Unit – 3
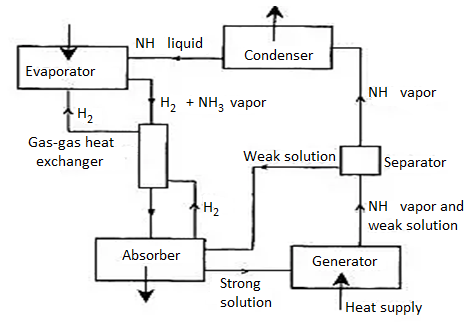
Vapour Absorption system
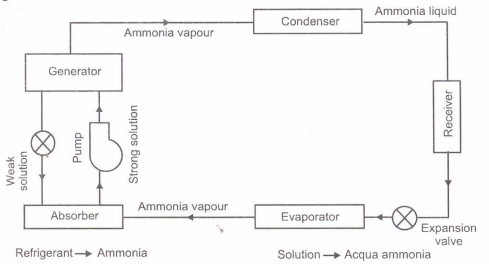
Fig. Simple vapour absorption system
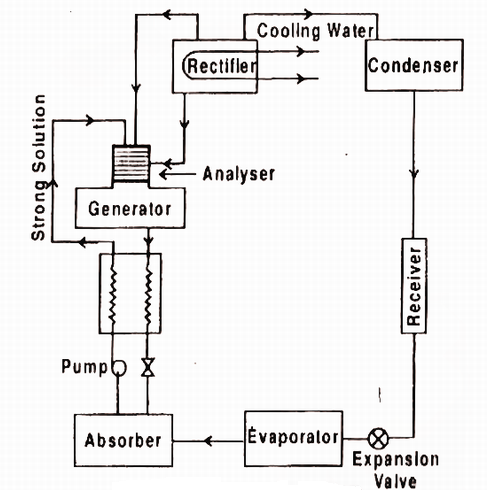
Fig. Practical Absorption system
Principle of Vapour Absorption System:
- There is the peculiar property of some substances to have affinity for another substances at some temperature and pressure conditions and less affinity at another conditions.
- This idea for the working principle of a vapour absorption system was generated by Michael Faraday in 1824.
- He knew that silver chloride (AgCl)m a white powder, had a property of absorbing large amount of ammonia gas at the normal temperature and pressure.
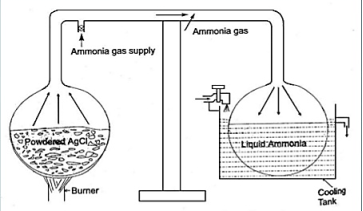
Fig. Intermittent vapour system
- Two chambers are combined with the help of a tube.
- The white powder was kept inside the first chamber to which ammonia gas was supplied and sealed.
- The powder was heated up while other end was cooled using circulating water.
- Liquid ammonia was obtained in the cool end of the apparatus. After stopping heat, it was observed that, the liquid ammonia instead of sitting there, started boiling (bubbles produced) and vapour was reabsorbed by the white powder.
- Upon touching the boiling end, it was astonished to find that the vessel was very cold.
- He repeated the experiments and cooling was observed again.
- This led to invention of the intermittent
Key Takeaways:
- This idea for the working principle of a vapour absorption system was generated by Michael Faraday in 1824.
- The white powder was kept inside the first chamber to which ammonia gas was supplied and sealed.
- He repeated the experiments and cooling was observed again.
Vapour Absorption system | Vapour Compression system |
Uses low grade energy like heat. Therefore, may be worked on exhaust system from I.C Engine, etc. | Uses high grade energy like mechanical work. |
Moving parts are only in the pump, which is a small element of the system. Hence operation is smooth. | Moving parts are in the compressor. Therefore, more tear, wear and noise. |
The system can work on lower evaporator pressure also without affecting COP. | The COP decreases considerably with decrease in evaporator pressure. |
No effect of reducing the load on the performance. | Performance is adversely affected at partial loads. |
Liquid traces of refrigerant present in piping at the exit of evaporator. | Liquid traces in suction line may damage the compressor. |
Fig. Liquid absorbent system
- Solubility requirement: The refrigerant should have proper solubility in the absorbent so that a strong solution, highly rich in the refrigerant, is formed in the absorber by the absorption of the refrigerant vapour.
- Boiling point requirement: There should be a large difference, about 200 degree C, in the boiling points of the two substances, thus absorbent free refrigerant is boiled off from the generator.
Some other Properties required:
- The refrigerant should have high affinity for the absorber at low temp and less affinity at high temp.
- It should have low freezing point.
- It should have good thermal and chemical stability
- Irreversible chemical reactions of all kinds are to be avoided.
Key Takeaways:
- There should be a large difference, about 200 degree C, in the boiling points of the two substances, thus absorbent free refrigerant is boiled off from the generator.
- The refrigerant should have high affinity for the absorber at low temp and less affinity at high temp.
In vapors absorption refrigeration structures primarily based totally on ammonia-water pair, ammonia is the refrigerant and water is the absorbent.
These structures are greater versatile than structures primarily based totally on water-lithium bromide as they may be used for each sub-zero (refrigeration) as nicely above 0o C (air conditioning) applications.
However, those structures are greater complicated in layout and operation because of the smaller boiling factor temperature distinction among the refrigerant and absorbent (approximately 133o C).
Due to the smaller boiling factor temperature distinction the vapors generated with inside the generator is composed of each ammonia in addition to water. If water is permitted to flow into with ammonia with inside the refrigerant circuit, then:
i. Heat switch in condenser and evaporator will become non-isothermal
Ii. Evaporator temperature will increase
Iii. Evaporation will now no longer be complete
Iv. Water may also get gathered with inside the evaporator main to malfunctioning of the plant
Iv. Circulation ratio will increase
Since all of the above results are unfavorable to the overall performance of the machine, it is essential to decrease the attention of water vapor in ammonia on the inlet to the condenser. This calls for extra components, specifically a rectification column and a depth legato among generator and absorber, which will increase the layout complexity and value and additionally reduces the machine COP as compared to water-lithium bromide machine.
