Unit-4
Introduction, shapes and characteristics of wells
INTRODUCTION SHAPES
CAISSONS
Introduction:
French word caissons mean that too and might be open at either finish on at one end. Such box with shut bottom may be prefabricated onshore so floated to the required site and is allowed to seat on a prepared base
Types of Caissons
There are three sorts of caissons
Types of caisson
(a) Box caisson
(b) The open caisson
(c) Pneumatic caisson
(a) Box Caisson
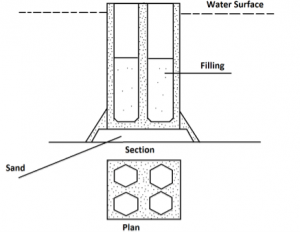
Fig no. 1 Box caisson
1. Box caisson may be provided just in case alternative sorts prove pricey or don't seem to be possible.
2. It may be extended up to massive depths.
3. It may be created onshore and floated to the place installation.
Disadvantages of Box Caisson
1 It needs exhausting strata for the bearing, therefore appropriate if such stratum is offered at shallow depth
2 Provision is needed for defense from scouring.
3. Progress is delayed if there's an obstruction like a log or boulders deep down of the caisson.
4. Inspection and excavation deep down is tough and needs different for such work
5. At bearing strata concrete scale provided might not be satisfied being placed beneath the water
(b) Open Caisson
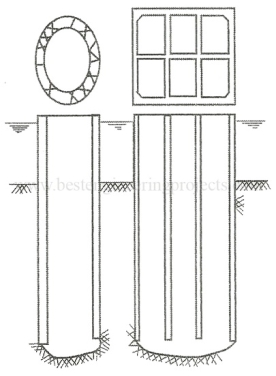
Fig no 2 Open caisson
1. The caisson may be created to nice depths.
2 the development value is comparatively sawed.
Disadvantages of Open Caisson
1. The clearing and scrutiny of the bottom of the caisson cannot be done
2 Concrete seal placed in water won't be satisfactory.
3. The speed of progress is going to be delayed if boulders are met throughout the construction.
(c) Pneumatic caisson
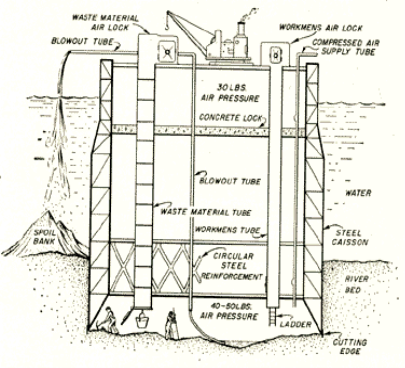
Fig no 3 Pneumatic caisson
Advantages of pneumatic Caisson
2 The caisson may be done vertically as careful superintendence is feasible.
3. The bottom of the chamber may be sealed effectively with concrete because it may be placed dry.
4. Obstruction to sinking such as boulders east northeast maybe considerd.
Disadvantages of gas Caisson
1 Construction value is kind of huge amount.
2 The depth of penetration below water is restricted to concerning higher costs are on the far side the endurance of the shape.
SHAPES
Caissons may be completely different shapes
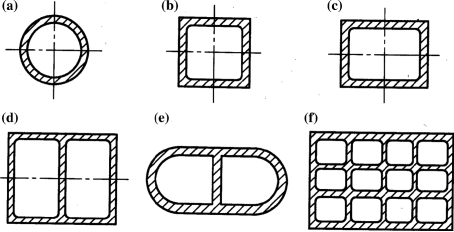
Fig No 4 Shapes of Caissons
Circular form
Caisson Diseases
Thereafter only working person is permissible to travel out.
CHARACTERISTICS OF WELLS
Well foundation
Advantages of Well foundation
Key takeaways
SHAPES
Types of caissons
Cutting Edge
Steining
Curb
Concrete seal or bottom plug
Top Plug
Well cap
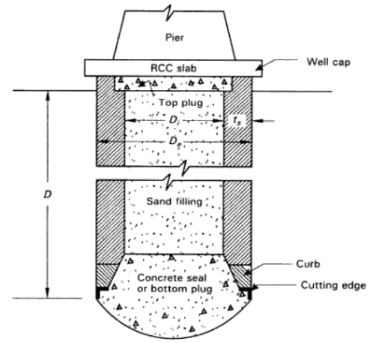
Fig no 5 Components of well foundation
1. Dead Loads
2. Live Loads
The live hundreds within the case of main road bridges are fixed by IRC. For the style of railway bridges, Indian railways follow-
The Indian Railway Bridge Rules (1963) are given by research, style, and Standards Organization (RDSO), Lucknow of the Ministry of Railway, Government of India.
