Unit 6
Steam Boilers
Content:
A steam boiler or steam generator is a closed vessel in which water is heated, vaporized and converted into steam at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure. Boiler is a closed vessel in which heat produced by combustion of fuel is transferred to water for its conversion in to steam at the desired temperature and pressure. According to IBR a boiler is closed pressure vessel with capacity exceeding 25.75 litres used for IBR a boiler is closed pressure vessel with capacity exceeding 25.75 Litres used for generating steam under pressure it includes all the mountings fitted to such vessels which remains wholly or partly under pressure when steam is shut off.
Working Principle of a Boiler
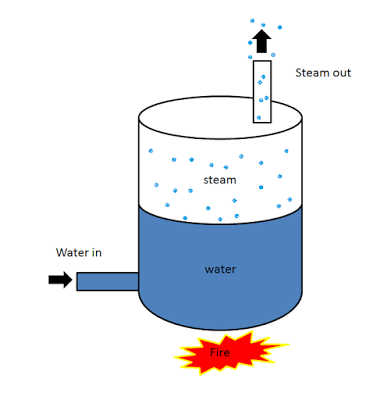
The boiler works on the same principle as the water is heated in a closed vessel and due to heating, the water changes into steam. This steam possesses high-pressure kinetic energy. The boiler contains water. The water is heated to its boiling temperature by the use of heat from the furnace. Due to the heating of water, it gets converted into high-pressure steam. The steam generated is passed through the steam turbines. As the high-pressure steam strikes the turbine, it rotates the turbine. A generator is attached to the turbine and the generator also starts to rotate with the turbine and produces electricity.
Classifications or Types of Boiler:
There is large number of boiler designs, but they may be classified according to the following ways:
1) According to the circulation of gases:
- Fire-tube boiler
- Water-tube boiler
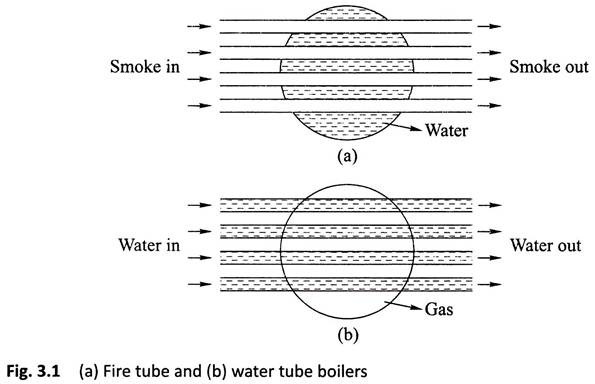
Fire Tube Boiler:
As it indicated from the name, the fire tube boiler consists of numbers of tubes through which hot gasses are passed. These hot gas tubes are immersed into water, in a closed vessel. Actually, in fire tube boiler one closed vessel or shell contains water, through which hot tubes are passed. These fire tubes or hot gas tubes heated up the water and convert the water into steam and the steam remains in same vessel. As the water and steam both are in same vessel a fire tube boiler cannot produce steam at very high pressure. Generally, it can produce maximum 17.5 kg/cm2 and with a capacity of 9 Metric Ton of steam per hour.
(a) Hot gases formed after the combustion of fuel flow through tubes and water surrounds these tubes.
(b) Internally fired.
(c) Working pressure limited to 20 bars.
(d) Steam generation rate is lower.
(e) For a given power, it occupies large floor area.
(f) Not suitable for large power plants.
(g) It carries lot of risk on less working pressure.
(h) Different parts cannot be separated easily, hence it becomes difficult to transport.
(i) Water treatment is not necessary.
(j) Parts are not so accessible for cleaning and inspection.
Fire tube boilers are classified as follows.
l. External furnace:
(i) Horizontal return tubular
(ii) Short fire box
(iii) Compact.
2. Internal furnace:
(i) Horizontal tubular
(a) Short firebox (b) Locomotive (c) Compact (d) Scotch.
(ii) Vertical tubular.
(a) Straight vertical shell, vertical tube
(b) Cochran (vertical shell) horizontal tube.
Advantages of Fire Tube Boiler
- It is quite compact in construction.
- Fluctuation of steam demand can be met easily.
- It is also quite cheap.
Disadvantages of Fire Tube Boiler
- As the water required for operation of the boiler is quite large, it requires long time for rising steam at desired pressure.
- As the water and steam are in same vessel the very high pressure of steam is not possible.
- The steam received from fire tube boiler is not very dry.
Water Tube Boiler:
A water tube boiler is such kind of boiler where the water is heated inside tubes and the hot gasses surround them.
This is the basic definition of water tube boiler. Actually, this boiler is just opposite of fire tube boiler where hot gasses are passed through tubes which are surrounded by water.
(a) Water flows inside the tubes and gas surrounds these tubes.
(b) Externally fired.
(c) Working pressure may be as high as 150 bars.
(d) Steam generation rate is higher.
(e) For a given power, it occupies lesser floor area.
(f) Suitable for large power plants
(g) Less risk on explosion due to high working pressure.
(h) Each and every part can be separated easily, so transportation is easier.
(i) In this boiler, water treatment is necessary.
