Unit - 5
Application Layer
FTP
- FTP stands for File transfer protocol.
- FTP is a standard internet protocol provided by TCP/IP used for transmitting the files from one host to another.
- It is mainly used for transferring the web page files from their creator to the computer that acts as a server for other computers on the internet.
- It is also used for downloading the files to computer from other servers.
Objectives of FTP
- It provides the sharing of files.
- It is used to encourage the use of remote computers.
- It transfers the data more reliably and efficiently.
Why FTP?
Although transferring files from one system to another is very simple and straightforward, but sometimes it can cause problems. For example, two systems may have different file conventions. Two systems may have different ways to represent text and data. Two systems may have different directory structures. FTP protocol overcomes these problems by establishing two connections between hosts. One connection is used for data transfer, and another connection is used for the control connection.
Mechanism of FTP
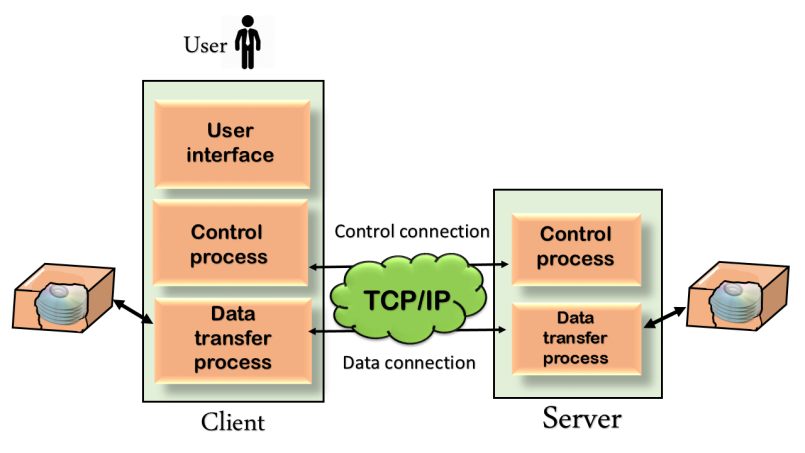
Fig – Mechanism of FTP
The above figure shows the basic model of the FTP. The FTP client has three components: the user interface, control process, and data transfer process. The server has two components: the server control process and the server data transfer process.
There are two types of connections in FTP:
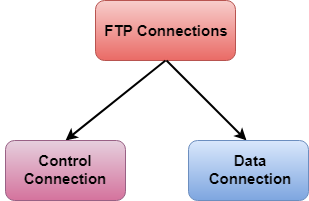
Fig – FTP Connections
- Control Connection: The control connection uses very simple rules for communication. Through control connection, we can transfer a line of command or line of response at a time. The control connection is made between the control processes. The control connection remains connected during the entire interactive FTP session.
- Data Connection: The Data Connection uses very complex rules as data types may vary. The data connection is made between data transfer processes. The data connection opens when a command comes for transferring the files and closes when the file is transferred.
FTP Clients
- FTP client is a program that implements a file transfer protocol which allows you to transfer files between two hosts on the internet.
- It allows a user to connect to a remote host and upload or download the files.
- It has a set of commands that we can use to connect to a host, transfer the files between you and your host and close the connection.
- The FTP program is also available as a built-in component in a Web browser. This GUI based FTP client makes the file transfer very easy and also does not require to remember the FTP commands.
Advantages of FTP:
- Speed: One of the biggest advantages of FTP is speed. The FTP is one of the fastest way to transfer the files from one computer to another computer.
- Efficient: It is more efficient as we do not need to complete all the operations to get the entire file.
- Security: To access the FTP server, we need to login with the username and password. Therefore, we can say that FTP is more secure.
- Back & forth movement: FTP allows us to transfer the files back and forth. Suppose you are a manager of the company, you send some information to all the employees, and they all send information back on the same server.
Disadvantages of FTP:
- The standard requirement of the industry is that all the FTP transmissions should be encrypted. However, not all the FTP providers are equal and not all the providers offer encryption. So, we will have to look out for the FTP providers that provides encryption.
- FTP serves two operations, i.e., to send and receive large files on a network. However, the size limit of the file is 2GB that can be sent. It also doesn't allow you to run simultaneous transfers to multiple receivers.
- Passwords and file contents are sent in clear text that allows unwanted eavesdropping. So, it is quite possible that attackers can carry out the brute force attack by trying to guess the FTP password.
- It is not compatible with every system.
Key takeaway
The FTP client has three components: the user interface, control process, and data transfer process. The server has two components: the server control process and the server data transfer process. One of the biggest advantages of FTP is speed. The FTP is one of the fastest way to transfer the files from one computer to another computer.
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) in Application Layer
When DNS (Domain Name System) was designed, nobody expected that there would be so many address changes such as adding a new host, removing a host, or changing an IP address. When there is a change, the change must be made to the DNS master file which needs a lot of manual updating and it must be updated dynamically.
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS):
It is a method of automatically updating a name server in the Domain Name Server (DNS), often in real-time, with the active DDNS configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses, or other information. In DDNS, when a binding between a name and an address is determined, the information is sent, usually by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to a primary DNS server.
The primary server updates the zone. The secondary servers are notified either actively or passively. Inactive notification, the primary server sends a message to secondary servers, whereas, in the passive notification, the secondary servers periodically check for any changes. In either case, after being notified about the change, the secondary requests information about the entire zone (zone transfer).
DDNS can use an authentication mechanism to provide security and prevent unauthorized changes in DNS records.
Advantages:
- It saves time required by static addresses updates manually when network configuration changes.
- It saves space as the number of addresses are used as required at one time rather than using one for all the possible users of the IP address.
- It is very comfortable for users’ point of view as any IP address changes will not affect any of their activities.
