Unit -5
Organic reactions and synthesis of drug molecule
A single displacement reaction or single substitution reaction or substitution reaction is a chemical reaction in which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. Substitution reaction is classified as the electrophilic or nucleophilic reaction that is dependent on the type of reagent involved i.e.; the reactive intermediate involved in reaction is carbocation, a carbanion or free radical.
Free radical-chlorination of molecule:
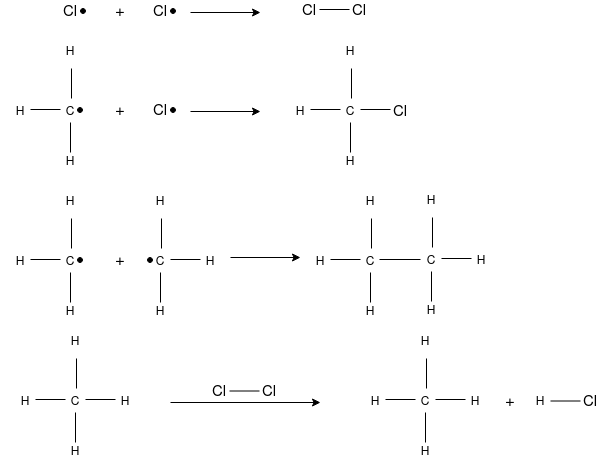
This is the substitution reaction in which the existing hydrogen atom of carbon atom is replaced by the chlorine atom. The mechanism completed in three steps starting with the hemolytic cleavage of a molecule to form free-radical. A free- radical is a reactive intermediate that contains an odd number of electrons, one of which is unpaired. This reactive intermediate is highly reactive due to its relative instability and is short-lived in an actual reaction. The second stage of free-radical chlorination is propagation. Propagation is a two step process where, first, the free-radical abstracts a hydrogen from a alkane, producing a free-radical alkane and a molecule of hydrogen chloride. This new free-radical alkane reacts with a molecule of chlorine forming a chlorinated alkane and free-radical chlorine. The chain reactions continue, propagate, until the supply of reactants is consumed or until side-reactions consume the free-radical intermediates. The latter, called termination are side reactions of the free-radicals that form stable products, but do not produce any other free-radicals. This prevents the formation of reactive intermediates to drive the propagation stage.
Chain Initiation: Splitting of a chlorine molecule to form two chlorine atoms, initiated by ultraviolet radiation or sunlight. A chlorine atom has an unpaired electron and acts as a free radical.

Chain Propagation: A hydrogen atom is pulled off from methane leaving a primary methyl radical. The methyl radical then pulls a Cl• from Cl2.
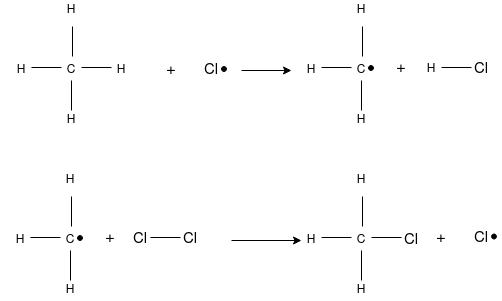
Chain Termination: Recombination of two free radicals
Nucleophilic reaction(SN1,SN2):
It is the reaction of electron pair donor with an electron pair acceptor. An sp3 hybridized electrophile must have a leaving group in order for the reaction to take place.
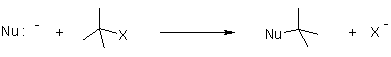
Mechanism of Nucleophilic substitution:
In the SN2 the term means that there are two molecules involved for the process of reaction.
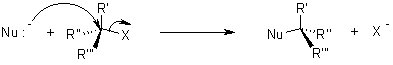
The nucleophile attacks form the backside that tends to the exit of leaving group from the reaction.
While in SN1 reaction a planar carbenium ion is formed first which then react further with the nucleophile. Since the nucleophile is free to attack from either side this reaction is associated with racemization.
