Unit 4
Writing Practices
Comprehension simply means the ability to understand something. It comprises of the multiple processes involved in hearing, understanding and making sense of the spoken language. This includes grasping various speech sounds and understanding the syntax of sentences. Comprehension can also include the process of understanding how the presentation of sentences changes meaning.
Comprehension is the correct association of meanings with word symbols. It is the selection of the correct meaning suggested by the text It is a thinking process. It is thinking through reading. Students should lead and get complete meaning. There are two situations that arise while reading a passage. The pupils may find a reading comprehension passage difficult for them. The teacher should know about the difficulties beforehand and prevent their occurrence.
It is often contested that speaking as a skill is more important than listening which is a common misconception. Listening is as important a skill as speaking if not more, as it is only by listening one can learn proper pronunciation and intonation of words which allows him to speak fluently.
Oral language skills including listening comprehension also are important for writing development. Although oral language skills aren't explicitly laid out in the developmental models of writing, they are essential component skills as writing requires generation of ideas, which then need to be translated into oral language.
There are two ways in which a person can listen to something being said to them – active and passive. Passive listening is listening without giving the speaker your full attention. Passive listening is like not listening at all therefore one must always give the speaker their full attention and practice active listening in order to fully grasp the meaning of what the speaker wants to say.
Some common difficulties with comprehension are:
- Students are not able to concentrate on what they read.
- They are not able to recognize words. Noisy surroundings, inadequate lighting and uncomfortable seating arrangements.
- Unfamiliarity of the subject matter (eg) a child from a city may not understand a passage on farming and a village child about road signal systems.
- In effective questioning and answering techniques.
- Lack of appropriate guidance by the teacher Steps for the comprehension skills. These are various steps followed for the construction of comprehension.
The term precis comes from a French word “précis”, which can be translated as "precise, clear, up to the point”. Therefore, the word precis in the context of writing means a summary of any writing piece, be it a book, an article, or a novel. What is typical while writing a precis is the outline of the main points and arguments presented in the given text. A precis does not contain a deep or critical analysis of the text, but it nevertheless objectively explains the situation narrated in a text.
Precis vs. Summary
A precis and a summary are quite similar to each other but they do contain certain major differences which set them apart. Below are the two main differences between a precis and a summary:
- A summary consists of a number of brief statements which covers the main points of the text. It has no pre-defined word limit. A precis on the other hand, has its own title and should be 1/3 of the total words of the original passage.
- A summary is a sort of general overview of the contents of a passage. Here only the main events in the passage are discussed. A precis, however, focuses on every detail and analyses a particular situation.
Rules
Below are the fundamental rules to be followed while writing a precis:
- Understand the theme of the passage
The first and the most important thing is to thoroughly read and comprehend the purpose of the passage. Once you understand the theme, it is easier to grasp the key ideas in the passage, which will help you remember them while writing the precis.
b. No copying from the passage
It is important in precis writing to use your own words and not copy from the passage. If you find certain sentences in the passage that you would like to incorporate in your precis, you need to understand them and then craft that sentence in your own words. Key words can be used but entire sentences should always be avoided.
c. Carry clarity and conciseness
One of the most fundamental rules of writing a precis is clarity. The sentences should be clear, concise, meaningful and too the point. They should reflect the central ideas from the passage.
d. A reflection of your intelligence
The precis should be written in such a way that it flaunts your writing skills. The use of language, vocabulary and structure of sentences should be perfect. A good precis will provide the readers a good impression of your writing skills and it will also make the precis comprehensible to the readers.
e. Be original
Each and every sentence in the precis should be one's own creation with no plagiarism whatsoever. If you find a significant idea or motif from the passage that you want to include in your precis, read the passage again and again and try to re-construct the idea from your memory using your own words.
f. Use of indirect speech
A precis must always be written in indirect speech since it employs the perspective of a third person. Direct speech leaves a personal impact and should be avoided while writing a precis.
g. Use facts and statistics
To maintain the credibility of the text, try to include all the numbers and facts you read in the text. It will also help you enhance the quality of your writing and will build the interest of the reader in your precis. Therefore, any of the facts and numbers should not be missed while writing the Precis.
h. An analysis of the various sections
Divide the text into sections and try to analyse each section carefully. A careful analysis of each section will let you draw in closer to the main themes and concepts in the text. Further, you can only mention the crucial content of the passage, if you have read it thoroughly and have identified the areas which carry high proportional value.
i. An interpretation of the original passage
Always conclude the passage by providing your own understand instead of the writer's perspective. The conclusion has to be from your own point of view but should still be in the third person as if spoken by a third party. It is your interpretation of the text that gives meaning to the precis.
j. The size of the precis
The size of a precis should always be one third of the original passage. While writing the precis one should always be aware of the word count but one should also be able to retain the individuality of the passage in the prescribed word limit.
Precis Format
A precis should be short and concise and comprises of three parts: The introduction, the main body and the conclusion.
The Introduction
- The introductory sentence of a precis should mention the author’s name along with the article/book title. It should also include the date of publishing in parenthesis. After that, the topic that you want to discuss in your precis has to be elaborated using a few key words. Extravagant detailing of the topic should be avoided.
- In the introduction, try to include a rhetorical verb outlining the author’s primary purpose (e.g., “assert,” “argue,” “deny,” “refute,” “prove,” disprove,” “explain”). This will give a strong definition to the facts and concepts you are about to present in the main body of your precis.
- It is important to include the thesis statement of the text in the introduction. A thesis statement is the main idea or crux of a particular text. This thesis statement will be elaborated in the main body by providing facts and evidence in its favour.
The Main Body
- The main body should include clarification of how the author formulates and further explains the main themes in the text. It should be informative enough to incite the reader's interest and short enough to retain that interest.
- It should include a sentence that states the purpose of the author in writing the text. Phrases such as “in order” are helpful in developing this sentence.
- Describe how the author establishes his connection with the readers. Always keep the audience for whom you are writing in mind while writing a precis. This includes the using vocabulary and structuring sentences according to the needs of your audience.
- All key points and arguments must be contained in this section.
