may consist of one or more directory or folder names. Each directory name is separated by forward slash characters and the file path may end with a filename at the end. Here index.htm is the filename which is available in html directory:
Https://www.tutorialspoint.com/html/index.htm
Other Parts of the URL
Using credentials is a way of specifying a username and password for a password-protected part of a site. The credentials come before the host address, and they are separated from the host address by an @ sign. Note how the username is separated from the password by a colon. The following URL shows the username admin and the password admin123:
Https://admin:admin123@tutorialspoint.com/admin/index.htm
Using the above URL, you can authenticate administrator and if provided ID and Password are correct then administrator will have access on index.htm file available in admin directory.
You can use a telnet URL to connect to a server as follows :
Telnet://user:password@tutorialspoint.com:port/
Another important information is Web Server Port Number. By default HTTP Server runs on port number 80. But if you are running a server on any other port number then it can be provided as follows, assuming server is running on port 8080:
Https://www.tutorialspoint.com:8080/index.htm
Fragment identifiers can be used after a filename to indicate a specific part of the page that a browser should go immediately. Following is an example to reach to the top of page html_text_links.htm.
Https://www.tutorialspoint.com/html/html_text_links.htm#top
You can pass some information to the server using URL. When you use a form on a webpage, such as a search form or an online order form, the browser can append the information you supply to the URL to pass information from your browser to the server as follows −
Https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cgi-bin/search.cgi?searchTerm=HTML
Here, search Term=HTML is passed to the server where search.cgi script is used to parse this passed information and take further action.
Absolute and Relative URLs
You may address a URL in one of the following two ways:
- Absolute −An absolute URL is the complete address of a resource. For example http://www.tutorialspoint.com/html/html_text_links.htm
- Relative − A relative URL indicates where the resource is in relation to the current page. Given URL is added with the <base> element to form a complete URL. For example /html/html_text_links.htm
Reserved and Unsafe Characters
Reserved characters are those have a specific meaning within the URL. For example, the slash character separates elements of a pathname within a URL. If you need to include a slash in a URL that is not intended to be an element separator then you need to encode it as %2F:
Unsafe characters are those have no special meaning within the URL but may have a special meaning in the context the URL is written. For example, double quotes ("") delimit URL attribute values in tags. If you need to include a double quotation mark directly in a URL, you would probably confuse the browser. Instead, you should encode the double quotation mark to avoid any possible conflict.
An application layer protocol defines how the application processes running on different systems; pass the messages to each other.
- DNS stands for Domain Name System.
- DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its numerical address.
- DNS is required for the functioning of the internet.
- Each node in a tree has a domain name, and a full domain name is a sequence of symbols specified by dots.
- DNS is a service that translates the domain name into IP addresses. This allows the users of networks to utilize user-friendly names when looking for other hosts instead of remembering the IP addresses.
- For example, suppose the FTP site at EduSoft had an IP address of 132.147.165.50, most people would reach this site by specifying ftp.EduSoft.com. Therefore, the domain name is more reliable than IP address.
DNS is a TCP/IP protocol used on different platforms. The domain name space is divided into three different sections: generic domains, country domains, and inverse domain.
Generic Domains
- It defines the registered hosts according to their generic behavior.
- Each node in a tree defines the domain name, which is an index to the DNS database.
- It uses three-character labels, and these labels describe the organization type.
Label | Description |
Aero | Airlines and aerospace companies |
Biz | Businesses or firms |
Com | Commercial Organizations |
Coop | Cooperative business Organizations |
Edu | Educational institutions |
Gov | Government institutions |
Info | Information service providers |
Int | International Organizations |
Mil | Military groups |
Museum | Museum & other nonprofit organizations |
Name | Personal names |
Net | Network Support centers |
Org | Nonprofit Organizations |
Pro | Professional individual Organizations |
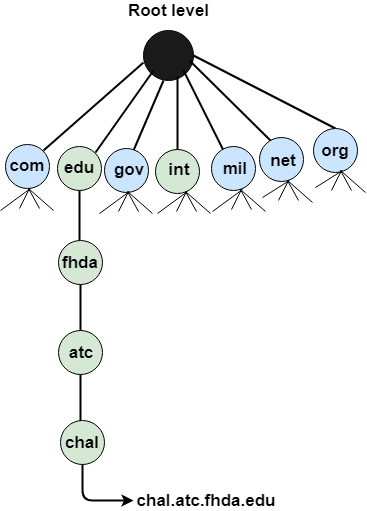
Country Domain
The format of country domain is same as a generic domain, but it uses two-character country abbreviations (e.g., us for the United States) in place of three character organizational abbreviations.
Inverse Domain
The inverse domain is used for mapping an address to a name. When the server has received a request from the client, and the server contains the files of only authorized clients. To determine whether the client is on the authorized list or not, it sends a query to the DNS server and ask for mapping an address to the name.
Working of DNS
- DNS is a client/server network communication protocol. DNS clients send requests to the. Server while DNS servers send responses to the client.
- Client requests contain a name which is converted into an IP address known as a forward DNS lookups while requests containing an IP address which is converted into a name known as reverse DNS lookups.
- DNS implements a distributed database to store the name of all the hosts available on the internet.
- If a client like a web browser sends a request containing a hostname, then a piece of software such as DNS resolver sends a request to the DNS server to obtain the IP address of a hostname. If DNS server does not contain the IP address associated with a hostname, then it forwards the request to another DNS server. If IP address has arrived at the resolver, which in turn completes the request over the internet protocol.
- Network Addressing is one of the major responsibilities of the network layer.
- Network addresses are always logical, i.e., software-based addresses.
- A host is also known as end system that has one link to the network. The boundary between the host and link is known as an interface. Therefore, the host can have only one interface.
- A router is different from the host in that it has two or more links that connect to it. When a router forwards the datagram, then it forwards the packet to one of the links. The boundary between the router and link is known as an interface, and the router can have multiple interfaces, one for each of its links. Each interface is capable of sending and receiving the IP packets, so IP requires each interface to have an address.
- Each IP address is 32 bits long, and they are represented in the form of "dot-decimal notation" where each byte is written in the decimal form, and they are separated by the period. An IP address would look like 193.32.216.9 where 193 represents the decimal notation of first 8 bits of an address, 32 represents the decimal notation of second 8 bits of an address.
Let’s understand through a simple example
.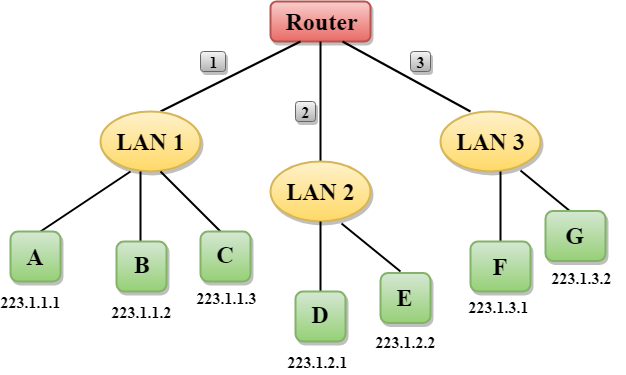
- In the above figure, a router has three interfaces labeled as 1, 2 & 3 and each router interface contains its own IP address.