3. Impact loads
The live hundreds cause impact result and it's thought-about within the style of pier cap and bridge seat on the abutment. Impact results could also be neglected for the elements of the well.
4. Wind Loads
Wind loads working on, superstructure and therefore the part of substructure situated higher than the water level are calculated supported "Indian customary Code of following for Structural Safety of Buildings Loading Standard" Wind hundreds act on the exposed space virtually.
5. Water pressure
Water pressure is thanks to the water current working on the part of the substructure between the water level and therefore the maximum scour level.
The intensity of Water pressure on piers parallel to the direction of flow is given by
P = K v 2
Where p = Intensity of Water Pressure (N/m);
V = speed of the water current (m/s).and
K = a constant, that depends upon the form of the well (maximum 788 for sq. over piers, and minimum 237 for piers with cutwaters and case-water)
Vis took to be the most at the free surface of flow and 0 at the deepest scour level, the variation is assumed to be linear. The most worth is taken to be v times the typical worth.
A crosswise force of 2 hundredths of that parallel to the flow is assured to permit for occasion obliquity of flow.
6. Longitudinal Force
Longitudinal force happens thanks to rubbing and braking forces. These are transmitted to the substructure in the main through fastened bearing and thru friction on movable bearings per IRC code, a Longitudinal force of  W is taken on the free bearing and therefore the balance on the fastened bearing, wherever W is that the total reaction and the constant of friction.
W is taken on the free bearing and therefore the balance on the fastened bearing, wherever W is that the total reaction and the constant of friction.
7. Earth Pressure
The earth pressure is calculated supported by one in every of classical earth pressure theories by temperature unit or Coulomb. Passive earth resistance of the soil is taken under consideration for the soundness of foundations below the scour level. The result of the live load on the abutment on the planet pressure is taken into account by taking the constant height of surcharge.
8. Centrifugal force
A force is taken to be transmitted through the bearing the construction is bowed in set up.
9. Buoyancy Force
Buoyancy reduces the effective weight of the well. In masonry or concrete staining 15% of the load is taken the buoyancy force to account for the consistency.
When the well is supported on coarse and, full buoyancy capable the weight of the displaced volume of water is taken into account for semi receptive foundation, the applicable reduction could also be created supported the situation of groundwater level.
10. Temperature Stresses
Longitudinal forces are induced thanks to temperature changes. The movements thanks to temperature changes are partly restrained in beam bridges as a result of friction.
11. Seismic Forces
These are to be considered in an applicable seismic zone. It's capable of a W. wherever W is that the weight of the element, and because of the seismic constant. The worth depends upon the Zone and is given in IS: 1893 1975 Indian customary Criteria of "Earthquake Resistance style on Structures".
It is worth ranges from zero.10 0.08. The seismic force acts through the center of gravity of the element. it should act in any one direction at a time. Separate seismic forces are thought-about on the axis of the pier and crosswise to its.
12. Resultant Force
The magnitude, direction, and therefore the purpose of application of all the applicable forces are found for the worst attainable combination. The resultant will be purported to get replaced by constant vertical force W, and lateral forces, P and letter of the alphabet within the longitudinal and crosswise direction of the pier, severally. The action of letter of the alphabet is going to be additional crucial within the thought of lateral stability of the well.
1. Preparatory work
2 Construction of the sand stand
3. Laying of curb
4. Providing shuttering reinforcement and concreting
5. Well staining
6. Measures to increase the speed of sinking
1. Preparatory work
2. Construction of the sand island
At the desired location if the depth of water is less than 5 m, then a sand island is created to facilitate the sinking of well as it is easier to control vertically of well by sand island. The size of the island is adequate to accommodate the well and to have some working area around.