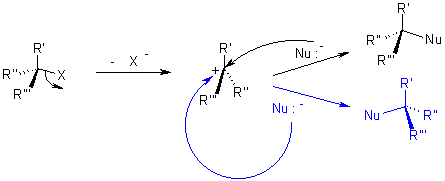
In both reactions, the nucleophile competes with the leaving group. Because of this, one must realize the properties of a leaving group should have, and what constitutes a good nucleophile. For this reason, it is worthwhile to know which factors will determine whether a reaction follows an SN1 or SN2 pathway.
Electrophilic Reaction:
It is the chemical reaction in which functional group is displaced by the electrophile in a compound probably that will be the hydrogen atom.
Addition Reaction
Morkownihoff Rule:
On addition of HX(X= Halide elements) to an asymmetrically substituted alkenes, addition of acidic hydrogen takes place at the less substituted carbon atom of the double bond, while halide X is added to the more alkyl substituted carbon atom. In other words, hydrogen is added to the carbon atom with more number of hydrogen atoms attached to it and halide is added to the carbon atom with least number of hydrogen atoms.
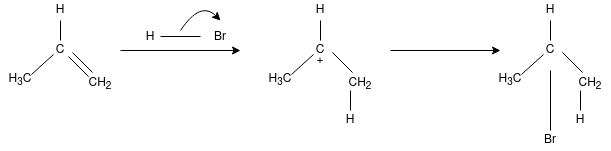
The reaction proceeds for the formation of carbocation by the addition of H to the alkenes, in the first step of reaction. The most stable carbocation is formed when H is added to carbon having more number of hydrogen atoms already attached – due to factors like induction and hyper conjugation – which gives the major product with Br added to less hydrogen – rich carbon. The less stable carbocation is also present in small quantity forming minor product on addition of Br to carbon having more hydrogen attached to it.
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction:
A nucleophilic addition reaction is a chemical addition reaction in which a nucleophile forms a sigma bond with an electron deficient species. These reactions are considered very important in organic chemistry since they enable the conversion of carbonyl groups into a variety of functional groups. Generally, nucleophilic addition reactions of carbonyl compounds can be broken down into the following three steps.
- The electrophilic carbonyl carbon forms a sigma bond with the nucleophile.
- The carbon-oxygen pi bond is now broken, forming an alkoxide intermediate
- The subsequent protonation of the alkoxide yields the alcohol derivative.
The carbon-oxygen double bond is directly attacked by strong nucleophiles to give rise to the alkoxide. However, when weak nucleophiles are used, the carbonyl group must be activated with the help of an acid catalyst for the nucleophilic addition reaction to proceed.
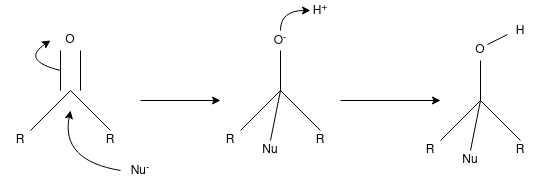
The carbonyl group has a coplanar structure and its carbon is sp2 hybridized. However, the attack of the nucleophile on the C=O group results in the breakage of the pi bond. The carbonyl carbon is now sp3 hybridized and forms a sigma bond with the nucleophile.
Elimination Reaction:
Elimination reaction is the type of reaction that is mainly used to convert saturated compounds to the unsaturated compounds that is organic compounds which contain single carbon bonds to the compound which features double or triple carbon bonds. It is a chemical reaction where several atoms either pair or groups are removed from a molecule. The removal usually takes place due to the action of acids and bases or action of metals. It can also happen through the process of heating at high temperatures.
Mechanism
The elimination reaction consists of three fundamental events they are:
- C-C pi bond is formed.
- Proton removal.
- There is a breakage in the bond of the leaving group.
Depending on the reaction kinetics, elimination reactions can occur mostly by two mechanisms namely E1 or E2 where E is referred to as elimination and the number represent the molecularity.
E1 Reaction
- This is also called as uni molecular elimination reaction, there are usually two steps involved – ionization and deprotonation.
- During ionization, there is a formation of carbocation as an intermediate. In de protonation, a proton is lost by the carbocation.
- This happens in the presence of a base which further leads to the formation of a pi-bond in the molecule.