- Each host contains its own interface and IP address.
- All the interfaces attached to the LAN 1 is having an IP address in the form of 223.1.1.xxx, and the interfaces attached to the LAN 2 and LAN 3 have an IP address in the form of 223.1.2.xxx and 223.1.3.xxx respectively.
- Each IP address consists of two parts. The first part (first three bytes in IP address) specifies the network and second part (last byte of an IP address) specifies the host in the network.
Classful Addressing
An IP address is 32-bit long. An IP address is divided into sub-classes:
- Class A
- Class B
- Class C
- Class D
- Class E
An ip address is divided into two parts:
- Network ID: It represents the number of networks.
- Host ID: It represents the number of hosts.
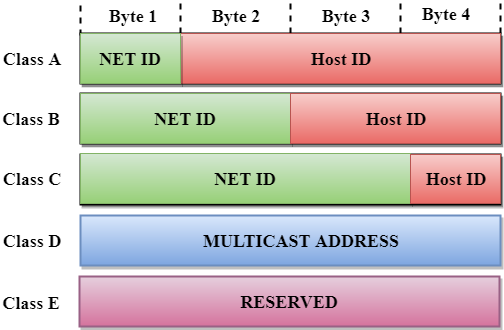
In the above diagram, we observe that each class have a specific range of IP addresses. The class of IP address is used to determine the number of bits used in a class and number of networks and hosts available in the class.
Class A
In Class A, an IP address is assigned to those networks that contain a large number of hosts.
- The network ID is 8 bits long.
- The host ID is 24 bits long.
In Class A, the first bit in higher order bits of the first octet is always set to 0 and the remaining 7 bits determine the network ID. The 24 bits determine the host ID in any network.
The total number of networks in Class A = 27 = 128 network address
The total number of hosts in Class A = 224 - 2 = 16,777,214 host address

Class B
In Class B, an IP address is assigned to those networks that range from small-sized to large-sized networks.
- The Network ID is 16 bits long.
- The Host ID is 16 bits long.
In Class B, the higher order bits of the first octet is always set to 10, and the remaining14 bits determine the network ID. The other 16 bits determine the Host ID.
The total number of networks in Class B = 214 = 16384 network address
The total number of hosts in Class B = 216 - 2 = 65534 host address

Class C
In Class C, an IP address is assigned to only small-sized networks.
- The Network ID is 24 bits long.
- The host ID is 8 bits long.
In Class C, the higher order bits of the first octet is always set to 110, and the remaining 21 bits determine the network ID. The 8 bits of the host ID determine the host in a network.
The total number of networks = 221 = 2097152 network address
The total number of hosts = 28 - 2 = 254 host address

Class D
In Class D, an IP address is reserved for multicast addresses. It does not possess subnetting. The higher order bits of the first octet is always set to 1110, and the remaining bits determines the host ID in any network.
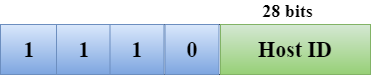
Class E
In Class E, an IP address is used for the future use or for the research and development purposes. It does not possess any subnetting. The higher order bits of the first octet is always set to 1111, and the remaining bits determines the host ID in any network.

Rules for assigning Host ID:
The Host ID is used to determine the host within any network. The Host ID is assigned based on the following rules:
- The Host ID must be unique within any network.
- The Host ID in which all the bits are set to 0 cannot be assigned as it is used to represent the network ID of the IP address.
- The Host ID in which all the bits are set to 1 cannot be assigned as it is reserved for the multicast address.
Rules for assigning Network ID:
If the hosts are located within the same local network, then they are assigned with the same network ID. The following are the rules for assigning Network ID:
- The network ID cannot start with 127 as 127 is used by Class A.
- The Network ID in which all the bits are set to 0 cannot be assigned as it is used to specify a particular host on the local network.
- The Network ID in which all the bits are set to 1 cannot be assigned as it is reserved for the multicast address.
Classful Network Architecture
Class | Higher bits | NET ID bits | HOST ID bits | No.of networks | No.of hosts per network | Range |
A | 0 | 8 | 24 | 27 | 224 | 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 |
B | 10 | 16 | 16 | 214 | 216 | 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 |
C | 110 | 24 | 8 | 221 | 28 | 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 |
D | 1110 | Not Defined | Not Defined | Not Defined | Not Defined | 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 |
E | 1111 | Not Defined | Not Defined | Not Defined | Not Defined | 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 |
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity.
Wi-Fi It is based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards and is primarily a local area networking (LAN) technology designed to provide in-building broadband coverage.
Current Wi-Fi systems support a peak physical-layer data rate of 54 Mbps and typically provide indoor coverage over a distance of 100 feet.
Wi-Fi has become the de facto standard for last mile broadband connectivity in homes, offices, and public hotspot locations. Systems can typically provide a coverage range of only about 1,000 feet from the access point.

Wi-Fi offers remarkably higher peak data rates than do 3G systems, primarily since it operates over a larger 20 MHz bandwidth, but Wi-Fi systems are not designed to support high-speed mobility.
One significant advantage of Wi-Fi over WiMAX and 3G is its wide availability of terminal devices. A vast majority of laptops shipped today have a built-in Wi-Fi interface. Wi-Fi interfaces are now also being built into a variety of devices, including personal data assistants (PDAs), cordless phones, and cellular phones, cameras, and media players.
Wi-Fi is Half Duplex
All Wi-Fi networks are contention-based TDD systems, where the access point and the mobile stations all vie for use of the same channel. Because of the shared media operation, all Wi-Fi networks are half duplex.
There are equipment vendors who market WiFi mesh configurations, but those implementations incorporate technologies that are not defined in the standards.
Channel Bandwidth
The WiFi standards define a fixed channel bandwidth of 25 MHz for 802.11b and 20 MHz for either 802.11a or g networks.
Wi-Fi - Working Concepts
Radio Signals
Radio Signals are the keys, which make WiFi networking possible. These radio signals transmitted from WiFi antennas are picked up by WiFi receivers, such as computers and cell phones that are equipped with WiFi cards. Whenever, a computer receives any of the signals within the range of a WiFi network, which is usually 300 — 500 feet for antennas, the WiFi card reads the signals and thus creates an internet connection between the user and the network without the use of a cord.

Access points, consisting of antennas and routers, are the main source that transmit and receive radio waves. Antennas work stronger and have a longer radio transmission with a radius of 300-500 feet, which are used in public areas while the weaker yet effective router is more suitable for homes with a radio transmission of 100-150 feet.
Wi-Fi Cards
You can think of Wi-Fi cards as being invisible cords that connect your computer to the antenna for a direct connection to the internet.