(j) Parts are easily accessible for inspection.
There are many types of water tube boilers, such as
- Horizontal Straight Tube Boiler.
- Bent Tube Boiler.
- Cyclone Fired Boiler.
Horizontal Straight Tube Boiler again can be sub-divided into two different types,
- Longitudinal Drum Water Tube Boiler.
- Cross Drum Water Tube Boiler.
Bent Tube Boiler also can be sub divided into four different types,
- Two Drum Bent Tube Boiler.
- Three Drum Bent Tube Boiler.
- Low Head Three Drum Bent Tube Boiler.
- Four Drum Bent Tube Boiler.
Advantages of Water Tube Boiler
There are many advantages of water tube boiler due to which these types of boiler are essentially used in large thermal power plant.
- Larger heating surface can be achieved by using more numbers of water tubes.
- Due to convectional flow, movement of water is much faster than that of fire tube boiler; hence rate of heat transfer is high which results into higher efficiency.
- Very high pressure in order of 140 kg/cm2 can be obtained smoothly.
Disadvantages of Water Tube Boiler
- The main disadvantage of water tube boiler is that it is not compact in construction.
- Its cost is not cheap.
- Size is a difficulty for transportation and construction.
2) According to Circulation of water:
- Free circulation
- Forced circulation
Free circulation:
In any water heating vessel heat is transmitted from one place to another not by condition but by convection because water is a bad conductor of heat. Let vessel containing water be heated at its bottom, as the water in the bottom portion is heated therefore its density becomes reduced in comparison to the density of water in the upper portion of the vessel, as a result, the less dense water at the bottom portion of the vessel rise up and comparatively more dense and cold water at the upper portion of the vessel comes down to take its place and thus a convection current is set up in the water until temperature off all water becomes the same.
The method of circulation of water described above is known as free circulation.
In boilers like Lancashire, Babcock, and Wilcox, etc. free circulation of water takes place.
- Advantages of free circulation:
The advantages of free circulation are:
- Free circulation of water helps to maintain a uniform temperature true everywhere within the boiler so that unequal expansion of various parts of the boiler is prevented.
- Free circulation of water facilities the escape of steam from the heating surface as soon as it formed. If steam does not escape quickly after its formation the boilerplates do not remain constantly in touch with water and as a result, these plates may be overheated.
Forced Circulation:
In forced circulation, pumps are used to maintains the continuous flow of water in the boiler. In such a case, the circulation of water takes place due to pressure created by the pump.
The forced circulation system is adopted in more high pressure, high capacity boilers of all of which are water tube type boiler
- Advantages of forced circulation:
The advantages of forced circulation are:
- The rate of heat transfer from the flue gases to the water higher.
- Tubes having comparatively smaller diameters can be used. This reduces the overall weight of the boiler.
- The number of boiler drums required may be reduced.
- Less scale formation in the boilers is required.
- Steam can be quickly generated.
- The fluctuation of load can be easily met without taking the help of any complicated controlled device.
- Chance of overheating of the boilerplates in minimum.
- Weight per unit mass of steam generated is less.
3) According to the number of tubes used:
According to the number of tubes, Boilers may be classified as:
- Single tube boiler
- Multi-tube boiler
Single tube boiler:
The boiler having only one fire tube or water tube is called single tube boiler.
Example: Cornish boiler
Multi tube boiler
The boiler having two or more fire or water tubes for the circulation of hot gases or water are called multi tube boiler.
Example: Lancashire boiler, Locomotive boiler, Cochran boiler, Babcock and Wilcox boiler etc.
4) According to the nature of use:
According to nature use, boilers are classified as
- Stationary boilers
- Locomotive boilers
- Marine boilers.
Stationary boilers:
For the generation of thermal power and for process work (in chemical, sager and textile industries) boilers used are called stationary boiler.
Locomotive boilers:
Boilers used in locomotive steam engines are called locomotive boilers.
Marine boilers:
Boilers used in steamships are called marine boilers.
5) According to the nature of the fuels used:
According to the nature of the fuel used boiler may be:
- Fuel-fired
- Gas fired
- Liquid fuel fired
- Electrically fired
- Nuclear fired
NOTE: Babcock and Wilcox boilers use solid or gaseous fuel.
Volex boilers use oil fuel.
6) According to the pressure of the boiler:
- High-pressure boiler
- Medium-pressure boiler
- Low-pressure boiler
High-pressure boiler:
The pressure of the boiler above 80 bar.
Medium-pressure boiler:
It has a working pressure of steam from 20 bar to 80 bar. It is used for power generation or process heating.
Low-pressure boiler:
This type of boiler produces steam at 15-20 bar pressure. This is used for process heating.
7) According to the position of the axis of the boiler shell:
According to the position of the axis of the boiler shell, boilers are classified as:
- Vertical boiler
- Horizontal boiler
Vertical boiler:
If the boiler axis is vertical, it is called a vertical boiler. For example, Cochran boiler.
Horizontal boiler:
If the boiler axis is horizontal, it is called a horizontal boiler.
For example, Lancashire boiler.
8) Stationary boiler and Portable boiler
a) Stationary boilers: The boilers which cannot be transported easily from one place to another are called stationary boilers.