- In E1, the reaction rate is also proportional to the concentration of the substance to be transformed.
- It exhibits first-order kinetics.
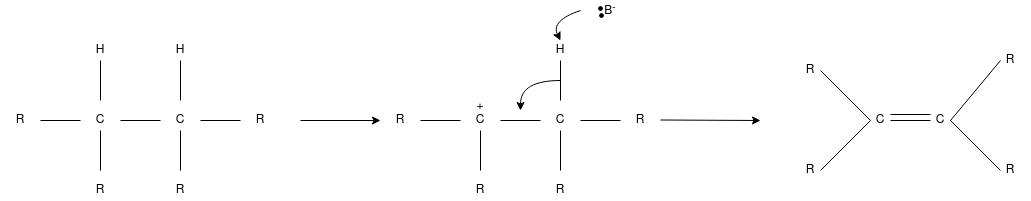
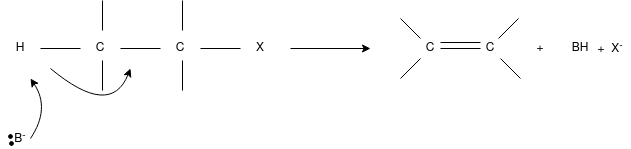
E2 Reaction:
- In an E2 mechanism which refers to bimolecular elimination is basically a one-step mechanism.
- Here, the carbon-hydrogen and carbon-halogen bonds mostly break off to form a new double bond.
- However, in the E2 mechanism, a base is part of the rate-determining step and it has a huge influence on the mechanism.
- The reaction rate is mostly proportional to the concentrations of both the eliminating agent and the substrate.
