Unit - 5
IC Engine Parts
The selection of the type of IC engine depends upon the following factors:
- Type of process.
- Type of cycle.
- Numbers of cylinders.
- Arrangements of cylinders.
- Engine speed, and
- Stroke bore ratio.
The general design considerations of the design of an IC engine depend on the following type of loads:
- Load due to gas pressure in the cylinder.
- Load due to inertia and centrifugal forces.
- Load due to frictional forces.
- Load due to torsional moment reaction and weight.
- Load due to vibrations, especially of the crankshaft.
- Thermal loads.
Step I: Thickness of cylinder wall:
The cylinder wall is subjected to gas pressure and piston side thrust. There may be bending of the wall due to piston side thrust.
The thickness of the wall is usually calculated by applying the following formula for a thin cylinder as
t=[(pmaxD)/2σc]+K
Where t=wall thickness in mm,
pmax=Maximum gas pressure, D= Cylinder bore σc=Permissible circumferential stress (MPa), K=reboring factor(mm)
Following empirical relations may be used to find various thicknesses:
- The thickness of the cylinder wall, t=0.145D+1.6mm
- The thickness of dry liner=0.030D to 0.035 D
- The thickness of the water jacket wall=0.032D+1.6mm
Step II: Cylinder Diameter (or bore) and length:
1. The output of a cylinder can be given as,
IP=pmLAn/60, where,
IP=Indicated power, pm=Indicated mean effective pressure(N/mm2), L=Length of stroke, A=Cross-sectional area of the cylinder, n=Number of working strokes per minute.
2. Output power can also be written in terms of brake power as
BP=2πNT/60
Where, BP= brake power, N=Number of rotation (rpm), and T= torque
- Mechanical efficiency=(BP)/(IP), from the above equations, the length of the cylinder can be evaluated.
Step III: Cylinder Flange and studs:
- The diameter of the studs may be obtained by equating the gas load due to maximum pressure in the cylinder to the resisting force offered by all the studs or bolts.
- Mathematically, (π/4)D2pmax=ns*( π/4)d2cσt
Where, σt=Allowable tensile stress (35 to 75 N/mm2), dc=core diameter of stud, ns=Number of studs or bolts.
Step IV: Cylinder Head:
- The thickness of the cylinder head may be obtained as, th=0.316D

- The value of allowable circumferential stress may be taken as 30 to 50 MPa.
Key Takeaway:
- The thickness of the cylinder wall is given by t=[(pmaxD)/2σc]+K.
- (π/4)D2pmax=ns*( π/4)d2cσt, For cylinder flange and stud.
1. Piston Head:
(i). The thickness of the piston head or crown is calculated based on strength and heat dissipation as follows:
The head thickness based on strength can be calculated by assuming the head to be a flat plate for uniform thickness and fixed at the edges.
The thickness of the pinhead, according to Grashof’s formula is given as
tH=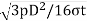
(ii). Based on heat dissipation, heat thickness is given as,
tH=H/[12.56k(TC-TE)],
Where, H=Heat flowing through the piston head (W), TC=Temperature at the center of the piston head, TE= Temperature at the edges of the piston head, and, k=Thermal conductivity factor (W/m/0C).
The heat following through the piston head (H) may also be estimated by the following formula:
H=C*V*m*HCV*BP
Where m=mass of the fuel used (kg/kW-s),
HCV= Higher calorific value of fuel, C= Constant representing that portion of heat supplied to the engine which is absorbed by the piston. Its value is taken as 0.05
2. Piston Rings:
The radial thickness (t1) of the ring may be obtained by considering the radial pressure between the cylinder wall and the ring. From bending stress considerations in the ring, the radial thickness is given by
t1=D(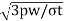
D= cylinder bore in mm, pw=[pressure of the gas on the wall
The axial thickness (t2) of the rings may be taken as 0.7t1 to t2.
The minimum axial thickness (t2) may also be obtained from the following empirical relation.
i2=D/10nR
Where, nR= number of rings, the width of top land, b1=tH to 1.2tH
3. Piston Barrel:
The thickness of the piston barrel at the top end is calculated,
t3=0.03D +b+4.9mm where, b=Radial width of ring (mm)
Step IV: Piston Skirt:
- We know that maximum gas load on the piston,
Fg=p*(πD2/4)
Where, p=maximum gas pressure in N/mm2
Step V: Piston Pin
The piston pin should be designed for the maximum gas load or the inertia force, whichever is larger. Bearing pressure is the design criteria and the diameter of the pin is determined by equating the gas load and bearing load.
So, l1dpb1=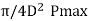
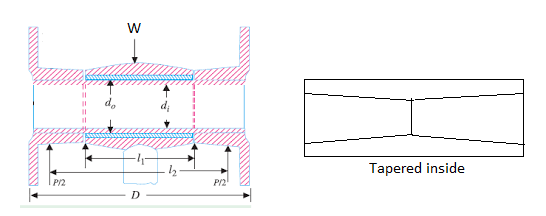
Fig. 1: Piston pin
The piston pin may be checked in bending by assuming the gas load to be uniformly distributed over the length l1 and pin supported at the center of the bosses at two ends.
The length between supports is
l2=l1+(D-l1)/2=(l1+D)/2
Key Takeaways:
Fg=p*(πD2/4) maximum gas load on the piston, for piston skirt
l2=l1+(D-l1)/2=(l1+D)/2 is important formula for design of piston pin
Mechanism which enables rotary motion of shaft to be transmitted to the second shaft axis, which is coincident with the first. OR
Clutch is a device to connect driving and driven shafts of a machine, where the driven shaft can be disconnected almost instantaneously from the driving shaft as desired by the operator or driver.
Requirements of clutch:
- Torque Transmission
- Gradual Engagements
- Heat Dissipation
- Dynamic Balancing
- Vibration Damping
- Size
- Inertia
- Ease of operation
1. Torque Transmission
- The clutch should be able to transfer the maximum torque of engine under all conditions.
- Usually designed to transmit 125 to 150% of maximum engine torque.
2. Gradual Engagement: Clutch should take the drive gradually without occurrence of sudden jerks.
3. Heat Dissipation: During clutch application large amount of heat is generated, the rubbing surfaces should have sufficient area and mass to absorb the heat generated. The design of clutch should ensure proper ventilation or cooling for adequate dissipation of heat.
The friction clutches work on the fact that friction is caused when two rotating discs come into contact with each other.
Principle for friction clutches:
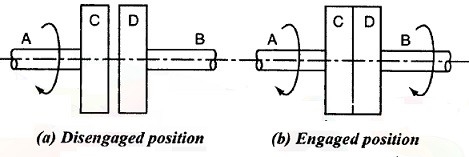
Figure 2: Principle for friction clutch
Let the shaft A and Disc C be revolving at some speed say N rpm. Shaft B and disc D keyed to it are stationary, initially when the clutch is not engaged.
Now apply some axial force W to disc D, so that it comes in contact with Disc C. As soon as the contact is made the force of friction between C and D will come into play and consequently the disc D will also start revolving.
The speed of D depends upon friction force present, which in turn is proportional to the force W applied.
If W is increased gradually, the speed of D will be increased correspondingly till the stage comes when speed of D becomes equal to speed of C.
Then clutch is said to be fully engaged.
Let W = axial load applied. µ= coefficient of friction R= effective mean radius of friction surface. Then, T = W R
Key Takeaways:
Clutch is a device to connect driving and driven shafts of a machine, where the driven shaft can be disconnected almost instantaneously from the driving shaft as desired by the operator or driver.
The friction clutches work on the fact that friction is caused when two rotating discs come into contact with each other.
Clutch | Coupling |
Clutch is a device that provides a temporary connection between the driver and driven shaft.
| Coupling makes the permanent and semi-permanent connection between two shaft ends.
|
Used where driven shaft/ driven machine required to be in intermittent service.
| Coupling used where driven shaft required to be in continuous service.
|
Clutch allow disconnection during the operation. Provide a mechanism for rapid engagement and disengagement during the operation at the operator will.
| It does not allow disconnection of the shaft during the normal operation (Torque limiting coupling allow slipping when torque limit is exceeded). Connection is in permanent nature, so there is no mechanism for quick connection and disconnection.
|
Clutch transmit power between two collinear shafts.
| Coupling used to transmit power between collinear as well as non-collinear shafts.
|
The driven shaft can run at variable speed.
| In coupling, the driven shaft run at the same speed as the driveshaft.
|
Example: Disc clutch, Cone clutch, Centrifugal clutch, Electromagnetic clutch
| Example: Universal coupling, Oldham coupling |
Working:
An unmarried plate take hold of has one take hold of plate. This take hold of works at the precept of friction.
It is the maximum not unusual place kind of take hold of utilized in motor vehicles. The take hold of frequently includes members, one set up at the using shaft and the opposite at the pushed shaft.
These shafts are parallel and concentric with every different; one shaft is constant to its housing even as the opposite is splined in order that it may circulate axially. The using torque can growth with the aid of using growing the powerful radius of contact. In the transmission device, the device with the aid of using which energy develops with the aid of using the engine transmits to avenue wheels to propel the car.
In motors, the energy develops with the aid of using the engine which use to show wheels. Therefore, the engine is to hook up with the transmission structures for transmitting energy to wheels.
Also, there ought to be a device the usage of which the engine may be engaged and disengaged with the transmission device easily and without surprise in order that the car mechanism isn't broken and passengers do now no longer experience inconvenience.
A take hold of is hired in motors for this purpose. A Clutch is a mechanism used to attach or disconnect the engine from the relaxation of the transmission elements. It is positioned among the engine and gearbox.
The take hold of disengages for starting, converting gears, stopping, and idling. The feature of the Clutch is to allow the engagement or disengagement of equipment whilst the car is desk bound and the engine is strolling without destructive equipment wheels. So, we come again to our factor of Single Plate Clutch and allow us to start.
