UNIT I
Macro Economics
Concept
Introduction:
The term "macro" was first used in economics by Ragnar Frisch in 1933. However, it originated in the 16th and 17th century mercantilists as a methodological approach to economic problems. They were interested in the entire economic system. In the 18th century,
Physiocrats adopted it in the table economy, demonstrating a "wealth cycle" (i.e., net production) among the three classes represented by the peasant, landowner, and barren classes.
Malthus, Sismondi and Marx in the 19th century dealt with macroeconomic issues. Walras, Wicksell and Fisher contributed modernly to the development of pre-Keynes macroeconomic analysis.
Certain economists such as Kassel, Marshall, Pigovian, Robertson, Hayek, and Hortley developed the Quantity Theory of Money and General Price Theory in the decade following World War I. But Keynes, who eventually developed the general theory of income, output, and employment in the wake of the Great Depression, has credit.
Economics is a science that deals with the production, Exchange and consumption of various goods in the economic system. It is a scarce resource that can lessen the abundance of human welfare. The central focus of Economics lies in the choice between resource scarcity and its alternative uses. The word "economics" is derived from two the Greek words oikos (House) and nemein (to manage) mean to manage the household budget "using the limited funds possible.

Scope of Macro Economics
Economics is the subject of dealing with every situation happening all over the world. This subject is used in many stances in our lives. For example, your mom does all the work in your home. From doing all the housework to maintaining a budget for rations to meeting all your needs. Thus, it is one subject that deals with the daily work of our lives. There are two major categories on the same subject: microeconomics and macroeconomics. One deals with individual units of the economy, such as consumers and households. But the latter deals with the whole economy. It deals with research on national income and output. This understanding of science is vast and of varying lengths. However, for simplicity, this article will only focus on the scope and need for macroeconomics.
Microeconomics:
As mentioned above, microeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with individual units of the economy. It includes research areas on individual units such as consumers and homes. The subject deals with issues related to determining the price of goods. These direct or indirect factors affect the supply and demand of goods and the procurement of individual satiety levels. The main purpose of microeconomics is to maximize profits and minimize costs incurred. It is used for future generations to be available and balanced.
Macroeconomics
The term macroeconomics was coined by Ragnar Frisch in 1933. However, the approach to economic problems began in the 16th and 17th centuries. As a result, this originated from mercantilists. It is the field of science that deals with the whole economy or the whole, including macro factors. The hope of macroeconomics does not involve studying individual units of the economy. But the whole economy studies the whole economy and the average National income, total employment, total savings and investment, aggregate supply and demand, and general price levels.
The subject of macroeconomics revolves around income and employment decisions.
Controlling the cycle of inflation and deflation was only possible by choosing current economic policies. These policies were developed at the macro level. Research on individual units has also become impossible. In addition, government participation through financial and fiscal measures in the economy is increasing. Therefore, the use of macro analysis is irrefutable.
Now we know that macroeconomics is a specialty of economics. Focus on the economy through the sum of the individual units and determine if it will have a significant impact on the country as a whole. All prominent policies and measures are based on this concept. For example, per capita income determines national income. This is nothing but the average of the total income of the people of the whole country.
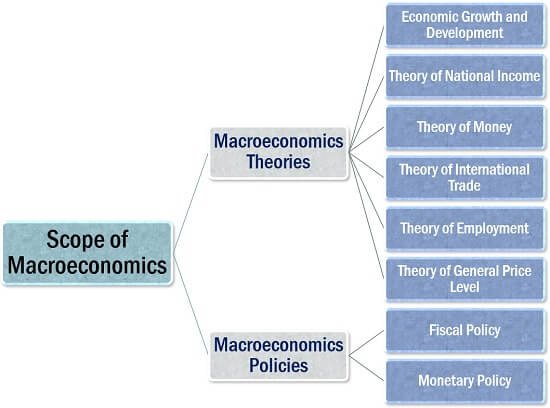
Fig 1
Scope of Macroeconomics:
Governments, financial institutions and researchers analyse the general problems of the people and the economic well-being of the people.
It mainly covers the foundations of macroeconomic theory and measure theory, which is macroeconomic policy. Here, macroeconomic theories include theories of economic growth and development, national income, money, international trade, employment, and general price levels. In contrast, macroeconomic policy covers fiscal and monetary policy.
Research on issues such as India's unemployment, general price levels and balance of payments (BOP) issues is part of macroeconomic research as it is relevant to the economy as a whole.