The Conclusion
- Present a finishing remark of 2-3 sentences to shed light on the author’s intended idea for the book or passage.
- Give a 1-sentence restatement of the major claim which the author used to develop their evidence in the reading.
Steps for Writing a Precis
Below are the steps involved in writing a precis
Step 1: As discussed, the very first step of Precis writing is to form a clear understanding of the passage. You should fully acquaint yourself with the subject first in order to get the meaning behind a passage before starting to write a precis.
Step 2: While reading the content, make sure you highlight the important points of the passage. It will help you in keeping track of the important information that needs to be written in your Precis. Also, you should omit the information, which you feel is not important for your Precis.
Step 3: Further, you need to remember that logical ordering is highly important when it comes to precis writing. Additionally, a logically organised text helps in making things much clearer to your audience and they tend to understand your take in a processed way.
Step 4: If you have some names to be mentioned in your Precis, remember, they should be with the designations, as it helps to increase the credibility of the content. In case, the designations are not mentioned in the passage, you can write the first name.
Step 5: Moving on, the word count of the passage should be taken into account, because one- third of the same has to be written in Precis. Therefore, conducting a word count before beginning the precis could be beneficial.
Step 6: Now, prepare the draft of your Precis by jotting all the important points together. While writing always remember to maintain the flow of your concepts and you should not miss any important information you have gathered while reading the passage.
Step 7: Before finally submitting your Precis, make sure you review all the details carefully. Also, you must do a thorough check of your grammatical and structural errors. Furthermore, one thing not to miss is to mention the total count in a bracket after the end point of your Precis.
Dimension of Essay Writing
There are many types of essays and papers you can write as a student. The content and length of the essay varies depending on your level, subject of study, and the requirements of a particular course.
However, many subject bodies share the same goal. They aim to convince students of a position or perspective through informed, evidence-based, analytical and interpretive debates.
In addition, every story has an introduction, body and ending that always do the same or few things.
Essay Writing Process:
The essay writing process consists of three stages: preparation, writing and revision. These categories apply to each article or paper. However, the time and energy spent in each category depends on the sort of essay, for instance a private statement, a press release of intent, a high school essay or a grad school essay.
Preparation:
- Understand the assignment
- Understand your audience
- Select a topic
- Do some initial research
- Name the thesis statement
- Create an outline
Writing:
- Write an introduction
- Organize your arguments and give evidence
- Write the conclusion
Review:
- Analyse the organization
- Review the content of each paragraph
- Proofread for language errors
- Check for plagiarism
Introduction of an Essay:
The introduction is important to both capture the reader's interest and inform them of what will be found in the story. The introduction usually contains 10-20% of the text. To learn how to write an article introduction, first become familiar with its most important objectives.
- Move your student by chasing curiosity and curiosity:
The first sentence of the introduction should draw your student's wish. This sentence is sometimes referred to as a hook. It can be a question, quote, a surprising number, or a bold statement that emphasizes the importance of a topic.
Let's say you write an article about the development of Braille (a literacy program used by the visually impaired). A boat can be something like:
The introduction of Braille marked the biggest turning point in the history of disability.
- Provide background and context for your topic:
After you dismiss the student, it is important to provide context that will help your student understand your argument. This may include providing background information, providing an overview of important academic work or arguments on a topic, as well as explaining difficult words. Do not give too many details in the introduction - you can adequately describe the content of your essay.
- Explain the purpose and create a thesis statement:
Next, you have to explain your basic argument or thesis statement. The thesis statement provides focus and reflects your position on the topic. Usually one or two sentences long. An example of a thesis statement from Braille essay can be seen as follows:
The idea of orthopaedics was not entirely new; Louis Braille adapted simple ways to create the first system for writing to the blind. But its success depended on the reception of people who had sinned before the social status of blindness was reversed, and the process was shaped by widespread debates about the place of people with disabilities in society.
- Provide a content map:
Finish the introduction with an overview of your site structure. An overview should give the reader a general idea of what each paragraph of your article is examining.
The Body of the Essay:
The theme of your article is when you make arguments that support your thesis statement, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. His main purpose is to present, interpret and analyse the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
- Length of body text:
The length of the body depends on the type of description. On average, the body comprises 60-80% of your material. In a high school essay, this can be just three paragraphs, but with a 6,000-word graduate essay, the body can take 8-10 pages.
- Section layout/Paragraph Structure:
In order to give your essay a clear structure, it is important to use paragraphs and topics. This makes the content unwanted and easy to digest. Each section should focus on a point of view or a single point of view.
The purpose of each paragraph is presented using topic sentences. The topic clause creates a transition from the previous paragraph and informs the argument to be made in this paragraph. Change words can be used to create smooth transitions between sentences.
After the topic sentence, demonstrate evidence by providing the reader with data, examples or quotes. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how the paragraph helps improve your overall argument.
Conclusion of an Essay:
Conclusion The last paragraph of the article or paper. It takes about 10-20% of your article. Strong conclusion:
- Draws connections between the arguments made in the body of the story.
- State the consequences of your argument.
- Emphasize the importance and importance of a thesis statement of policy, education or the wider world.
- Evaluates key findings and the importance of the topic
A good conclusion should end with a memorable or impactful sentence that emphasizes the importance of your work and leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What you must not write in the conclusion
To make the end of your article as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid including. The most common errors are:
Includes new argument or evidence.
Minimize your conflicts (e.g. "This is one way for many").
Concluding phrases such as “Conclusion…” are used.
How to write an essay
- The story begins with a hook that catches your reader's interest.
- Introduction provides background and context that help your reader understand the topic.
- The introduction contains a thesis statement that provides focus and reflects your position on the topic.
- Paragraphs and titles are used for story planning.
- Each paragraph deals with a single idea, debate or issue.
- Subject sentences are used to create a smooth transition between paragraphs.
- The conclusion is not only brief, but draws a link between issues.
- The significance of the thesis statement is emphasized in the conclusion.
- Conclusion does not contain new ideas, arguments or evidence.