Example: Lancashire boiler, Babcock and Wilcox boiler
(b) Portable boiler: The boilers which can be easily transported (moved) from one place to another are called portable boilers.
Example: Locomotive boiler.
9) Externally tired and internally tired boilers
(a) Externally fired boiler: - In the boiler if the fire is outside the shell, that boiler is known as externally fired boiler. Example: Babcock & Wilcox boiler
(b) Internally fire boiler:- In the boiler in which the furnace is located inside the boiler shell it is known as internally fired boiler. Example: Cochran boiler, Lancashire boiler etc.
Cochran Boiler is a multi-tubular vertical fire tube boiler having a number of horizontal fire tubes. It is the modification of a simple vertical boiler where the heating surface has been increased by means of a number of fire tubes. The efficiency of this boiler is much better than the simple vertical boiler.
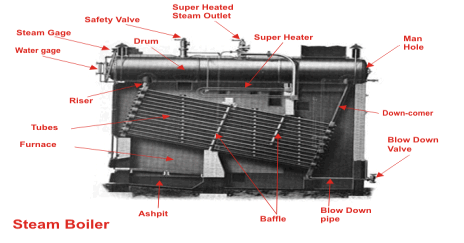
Parts of Cochran Boiler:
A Cochran Boiler is consisted of following parts:
- Shell
- Grate
- Combustion Chamber
- Fire tubes
- Fire hole
- Firebox (Furnace)
- Chimney
- Man Hole
- Flue pipe
- Fire Brick Lining
- Feed Check Valve
- Blow Off Valve
- Ash Pit
- Smoke Box Door
- Anti-Priming Pipe
- Crown
- Pressure Gauge
- Safety Valve
- Water Level Indicator
- Water Level Gauge
- Fusible Plug
- Stop Valve
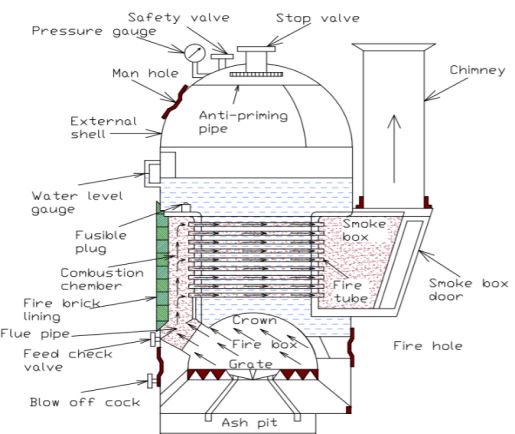
Diagram of Cochran Boiler
1 Shell:
The main body of the boiler is known as a shell. It is hemispherical on the top, where space is provided for steam.
This hemispherical top gives a higher volume to area ratio which increases the steam capacity.
2 Grates:
In the grate section, solid fuel is stored, it is designed so well that air can easily flow through it, and also the ashes fall from the grate quite easily. In this section, the fire is placed.
3 Combustion Chamber:
It is lined with fire bricks on the side of the shell to prevent overheating of the boiler. Hot gases enter the fire tubes from the flue pipe through the combustion chamber. The combustion chamber is connected to the furnace.
4 Fire Tubes:
There are various fire tubes whose one end is connected to the furnace and other to the chimney. Several horizontal fire tubes are provided to increase the heating surface.
5 Fire Hole:
The small hole is provided at the bottom of the combustion chamber to place fuel is known as a fire hole.
6 Fire Box (Furnace):
It works as a mediator of fire tubes and combustion chamber.
It is also dome-shaped like the shell so that the gases can be deflected back till they are passed out through the flue pipe to the combustion chamber.
7 Chimneys:
It is provided for the exit of flue gases to the atmosphere from the smoke box.
8 Man Hole:
It is provided for the inspection and repair of the interior of the boiler shell.
9 Flue Pipe:
It is a short passage connecting the firebox with the combustion chamber.
10 Fire Brick Lining:
It is a special type of brick ling use in Cochran Boiler to reduce the convection of heat from the outer surface of the boiler. Fire Brick is generally made of fire clay.
11 Feed Check Valve:
It is used to control the flow of water inside the boiler, it also helps to restrict the backflow of water.
12 Blow Off Valve:
It is used to blow off the settle down impurities, mud, and sediments present in the boiler water.
13 Ash Pit:
It is a chamber inside a boiler where ashes are stored.
14 Smoke Box Door:
It is used to clean the smoke box deposits materials.
15 Anti Priming Pipe:
Sometimes water droplets come out with the steam, so to prevent the droplets from carried out by the steam the Anti-Priming Pipe is used.
16 Crown:
It is hemispherical dome-shaped section of a boiler, where burning of fuel happens.
17 Pressure Gauges:
It measures the pressure of steam inside the boiler.
18 Safety Valves:
It blows off the extra steam when the steam pressure inside the boiler reaches above safety level.
19 Water Level Indicators:
The position of the water level in the Cochran boiler is indicated by the water level indicator.
20 Water Level Gauge:
It glass tube fitted outside of the boiler to check the water level inside the boiler.