- In the Clutch the 3 elements needs.
- These are the engine flywheel, a friction disc or a snatch plate and a stress plate. Some springs supply axial pressure to live the snatch with inside the engaged position.
- When the engine is strolling and consequently the flywheel is rotating, the stress plate additionally rotates due to the fact the stress plate attaches to the flywheel.
- The friction disc is positioned among the flywheel and the stress plate.
- When the using pressure has driven down the snatch is released.
- This movement forces the stress plate to transport far from the friction disc in opposition to the pressure of stress springs.
- With this motion of the stress plate, the friction plate is released, and consequently the snatch disengaged.
- When your foot is off the pedal, the springs push the stress plate in opposition to the snatch disc, which successively presses in opposition to the flywheel.
- This locks up the engine to the transmission enter shaft, inflicting them to spin on the identical speed.
- The amount of pressure the snatch can maintain relies upon at the friction among the snatch plate and the flywheel, and on this way, a good deal pressure the spring places at the stress plate.
- When the snatch presses, the piston pushes on the discharge fork, which presses the throw-out bearing in opposition to the middle of the diaphragm spring.
- As the centre of the diaphragm spring pushes in, a chain of pins close to the outdoor floor of the spring reasons the spring to tug the stress plate Forfar from the snatch plate.
- This releases the snatch from the spinning engine.
Construction:
An unmarried plate take hold of is composed of various components for correct working. They are organized in a scientific order.
Mainly it includes a take hold of plate with each facet friction lining and a few different components which assist with inside the right functioning of a take hold of like a flywheel, stress plate, thrust bearing, hub, springs, and enter mechanism for engagement and disengagement of the take hold of.
The take hold of plate attaches to the hub among the flywheel and the stress plate, it movements axially at the pushed shaft.

In an unmarried plate take hold of, the take hold of plate ought to have each facet friction lining as it mounts among the stress plate and flywheel, friction is chargeable for the torque transmission.
The stress plate engages with the flywheel and springs. Pressure plate enables to push the take hold of plate with the flywheel. A lever attaches to thrust bearings with a few mechanism at the pushed shaft which transmits enter and output movement from the take hold of pedal.
Parts:
1. Flywheel
The flywheel is a quintessential a part of the engine, which additionally use as part of the grasp. It is a using member and connects to the stress plate of the grasp shaft is homes with bearings in a flywheel. The flywheel rotates because the engine crankshaft rotates.
2. Pilot Bearing
The pilot bearing or bushing press into the quilt of the crankshaft to guide the quit of the transmission enter shaft. The pilot bearing prevents the transmission shaft and grasp disc from wobbling up and down while the grasp releases. It additionally assists the enter shaft middle of the disc at the flywheel.
3. Clutch plate or Disc plate
It is the pushed member of the single-plate grasp and line with friction cloth on each surfaces. It has an important hub with inner splines to restrict the axial journey alongside the splined gearbox using shaft.
This facilitates to offer damping movements in opposition to torsional vibrations or versions of the using torque among engine and transmission. A grasp disc is a plate among flywheel and friction or stress plate. It has a chain of facings inverters on every facet to extend the friction. These grasp facings are fabricated from asbestos cloth. They are relatively worn and warmth resistant.
4. Pressure plate
The stress plate is fabricated from unique solid iron. It is the heaviest a part of the grasp meeting. The essential characteristic of the stress plate is to set up even touch with the pushed plate dealing with thru which the stress springs can exert a enough pressure to transmit the total torque of the engine. The stress plate presses the grasp plate directly to the flywheel from its machined surface. Between the stress plate and grasp cowl meeting, stress springs are fitted. The stress may be withdrawn from the flywheel every time launch levers are depressed via way of means of the toggle or launch levers are pivoted accordingly.
5. Clutch cowl
The grasp cowl meeting bolts to the flywheel. It includes a stress plate, launch lever mechanism, grasp cowl, and stress springs. Generally, the grasp plate revolves with the flywheel. However, while the grasp has disengaged, the flywheel, in addition to the stress plates, are loose to rotate independently from the pushed plate and using shaft.
6. Release levers
These pivots on pins to the grasp cowl, their outer ends find and positions on stress plate legs, and the internal ends are projecting closer to the grasp shaft. A cautious and correct adjustment of the discharge mechanism is one of the maximum crucial elements governing the overall performance of a grasp meeting.
7. Clutch shaft
It is part of the gearbox. Since its miles a splined shaft to the hub of the grasp plate, that is sliding on it. One quit of the grasp shaft attaches to the crankshaft or flywheel and the opposite quit connects to the gearbox or paperwork part of the gearbox.
Advantages of Single Plate Clutch
The running of engagement and disengagement may be very clean in an unmarried plate snatch.
Power losses are very much less.
As enough floor location is to be had for warmth dissipation in such clutches, no cooling oil is required.
Therefore, unmarried plate clutches are dry type.
Single plate clutches have a short operation and reply fast.
It makes it less complicated to extrude gears than a cone type.
Disadvantages of Single Plate Clutch
Single plate clutches have excessive put on and tear rate.
It has much less torque transmitting capacity.
The springs should be the greater stiff as a result more pressure calls for to disengage.
It calls for excessive maintenance.
The area required to deal with the snatch is greater in comparison to the multi-plate snatch.
Key Takeaways:
- An unmarried plate take hold of has one take hold of plate. This take hold of works at the precept of friction.
- It is positioned among the engine and gearbox.
- The friction disc is positioned among the flywheel and the stress plate.
- An unmarried plate take hold of is composed of various components for correct working. They are organized in a scientific order.
The torque potential of the snatch is the quantity of torque that may be transmitted via way of means of the snatch whilst it is slipping or whilst it is completely closed.
The torque potential of a snatch relies upon on a chain of factors: general vicinity of the friction floor.
Friction coefficient
Modern automobile powertrain and drivetrain structures have as a minimum one snatch as an aspect.
An AWD or four wheel drive car will have numerous clutches, relying at the structure and form of the powertrain and drivetrain.
A snatch may be a standalone aspect, used to attach the inner combustion engine (ICE) to the transmission, or may be the sub-aspect or every other most important aspect: torque converter, automated transmission, switch case, limited-slip differential (LSD), etc.
Depending at the variety of friction plates, a snatch may be: unmarried plate snatch multi-disc snatch Depending at the form of friction, we are able to have: dry clutches moist (oil) clutches Usually, unmarried plate clutches (besides torque converter lock-up clutches) have dry friction and multi-disc clutches are with moist friction.
Regardless of the type, each snatch has a torque potential. The torque potential of the snatch is the quantity of torque that may be transmitted via way of means of the snatch whilst it’s slipping or whilst it’s completely closed.
The torque potential of a snatch relies upon on a chain of factors: general vicinity of the friction floor friction coefficient everyday pressure performing at the snatch variety of friction elements
To calculate the torque potential of the snatch we’ll have a examine the geometry of the snatch (friction) disc. Within the vicinity of the friction floor we're going to constitute a standard vicinity dx, at the gap x from the centre.
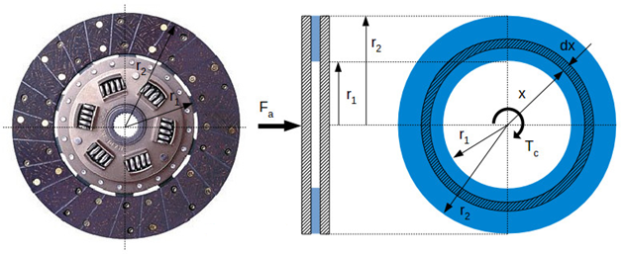
Fig 3: Clutch torque capacity calculation
Where:
Fa [N] – the normal force pressing the clutch plate
Tc [Nm] – the torque capacity of the clutch
r1 [m] – the inner radius of the friction surface
r2 [m] – the outer radius of the friction surface
The pressure p [Pa] acting on the clutch is equal with the ratio between the normal force Fa and the area of the friction surface S [m2]:
p=FaS(1)
Assuming that the area of the rivets is negligible, the area of the friction surface is calculated as:
S=S2–S1=πr22–πr21=π(r22–r21)(2)
Replacing (2) in (1), we get the expression for the clutch pressure:
p=Faπ(r22–r21)(3)
The elementary area dA is calculated as:
DA=2πxdx(4)
The elementary normal force dN, acting on the elementary area is calculated as:
DN=pdA(5)
Replacing (3) and (4) in (5), we get:
DN=2Faxdxr22–r21(6)
The elementary friction force dF is calculated as:
DF=μdN(7)
Where μ [-] is the friction coefficient of the clutch disc.
Replacing (6) in (7), we get:
DF=2μFaxdxr22–r21(8)
The elementary friction torque dT is calculated as:
DT=xdF(9)
Replacing (8) in (9), we get:
DT=2μFax2dxr22–r21(10)
Integrating equation (10) from r1 to r2, we get the mathematical expression of the torque capacity of the clutch:
Tc=∫r2r1dT=2μFar21–r22∫r2r1x2dx=23μr32–r31r22–r21Fa
Since a clutch has two friction surfaces, the resulting mathematical expression for the torque capacity of a single plate clutch is:
Tc=2⋅23μr32–r31r22–r21Fa(11)
For a multi-disc clutch expression (11) becomes:
Tc=z23μr32–r31r22–r21Fa(12)
Where z [-] is the number of friction surfaces (e.g. 2 – for a single friction disc, 4 – for two friction discs, etc.).
Assuming a mean radius rm [m] of the clutch calculated as:
Rm=r2+r12
We can deduce a simplified expression, with an acceptable error, for the torque capacity of the clutch:
Tc=zμFarm
Example 1
Calculate the torque capacity of single plate dry clutch, which has: the normal force 250 N, the outer radius 0.3 m, the inner radius 0.2 m and the friction coefficient 0.4.