Wi-Fi cards can be external or internal. If a Wi-Fi card is not installed in your computer, then you may purchase a USB antenna attachment and have it externally connect to your USB port, or have an antenna-equipped expansion card installed directly to the computer (as shown in the figure given above). For laptops, this card will be a PCMCIA card which you insert to the PCMCIA slot on the laptop.
Wi-Fi Hotspots
A Wi-Fi hotspot is created by installing an access point to an internet connection. The access point transmits a wireless signal over a short distance. It typically covers around 300 feet. When a Wi-Fi enabled device such as a Pocket PC encounters a hotspot, the device can then connect to that network wirelessly.
Most hotspots are located in places that are readily accessible to the public such as airports, coffee shops, hotels, book stores, and campus environments. 802.11b is the most common specification for hotspots worldwide. The 802.11g standard is backwards compatible with .11b but .11a uses a different frequency range and requires separate hardware such as an a, a/g, or a/b/g adapter. The largest public WiFi networks are provided by private internet service providers (ISPs); they charge a fee to the users who want to access the internet.

Hotspots are increasingly developing around the world. In fact, T-Mobile USA controls more than 4,100 hotspots located in public locations such as Starbucks, Borders, Kinko's, and the airline clubs of Delta, United, and US Airways. Even select McDonald's restaurants now feature Wi-Fi hotspot access.
Any notebook computer with integrated wireless, a wireless adapter attached to the motherboard by the manufacturer, or a wireless adapter such as a PCMCIA card can access a wireless network. Furthermore, all Pocket PCs or Palm units with Compact Flash, SD I/O support, or built-in Wi-Fi, can access hotspots.
Some Hotspots require WEP key to connect, which is considered as private and secure. As for open connections, anyone with a Wi-Fi card can have access to that hotspot. So in order to have internet access under WEP, the user must input the WEP key code.
Wireless Communication - Bluetooth
Bluetooth wireless technology is a short range communications technology intended to replace the cables connecting portable unit and maintaining high levels of security. Bluetooth technology is based on Ad-hoc technology also known as Ad-hoc Pico nets, which is a local area network with a very limited coverage.
History of Bluetooth
WLAN technology enables device connectivity to infrastructure based services through a wireless carrier provider. The need for personal devices to communicate wirelessly with one another without an established infrastructure has led to the emergence of Personal Area Networks (PANs).
- Ericsson's Bluetooth project in 1994 defines the standard for PANs to enable communication between mobile phones using low power and low cost radio interfaces.
- In May 1988, Companies such as IBM, Intel, Nokia and Toshiba joined Ericsson to form the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) whose aim was to develop a defacto standard for PANs.
- IEEE has approved a Bluetooth based standard named IEEE 802.15.1 for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs). IEEE standard covers MAC and Physical layer applications.
Bluetooth specification details the entire protocol stack. Bluetooth employs Radio Frequency (RF) for communication. It makes use of frequency modulation to generate radio waves in the ISM band.

The usage of Bluetooth has widely increased for its special features.
- Bluetooth offers a uniform structure for a wide range of devices to connect and communicate with each other.
- Bluetooth technology has achieved global acceptance such that any Bluetooth enabled device, almost everywhere in the world, can be connected with Bluetooth enabled devices.
- Low power consumption of Bluetooth technology and an offered range of up to ten meters has paved the way for several usage models.
- Bluetooth offers interactive conference by establishing an adhoc network of laptops.
- Bluetooth usage model includes cordless computer, intercom, cordless phone and mobile phones.
Piconets and Scatternets
Bluetooth enabled electronic devices connect and communicate wirelessly through short range devices known as Piconets. Bluetooth devices exist in small ad-hoc configurations with the ability to act either as master or slave the specification allows a mechanism for master and slave to switch their roles. Point to point configuration with one master and one slave is the simplest configuration.
When more than two Bluetooth devices communicate with one another, this is called a PICONET. A Pico net can contain up to seven slaves clustered around a single master. The device that initializes establishment of the Piconet becomes the master.
The master is responsible for transmission control by dividing the network into a series of time slots amongst the network members, as a part of time division multiplexing scheme which is shown below.
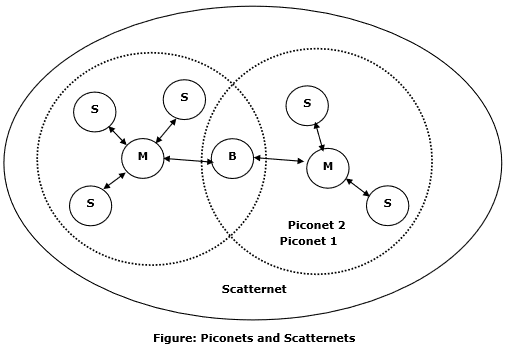
The features of Piconets are as follows –
- Within a Piconet, the timing of various devices and the frequency hopping sequence of individual devices is determined by the clock and unique 48-bit address of master.
- Each device can communicate simultaneously with up to seven other devices within a single Piconet.
- Each device can communicate with several piconets simultaneously.
- Piconets are established dynamically and automatically as Bluetooth enabled devices enter and leave piconets.
- There is no direct connection between the slaves and all the connections are essentially master-to-slave or slave-to-master.
- Slaves are allowed to transmit once these have been polled by the master.
- Transmission starts in the slave-to-master time slot immediately following a polling packet from the master.
- A device can be a member of two or more piconets, jumping from one piconet to another by adjusting the transmission regime-timing and frequency hopping sequence dictated by the master device of the second piconet.
- It can be a slave in one piconet and master in another. It however cannot be a master in more than once piconet.
- Devices resident in adjacent piconets provide a bridge to support inner-piconet connections, allowing assemblies of linked piconets to form a physically extensible communication infrastructure known as Scatternet.
Spectrum
Bluetooth technology operates in the unlicensed industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band at 2.4 to 2.485 GHZ, using a spread spectrum hopping, full-duplex signal at a nominal rate of 1600 hops/sec. The 2.4 GHZ ISM band is available and unlicensed in most countries.
Range
Bluetooth operating range depends on the device Class 3 radios have a range of up to 1 meter or 3 feet Class 2 radios are most commonly found in mobile devices have a range of 10 meters or 30 feet Class 1 radios are used primarily in industrial use cases have a range of 100 meters or 300 feet.
Data rate
Bluetooth supports 1Mbps data rate for version 1.2 and 3Mbps data rate for Version 2.0 combined with Error Data Rate.
What is Internet?
The internet is a global system that uses TCP/IP protocol suite to link various types of electric devices worldwide. The internet is a collection of interconnected devices that are spread across the globe. The internet is a network of networks which consist of public, private, sales, finance, academic, business, and government networks. The internet is a type of network and called a network of networks.
What is Intranet?
An intranet is a private network which gives employees in a company the ability to organise information, manage documents, shares calendars and to-do list. It normally runs in a client/server environment in a local area network.
In Intranet, every computer is connected via the LAN and has something known as an MAC address. It is a number that allows you to identify the place where the computer is located.
