Unit – 4
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning is the process of treating air so as to control its temperature, humidity, cleanliness.
Applications:
1. Promoting the human comfort.
2. In manufacturing areas such as for tablets, capsules and sterile products.
3. Testing chambers
4. Maintenance of animals and equipment
- Dry Air: - The mixture of Nitrogen the oxygen neglecting water vapour is known as Dry Air.
- Wet Air: - It is the mixture of Dry Air and Water Vapour is known as Wet Air.
- Saturated Air: - It is the mixture of Dry Air and Water Vapour and it is said saturated when it diffused maximum amount of water vapour depends on absolute pressure and temperature
- Dry Bulb Temperature: - It is the temperature recorded by ordinary thermometer with a clean, dry sensing element when bulb of thermometer is expose to air.
- Wet Bulb Temperature: - it is the temperature recorded by ordinary thermometer when its bulb is covered by a wet cloth exposed to the air.
- Dew Point Temperature: - It is the temperature of air recorded by ordinary thermometer when the mixture present in air start to condensed
- Specific Humidity: - The mass of water vapour present in 1 kg of moist air it known as Specific Humidity.
- Absolute Humidity: - It is defined as the mass of water vapour in unit volume of moist air is called as Absolute Humidity.
- Relative Humidity: - It is defined as the ratio of actual mass of water vapour in unit volume of moist air to the mass of water vapour in the same volume of saturated Air at the same temperature and pressure.
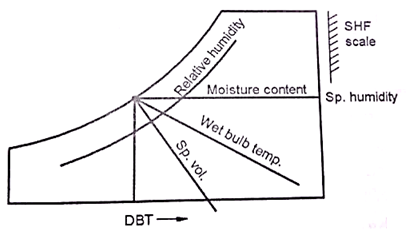
The properties of atmospheric air at a specified total pressure are presented in the form of easily readable charts called Psychrometric Chart.
The dry – bulb temperature are shown on the horizontal axis.
The specific humidity is shown on the vertical axis.
Key takeaways:
- 2. In manufacturing areas such as for tablets, capsules and sterile products.
- Wet Air: - It is the mixture of Dry Air and Water Vapour is known as Wet Air.
- Dew Point Temperature: - It is the temperature of air recorded by ordinary thermometer when the mixture present in air start to condensed
- Sensible Heating
- Sensible Cooling
- Dehumidification
- Humidifying
- Adiabatic Cooling
- Chemical Dehumidification
- Adiabatic Mixing (Moist Air & Water Vapor)
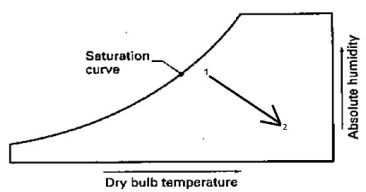
- Sensible Heating: It is addition of heat to moist air without the addition of moisture. It follows a constant humidity ratio line on the psychrometric chart.
- Sensible Cooling: It is the removal of heat from moist air without the removal of moisture. It also follows a constant W on the psychrometric chart.
- Heating & Cooling process – addition or removal of sensible heat without change in absolute moisture content.
NOTE: RH changes as temperature changes.
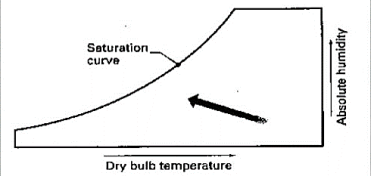
4. Dehumidification: Dehumidification by cooling – in cooling coils temp of air reduces and the saturation point (dew point) is reached.
Further cooling results in reduction of absolute humidity.
5. Cooling and Dehumidifying: It is the removal of heat and moisture from moist air, it involves sensible and latent heat transfer.
6. Humidifying: It is the addition of moisture to moist air without the addition of heat.
7. Adiabatic or evaporative cooling: A psychrometric process which involves the cooling without heat loss or gain.
Sensible heat lost by air is converted to latent heat in the added water vapor.