- It does not affect accessibility as changed IP addresses are configured automatically against URL’s.
Disadvantages:
- It is less reliable due to lack of static IP addresses and domain name mappings.
- Dynamic DNS services alone cannot make any guarantee about the device you are attempting to connect is actually your own.
Uses:
- It is used for Internet access devices such as routers.
- It is used for security appliance manufacturers and even required for IP-based security appliances like DVRs.
Telnet
- The main task of the internet is to provide services to users. For example, users want to run different application programs at the remote site and transfers a result to the local site. This requires a client-server program such as FTP, SMTP. But this would not allow us to create a specific program for each demand.
- The better solution is to provide a general client-server program that lets the user access any application program on a remote computer. Therefore, a program that allows a user to log on to a remote computer. A popular client-server program Telnet is used to meet such demands. Telnet is an abbreviation for Terminal Network.
- Telnet provides a connection to the remote computer in such a way that a local terminal appears to be at the remote side.
There are two types of logins:
Local Login
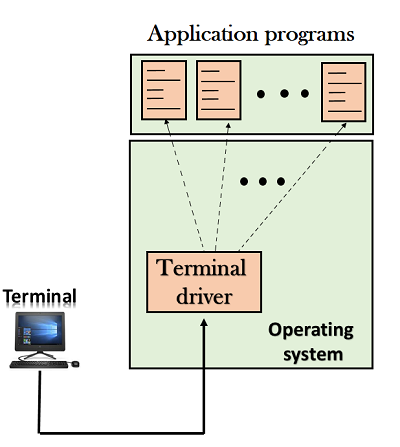
Fig – Local login
o When a user logs into a local computer, then it is known as local login.
o When the workstation running terminal emulator, the keystrokes entered by the user are accepted by the terminal driver. The terminal driver then passes these characters to the operating system which in turn, invokes the desired application program.
o However, the operating system has special meaning to special characters. For example, in UNIX some combination of characters have special meanings such as control character with "z" means suspend. Such situations do not create any problem as the terminal driver knows the meaning of such characters. But it can cause the problems in remote login.
Remote login
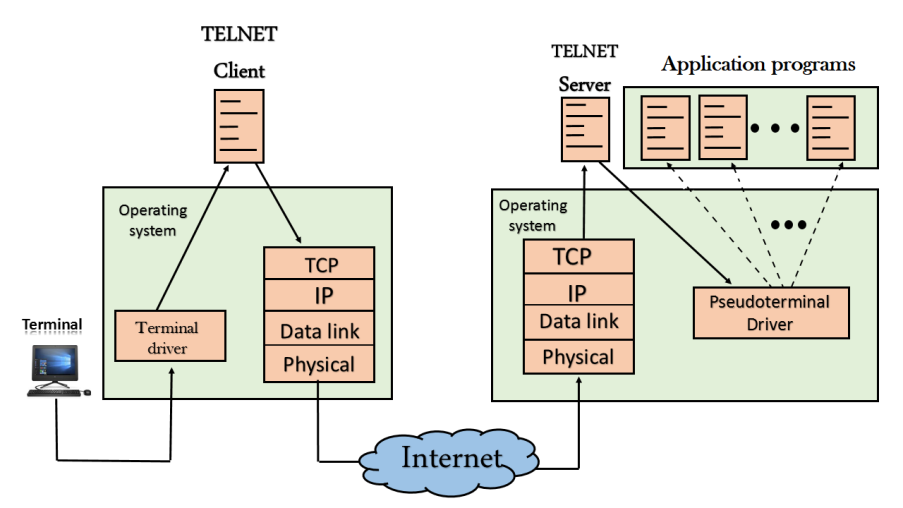
Fig – Remote login
- When the user wants to access an application program on a remote computer, then the user must perform remote login.
How remote login occurs
At the local site
The user sends the keystrokes to the terminal driver, the characters are then sent to the TELNET client. The TELNET client which in turn, transforms the characters to a universal character set known as network virtual terminal characters and delivers them to the local TCP/IP stack
At the remote site
The commands in NVT forms are transmitted to the TCP/IP at the remote machine. Here, the characters are delivered to the operating system and then pass to the TELNET server. The TELNET server transforms the characters which can be understandable by a remote computer. However, the characters cannot be directly passed to the operating system as a remote operating system does not receive the characters from the TELNET server. Therefore it requires some piece of software that can accept the characters from the TELNET server. The operating system then passes these characters to the appropriate application program.
Network Virtual Terminal (NVT)
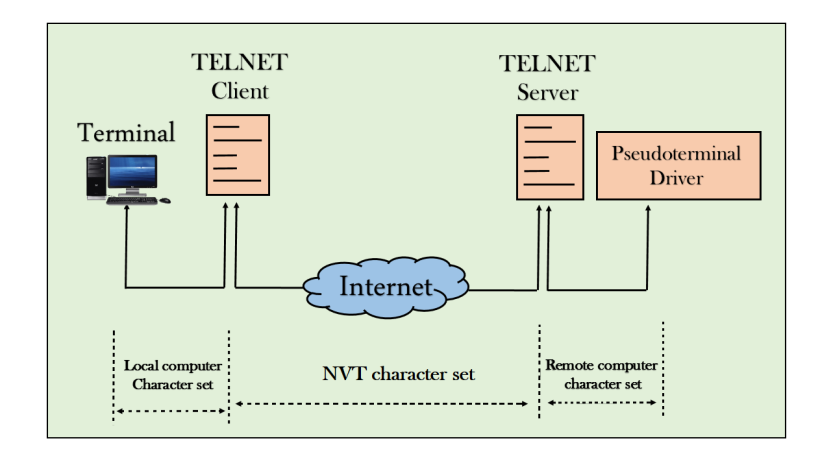
Fig - NVT
- The network virtual terminal is an interface that defines how data and commands are sent across the network.