KEY DIFFERENCES:
- The Internet is a wide network of computers that is available to all whereas Intranet is a network of computers designed for a certain group of users.
- Internet is a public network and Intranet is a private network.
- Internet contains various source of information while Intranet only contains group-specific information.
- Number of internet users are very high but the number of users of Intranet is limited.
- Anyone can access the internet while Intranet is accessible only by the organization employees or admin who have login details.
How Does Internet Works?
The Internet is a network build by the interconnection of a large number of computer networks that is not owned by any entity. It is not admin by any administration any person in the world can join it.
TCP/IP protocol is the main impelling agent for the internet used by the connected networks apart from other protocols like FTP, HTTP, and SMTP.
How Does Intranet Works?
An intranet is a private computer network that uses internet protocols, network connectivity to access and share an enterprise information and operations securely with its staff.
It uses the same client-server model that runs on the TCP/IP protocol suite, which is very much similar to the internet. Information within an organization can be retrieved with the help of browsers. It could also work without the need to installing special software on the user's machines.
Features of the Internet
Here are some important features of the Internet:
- A global network which connects millions of computers
- The internet is decentralized
- Every computer over the internet is independent
- There are various ways to access the internet
Features of Intranet
Here, are important features of Intranet
- Intranet is fast and accurate.
- Most website with large graphical images, videos, and sound, process fast on Intranet
- Your firewall protects it from external threats.
- It is easy to monitor with your organization
- Easy communication across the company from all levels
- Helps to share ideas and discussions
Difference between Internet and Intranet
Here, are important differences between Internet and Intranet:
Internet | Intranet |
The Internet is a wide network of computers and is available to all. | Intranet is a network of computers designed for a certain group of users. |
Internet contains a large number of intranets. | Intranet can be accessed from the Internet with specific restrictions. |
Number of internet users are very high. | Number of users is limited. |
Internet contains various source of information. | Intranet only contains group-specific information. |
Anyone can access the internet | Accessible only by the organization employees or admin who have login details. |
It is not as safe as compared to intranet | Safe and secure network. |
It is a public network. | It is a private network. |
Application of Internet
Here, are important applications of Internet
- Download programs and files
- To send and receive E-Mails
- Voice and video Conferencing
- E-Commerce
- File sharing
- Browsing various types of Information
- Search the web addresses for access through the search engine and chatting
Application of Intranet
Here, are important applications of internet
- Sharing the detail of company rules/policies & regulations
- Access employee database
- Access product & customer data
- Sharing some common information
- Intranet also use for launching personal or department-specific home pages
- Submission of reports
- Corporate telephone directories
Advantages of Internet
Here, are pros/benefits of using the Internet
- The Internet is a network of computers at different locations around the world.
- Allows you to send an email message from every location
- Helps you to send or receive files between different computers
- Using the Internet, you can participate in discussion groups, such as mailing lists and newsgroups.
- It allows all small, medium, and large size businesses to sell their products with small investments.
- It makes information available worldwide
- It helps you updated with the latest news and technologies.
- It helps us meet people with the same interests as communities, forums, chats, websites, etc.
Advantages of Intranet
Here, are pros/benefits of Intranet:
- Fast, easy, low-cost to implement
- Based on open standards
- Allows connectivity with other systems
- Access to internal and external information
- Improves communication
Disadvantages of Internet
Here, are important cons/drawback of using the internet:
- It allows everybody to speak about everything without any limitations or censorship. That could be a bad influence on impressionable minds.
- The search engines may display some fake news results.
- Internet could replace face to face collaborations and make us lose the human touch.
- Working or on the internet is surely tiring.
- The Internet makes us lazier – as for common things like search the nearest restaurant or finding the best hotel.
Disadvantages of Intranet
Here, are drawbacks/cons of Intranet
- Threat of sharing information and the loss of control
- Unauthorized access
- Limited bandwidth for the business
- Information overload lowers productivity
- Hidden or unknown complexity and costs
The Internet has many important applications. Of the various services available via the Internet, the three most important are e-mail, web browsing, and peer-to-peer services. E-mail, also known as electronic mail, is the most widely used and successful of Internet applications. Web browsing is the application that had the greatest influence in dramatic expansion of the Internet and its use during the 1990s. Peer-to-peer networking is the newest of these three Internet applications, and also the most controversial, because its uses have created problems related to the access and use of copyrighted materials.
Whether judged by volume, popularity, or impact, e-mail has been and continues to be the principal Internet application. This is despite the fact that the underlying technologies have not been altered significantly since the early 1980s. In recent years, the continuing rapid growth in the use and volume of e-mail has been fuelled by two factors. The first is the increasing numbers of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offering this service, and secondly, because the number of physical devices capable of supporting e-mail has grown to include highly portable devices such as personal digital assistants (PDAs) and cellular telephones.
The volume of e-mail also continues to increase because there are more users, and because users now have the ability to attach documents of various types to e-mail messages. While this has long been possible, the formulation of Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) and its adoption by software developers has made it much easier to send and receive attachments, including word-processed documents, spreadsheets, and graphics. The result is that the volume of traffic generated by e-mail, as measured in terms of the number of data packets moving across the network, has increased dramatically in recent years, contributing significantly to network congestion.
E-mail has become an important part of personal communications for hundreds of millions of people, many of whom have replaced it for letters or telephone calls. In business, e-mail has become an important advertising medium, particularly in instances where the demand for products and services is time sensitive. For example, tickets for an upcoming sporting event are marketed by sending fans an e-mail message with information about availability and prices of the tickets. In addition, e-mail serves, less obviously, as the basis for some of the more important collaborative applications that have been developed, most notably Lotus Notes.
In the near future, voice-driven applications will play a much larger role on the Internet, and e-mail is sure to be one of the areas in which voice-driven applications will emerge most rapidly. E-mail and voice mail will be integrated, and in the process it seems likely that new models for Internet- based messaging will emerge.
Synchronous communication, in the form of the highly popular "instant messaging," may be a precursor of the messaging models of the near future. Currently epitomized by AOL Instant Messenger and Microsoft's Windows Messenger, instant messaging applications generally allow users to share various types of files (including images, sounds, URLs ), stream content, and use the Internet as a medium for telephony, as well as exchanging messages with other users in real time and participating in online chat rooms.
Web Browsing
The web browser is another Internet application of critical importance. Unlike e-mail, which was developed and then standardized in the early, non-commercial days of the Internet, the web browser was developed in a highly commercialized environment dominated by such corporations as Microsoft and Netscape, and heavily influenced by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). While Microsoft and Netscape have played the most obvious parts in the development of the web browser, particularly from the public perspective, the highly influential role of the W3C may be the most significant in the long term.