8. Heating and Humidifying: It is the addition of heat and moisture to moist air, it also involves sensible and latent heat transfer.
Key takeaways:
- Sensible Heating: It is addition of heat to moist air without the addition of moisture. It follows a constant humidity ratio line on the psychrometric chart.
- Humidifying: It is the addition of moisture to moist air without the addition of heat.
- Heating and Humidifying: It is the addition of heat and moisture to moist air, it also involves sensible and latent heat transfer.
An air washer may be thought of as an enclosure in which air is drawn or forced through a spray of water in order to cleanse, humidity, or dehumidify the air. Cleansing the air refers to the removal of airborne impurities such as dusts, gases, vapors, fumes, and smoke. The increase in water vapor in a given space is called humidification, and the decrease of water vapor in a given space is the process of dehumidification.
The cooling tower is one of the most important devices in chemical industries for example when the hot water come from heat exchanger, we use the cooling tower to cool it. The purpose of cooling tower is to cool relatively warm water by contacting with unsaturated air. The evaporation of water mainly provides cooling.
Cooling tower performance depends on four factors:
(1) Range
(2) Heat load
(3) Ambient wet-bulb temperature or relative humidity and
(4) Approach.
Range is the temperature difference between the hot water inlet and cold-water outlet at the tower.
Cooling tower efficiency is limited by the ambient wet bulb temperature. Ideally, cold water temperature will be equal to the wet-bulb temperature which is practically impossible to achieve. Hence, cooling tower efficiency will be in between 70 to 75%.
Humidification efficiency was evaluated by:
(a) measuring the water content of the inspiratory air on perfusion with different gas flows,
(b) measuring the water loss of a lung model, and
(c) simultaneous measurement of the in- and expiratory water content with a capacitive hybrid sensor.
The humidification efficiency of HHs is a function of gas flow and design characteristics.
Key takeaways:
- The increase in water vapor in a given space is called humidification, and the decrease of water vapor in a given space is the process of dehumidification.
- The evaporation of water mainly provides cooling.
- Humidification efficiency was evaluated by:
Thermal Analysis (TA)is a group of techniques that study the properties of materials as they change with temperature Thermal analysis. Includes several different methods. These are distinguished from one another by the property which is measured.
- Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA): mass
- Differential thermal analysis (DTA): temperature difference
- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC): heat difference
Concepts of Thermal Analysis:
Temperature: A measure of kinetic energy of molecular motion.
Temperature Scales:
• Newton (1701): freezing point of water 0, human body 12
• Fahrenheit (1714): freezing point of water mixed with NaCl 0, human body 96, freezing point of water 32, boiling point of water 212
• Celsius (1742): freezing point of water 0, boiling point of water 100
• Kelvin (1848): absolute zero is the temperature at which molecular energy is a minimum and it corresponds to a temperature of -273.15°C.
Thermal comfort is the condition of mind that expresses satisfaction with the thermal environment and is assessed by subjective evaluation.
It is defined as the temperature of a still and saturated atmosphere which would, in the absence of radiation, produce the same effect as the temperature in question.
• The first comfort scale was produced by Houghton and Yaglou in 1923, working at the American Society of Heating and Ventilating Engineers.
• Their findings were plotted on a psychrometric chart, producing ‘equal comfort lines’.
• This new scale was named Effective Temperature (ET Scale).
• The different factors determining thermal comfort – air temperature, humidity and air movements are combined together into a single index – Effective temperature
• Effective temperature is the temperature in an environment with 100% humidity and no air movements which will induce the same level of thermal comfort as in the present situation
• For example, if the effective temperature is said to be 30°C, it means that the thermal comfort is equivalent to one is an environment with temperature 30°C, 100% humidity and no air movements
• But effective temperature does not take into consideration, the effect of radiant heat energy.
The Comfort Chart is a tool that helps operators determine how well air-handling equipment is providing thermal comfort for the building occupants or for a process within the facility.
Key takeaways:
- These are distinguished from one another by the property which is measured.