- In today's world, systems are heterogeneous. For example, the operating system accepts a special combination of characters such as end-of-file token running a DOS operating system ctrl+z while the token running a UNIX operating system is ctrl+d.
- TELNET solves this issue by defining a universal interface known as network virtual interface.
- The TELNET client translates the characters that come from the local terminal into NVT form and then delivers them to the network. The Telnet server then translates the data from NVT form into a form which can be understandable by a remote computer.
What is E-mail?
E-mail is defined as the transmission of messages on the Internet. It is one of the most commonly used features over communications networks that may contain text, files, images, or other attachments. Generally, it is information that is stored on a computer sent through a network to a specified individual or group of individuals.
Email messages are conveyed through email servers; it uses multiple protocols within the TCP/IP suite. For example, SMTP is a protocol, stands for simple mail transfer protocol and used to send messages whereas other protocols IMAP or POP are used to retrieve messages from a mail server. If you want to login to your mail account, you just need to enter a valid email address, password, and the mail servers used to send and receive messages.
Although most of the webmail servers automatically configure your mail account, therefore, you only required to enter your email address and password. However, you may need to manually configure each account if you use an email client like Microsoft Outlook or Apple Mail. In addition, to enter the email address and password, you may also need to enter incoming and outgoing mail servers and the correct port numbers for each one.
Email messages include three components, which are as follows:
- Message envelope: It depicts the email's electronic format.
- Message header: It contains email subject line and sender/recipient information.
- Message body: It comprises images, text, and other file attachments.
The email was developed to support rich text with custom formatting, and the original email standard is only capable of supporting plain text messages. In modern times, email supports HTML (Hypertext markup language), which makes it capable of emails to support the same formatting as websites. The email that supports HTML can contain links, images, CSS layouts, and also can send files or "email attachments" along with messages. Most of the mail servers enable users to send several attachments with each message. The attachments were typically limited to one megabyte in the early days of email. Still, nowadays, many mail servers are able to support email attachments of 20 megabytes or more in size.
In 1971, as a test e-mail message, Ray Tomlinson sent the first e-mail to himself. This email was contained the text "something like QWERTYUIOP." However, the e-mail message was still transmitted through ARPANET, despite sending the e-mail to himself. Most of the electronic mail was being sent as compared to postal mail till 1996.
Differences between email and webmail
The term email is commonly used to describe both browser-based electronic mail and non-browser-based electronic mail today. The AOL and Gmail are browser-based electronic mails, whereas Outlook for Office 365 is non-browser-based electronic mail. However, to define email, a difference was earlier made as a non-browser program that needed a dedicated client and email server. The non-browser emails offered some advantages, which are enhanced security, integration with corporate software platforms, and lack of advertisements.
Uses of email
Email can be used in different ways: it can be used to communicate either within an organization or personally, including between two people or a large group of people. Most people get benefit from communicating by email with colleagues or friends or individuals or small groups. It allows you to communicate with others around the world and send and receive images, documents, links, and other attachments. Additionally, it offers benefit users to communicate with the flexibility on their own schedule.
There is another benefit of using email; if you use it to communicate between two people or small groups that will beneficial to remind participants of approaching due dates and time-sensitive activities and send professional follow-up emails after appointments. Users can also use the email to quickly remind all upcoming events or inform the group of a time change. Furthermore, it can be used by companies or organizations to convey information to large numbers of employees or customers. Mainly, email is used for newsletters, where mailing list subscribers are sent email marketing campaigns directly and promoted content from a company.
Email can also be used to move a latent sale into a completed purchase or turn leads into paying customers. For example, a company may create an email that is used to send emails automatically to online customers who contain products in their shopping cart. This email can help to remind consumers that they have items in their cart and stimulate them to purchase those items before the items run out of stock. Also, emails are used to get reviews by customers after making a purchase. They can survey by including a question to review the quality of service.
History of E-mail
As compared to ARPANet or the Internet, email is much older. The early email was just a small advance, which is known as a file directory in nowadays. It was used to just put a message in other user's directory in the place where they were able to see the message by logging in. For example, the same as leaving a note on someone's desk. Possibly MAILBOX was used at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, which was the first email system of this type from 1965. For sending messages on the same computer, another early program was SNDMSG.
Users were only able to send messages to several users of the same computer through email when the internetworking was not beginning. And, the problem became a little more complex when computers began to talk to each other over networks, we required to put a message in an envelope and address it for the destination.
Later in 1972, Ray Tomlinson invented email to remove some difficulties. Tomlinson worked (Like many of the Internet inventors) for Newman and Bolt Beranek as an ARPANET contractor. To denote sending messages from one computer to another, he picked up the @ symbol from the keyboard. Then, it became easy to send a message to another with the help of Internet standards; they were only required to propose name-of-the-user@name-of-the-computer. One of the first users of the new system was Internet pioneer Jon Postel. Also, describing as a "nice hack," credited goes to Jon Postel.
Although the World Wide Web offers many services, email is the most widely used facility and remains the most important application of the Internet. On the international level, over 600 million people use email. There were hundreds of email users by 1974, as ARPANET ultimately encouraged it. Furthermore, email caused a radical shift in Arpa's purpose, as it became the savior of Arpanet.
From there were rapid developments in the field of the email system. A big enhancement was to sort emails; some email folders for his boss were invented by Larry Roberts. To organize an email, John Vittal developed some software in 1976. By 1976 commercial packages began to appear, and email had really taken off. The email had changed people and took them from Arpanet to the Internet. Here was appeared some interesting features that ordinary people all over the world wanted to use.
Some years later, Ray Tomlinson observed about email. As compared to the previous one, any single development is stepping rapidly and nearly followed by the next. I think that all the developments would take a big revolution.