Macroeconomic Theories:
The government is understood to be the national regulator. Consider various aspects that are important and have a direct impact on the lives of citizens. There are six theories within the scope of macroeconomics.
Theory of Economic Growth and Development:
Economic growth is also under the study of macroeconomics. Economic resources and capabilities are assessed based on the scope of macroeconomics. It plans to increase levels of national income, output, and environmental levels. They have a direct impact on the economic development of the economy.
Money theory:
Macroeconomics assesses the impact of reserve banks on the economy, capital inflows and outflows, and its impact on employment rates. Frequent changes in the value of money caused by inflation and deflation have many negative effects on the country's economy. They can be exacerbated by monetary policy, fiscal policy, and direct control of the economy as a whole.
National Income Theory:
This includes various topics related to measuring national income, such as revenue, spending, and budget. As a macroeconomic study, it is essential to assess the overall performance of the economy in terms of national income. At the beginning of the Great Depression of the 1930s, it was essential to investigate the triggers of general overproduction and general unemployment.
This led to the creation of data on national income. Helps predict the level of economic activity. It also helps to understand the income distribution among different classes of citizens.
International Trade Theory:
This is a research area focused on the import and export of products or services. Simply put, it points to the economic impact of cross-border commerce and tariffs.
Employment theory:
This macroeconomic scope helps determine the level of unemployment. It also determines the conditions that lead to such unemployment. Therefore, this affects production supply, consumer demand, consumption, and spending behaviour.
General Price level theory:
The most important of these are research on commodity prices and how inflation or deflation fluctuates a particular price rate.
Macroeconomic policy:
The RBI and the Government of India are working together to imply macroeconomic policies for national improvement and development.
It falls into two sections:
Fiscal policy:
It refers to how spending fills deficit income and describes itself as a form of budgeting under macroeconomics.
Financial policy:
The Reserve Bank is working with the government to establish monetary policy. These policies are measures taken to maintain the stability and growth of a country's economy by regulating various interest rates.
Importance of macroeconomics:

Fig 2
Macroeconomics is an important concept that considers the whole country and works for the welfare of the economy.
1. Business cycle analysis
Timing of economic fluctuations helps prevent or prepare for financial crises and long-term negative situations.
2. Formulation of economic policy
The fiscal and monetary policy system relies entirely on the widespread analysis of macroeconomic conditions in the country.
3. Reduce the effects of inflation and deflation
Macroeconomics is primarily aimed at helping governments and financial institutions prepare for economic stability in a country.
4. Promote material welfare
This stream of economics provides a broader perspective on social or national issues. Those who want to contribute to the welfare of society need to study macroeconomics.
5. Regulate the economic system
It continues to guarantee or check the proper functioning and actual position of the country's economy.
6. Solve economic problems
Macroeconomic theory and problem analysis help economists and governments understand the causes and possible solutions to such macro-level problems.
7. Economic development
By utilizing macroeconomic data to respond to various economic conditions, the door to national growth will be opened.
Problems related to macroeconomics

Fig 3
Economists need to analyse the following issues while studying macroeconomics.
1. Issues related to government policy
Business activities also bring social costs such as deforestation and land degradation. To regulate this social cost, the government has clear laws and laws in place. These regulations act as barriers for corporate organizations.
2. Problems related to macroeconomic trends in the economy
The economic situation of a country has immeasurable impact on the activities of all organizations, directly or indirectly. The various economic patterns or variables that affect the industry include gross domestic product (GDP), employment rates and conditions, revenue incentives, banks, and pricing policies.
3. Problems related to foreign trade
Many organizations trade (export or import goods) in the international market. They are sensitive to economic fluctuations, exchange rates, prices, and many other factors in other countries. Therefore, such changes can affect the economic situation of the country. This can also affect your business organization.
Conclusion
Macroeconomics is the basis of many economic policies. It lays the foundation for the regional decision-making mechanism of the country. However, policies backed by this concept usually have a dual impact on society as a whole and on individual citizens. It requires an observing, logical and incredible approach.
Limitations
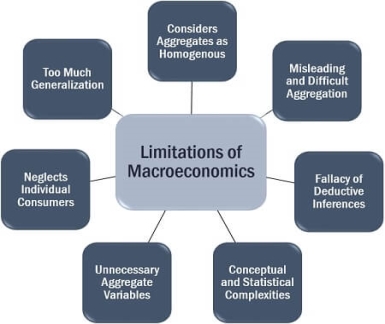
Fig 4
The next drawback of this approach should lead to its criticism:
- Consider aggregates as homogeneous: individual data may not be similar in structure or composition. It is useful to look at aggregated values by such a single aggregation.