- Celsius (1742): freezing point of water 0, boiling point of water 100
- The first comfort scale was produced by Houghton and Yaglou in 1923, working at the American Society of Heating and Ventilating Engineers.
- For example, if the effective temperature is said to be 30°C, it means that the thermal comfort is equivalent to one is an environment with temperature 30°C, 100% humidity and no air movements
- It is the thermal energy that must be removed from the space in order to maintain the desired comfort conditions.
- HVAC systems are used to maintain thermal conditions in comfort range.
Purpose of Load Estimate:
- Load profile over a day
- Peak load (basis for equipment sizing)
- Operation Energy analysis
- HVAC Construction cost
Principles of cooling Load Estimate:
- Enclosure heat transfer characteristics – Conduction – Convection – radiation
- Design conditions – Outdoor & indoor
- Heat Gains – Internal – External or Solar
- Thermal capacity
Indoor Design Conditions:
- Indoor air quality
- Air contaminants
- Air cleaning
2. Acoustic requirements
3. Pressurization requirements
4. Outdoor Design Conditions:
- Weather data required for load calculation
- Temperature & humidity
- Wind speed, sky clearness, ground reflectance etc.
ASHRAE Fundamentals 2001:
– Design severity based on 0.4%, 1%, & 2% level annually (8760h)
– For example, at 1% level, the value is exceeded in 0.01x8760h = 87.6 h in a year
Heat flow- Heat energy tends to distribute itself evenly until a perfectly diffused uniform thermal field is achieved. It tends to flow from high temperature to lower temperature zones, by any or all of the following ways:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
The 'motive force' of heat flow in any of these forms is the temperature difference between the two zones or areas considered. The greater the temperature difference, the faster the rate of heat flow. The rate of heat flow is measured in Watts (W). In most practical applications, the multiple of watt 'kilowatt' (kW), will be used. (1 kW = 1000 W)
Convection:
In convection, heat is transferred by the bodily movement of a carrying medium, usually a gas or a liquid. The rate of heat transfer in convection depends on three factors:
- Temperature difference (difference in temperature of the medium at the warmer and cooler points).
- The rate of movement of the carrying medium in terms of kg/s or m3/s.
- The specific heat of the carrying medium in J/kg deg C or J/m3 deg C.
These quantities will be used in ventilation heat loss or cooling calculations.
Radiation:
In radiation heat transfer, the rate of heat flow depends on the temperatures of the emitting and receiving surfaces and on certain qualities of these surfaces: the emittance and absorbance.
Radiation received by a surface can be partly absorbed and partly reflected:
The proportion of these two components is expressed by the coefficients absorbance (a) and reflectance (r). The sum of these two coefficients is always one: a + r = 1 Light colored, smooth and shiny surfaces tend to have a higher reflectance.
For the perfect reflective theoretical white surface: r = 1, a = O. The perfect absorber, the theoretical 'black body', would have the coefficients: r = 0, a = 1
Key takeaways:
- HVAC systems are used to maintain thermal conditions in comfort range.
- Enclosure heat transfer characteristics – Conduction – Convection –
- Wind speed, sky clearness, ground reflectance etc.
- It tends to flow from high temperature to lower temperature zones, by any or all of the following ways:
Infiltration is the unwanted and unintentional flow of air through a building’s fabric. It’s caused by gaps and cracks, typically at junctions between different building elements. Some are big, for example a visible gap between a window frame and ill-fitting openable casement, and some are small, such as an almost imperceptible flow of air where an external wall meets a ground floor.
Ventilation is the deliberate movement of air to remove contaminants such as water vapour, airborne chemicals (VOCs), CO2, NOx, and odours from an indoor environment, and to keep everything feeling ‘fresh’. Kitchen and bathroom extractors and opening a window are simple forms of ventilation.
Internal heat gain is the sensible and latent heat emitted within an internal space from any source that is to be removed by air conditioning or ventilation, and/or results in an increase in the temperature and humidity within the space.