When personal computers came on the scene, the offline reader was one of the first new developments. Then, email users became able to store their email on their own personal computers with the help of offline reader and read it. Also, without actually being connected to the network, they were able to prepare replies like Microsoft Outlook can do today. In parts of the world, this was specifically useful for people where the telephone was expensive as compared to the email system.
Without being connected to a telephone, it was able to prepare a reply with connection charges of many dollars a minute and then get on the network to send it. Also, it was useful as the offline mode allowed for more simple user interfaces. In this modern time of very few standards being connected directly to the host email system often resulted in no capacity for text to wrap around on the screen of the user's computer, and backspace keys and delete keys may not work and other such annoyances. Offline readers helped out more to overcome these kinds of difficulties.
The SMTP (simple mail transfer protocol) was the first important email standard. It was a fairly naïve protocol that is still in use. And, it was made in terms of no attempt to find the person who sent a message that was the right or not what they claimed to be. In the email addresses, fraudulent was very easy and is still available. Later, these basic flaws were used in the protocol by security frauds, worms and viruses, and spammers forging identities. From 2004, some of these problems are still being processed for a solution.
But as developed email system offered some important features that helped out people to understand easily about email. In 1988, Steve Dorner developed Eudora that was one of the first good commercial systems. But it did not appear for a long time after Pegasus mail come. Servers began to appear as a standard when Internet standards POP (Post office protocol) for email began to mature. Each server was a little different before standard post office protocol (POP). POP was an important standard that allowed users to work together.
Individual dialup users were required to charges for an email per-minute in those days. Also, on the Internet, email and email discussion groups were the main uses for most people. There were several issues on a wide variety of subjects; they became USENET as a body of newsgroups.
With the World Wide Web (WWW), email became available with a simple user interface that was offered by providers like Hotmail and Yahoo. And, users did not require to pay any charges on these platforms. Now everyone wanted at least one email address as it is much simple and affordable, and the medium was adopted by millions of people.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) started to connect people with each other all over the world by the 1980s. Also, by 1993 the use of the Internet was becoming widespread, and the word electronic mail was replaced by email.
Today, email has become a primary platform to communicate with people all over the world. There are continuing updates to the system with so many people using email for communication. Although email has some security issues, there have been laws passed to prevent the spread of junk email over the years.
Advantages of Email
There are many advantages of email, which are as follows:
- Cost-effective: Email is a very cost-effective service to communicate with others as there are several email services available to individuals and organizations for free of cost. Once a user is online, it does not include any additional charge for the services.
- Email offers users the benefit of accessing email from anywhere at any time if they have an Internet connection.
- Email offers you an incurable communication process, which enables you to send a response at a convenient time. Also, it offers users a better option to communicate easily regardless of different schedules users.
- Speed and simplicity: Email can be composed very easily with the correct information and contacts. Also, minimum lag time, it can be exchanged quickly.
- Mass sending: You can send a message easily to large numbers of people through email.
- Email exchanges can be saved for future retrieval, which allows users to keep important conversations or confirmations in their records and can be searched and retrieved when they needed quickly.
- Email provides a simple user interface and enables users to categorize and filter their messages. This can help you recognize unwanted emails like junk and spam mail. Also, users can find specific messages easily when they are needed.
- As compared to traditional posts, emails are delivered extremely fast.
- Email is beneficial for the planet, as it is paperless. It reduces the cost of paper and helps to save the environment by reducing paper usage.
- It also offers a benefit to attaching the original message at the time you reply to an email. This is beneficial when you get hundreds of emails a day, and the recipient knows what you are talking about.
- Furthermore, emails are beneficial for advertising products. As email is a form of communication, organizations or companies can interact with a lot of people and inform them in a short time.
Disadvantages of Email
- Impersonal: As compared to other forms of communication, emails are less personal. For example, when you talk to anyone over the phone or meeting face to face is more appropriate for communicating than email.
- Misunderstandings: As email includes only text, and there is no tone of voice or body language to provide context. Therefore, misunderstandings can occur easily with email. If someone sends a joke on email, it can be taken seriously. Also, well-meaning information can be quickly typed as rude or aggressive that can impact wrong. Additionally, if someone types with short abbreviations and descriptions to send content on the email, it can easily be misinterpreted.
- Malicious Use: As email can be sent by anyone if they have an only email address. Sometimes, an unauthorized person can send you mail, which can be harmful in terms of stealing your personal information. Thus, they can also use email to spread gossip or false information.
- Accidents Will Happen: With email, you can make fatal mistakes by clicking the wrong button in a hurry. For instance, instead of sending it to a single person, you can accidentally send sensitive information to a large group of people. Thus, the information can be disclosed, when you have clicked the wrong name in an address list. Therefore, it can be harmful and generate big trouble in the workplace.
- Spam: Although in recent days, the features of email have been improved, there are still big issues with unsolicited advertising arriving and spam through email. It can easily become overwhelming and takes time and energy to control.
- Information Overload: As it is very easy to send email to many people at a time, which can create information overload. In many modern workplaces, it is a major problem where it is required to move a lot of information and impossible to tell if an email is important. And, email needs organization and upkeep. The bad feeling is one of the other problems with email when you returned from vacation and found hundreds of unopened emails in your inbox.
- Viruses: Although there are many ways to travel viruses in the devices, email is one of the common ways to enter viruses and infect devices. Sometimes when you get a mail, it might be the virus come with an attached document. And, the virus can infect the system when you click on the email and open the attached link. Furthermore, an anonymous person or a trusted friend or contact can send infected emails.
- Pressure to Respond: If you get emails and you do not answer them, the sender can get annoyed and think you are ignoring them. Thus, this can be a reason to make pressure on your put to keep opening emails and then respond in some way.