- Misleading: the widespread application of macroeconomic measures seems to be irrelevant when aimed at 100% results.
- The fallacy of deductive reasoning: the function of macroeconomics on aggregate values. However, the interpretation of individual activities may not be the same in comparison with the conclusions drawn at the mass level.
- Conceptual and statistical complexity: when individual data have different units, their aggregation becomes difficult and does not retain significance.
- Unnecessary aggregate variables: aggregate values cannot be used for purpose when you need to examine individual elements individually.
- Ignore individual consumers: the concept of macroeconomics overlooks the importance of individual units or consumers, since the basis is to utilize aggregates.
- Too many generalizations: conclusions drawn from the aggregation of data are generally considered true for all individuals.
Conclusion
Macroeconomics is the basis of various economic reforms and national decision models in a country.
However, the policy enclosed under this concept usually has a double impact as a whole society and as an individual citizen.
Therefore, while reaching such interference, a highly analytical, logical and special approach is required.
Difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics:
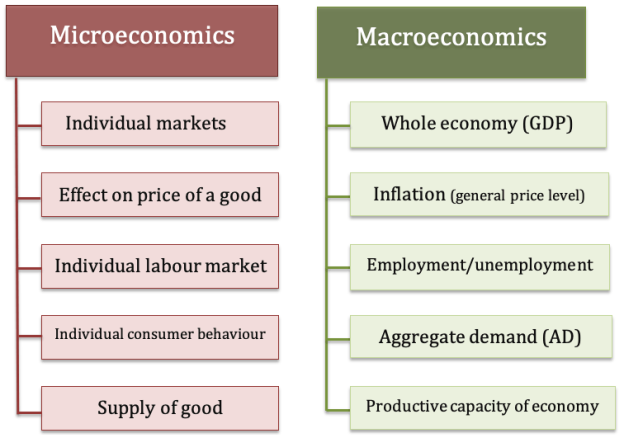
Fig 5
The differences between microeconomics and macroeconomics can be seen in the following points. Microeconomics is the study of the economic activity of individuals and small groups of individuals. This includes specific households, specific companies, specific industries, specific products, and individual prices.
Macroeconomics is also derived from Macross, which means "big" in Greek. The purpose of microeconomics on the demand side is to maximize utility, while on the supply side it is to minimize profits at the lowest cost. On the other hand, the main objectives of macroeconomics are full employment, price stability, economic growth and a good balance of payments.
The basis of microeconomics is a price mechanism that works with the help of the power of supply and demand. These forces help determine the equilibrium price of the market. On the other hand, the basis of macroeconomics is national income, output, and employment, which are determined by aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
Microeconomics is based on various assumptions about the rational behaviour of individuals. In addition, the phrase "ceteris paribus" is used to describe economic law. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, makes assumptions based on variables such as the total output of the economy, the extent to which its resources are used, the size of national income, and general price levels.
Microeconomics is based on partial equilibrium analysis that helps explain the equilibrium conditions of individuals, businesses, industries, and factors. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, is based on general equilibrium analysis, which is an extensive study of many economic variables, their interrelationships and their interdependencies, to understand the workings of the entire economic system.
In microeconomics, equilibrium studies are analysed at specific times. But it does not explain the time element. Therefore, microeconomics is considered static analysis. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, is based on time lags, rate of change, past and expected values of variables. This rough division between microeconomics and macroeconomics is not rigorous, as parts affect the whole and whole influences the parts.