Types of Essays
Below are the various types of essays:
Scientific Essay
Before writing your essay, first and foremost, you need to know and understand what an essay on science is. So, what is a scientific essay? A scientific essay is an article whereby you have to analyse a scientific issue or problem and then try to develop a solution on the basis of factual information and perhaps provide some of your opinions from your own perspective on the matter as well. Essays on science can be considered different from other types of essays considering the freedom they allow. In other types of essays, you can express yourself. But, in scientific essays, there is little to no room to do so. Contrariwise, science essays seek out impartial logicality and accurate knowledge. Also, these essays test your judgment skills and analysis.
Literary Essay
A literary essay is a type of essay which involves closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not just a summarized version of the plot or a book review. Rather, it is a type of argumentative and analytical essay where you need to analyse various textual elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create meaning and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and come up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. A literary essay follows the same structure as any academic essay:
- An introduction that defines what the rest of the essay is focused on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs, that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Narrative Essay
The first step in writing an outstanding narrative essay is learning the narrative essay definition. There is no universal definition of narrative essay simply because of how broad and all-encompassing this genre of writing is.
However, when asked to define narrative essay, most academic writers will say that it’s a piece of writing telling a story using a variety of literary device. The narrative essay format is one of the most personal ones in academic writing, but it also requires you to have extensive knowledge of the writing process, not just rely on your own experiences.
Descriptive Essay
Description is a tool that writers use to keep things live for their readers, to make sure their audience is fully immersed in the words on the page. Every time you tell someone a story, or when you tell someone something, you either use the description or you don't know it. The description is basically "I have a blue car" or "That beautiful baby" or "Flowers soften the sun's golden rays and start showing their bright colours". Descriptive words are used to provide more detail and provide more insight. In fact, commentary is a tool that allows many authors (and speakers) to show up instead of just saying, and enabling our readers to interpret our material.
There are two basic types of Objective and Subjective. The meaning of purpose is shown in the first two examples above; Provides a true account of the item. Co-explanation provides a personal examination of the details by selecting specific words and phrases, such as clarifying the colours in the example above. Vibration not only provides information on colours, but also gives the idea or judgment of the value in the description. Many interpretations provide a mixture of both, giving the audience an idea of the emotional state of the subject being described.
Descriptive essays often describe a person, place, or thing that uses sensitive information. The structure of the descriptive text is more flexible than other filtering methods. The introduction of a descriptive article should set the tone and point of the essay. The thesis should convey the author's general opinion of the person, place, or thing described in the body paragraphs.
Article organization can better track spatial order, classification of ideas according to physical characteristics or appearance. Depending on the author's description, the movement can move from top to bottom, left to right, near and far, warm, cold, inviting, and so on.
Example, if the theme was the customer's kitchen during the renovation, you could start heading to one side of the room and then slowly to the other side, explaining materials, cabinetry, and so on. Or, you can choose to start with the old kitchen remnants and move on to new installations. Maybe start at the bottom and climb up to the roof.
Reflective Essay
A reflective essay is a type of written assignment where the author analyses the event from the past using a present point of view. The purpose of a reflective essay is to demonstrate the effect of the past event — specifically, what can be learned from the event and how the event helped shape the personality of the individual writing the paper.
In a way, a descriptive essay is somewhat similar to a reflective essay. Both refer to an event from the writer’s past and both can be equally rewarding for the writer, allowing them to relive the event in their thoughts and possibly even get some closure.
However, there is one key difference between a descriptive essay and a reflective essay is that the purpose of a descriptive essay is to simply describe a past event without providing an in-depth look on the effect of the event on the writer’s personality and present life.
You can use rich language and various literary devices to describe the event, but a descriptive essay barely requires the writer to do any analysis at all. A reflective essay also describes a past event in great detail, but its main purpose is to express the consequences of the event and how they changed the writer’s life and outlook.
The subject of a reflective essay can be nearly anything that influenced your life in a major way. The most popular thing to focus on when writing a reflective essay is a past experience — anything that occurred to you some time in the past. It can be a meeting or conversation with someone that left a lasting impression on you.
Expository Essay
An expository essay is a piece of writing where the author’s job is to introduce the audience to a particular concept.
The big and key difference between an expository essay and a persuasive essay is that the expository essay does not require the author to address his personal attitude to the subject, whereas writing a persuasive essay means expressing an opinion and attempting to convince the audience that it’s the only possibly correct opinion.
After learning the expository essay definition, it’s easy to think that this written assignment is pretty straightforward and can be mastered very quickly. That is why many students are surprised to learn that there are actually six main types of expository essays that are commonly used in modern schools:
- Definition essay, where the writer attempts to give a more precise definition to a concept that has been already defined by other scholars;
- Classification essay, where the writer takes a complete concept and breaks it down into groups and pieces:
- Problem and solution essay, which requires the writer to define a problem and then offer a solution that has the highest chance of solving the problem:
- Cause and effect essay, where the writer needs to cover the reasons for the subject in question happening and the possible results of the event:
- Process essay, also known as the “how-to essay”, where the writer describes the steps in a particular procedure that will lead to the desired result:
- Comparison and contrast essay, where the writer compares two subjects and defines their differences and similarities.
On paper, the assignment of writing an expository essay seems easy, but, as we have already established, there are six types and even more variations of expository essays that you may encounter throughout your academic journey.
The purpose of an expository essay, in general, is to give the readers a detailed introduction of the subject of the paper, but in reality, your job can be different. Always carefully check the writing prompt to see which type of essay you are required to write — only then will you be able to choose the appropriate expository essay format, structure, and content.
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay is a type of essay where the writer’s objective is to convince the reader that his opinion is correct by providing compelling arguments backed up by strong evidence.
An argumentative essay follows the same format as other academic essays. However, it is often believed that writing an argumentative essay is as easy as simply voicing your opinion. In reality, even though a personal opinion is an important part of the essay, it’s the arguments and evidence that make the work complete.
When learning how to write argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that the focus and most vital point of an argumentative essay is the argument itself. The rest of the paper, including the introduction, conclusion, and most of the body paragraphs, are simply there to set the context for the subject of the essay and offer support to the argument.