- Time Consuming: When you get an email and read, write, and respond to emails that can take up vast amounts of time and energy. Many modern workers spend their most time with emails, which may be caused to take more time to complete work.
- Overlong Messages: Generally, email is a source of communication with the intention of brief messages. There are some people who write overlong messages that can take much time than required.
- Insecure: There are many hackers available that want to gain your important information, so email is a common source to seek sensitive data, such as political, financial, documents, or personal messages. In recent times, there have various high-profile cases occurred that shown how email is insecure about information theft.
Different types of Email
There are many types of email; such are as follows:
Newsletters: It is studying by Clutch, the newsletter is the most common type of email that are routinely sent to all mailing list subscribers, either daily, weekly, or monthly. These emails often contain from the blog or website, links curated from other sources, and selected content that the company has recently published. Typically, Newsletter emails are sent on a consistent schedule, and they offer businesses the option to convey important information to their client through a single source. Newsletters might also incorporate upcoming events or new, webinars from the company, or other updates.
Lead Nurturing: Lead-nurturing emails are a series of related emails that marketers use to take users on a journey that may impact their buying behavior. These emails are typically sent over a period of several days or weeks. Lead-nurturing emails are also known as trigger campaigns, which are used for solutions in an attempt to move any prospective sale into a completed purchase and educate potential buyers on the services. These emails are not only helpful for converting emails but also drive engagement. Furthermore, lead-nurturing emails are initiated by a potential buyer taking initial action, such as clicking links on a promotional email or downloading a free sample.
Promotional emails: It is the most common type of B2B (Business to Business) email, which is used to inform the email list of your new or existing products or services. These types of emails contain creating new or repeat customers, speeding up the buying process, or encouraging contacts to take some type of action. It provides some critical benefits to buyers, such as a free month of service, reduced or omitted fees for managed services, or percentage off the purchase price.
Standalone Emails: These emails are popular like newsletters emails, but they contain a limitation. If you want to send an email with multiple links or blurbs, your main call-to-action can weaken. Your subscriber may skip your email and move on, as they may click on the first link or two in your email but may not come back to the others.
Onboarding emails: An onboarding email is a message that is used to strengthen customer loyalty, also known as post-sale emails. These emails receive users right after subscription. The onboarding emails are sent to buyers to familiarize and educate them about how to use a product effectively. Additionally, when clients faced with large-scale service deployments, these emails help them facilitate user adoption.
Transactional: These emails are related to account activity or a commercial transaction and sent from one sender to one recipient. Some examples of transactional email are purchase confirmations, password reminder emails, and personalized product notifications. These emails are used when you have any kind of e-commerce component to your business. As compared to any other type of email, the transactional email messages have 8x the opens and clicks.
Plain-Text Emails: It is a simple email that does not include images or graphics and no formatting; it only contains the text. These types of emails may worth it if you try to only ever send fancy formatted emails, text-only messages. According to HubSpot, although people prefer fully designed emails with various images, plain text emails with less HTML won out in every A/B test. In fact, HTML emails contain lower open and click-through rates, and plain text emails can be great for blog content, event invitations, and survey or feedback requests. Even if you do not send plainer emails, but you can boost your open and click through rates by simplifying your emails and including fewer images.
Welcome emails: It is a type of B2B email and common parts of onboarding emails that help users get acquainted with the brand. These emails can improve subscriber constancy as they include additional information, which helps to the new subscriber in terms of a business objective. Generally, welcome emails are sent buyers who got a subscription to a business's opt-in activities, such as a blog, mailing list, or webinar. Also, these emails can help businesses to build a better relationship between customers.
Examples of email attacks
Although there are many ways to travel viruses in the devices, email is one of the most common vectors for cyberattacks. The methods include spoofing, spamming, spear-phishing, phishing, ransomware, and business email compromise (BEC).
There are many organizations (around 7710) hit by a BEC attack every month, as one out of every 412 emails contains a malware attack. According to the Symantec Internet Threat Security Report, spear-phishing is the most widely used infection vector. Below is given a complete description of these types of attacks:
- Phishing: A form of fraud in which the attacks are the practice of sending fraudulent communications that appear to come from a reputable entity or person in email or other communication channels. Usually, it is done through the email; phishing emails are used by attackers to steal sensitive data like credit card and login information or to install malware on the victim's machine. Additionally, everyone should learn about a phishing attack in order to protect themselves, as it is a common type of cyberattack. The common features of phishing emails are Sense of urgency, Hyperlinks, Too Good to Be True, Unusual sender, Attachments.
- Spamming: Spam email is unsolicited bulk messages sent without explicit consent from the recipient, which is also known as junk email. Since the 1990s, spam is a problem faced by most email users and has been increasing in popularity. Obtained by spambots, spam mail recipients have had their email addresses (automated programs), which crawl the Internet to find email addresses. This is the dark side of email marketing in which spammers use spambots to create email distribution lists. Typically, an email is sent by a spammer to millions of email addresses with the expectation that only a few numbers of an email address will respond or interact with the message.
- Spoofing: Email spoofing is an email message that could be obtained from someone or somewhere other than the intended source. It is a popular strategy that is used in spam and phishing campaigns as core email protocols do not have a built-in method of authentication. And, when people think the email has been sent by a legitimate or familiar source, they are more likely to open an email. Thus, it is a common tactic used for spam and phishing emails. The email spoofing is used with the purpose of getting mail recipients to open emails and possibly respond to a solicitation.
- Business email compromise (BEC): A BEC is an exploit in which an authorized person or attacker hacks to a business email account and spoofs the owner's identity to defraud the company, its customers, partners of money. Often, an attacker simply creates an account with an email address that is almost identical to one on the corporate network, which creates trust between the victim and their email account. Sometimes, a BEC is also known as a man-in-the-email attack. Some samples of BEC email messages that contain the word in subject, such as urgent, transfer, request, payment, and more. There are five types of BEC scams on the basis of the FBI, which are False Invoice Scheme, CEO Fraud, Data Theft, Attorney Impersonation, Account Compromise.