Replacing the given parameters in equation (11), we get:

Key Takeaways:
The torque potential of a snatch relies upon on a chain of factors: general vicinity of the friction floor.
Within the vicinity of the friction floor we're going to constitute a standard vicinity dx, at the gap x from the centre
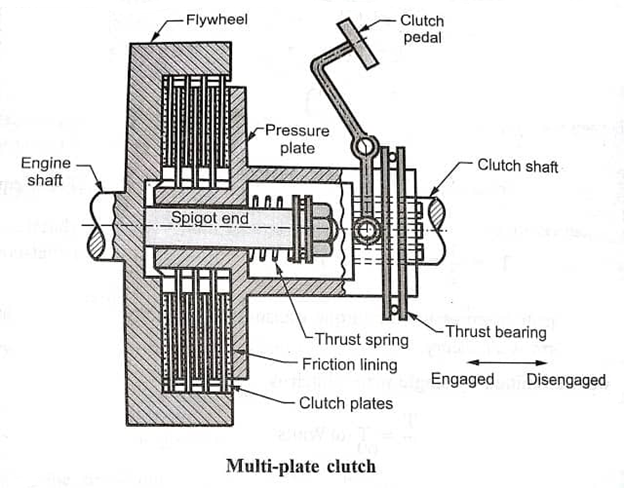
The Multi Plate Clutch makes use of more than one grasp plates to make touch with the engine flywheel to switch electricity among the engine shaft and the transmission shaft.
A multi-plate grasp utilized in vehicles and equipment in which excessive torque output is needed. It is a form of grasp that transmits extra electricity from the engine to the transmission shaft of a car and also, makes up for the torque loss because of slippage.
Multiple clutches encompass extra than 3 discs or plates in an effort to offer extra torque output. Multi-plate clutches are utilized in heavy motors with racing vehicles and bikes for transmitting excessive torque.
As compared to unmarried plate clutches, those are clean and clean to function because of their meeting of friction surface’s touch. It can be used in which the gap may be very limited.
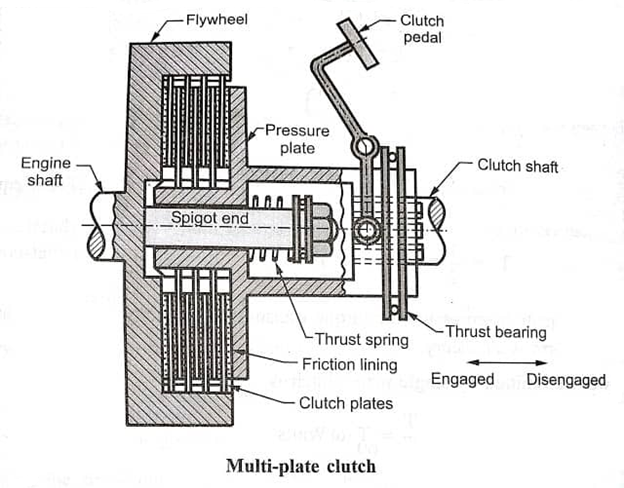
Parts of Multi Plate Clutch
The additives of all of the clutches utilized in car motors are nearly the identical. But with a few modifications, so let’s talk the primary elements of various sorts of multi-plate clasps used.
- Pressure Plate
- Clutch Plate
- Thrust Spring
- Clutch Paddle
- Inner Splined
- Sleeves
- Flywheel
- Diaphragm
Spring Pressure Plate:
A plate connected to the splined sleeves which similarly related to the pedal fulcrum. Such that after the grasp pedal pressed, the sleeves connected to the pedal fulcrum pass outward, which in flip drives the strain plate connected with this splined sleeve.
Clutch Plate:
It is a steel plate having frictional strains at its outer surfaces. It makes use of frictional touch with the flywheel to transmit electricity among the engine shaft and the transmission shaft.
Thrust Springs:
These are springs used at the back of the strain plate, and the stiffness of those springs is utilized by the strain plate to preserve frictional touch with grasp plates, which in flip helps the grasp engagement.
Clutch Pedal:
A grasp pedal operated through the driving force of the car used to manipulate the engagement and disengagement of the grasp.
Splined Shaft & Inner Splined Sleeves:
An outer splined transmission enter shaft over which the whole grasp meeting. That consists of grasp plates, strain plates, internal splined sleeve, and the grasp casing area and rotates with it.
Flywheel:
It is a part of the engine. We also can recollect it as a part of the grasp gadget because the transmission of electricity from the engine output shaft to the transmission shaft gain through the frictional touch among a grasp and the flywheel of an engine.
Diaphragm Spring:
In the diaphragm kind grasp gadget, the thrust springs used with inside the spring kind grasp update with an unmarried diaphragm kind spring.
Construction of Multi Plate Clutch:
The multi-plate clutches production is just like a unmarried plate clutches besides for the wide variety of clutches plates. The overall wide variety of grasp plates divides into units wherein one from every set is as a substitute arranges.
One set of the plate slides in grooves at the flywheel and the opposite one slides on splines at the strain plate hub. These plates are reliably pressed through a robust coil spring and assembled in a drum.
Working of Multi Plate Clutch
Engagement of Clutch
During the engaged function of the grasp, i.e., whilst the grasp pedal isn't pressed. The thrust springs do now no longer pass because of which the stiffness furnished through those springs keeps the strain over the strain, the plate having friction strains on its internal surface.
Due to this strain over the strain surface, the frictional touch among the friction strains of the strain plate and the friction strains of more than one grasp plates is maintained because of which frictional pressure is carried out over the flywheel.
Due to this frictional pressure, the frictional touch among the diverse grasp plates and the wheel is supported, which in flip ultimately affords grasp engagement.
Disengagement of Clutch
When the grasp pedal is pressed, the fulcrum connected at its internal quit rotates because of which the internal splined sleeve via which the strain plate connects movements outward, which in flip applies strain over the thrust springs.
Due to this pressure, the thrust springs pass, which in flip releases the anxiety over the strain plate, and ultimately, the frictional pressure among the strain plate, grasp plate, and flywheel is removed.
For the motive that the elimination of the frictional pressure, frictional touch among the strain plate, grasp plate, and flywheel breaks, and ultimately the disengagement of the grasp obtained.
Application of Multi-Plate Clutch
It may be utilized in commercial machines and vehicles in which excessive overall performance is needed.
Due to the compact gearbox and excessive acceleration is needed and the standards for torque switch are maximum, it could be utilized in motorbike or drag racing races, in addition to in F1 motors.
Due to the compact gearbox design, it could be utilized in ships, trucks, and locomotives.
It is appropriate for heavy sorts of machines together with bulldozers, excavators, tanks and caterpillars, and others due to the fact the multi-disc grasp is heavy and produces excessive electricity.
Because of this, the heavy system elements effortlessly elevate heavyweights. The multi-plate lock is utilized in heavy industrial motors to transmit excessive torque.
The multi-disc grasp is used in which the desired area wherein the grasp needs to be set up is a whole lot much less than with bikes and scooters.
Key Takeaways:
- It is a form of grasp that transmits extra electricity from the engine to the transmission shaft of a car and also, makes up for the torque loss because of slippage.
- The additives of all of the clutches utilized in car motors are nearly the identical.
- A grasp pedal operated through the driving force of the car used to manipulate the engagement and disengagement of the grasp.
Friction substances are materials that produce friction among strong surfaces which will manage or save you ahead or backward movement.
The substances used to provide friction substances encompass natural and non-natural materials which includes resin, ceramics, fibres, and metals. Friction substances have a restricted lifespan because of the individual in their function.
This detail calls for that they be carefully monitored and that plans be in location for his or her replacement. The essential use for friction substances is in transportation as braking fabric, components of clutching systems, and transmissions. Since their discovery, friction substances have end up a vital a part of a number of product developments.
Uses for Friction Materials
Friction is the resistance to movement of an item thru an opposing item transferring with inside the other course or is static. This function of friction is the reason that friction substances are used as braking, preventing, and course converting devices.
Though preventing is a now not unusual place use of friction substances, developing a connection among surfaces is some exclusive in their makes use of. Since friction substances are available a number of types and shapes, they're adaptable to any shape of application. The makes use of friction substances are decided thru the shape they take. Each of the shapes and configurations is designed to carry out a particular function.
Friction Material
Uses Friction Disc Friction discs, take hold of discs, or brake discs are an awesome a part of a disc brake gadget. They are designed to gradual or save you movement of a vehicle such that it may flip or save you. The friction fabric is installation to a metal plate with an adhesive or rivets. Friction discs are components of motors and business agency gadget.
Clutch Disc
The take hold of discs, or linings, are the maximum crucial a part of the take hold of. Its hub is installation to the shaft of the transmission and engages the engines on the identical time because the take hold of is released. When the take hold of is disengaged, the transmission is disengaged and lets in for the converting of gears. Clutch discs are decided on production gadget, big machines, and maximum motors. Regardless if the gadget is electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic, take hold of discs are used to attach and disconnect the transmission of the motor.
Clutch Facing
Clutch facings lessen the quantity of noise produced thru the take hold of. It lets in for clean and consistent operation of the take hold of, which results in a smoother engagement of the take hold of. Like all friction substances, take hold of facings are crafted from a number of substances with asbestos being the maximum now not unusual place. The kinetic electricity from the engagement of the take hold of creates a splendid deal of heat. Clutch facings are designed to undergo and face up to the stressful conditions.