3. Laying of curb
If the depth of water is less than 5 m, the curb is laid on a sand island constructed. However, if it is more, then curt is precast on the store and then floated to site. The cutting curb is supported on wooden sleepers laid on the sand island while the cart is placed below the curbin by one. By providing sleepers a load of curt is distributed uniformly.
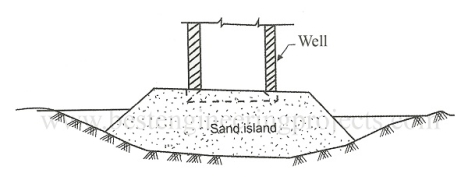
Fig no 6 Sand island for sinking a well
4. Providing shuttering reinforcement and concreting
5. Well steining
1.5 m steining constructed and is allowed to sink after attaining sufficient strength. The probability of the well is checked from time to time and suitable connection measures are taken. In the initial stages, steining is cast at a height of 1.5 m and later on, these can be increased to 3 m to overcome frictional resistance.
6. Measures to increase the speed of sinking
For safe and curly sinking of well, the following measurements are taken
Tilting well will cause unequal stresses and the speed of sinking will reduce
2. By removing the soil uniformly
Vertically speed can be maintained
3. Jetting of water
Inside and outside the periphery of will reduce frictional resistance this is attained by jetting water through pipes with nozzles all along water periphery.
4. Providing kentledge
Suitable platform resisting on steining is constructed and on this platform kentledge in the form of RSJ /heavy block plates sandbags etc are placed to overcome frictional resistance.
5. Chiseling and Light blasting
In Case, during the sinking of well meets a boulder, which can be taken out by grab or which can obstruct the cutting edge, divers send down and used to call it by ordinary chisels and hammers. This was not successful a hole is to be drilled into the boulder by ordinary chisel und hammer and about I/4 charge (gelignite) is to be deposited is it by divers. The blasting of the charge is to be done electrically from the top of the well with 12 volts battery. This makes the boulder and facilitates the sinking operation.
6. Use of Drop Chisel
When soil strata are hard the excavation operations of the dredger could be aided by the use of a drop chisel The chisel could be just double sections welded together and strengthened by rails co either side of the sections. The chisels should have pointed and at the bottom and a bole sear the top. Through a power winch and steel wire rope, the chisel which may be 3 meters long is held and dropped from a height.
Key takeaways
In the sinking of wells, there are different steps
1. Preparatory work
2 Construction of the sand stand
3. Laying of curb
4. Providing shuttering reinforcement and concreting
5. Well staining
6. Measures to increase the speed of sinking
Measure to increase of speed of sinking
The tilt of the Well
Difficulties in well sinking
Difficulties in well sinking are
During the sinking process of the well, the well can tilt. The magnitude of the tilt that can be allowed is 1 in 60.
The general causes of the tilt of the well
The general causes of the tilt of the wall are
(a) Meeting hand strata such as boulder on one side and soft soil such as sand or weak clay on the other side of the well.
(b) Unequal or eccentric Kentledge.
(c) Slopping bed given tilt p initial stages of sinking operations.
(d) Usual rubbing or excavation inside the dredge hole or outside the well.
(e). The sudden sinking of the caisson. The tilt of the well having once started, it is difficult to arrest it when it is occurring we can only rectify the tilt that has occurred.
Usual methods for the rectification of tilt
Methods for the rectification of the tilt
(a) Control of dredging
(b) Packing on the low side
(c) Water Jet method
(d) The method of wedges
(e) Unequal loading
(f) Explosives
(g) Unequal excavation
(a) Control of Dredging
(b) Packing on Low side
(c) Water Jet technique
(d) The methods of Wedges
(e) Unequal Loading
(f) Explosives
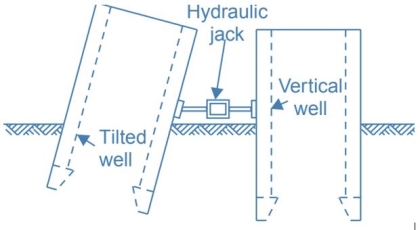
Fig no 7 Rectification of tilt
(g) Unequal Excavation
Sand blowing
Precautions to be determined to stop sand processing tilt and shift
(1). Care to be taken throughout dewatering operations, so that important gradient ne'er exceeded.