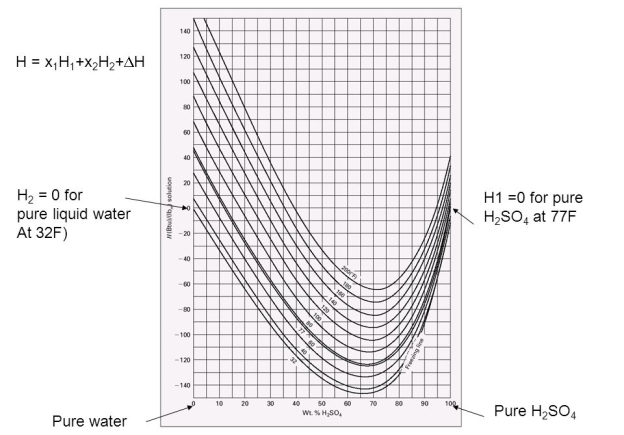
Fig. The enthalpy/concentration (Hx) diagram
A psychometric process that involves no net heat loss or gain during the mixing of two air streams.
Two wet inlet air streams are blended adiabatically. This Demonstration makes use of mass and power stability equations to decide the whole air circulate.
You can set the dry-bulb and wet-bulb temperatures of the primary inlet circulate and the dry-bulb temperature and relative humidity of the second one inlet circulate. You can extrude the values of the volumetric waft costs of the inlet air streams.
The facts consists of the dry-bulb, wet-bulb and dew factor temperatures expressed in , the relative humidity in , absolutely the humidity or moisture content material in , the humid quantity in and the unique enthalpy in .
Two wet inlet air streams are blended adiabatically.
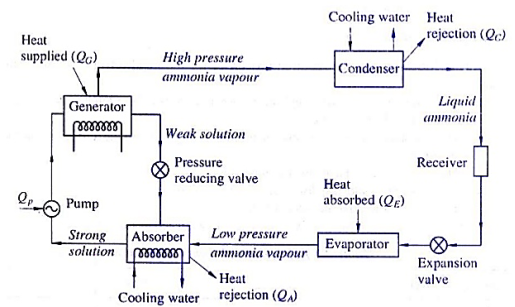
The running of ammonia-water absorption refrigeration device is primarily based totally at the easy vapor absorption refrigeration device. In this device ammonia is used because the refrigerant and water is used because the absorbent.
The ammonia-water absorption device is used with inside the home as nicely the economic programs wherein the requirement of the temperature is above 32 diploma F. The main gain of the ammonia-water answer is that water has sturdy affinity for ammonia and they're soluble with every different in extensive running situations that arise in exclusive refrigeration programs.
Further, the ammonia-water answer is enormously strong and works nicely with many substances besides copper and its alloys that get corroded with inside the presence of ammonia.
The numerous components of the ammonia-water vapor absorption refrigeration device and their running are defined below (please refer the determine above):
1) Evaporator:
It is with inside the evaporator wherein the refrigerant natural ammonia (NH3) in liquid nation produces the cooling effect. It absorbs the warmth from the substance to be cooled and receives evaporated. From here, the ammonia passes to the absorber with inside the gaseous nation.
2) Absorber:
In the absorber the vulnerable answer of ammonia-water is already present. The water, used because the absorbent with inside the answer, is unsaturated and it has the capability to take in extra ammonia gas. As the ammonia from evaporator enters the absorber, it's far effortlessly absorbed with the aid of using water and the sturdy answer of ammonia-water is fashioned. During the method of absorption warmness is liberated that may lessen the ammonia absorption capability of water; subsequently the absorber is cooled with the aid of using the cooling water. Due to absorption of ammonia, sturdy answer of ammonia-water is fashioned with inside the absorber.
3) Pump:
The sturdy answer of ammonia and water is pumped with the aid of using the pump at excessive stress to the generator.
4) Generator:
The sturdy answer of ammonia refrigerant and water absorbent are heated with the aid of using the outside supply of warmth inclusive of steam or warm water. It also can be heated with the aid of using different reasserts like herbal gas, electric powered heater, waste exhaust warmness etc. Due to heating the refrigerant ammonia receives vaporized and it leaves the generator. However, seeing that water has sturdy affinity for ammonia and its vaporization factor is pretty low a few water debris additionally get over excited with ammonia refrigerant, so it's far essential to by skip this refrigerant thru analyzer.
5) Analyzer:
One of the main risks of the ammonia-water vapor absorption refrigeration device is that the water with inside the answer has pretty low vaporizing temperature, subsequently whilst ammonia refrigerant receives vaporized with inside the generator a few water additionally receives vaporized. Thus the ammonia refrigerant leaving the generator contains considerable quantity of water vapor. If this water vapor is permitted to be carried to the evaporator, the capability of the refrigeration device might lessen. The water vapor from ammonia refrigerant is eliminated with the aid of using analyzer and the rectifier.
Key Takeaways:
- In this device ammonia is used because the refrigerant and water is used because the absorbent.
- From here, the ammonia passes to the absorber with inside the gaseous nation.
- Due to absorption of ammonia, sturdy answer of ammonia-water is fashioned with inside the absorber.
The Li-Br answer has a sturdy affinity for water vapor due to its very low vapor stress. Also it's far corrosive, for this reason Lithium chromate is regularly used as an inhibitor.
The absorber and evaporator are positioned in a single shell which operates at identical low stress of device, whilst generator and condenser are positioned in every other shell which operates at identical excessive stress of device.
Water for air con coils pumped thru chilled water tubes, is chilled in evaporator via way of means of giving up warmth to refrigerant water sprayed over the tubes.
Since evaporator stress is maintained very low, consequently refrigerant water evaporates and the vapors are absorbed via way of means of sturdy Li-Br answer that's sprayed in absorber. This absorption makes the answer susceptible and continues excessive vacuum in evaporator.