Brake Pads
There are 3 styles of friction substances which might be used with inside the manufacture of brake pads, which might be semi-metal, non-asbestos natural, and ceramic. Each of the one-of-a-type substances have their blessings and disadvantages. The first brakes had been drum brakes and had friction fabric completed to the brake shoe. When the brake on a tool have emerge as completed, the shoe have emerge as activated and made touch with the braking floor or drum.
Later, disc brakes had been advanced with brake pads that use the same gadget to brake a tool thru the usage of friction to the rotor. A in addition development in friction substances have emerge as the improvement of semi-metal substances which have metal fibres to offer friction.
Brake Lining
The brake lining assists with inside the reduce rate of braking or preventing movement. They function a barrier among braking additives and beautify friction levels. Brake linings amplify the lifestyles of braking additives thru keeping them from breaking down too rapid and are a buffer area among additives. In essence, the brake lining is some exclusive call for brake pads and serves the same function.
Brake Shoes
Brake footwear are drastically carried out in a collection of gadget as a technique for preventing movement. Drum brakes use hydraulic pressure to transport small pistons that push the footwear towards the indoors floor of the spinning part of the mechanism.
The friction fabric slows the movement of the tool. Brake footwear are crescent fashioned with the friction fabric completed at the rounded floor of the shoe. Though brake footwear serve the same function as brake pads, they take a look at pressure differently. While brake pads by skip inwardly towards the rotor, brake footwear by skip upward and outward to make touch with the drum.
Brake Block
A block brake is a difficult fabric this is pressed towards a wheel to save you movement. They may be crafted from a number of substances further to from chunks of rubber. Block brakes are a crude shape of braking tool that may be completed to a large type of applications. In their high-quality shape, they will be decided on bicycles which have hand brakes. Block brakes are a shape of friction fabric that may be associated with the out of doors of a brake shoe with rivets or screws.
Melded brake blocks are carried out in slowing mining, engineering, and business agency machines. They are made from resin, wire, or viscose, glass, or yarn fibres.
Key Takeaways:
- Since their discovery, friction substances have end up a vital a part of a number of product developments.
- Each of the shapes and configurations is designed to carry out a particular function.
- Drum brakes use hydraulic pressure to transport small pistons that push the footwear towards the indoors floor of the spinning part of the mechanism.
References:
1. Mechanical Engineering Design, 9e – Joseph E. Shigely, McGraw Hill Education.
2. Machine Design‐Maleev and Hartman, CBS Publishers.
3. Design of Machine Design‐M.F. Spott, Pearson Education.
4. Elements of Machine Component Design, Juvinal & Marshek, John Wiley & Sons.
5. Machine design, Robert L. Norton, Pearson Education
Unit - 5
IC Engine Parts
The selection of the type of IC engine depends upon the following factors:
- Type of process.
- Type of cycle.
- Numbers of cylinders.
- Arrangements of cylinders.
- Engine speed, and
- Stroke bore ratio.
The general design considerations of the design of an IC engine depend on the following type of loads:
- Load due to gas pressure in the cylinder.
- Load due to inertia and centrifugal forces.
- Load due to frictional forces.
- Load due to torsional moment reaction and weight.
- Load due to vibrations, especially of the crankshaft.
- Thermal loads.
Unit - 5
IC Engine Parts
The selection of the type of IC engine depends upon the following factors:
- Type of process.
- Type of cycle.
- Numbers of cylinders.
- Arrangements of cylinders.
- Engine speed, and
- Stroke bore ratio.
The general design considerations of the design of an IC engine depend on the following type of loads:
- Load due to gas pressure in the cylinder.
- Load due to inertia and centrifugal forces.
- Load due to frictional forces.
- Load due to torsional moment reaction and weight.
- Load due to vibrations, especially of the crankshaft.
- Thermal loads.
Step I: Thickness of cylinder wall:
The cylinder wall is subjected to gas pressure and piston side thrust. There may be bending of the wall due to piston side thrust.
The thickness of the wall is usually calculated by applying the following formula for a thin cylinder as
t=[(pmaxD)/2σc]+K
Where t=wall thickness in mm,
pmax=Maximum gas pressure, D= Cylinder bore σc=Permissible circumferential stress (MPa), K=reboring factor(mm)
Following empirical relations may be used to find various thicknesses:
- The thickness of the cylinder wall, t=0.145D+1.6mm
- The thickness of dry liner=0.030D to 0.035 D
- The thickness of the water jacket wall=0.032D+1.6mm
Step II: Cylinder Diameter (or bore) and length:
1. The output of a cylinder can be given as,
IP=pmLAn/60, where,
IP=Indicated power, pm=Indicated mean effective pressure(N/mm2), L=Length of stroke, A=Cross-sectional area of the cylinder, n=Number of working strokes per minute.
2. Output power can also be written in terms of brake power as
BP=2πNT/60
Where, BP= brake power, N=Number of rotation (rpm), and T= torque
- Mechanical efficiency=(BP)/(IP), from the above equations, the length of the cylinder can be evaluated.
Step III: Cylinder Flange and studs:
- The diameter of the studs may be obtained by equating the gas load due to maximum pressure in the cylinder to the resisting force offered by all the studs or bolts.
- Mathematically, (π/4)D2pmax=ns*( π/4)d2cσt
Where, σt=Allowable tensile stress (35 to 75 N/mm2), dc=core diameter of stud, ns=Number of studs or bolts.
Step IV: Cylinder Head:
- The thickness of the cylinder head may be obtained as, th=0.316D
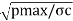
- The value of allowable circumferential stress may be taken as 30 to 50 MPa.
Key Takeaway:
- The thickness of the cylinder wall is given by t=[(pmaxD)/2σc]+K.
- (π/4)D2pmax=ns*( π/4)d2cσt, For cylinder flange and stud.
1. Piston Head:
(i). The thickness of the piston head or crown is calculated based on strength and heat dissipation as follows:
The head thickness based on strength can be calculated by assuming the head to be a flat plate for uniform thickness and fixed at the edges.
The thickness of the pinhead, according to Grashof’s formula is given as
tH=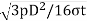
(ii). Based on heat dissipation, heat thickness is given as,
tH=H/[12.56k(TC-TE)],
Where, H=Heat flowing through the piston head (W), TC=Temperature at the center of the piston head, TE= Temperature at the edges of the piston head, and, k=Thermal conductivity factor (W/m/0C).
The heat following through the piston head (H) may also be estimated by the following formula:
H=C*V*m*HCV*BP
Where m=mass of the fuel used (kg/kW-s),
HCV= Higher calorific value of fuel, C= Constant representing that portion of heat supplied to the engine which is absorbed by the piston. Its value is taken as 0.05
2. Piston Rings:
The radial thickness (t1) of the ring may be obtained by considering the radial pressure between the cylinder wall and the ring. From bending stress considerations in the ring, the radial thickness is given by
t1=D(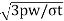
D= cylinder bore in mm, pw=[pressure of the gas on the wall
The axial thickness (t2) of the rings may be taken as 0.7t1 to t2.
The minimum axial thickness (t2) may also be obtained from the following empirical relation.
i2=D/10nR
Where, nR= number of rings, the width of top land, b1=tH to 1.2tH
3. Piston Barrel:
The thickness of the piston barrel at the top end is calculated,
t3=0.03D +b+4.9mm where, b=Radial width of ring (mm)
Step IV: Piston Skirt:
- We know that maximum gas load on the piston,
Fg=p*(πD2/4)
Where, p=maximum gas pressure in N/mm2
Step V: Piston Pin
The piston pin should be designed for the maximum gas load or the inertia force, whichever is larger. Bearing pressure is the design criteria and the diameter of the pin is determined by equating the gas load and bearing load.
So, l1dpb1=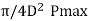
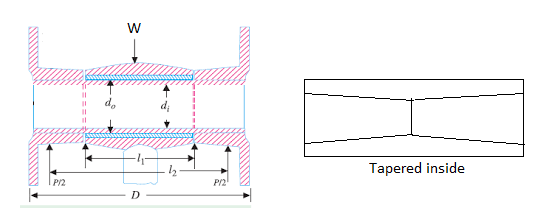
Fig. 1: Piston pin
The piston pin may be checked in bending by assuming the gas load to be uniformly distributed over the length l1 and pin supported at the center of the bosses at two ends.
The length between supports is
l2=l1+(D-l1)/2=(l1+D)/2
Key Takeaways:
Fg=p*(πD2/4) maximum gas load on the piston, for piston skirt
l2=l1+(D-l1)/2=(l1+D)/2 is important formula for design of piston pin
Mechanism which enables rotary motion of shaft to be transmitted to the second shaft axis, which is coincident with the first. OR
Clutch is a device to connect driving and driven shafts of a machine, where the driven shaft can be disconnected almost instantaneously from the driving shaft as desired by the operator or driver.
Requirements of clutch:
- Torque Transmission
- Gradual Engagements
- Heat Dissipation
- Dynamic Balancing
- Vibration Damping
- Size
- Inertia
- Ease of operation
1. Torque Transmission
- The clutch should be able to transfer the maximum torque of engine under all conditions.
- Usually designed to transmit 125 to 150% of maximum engine torque.
2. Gradual Engagement: Clutch should take the drive gradually without occurrence of sudden jerks.
3. Heat Dissipation: During clutch application large amount of heat is generated, the rubbing surfaces should have sufficient area and mass to absorb the heat generated. The design of clutch should ensure proper ventilation or cooling for adequate dissipation of heat.
The friction clutches work on the fact that friction is caused when two rotating discs come into contact with each other.
Principle for friction clutches:
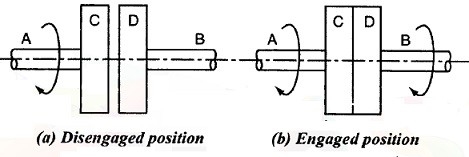
Figure 2: Principle for friction clutch
Let the shaft A and Disc C be revolving at some speed say N rpm. Shaft B and disc D keyed to it are stationary, initially when the clutch is not engaged.