Founded in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the original architect of the web, the goal of the W3C has been to develop interoperable technologies that lead the web to its full potential as a forum for communication, collaboration, and commerce. What the W3C has been able to do successfully is to develop and promote the adoption of new, open standards for web-based documents. These standards have been designed to make web documents more expressive (Cascading Stylesheets), to provide standardized labeling so that users have a more explicit sense of the content of documents (Platform for Internet Content Selection, or PICS), and to create the basis for more interactive designs (the Extensible Markup Language, or XML ). Looking ahead, a principal goal of the W3C is to develop capabilities that are in accordance with Berners-Lee's belief that the web should be a highly collaborative information space.
Microsoft and Netscape dominate the market for web browsers, with Microsoft's Internet Explorer holding about three-quarters of the market, and Netscape holding all but a small fraction of the balance. During the first few years of web growth, the competition between Microsoft and Netscape for the browser market was fierce, and both companies invested heavily in the development of their respective browsers. Changes in business conditions toward the end of the 1990s and growing interest in new models of networked information exchange caused each company to focus less intensely on the development of web browsers, resulting in a marked slowing of their development and an increasing disparity between the standards being developed by W3C and the support offered by Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
Now, the future of the web browser may be short-lived, as standards developers and programmers elaborate the basis for network-aware applications that eliminate the need for the all-purpose browser. It is expected that as protocols such as XML and the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) grow more sophisticated in design and functionality, an end user's interactions with the web will be framed largely by desktop applications called in the services of specific types of documents called from remote sources.
The open source model has important implications for the future development of web browsers. Because open source versions of Netscape have been developed on a modular basis, and because the source code is available with few constraints on its use, new or improved services can be added quickly and with relative ease. In addition, open source development has accelerated efforts to integrate web browsers and file managers. These efforts, which are aimed at reducing functional distinctions between local and network-accessible resources, may be viewed as an important element in the development of the "seamless" information space that Berners-Lee envisions for the future of the web.
Peer-To-Peer Computing
One of the fastest growing, most controversial, and potentially most important areas of Internet applications is peer-to-peer (P2P) networking. Peer-to-peer networking is based on the sharing of physical resources, such as hard drives, processing cycles, and individual files among computers and other intelligent devices. Unlike client-server networking, where some computers are dedicated to serving other computers, each computer in peer-to-peer networking has equivalent capabilities and responsibilities.
Internet-based peer-to-peer applications position the desktop at the center of a computing matrix, usually on the basis of "cross-network" protocols such as the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) or XML-RPC (Remote Procedure Calling), thus enabling users to participate in the Internet more interactively.
There are two basic P2P models in use today. The first model is based on a central host computer that coordinates the exchange of files by indexing the files available across a network of peer computers. This model has been highly controversial because it has been employed widely to support the unlicensed exchange of commercial sound recordings, software, and other copyrighted materials. Under the second model, which may prove ultimately to be far more important, peer-to-peer applications aggregate and use otherwise idle resources residing on low-end devices to support high-demand computations. For example, a specially designed screensaver running on a networked computer may be employed to process astronomical or medical data.
Creating an e-mail account
To create an e-mail account in cPanel, follow these steps:
- In the Email section of the cPanel home screen, click Email Accounts.
- Click Create. A new interface will appear.
- From the Domain menu, select the domain on which you wish to create the email account.
If the desired domain does not appear in the menu, click Manage Subdomains or Manage Aliases to check your account's domain configuration. The domain menu does not appear if only one domain is present in the account.
4. Enter a new email address in the Username text box.
You cannot enter cpanel as an account name when you create an email account.
5. In the Security section, perform either of the following actions:
-Select Provide alternate email and enter an email address for the system to send a password configuration link.
-Select Set password now.and enter a password in the Password text box.
You can click and cPanel generates a random, strong password for you.
6. In the Storage Space section, enter a custom Mailbox Quota storage size or select Unlimited to set the amount of disk space that the account may use to store email.
7. To send a message with client configuration instructions to the account, select the Send welcome email with instructions to set up a mail client check box.
If you selected Provide alternate email in the Security section, the system will send the instructions to that alternate email address. Otherwise, the user can access the welcome message via Webmail.
8. Select Stay on this page after I click Create to create another email account after you create this one (if necessary.) Otherwise, click Create to create the account and return to the Email Accounts interface.
Modifying an e-mail account
To modify an e-mail account in cPanel, follow these steps:
- In the Email section of the cPanel home screen, click Email Accounts.
- Click the setting that you want to change for the account:
- To change the account's password, click Manage. Then type the new password into the New Password field under Security.
For security reasons, you should occasionally change e-mail account passwords. You should always change an e-mail account password if you think an unauthorized user has accessed the account. When you change an e-mail account password, make sure that you also update the password in your e-mail client application (if you are using one). Otherwise, you will not be able to access the account.
- To change the account's quota, click Manage. Then allocate the storage allowed under Allocated Storage Space under Storage.
- To access the account's webmail, click Check Email.
Deleting an e-mail account
You can delete an e-mail account when you no longer need it. However, you cannot delete your default e-mail account.
Deleting an e-mail account deletes all e-mail currently in the account, including new messages, sent messages, and so on. Make sure that you download any e-mail that you want to retain before you delete an account. After you delete an account, the information is unrecoverable.
To delete an e-mail account in cPanel, follow these steps:
- In the Email section of the cPanel home screen, click Email Accounts.
- Locate the e-mail account that you want to delete, and then click Manage.
- Navigate to the bottom of the page to Delete Email Account. Click Delete Email Account to confirm.
What is good email Netiquette?
Proper Internet etiquette is often referred to as Netiquette. Students and teachers can avoid embarrassing situations by adhering to some simple guidelines for electronic communication. The following is a list of standards for Netiquette:
- Always identify yourself and keep your messages brief and to the point. Remember that not everyone accesses email from a computer these days. Many people use portable devices such as cell phones to quickly check their email while they are away from a computer. They will appreciate not having to wait for the long messages to download.
- Include a concise subject line with all of your emails. This will allow the recipient to quickly scan their mailbox to see if the message is something they need to act on or “junk” email.
- Let your recipient know right away if any action is required of them. The easiest way to do this is by marking emails that do not require a reply or other action as FYI emails. This can be indicated in the subject line.
- Avoid “flaming” (inflammatory or antagonistic criticism) or sending insulting, abusive, or threatening remarks. There is no “unsend” option in email. Once a “flame war” starts, it tends to escalate quickly, often leading to hurt feelings and tension among those involved. A good rule to follow is to ask yourself “would I say this to the person’s face?” If you wouldn’t feel comfortable saying it to their face then it’s probably not appropriate for email either.
- Avoid using all capital letters in a message. This is perceived as SHOUTING and may cause hard feelings.
- Remember that email is not necessarily private. Your messages can be forwarded to many people without your knowledge. Before sending a message, read it over, double check the recipient(s) and make sure it would not become an embarrassment if it were forwarded to others not on your recipient list.
- Do not spam others. Spam is the practice of sending unsolicited email messages in bulk or overloading someone’s mailbox or server with messages. Spamming may be as simple as forwarding chain letters. Forwarding these chain letters not only creates work for the people on the other end, who have to spend more time going through their messages to separate the good messages from spam, but it also generates unnecessary network traffic.