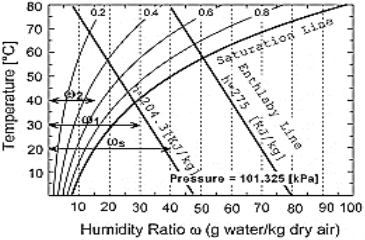
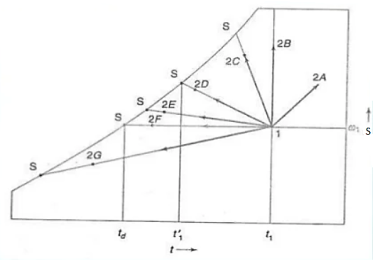
SHF: The heat added during psychometric process may be split into sensible heat and latent heat. The ratio of sensible heat to total heat is called sensible heat factor,
SHF = SHSH+LH
Where, SH = sensible heat and LH = latent heat
Importance of SHF factor:
Total heat is comprised of sensible heat and latent heat.
SHF (Sensible Heat Factor) is the ratio between the sensible and the total heat.
The factor comes handy for the ‘building specifications’ point of view. The factor is greatly influenced by the relative humidity and the working conditions of the air coolers.
By SHF the latent and sensible cooling or heating loads on a building can be estimated. It’s the basic ratio and yet the a very important one whenever cooling load is estimated for a room.
Key takeaways:
- Kitchen and bathroom extractors and opening a window are simple forms of ventilation.
- The ratio of sensible heat to total heat is called sensible heat factor,
- SHF = SHSH+LH
- It’s the basic ratio and yet the a very important one whenever cooling load is estimated for a room.
Bypass factor is an important coil characteristic on moisture removal performance. Its value depends on:
• Number of rows/fins per inch
• Velocity of air
Bypass Factor of the coil:
- When air streams across the cooling, portion of air may not come into contact with the coil surface.
- BPF = un-contacted air flow/ total flow
- BPF is normally selected at 0.1 for offshore cooling and dehumidification.
Great Sensible Heat Factor is the ratio between sensible and total heat in a cooling coil.
A cooling coil should have the capacity to handle the heat load generated in the room in addition the capacity to cool down the fresh make up air.
The Great Sensible Factor is independent of the total air flow and can be expressed as:
GSHF = [Qs + mf cp (tf - tr)] / [Qt + mf (hf - hr)]
Where,
GSHF = Great Sensible Heat Factor
If the GSHF line is extended, it strikes the saturation curve known as apparatus dew point (ADP).
Apparatus Dew Point (ADP) is the effective surface temperature of the cooling coil. It is also the temperature at a fixed flow rate at which both sensible and latent heat gains are removed (from the conditioned space) at the required rates. It is also often called as the 'Coil Temperature’.
Window air conditioner is now and again called room air conditioner as well. It is the most effective shape of a zircon machine and is hooked up on home windows or walls.
It is an unmarried unit this is assembled in a casing in which all of the additives are placed. This refrigeration unit has a double shaft fan motor with fanatics hooked up on each facets of the motor. One on the evaporator facet and the opposite on the condenser facet.
The evaporator facet is placed going through the room for cooling of the distance and the condenser facet out of doors for warmth rejection. There is an insulated partition keeping apart this facets with inside the identical casing.
Front Panel
The front panel is the only this is visible via way of means of the person from within the room in which it's miles hooked up and has a person interfaced manipulate be it electronically or mechanically. Older unit generally are of mechanical manipulate kind with rotary knobs to manipulate the temperature and fan velocity of the air conditioner
The more modern gadgets include digital manipulate machine in which the features are managed the use of far flung manipulate and contact panel with virtual display. The front panel has adjustable horizontal and vertical (a few models) louvers in which the path of air waft are adjustable to healthy the consolation of the users.
The mechanical kind is generally decrease in fee in comparison to the digital kind. If you simply need to chill the room and aren't too precise approximately aesthetic or extra features, the mechanical kind will do the work.