Now apply some axial force W to disc D, so that it comes in contact with Disc C. As soon as the contact is made the force of friction between C and D will come into play and consequently the disc D will also start revolving.
The speed of D depends upon friction force present, which in turn is proportional to the force W applied.
If W is increased gradually, the speed of D will be increased correspondingly till the stage comes when speed of D becomes equal to speed of C.
Then clutch is said to be fully engaged.
Let W = axial load applied. µ= coefficient of friction R= effective mean radius of friction surface. Then, T = W R
Key Takeaways:
Clutch is a device to connect driving and driven shafts of a machine, where the driven shaft can be disconnected almost instantaneously from the driving shaft as desired by the operator or driver.
The friction clutches work on the fact that friction is caused when two rotating discs come into contact with each other.
Clutch | Coupling |
Clutch is a device that provides a temporary connection between the driver and driven shaft.
| Coupling makes the permanent and semi-permanent connection between two shaft ends.
|
Used where driven shaft/ driven machine required to be in intermittent service.
| Coupling used where driven shaft required to be in continuous service.
|
Clutch allow disconnection during the operation. Provide a mechanism for rapid engagement and disengagement during the operation at the operator will.
| It does not allow disconnection of the shaft during the normal operation (Torque limiting coupling allow slipping when torque limit is exceeded). Connection is in permanent nature, so there is no mechanism for quick connection and disconnection.
|
Clutch transmit power between two collinear shafts.
| Coupling used to transmit power between collinear as well as non-collinear shafts.
|
The driven shaft can run at variable speed.
| In coupling, the driven shaft run at the same speed as the driveshaft.
|
Example: Disc clutch, Cone clutch, Centrifugal clutch, Electromagnetic clutch
| Example: Universal coupling, Oldham coupling |
Working:
An unmarried plate take hold of has one take hold of plate. This take hold of works at the precept of friction.
It is the maximum not unusual place kind of take hold of utilized in motor vehicles. The take hold of frequently includes members, one set up at the using shaft and the opposite at the pushed shaft.
These shafts are parallel and concentric with every different; one shaft is constant to its housing even as the opposite is splined in order that it may circulate axially. The using torque can growth with the aid of using growing the powerful radius of contact. In the transmission device, the device with the aid of using which energy develops with the aid of using the engine transmits to avenue wheels to propel the car.
In motors, the energy develops with the aid of using the engine which use to show wheels. Therefore, the engine is to hook up with the transmission structures for transmitting energy to wheels.
Also, there ought to be a device the usage of which the engine may be engaged and disengaged with the transmission device easily and without surprise in order that the car mechanism isn't broken and passengers do now no longer experience inconvenience.
A take hold of is hired in motors for this purpose. A Clutch is a mechanism used to attach or disconnect the engine from the relaxation of the transmission elements. It is positioned among the engine and gearbox.
The take hold of disengages for starting, converting gears, stopping, and idling. The feature of the Clutch is to allow the engagement or disengagement of equipment whilst the car is desk bound and the engine is strolling without destructive equipment wheels. So, we come again to our factor of Single Plate Clutch and allow us to start.
- In the Clutch the 3 elements needs.
- These are the engine flywheel, a friction disc or a snatch plate and a stress plate. Some springs supply axial pressure to live the snatch with inside the engaged position.
- When the engine is strolling and consequently the flywheel is rotating, the stress plate additionally rotates due to the fact the stress plate attaches to the flywheel.
- The friction disc is positioned among the flywheel and the stress plate.
- When the using pressure has driven down the snatch is released.
- This movement forces the stress plate to transport far from the friction disc in opposition to the pressure of stress springs.
- With this motion of the stress plate, the friction plate is released, and consequently the snatch disengaged.
- When your foot is off the pedal, the springs push the stress plate in opposition to the snatch disc, which successively presses in opposition to the flywheel.
- This locks up the engine to the transmission enter shaft, inflicting them to spin on the identical speed.
- The amount of pressure the snatch can maintain relies upon at the friction among the snatch plate and the flywheel, and on this way, a good deal pressure the spring places at the stress plate.
- When the snatch presses, the piston pushes on the discharge fork, which presses the throw-out bearing in opposition to the middle of the diaphragm spring.
- As the centre of the diaphragm spring pushes in, a chain of pins close to the outdoor floor of the spring reasons the spring to tug the stress plate Forfar from the snatch plate.
- This releases the snatch from the spinning engine.
Construction:
An unmarried plate take hold of is composed of various components for correct working. They are organized in a scientific order.
Mainly it includes a take hold of plate with each facet friction lining and a few different components which assist with inside the right functioning of a take hold of like a flywheel, stress plate, thrust bearing, hub, springs, and enter mechanism for engagement and disengagement of the take hold of.
The take hold of plate attaches to the hub among the flywheel and the stress plate, it movements axially at the pushed shaft.

In an unmarried plate take hold of, the take hold of plate ought to have each facet friction lining as it mounts among the stress plate and flywheel, friction is chargeable for the torque transmission.
The stress plate engages with the flywheel and springs. Pressure plate enables to push the take hold of plate with the flywheel. A lever attaches to thrust bearings with a few mechanism at the pushed shaft which transmits enter and output movement from the take hold of pedal.
Parts:
1. Flywheel
The flywheel is a quintessential a part of the engine, which additionally use as part of the grasp. It is a using member and connects to the stress plate of the grasp shaft is homes with bearings in a flywheel. The flywheel rotates because the engine crankshaft rotates.
2. Pilot Bearing
The pilot bearing or bushing press into the quilt of the crankshaft to guide the quit of the transmission enter shaft. The pilot bearing prevents the transmission shaft and grasp disc from wobbling up and down while the grasp releases. It additionally assists the enter shaft middle of the disc at the flywheel.
3. Clutch plate or Disc plate
It is the pushed member of the single-plate grasp and line with friction cloth on each surfaces. It has an important hub with inner splines to restrict the axial journey alongside the splined gearbox using shaft.
This facilitates to offer damping movements in opposition to torsional vibrations or versions of the using torque among engine and transmission. A grasp disc is a plate among flywheel and friction or stress plate. It has a chain of facings inverters on every facet to extend the friction. These grasp facings are fabricated from asbestos cloth. They are relatively worn and warmth resistant.
4. Pressure plate
The stress plate is fabricated from unique solid iron. It is the heaviest a part of the grasp meeting. The essential characteristic of the stress plate is to set up even touch with the pushed plate dealing with thru which the stress springs can exert a enough pressure to transmit the total torque of the engine. The stress plate presses the grasp plate directly to the flywheel from its machined surface. Between the stress plate and grasp cowl meeting, stress springs are fitted. The stress may be withdrawn from the flywheel every time launch levers are depressed via way of means of the toggle or launch levers are pivoted accordingly.
5. Clutch cowl
The grasp cowl meeting bolts to the flywheel. It includes a stress plate, launch lever mechanism, grasp cowl, and stress springs. Generally, the grasp plate revolves with the flywheel. However, while the grasp has disengaged, the flywheel, in addition to the stress plates, are loose to rotate independently from the pushed plate and using shaft.
6. Release levers
These pivots on pins to the grasp cowl, their outer ends find and positions on stress plate legs, and the internal ends are projecting closer to the grasp shaft. A cautious and correct adjustment of the discharge mechanism is one of the maximum crucial elements governing the overall performance of a grasp meeting.
7. Clutch shaft
It is part of the gearbox. Since its miles a splined shaft to the hub of the grasp plate, that is sliding on it. One quit of the grasp shaft attaches to the crankshaft or flywheel and the opposite quit connects to the gearbox or paperwork part of the gearbox.
Advantages of Single Plate Clutch
The running of engagement and disengagement may be very clean in an unmarried plate snatch.
Power losses are very much less.
As enough floor location is to be had for warmth dissipation in such clutches, no cooling oil is required.
Therefore, unmarried plate clutches are dry type.
Single plate clutches have a short operation and reply fast.
It makes it less complicated to extrude gears than a cone type.
Disadvantages of Single Plate Clutch
Single plate clutches have excessive put on and tear rate.
It has much less torque transmitting capacity.
The springs should be the greater stiff as a result more pressure calls for to disengage.
It calls for excessive maintenance.
The area required to deal with the snatch is greater in comparison to the multi-plate snatch.
Key Takeaways:
- An unmarried plate take hold of has one take hold of plate. This take hold of works at the precept of friction.
- It is positioned among the engine and gearbox.
- The friction disc is positioned among the flywheel and the stress plate.
- An unmarried plate take hold of is composed of various components for correct working. They are organized in a scientific order.
Unit - 5
IC Engine Parts
The selection of the type of IC engine depends upon the following factors:
- Type of process.
- Type of cycle.
- Numbers of cylinders.
- Arrangements of cylinders.
- Engine speed, and
- Stroke bore ratio.
The general design considerations of the design of an IC engine depend on the following type of loads:
- Load due to gas pressure in the cylinder.
- Load due to inertia and centrifugal forces.
- Load due to frictional forces.
- Load due to torsional moment reaction and weight.
- Load due to vibrations, especially of the crankshaft.
- Thermal loads.
Step I: Thickness of cylinder wall:
The cylinder wall is subjected to gas pressure and piston side thrust. There may be bending of the wall due to piston side thrust.
The thickness of the wall is usually calculated by applying the following formula for a thin cylinder as
t=[(pmaxD)/2σc]+K
Where t=wall thickness in mm,
pmax=Maximum gas pressure, D= Cylinder bore σc=Permissible circumferential stress (MPa), K=reboring factor(mm)
Following empirical relations may be used to find various thicknesses:
- The thickness of the cylinder wall, t=0.145D+1.6mm
- The thickness of dry liner=0.030D to 0.035 D
- The thickness of the water jacket wall=0.032D+1.6mm
Step II: Cylinder Diameter (or bore) and length:
1. The output of a cylinder can be given as,
IP=pmLAn/60, where,
IP=Indicated power, pm=Indicated mean effective pressure(N/mm2), L=Length of stroke, A=Cross-sectional area of the cylinder, n=Number of working strokes per minute.