The argument of the argumentative essay is the backbone of the paper that holds it together. You should first state your main argument right in the introduction of the essay and then refer to it several times in the paper, so make sure to make it clear, concise, and able to resonate with the audience.
Imaginative Essay
An imaginative essay is an essay which is fictional in nature and is written completely from the author’s imagination. It may involve partial real-life events but the overall outcome is fictional. It tests the creative ability of a writer in formulating new thoughts, ideas and concepts.
An imaginative essay is narrative and descriptive in style and follows the same format as most academic essays including an introduction, the main body and the conclusion.
Business Letters
Writing letters is an art and a strategy. The latter can be followed by following formal meetings; the former must be nurtured with the care and deepest interest of man. The letters are generally divided into the following four categories: friendly or informal letters, business letters; invitations and responses, as well as the use of functions.
Importance of a Business Letter
Promotional Function: By promoting new products and providing better services to business organizations, improving and enhancing the quality of their products. Customers should be informed through these developments. Business organizations have to expand their market by tapping new areas. All-round expansion is possible only if the organization continues to be well-informed by letters to those people and letters promoting them.
Informational work: Business letters provide valuable data about previous policies, transactions and all other activities of the organization. Modern businesses cannot depend on memory like the old days. If they are available then the letters are ready reference. New policies can be developed by studying earlier. Not only is it necessary to maintain good correspondence, but it is also more necessary to make them available in the files.
Legal work: Business letters can provide evidence in legal disputes, if any, which is in a transaction. They are useful as legal documents in quotes and offers.
Goodwill work: Business letters promote goodwill among business parties that trade. They make a good rapport between the parties in business transactions.
Convey information: The fundamental reason for any business letter is to pass on information in regards to practice business exercises. Information can be transmitted through the business letter to clients, providers, indebted individuals, government experts, monetary organizations, bank, and insurance agencies and to any different gatherings related to the business.
Conclude exchange: One of the particular functions of a business letter is to finish up an exchange. In finished exchanges business letter are as often as possible utilized.
Creation of markets: Business letter are particularly significant for creating interest for new products and services and market creation.
Creation of generosity: In this electronic period, messages can be sent inside a couple of moments through electronic media however a very much beautified business letter has its own significance in creating a positive picture of the company.
Features of business letters
- Knowing What to Say:
Nothing is more harmful to good communication than muddle-headedness resulting in not being able to make one's point. Before writing a letter one should be sure of what one wants to say and accordingly one should be in command of all the necessary facts and information arranged logically and systematically.
2. Clarity:
Knowing what one wants to say is not enough unless one says it in as clear a Language as possible. Here comes the importance of the right word and the right expression put in a sentence constructed neatly and with precision. It should, however, be remembered that right words and write expressions become relevant only when they occur in the right place. Thus, emotional and even flowery language may be apposite to a personal Letter but it will be completely out of place in a business letter.
3. Brevity:
A few generations ago, when man enjoyed unlimited space and time, prolixity in language would not have been unwelcome, at Least in certain kinds of correspondence. In the modern age, however, addition of even one extra word cost time and energy most people will like to avoid. It is all the more the business correspondence. It means that all redundancy, be it a quotation illustration, an elaboration, in short, padding of any kind, must be avoided at all costs.
4. Accuracy:
Avoidance of redundant helps achieve accuracy of statement. For much unwanted language in letters is the direct result of inaccurate and inconsistent thoughts and statements. A little care, particularly habitual revision of what one has written, will go a long way towards making writing accurate.
5. Courtesy:
As remarked earlier, a letter reveals its writer's personality and character. Since there is always a 'you' in every letter, it is necessary that this 'you' or the addressee be shown all the courtesy and respect that language can express. Even when a complaint is lodged or a statement or application rejected, care should be taken that it is couched in polite and civilized language. It is worth remembering that while courtesy costs nothing, there is hardly anything more abrasive than impolite language.
6. Good Looks:
Finally, a letter must be a visual attraction to the reader. It can displease either through wrong spelling and punctuation or bad writing and typing. These are not matters merely of form as even a well-thought out-letter, rich in ideas and having all the qualities of clarity, brevity, accuracy and courtesy may not only fail to make proper impact on the reader, but may even defeat its purpose by causing him unnecessary annoyance.
Parts of a business letter
It is convenient to divide all letters into 10 parts:
- Sender's address
- Date
- Direction (the address of the person(s) to whom you are writing)
- Salutation
- Reference (not always necessary in intimate, personal letters)
- Body
- Subscription
- Signature
- Postscript (to be as a rule avoided, unless absolutely necessary)
- The envelope.
As these are mostly (except for the body of the letter) matters of form, we will illustrate each one of them. Often there are alternative forms, but you must choose one of them and use it consistently.
- Sender's address:
(a) Laxmi Niwas,
52 Mall Road,
Civil Lines,
Kanpur 208 016
(b) D 64 Press Road,
Nauroji Nagar,
Mysore 570 006
(c) Department of Linguistics,
University of Delhi,
Delhi 110 007.
- Date:
(a) October 25, 1988
(b) 25th October, 1988
- Direction:
(a) The Personnel Manager,
Life Insurance Corporation of India,
Bhubaneshwar, 751 006.
(b) Messrs Atma Ram & Sons,
3B Asaf Ali Roa,
New Delhi 110 001.
(c) Professor N. G. Arunachalam,
Department of Civil Engineering,
University Engineering College,
Hyderabad 500 007.
(d) Ms. Kavita Swaroop,
4/D Indira Colony,
Jawahar Nagar,
Agra 282 005.
(Messrs is used for an unlimited company or partnership of traders) (The same address is to be repeated on the envelope.)
- Salutation:
(a) Dear Sir/Madam,
(b) Sir/Madam, (in strictly formal letters to and from government departments or officials)
(c) Dear Sirs/Gentlemen, (in the case of unlimited company, firm or partnership of traders or from a clerk to the Board of Directors, when 'Gentlemen' is preferred)
(d) Dear Mr. Swaminathan,
(e) Dear Swaminathan,
(f) My dear Swaminathan/My dear Mr. Swaminathan, ('My dear' shows extra intimacy)
(g) My dear Ravi, (very intimate and friendly)
(a) Reference:( in professional or business letters)
(b) Sale of Old Stock (between salutation and the body of the letter) (usually placed above the direction)
(c) Our ref...