The susceptible answer is pumped to generator wherein it's far heated up the usage of steam or warm water in heating coils. This ends in evaporation of a few part of water thereby making the answer sturdy. Now this answer is dispatched returned to absorber for spraying as noted above.
The susceptible answer going to generator is exceeded thru warmth exchanger wherein it absorbs warmth from the sturdy answer coming from generator. This reduces steam requirement for the generator to warmth the susceptible answer.
The refrigerant water vapors shaped in generator are exceeded to condenser. Cooling water for condensing is pumped from cooling water pond or tower, and this water is going first to the absorber for doing away with warmth of condensation and dilution, after which to the condenser.
The condensate from condenser is dispatched to evaporator to compensate the lack of refrigerant water thru evaporation and is pumped and sprayed at the chilled tubes, therefore finishing the cycle.
The stress lowering valve reduces the condensate stress from condenser to evaporator stress. The stress for spray is created the usage of the stress distinction among generator and absorber, and the gravity because of peak distinction of the 2 shells.
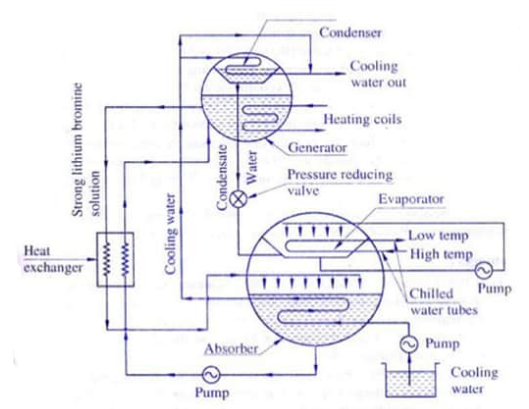
LiBr is non-toxic, readily available and inexpensive. This solution is confined to the absorber and generator sections of the cycle. It is used to move the refrigerant (distilled water) from low pressure to high pressure.
The absorbent (LiBr) should have a strong affinity to absorb the refrigerant (H2O). The solution of absorbent and refrigerant should have a boiling point that is much higher than the refrigerant (water) alone. This makes it easy to separate the absorbent from the refrigerant at high temperatures. A pump is used to circulate the absorbent-refrigerant solution between the absorber and generator. The pump also increases the pressure.
Another common refrigerant-absorbent combination is ammonia as the refrigerant and water as the absorbent. This combination is sometimes used in small residential application. This discussion assumes the refrigerant is Distilled Water (H2O) and the absorbent is Lithium Bromide (LiBr).
The two fluids, refrigerant and absorbent, are mixed inside the chiller in various concentrations. The term "dilute solution" refers to a mixture that is high in refrigerant (H2)) and low in absorbent (LiBr). "Concentrated solution" refers to a mixture that is low in H2O and high in LiBr. "Intermediate solution" is somewhere in between.
The components of the absorption refrigeration cycle are the evaporator-absorber on the low-pressure side and the generator-condenser on the high-pressure side. The pressure on the high-pressure side is about ten times the low-pressure side.
Advantages:
• Feasible to separate refrigerant from absorbent, as water is more volatile compared to Li-Br.
• Operating pressures are low so pumping cost is low.
• Wall thickness of the system less compared to VCR.
• Water as refrigerant is nontoxic, so can be directly used for chilled coil.
• Can be built up to 1,00,000 TR capacity plants.
• Operation and maintenance cost is very low.
Disadvantages:
• Evaporation temperature must be kept above the freezing point of water and hence the temperature of chilled water cannot be less than 5oC.
• Li-Br solution is corrosive. So, inhibitors need to be added to the system to prevent the metal parts from corrosion.
Key Takeaways:
- The pump also increases the pressure.
- This discussion assumes the refrigerant is Distilled Water (H2O) and the absorbent is Lithium Bromide (LiBr).
- The pressure on the high-pressure side is about ten times the low-pressure side.
The three-fluid refrigeration system has three fluids as follows:
- Ammonia
- Water
- Hydrogen
This is basically vapour absorption refrigeration system and here ammonia is refrigerant and water is absorbent. Hydrogen gas circulated in evaporator and absorber to increase the rate of evaporation of ammonia in evaporator.
Three fluid refrigeration is a system which does not needs any mechanical work or electrical works (no pump or compressor).
This was found by two students from Sweden.
This is designed to overcome the drawbacks of conventional two fluid VAR systems. There we will use a pump to pump the solution from absorber to the generator.
This system has Hydrogen as third fluid along with Ammonia(refrigerant), Water(absorber).
Key Takeaways:
- Hydrogen gas circulated in evaporator and absorber to increase the rate of evaporation of ammonia in evaporator.
- This was found by two students from Sweden.
Refrigerants:
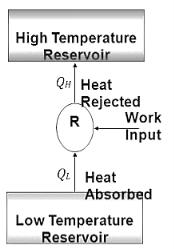
The transfer of heat from a low-temperature region to a high-temperature one requires special devices called refrigerators.
The objective of a refrigerator is to remove heat (QL) from the cold medium; the objective of a heat pump is to supply heat (QH) to a warm medium.
Device used to maintain low temperature below atmospheric temperature within required space.
‘Method of reducing the temperature of a system below surrounding temperature and maintains it at lower temperature by continuously abstracting heat from it.’
Refrigerants are classified as follows:
- Primary refrigerants are those working mediums or heat carries which directly take part in refrigeration system and cool the substance by the absorption of latent heat e.g., Ammonia, Carbon dioxide, Methyl chloride etc.
- Secondary refrigerants are those circulating substances which are first cooled with the help of the primary refrigerants and are then employed for cooling purposes, e.g., ice, Carbon dioxide etc. These refrigerant cool substances by absorption of their sensible heat.