2. Output power can also be written in terms of brake power as
BP=2πNT/60
Where, BP= brake power, N=Number of rotation (rpm), and T= torque
- Mechanical efficiency=(BP)/(IP), from the above equations, the length of the cylinder can be evaluated.
Step III: Cylinder Flange and studs:
- The diameter of the studs may be obtained by equating the gas load due to maximum pressure in the cylinder to the resisting force offered by all the studs or bolts.
- Mathematically, (π/4)D2pmax=ns*( π/4)d2cσt
Where, σt=Allowable tensile stress (35 to 75 N/mm2), dc=core diameter of stud, ns=Number of studs or bolts.
Step IV: Cylinder Head:
- The thickness of the cylinder head may be obtained as, th=0.316D
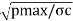
- The value of allowable circumferential stress may be taken as 30 to 50 MPa.
Key Takeaway:
- The thickness of the cylinder wall is given by t=[(pmaxD)/2σc]+K.
- (π/4)D2pmax=ns*( π/4)d2cσt, For cylinder flange and stud.
1. Piston Head:
(i). The thickness of the piston head or crown is calculated based on strength and heat dissipation as follows:
The head thickness based on strength can be calculated by assuming the head to be a flat plate for uniform thickness and fixed at the edges.
The thickness of the pinhead, according to Grashof’s formula is given as
tH=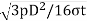
(ii). Based on heat dissipation, heat thickness is given as,
tH=H/[12.56k(TC-TE)],
Where, H=Heat flowing through the piston head (W), TC=Temperature at the center of the piston head, TE= Temperature at the edges of the piston head, and, k=Thermal conductivity factor (W/m/0C).
The heat following through the piston head (H) may also be estimated by the following formula:
H=C*V*m*HCV*BP
Where m=mass of the fuel used (kg/kW-s),
HCV= Higher calorific value of fuel, C= Constant representing that portion of heat supplied to the engine which is absorbed by the piston. Its value is taken as 0.05
2. Piston Rings:
The radial thickness (t1) of the ring may be obtained by considering the radial pressure between the cylinder wall and the ring. From bending stress considerations in the ring, the radial thickness is given by
t1=D(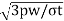
D= cylinder bore in mm, pw=[pressure of the gas on the wall
The axial thickness (t2) of the rings may be taken as 0.7t1 to t2.
The minimum axial thickness (t2) may also be obtained from the following empirical relation.
i2=D/10nR
Where, nR= number of rings, the width of top land, b1=tH to 1.2tH
3. Piston Barrel:
The thickness of the piston barrel at the top end is calculated,
t3=0.03D +b+4.9mm where, b=Radial width of ring (mm)
Step IV: Piston Skirt:
- We know that maximum gas load on the piston,
Fg=p*(πD2/4)
Where, p=maximum gas pressure in N/mm2
Step V: Piston Pin
The piston pin should be designed for the maximum gas load or the inertia force, whichever is larger. Bearing pressure is the design criteria and the diameter of the pin is determined by equating the gas load and bearing load.
So, l1dpb1=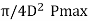
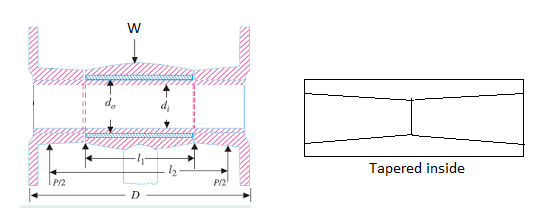
Fig. 1: Piston pin
The piston pin may be checked in bending by assuming the gas load to be uniformly distributed over the length l1 and pin supported at the center of the bosses at two ends.
The length between supports is
l2=l1+(D-l1)/2=(l1+D)/2
Key Takeaways:
Fg=p*(πD2/4) maximum gas load on the piston, for piston skirt
l2=l1+(D-l1)/2=(l1+D)/2 is important formula for design of piston pin
Mechanism which enables rotary motion of shaft to be transmitted to the second shaft axis, which is coincident with the first. OR
Clutch is a device to connect driving and driven shafts of a machine, where the driven shaft can be disconnected almost instantaneously from the driving shaft as desired by the operator or driver.
Requirements of clutch:
- Torque Transmission
- Gradual Engagements
- Heat Dissipation
- Dynamic Balancing
- Vibration Damping
- Size
- Inertia
- Ease of operation
1. Torque Transmission
- The clutch should be able to transfer the maximum torque of engine under all conditions.
- Usually designed to transmit 125 to 150% of maximum engine torque.
2. Gradual Engagement: Clutch should take the drive gradually without occurrence of sudden jerks.
3. Heat Dissipation: During clutch application large amount of heat is generated, the rubbing surfaces should have sufficient area and mass to absorb the heat generated. The design of clutch should ensure proper ventilation or cooling for adequate dissipation of heat.
The friction clutches work on the fact that friction is caused when two rotating discs come into contact with each other.
Principle for friction clutches:
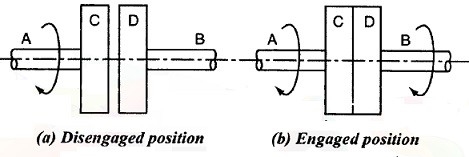
Figure 2: Principle for friction clutch
Let the shaft A and Disc C be revolving at some speed say N rpm. Shaft B and disc D keyed to it are stationary, initially when the clutch is not engaged.
Now apply some axial force W to disc D, so that it comes in contact with Disc C. As soon as the contact is made the force of friction between C and D will come into play and consequently the disc D will also start revolving.
The speed of D depends upon friction force present, which in turn is proportional to the force W applied.
If W is increased gradually, the speed of D will be increased correspondingly till the stage comes when speed of D becomes equal to speed of C.
Then clutch is said to be fully engaged.
Let W = axial load applied. µ= coefficient of friction R= effective mean radius of friction surface. Then, T = W R
Key Takeaways:
Clutch is a device to connect driving and driven shafts of a machine, where the driven shaft can be disconnected almost instantaneously from the driving shaft as desired by the operator or driver.
The friction clutches work on the fact that friction is caused when two rotating discs come into contact with each other.
Clutch | Coupling |
Clutch is a device that provides a temporary connection between the driver and driven shaft.
| Coupling makes the permanent and semi-permanent connection between two shaft ends.
|
Used where driven shaft/ driven machine required to be in intermittent service.
| Coupling used where driven shaft required to be in continuous service.
|
Clutch allow disconnection during the operation. Provide a mechanism for rapid engagement and disengagement during the operation at the operator will.
| It does not allow disconnection of the shaft during the normal operation (Torque limiting coupling allow slipping when torque limit is exceeded). Connection is in permanent nature, so there is no mechanism for quick connection and disconnection.
|
Clutch transmit power between two collinear shafts.
| Coupling used to transmit power between collinear as well as non-collinear shafts.
|
The driven shaft can run at variable speed.
| In coupling, the driven shaft run at the same speed as the driveshaft.
|
Example: Disc clutch, Cone clutch, Centrifugal clutch, Electromagnetic clutch
| Example: Universal coupling, Oldham coupling |
Working:
An unmarried plate take hold of has one take hold of plate. This take hold of works at the precept of friction.
It is the maximum not unusual place kind of take hold of utilized in motor vehicles. The take hold of frequently includes members, one set up at the using shaft and the opposite at the pushed shaft.
These shafts are parallel and concentric with every different; one shaft is constant to its housing even as the opposite is splined in order that it may circulate axially. The using torque can growth with the aid of using growing the powerful radius of contact. In the transmission device, the device with the aid of using which energy develops with the aid of using the engine transmits to avenue wheels to propel the car.
In motors, the energy develops with the aid of using the engine which use to show wheels. Therefore, the engine is to hook up with the transmission structures for transmitting energy to wheels.
Also, there ought to be a device the usage of which the engine may be engaged and disengaged with the transmission device easily and without surprise in order that the car mechanism isn't broken and passengers do now no longer experience inconvenience.
A take hold of is hired in motors for this purpose. A Clutch is a mechanism used to attach or disconnect the engine from the relaxation of the transmission elements. It is positioned among the engine and gearbox.
The take hold of disengages for starting, converting gears, stopping, and idling. The feature of the Clutch is to allow the engagement or disengagement of equipment whilst the car is desk bound and the engine is strolling without destructive equipment wheels. So, we come again to our factor of Single Plate Clutch and allow us to start.
- In the Clutch the 3 elements needs.
- These are the engine flywheel, a friction disc or a snatch plate and a stress plate. Some springs supply axial pressure to live the snatch with inside the engaged position.
- When the engine is strolling and consequently the flywheel is rotating, the stress plate additionally rotates due to the fact the stress plate attaches to the flywheel.
- The friction disc is positioned among the flywheel and the stress plate.
- When the using pressure has driven down the snatch is released.
- This movement forces the stress plate to transport far from the friction disc in opposition to the pressure of stress springs.
- With this motion of the stress plate, the friction plate is released, and consequently the snatch disengaged.
- When your foot is off the pedal, the springs push the stress plate in opposition to the snatch disc, which successively presses in opposition to the flywheel.
- This locks up the engine to the transmission enter shaft, inflicting them to spin on the identical speed.
- The amount of pressure the snatch can maintain relies upon at the friction among the snatch plate and the flywheel, and on this way, a good deal pressure the spring places at the stress plate.