(d) Your ref...
- Body: (the main part of the Letter, the subject matter of which will differ in each case)
- Subscription:
(a) Yours faithfully. (most common form in formal, official and business letters)
(b) Yours truly. (somewhat warmer than the above)
(c) Yours sincerely, (cordial and friendly)
(d) Yours affectionately. Very sincerely yours, Yours ever, in very intimate personal letter
Layout of a Business Letter
1. Font and Margins
Before writing an official letter, it must be kept in mind that the letter should not only be simple to understand but easy to read as well. Set your margins to be one or one and a half inches per each side of the document, this will help your letter look professional. Using simple fonts like Verdana, Arial, Calibri or Times New Roman with a 12-point size will give your official letter a clean look as well.
2. Heading and Subject
Once your fonts are set, you can begin addressing your letter. First, write your name in the top left-hand corner of the page. Include your name, address and the current date. You can also include your phone number and email if you are requesting further contact.
While writing the recipient's address information, remember to put it directly beneath yours. Write their name, title of their organization if they are representing one, followed by the address. Review the name and address of your recipient more than once to ensure you've written the correct address and spelled their name right.
3. Salutation
You can now professionally greet your reader. A common salutation used in official letters is, "Dear Ms. Or Mr. Last name". If you know both their first name or last name, you can include that in the salutation. For example, you can write, "Dear Alex Smith". If you know their gender, you can write, "Dear Mr. Alex Smith" or "Dear Ms. Alex Smith". If you're unaware of the name of the recipient, you can write, "Dear Sir or Madam".
4. The Body
The body paragraphs are where you can capture your main points and professionally explain your concerns, opinions or other information to your recipient. This is the part where your introduction and the purpose of the letter comes in. You can use verbiage such as, "I am writing to you today because..."
Once you've explained what the recipient will read, you can expand further throughout the next paragraph. Include details that support your first statement. For example, if you were writing a recommendation letter, you could expand on the skills of the person your recommending by saying, "Avery's time-management and organizational skills have improved the efficiency of my business by 12% since the beginning of the quarter."
You can continue giving examples until you believe your point has been clearly understood by the reader. Keep your sentences short, simple and easy for the reader to understand.
5. Conclusion and Signature
After finishing the body of the letter, the conclusion should be written. This paragraph can be short and will finalize the document by repeating your main point, explaining any possible next steps or thanking the recipient for taking the time to read your letter.
After closing the letter, you can provide your closing signature at the end of the document. Examples of common letter signatures are:
Sincerely
Sincerely yours
With appreciation
Thank you
Regards
Yours truly
Respectfully yours
Carefully select your closing signature as per the requirements and input name at the bottom of the letter.
6. Enclosures
Enclosures are additional materials added to your letter to support your document, similar to when you attach a file to an email. If you're attaching a document to complement your letter, you should mention it near the end of your letter. To inform the reader that an additional document is attached, you can include the word "enclosure" at the end of the letter after your name. You can also shorten the word by writing, "encl."
Write your name and address in the top left-hand corner of the envelope followed by the recipient's name and address in the middle. Now your letter is ready to be sent to the recipient.
Sales and Credit Letters
A sales letter is a type of business letter which is written with the intent of selling a product. Sales letters are an effective way to communicate with clients.
Sales letters are designed in such a way that they immediately grab the attention of the reader. It is like a salesman discussing the purpose but in the form of a letter. A sales letter could be general or particular in nature depending upon the person(s) it is addressed to.
Objectives of Sales Letter
- The main purpose of every sale letter is to convince the reader to purchase a product.
- Introduction and marketing of new products and services.
- To reach potential customers.
- Expansion of the market.
Advantages of Sales Letter
- A sales letter is less expensive.
- Reach a client where a salesman cannot.
- Reach a number of clients all at the same time.
- Ease of understanding and availability of full details.
- More convenient, efficient, and comprehensive.
Elements and Format of Sales Letter
Below is the format of a sales letter
Headline: Here the writer wants to grab the reader’s attention toward the main purpose of the letter.
Introduction: The first paragraph serves the purpose of introduction the product or service to the reader. It provides the reader with the details of the product or service. These details include the cost of the product or service, the quality, the savings and any other information associated with it.
Body: This is the part where the writer needs to build his credibility and convince the reader. Here, the content includes the worth of the product, its similarities and differences from other products, a list of satisfied customers who are already happily using the product, and the terms of contract related to the product etc.
Call to Action: Here the writer tries to incite an appropriate response from the reader. Details such as warranties and discounts are often added in the concluding part of the letter.
Writing Tips for Writing Sales Letter
- Introduce the ideas in a way that compels the reader to take a positive action.
- Introduce yourself and the product well.
- Be clear in what you are offering.
- Choose your words as per the targeted audience.
- Always use a headline.
- Make the first sentence of each paragraph count.
- Use of font styles, font sizes, bullets, and numbering etc.
- Strongly describe the credibility of the product using relevant statements and examples.
- Suitable closing sentences.
- Correct use of salutation.
- Proper and complete details of the product and availability.
- Always ask for the reader's attention, build interest and desire in the reader's mind, and finally incite the call of action.
- Have a simple and convincing tone.
- Avoid creating confusion and uncertainty.
- Avoid being clever and funny.
- Include your name, signature, and other contact details.
- Do not use fancy words or slang.
- Always revise and edit the letter.
Letters of Quotation
A quotation is an offer from the seller to sell products or services at a certain price. A quotation is not a legally binding contract but only an offer. In businesses such offers are often made through letters. These letters are known as quotation letters or voluntary offers.
Quotation letters are written in formal style and follow the same format as other business letters with a change in the main content of the letter.