- It exhibits second-order kinetics.
The E2 mechanism can generally be represented as below. In the below-mentioned representation, B stands for base and X stands for the halogen.
The oxidation of ketone to a carboxylic acid ester by the help of peroxy acid as the oxidizing agent.
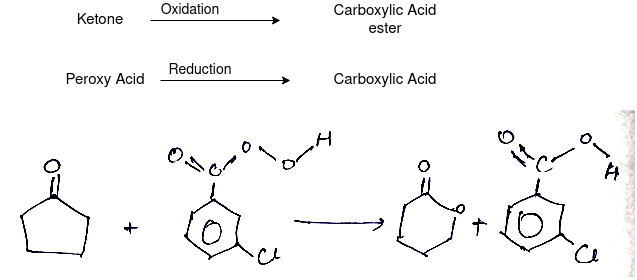
Mechanism:
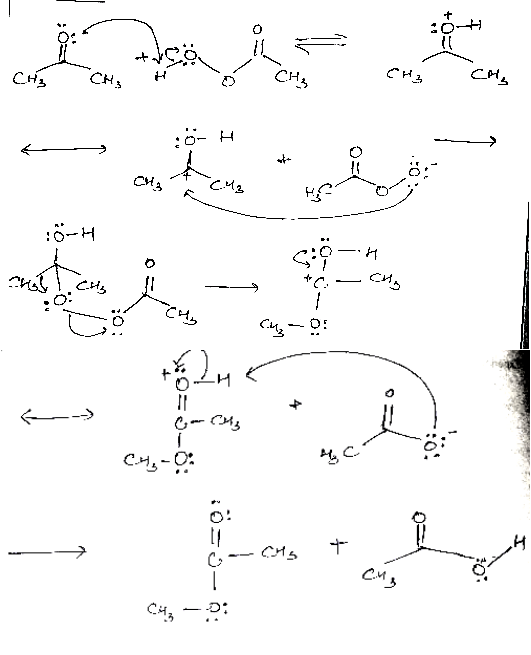
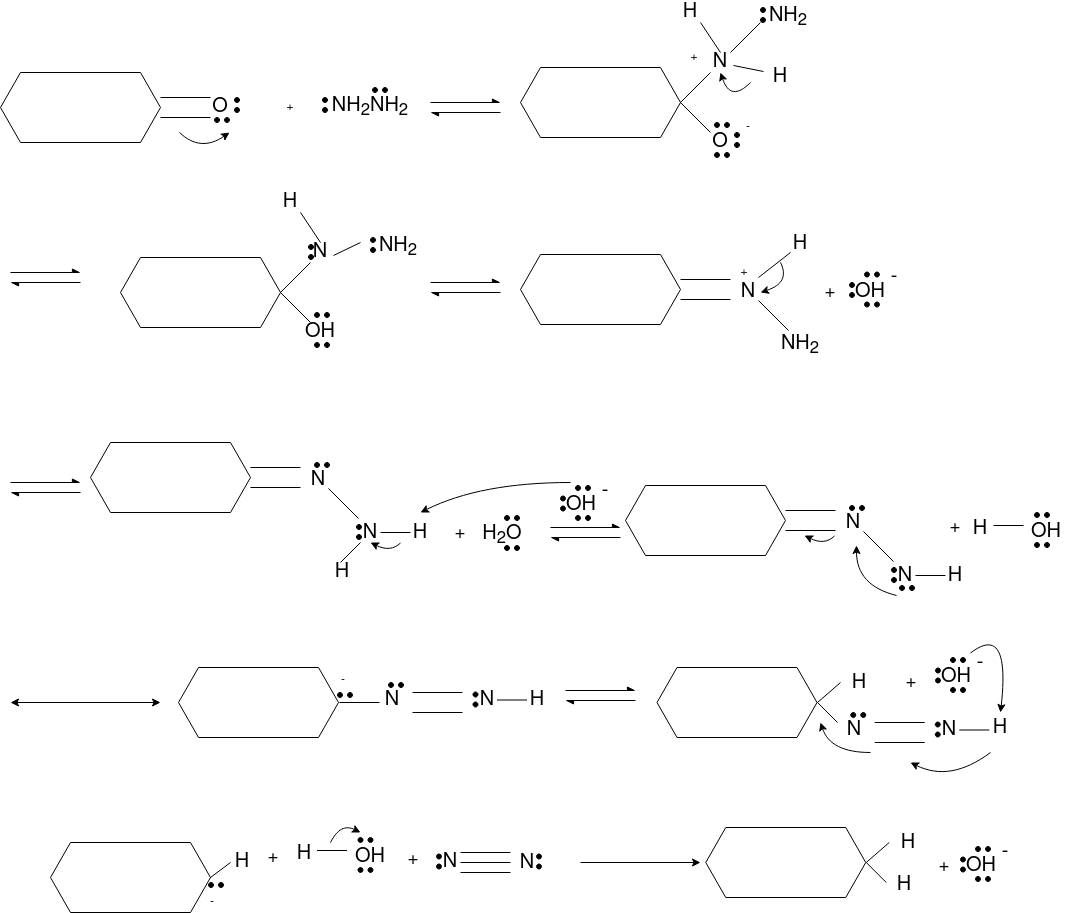
The aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine in basic medium, which reduces the aldehyde or the ketone to a hydrocarbon, is called Wolff-Kishner reduction.