Parameters of Differentiation | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
Meaning | Microeconomics studies the particular market segment of the economy | Macroeconomics studies the whole economy, that covers several market segments |
Deals with | Microeconomics deals with various issues like demand, supply, factor pricing, product pricing, economic welfare, production, consumption, etc. | Macroeconomics deals with various issues like national income, distribution, employment, general price level, money, etc. |
Business Application | Applied to internal issues | Environment and external issues |
Scope | Covers several issues like demand, supply, factor pricing, product pricing, economic welfare, production, consumption, etc. | Covers several issues like distribution, national income, employment, money, general price level, etc. |
Significance | Useful in regulating the prices of a product alongside the prices of factors of production (labour, land, entrepreneur, capital, etc) within the economy | Perpetuates firmness in the broad price level and solves the major issues of the economy like deflation, inflation, rising prices (reflation), unemployment and poverty as a whole |
Limitations | It is based on impractical presuppositions, i.e., in microeconomics, it is presumed that there is full employment in the community, which is not at all feasible | It has been scrutinized that Misconception of Composition’ incorporates, which sometimes fails to prove accurate because it is feasible that what is true for aggregate (comprehensive) may not be true for individuals too |
Dependence of Microeconomics on Macroeconomics:
For example, when aggregate demand increases during the prosperous period, so does the demand for individual products. If this increase in demand is due to lower interest rates, then "the demand for different types of capital goods will increase, which will lead to an increase in the demand for certain types of labor required by the capital goods industry. If the supply of such a labor force is inflexible, its wage rate will rise.
Wage rates can be raised by increasing profits from increased demand for capital goods.
Similarly, the overall size of income, output, employment, cost, etc. in an economy affects the composition of individual income, output, employment, and cost of individual companies and industries. To give another example, when total production declines during a recession, capital goods production is lower than consumer goods production. In the capital goods industry, profit and wage employment declines more rapidly than in the consumer goods industry.
Reliance of macroeconomics on microeconomic theory:
On the other hand, macroeconomic theory also relies on microeconomic analysis. The total is made up of parts. National income is the sum of personal, household, corporate and industrial incomes. Total savings, total investment and total consumption are the result of individual industry, business, household and individual savings, and investment and consumption decisions.
A typical price level is the average of all prices for individual goods and services. Similarly, the economic output is the sum of the outputs of all individual production units.
Let's look at some concrete examples of this macro dependence on microeconomics. When the economy concentrates all its resources on the production of agricultural products only, the total production of the economy decreases because other parts of the economy are ignored.
The total level of output, income and employment in the economy also depends on income distribution. If there is an unequal distribution of income and the income is concentrated in the hands of a few rich people, it tends to reduce the demand for consumer goods.
Profit, investment and output will decline, unemployment will widen and the economy will eventually face a recession. Therefore, both macro and micro approaches to economic problems are interrelated and interdependent.
Macro dynamics:
Economic dynamics, on the other hand, is the study of changes in acceleration or deceleration. It is an analysis of the process of change that continues over time.
The economy can change over time in two ways.
(A) Without changing the pattern
(B) By changing the pattern.
Economic dynamics are associated with the latter type of change. When there are changes in population, capital, production technology, the form of business organizations, and people's tastes, the economy takes different patterns in any or all of them, and the economic system changes its direction.
In the attached figure, given the initial value of the economy, D was moving along path AB, but suddenly at A the index changed pattern and the direction of equilibrium changed towards C. Proceed to D again. But in C, the pattern and orientation change to E. Therefore, economic dynamics investigates the path from one equilibrium position to another, that is, the path from A to C and from C to E.
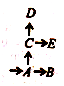
Therefore, economic dynamics is related to time lag, rate of change, past and expected values of variables. In a dynamic economy, data changes and the economic system take time to adjust accordingly. . It can be seen as a" movie "of the progressive overall economic function. "
In Figure 2, C + 1 is the aggregate demand function and the 45 ° line is the aggregate supply function. Starting from a period when the income equilibrium level is OY0, the investment increases by ∆I, and in the period t, the income increases by the amount of increased investment (t0 to t). The increase in investment is indicated by the new aggregate demand function C + I + ∆I.
However, in period t, consumption is delayed and is the same as income at E0. In period t + I, consumption increases and new investment increases even higher income up to OY1.
This process of income propagation continues until the aggregate demand function C + I + ∆I crosses the line of aggregate supply function 45 ° at En in the nth period, and the new equilibrium level is determined by OYn. Curve step t0 to En shows the macrodynamic equilibrium path.

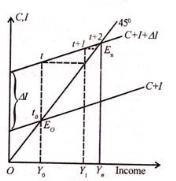
Fig 6
References:
- Https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/6796/economics/difference-between-microeconomics-and-macroeconomics/
- Https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/difference-between-microeconomics-and-macroeconomics/
- Https://www.cheggindia.com/blog/career-guidance/scope-of-macroeconomics-meaning-nature-and-importance/
- Https://theinvestorsbook.com/macroeconomics.html
- Https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/6796/economics/difference-between-microeconomics-and-macroeconomics/