Format of a quotation letter
Your name, address, city, zip code, phone number and email address should be included in the contact information. Following the contact info is the date. After writing these, you have to write the contact information of the person or organization you are writing to, the salutation, The introduction as to why you are writing the letter, the body comprising of various specifications regarding the products or services along with the price list, a few concluding statements and your signature (handwritten signature if the letter is mailed).
These are the basic steps of writing a business quotation letter. To summarize, a business quotation letter should consist of short and to the point sentence, the focus should always be on the numbers, it should attract the attention of the reader, it should be respectful and should not contain errors.
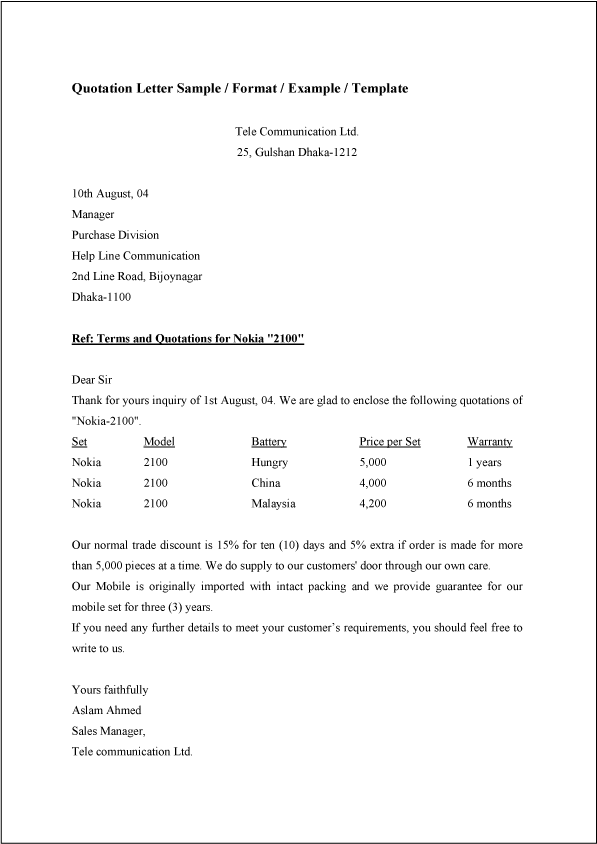
Sample
Below is a sample letter of quotation which will help you understand the basic template of a quotation letter
Order Letter
An order letter is a type of business letter which is written for the purpose of placing orders for products and services. An order letter is written by the buyer when the seller has provided them with a quote and it is in accordance with their budget.
An order letter is important step towards initiating a business transaction. This letter demonstrates interest in the merchandise and the need to start a business deal. This letter also shows that a customer is satisfied with the details provided in the quote like prices, specifications and other details.
An order letter is also used to specify the timeline around which the ordered products are to be delivered. It also provides other relevant information on quantity, the things ordered, and the mode of payment.
Below is a template of how an order letter should be written. In this template, the buyer is placing an order after receiving a quotation from the seller and agreeing to it.
From,
_____________
_____________
Date (date on which letter is written)
To,
________________
Subject:_________________________________________
Dear _________________,
My name is ____________ and I am writing as ____________ on behalf of ____________. With regard to a request for a quote dated ____________, I wish to order ____________ fabrics that are ____________ in colour and ____________ design. This order is for a client who is preparing for a wedding on ____________ and I wish to have the order urgently. The reference number of this order is ____________, please include it in all transactions for this order.
The first order will be for ____________ pieces so that we can examine the quality of the fabric and the design before making the second order. The second order will be for ____________ pieces upon approval of the first order. Kindly receive a check of ____________ for the first order. I would appreciate if you sent me a confirmation of receipt through my email ____________.
I hope to receive the shipment by latest ____________ in our office located on this address ____________.
Thank you in advance.
Your Truly,
__________
(__________________)
Claim Letter
A claim letter is essentially a complaint letter which a buyer writes to a seller to resolve grievances. Claim letters are formal business letters in which an individual or company demands the fulfilment of their claims.
In a claim letter the buyer asks for a refund or replacement for the faulty products or services provided by the seller. The seller then sends an adjustment letter where he tries to find a solution for the buyer’s problem.
Below is a sample claim letter which can be used as a template while writing a claim letter:

Adjustment Letter
An adjustment letter is a response to a buyer’s complaint or claim letter. Th main objective of writing an adjustment letter is to rectify the problem and provide the buyer with an appropriate solution.
Steps on How to Write an Adjustment Letter
1. Write the salutation.
Always address the letter to a particular person. Usually, people that send a complaint letter leave their name and address. Make sure that you spell the name correctly. For example, “Dear Mr. Jones” or “Dear Michael Robertson.”
2. Write the introduction.
Start the first sentence with a positive note. Write that you are pleased to hear from the client or express regret over the troublesome situation, or both. Address the date of the customer’s complaint letter and tell why you are writing. Don’t repeat the content of the complaint in detail.
Try to avoid such words as “complaint” or “claim.” These words may sound accusatory for the client. It will be better to say something like “Your report/message/notice from 2nd November has been received.”
3. Write the main part of the letter.
This section will consist of several parts. First, you need to restate the essence of the problem, so the reader will clearly understand that you have understood their problem well. Then you need to explain why the situation has occurred. Avoid long explanations, and be specific and brief. Clients don’t care about the company’s difficulties and simply want the situation to be fixed.
Second, present the solution to the problem. If the client is right, admit the mistake and provide a compensation or guarantee that the error will be resolved. Provide a list of steps that you are going to take (or have already taken). In some cases, when the claim is unwarranted, the company needs to write a careful and tactful denial to maintain good relations with the customer. Always try to persuade the client that you always have their needs in mind.
4. Write a conclusion.
End the letter with kind words. Thank for the client’s patience and offer further cooperation. Assure the client that such situations are rare and the company will do all possible to prevent this in the future. Express hope that the client will continue to enjoy products or services of the company. Don’t restate the essence of the problem at the end of the letter, as it will leave a feeling of incompleteness rather than your goodwill.
Add a hot-line phone number and website at the end of your letter, so the client can contact your company if needed.