- Spear-phishing: Email spoofing is an attack where hackers target an individual or specific organization to gain sensitive information through unauthorized access. Spear phishing is not initiated by random hackers but attempted by perpetrators to gain financial benefits or secrets information. It is an attack in which attackers send emails to specific and well-researched targets while purporting to be a trusted sender. The main objective of spear phishing is to convince victims to hand over information or money and infect devices with malware.
- Ransomware: It is a subset of malware that is used to encrypt a victim's files. Typically, it locks data by encryption on the victim's system. Typically, it locks data by encryption on the victim's system, and attackers demand payments before the ransomed data is decrypted. Unlike other types of attacks, the primary goal of ransomware attacks is just about always monetary. Usually, when the exploit occurs, a victim is notified about the attack and is given instructions for how to recover from the attack.
Popular email sites
There are some free email website examples include the following:
- AOL
- Zoho
- Gmail
- ProtonMail
- Com
- Microsoft Outlook
- Yahoo Mail
Email is a platform that allows users to communicate with people or groups of people around the world. As email security is more important but consequent, it is not inherently secure.
There are many techniques that can be used by individuals, organizations, and service providers. These techniques provide how to protect sensitive information with email communication and accounts from unauthorized access, loss, or destruction.
Individuals can protect their account with the help of creating strong passwords and changing them frequently. They can use alphabetical, numerical, special symbols to make a strong password that helps to protect your account. Users can also install and run an antivirus and antimalware software on their computer, as well as create spam filters and folders to separate potentially malicious emails and junk mail.
Also, there are some techniques the helps organizations to secure email include implementing an email security gateway, training employees on deploying automated email encryption solutions, and proper email usage. By processing and scanning all received emails, email gateways check emails for threats, and analyze that should be allowed into the system or not. A multilayered gateway is a powerful technique since attacks are increasing rapidly and becoming complicated and sophisticated. Some emails that cannot be caught by the gateway, training employees on how to differentiate malicious messages, and properly use email are the best approach, which helps users avoid threatening mails.
For potentially sensitive information, the automated email encryption solutions are used that scans all outgoing messages; it will encrypt the sensitive information before it is sent to the intended recipient. This process helps to send email securely and prevent hackers from gaining access to the secret information, even if they stop it. The only intended recipient can view the original information with permission.
Email service providers can also help to enhance security with the help of accessing control standards and mechanisms and establishing a strong password. Additionally, providers should also offer digital signatures and encryption solutions to secure emails in transit and in users' inboxes. Finally, to protect users from malicious, unrecognized, and untrustworthy messages, service providers should implement firewalls and spam-filtering software applications.
E-mail address breakdown
Let's take an example of Help@javatpoint.com to describe the breakdown of an email.
In the email address, before the part of the @ symbol, contains the department of an organization, alias, user, or group. As shown in the above example, help is the support department at our company javatpoint.
Next, the @ (at sign) is required for all SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) email address that is a divider in the email address, since the first message was sent by Ray Tomlinson.
Finally, users belong to the domain name, javatpoint.com. For the domain, the .com is the top-level domain (TLD).
What can be sent in an e-mail?
An email is a platform that enables users to communicate with each other. It allows users to send text messages, including a file or other data on the e-mail all over the world. It is also possible to attach a picture, word processor document, PDF, program, movie, or any file stored on your computer in an e-mail. However, due to some security issues, it may not be possible to send certain types of files on the email; they need some additional steps. For example, the .exe file can be blocked by many companies from being sent over the email, and you will need to compress the file into a .zip file format. Additionally, you may be unable to send any large files or programs from being sent over e-mail as most e-mail providers have file size restrictions.
What should be write e-mail or email?
You can use any word email or e-mail according to the style guide you are following as both are valid and have the same meaning. However, the e-mail word has a hyphen and is a compound noun that describes "electronic" and "mail."
How to send and receive e-mail
E-mail program
You can use an email program to send and receive an email. An email program is also known as an e-mail client. There are many email programs available to send and receive an email, including Mozilla Thunderbird and Microsoft Outlook. A server is used to store and deliver your messages while you use an email client. Often, your ISP (Internet service provider) host this server but can be another Internet company to host this server. To download the new emails, an email client requires connecting a server, whereas online stored emails are always available on Internet-connected devices.
Online e-mail
An online e-mail service or webmail is an alternative way and the popular solution for most people in sending and receiving e-mail. Examples of online emails are Yahoo Mail, Gmail, and Hotmail (now Outlook.com).
Some of the popular e-mail clients?
Today, there are different software-based e-mail clients available for users, but these are not online. Below is given a list that contains the most popular clients.
- Microsoft Outlookv
- Mail for Windows 10
- DreamMail
- Mozilla Thunderbird
- EM Client
- Mailbird
What makes a valid e-mail address?
Users need to follow the various rule that is given below to make valid email address:
- A username followed by @ (the at sign) is most important for an email address, which is followed by the domain name with a domain suffix. Hence, an e-mail must have a username.
- The domain name cannot be longer than 254 characters, and the username cannot be longer than 64 characters long.
- An email must have only one @ sign.
- An email should not have space and special characters like \ [ ] ( ) , : ; < >. Sometimes, few symbols such as backslash, space, and quotation mark work must be preceded with a forward slash. But these characters are not allowed by some email providers.
- In the email, the email address and username cannot start or end with a period.
- The two or more successive periods are not allowed in the email.