- When the snatch presses, the piston pushes on the discharge fork, which presses the throw-out bearing in opposition to the middle of the diaphragm spring.
- As the centre of the diaphragm spring pushes in, a chain of pins close to the outdoor floor of the spring reasons the spring to tug the stress plate Forfar from the snatch plate.
- This releases the snatch from the spinning engine.
Construction:
An unmarried plate take hold of is composed of various components for correct working. They are organized in a scientific order.
Mainly it includes a take hold of plate with each facet friction lining and a few different components which assist with inside the right functioning of a take hold of like a flywheel, stress plate, thrust bearing, hub, springs, and enter mechanism for engagement and disengagement of the take hold of.
The take hold of plate attaches to the hub among the flywheel and the stress plate, it movements axially at the pushed shaft.
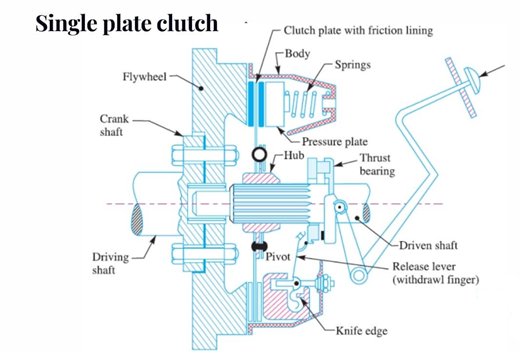
In an unmarried plate take hold of, the take hold of plate ought to have each facet friction lining as it mounts among the stress plate and flywheel, friction is chargeable for the torque transmission.
The stress plate engages with the flywheel and springs. Pressure plate enables to push the take hold of plate with the flywheel. A lever attaches to thrust bearings with a few mechanism at the pushed shaft which transmits enter and output movement from the take hold of pedal.
Parts:
1. Flywheel
The flywheel is a quintessential a part of the engine, which additionally use as part of the grasp. It is a using member and connects to the stress plate of the grasp shaft is homes with bearings in a flywheel. The flywheel rotates because the engine crankshaft rotates.
2. Pilot Bearing
The pilot bearing or bushing press into the quilt of the crankshaft to guide the quit of the transmission enter shaft. The pilot bearing prevents the transmission shaft and grasp disc from wobbling up and down while the grasp releases. It additionally assists the enter shaft middle of the disc at the flywheel.
3. Clutch plate or Disc plate
It is the pushed member of the single-plate grasp and line with friction cloth on each surfaces. It has an important hub with inner splines to restrict the axial journey alongside the splined gearbox using shaft.
This facilitates to offer damping movements in opposition to torsional vibrations or versions of the using torque among engine and transmission. A grasp disc is a plate among flywheel and friction or stress plate. It has a chain of facings inverters on every facet to extend the friction. These grasp facings are fabricated from asbestos cloth. They are relatively worn and warmth resistant.
4. Pressure plate
The stress plate is fabricated from unique solid iron. It is the heaviest a part of the grasp meeting. The essential characteristic of the stress plate is to set up even touch with the pushed plate dealing with thru which the stress springs can exert a enough pressure to transmit the total torque of the engine. The stress plate presses the grasp plate directly to the flywheel from its machined surface. Between the stress plate and grasp cowl meeting, stress springs are fitted. The stress may be withdrawn from the flywheel every time launch levers are depressed via way of means of the toggle or launch levers are pivoted accordingly.
5. Clutch cowl
The grasp cowl meeting bolts to the flywheel. It includes a stress plate, launch lever mechanism, grasp cowl, and stress springs. Generally, the grasp plate revolves with the flywheel. However, while the grasp has disengaged, the flywheel, in addition to the stress plates, are loose to rotate independently from the pushed plate and using shaft.
6. Release levers
These pivots on pins to the grasp cowl, their outer ends find and positions on stress plate legs, and the internal ends are projecting closer to the grasp shaft. A cautious and correct adjustment of the discharge mechanism is one of the maximum crucial elements governing the overall performance of a grasp meeting.
7. Clutch shaft
It is part of the gearbox. Since its miles a splined shaft to the hub of the grasp plate, that is sliding on it. One quit of the grasp shaft attaches to the crankshaft or flywheel and the opposite quit connects to the gearbox or paperwork part of the gearbox.
Advantages of Single Plate Clutch
The running of engagement and disengagement may be very clean in an unmarried plate snatch.
Power losses are very much less.
As enough floor location is to be had for warmth dissipation in such clutches, no cooling oil is required.
Therefore, unmarried plate clutches are dry type.
Single plate clutches have a short operation and reply fast.
It makes it less complicated to extrude gears than a cone type.
Disadvantages of Single Plate Clutch
Single plate clutches have excessive put on and tear rate.
It has much less torque transmitting capacity.
The springs should be the greater stiff as a result more pressure calls for to disengage.
It calls for excessive maintenance.
The area required to deal with the snatch is greater in comparison to the multi-plate snatch.
Key Takeaways:
- An unmarried plate take hold of has one take hold of plate. This take hold of works at the precept of friction.
- It is positioned among the engine and gearbox.
- The friction disc is positioned among the flywheel and the stress plate.
- An unmarried plate take hold of is composed of various components for correct working. They are organized in a scientific order.
The torque potential of the snatch is the quantity of torque that may be transmitted via way of means of the snatch whilst it is slipping or whilst it is completely closed.
The torque potential of a snatch relies upon on a chain of factors: general vicinity of the friction floor.
Friction coefficient
Modern automobile powertrain and drivetrain structures have as a minimum one snatch as an aspect.
An AWD or four wheel drive car will have numerous clutches, relying at the structure and form of the powertrain and drivetrain.
A snatch may be a standalone aspect, used to attach the inner combustion engine (ICE) to the transmission, or may be the sub-aspect or every other most important aspect: torque converter, automated transmission, switch case, limited-slip differential (LSD), etc.
Depending at the variety of friction plates, a snatch may be: unmarried plate snatch multi-disc snatch Depending at the form of friction, we are able to have: dry clutches moist (oil) clutches Usually, unmarried plate clutches (besides torque converter lock-up clutches) have dry friction and multi-disc clutches are with moist friction.
Regardless of the type, each snatch has a torque potential. The torque potential of the snatch is the quantity of torque that may be transmitted via way of means of the snatch whilst it’s slipping or whilst it’s completely closed.
The torque potential of a snatch relies upon on a chain of factors: general vicinity of the friction floor friction coefficient everyday pressure performing at the snatch variety of friction elements
To calculate the torque potential of the snatch we’ll have a examine the geometry of the snatch (friction) disc. Within the vicinity of the friction floor we're going to constitute a standard vicinity dx, at the gap x from the centre.
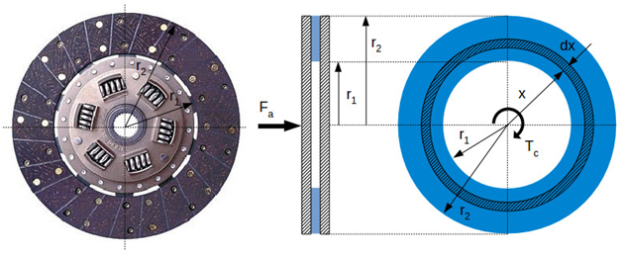
Fig 3: Clutch torque capacity calculation
Where:
Fa [N] – the normal force pressing the clutch plate
Tc [Nm] – the torque capacity of the clutch
r1 [m] – the inner radius of the friction surface
r2 [m] – the outer radius of the friction surface
The pressure p [Pa] acting on the clutch is equal with the ratio between the normal force Fa and the area of the friction surface S [m2]:
p=FaS(1)
Assuming that the area of the rivets is negligible, the area of the friction surface is calculated as:
S=S2–S1=πr22–πr21=π(r22–r21)(2)
Replacing (2) in (1), we get the expression for the clutch pressure:
p=Faπ(r22–r21)(3)
The elementary area dA is calculated as:
DA=2πxdx(4)
The elementary normal force dN, acting on the elementary area is calculated as:
DN=pdA(5)
Replacing (3) and (4) in (5), we get:
DN=2Faxdxr22–r21(6)
The elementary friction force dF is calculated as:
DF=μdN(7)
Where μ [-] is the friction coefficient of the clutch disc.
Replacing (6) in (7), we get:
DF=2μFaxdxr22–r21(8)
The elementary friction torque dT is calculated as:
DT=xdF(9)
Replacing (8) in (9), we get:
DT=2μFax2dxr22–r21(10)
Integrating equation (10) from r1 to r2, we get the mathematical expression of the torque capacity of the clutch:
Tc=∫r2r1dT=2μFar21–r22∫r2r1x2dx=23μr32–r31r22–r21Fa
Since a clutch has two friction surfaces, the resulting mathematical expression for the torque capacity of a single plate clutch is:
Tc=2⋅23μr32–r31r22–r21Fa(11)
For a multi-disc clutch expression (11) becomes:
Tc=z23μr32–r31r22–r21Fa(12)
Where z [-] is the number of friction surfaces (e.g. 2 – for a single friction disc, 4 – for two friction discs, etc.).
Assuming a mean radius rm [m] of the clutch calculated as:
Rm=r2+r12
We can deduce a simplified expression, with an acceptable error, for the torque capacity of the clutch:
Tc=zμFarm
Example 1
Calculate the torque capacity of single plate dry clutch, which has: the normal force 250 N, the outer radius 0.3 m, the inner radius 0.2 m and the friction coefficient 0.4.
Replacing the given parameters in equation (11), we get:
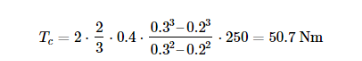
Key Takeaways:
The torque potential of a snatch relies upon on a chain of factors: general vicinity of the friction floor.