- Include a signature that has your phone number or if you are sending internal email, your extension. This will make it easier for your recipient to contact you if they need to speak to you in person. Avoid recalling messages. Take the time to really determine if a message is necessary or not before sending it in the first place. By the time you send out a recall for your messages they have already arrived in the recipients’ mailboxes and they have probably already been read. The recall notice will just be one more message that has to be deleted.
What is Instant Messaging?
Instant Messaging, also known as IM, has soared in popularity in recent years. In fact, the number of worldwide instant messaging accounts Despite so many using instant messaging in their everyday lives, many would struggle to answer the question of what exactly IM is. Answers to this question would not only have a wide range, but fail to capture all of the different elements and uses of IM.
The answer to this question is important, though, as it can provide good insights into the potential uses for IM both personally and in the business world.
Direct Online Communication
At its core, instant messaging is a real-time online communication method used to connect two or more people.
Instant messaging software is best known for its direct peer to peer connections, such as the messaging pioneered by the now-defunct AOL Instant Messenger (AIM). AIM, and other similar programs, initially allowed two ‘contacts’ to directly send and receive real-time text-based messages as long as they were both online and logged on.
Today, when people think of instant messaging they tend to stop at peer-to-peer chat, thus viewing IM solely as a vehicle for sending direct messages.
In the past decade, however, IM has expanded to include a variety of communication features, not just for personal use, but for business environments, too. This growth has brought a range of benefits to both individuals and businesses, like greater transparency and networking opportunities.
A Brief History of Instant Messaging
Who could forget the days of buddy lists on America Online (AOL) or even ICQ (I Seek You) before that? Other platforms like Yahoo Messenger and Microsoft’s MSN brought instant messaging into the mainstream in the 90s.
You’d be forgiven, however, for not knowing that instant messaging systems date back to the 1960s. MIT’s pioneering Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) allowed up to 30 users to log in and send messages to each other, all the way back in 1961!
While rudimentary messaging programs like CTSS connected universities and research labs, those early days have since morphed into an industry spanning myriad platforms, social media, mobile IM, business environments, billions of users, and even more instant messages.
Real-Time Communication Features
Today’s instant messaging couldn’t be further from the original CTSS, or even the groundbreaking platforms of the 90s. IM has evolved to include a range of real-time communication features with implications for both personal and business use.
Consumer-grade instant messengers like WhatsApp, Viber, and Telegram have exploded in popularity. Thanks to their mobile capabilities, users can chat and share media and content from the palm of their hands.
One of the most common features of modern-day IM is the ability to chat in groups. Group chat, a shared space for communication between more than two users, enhances communication in situations – like the workplace, for instance – which require the exchange of information among multiple individuals. Just remember to consider this tips when chatting in groups.
By way of Voice over Internet Protocol technology, voice and video capabilities facilitate more personal communication. Audible and visual interactions can serve a variety of use cases, like empowering more dynamic meetings for remote workers.
For both consumer and enterprise-grade instant messengers, file sharing and peer-to-peer file transfers facilitate the distribution of large media and content files, albeit via different routes and technologies.
Instant Messaging Helps You Work Smarter
Today’s instant messaging isn’t just about the individual power to communicate quickly and conveniently in real time. It also serves to boost the work environment, from the ability of a team to communicate efficiently, all the way down to the workplace culture.
“Powerful tools are giving leaders deeper understanding of their organization’s culture and work dynamics. They also provide a way to get ahead of issues that could handicap success.”
Carefully tailor internal communication channels for feedback or team-building. Doing so better aligns team communication and helps foster more wholesome connections – boosting effectiveness and driving results.
All in one communication and collaboration platforms enhance internal processes and productivity while helping you streamline operating procedures and overhead.
Tools like screen-sharing, instant screenshot, virtual whiteboards, and unlimited size file transfers transform how teams approach and resolve issues from collaboration on copy and content to IT and tech support.
What’s more, all-in-one platforms allow you to:
- Consolidate the software in your arsenal;
- Reduce instances of multitasking;
- And cut back on costly applications and upgrades
Despite their prevalence, many free instant messengers are fraught with privacy and security issues, bugs and ads and solicitations. IM for business, on the other hand, often offers more Robust security protocol.
Private team networks allow teams to communicate over an enterprise-exclusive network. Peer-to-peer channels, end-to-end encryption and anti-virus and malware integration facilitate more secure chat while bypassing potentially vulnerable or malicious third-party servers.
What is Skype?
Skype is software that enables the world's conversations. Millions of individuals and businesses use Skype to make free video and voice one-to-one and group calls, send instant messages and share files with other people on Skype. You can use Skype on whatever works best for you – on your mobile, computer or tablet.
Skype is free to download and easy to use.
If you pay a little, you can do more – like call phones and send SMS. You can pay as you go or buy a subscription, whatever works for you. And in the world of business, this means you can bring your entire ecosystem of workers, partners and customers together to get things done.
Try Skype today and start adding your friends, family and colleagues. They won’t be hard to find; hundreds of millions of people are already using Skype to do all sorts of things together.
What is Messenger Service?
A Microsoft Windows NT and Windows 2000 service that sends and receives pop-up messages. These messages can be generated by the Alerter service, which generates Windows NT alerts when conditions warrant it. Or, an administrator can generate pop-up messages in one of the following ways:
- In Server Manager, choosing Send Message from the Computer menu to send a message to all users currently connected to the selected server
- Using the Net Send command at the Windows NT command prompt
Atomi Smart 12-Cup Coffee Maker
Can't function without a first cup of coffee? No problem. Atomi's Smart Coffee Maker allows you to schedule or adjust brew time right from your smartphone, Alexa speaker, or Google Assistant whenever you think of it—while entering an early meeting into your calendar or setting your phone alarm just before sleep. Set up brewing times in advance, and you can have a fresh brew ready and waiting
O-Cedar O-Duster Robotic Floor Cleaner
Meet the bot that may make dusting floors your new favourite chore: the O-Duster Robotic Floor Cleaner. Charge its batteries, and watch it navigate your hard floors on autospin, gathering up all the lint, dust, and hair on an attached electrostatic cloth. All you’ll need to do is recharge your new robot friend and swap out the disposable cloths as needed.
IDevices Kitchen Thermometer
Finally, there’s a way to get a precise temperature read on your turkey without having to hover outside the oven window for half the afternoon. The iDevices Kitchen Thermometer allows you to shift your focus to the other parts of the meal, confident that it will alert your smart phone when the bird is thoroughly cooked. An additional LED-screened device sits on the countertop or mounts magnetically to your oven, letting you monitor the temperature whenever you pass by.
Crock-Pot® 6-Quart. Smart Slow Cooker with Alexa
As if slow cooking couldn't get an easier, this smarter Crock-Pot puts control in your hands and your voice via an integration with any Alexa-enabled device. Shift from high to warm to off with the tap of your finger or a voice command and dinner will be ready with minimal effort.