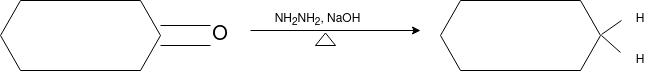
Mechanism:
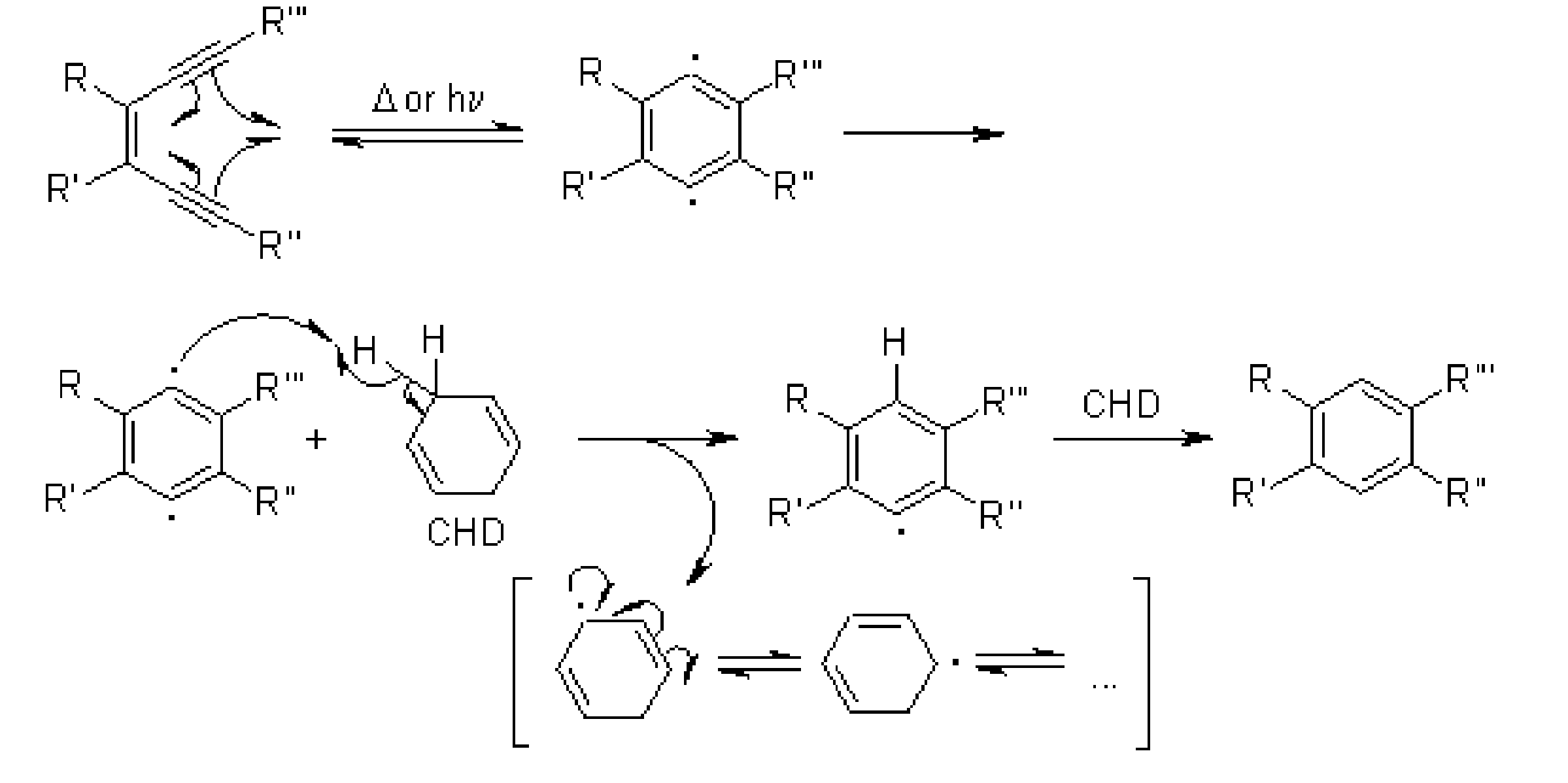
The Bergman cyclization is an organic reaction and more specifically a rearrangement reaction taking place when an enediyne is heated in presence of a suitable hydrogen donor. It is the most famous and well-studied member of the general class of cycloaromatization reactions.
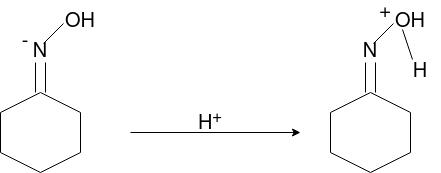
Beckmann reaction:
Oximes generally have a high barrier to inversion, and accordingly this reaction is envisioned to proceed by protonation of the oxime hydroxyl, followed by migration of the alkyl substituent "trans" to nitrogen. The N-O bond is simultaneously cleaved with the expulsion of water, so that formation of a free nitrene is avoided.