Key Takeaways:
- The objective of a refrigerator is to remove heat (QL) from the cold medium;
- Primary refrigerants are those working mediums or heat carries which directly take part in refrigeration system and cool the substance by the absorption of latent heat e.g., Ammonia, Carbon dioxide, Methyl chloride etc.
Designation of Refrigerants: - The international designation committee of refrigerants uses Refrigerant or R as the designation followed by certain numbers (e.g., R-21, R-40, R-30, R-744 etc.)
A refrigerant followed by a two-digit number indicates that the refrigerant is derived methane base while a three-digit number represents ethane base.
The general chemical formula for a compound derived from a saturated hydrocarbon is given by as: CaHbFcCld
Where, b + c + d=2a+2, and,
a= Number of carbon atoms,
b= Number of hydrogen atoms,
c= Number of fluorine atoms,
d= Number of chlorine atoms, the complete designation of the refrigerant is given by: R (a-1) (b+1) (c)
Example: In case of Dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2): a=1, b=0, c=2, d=2 So, the designation is: R (1-1) (0+1) (2) i.e., R-12.
Few refrigerants and their use:
A refrigerant is a substance used for refrigeration. The best refrigerant has good thermodynamic properties, is chemically non-reactive, and is safe. Because some refrigerants can cause severe damage to the ozone layer, it was decided in 1992 to make it illegal to release refrigerants into the atmosphere.
Refrigerants used in refrigeration systems are as follows:
RefrigerantR11: R11 is a CFC refrigerant, which means it is made of chlorine, fluorine, and carbon. R11 is typically used in the refrigerators found in office building and hotel air conditioning systems because it allows large refrigerators to cool large amounts of water at low costs. In the past, when air would leak into R11 systems, that air had to be purged, and usually some of the refrigerant would be lost. Through newer technological advances and better maintenance, less R11 has been lost in these large refrigerators. In view of the global environmental problem resulting from global warming, depletion of the ozone layer, this CFC refrigerant is currently being pursued internationally.
RefrigerantR22: R22 belongs to the HCFC group of refrigerants, which means it's made of hydrogen, chlorine, fluorine, and carbon. R22 is the most common refrigerant on the market as it is used in most residential and commercial air conditioning systems and even in some large centrifugal refrigerators. R22 is also pursued internationally for its GWP (Global warming potential) and ODP (Ozone depletion potential).
Although it is a popular refrigerant, it will be phased out in new refrigeration equipment that is made in 2010, and it will stop being produced in 2020.
RefrigerantR422B: R422B is a refrigerant made by ICOR to be similar to the R22 refrigerant. Like the R22 it is made for residential and commercial air conditioners. R422B is an HFC refrigerant, which means that it is made of hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon. This hydrogen and carbon in refrigerant help oil return in those refrigeration systems that have mineral oil or alkyl benzene in them. R422B won't mix with these oils, but the hydrogen and carbon allow the oil to thin out and keep moving in these systems.
RefrigerantR717: R717 is the refrigerant free from any halogen atoms. It is named as ammonia. The ammonia–water absorption refrigerator has been used widely in refrigeration and air-conditioning applications. R717 has a wide range of applications. It is particularly suited to working in the range approximately 0°C to -30°C and hence is widely used for food preservation. This includes the chilling of liquids such as milk, beer and soft drinks, enlarge cold storage facilities, meat processing and packing plants, large ice-making plants and commercial refrigeration. Other common applications include large air conditioning systems (refrigerators), industrial heat extraction and ice rinks.
An advantage of using R717 is its zero-ozone depletion potential and zero global warming potential.
RefrigerantR718: R718 is nothing but water. Water can be used as a refrigerant in refrigerators without any safety measurement which is cheap, environmentally neutral. Its maintenance cost is very low since leakages can be accommodated from the system.
Key Takeaways:
- A refrigerant followed by a two-digit number indicates that the refrigerant is derived methane base while a three-digit number represents ethane base.
- A refrigerant is a substance used for refrigeration.
- Refrigerants used in refrigeration systems are as follows:
- Although it is a popular refrigerant, it will be phased out in new refrigeration equipment that is made in 2010, and it will stop being produced in 2020.
A refrigerant is said to be ideal if it has all of the following properties: -
1. Low boiling point and High critical temperature.
2. High latent heat of vaporization and Low specific heat of liquid.
3. Low specific heat of liquid and Low specific volume of vapour.
4. Low specific volume of vapour.
5. Non-corrosive to metal.
6. Non-flammable and non-explosive, non-toxic.
7. Low cost.
8. Easy to liquidate moderate pressure and temperature.
9. Easy of locating leaks by suitable indicator, and
10. Mixes well with oil.
The refrigerants which are available commercially in the market are numerous. Some of them which are in common use are mentioned below:
- Air: Air (molecular weight 28.97, specific heats cp = 1.04 kJ/kgK and cv = 0.712 kJ/kg-K) is one of the earliest refrigerants to be used in the refrigeration systems. Its advantages are that it is available free of cost, is non-toxic and non-flammable and does not affect the commodity if pure. However, air suffers from a number of drawbacks. Air contains moisture and this reacts with the material of the evaporator and condenser severely affecting their working capacity. Further, there is a possibility that the passages may be blocked by the formation of ice from this moisture. The COP of air is of the order of 0.6 and thus, not suitable for use in refrigeration systems on a Refrigerants commercial scale. It is mainly used for air conditioning in aircrafts where efficiency of operation is of secondary importance.
- Ammonia: Ammonia (molecular weight 17) is one of the oldest refrigerants and it was commonly employed in places where toxicity effects were of secondary importance. Its advantages are its low cost, low specific volume, high COP (of the order of 4.0) and high refrigeration effect per unit mass of the refrigerant. Its primary drawback is its toxicity which prevents its use in air- conditioning and food preservation systems. Ammonia has a boiling point of -33 0 C at atmospheric pressure.