21 Fusible Plugs:
It is one type of safety measure. If the inside temperature of the boiler cross the limit, then for safety purpose this Fusible Plug melts and the water comes into the boiler furnace and extinguish the fire.
22 Stop Valve:
Stop valve is used to transfer steam to the desired location when it is required. Otherwise, it stops the steam in the boiler.
Working Principle of Cochran Boiler:
The Cochran boiler works as same as other fire tube boiler.
First, the coal is placed at the grate through the fire hole.
Then the air is entering into the combustion chamber through the atmosphere and fuel is sparked through fire hole.
Then flue gases start flowing into the hemispherical dome-shaped combustion chamber. This flue gases further moves into the fire pipes.
Heat is exchanged from flue gases to the water into the fire tubes.
The steam produce collected into the upper side of the shell and taken out by when the required pressure generated.
The flue gases now send to the chimney through a firebox where it leaves into the atmosphere.
Now, this process repeats and runs continuously. The steam generates used into the small industrial processed.
Applications of Cochran Boiler:
The application of Cochran boiler is:
- Variety of process applications industries.
- Chemical processing divisions.
- Pulp and Paper manufacturing plants.
- Refining units.
Besides, they are frequently employed in power generation plants where large quantities of steam (ranging up to 500 kg/s) having high pressures i.e. approximately 16 mega Pascal’s (160 bar) and high temperatures reaching up to 550 °C are generally required.
Features of Cochran boiler:
These are some features of Cochran Boiler:
- In the Cochran boiler, any type of fuel can be used.
- It is best suitable for small capacity requirements.
- It gives about 70% thermal efficiency with coal firing and about 75% thermal efficiency with oil firing.
- The ratio of the grate area to the heating surface area varies from 10: 1 to 25:1.
Advantages of Cochran Boiler:
The advantages of Cochran Boiler are following:
- Low floor area required.
- Low initialization cost.
- It is easy to operate.
- Transport from one place to another is very easy.
- It has a higher volume to area ratio.
Disadvantages of Cochran Boiler:
There are some disadvantages of Cochran Boiler and those are:
- Low steam generation rate.
- Limited pressure handles capacity.
- It is difficult to inspect and maintain.
So, this is all about Cochran boiler, I hope you like this article, if so then don't forget to share this article on your favourite social media platform. See you in some other article till then, stay safe and keep learning.
Lancashire Boiler is a horizontal type and stationary fire tube boiler. This boiler was invented in the year 1844, by William Fairbairn.
This is an internally fired boiler because the furnace uses to present inside the boiler. This boiler generates low-pressure steam and it is a natural circulation boiler.
It has high thermal efficiency of about 80 to 90 percent.
The size is approximately 7-9 meters in length and 2-3 meters in diameter.
It is mostly used in locomotive engines and marines etc.
Parts of a Lancashire Boiler:
A Lancashire Boiler consists of following parts:
- Safety valve
- Pressure Gauge
- Feed check valve
- Water Level Indicator
- Blow off valve
- Steam stop valve
- Manhole
- Fire door
- Fusible Plug
- Ash pit
- Economizer
- Air preheater
- Superheater
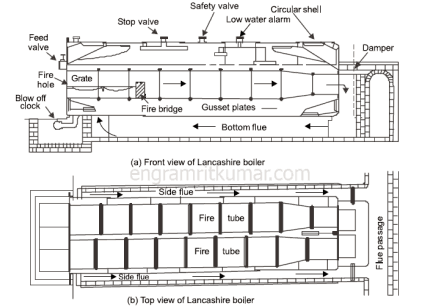
Lancashire Boiler
Safety valve:
The safety valve is used to blow off the steam when the pressure of the steam inside the boiler exceeds the working pressure.
Pressure gauge:
The function of the pressure gauge is to indicate the pressure of the steam inside the boiler.
Feed check valve:
It stops and allows the flow of water inside the boiler.
Water level indicator:
It indicates the level of water in the boiler. It is placed in front of the boiler. Two water level indicators are used in the boiler.
Blow off Valve:
Its function is to remove the sediments or mud periodically that is collected at the bottom of the boiler.
Steam stop valve:
The function of a steam stop valve is to stop and allows the flow of steam from the boiler to the steam pipe.
Manhole:
The hole is provided on the boiler so that a man can easily enter inside the boiler for the cleaning and repairing purpose.
Fire door:
This is used to ignite the present fuel inside or outside the boiler.
Fusible plug:
It is used to extinguish the fire inside the boiler when the water level inside the boiler falls to an unsafe level and prevent an explosion.
It also prevents the damage that may happen due to the explosion.
Ash pit:
The Ash-pit used to collect the ash of the burnt fuel.
The other various accessories that are also used in Lancashire boiler are:
Economizer:
An economizer is a mechanical device that is used as a heat exchanger in the steam power plant.
It is used to pre-heat the fluid or water by taking the residual heat from the combustion products ( flue gases).
It is installed to increase the efficiency of the boiler.
Air pre-heater:
Air preheater is also a mechanical device that abstracts the heat from the flue gases and transfers it to the air(atmosphere).
Superheaters:
The main purpose of the super heater is to increase the temperature of the saturated steam without any change in the pressure.