(2) Outer surface of well curb and steining ought to be as swish as attainable.
(3) Radius of curb ought to be unbroken a pair of to four cm larger than the Suicide radius of well steining.
(4) Uniform dredging and uniform kentledge.
(5) Leading edge of the curb to be of uniform thickness and sharpness.
Key takeaways
Introduction
Gravity wall
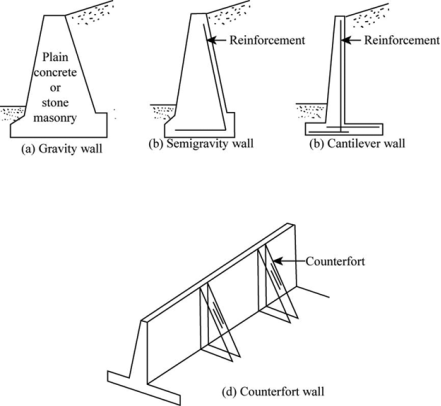
Fig no 8 Types of walls
Cantilevered wall
Diaphragm wall
Diaphragm walls area unit a kind of retentive walls that area unit terribly stiff and usually watertight. Diaphragm walls area unit pricy walls, however, they save time and house, and thus area unit utilized in urban constructions.
Sheet pile wall
Bored pile wall
Bored pile retentive walls area unit designed by grouping a sequence of bored piles, followed by excavating away the surplus soil. Reckoning on the project, the bored pile wall might embrace a series of earth anchors, reinforcing beams, soil improvement operations reinforcement layer. This construction technique tends to be used in eventualities wherever sheath pile could be a valid construction resolution, however wherever the vibration or noise levels generated by a machine aren't acceptable.
Anchored wall
An anchored wall will be made in any of the aforesaid designs however conjointly includes extra strength victimization cables or different stays anchored within the rock or soil behind it. typically driven into the fabric with boring, anchors area unit then expanded at the tip of the cable, either by mechanical suggests that or usually by injecting pre stressed concrete, that expands to create a bulb within the soil. Technically advanced, this methodology is incredibly helpful wherever high hundreds area unit expected, or wherever the wall itself must be slender and would preferably be too weak.
Key takeaways
Types of retaining walls
A. General
B. Analysis
C. Constructability
FLEXIBLE ANCHORED WALLS
B. Analysis
2. Multiple Row of Anchors:
C. Anchor sorts
The following are possible types of anchor support system:
A grouted tieback is a system used to transfer the tensile load from the flexible wall to soil or rock. It consists of all pre stressing steel or tendons the anchorage grout coating sheathings couplers and encapsulation.
2. Deadman
A dead man might encompass giant plenty of formed or cast-in-place concrete, driven soldier piles, or a nonstop cloth wall. The specified depth of the dead man shall be analyzed supported by the active and passive earth pressures exerted on the dead man.
Deadman anchors should be settled a distance from the anchored wall such they'll mobilize their passive pressure resistance outside of the anchored wall's active zone this is often delineated in such references as USS Steel pile Manual and Foundation Analysis.
3. Struts or Braces
D. Constructability
The mass stability of the earth-tieback wall system is checked by the Geotechnical Engineering Bureau unless the adviser agreement states that the adviser can do all the geotechnical style work for the project. The designer is notified of any special necessities that have to be compelled to be enclosed within the contract to confirm mass stability.
Sheeting Walls:
In the case of permanently anchored cloth walls (not H-pile and walls with avoidance zones) while not special options that will allow water to empty from behind the wall (weep holes alone square measure ineffective). The consequences of associate the blue rise in water level in periods of serious precipitation ought to be thought-about. Unless careful water level analyses indicate Otherwise, the ultimate anchor style ought to be supported a ten-foot. (3 m) rise within the water level compared to the best water level determined from belowground explorations. To account for attainable alert water conditions, multiply by one.25 the calculated anchor masses on top of the water level (after adding the ten-foot. (3 m)
Soldier Pile and lagging Walls:
H-pile (or an alternative style of the solider pile) and lagging walls mustn't be employed in excavations below water level unless the look includes acceptable positive strategies to regulate flow.