Key takeaways
- It is a method of automatically updating a name server in the Domain Name Server (DNS), often in real-time, with the active DDNS configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses, or other information. In DDNS, when a binding between a name and an address is determined, the information is sent, usually by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to a primary DNS server.
- The primary server updates the zone. The secondary servers are notified either actively or passively. Inactive notification, the primary server sends a message to secondary servers, whereas, in the passive notification, the secondary servers periodically check for any changes. In either case, after being notified about the change, the secondary requests information about the entire zone (zone transfer).
- DDNS can use an authentication mechanism to provide security and prevent unauthorized changes in DNS records.
A network virtual terminal is a communications concept describing a variety of data terminal equipment (DTE), with different data rates, protocols, codes and formats, accommodated in the same network. This is done as a result of network processing where each device’s data is converted into a network standard format, then converted into the format of the receiving device at the destination end. A virtual terminal allows a PC to connect to a remote server, usually to perform a file transfer or run an application. In the past, this functionality used to be performed by a physical terminal, but is now emulated in software. The PC and the server may be running different operating systems, but can communicate using well-known network protocols such as Telnet, SSH, FTP, etc. A virtual terminal normally has a command-line interface, which requires typing cryptic commands to communicate with a server. Putty is a well-known example of a virtual terminal.
Telnet is designed for terminal-to-terminal communication and distributed computer processing. Each host sets up a Network Virtual Terminal (NVT) and a host at one end assumes that an NVT has been set up at the other end. This save having to share information about each other's terminals. There is the mechanism to negotiate options so that the hosts can operate a more elaborate interface at each end using different fonts etc. than the NVT. Each host has the right to reject requests to 'upgrade'. Option requests will fly back and forth until the optimum session is established. A request for an option that the other is already running, will not be responded to.
Communication is established using the TCP/IP protocols and communication is based on a set of facilities known as a Network Virtual Terminal (NVT). At the user or client end the telnet client program is responsible for mapping incoming NVT codes to the actual codes needed to operate the user's display device and is also responsible for mapping user generated keyboard sequences into NVT sequences.
The NVT uses 7-bit codes for characters, the display device, referred to as a printer, is only required to display the "standard" printing ASCII characters represented by 7-bit codes and to recognize and process certain control codes. The 7-bit characters are transmitted as 8-bit bytes with most significant bit set to zero. An end-of-line is transmitted as the character sequence CR (carriage return) followed by LF (line feed). If it is desired to transmit an actual carriage return this is transmitted as a carriage return followed by a NUL (all bits zero) character.
Origin of Cryptography
Human being from ages had two inherent needs − (a) to communicate and share information and (b) to communicate selectively. These two needs gave rise to the art of coding the messages in such a way that only the intended people could have access to the information. Unauthorized people could not extract any information, even if the scrambled messages fell in their hand.
The art and science of concealing the messages to introduce secrecy in information security is recognized as cryptography.
The word ‘cryptography’ was coined by combining two Greek words, ‘Krypto’ meaning hidden and ‘graphene’ meaning writing.
History of Cryptography
The art of cryptography is considered to be born along with the art of writing. As civilizations evolved, human beings got organized in tribes, groups, and kingdoms. This led to the emergence of ideas such as power, battles, supremacy, and politics. These ideas further fueled the natural need of people to communicate secretly with selective recipient which in turn ensured the continuous evolution of cryptography as well.
The roots of cryptography are found in Roman and Egyptian civilizations.
Hieroglyph − The Oldest Cryptographic Technique
The first known evidence of cryptography can be traced to the use of ‘hieroglyph’. Some 4000 years ago, the Egyptians used to communicate by messages written in hieroglyph. This code was the secret known only to the scribes who used to transmit messages on behalf of the kings. One such hieroglyph is shown below.

Later, the scholars moved on to using simple mono-alphabetic substitution ciphers during 500 to 600 BC. This involved replacing alphabets of message with other alphabets with some secret rule. This rule became a key to retrieve the message back from the garbled message.
The earlier Roman method of cryptography, popularly known as the Caesar Shift Cipher, relies on shifting the letters of a message by an agreed number (three was a common choice), the recipient of this message would then shift the letters back by the same number and obtain the original message.
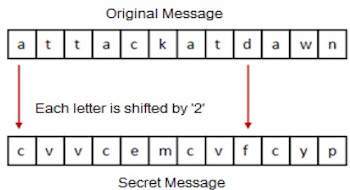
Steganography
Steganography is similar but adds another dimension to Cryptography. In this method, people not only want to protect the secrecy of an information by concealing it, but they also want to make sure any unauthorized person gets no evidence that the information even exists. For example, invisible watermarking.
In steganography, an unintended recipient or an intruder is unaware of the fact that observed data contains hidden information. In cryptography, an intruder is normally aware that data is being communicated, because they can see the coded/scrambled message.

Evolution of Cryptography
It is during and after the European Renaissance, various Italian and Papal states led the rapid proliferation of cryptographic techniques. Various analysis and attack techniques were researched in this era to break the secret codes.
- Improved coding techniques such as Vigenere Coding came into existence in the 15th century, which offered moving letters in the message with a number of variable places instead of moving them the same number of places.
- Only after the 19th century, cryptography evolved from the ad hoc approaches to encryption to the more sophisticated art and science of information security.
- In the early 20th century, the invention of mechanical and electromechanical machines, such as the Enigma rotor machine, provided more advanced and efficient means of coding the information.
- During the period of World War II, both cryptography and cryptanalysis became excessively mathematical.
With the advances taking place in this field, government organizations, military units, and some corporate houses started adopting the applications of cryptography. They used cryptography to guard their secrets from others. Now, the arrival of computers and the Internet has brought effective cryptography within the reach of common people.
Modern Cryptography
Modern cryptography is the cornerstone of computer and communications security. Its foundation is based on various concepts of mathematics such as number theory, computational-complexity theory, and probability theory.