Within the vicinity of the friction floor we're going to constitute a standard vicinity dx, at the gap x from the centre
The Multi Plate Clutch makes use of more than one grasp plates to make touch with the engine flywheel to switch electricity among the engine shaft and the transmission shaft.
A multi-plate grasp utilized in vehicles and equipment in which excessive torque output is needed. It is a form of grasp that transmits extra electricity from the engine to the transmission shaft of a car and also, makes up for the torque loss because of slippage.
Multiple clutches encompass extra than 3 discs or plates in an effort to offer extra torque output. Multi-plate clutches are utilized in heavy motors with racing vehicles and bikes for transmitting excessive torque.
As compared to unmarried plate clutches, those are clean and clean to function because of their meeting of friction surface’s touch. It can be used in which the gap may be very limited.
Parts of Multi Plate Clutch
The additives of all of the clutches utilized in car motors are nearly the identical. But with a few modifications, so let’s talk the primary elements of various sorts of multi-plate clasps used.
- Pressure Plate
- Clutch Plate
- Thrust Spring
- Clutch Paddle
- Inner Splined
- Sleeves
- Flywheel
- Diaphragm
Spring Pressure Plate:
A plate connected to the splined sleeves which similarly related to the pedal fulcrum. Such that after the grasp pedal pressed, the sleeves connected to the pedal fulcrum pass outward, which in flip drives the strain plate connected with this splined sleeve.
Clutch Plate:
It is a steel plate having frictional strains at its outer surfaces. It makes use of frictional touch with the flywheel to transmit electricity among the engine shaft and the transmission shaft.
Thrust Springs:
These are springs used at the back of the strain plate, and the stiffness of those springs is utilized by the strain plate to preserve frictional touch with grasp plates, which in flip helps the grasp engagement.
Clutch Pedal:
A grasp pedal operated through the driving force of the car used to manipulate the engagement and disengagement of the grasp.
Splined Shaft & Inner Splined Sleeves:
An outer splined transmission enter shaft over which the whole grasp meeting. That consists of grasp plates, strain plates, internal splined sleeve, and the grasp casing area and rotates with it.
Flywheel:
It is a part of the engine. We also can recollect it as a part of the grasp gadget because the transmission of electricity from the engine output shaft to the transmission shaft gain through the frictional touch among a grasp and the flywheel of an engine.
Diaphragm Spring:
In the diaphragm kind grasp gadget, the thrust springs used with inside the spring kind grasp update with an unmarried diaphragm kind spring.
Construction of Multi Plate Clutch:
The multi-plate clutches production is just like a unmarried plate clutches besides for the wide variety of clutches plates. The overall wide variety of grasp plates divides into units wherein one from every set is as a substitute arranges.
One set of the plate slides in grooves at the flywheel and the opposite one slides on splines at the strain plate hub. These plates are reliably pressed through a robust coil spring and assembled in a drum.
Working of Multi Plate Clutch
Engagement of Clutch
During the engaged function of the grasp, i.e., whilst the grasp pedal isn't pressed. The thrust springs do now no longer pass because of which the stiffness furnished through those springs keeps the strain over the strain, the plate having friction strains on its internal surface.
Due to this strain over the strain surface, the frictional touch among the friction strains of the strain plate and the friction strains of more than one grasp plates is maintained because of which frictional pressure is carried out over the flywheel.
Due to this frictional pressure, the frictional touch among the diverse grasp plates and the wheel is supported, which in flip ultimately affords grasp engagement.
Disengagement of Clutch
When the grasp pedal is pressed, the fulcrum connected at its internal quit rotates because of which the internal splined sleeve via which the strain plate connects movements outward, which in flip applies strain over the thrust springs.
Due to this pressure, the thrust springs pass, which in flip releases the anxiety over the strain plate, and ultimately, the frictional pressure among the strain plate, grasp plate, and flywheel is removed.
For the motive that the elimination of the frictional pressure, frictional touch among the strain plate, grasp plate, and flywheel breaks, and ultimately the disengagement of the grasp obtained.
Application of Multi-Plate Clutch
It may be utilized in commercial machines and vehicles in which excessive overall performance is needed.
Due to the compact gearbox and excessive acceleration is needed and the standards for torque switch are maximum, it could be utilized in motorbike or drag racing races, in addition to in F1 motors.
Due to the compact gearbox design, it could be utilized in ships, trucks, and locomotives.
It is appropriate for heavy sorts of machines together with bulldozers, excavators, tanks and caterpillars, and others due to the fact the multi-disc grasp is heavy and produces excessive electricity.
Because of this, the heavy system elements effortlessly elevate heavyweights. The multi-plate lock is utilized in heavy industrial motors to transmit excessive torque.
The multi-disc grasp is used in which the desired area wherein the grasp needs to be set up is a whole lot much less than with bikes and scooters.
Key Takeaways:
- It is a form of grasp that transmits extra electricity from the engine to the transmission shaft of a car and also, makes up for the torque loss because of slippage.
- The additives of all of the clutches utilized in car motors are nearly the identical.
- A grasp pedal operated through the driving force of the car used to manipulate the engagement and disengagement of the grasp.
Friction substances are materials that produce friction among strong surfaces which will manage or save you ahead or backward movement.
The substances used to provide friction substances encompass natural and non-natural materials which includes resin, ceramics, fibres, and metals. Friction substances have a restricted lifespan because of the individual in their function.
This detail calls for that they be carefully monitored and that plans be in location for his or her replacement. The essential use for friction substances is in transportation as braking fabric, components of clutching systems, and transmissions. Since their discovery, friction substances have end up a vital a part of a number of product developments.
Uses for Friction Materials
Friction is the resistance to movement of an item thru an opposing item transferring with inside the other course or is static. This function of friction is the reason that friction substances are used as braking, preventing, and course converting devices.
Though preventing is a now not unusual place use of friction substances, developing a connection among surfaces is some exclusive in their makes use of. Since friction substances are available a number of types and shapes, they're adaptable to any shape of application. The makes use of friction substances are decided thru the shape they take. Each of the shapes and configurations is designed to carry out a particular function.
Friction Material
Uses Friction Disc Friction discs, take hold of discs, or brake discs are an awesome a part of a disc brake gadget. They are designed to gradual or save you movement of a vehicle such that it may flip or save you. The friction fabric is installation to a metal plate with an adhesive or rivets. Friction discs are components of motors and business agency gadget.
Clutch Disc
The take hold of discs, or linings, are the maximum crucial a part of the take hold of. Its hub is installation to the shaft of the transmission and engages the engines on the identical time because the take hold of is released. When the take hold of is disengaged, the transmission is disengaged and lets in for the converting of gears. Clutch discs are decided on production gadget, big machines, and maximum motors. Regardless if the gadget is electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic, take hold of discs are used to attach and disconnect the transmission of the motor.
Clutch Facing
Clutch facings lessen the quantity of noise produced thru the take hold of. It lets in for clean and consistent operation of the take hold of, which results in a smoother engagement of the take hold of. Like all friction substances, take hold of facings are crafted from a number of substances with asbestos being the maximum now not unusual place. The kinetic electricity from the engagement of the take hold of creates a splendid deal of heat. Clutch facings are designed to undergo and face up to the stressful conditions.
Brake Pads
There are 3 styles of friction substances which might be used with inside the manufacture of brake pads, which might be semi-metal, non-asbestos natural, and ceramic. Each of the one-of-a-type substances have their blessings and disadvantages. The first brakes had been drum brakes and had friction fabric completed to the brake shoe. When the brake on a tool have emerge as completed, the shoe have emerge as activated and made touch with the braking floor or drum.
Later, disc brakes had been advanced with brake pads that use the same gadget to brake a tool thru the usage of friction to the rotor. A in addition development in friction substances have emerge as the improvement of semi-metal substances which have metal fibres to offer friction.
Brake Lining
The brake lining assists with inside the reduce rate of braking or preventing movement. They function a barrier among braking additives and beautify friction levels. Brake linings amplify the lifestyles of braking additives thru keeping them from breaking down too rapid and are a buffer area among additives. In essence, the brake lining is some exclusive call for brake pads and serves the same function.
Brake Shoes
Brake footwear are drastically carried out in a collection of gadget as a technique for preventing movement. Drum brakes use hydraulic pressure to transport small pistons that push the footwear towards the indoors floor of the spinning part of the mechanism.
The friction fabric slows the movement of the tool. Brake footwear are crescent fashioned with the friction fabric completed at the rounded floor of the shoe. Though brake footwear serve the same function as brake pads, they take a look at pressure differently. While brake pads by skip inwardly towards the rotor, brake footwear by skip upward and outward to make touch with the drum.
Brake Block
A block brake is a difficult fabric this is pressed towards a wheel to save you movement. They may be crafted from a number of substances further to from chunks of rubber. Block brakes are a crude shape of braking tool that may be completed to a large type of applications. In their high-quality shape, they will be decided on bicycles which have hand brakes. Block brakes are a shape of friction fabric that may be associated with the out of doors of a brake shoe with rivets or screws.
Melded brake blocks are carried out in slowing mining, engineering, and business agency machines. They are made from resin, wire, or viscose, glass, or yarn fibres.
Key Takeaways:
- Since their discovery, friction substances have end up a vital a part of a number of product developments.
- Each of the shapes and configurations is designed to carry out a particular function.
- Drum brakes use hydraulic pressure to transport small pistons that push the footwear towards the indoors floor of the spinning part of the mechanism.
References:
1. Mechanical Engineering Design, 9e – Joseph E. Shigely, McGraw Hill Education.
2. Machine Design‐Maleev and Hartman, CBS Publishers.
3. Design of Machine Design‐M.F. Spott, Pearson Education.
4. Elements of Machine Component Design, Juvinal & Marshek, John Wiley & Sons.
5. Machine design, Robert L. Norton, Pearson Education