Indoor Side Components
The indoor elements of a window air conditioner include: Cooling Coil with an air clear out hooked up on it. The cooling coil is in which the warmth change occur among the refrigerant with inside the machine and the air with inside the room.
Fan Blower is a centrifugal evaporator blower to discharge the cool air to the room. Capillary Tube is used as a growth device. It may be noisy at some stage in operation if hooked up too close to the evaporator. Operation Panel is used to manipulate the temperature and velocity of the blower fan.
A thermostat is used to experience the go back air temperature and every other one to screen the temperature of the coil. Type of manipulate may be mechanical or digital kind.
Filter Drier is used to get rid of the moisture from the refrigerant. Drain Pan is used to incorporate the water that condensate from the cooling coil and is discharged out to the out of doors via way of means of gravity.
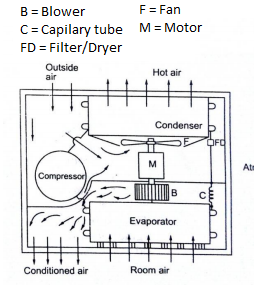
Outdoor Side Components
The out of doors facet elements include: Compressor is used to compress the refrigerant. Condenser Coil is used to reject warmth from the refrigeration to the out of doors air.
Propeller Fan is utilized in air-cooled condenser to assist pass the air molecules over the floor of the condensing coil. Fan Motor is placed here. It has a double shaft in which the indoor blower and out of doors propeller fan are related together.
Operations During operation, a thermostat is hooked up at the go back air of the unit. This temperature is used to manipulate the on or off of the compressor. Once the room temperature has been achieved, the compressor cuts off.
Usually, it must be off for as a minimum three mines earlier than turning on once more to save you it from being damaged.
For mechanical manipulate kind, there is mostly a warning to show at the unit after the unit has become off for as a minimum three mines.
For digital manipulate, there is mostly a timer to routinely manipulate the cut-in and cut-out of compressor. The evaporator blower fan will suck the air from the room to be conditioned via the air clear out and the cooling coil.
Air that has been conditioned is then discharge to supply the cool and dehumidified air lower back to the room. This air mixes with the room air to convey down the temperature and humidity stage of the room.
The advent of sparkling air from out of doors the room is accomplished via the damper that is then combined with the go back air from the room earlier than passing it over the air clear out and the cooling coil.
The air clear out that is hooked up in the front of the evaporator acts as a clear out to preserve the cooling coil smooth to gain excellent warmth-switch from the coil. Hence, ordinary washing and cleansing of the air clear out is a superb exercise to make sure green operation of the air conditioner.
Key takeaways:
- If the GSHF line is extended, it strikes the saturation curve known as apparatus dew point (ADP).
- There is an insulated partition keeping apart this facets with inside the identical casing.
- The front panel has adjustable horizontal and vertical (a few models) louvers in which the path of air waft are adjustable to healthy the consolation of the users.
- It has a double shaft in which the indoor blower and out of doors propeller fan ate related together
- Once the room temperature has been achieved, the compressor cuts off.
Air conditioners are available loads of shapes and sizes, however all of them perform at the identical fundamental premise. An air conditioner gives bloodless air inner your house or enclosed area with the aid of using genuinely getting rid of warmness and humidity from the indoor air.
It returns the cooled air to the indoor area, and transfers the undesirable warmness and humidity out of doors. A preferred air conditioner or cooling device makes use of a specialized chemical referred to as refrigerant, and has 3 important mechanical additives: a compressor, a condenser coil and an evaporator coil.
The compressor increases the stress and temperature of the refrigerant fuelling and sends it to the condenser coil in which its miles transformed to a liquid. Then the refrigerant travels returned interior and enters the evaporator coil. Here the liquid refrigerant evaporates, and cools the indoor coil.
A fan blows indoor air throughout the bloodless evaporator coil in which the warmth in the domestic is absorbed into the refrigerant.
The cooled air is then circulated for the duration of the house whilst the heated evaporated fuelling is dispatched returned out of doors to the compressor.