Working Principle of Lancashire Boiler:
This Lancashire boiler works on the basic principle of the heat exchanger.
It is basically a shell and tube type heat exchanger in which the flue gases flow through the tubes and the water flows through a shell.
The heat is transfer from flue gases to the water through convection.
It is a natural circulation boiler that uses the natural current to flow the water inside the boiler.
Applications of Lancashire Boiler:
Lancashire Boiler can be used in several filed like:
- The Lancashire boiler is used to drive steam turbines, locomotives, marines, etc.
- It is used in industries like paper industries, textile industries, sugar industries, tire industries, etc.
Advantages of Lancashire Boiler:
These are some advantages of Lancashire boiler:
- This has high thermal efficiency. Thermal efficiency is about 80 to 90%.
- This is easy to operate.
- It can easily meet the load requirement.
- Easy to maintain.
- Low consumption of electricity due to natural circulation.
Disadvantages of Lancashire boiler:
Although a Lancashire boiler has some disadvantages and those are:
- This is a low-pressure type boiler, so high-pressure steam is not produced.
- It has a limited grate area due to the small diameter of the flue tubes.
- The steam production rate is low. It is about 9000 kg/hr.
- Corrosion occurs in the water legs.
- This boiler requires more floor space.
Babcock and Wilcox Boiler
It was discovered by George Herman Babcock and Stephen Wilcox in the year 1967.
This is a water tube boiler, used in steam power plants. In this type of boiler, water is circulated inside the tubes and hot gases flow over the tubes.
This is a Horizontal drum axis, natural draft, natural circulation, multi-tubular, stationary, high pressure, solid fuel fired, externally fired Water tube boiler.
Babcock and Wilcox Boiler Parts:
A Babcock and Willcox Boiler Parts or Construction consists of:
- Drum
- Water Tubes
- Uptake and Down take header
- Grate
- Furnace
- Baffles
- Superheater
- Mud box
- Inspection Door
- Water Level Indicator
- Pressure Gauge
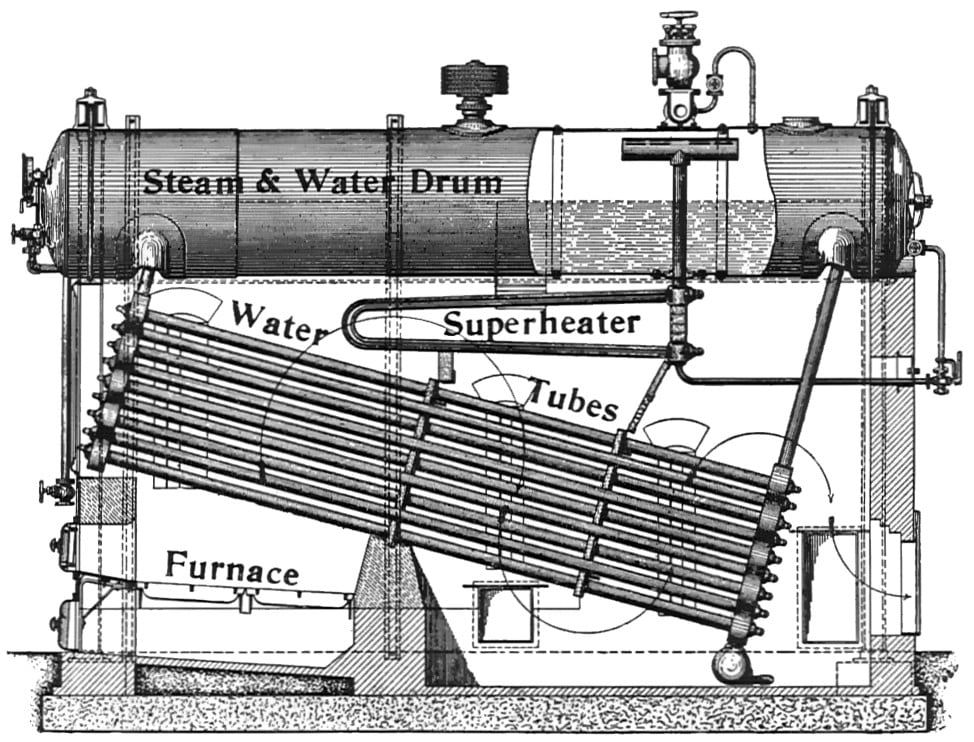
Drum:
This is a horizontal axis drum which contains water and steam.
Water tubes:
Water tubes are placed between the drum and furnace in an inclined position (at an angle of 10 to 15 degrees) to promote water circulation.
Uptake and Down take Header:
This is present at the front end of the boiler and connected to the front end of the drum. It transports the steam from the water tubes to the drum. And
This is present at the rear end of the boiler and connects the water tubes to the rear end of the drum.
It receives water from the drum.
Grate:
Coal is fed to the grate through the fire door.
Furnace:
The furnace is kept below the uptake-header.
Baffles:
The fire-brick baffles, two in number, are provided to deflect the hot flue gases.
Superheater:
It increases the temperature of saturated steam to the required temperature before discharging it from the steam stop valve.
Mud Box:
This is used to collect the mud present in the water.