- Carbon Dioxide: Carbon dioxide (molecular weight 44) is a non-toxic and non-poisonous refrigerant. Also, it is not only non-flammable but and is an excellent extinguishing agent as well. Its other advantages are that it is chemically stable, immiscible with the lubricating oil and does not affect the metal used in the system. It has a low specific volume and this requires volume displacement per ton of refrigeration. However, its critical pressure is too high. Also, its critical temperature is only 31 0 C which makes it unsuitable for use in countries with a hot climate like India. It is an excellent refrigerant for low temperature refrigeration.
- Sulphur Dioxide: Sulphur dioxide (molecular weight 64) is a colourless, suffocating and irritating gas and is twice as heavy as air at atmospheric conditions. It was mostly used as a household refrigerant in the older days, but has since been discarded for better refrigerants. It suffers from a lot of disadvantages. Sulphur dioxide reacts with water forming sulphurous acid, which in presence of oxygen becomes sulphuric acid, a corrosive compound for metals. It is non-flammable but attacks foodstuff on coming in contact with it. It is also partially miscible with the lubricating oil.
- Hydrocarbons: This group consists of colourless fluids normally in gaseous state and made up of various combinations of carbon and hydrogen. Most of the refrigerants from this category are suitable for low temperature refrigeration. Isobutane falls in this category and has been suitable for domestic refrigeration. They are non-poisonous, but are flammable and highly explosive when exposed to air. The molecular weight and boiling point of each gas varies according to the number of hydrogen and carbon atoms. The larger the number of hydrogen and carbon atoms, the heavier is the gas and higher is its boiling point.
- Halocarbon Refrigerants: The halocarbon refrigerants are formed by replacing one or more of hydrogen atoms of methane or ethane by one or more atoms of the three halogens: fluorine, chlorine or bromine. Some of the refrigerants coming under this category are mentioned below:
- Refrigerant R12: The refrigerant R12 is the most widely used refrigerant in the domestic and large commercial establishments. Its chemical formula is CCl2F2 and its boiling point is -300 C at 1 bar. It is a non-flammable, non-explosive, non-irritating, non-toxic and odourless refrigerant.
- Refrigerant R13: Its chemical formula is CClF3. It is a non-flammable, non-toxic and stable refrigerant. It is very suitable for achieving low temperatures in a cascade refrigeration system. Its specific volume is high and therefore, it is suitable for centrifugal compressors. However, it also has a negative effect on ozone depletion.
- Refrigerant R22: Its chemical formula is CHClF2. It is also a non-toxic, non-flammable, non-corrosive and non-irritating refrigerant. It is the most common refrigerant for use in large refrigeration systems and is preferred to R12.
- Refrigerant R114: Its chemical formula is C2Cl2F4. Its boiling point corresponding to 1 bar is about 30 C. It has properties very similar to those of R12 with respect to water and oil combination. It is not suitable for low temperature refrigeration since it has negative evaporator pressure even at around 9 0 C. It is non-toxic, non-explosive and non-corrosive even in the presence of water.
Key Takeaways:
- Non-flammable and non-explosive, non-toxic.
- Easy of locating leaks by suitable indicator, and
- It is mainly used for air conditioning in aircrafts where efficiency of operation is of secondary importance.
- . It is an excellent refrigerant for low temperature refrigeration.
- However, it also has a negative effect on ozone depletion.
Secondary refrigerants are those circulating substances which are first cooled with the help of the primary refrigerants and are then employed for cooling purposes, e.g., ice, Carbon dioxide etc. These refrigerant cool substances by absorption of their sensible heat.
In some refrigeration systems, the refrigerant is not put into direct use. This is done mainly out of safety considerations. As an example, it is not desirable to use toxic refrigerants like ammonia in home air- conditioning and home refrigeration systems. Also, in some cases the size of the refrigerated space may be so large that direct refrigeration may be uneconomical. In such case, an indirect way is employed. The refrigerants used in this way do not pass through the cyclic process and are referred to as secondary refrigerants. The refrigerants commonly used in this way are water and brine solutions of calcium or sodium. This 1. UV radiation hits CFC molecule 2. Chlorine atom breaks away. 3. Chlorine atom hits ozone molecule. 4. Chlorine atom takes one oxygen atom to form chlorine monoxide and one molecule of oxygen. 5. Oxygen atom hits chlorine monoxide molecule. 6. Two oxygen atoms form an oxygen molecule. Chlorine atom is free and repeats the depletion process.
Antifreeze Solution is an additive which lowers the freezing factor of a water-primarily based totally liquid that may be a fluid, which includes methanol or ethylene glycol, introduced to automobile engine coolant, or utilized in sun heating device warmth switch fluids, to defend the structures from freezing.
Antifreeze, any substance that lowers the freezing factor of water, defensive a device from the unwell results of ice formation.
Antifreezes, which includes ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, normally introduced to water in vehicle cooling structures save you harm to radiators. Additives to save you freezing of water in gasoline (e.g., Dry gas) normally include methanol or isopropanol.
Organisms that ought to live on freezing temperatures use numerous chemical compounds to inhibit ice crystal formation of their cells and tissues: glycerol or dimethyl sulfide in insects, glycerol or trehalose in different invertebrates (nematodes, rotifers), and proteins in Antarctic fishes.
Freezing factor, temperature at which a liquid will become a strong. As with the melting factor, expanded strain normally increases the freezing factor. The freezing factor is decrease than the melting factor with inside the case of combinations and for sure natural compounds which includes fats.
- As a combination freezes, the strong that paperwork first normally has a composition specific from that of the liquid, and formation of the strong modifications the composition of the closing liquid, normally in a manner that step by step lowers the freezing factor.
- This precept is utilized in purifying combinations, successive melting and freezing step by step isolating the components.
- The warmth of fusion (see thermal fusion), the warmth that ought to be carried out to soften a strong, ought to be eliminated from the liquid to freeze it.