Characteristics of Modern Cryptography
There are three major characteristics that separate modern cryptography from the classical approach.
Classic Cryptography | Modern Cryptography |
It manipulates traditional characters, i.e., letters and digits directly. | It operates on binary bit sequences. |
It is mainly based on ‘security through obscurity’. The techniques employed for coding were kept secret and only the parties involved in communication knew about them. | It relies on publicly known mathematical algorithms for coding the information. Secrecy is obtained through a secrete key which is used as the seed for the algorithms. The computational difficulty of algorithms, absence of secret key, etc., make it impossible for an attacker to obtain the original information even if he knows the algorithm used for coding. |
It requires the entire cryptosystem for communicating confidentially. | Modern cryptography requires parties interested in secure communication to possess the secret key only. |
Context of Cryptography
Cryptology, the study of cryptosystems, can be subdivided into two branches
- Cryptography
- Cryptanalysis
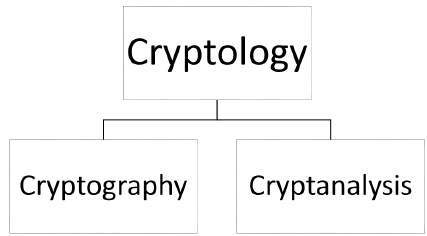
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the art and science of making a cryptosystem that is capable of providing information security.
Cryptography deals with the actual securing of digital data. It refers to the design of mechanisms based on mathematical algorithms that provide fundamental information security services. You can think of cryptography as the establishment of a large toolkit containing different techniques in security applications.
What is Cryptanalysis?
The art and science of breaking the cipher text is known as cryptanalysis.
Cryptanalysis is the sister branch of cryptography and they both co-exist. The cryptographic process results in the cipher text for transmission or storage. It involves the study of cryptographic mechanism with the intention to break them. Cryptanalysis is also used during the design of the new cryptographic techniques to test their security strengths.
Note − Cryptography concerns with the design of cryptosystems, while cryptanalysis studies the breaking of cryptosystems.
Security Services of Cryptography
The primary objective of using cryptography is to provide the following four fundamental information security services. Let us now see the possible goals intended to be fulfilled by cryptography.
Cryptography Primitives
Cryptography primitives are nothing but the tools and techniques in Cryptography that can be selectively used to provide a set of desired security services −
- Encryption
- Hash functions
- Message Authentication codes (MAC)
- Digital Signatures
The following table shows the primitives that can achieve a particular security service on their own.
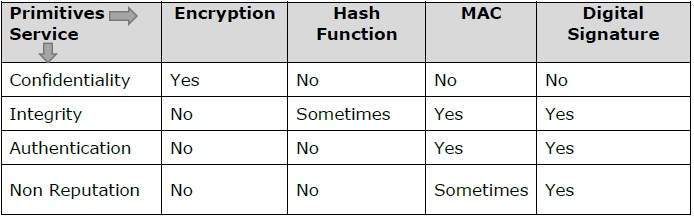
Note − Cryptographic primitives are intricately related and they are often combined to achieve a set of desired security services from a cryptosystem.
Computer network security consists of measures taken by business or some organizations to monitor and prevent unauthorized access from the outside attackers.
Different approaches to computer network security management have different requirements depending on the size of the computer network. For example, a home office requires basic network security while large businesses require high maintenance to prevent the network from malicious attacks.
Network Administrator controls access to the data and software on the network. A network administrator assigns the user ID and password to the authorized person.
Aspects of Network Security:
Following are the desirable properties to achieve secure communication:
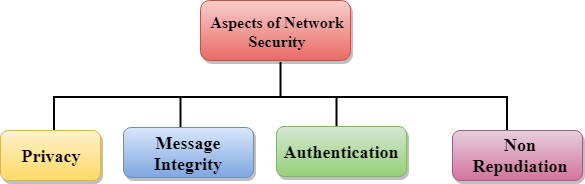
- Privacy: Privacy means both the sender and the receiver expects confidentiality. The transmitted message should be sent only to the intended receiver while the message should be opaque for other users. Only the sender and receiver should be able to understand the transmitted message as eavesdroppers can intercept the message. Therefore, there is a requirement to encrypt the message so that the message cannot be intercepted. This aspect of confidentiality is commonly used to achieve secure communication.
- Message Integrity: Data integrity means that the data must arrive at the receiver exactly as it was sent. There must be no changes in the data content during transmission, either maliciously or accident, in a transit. As there are more and more monetary exchanges over the internet, data integrity is more crucial. The data integrity must be preserved for secure communication.
- End-point authentication: Authentication means that the receiver is sure of the sender’s identity, i.e., no imposter has sent the message.
- Non-Repudiation: Non-Repudiation means that the receiver must be able to prove that the received message has come from a specific sender. The sender must not deny sending a message that he or she send. The burden of proving the identity comes on the receiver. For example, if a customer sends a request to transfer the money from one account to another account, then the bank must have a proof that the customer has requested for the transaction.
Key takeaway
Computer network security consists of measures taken by business or some organizations to monitor and prevent unauthorized access from the outside attackers. Aspects of network security are i) Privacy ii) Message Integrity iii) End Point authentication iv) Non-Repudiation.
References:
1. Forouzan, Data Communication & Networking, McGraw-Hill Education
2. Lathi, B. P. & Ding, Z., (2010), Modern Digital and Analog Communication Systems, Oxford University Press
3. Stallings, W., (2010), Data and Computer Communications, Pearson.
4. Andrew S. Tanenbaum, “Computer Networks” Pearson.
5. Ajit Pal, “Data Communication and Computer Networks”, PHI
6. Dimitri Bertsekas, Robert G. Gallager, “Data Networks”, Prentice Hall, 1992