Mud box is provided at the bottom end of the down-take header.
Inspection Door:
Inspection doors are provided for cleaning and inspection of the boiler.
Water Level Indicator:
The water level indicator shows the level of water within the drum.
Pressure Gauge:
The pressure gauge is used to check the pressure of steam within the boiler drum.
Working Principle of Babcock and Wilcox Boiler:
The working of Babcock and Wilcox boiler is first the water starts to come in the water tubes from the drum through down take header with the help of a boiler feed pump which continues to feed the water against the drum pressure.
The water present in the inclined water tubes gets heated up by the hot flue gases produced by the burning of coal on the fire grate.
These fuel gases are uniformly heated the water tube with the help of a baffle plate which works deflect the flues gas uniform throughout the tubes which absorbed the heating maximum from the flue gases.
As the hot flue gases come in contact with water tubes, it exchanges the heat with heater and converts into the steam.
Continuous circulation of water from the drum to the water tubes and water tubes to the drum is thus maintained.
The circulation of water is maintained by convective current and it's known as Natural Circulation.
The Steam generated is moved upward, due to density difference and through the up-take header, it gets collected at the upper side in the boiler drum.
Anti-priming pipe inside the drum which works separates the moisture from the steam and sends it's to the superheater.
The superheater receives the water-free steam from an anti-priming pipe. It increases the temperature of the steam to the desired level and transfers it to the main steam stop valve of the boiler.
The superheated steam stop valve is either collected in a steam drum or send it's inside the steam turbine for electricity generation.
Applications Babcock and Wilcox Boiler:
The main application Babcock and Wilcox boiler to produce high-pressure steam in power generation industries.
Advantages of Babcock and Wilcox:
The advantages of Babcock and Wilcox boiler are:
- The overall efficiency of this boiler is high.
- The steam generation rate is higher about 20 ton per hour at pressure 10 to 20 bars.
- The tubes can be replaced easily.
- The boiler can expand and contract freely.
- It is easy to repair maintenance and cleaning.
Disadvantages of Babcock and Wilcox Boiler:
These are some disadvantages of Babcock and Wilcox Boiler:
- It is less suitable for impure and sedimentary water, as a small deposit of scale may cause the overheating and bursting of tubes. Hence, water treatment is very essential for water tube boilers.
- Failure in feed water supply even for a short period is liable to make the boiler overheated. Hence the water level must be watched very carefully during the operation of a water tube boiler.
- The maintenance cost is high.
The boiler mountings are fittings which are mounted on the boiler for its proper functioning. Mountings are water level indicator, safety valve, pressure gauge, etc. It may be noted that a boiler cannot function safely without the mountings
Following are the important boiler mountings:
- Water level indicator
- Pressure gauge
- Safety valve
- Stop valve
- Blow off
- Feed check valve
- Fusible plug
1) Water Level Indicator
It is an main fitting in the boiler, Water level indicator indicates the water level inside the boiler. It is a safety device upon which safe working of the boiler depends.
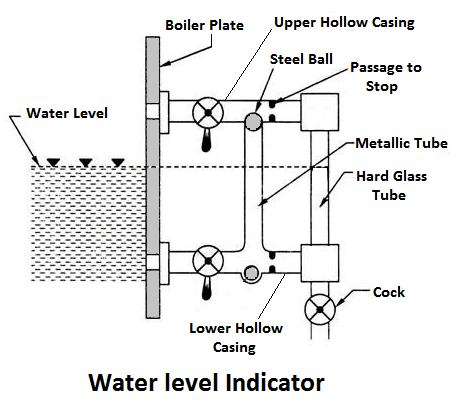
Working Principle
Water-tube indicator the water consists of a vertical hard glass tube G which is fitted with two gunmetal tubes A and B. The tubes A connects the steam space of the boiler with the glass tube and the tube B connects the water space of the boiler with the glass tube.
The tube A is provided with a valve ‘S’, called a steam valve, and tube B is fitted with another valve ‘W’, called a water valve. In addition to these valves, a third valveD, called drain valve, is fitted to the water level indicator through which water together with condensed steam from the gunmetal tube A is drained from time to time.
2) Pressure Gauge
Pressure gauges are used to measure the pressure of steam inside a steam boiler. The pressure gauge is fixed in front of a steam boiler.
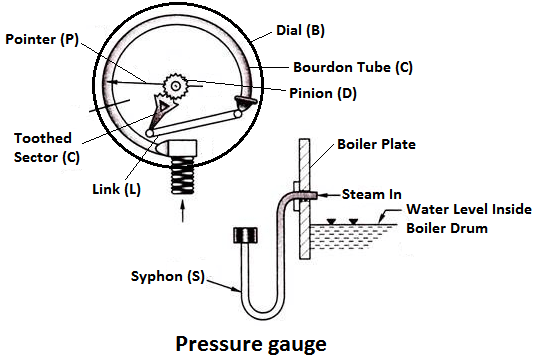
Working Principle
The pressure gauge shown in fig is bourdon pressure gauge. It consists of a circular spring tube A. One end of the bourdon tube is closed and connected to a link L and the other end is squared to a Hollow block B. The link L connects the closed end of the tube to the toothed sector C which is hinged at O. The toothed sector gears with pinion D which carries a pointer P. The pointer moves on a dial graduated in pressure units.