5. Proofread and send the letter.
Make sure that your text is free of mistakes and has a logical structure. When you are pleased with the result, send the letter to the client.
Tips on How to Write an Adjustment Letter
- Don’t forget to fill in the subject field if you are sending an email.
- Write the adjustment letter in the shortest time possible. The company improves its own reputation by responding quickly to all complaints.
- Focus more on the solution rather than on the details of the problem.
- Always write in a positive tone. You need to calm down the customer and cheer them up.
- Focus on the relevant and specific facts rather than emotions.
- Don’t use abusive language or a negative tone. Even if the customer is aggressive or rude, you need to keep a friendly attitude and understanding of the problem.
- Never promise the client to do what is impossible or something that violates the company’s policy.
- Don’t show your surprise about the problem, unless it is a truly unique case for your company.
- Don’t try to make excuses – provide only factual information in the explanation.
- Show that your company takes it seriously.
- If the client experiences a great inconvenience, be generous. For example, you can provide a discount for the next order or a gift if appropriate.
- Remember the classical rule: “The customer is always right.” Even if the customer is wrong, make sure the customer is satisfied with your response.
Business Emails
Emails are basically letters sent electronically. They can be long or short, formal or informal. Although for business purposes only formal emails are considered important.
Emails have become a dominant form of communication. Being able to write polished, relevant email is now a critical skill in college and work.
Formal Email:
- Written for a professor, colleague, manager, etc.
- Must always be professional.
- Accurate grammar, punctuation, and spelling necessary
Example:
Dear Professor Johnson,
I was unable to attend class today due to a doctor’s appointment. If you have a moment, can you let me know what I missed and what homework I need to complete on Friday?
Thank you,
Julia Smith.
Business Email Format:
- Greetings / Salutation:
A formal email greeting is similar to a letter greeting. When you write a letter to a stranger, you put the question “Who Can Worry About You”? When applying for a job, you were addressing the person, “Dear Hiring Manager.” If you know the name of the recipient, you put “Mr. Dear Mr.M /. Smith. "For formal greetings, you should not use the recipient's first name or the informal greetings" Hello "or" Hello."
- Physical Categories/ Body Paragraphs:
It is important to remember that the email needs to be shorter.
I hope that all goes well for you.
Thank you for your prompt response.
However, in official emails it is best to understand the point. Depending on the topic, you should have four main roles and each paragraph should have one point. In your last paragraph you should provide a "thank you" or "call to action" depending on the topic of your email.
Thank you for your help with
Thank you for your time and look forward to hearing from you.
Please feel free to call me or email me if you have any questions. If this can be taken care of immediately.
- Closing:
As a greeting, the closing of the official email can be the same as the closing of the book. However, unlike mourning, there are many ways to close.
Thank you
Very humbly
Sincerely
It is also helpful to add your post (if any) and a phone number under your name in paragraph 4.
For example:
Yours sincerely,
Julia Smith
President of Student Body
Menlo College
(555) 555-5555
- Tips:
DO NOT use a contract.
Example: no, no, I'm not, I'm not.
DO NOT write about all the coins.
Use structured vocabulary and sentence structure. DO NOT use slang.
Close email at least twice and get a second opinion if possible.
Report Writing
The success of a business or industrial organization lies in doing its job for this purpose, gathering information and passing it on to those who need it is important. In the broader collection and transfer of information is happening all the time in every area of formal life. So scientists, working brokers, testers, journalists, and various professionals, government and private organizations are asked to write and report to their management on important topics at the institution or the person involved.
Reports can be as short as a few sentences and as long as a few large pages. Although reports can be verbal and informal, here we are concerned with written and formal reports.
Features of Writing a Good Report
- Requirement:
When organizing and preparing your reports you need to know who your audience is and whether or not your content meets their interests and needs.
- Accessibility:
Legitimacy has to do with how easy or readable it is. As most reports in normal cases type, all meetings with good typing should be followed. If there are handwritten reports, special attention should be given to writing clearly and clearly. Any departure from the above requirement will prove displeasing to your audience.
- Clarity and Readability:
Clarity, durability and systematic presentation of readable content. The concept is summarized better than the following:
The author does a lot by giving his reader a lot of information and taking away from him a little time.
In this regard the following five goals are met:
a) Use short sentences.
b) Prefer quality over quantity.
c) Choose a common name.
d) Use the economy and avoid unnecessary words.
e) Act actions as far as possible
- Conciseness:
Just like unwanted fat in the body, padding, prolixity and repetition violates the respect of good writing, not to mention the respect they wrote for you. So 'agree' and 'prefer' will be more acceptable than pompous 'agree with' and 'prefer'. As such, why use 'at that point in time' and at a time when we have the best and most economical holdings at that time 'and' when '. Viewed from the point of view of the report, or requested for the report, a good report will contain four important details, an analysis of the information, conclusions and recommendations. It should always be remembered that effective reporting requires special attention to the needs and expectations of the reader. It means that the author of the report has to 'snap a picture', he must think and understand himself.
Structure of a Formal Report
A formal report is comprised of the following sections:
- Title Page
The title page includes the main title of the report, it must be short and concise. You can also include the word counts of your summary and main body.
B. Table of Contents
Help your reader quickly and easily find what they are looking for by using informative headings and careful numbering of your sections and sub-sections.
For example:

C. Introduction
The introductory part of the report comprises of statement of the objectives of the report and how the report should be treated by the readers. It should indicate towards the problem that is going to be addressed in the main body. It should be catchy and interesting to grasp the attention of the reader from the very start.
D. The Body
The main body consists of the central theme or the main idea of the report. It can be divided into a number of sections and subsections to separate your research and subsequent findings in a logical order.
E. Figures, Graphs, Formulae and Tables
This section consists of the statistical representation of the data you have collected. Ideas should be conveyed in the form which is most suitable to the reader and easily understandable by the reader. Excessive use of these tools should be avoided.
F. Conclusion
The conclusion is a kind of summing up of all the points you have stated in the main text. It should be a definite solution to the problem introduced during the introductory part of the report. The conclusion must be short and to the point.