- Some beverages may be supercoiled—i.e., cooled under the freezing factor—without strong crystals forming. Putting a seed crystal right into a super cooled liquid triggers freezing, whereupon the discharge of the warmth of fusion increases the temperature unexpectedly to the freezing factor.
- The addition of 1 mole (molecular weight in grams) of any nonionic (does now no longer shape ions) solute to 1,000 grams of water lowers the freezing factor of the water with the aid of using 1. 885 °C, and this has been used as a correct approach for figuring out molecular weights.
- River water, properly water, spring etc. improve water with the mineral cloth as tough water, being subjected to warm empress the mineral excellent sink wall to come to be water dust in water set with unfold the new device, death down diesel engine to unfold thermal power dint, the critical hour will seem an um of set and stay bloodless wreath to chafe, the piston choked to death.
- But the water tank knot dust hereafter will motive the water temperature cross up and open a pot.
- Therefore need to use the gentle water because the anti — freeze. The in not unusual place answer of moving the tough water into gentle water is to boil tough water to eliminates sediments
- The greater exhaustive approach is to feature to melt with inside the tough water, including 0.five baking sodas of ~ lg( natural alkali) or the 0. Five–0. Eight g hydrogen to oxidize NA (caustic soda). There is tons weak spot the use of the water because the anti — freeze.
- It is straightforward to, come to be water dust
- The freezing factor of water is an 0 ℃, it is straightforward to freeze a jelly crack an air cylinder frame and unfold a warm device without difficulty in iciness.
- The boiling factor of water is 100 ℃, due to the fact the device large undertake approach of turbo — charger, the everyday water temperature is 105 ℃s for 95℃s, will typically seem to open a pot in summer.
The cooling machine is sewn a medium soldering via way of means of six styles of metals iron castings, aluminum, steels, crimson coppers, brasses and the water tank to constitute, water, mean water of miscellaneous excellent especially, as to its have a corrosion function, seem rusty with cave eclipse As having been conquer many risks of the water — coolant, the anti — freeze answer will become the best coolant which may be utilized in every season of the year.
At the primary time, human beings introduced the inorganic salts into the water to decrease the freezing factor or increase the boiling factor; then the natural alcohols (including ethanol, methanol, etc.) had been introduced further. And with inside the current years, the anti — freeze answer has advanced to come to be the glycol and glycerol primarily based totally anti — freeze answers.
But for the rate reason, the utility of the brand new advanced answers become restricted. Nowadays, its miles the glycol primarily based totally anti — freeze answers which have been ordinary broadly.
Key Takeaways:
- The refrigerants commonly used in this way are water and brine solutions of calcium or sodium.
- Chlorine atom is free and repeats the depletion process.
- Antifreeze, any substance that lowers the freezing factor of water, defensive a device from the unwell results of ice formation.
- The freezing factor is decrease than the melting factor with inside the case of combinations and for sure natural compounds which includes fats.
- A section alternate cloth (PCM) is a substance which releases/absorbs enough strength at section transition to offer beneficial warmth/cooling.
- Generally the transition can be from one of the first essential states of matter - strong and liquid - to the different.
- The section transition will also be among non-classical states of matter, along with the conformity of crystals, in which the cloth is going from conforming to at least one crystalline shape to conforming to another, which can be a better or decrease strength state.
- The strength launched/absorbed via way of means of section transition from strong to liquid, or vice versa, the warmth of fusion is typically lots better than the practical warmth. Ice, for example, calls for 333.fifty five J/g to melt, however then water will upward push one diploma similarly with the addition of simply 4.18 J/g.
- Water/ice is consequently a completely beneficial section alternate cloth and has been used to shop iciness bloodless to chill homes in summer time season on account that as a minimum the time of the Achaemenid Empire.
- By melting and solidifying on the section alternate temperature (PCT), a PCM is able to storing and freeing massive quantities of strength as compared to practical warmth garage.
- Heat is absorbed or launched whilst the cloth modifications from strong to liquid and vice versa or whilst the inner shape of the cloth modifications; PCMs are hence known as latent warmth garage (LHS) substances.
- There are predominant training of section alternate cloth: organic (carbon-containing) substances derived both from petroleum, from vegetation or from animals; and salt hydrates, which typically both use herbal salts from the ocean or from mineral deposits or are via way of means of-merchandise of different processes.
- A 1/3 magnificence is strong to strong section alternate. PCMs are used in lots of exceptional industrial packages in which strength garage and/or strong temperatures are required, including, amongst others, heating pads, cooling for cellphone switching boxes, and clothing.
- In North America, China, Japan, Australia, Southern Europe and different advanced international locations with warm summers top deliver is at noon whilst top call for is from round 17:00 to 20:00.
- This creates lots of call for garage media. Solid-liquid section alternate substances are typically encapsulated for set up in the long run software, to comprise with inside the liquid state.
- In a few packages, in particular whilst incorporation to textiles is required, section alternate substances are micro-encapsulated. Micro-encapsulation lets in the cloth to stay strong, with inside the shape of small bubbles, whilst the PCM center has melted.
The section alternate cloth have to own the subsequent thermodynamic properties:
- Melting temperature with inside the favored working temperature range
- High latent warmness of fusion in keeping with unit quantity
- High unique warmness, excessive density, and excessive thermal conductivity
- Small quantity modifications on section transformation and small vapor strain at working temperatures to lessen the containment problem
- Congruent melting
- Kinetic properties
- High nucleation price to keep away from super cooling of the liquid section
- High price of crystal growth, in order that the machine can meet needs of warmth restoration from the garage machine
- Chemical properties
- Chemical stability
- Complete reversible freeze/soften cycle
- No degradation after a huge range of freeze/soften cycle
Advantages
- Freeze without a great deal super cooling
- Ability to soften congruently
- Self-nucleating properties
- Compatibility with traditional fabric of construction
- No segregation
- Chemically stable
- Safe and non-reactive
Disadvantages
- Low thermal conductivity of their strong state.
- High warmness switch prices are required at some stage in the freezing cycle.