3) Safety valves
These are the devices attached in the steam boiler for preventing explosions due to excessive internal pressure of steam.
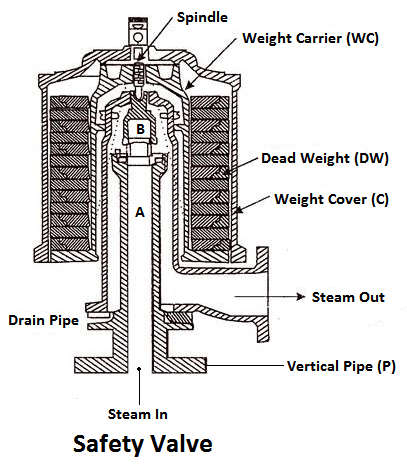
The safety valve is an instrument which prevents the boiler pressure from rising above its normal working pressure by automatically opening when the boiler pressure exceeds the normal working pressure, thus allowing excess steam to escape into the atmosphere until the pressure comes down to its normal valve. Thus, a safety valve ensures safety to a boiler from being damaged due to excessive steam pressure.
The safety valves commonly used are:
- Deadweight safety valve,
- Lever safety valve,
- Spring-loaded safety valve,
4) Steam stop valve
The function of a stop valve is to control the flow of the steam from within the boiler and to stop it completely when required. A stop valve or junction valve is used to regulate the flow of steam from the boiler.
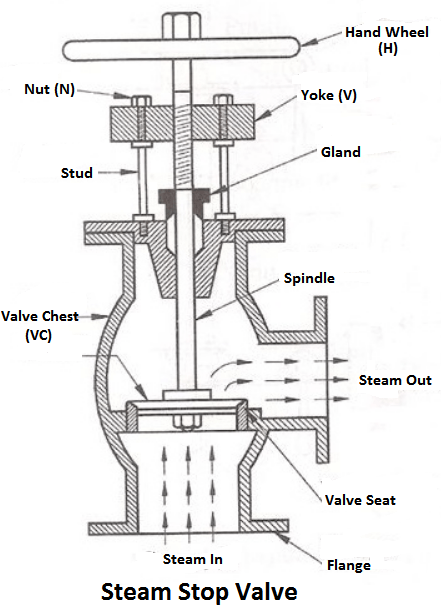
The valves mounted on the boilers, which change the direction of flow of steam by 90° are called junction valves, while valves fitted in pipelines which allowing the steam in the same direction are called stop valve.
5) Blow-off Valve
The function of a blow-off valve is to remove periodically the sediments deposited at the bottom of the boiler while the boiler is in operation and to empty the boiler while it is being cleaned or inspected.
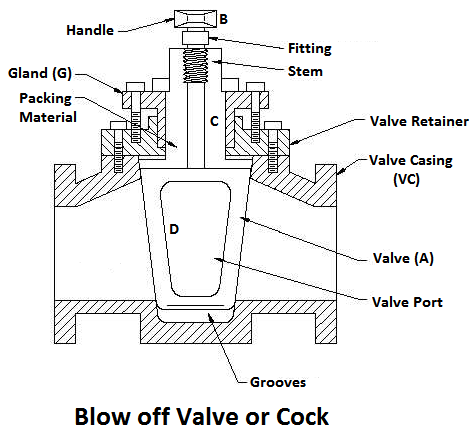
When the blow-off valve is opened the water, which is under the pressure of steam, rushes out with tremendous velocity thus carrying out the sediments along with it.
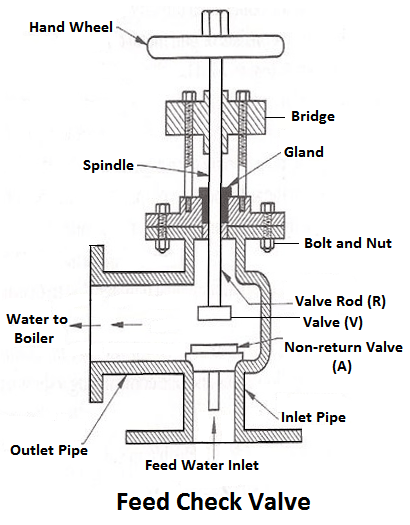
6) Feed Check Valve
When the level of water in the boiler falls, it is brought back to the specified level by supplying the additional water called feed water. The pressure inside the boiler will be high therefore the pressure of the feed water has to be raised by a pump before it is fed into the boiler. The feed water under high pressure is fed into the boiler through the feed check valve.
The function of a feed check valve is to control the flow of water from the feed pump to the boiler and to prevent the backflow of water from the boiler to the pump when the pump pressure is less than the pressure or when the feed pump ceases to work. Evidently feed check valve is placed at the boiler end of the delivery pipe of the feed pump.