The warmness is then launched into the out of doors air because the refrigerant returns to a liquid state. This cycle keeps till your house has reached the preferred temperature.
A common air on device, regularly called “crucial air” or “split-device air on”, commonly consists of the following: a thermostat that controls device operation an outside unit that homes a fan, condenser coil and compressor an indoor unit (generally both a furnace or fan coil) that homes the evaporator coil and fan to flow into the cooled air copper tubing that lets in refrigerant to waft among the indoor and out of doors units an growth valve the regulates the quantity of refrigerant going into the evaporator coil ductwork that lets in air to flow into from the indoor unit out to the diverse residing areas and returned to the indoor unit In its maximum fundamental description, the air on system entails movements that arise simultaneously, one in the domestic and one out of doors the house.
Inside the house (every now and then called the “bloodless side” of the device), heat indoor air is cooled because it blows throughout a chilly cooling coil complete of refrigerant. Heat from indoor air is absorbed into the refrigerant because the refrigerant turns from liquid to fuelling.
The cooled air is shipped returned to the residence. Outside the house (every now and then called the “warm side” of the device), the refrigerant fuel line is compressed earlier than coming into a huge coil with inside the out of doors unit.
Heat is launched out of doors because the refrigerant turns returned to a liquid and a huge fan pulls out of doors air via the out of doors coil rejecting the warmth absorbed from the residence.
The end result is a non-stop cycle of warmth and humidity being eliminated from indoor air, cool air returning to the house, and warmth and humidity exiting the house. Now which you have a fundamental expertise of ways air conditioners paintings, let’s dig a touch deeper and describe the complete system works.
The thermostat, that's generally set up on a wall in a crucial region in the domestic, video display units and controls the temperature of the indoor air. The cooling system begins off evolved whilst the thermostat senses the air temperature desires to be reduced and sends alerts to the air on device additives each outside and inside the house to begin running.
The fan from the indoor unit pulls warm air from in the residence via go back air ducts. This air passes via filters in which dust, lint and different airborne debris are collected.
The filtered, heat indoor air then passes over bloodless evaporator coil. As the liquid refrigerant in the evaporator coil converts to fuel line, warmness from the indoor air is absorbed into the refrigerant, for this reason cooling the air because it passes over the coil.
The indoor unit’s blower fan then pumps the chilled air returned via the house’s ductwork out into the diverse residing areas. The refrigerant fuelling leaves the house via a copper tube and passes into the compressor with inside the air conditioner unit out of doors.
Think of the compressor as a huge electric powered pump. The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant fuelling and sends the refrigerant into the out of doors unit’s condenser coil.
A huge fan pulls out of doors air via the condenser coil, permitting the air to soak up heating power from the house and launch it out of doors. During this system, the refrigerant is transformed returned to a liquid.
It then travels via a copper tube returned to the indoor unit in which it passes via a growth device, which regulates the waft of refrigerant into the evaporator coil. The bloodless refrigerant then absorbs greater warmness from the indoor air and the cycle keeps.
Key takeaways:
- A compressor, a condenser coil and an evaporator coil.
- Here the liquid refrigerant evaporates, and cools the indoor coil.
- The cooled air is then circulated for the duration of the house whilst the heated evaporated fuelling is dispatched returned out of doors to the compressor.
- Heat from indoor air is absorbed into the refrigerant because the refrigerant turns from liquid to fuelling.
Healthy and sparkling indoor air is fundamental to a terrific excellent of existence. It is a whole lot nicer to paintings whilst the excellent of the air is right without a consistent want to open the windows, and to move domestic to sparkling air.
Both air on and air flow assist enhance the excellent of indoor air. Although without problems pressured in regular language, the 2 have an effect on the air in special ways.
Ventilation makes it simpler for us citizens to be and to breathe. Ventilation additionally continues the systems of the rental in desirable condition.