Mechanism:
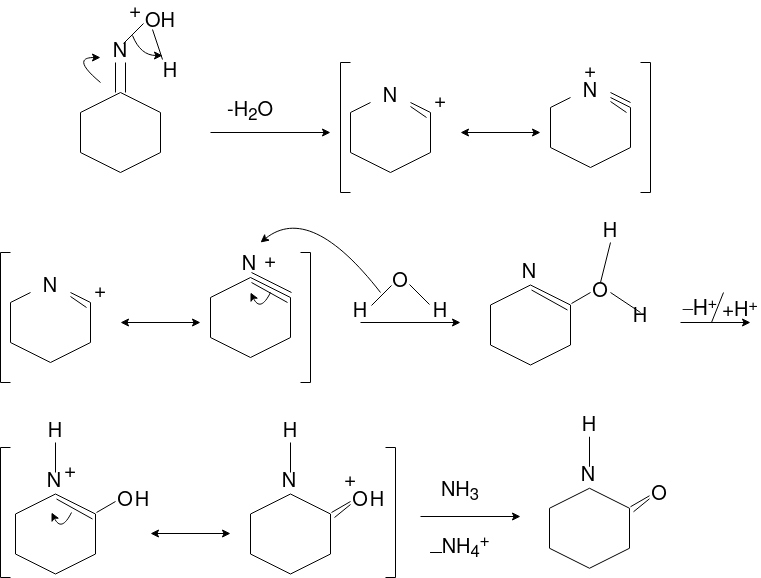
Reimer Tiemann reaction:
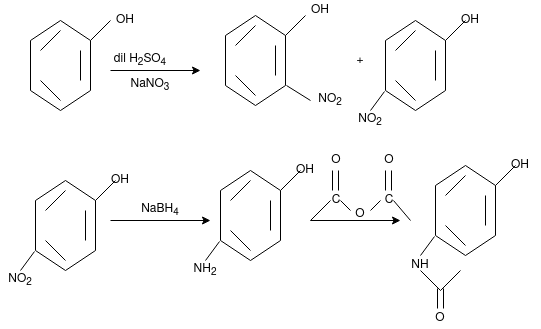
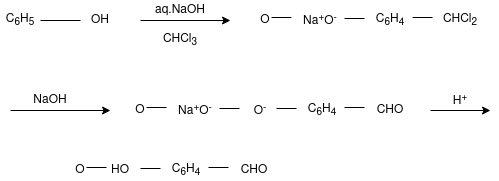 The conversion of Phenol into salicyadehyde (ortho hydroxy benzaldehyde)
The conversion of Phenol into salicyadehyde (ortho hydroxy benzaldehyde)
by the treatment with NaOH/chloroform. Thus Reimer-Tiemann reaction
involves ortho-formylation of phenols.
Major product is ortho isomer which is separated from para isomer by steam distillation. Ortho isomer predominates due to its stability due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
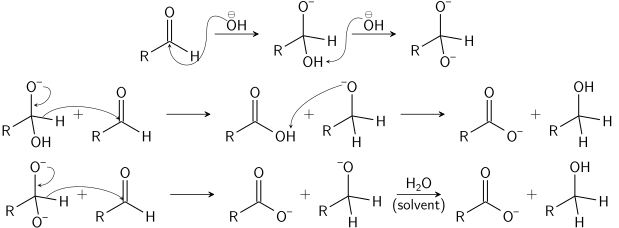
Cannizaro reaction:
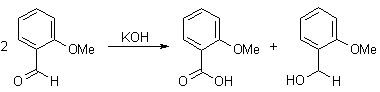
This redox disproportionate of non-enolizable aldehydes to carboxylic acids and alcohols is conducted in concentrated base.
α-Keto aldehydes give the product of an intramolecular disproportionate in excellent yields.
Mechanism:
The preparation of organic compound from the commercial chemicals. Chemical synthesis can also be used to prove the chemical structure of a compound. The structure of a compound isolated from natural sources was deduced by chemical reactions that converted the original compound into substances of known, smaller molecular arrangements.