7) Fusible Plug
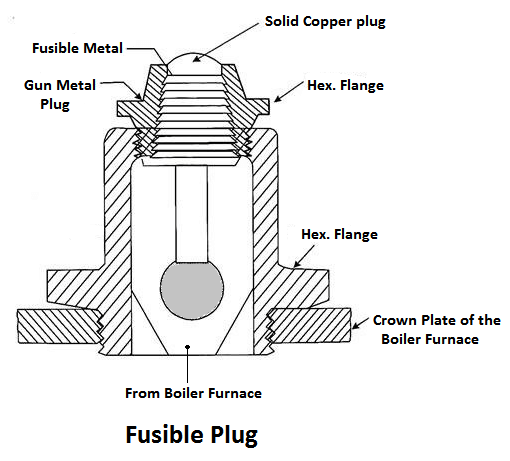
The plug is made up of tin or leads alloy, which has a low melting point. The function of the fusible plug is to put-off the fire in the furnace of the boiler when the water level falls below an unsafe level and thus avoids the explosion, which may take place due to overheating of the tubes and the shell. It is fitted over the crown of the furnace or the combustion chamber.
Boiler Accessories
The boiler accessories are required to improve the efficiency of the steam power plant and to enable for the proper working of the boiler. The boiler accessories are the devices, which form an integral part of a boiler but are not mounted on it. They include superheaters, economiser, feed pump etc. It may be noted the accessories help in controlling and running the boiler efficiently. The boiler accessories aren’t mounted directly on the boiler.
The essential boiler accessories are:
- Economiser
- Air pre-heater
- Superheaters
- Feed pump
- Steam Separator
- Steam trap
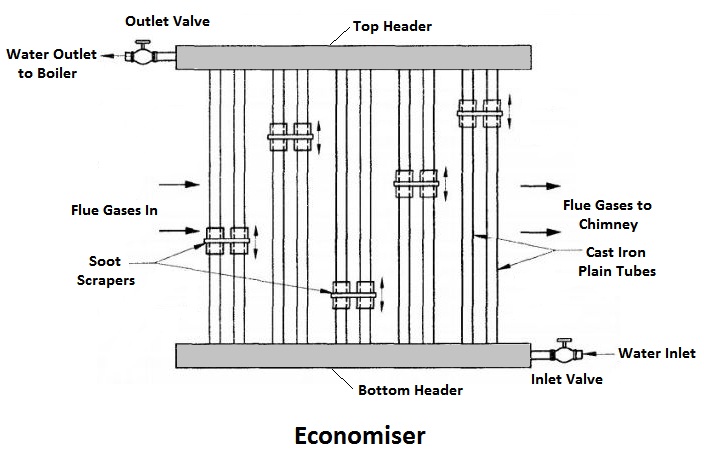
1) Economiser
The combustion gases coming out of the boiler contain a large quantity of heat. Therefore, the maximum amount of heat from the gases should be recovered before it escapes to the chimney.
In the economiser, heating the feed water does the recovery of heat in the flue gases. The economiser is placed in the path of the gases. They improve the overall efficiency of the boiler by reducing fuel consumption.
2) Air Pre-heater
The air preheater is an accessory that recovers the heat in the exhaust gas by heating the air supplied to the furnace of the boiler. Supplying preheated air into the furnace produces a high furnace temperature and accelerates the combustion of the fuel. Thus, the thermal efficiency of the plant will be increased.
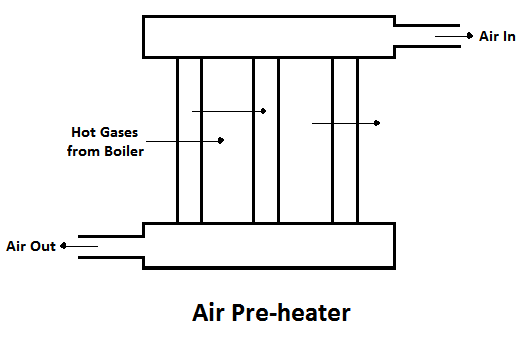
The advantages of air pre-heater are,
- Increase in the steam generation rate.
- Better combustion with less soot, smoke and ash, and
- Low-grade fuels can be used.
3) Superheaters
The superheaters are used in boilers to increase the temperature of the steam about the saturation temperature.
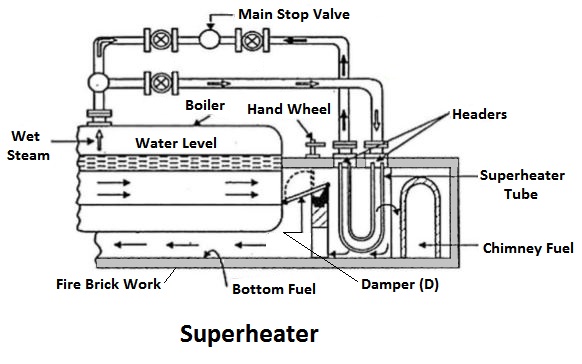
The dry saturated steam generated in the boiler is passed through a set of tubes placed in the path of the flue gases, in which it will be heated further by the hot gas to increase its temperature about the saturation temperature.
4) Feed Pump
A feed pump is a boiler accessory required to force the feed water at high pressure into the boiler. Commonly used pumps are,
- Reciprocating pumps
- Rotary pumps
The reciprocating pumps are driven directly by coupling them to the steam engine. The rotary pumps are driven by the steam turbines or by electric motors.
.