Air conditioning with a separate unit, on the opposite hand, way that indoor air is recycled and its traits are modified e.g. With the aid of using cooling it or casting off moisture.
Air conditioning does now no longer carry new air into the rental. If your mattress is soaked in sweat on summer time season mornings, an air cooler or the cooling feature of an air-to-air warmth pump could make you sense greater comfortable.
An air-to-air warmth pump additionally allows warmth the constructing in chillier months. Ventilation, on the opposite hand, continues the air sparkling and smooth to breath in any respect times- no matter the season. Its cooling capability is, however, limited.
Technically air flow and air on may be carried out both with the aid of one or absolutely separate devices. Air conditioning carried out with the aid of an air-to-air warmth pump does now no longer carry new air into the indoor premises.
Air conditioning may be carried out e.g. With the aid of an air-to-air warmth pump installed at the wall, a transportable air on unit, a fan convector, or a cooling beam.
These gadgets recycle indoor air and regulate its traits with the aid of using cooling and casting off moisture, however they do now no longer update the air.
Therefore, the processed air is usually the equal, best the traits change. When cooling, devices condensate water from the recycled indoor air, consequently casting off moisture from the air.
This is even greater critical for the consolation of dwelling than cooling, due to the fact humidity feels uncomfortable at the skin - very just like sweating. No one desires to sweat all of the time.
Because air on devices recycle the air, they do now no longer do away with smells regarding regular existence from it.
These smells are brought on e.g. With the aid of using cooking, respiratory, and the bathing of clothes.
While an air-to-air warmth pump allows warmth the constructing in cooler months, it can't lessen the humidity load due to showering and sauna - even if used for heating. Air conditioning may be carried out with the aid of a separate unit or it is able to be included with the air flow machine of the constructing.
For instance the bloodless geothermal warmth series circuit fluid may be used as a coolant.
Ventilation comes from the Latin ventilation meaning “an exposing to the air”. Used indoor air is eliminated and changed with new and sparkling air. A mechanical air flow machine is generally designed and carried out whilst the residence is constructed or in connection to renovations.
Ventilation pipes are hooked up with inside the systems and the air flow unit in a technical space, bathroom, or a few different appropriate location. Ventilation gets rid of impurities from the indoor air which might be due to regular dwelling, including cooking smells and moisture due to bathing and the bathing of clothes.
Modern mechanical air flow recovers the warmth of the extracted air and makes use of it to warmth the sparkling air this is blown into the rental. This is sensible in phrases of strength performance. Heating the deliver air prevents unsightly drafts.
The fashionable gadget of Val lox MV fashions consist of a humidity sensor that measures the relative humidity of indoor air. When the sensor detects immoderate humidity, the unit gets rid of it. A carbon dioxide sensor that detects carbon dioxide generated with the aid of using respiratory is likewise a fashionable gadget.
When the carbon dioxide degree will increase too high, the sensor boosts the air flow. Usually the air flow performance wishes to be boosted after a sauna and showering or whilst there's a big wide variety of humans gift with inside the constructing. The air flow performance may be decreased whilst the house is unoccupied.
Key takeaways:
- It is a whole lot nicer to paintings whilst the excellent of the air is right without a consistent want to open the windows, and to move domestic to sparkling air.
- Ventilation makes it simpler for us citizens to be and to breathe. Ventilation additionally continues the systems of the rental in desirable condition.
- Its cooling capability is, however, limited.
- Air conditioning carried out with the aid of an air-to-air warmth pump does now no longer carry new air into the indoor premises.
- Because air on devices recycle the air, they do now no longer do away with smells regarding regular existence from it.
- For instance the bloodless geothermal warmth series circuit fluid may be used as a coolant.
References:
1. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by C.P Arora, McGraw‐Hill
2. Refrigeration and Air conditioning, by Manohar Prasad, New Age International (P) Ltd. Pub.
3. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by R.C. Arora, PHI
4. Principles of Refrigeration by Roy J. Dossat. Pearson Education
5. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by Stoecker& Jones. McGraw‐Hill