In 1979, chemical synthesis was used as a tool to determine the molecular structure of periplanone B. C. J. Persons isolated 200 micrograms of periplanone B from the droppings of 75,000 virgin female cockroaches. He was able to deduce the gross chemical structure of the compound by modern analytical methods, but not its exact three dimensional structure. Without knowing the stereochemistry or three dimensional arrangements of the carbon atoms, larger quantities of the excitant could not be prepared and tested. In 1979, W. Clark Still at Columbia University in New York, set out to determine the structure of periplanone B. He noted that four compounds had to be made by chemical synthesis in order to determine the structure of the cockroach excitant. He chose an easily prepared starting material and by a series of chemical reactions was able to make three of the four compounds he needed to determine the chemical structure. One of the new substances matched all the analytical data from the natural material. Organic chemistry deals with the organic compounds that contain C, H, O. These are chemical reaction that involves organic compounds.
Substitution Reaction:
When a reactant A-B reacts; C comes out as the leaving group i.e.; it has taken a place of B or in other words it has substitution reaction. In other words a substitution reaction is a part of one molecular replaced by other atom or group without causing a change a change in rest of the molecule.
E.g.
A-B + C A-C + B
CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl
CH3Cl + Cl2 CH2Cl2 + HCl
CH2Cl2 + Cl2 CHCl3 + HCl
CHCl3 + Cl2 CCl4 + HCl
The substitution reaction may be brought by free radical nucleophilic or electrophilic reagent.
Mechanism:
The substitution reaction may be completed through following steps:
Chain Initiation:
The formation of chlorine free radical took place by the presence of sunlight or ultraviolet rays.
Cl : Cl Clo + Clo
Chain Propagation:
The Cl2 free radical replaces H2 atom forming an other free radical which can later again formed Cl2 free radical & thus this chain goes on till all the H2 atoms are reduced by the chlorine.
Clo + H:CH3 HCl + oCH3
oCH3 + Cl:Cl CH3Cl + oCl
oCl + H:CH2Cl HCl + oCH2Cl
oCH2Cl + Cl:Cl CH2Cl2 + oCl
oCl + H:CH2Cl2 HCl + oCHCL2
oCHCL2 + Cl:Cl CHCl3 + oCl
oCl + H:CCl3 HCl + oCCl3
oCCl3 + Cl:Cl CCl4 + oCl
Chain Termination:
When all hydrogen atom are replaced by Cl than finally 2Cl free radical combines & chains terminates to form Cl molecule.
Clo + oCl Cl:Cl
Addition Reaction: Addition reaction is one of the simplest term in the organic chemistry this involve the expansion of the chain by addition of different molecule.
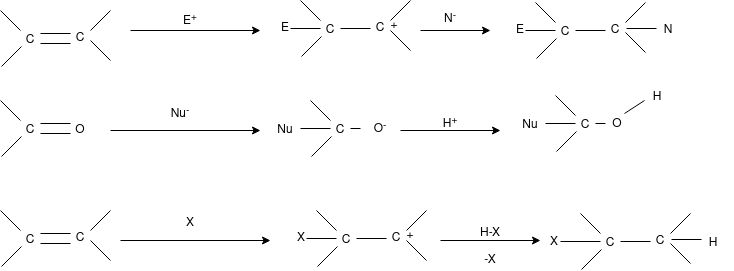
Elimination Reaction:
Elimination reaction is the type of reaction that is mainly used to convert saturated compounds to the unsaturated compounds that is organic compounds which contain single carbon bonds to the compound which features double or triple carbon bonds. It is a chemical reaction where several atoms either pair or groups are removed from a molecule. The removal usually takes place due to the action of acids and bases or action of metals. It can also happen through the process of heating at high temperatures.
Mechanism
The elimination reaction consists of three fundamental events they are:
4. C-C pi bond is formed.
5. Proton removal.
6. There is a breakage in the bond of the leaving group.
Depending on the reaction kinetics, elimination reactions can occur mostly by two mechanisms namely E1 or E2 where E is referred to as elimination and the number represent the molecularity.
E1 Reaction
- This is also called as unimolecular elimination reaction, thereare usually two steps involved – ionization and deprotonation.
- During ionization, there is a formation of carbocation as an intermediate. In deprotonation, a proton is lost by the carbocation.
- This happens in the presence of a base which further leads to the formation of a pi-bond in the molecule.