Click & Grow Indoor Smart Herb Garden
If you can operate a Keurig coffee machine, you can definitely grow kitchen herbs with the Click & Grow planter—no matter your previous track record with plants. Each kit contains everything you need, including seed cartridges filled with nutrients and a plant light to boost growth. Your job is simple: Fill the water reservoir. The planter will take care of the rest.
Smartphones are the friendly gadgets which have made everything reachable through a touch. They have occupied such a huge place in our daily lives that it is no wonder that for most of us, a smartphone is the first thing we look at in the morning and it is the last thing we see before going to bed.
Now, there will certainly be some advantages and a few disadvantages while using any electronic gadget. Let’s observe them:
Advantages
- Keep your loved ones in touch, either through calls, text or images, .which express the feeling in a sweet and amusing way.
- You may know where you are and find easy ways and routes to go anywhere, especially in an unknown place.
- You can make the world listen to your voice in a touch.
- You can spend your time wisely reading the news or doing some official work.
- Can entertain yourself with games, music or movies.
- Can always be available socially.
- Can avail the Customer service offers to be easily accessible.
- Food and groceries can be ordered online.
- Email and Banking become easy.
- Endless apps are available to make your dreams come true.
Disadvantages
- The electromagnetic radiation will be high because of the heavy internet usage and might lead to health problems such as a brain tumor and Skin Cancer.
- The HEV light emitted from the screen of a smartphone leads to severe eye-strain during long-time use and would slowly damage the retina.
- Even many psychological issues such as loneliness, being suspicious all the time, feeling self-centered etc. are caused by using a smartphone and being online, for most of the time.
- Spending most of the time on your phone creates neck problems and sleep deprivation.
- Exposure to unwanted things on the internet affects a child’s growth mentally and even physically.
- As too much of anything is good for nothing, depending on a smartphone for everything makes you addicted.
- Being online for most of the time keeps you away from having real experiences and having real friends, to share your mind.
- Having checked all the time for online security, you start losing trust in people around you.
- Forwarding the messages and sharing the videos online regarding humanity, one might forget the real meaning behind it.
- With all these things around, the family life gets affected.
- Few of them get really addicted that they text or watch videos while on roads and talk on the phone while driving, which causes serious trouble as being busy makes you react slow.
- Chances of losing money due to fraudulence on the internet.
- Usage of Apps by not having complete awareness might lead to the leakage of personal information, which could be really dangerous.
- With every emerging new model, there come new features which are really tempting to use and you may get into the crazy whirlpool of going for new models always.
However, there are two sides of a coin. No harm can be caused by anything if you do not get indulged into it blindly. Wiseness lies where you take the positive and helpful aspects of anything and leave the negative and unnecessary attachment to that. One should be careful and should not get involved completely into something. Hence, being aware of the pros and cons and having self-control could save you from many disasters, which is really necessary.
4K smart television gadgets
A whopping number of new TVs claim to be Smart TVs in some way or another, no matter how stupid the built-in “smart” features really are. In fact, Smart TV is such a vague term that just about any TV with built-in Internet connectivity and a couple of incredibly lame apps can boldly claim the label. Thankfully, there are also quite a few highly deserving Smart TVs with amazing capabilities on store shelves, too. Of course, just because this or that function is “incredible” doesn’t mean that you’re going to use it. The best Smart TV for most people lies somewhere between the two extremes of dim witted on one end and misunderstood genius on the other. If you’re shopping for a new Smart TV, here’s a list of 10 of the most important, must-have features.
1. Fast User Interface
One of the most must-have of the must-have features in a Smart TV is one that you won’t give a second thought—or a second’s thought to—if you already have it: speed. If you have a Blu-ray Disc player, you know how annoying it is to wait for what seems like an eternity for the disc’s main menu to load and finally appear on your screen. Likewise, some Smart TVs take eons (okay, maybe it’s only decades) to switch from one app, function, or input to another. A blazingly fast interface that lets you do what you want to do almost before you know you want to do it is a must if you don’t want to find yourself endlessly irritated by how sluggish your Smart TV is.
2. Streaming Video Services
If all you do is watch movies rented from a red kiosk or tune in to the local nightly news broadcast, then you don’t need a Smart TV. Frankly, if that’s the case, you need to get a life. The other option is to get a Smart TV and sign up for at least one (but probably more) online streaming video service, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Instant, Vudu, Hulu Plus, Crackle, or even Funny or Die. There’s also Showtime Anytime, HBO Now, and CBS All Access. If you have a fast Internet connection, there are more movies and TV shows to stream than you’ll ever have time to watch—but, you can only stream them if your Smart TV has an app(s) that supports the online service(s) you want to use. Sling TV for example, is an affordable alternative to your cable subscription, but it might as well not exist if your TV isn’t compatible with it.
3. 4K UHD Streaming Video
At the moment, there isn’t a deluge of 4K Ultra HD content available to stream from the Internet. There is a bit, though, mainly from Netflix, Amazon Instant, M-GO, and a few others. While it might seem logical that owning a 4K UHD Smart TV with a subscription to one of these services would automatically provide access to their particular 4K UHD selections, it doesn’t. Your Smart TV has to be compatible with that specific service. Not all TVs are, nor are all the services, and vice versa, and…confused? If 4K UHD streaming is important to you, check with the websites for these services to see which Smart TVs are compatible—and make sure you have a fast Internet connection. (Netflix recommends “at least 25 megabits per second to stream Ultra HD titles.”)
4. Music Streaming
Listening to music might not be the first activity you think about when considering a new Smart TV, but—if it’s available on your TV—you’ll be surprised at how much you’ll use it, especially if the TV is in a kitchen, a bedroom, or some other location in the house where you don’t already have an audio system. As with streaming video services, though, not all Smart TVs have apps for some of the most popular services, such as Pandora, Spotify, iHeartRadio, and TuneIn. Check the Smart TV’s app store to see if your favorite music streaming service is available. The speakers in nearly every TV—smart, average, or dumb as a brick—sound weak and wimpy, however, so we highly recommend using a set of bookshelf speakers or a decent sound bar with the TV to make the experience more enjoyable.
5. Media Player
It’s much more pleasant to look at family photos on a 50- or 60-inch screen in your living room instead of scrunching everyone together in front of a tiny computer screen—or, worse, passing around a smartphone. A basic DLNA-compliant media player can provide access to all of the digital videos, photos, and music located on a network-attached storage device or computer on your home network. More advanced media players and servers, such as Plex, can organize, categorize, and convert your content, making it super-easy to access all of your digital stuff.
6. Recommendation Engine
Netflix does it. Amazon does it. Even friends do it. “If you liked this,” they say, “then you might like…” or, “Other people who bought this also bought…” So why shouldn’t your Smart TV offer suggestions, too? It’s true that sometimes recommendations from these single-minded algorithms can be a little strange and creepy—especially when multiple people get swirled together under the same profile—but more often than not they can provide some very useful suggestions when the specific movie or TV show you want isn’t available to stream.