2. Grouted Tiebacks:
The presence of existing structures and utilities ought to be taken under consideration once deciding upon the placement and inclination of anchors. The installation of the grouted holding device, location, and inclination, ought to be surveyed against these existing web site constraints. The look shall meet the necessities for minimum ground protects the grouted holding device.
The minimum anchor free length is
a. 15 ft. (4.6 m) or
b. the length of the tieback from the face of the wall to the theoretical.
Plus H/5
3. Deadman:
Both the projected maintenance and protection of traffic theme and also the construction sequencing ought to be evaluated to confirm that there's no interference with the tactic and sequence of rod installation and its future functioning.
4. Struts or Braces
The location and spacing of struts or thought to be critiqued about the assigned operating area and projected construction thought ought to incline to access by staff, provides and instrumentation
The installation of the block ought to be evaluated with regard to the support of the wall system. The wall ought to be analyzed for any extra excavation or alternative construction impacts necessary to put in the block.
Key takeaways
Retaining Walls necessary Factors
Depth
The depth of the wall footings can primarily rely on the kind of soil or bedrock gift. In some cases, it'll conjointly rely on the frost depth in your area; the retentive wall’s depth ought to be below the frost line. For areas that don't have frost however have soils that are water retentive, the footings should even be mammary gland deeper.
Drains
Drains should even be integrated into the planning of retentive walls to attenuate the lateral pressure iatrogenic by water once it rains. A typical wall drain is put in by creating by removal a trench simply behind the wall. A geotechnical filter cloth is placed within the ditch and a slanted perforated voidance pipe is ordered on high of it. The pipe is then coated with gravel, once that the filter cloth is wrapped around it and therefore the trench is flat-topped with soil.
Building a wall is difficult, particularly once it involves side properties. However, you'll have confidence in Sinai Construction for quality work and work done right. Sinai Construction for a consultation currently.
Introduction
(1). Then types of labor, as an example. Whether it is permanent or temporary
(2). Site conditions.
(3).The required depth of piles.
(4). The bending moments concerned.
(5).The nature of the structure.
(6).The type of protection needed.
Timber sheet piles
Timber sheet piles square measure usually used for brief spans in temporary structures, and to resist lightweight lateral masses. they're generally connected along by tongue and groove joints. The disadvantage of timber piles is that they need preservative treatment and don't seem to be usually appropriate for soils consisting of stones.
Reinforced concrete sheet piles
Reinforced concrete sheet piles are formed by concrete members, sometimes connected along by tongue and groove joints. They are ordinarily employed in permanent stream embankments, canals, and different marine structures. The toes of the piles square measure sometimes cut with Associate in Nursing oblique face to facilitate simple driving and interlocking, whereas the heads square measure finished off by casting a capping beam.
Steel sheet piles
Steel is that the most typical variety of sheet piles because it has sensible resistance to high driving stresses, wonderful water-tightness, and may be exaggerated long either by attachment or bolting. They are connected by interlocking.
There square measure four basic varieties of steel sheet piles:
These embody Larssen and Frodingham sheet piles that are measure systems of interlocking steel piles. They need sensible driving qualities and a square measure designed to produce great strength for low weight.
The interlocking system facilitates simple positioning of the piles (pitching) and driving, additionally providing a tight joint to make a good water seal. In some cases, a sealing material is brushed into the joints before pitching that expands in thickness to make a watertight joint.
Larssen sheet piles square measure stronger and easier to drive owing to their uniform section form. Frodingham sheet piles square measure sometimes provided interlocked in pairs that make them easier and faster to handle and pitch.
These square measure piles that square measure interlocked and driven to make cellular cofferdams which can be full of material like gravel and little rocks.
These square measures are fashioned by 2 or a lot of piling sections welded along, and square measure appropriate once serious masses and high bending moments square measure anticipated.
These square measures are ordinarily employed in city district protection wherever massive bending moments and serious axial masses square measure anticipated. A typical composite pile may be a double-section welded to the rim of a universal girder.
Key takeaways
Type of sheet piles
Basic varieties of steel sheet piles
References
1. LH khan - a textbook of geotechnical engineering
2. VNS Murthy: soil mechanics and foundation engg; sai Krupa technical consultant
3. Das braja M: Principle of geotechnical engineering