- In E1, the reaction rate is also proportional to the concentration of the substance to be transformed.
- It exhibits first-order kinetics.
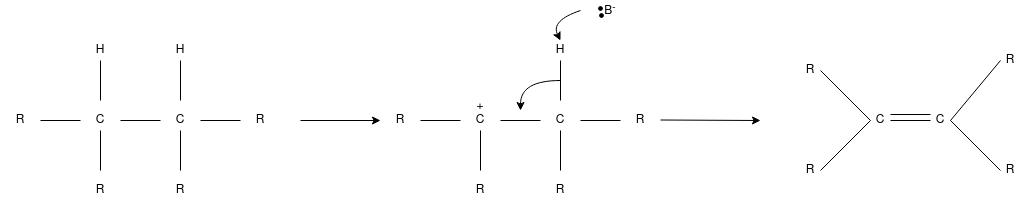
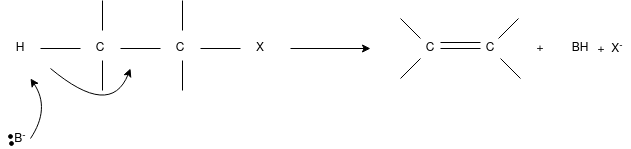
E2 Reaction:
- In an E2 mechanism which refers to bimolecularelimination is basically a one-step mechanism.
- Here, the carbon-hydrogen and carbon-halogen bonds mostly break off to form a new double bond.
- However, in the E2 mechanism, a base is part of the rate-determining step and it has a huge influence on the mechanism.
- The reaction rate is mostly proportional to the concentrations of both the eliminating agent and the substrate.
- It exhibits second-order kinetics.
The E2 mechanism can generally be represented as below. In the below-mentioned representation, B stands for base and X stands for the halogen.
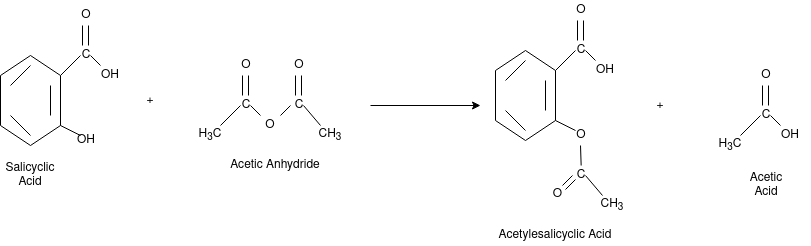
The chemical name for the Aspirin is Acetyl salicyclic acid. It is used as pain killer and fever reducer. Salicyclic acid derive from the willow family of plants which were widely used for treating headache. For the preparation of aspirin the salicyclic acid is reacted with the excess acetic anhydride. Phospohoric acid is used for boosting the procedure of reaction. The excess acetic acid will be quenched with the addition of water. The aspirin product is not very soluble in water so the aspirin product will precipitate when water is added. The synthesis reaction of aspirin is shown below:
Since acetic acid is very soluble in water, it is easily separated from the aspirin product. The aspirin isolated in this step is the “crude product”. A “purified product” can be obtained through re-crystallization of the crude product in hot ethanol. In this experiment, the crude product will be the desired product. The percent yield of the crude product will be determined for this reaction. The purity of the product will also be analyzed. The product will be analyzed by three different methods: melting point, titration, and spectroscopic assay. C and the melting point range of the salicylic acid. The melting point range of pure aspirin is 138-140 C. If impurities are present in your crude sample, the melting point rangestarting material is 158-161 for your product will be lower than the range of pure aspirin. Also, your melting point range may be greater than 2 degrees.
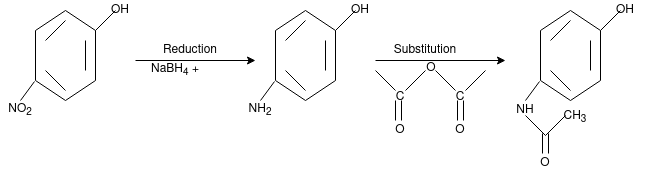
Synthesis of Paracetamol
From Phenol:
From Para nitro Phenol