7. Universal Search
One blessing of the Internet is that we have so many choices of online streaming services, but it’s also a curse because finding what you want to watch is often a daunting, time-consuming task of searching through each service one-by-one. Most Smart TVs have a built-in search engine or “guide” that will look for the particular movie, TV show, actor, genre, or whatever. They’re not all equally as thorough, though. While some look virtually everywhere, others only peruse certain services. If you want a really smart Smart TV, get one with the widest search capabilities.
8. Games
You can use your Smart TV to watch movies and listen to music, so why not use it to play games, too? Many Smart TVs have game apps, which is okay as long as you like playing Solitaire or Angry Birds. But gaming is getting more sophisticated on some of the newest Smart TVs. Several models from Sony and Samsung, for example, can access the PlayStation Now game streaming service. Take note: These require using a Sony Dualshock 3 or Dualshock 4 controller.
9. Transfer Smartphone Content to the Smart TV
Different companies call it different things, such as “flinging,” “casting,” “second screen experience,” or “swipe & share.” Whatever the name, the ability to send content from your smartphone or tablet to your TV can be priceless. (Well, maybe not priceless, but extremely valuable, at least.) With a compatible app on your phone or tablet, you can display photos, play videos, and transfer streaming content wirelessly from your smart device to the Smart TV. It’s not limited to just your smart device, either, so friends and family can “fling” their photos and videos to your Smart TV if their devices and apps are compatible.
10. App Store
Your Smart TV may be the smartest in the world today, but technology doesn’t stand still. It’s important that your Smart TV has access to an app store that offers a wide variety of applications so it can keep up to date with new services and features as time goes on by downloading new and updated apps. Some Smart TV companies, such as Samsung, Vizio, and LG, have their own proprietary app stores with different numbers of apps. Smart TVs from Sony and Sharp, which are based on the Android TV operating system, have access to over 600 apps. The recently developed Firefox OS, which Panasonic is beginning to use in its Smart TVs, will have its own app store, as well.
Extras: Of course, there are more than 10 Smart TV features that could be considered “must haves.” Skype capability, either built-in or with an optional camera, is a must-have feature, for example, but only for people who actively use Skype to make phone and video calls. Voice control and/or motion control is a feature on some Smart TVs that you should definitely check out because it’s a tremendously cool way to operate one. Not everyone likes using these methods, however. (Voice control can be finicky at times.) Another feature that’s helpful to have is a wired Ethernet connection in addition to the more common Wi-Fi connectivity that’s built into most Smart TVs. Although a wired connection is faster, more reliable, and can pass more data, a lot of people don’t have an Ethernet port near their TV.
Best gaming gadgets
Sony PS5 Next-Gen Console
With a 2020 holiday release, the Sony PS5 Next-Gen Console promises to upgrade your gaming experience with its bold and stunning design. Featuring white-and-black hardware that matches the new PS5 DualSense controller, the Sony PS5 console also stands vertically. The latest edition to the PlayStation family will be available in two versions: a pure digital edition and a 4K Blu-ray drive version. Also, it will be powered by and eight-core AMD Zen 2 CPU and a customer AMD RDNA 2-based GPU.
LEGO Nintendo Entertainment System Retro Mario Game
Step back in time with the LEGO Nintendo Entertainment System Retro Mario Game. This game comes with a vintage TV that you’ll construct to recreate the original Mario games. Just place the Pak cartridge into the console, plug in the controller, and turn the TV handle to move Mario along the screen. If you’re looking for a fun way to spend an afternoon and love video games, this is the project for you.
Razer Huntsman Mini Portable Gaming Keyboard
Play anywhere with the Razer Huntsman Mini Portable Gaming Keyboard. This item on our best gaming gadgets of 2020 list features Razer Optical Switches that give you fast, light, and smooth actuations. And with a 60% form factor, this keyboard can go anywhere with you. You’ll also enjoy clicky optical switches with 45g force. Get a personalized experience with lighting and onboard memory presets so that your keyboard operates in the way that’s best for you.
Samsung Odyssey G9 Detailed Gaming Monitor
Whether you’re playing a historical, science-fiction, or present-day game, the Samsung Odyssey G9 is a 49-inch monitor will immerse you. From the back, this curved display appears somewhat like a cyclops. Its sleek white exterior has a lit blue circle—the Infinity Core—in the center that has the look of an eyeball. That way, everyone around you knows you’re keeping an eye on them. Furthermore, the Odyssey G9 has a 1000R curved screen that allows it to match the contours of human eyes.
Razer DeathAdder V2 Mini Ergonomic Gaming Mouse
Another of our best gaming gadgets of 2020 is the Razer DeathAdder V2 Mini Ergonomic Gaming Mouse. This mouse comes with antislip tape to absorb sweat and keep it from slipping on a mat. Moreover, it’s comfortable to use and boasts a response time of just 0.2 milliseconds. You’ll love the infrared light beam that registers every click, which means it never makes an unintended one. Finally, the flexible cable won’t produce drag.
Fitness gadgets
Ozmo Active Smart Cup Hydration Tracker
Staying hydrated is one of the most overlooked aspects of working out, but with Ozmo’s Active Smart Cup, you’ll fill up when you need to. This BPA-free leak-proof smart water bottle tracks hydration levels, comes with an interactive app, and has a vibration alert system. You can even sync it with Fitbit and Apple Health for more personalization.
Tangram Smart Rope
Jumping rope is one of the best killer cardio workouts you can do and the Tangram Smart Rope will help you step it up a notch. As you’re skipping rope, this piece of workout equipment will display stats in mid-air via LED lights. The Tangram Smart Rope is able to store 100 sets of fitness data to help you get lean.
Upright Go Posture Trainer
Condition yourself to have a strong, healthy posture with the UpRight Go Posture Trainer. This trainer provides real-time posture feedback via a mobile app, allowing you to toughen up your core muscles. According to UpRight, this trainer is recommended by physiotherapists and chiropractors. Also, it comes with a 30-day 100% money back guarantee.
Skulpt Performance Training System
Measure your overall body fat percentage at any time with the Skulpt Performance Training System. Grab accurate data and analyze which of your muscle groups needs more attention so you can achieve peak performance. The system is capable of identifying the relative strength of 24 muscle groups in various areas of your body so you can personalize your workouts further.
IFit Sleep HR
Sleep definitely isn’t for the week, as getting the right amount will help you in dominating your workout the next day. The iFit Sleep HR will track the quality of your rest by monitoring your heart rate, respiratory rate, and nightly sleeping patterns. It also has a ‘Fresh Wake’ smart alarm system that will wake you up at the ideal part of your sleep cycle.
Text Books:
1. Computer Basics by IGNOU.
2. Suresh K Basendrea: Computers Today
3. Pradeep K. Sinha, Priti Sinha, “Computer Fundamentals”. BPB Publications.
4. Rajaraman, V., “Fundamental of Computers”. Prentice Hall India, New Delhi
5. Sanders Donald H Computers Today