- Nano composites have been determined to yield a powerful thermal conductivity growth as much as 216%.
- Volumetric latent warmness garage ability may be low Flammable.
Key Takeaways:
- Small quantity modifications on section transformation and small vapor strain at working temperatures to lessen the containment problem
- This creates lots of call for garage media. Solid-liquid section alternate substances are typically encapsulated for set up in the long run software, to comprise with inside the liquid state
An issue of growing concern for the present-day environment is the impact of the various refrigerants on the ozone depletion and global warming of the environment. The main culprits in this case are the chlorine containing halogenated hydrocarbons, commonly known as chlorofluorocarbons or CFC which are being used as refrigerants. The Earth’s atmosphere is made up of various layers. The layer just above the Earth’s surface is known as the troposphere. The troposphere extends up to 10 km from the surface. The ozone layer is just above the troposphere and located in the stratosphere. The stratospheric ozone is Earth’s natural protection to harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV radiation is harmful to human, plant and animal life. The ozone layer gets depleted by the action of these refrigerants. CFCs, when they are released from the surface of the Earth, rise slowly into the stratosphere. Here they are bombarded by the incoming UV light from the Sun, which releases the chlorine atoms from the parent compound. It is this chlorine atom which reacts with the ozone molecules.
The detailed reactions are given below:
Chlorofluorocarbon Irradiated with UV light free Cl
Cl + O3 ClO + O2
ClO + O Cl + O2
The free chlorine atom can again take part in the reaction with another ozone atom. A single chlorine atom, released by the action of UV radiation on CFCs,
Refrigerants can catalytically destroy tens of thousands of ozone molecules during its residence in the stratosphere. Ozone depletion will permit UV rays to reach earth which can result in several harmful effects on living creatures. The UV radiation can cause skin cancer, cataracts and destruction of the body’s immune system. Along with ozone depletion, CFC refrigerants also contribute to a large extent in the global warming of the planet. These gases create a greenhouse effect which traps the heat in the lower atmosphere. This makes the Earth warmer because the greenhouse gases do not allow infrared radiation to pass through them. The earth emits IR rays during its cooling when sun is not there. CO2 is the most important greenhouse gas but one molecule of CFC has warming potential which is more than 1000 times the warming potential of one molecule of CO2. Sun’s rays are allowed into the lower atmosphere, but the heat from these rays is not allowed to escape.
The “Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer” signed in 1987 by several countries stipulates the gradual phase-out of CFC refrigerants. Use of HCFC refrigerant is advocated as an interim measure, but even these are to be eventually phased out. This therefore necessitates the need for new refrigerants which can at least perform as well as the refrigerants they replace without harming the atmosphere. Based on this requirement, HFC 134a emerges as the refrigerant of the future.
Key Takeaways:
- The ozone layer is just above the troposphere and located in the stratosphere.
- It is this chlorine atom which reacts with the ozone molecules.
- Sun’s rays are allowed into the lower atmosphere, but the heat from these rays is not allowed to escape.
- There are 5 main elements that layout engineers have to recollect in deciding on a refrigerant for a specific software: overall performance, protection, reliability, environmental acceptability, and easy economics.
- In assessing those areas, layout engineers ought to preserve in thoughts that the relative significance of every relies upon the software and, of late, authorities regulations, which vary from one u. s. To another.
- Two of the number one standards with inside the overall performance of a refrigeration gadget are refrigeration capability and efficiency.
- The refrigeration capability is the quantity of cooling that the gadget can produce for a given volumetric glide price of the refrigerant.
- Volumetric capability relies now no longer best at the latent warmth of vaporization however additionally at the density of the refrigerant vapor that enters the compressor.
- One correct indicator of a refrigerant’s capability is its regular boiling point. The better the boiling point, the decrease the fluids volumetric cooling capability will be.
- On the alternative hand, fluids with better boiling factors generally tend to have more efficiency. However, additionally they generally tend to have a better stress drop and, in a few cases, decrease warmth switch coefficients.
- Thus there's a want for compromise. Other refrigeration gadget necessities consist of suitable working stress, smaller compressor size, and decrease compressor-discharge temperature. As a ways as protection is concerned, toxicity, flammability, and stress govern the right use of a refrigerant.
- Some of the gases which are obviously gift with inside the surroundings, which includes carbon dioxide, take in infrared radiation, main to the greenhouse impact that continues an electricity stability and the floor temperature of the Earth.
- However, improved emissions of carbon dioxide and different greenhouse gases, because of such human hobby because the burning of fossil fuels, modify this stability and cause the slow warming of the Earth’s floor.
- Refrigerants, mainly those who have lengthy atmospheric lifetimes, have additionally been discovered to make a contribution to this impact.
- The quantity of radiant electricity that the refrigerants take in is measured with the aid of using an index known as worldwide warming potential (GWP).
- GWP is the quantity of infrared radiation that the fuelling can take in, relative to carbon dioxide (with an assigned GWP of 1), incorporated over a duration of a hundred years.
However, there are 5 standards have to be taken into account:
- Thermo physical properties.
- Technological issues.
- Economic aspects.
- Safety.
- Environmental factors.
In addition to those standards, different issues along with; nearby rules and standards, maintainability and capability (along with having team of workers with abilities to help the units). User education necessities have to be taken into account.
The perfect traits of ‘ideal’ refrigerants are taken into consideration to be as follows:
- Normal boiling factor under 0°C.
- Non-flammable.
- Non-toxic.
- Easily detectable in case of leakage.
- Stable beneath running conditions.
- Easy to recycle after use.
- Relatively big location for warmth evaporation.
- Relatively cheaper to produce.
- Low environmental affects in case of unintended venting.
- Low fuel line waft charge according to unit of cooling at compressor.
As its miles not likely that there might be a refrigerant that suits the proper profile, it can be essential to priorities which of the standards for the best refrigerant is of maximum importance.
For example, if minimizing the environmental effect is a key standards, the performance of the refrigerant with inside the operational segment of the machine will outweigh the effect of the manufacturing and disposal stages.
Commercial companies have historically used an R12, CFC, R502, or CFC/HCFC blend.
To allow the authorities goals to be finished maximum producers have followed both R404A, an HFC blend, and R134a. However, those are effective greenhouse gases. An opportunity, and one of the destiny answers would possibly be 'herbal' refrigerants, however this can require a few layout adjustments to zircon and refrigeration equipment. The maximum not unusual place herbal refrigerants and their traits are proven below:
Isobutene (R600A)
Isobutene is a hydrocarbon, and subsequently is flammable. Its thermodynamic homes are very much like the ones of R134a. Isobutene provides different advantages, inclusive of its compatibility with mineral oil and higher power performance and it's far inexpensive than R134a. The use of isobutene calls for minimum layout adjustments, inclusive of the relocation of ability ignition reasserts outdoor the refrigerated compartment.
Propane (R290)
Propane has a boiling factor of –42°C, making it an high-quality opportunity to R22 because it calls for comparable running pressures. An introduced gain is that, apart from introduced protection measures due to its flammability, simply no layout alternate is needed in structures whilst switching from R22 to propane. The mixture of its suitable thermodynamic and thermo physical homes yields structures which might be at the least as power green as the ones running with R22. The use of propane is growing in international locations in which guidelines permit it.
AMMONIA (R171)
Ammonia has been constantly used at some point of cutting-edge refrigeration history, however has several drawbacks. It is poisonous and flammable in concentrations among 15.5% and 28% in air. It isn't like minded with copper, for this reason requiring different substances for construction. But ammonia’s thermodynamic and thermo physical homes additionally yield very green refrigeration structures.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide isn't a brand new refrigerant. The use of carbon dioxide as a refrigerant lasted for nicely over a century, however became deserted with inside the mid-1950s, with the big use of the CFC refrigerants, which have been extra green, extra strong and safer. It became ‘rediscovered’ with inside the early 1990s. Due to its low environmental impact, low toxicity and non-flammability, CO2 is now regaining recognition with refrigeration device designers at the same time as an opportunity to fluorocarbons is being sought.
Key Takeaways:
- Volumetric capability relies now no longer best at the latent warmth of vaporization however additionally at the density of the refrigerant vapor that enters the compressor.
- As a ways as protection is concerned, toxicity, flammability, and stress govern the right use of a refrigerant.
- The quantity of radiant electricity that the refrigerants take in is measured with the aid of using an index known as worldwide warming potential (GWP).
- Easily detectable in case of leakage.
These organ fluorine compound are of hobby as refrigerants. Unlike conventional hydro fluorocarbons (HFCs) and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), that are saturated, HFOs are olefins, in any other case called alkenes.
HFO refrigerants are labeled as having 0 ozone depletion potential (ODP) and occasional international warming potential (GWP) and so provide an extra environmentally pleasant opportunity to CFC, HCFC, and HFC refrigerants.
This short reactivity prevents them from achieving the stratosphere and collaborating with inside the depletion of precise ozone, main to sturdy hobby with inside the improvement and characterization of recent HFO blends to be used as refrigerants. Many refrigerants with inside the HFO elegance are inherently solid chemically and inert, nontoxic, and non-flammable or mildly flammable.
Many HFOs have the right freezing and boiling factors to be beneficial for refrigeration at not unusual place temperatures.
They additionally display promise as blowing agents, i.e. in manufacturing of insulation foams, meals industry, creation materials, and others.
The major kind of refrigerant that has ability as the subsequent famous refrigerant are Hydro fluoro olefins (HFOs) due to the fact they offer a decrease international warming ability and don’t burn up the Ozone.
In evaluation to a few HFCs its international warming ability is over three hundred instances decrease, at the same time as its far handiest four instances better than ordinary carbon dioxide.
There also are lots of herbal refrigerants that, even though won't be as green as others, have little to no international warming ability and no chlorine to burn up the Ozone.
For example, propane, ammonia, or even carbon dioxide make properly herbal refrigerants that may update lots of different refrigerants, together with R404A, a famous HFC blend
However, the charge of those refrigerants will begin increasing, so it can be useful to alternate structures or refrigerants.
You can both convert your current gadget, purchase a brand new one, or maintain working your present day gadget, however you have to be extraordinarily watchful for leaks or inefficiencies.
Also, in a few instances HFOs can healthy into current structures without requiring a whole lot retrofitting or blend with different refrigerants to create refrigerants that paintings in present day structures however nevertheless hugely lessen the worldwide warming and ozone depletion ability
Refrigerants play a giant however now no longer continually observed function in our lives, from air con to refrigerating food, and that they have extreme implications on destiny climates.
Although maximum human beings can maintain to apply their present day structures with the identical refrigerants, converting or changing current structures to healthy the refrigerants of the destiny may be useful or even fee powerful with inside the lengthy term.
If you pick out now no longer to alternate structures or refrigerants, it's far extraordinarily critical to take into account a way to save you refrigerant leaks from this gadget, as those leaks are how those materials are launched into the atmosphere, and to take into account the destiny boom in HCFC
Key Takeaways:
- Many refrigerants with inside the HFO elegance are inherently solid chemically and inert, nontoxic, and non-flammable or mildly flammable.
- However, the charge of those refrigerants will begin increasing, so it can be useful to alternate structures or refrigerants.
- Refrigerants play a giant however now no longer continually observed function in our lives, from air con to refrigerating food, and that they have extreme implications on destiny climates.
References:
1. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by C.P Arora, McGraw‐Hill
2. Refrigeration and Air conditioning, by Manohar Prasad, New Age International (P) Ltd. Pub.
3. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by R.C. Arora, PHI
4. Principles of Refrigeration by Roy J. Dossat. Pearson Education
5. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by Stoecker& Jones. McGraw‐Hill