G. Summary
Summarize all the key points stated in the report including your research, your findings and your conclusion. The summary should feel like a brief overview of your investigations and outcomes. The summary should be constructed in such a way that it can be called a stand-alone document on its own.
H. References
References must include detailed information of all your citations and the sources of material quoted in your texts. It can also include bibliography for further reading.
I. Appendices
This is the last element of a report. It refers to any material which can be useful in the detailed understanding of your subject. It is not meant for the casual reader but for readers who are highly interested in the subject.
Progress Report
A progress report is a type of report which is written in order to inform a supervisor, associate, or customer about progress you’ve made on a project over a certain period of time.
A progress report must answer the following questions:
- What percentage of the work is complete?
- Which part of the work is currently being performed?
- Which sections of the work are yet to be completed?
- What unexpected problems have arisen in the project?
- What is the overall status of the project?
- How much more time will be required to complete the work?
A progress report can be structured in three different ways:
a) Memo – An informal memo report to be sent to someone within the organization.
b) Letter – An informal or formal letter to be sent to someone outside of the organization.
c) Formal Report – A formal report to be sent to someone outside the organization
You should choose the type of progress report depending upon your requirements.
A progress report has no specific structure but should always include the following elements:
- The title and the words “Progress Report” on top of the document
- Section headings to simplify the reading process.
- The name of the writer along with their designation and the receiver’s name and designation.
- The opening should be titled “scope and purpose” where the introduction defines the purpose of the report.
- Two sections titled “Progress….” And “Remaining work” should always be included. The former defining how much work has been successfully completed and the latter describing what part of it is yet to be done.
- A section projecting results and the tentative timeline of completion should also be included.
- The paragraphs should be short and concise and the tone respectful.
Status Report
A status report is an informative piece of writing which keeps the clients, project managers, supervisors and team members up to date regarding a certain project.
It comprises of the efforts, progress and risk associated with a project. A project status report can be a weekly, monthly or quarterly formulated report.
A project status report may be used to:
- Streamline communication efforts across the organization and stakeholders
- Make it easier to gather and disseminate information about key elements of the project
- Ensure stakeholders have all necessary information for decision-making
- Amplify key messages and goals around the project
- Act as a logbook for past key events and actions
What is included in a status report:
- Summary of Work Completed
- A Plan for What Comes Next
- Updates on Budget and Timeline
- Any Action Items/To-Dos
- Report on Risks, Issues, and Mitigation
Below is the format of a status report:
1. Project Name / Client Name
This section should contain the title of the project along with the name of the client. Make sure you record WHO the report is for and WHAT the report entails (ie. What project).
2. Project Vision
Here the main objectives of the project are to be listed in a clear and to the point manner. This is the only static unchanging section of a status report.
Examples:
Drive qualified customers to “purchase” mobile devices based on an improved UI.
With this project, we hope to increase online sales through the implementation of a drip email marketing campaign.
Launch a website by June 2018 that allows customers to purchase the highest quality & best-tasting product in its category.
3. Project Health
Here the health status of the project can be highlighted. The use of colours could be very helpful for notifying the health status for example, green for successful, yellow for a few complications and red for issues requiring immediate and critical attention. A note to support is always helpful.
Examples:
Green: We’ve obtained approval on drip email designs. No budget concerns at this time.
Yellow: The drip email designs need significant revisions, therefore the final delivery date has been delayed by 1 week.
Red: The drip email campaign has drastically shifted direction since starting. We need to set-up a meeting to establish a wants/wishes for the project.
4. What We Completed This TIMEFRAME
These should be listed in bullet format. Keep these short & simple. Don’t explain the “how” just what.
Example:
Obtained approval for 3 drip email designs
5. What We Plan to Complete Next TIMEFRAME
This section should include what is planned in clear and precise bullet points.
Example:
Develop the three emails
Perform internal QA & testing
Pass off to client QA & testing
6. Issues/Roadblocks
This is where you can raise any red flags or obstacles keeping you from moving forward.
Example:
If we do not obtain client feedback by 06/02, we will be in jeopardy of not being able to send the email to consumers the same day as the product will be available in stores.
7. Upcoming Tasks & Milestones
This should include a set of goals to be achieved in the near future. Is there anything that the viewer should review? and what’s coming up next?
Examples:
Dd/mm: Client QA & Testing
Dd/mm: Email Deployment
Survey Report
A survey report is a document which elaborates the findings of a survey in an objective manner. Survey reports usually consist of detailed statistical analysis of the surveyed data divided into various sections. A survey report has no specific format and is curated as per the requirements of the surveyor.
Surveys can be conducted by means of questionnaires, door to door information gathering or by using internet surveying facilities. A survey report may be presented in factual form (numbers, percentages and proportions) along with its implications.
Like other reports, a survey report can also be broken up into several headings namely,
- To
- From
- Survey
- Date
- Purpose
- Introduction
- The Body
- Conclusion
Below is a basic survey report sample:
To: Mrs Joanna Brown
From: Liam Black Subject:
Survey "Ban on using and selling fireworks".
Date: 1st January 2008
Purpose
The aim of this report is to present results of the survey carried out to find out what is people's opinion on public displays and selling fireworks. That will help to decide if using and selling fireworks should be banned. The survey was carried out among people aged 25-50.
Ban on public displays of fireworks
Seventy two per cent of people asked if there should be a ban on public display of fireworks were of the opinion that public displays should not be banned five per cent were for banning public displays of fireworks while three percent were not sure of their opinion. The facts stated above suggest that people do not mind public displays of fireworks and they would not want any limits on them.
An overall ban on sale of fireworks
The majority of people asked if there should be an overall, ban on sale of fireworks replied 'yes'. One fifth of interviewed said 'no'. One out of ten reported that they would rather ban sale of fireworks while a small portion of people (5 per cent) answered that they would rather not ban the sale of fireworks. Seven per cent did not have any opinion on the subject. It shows that over half of viewers are for banning sale of fireworks.
Children buying and using fireworks
A significant percentage of people (eighty-three) asked if they would allow their children to buy and use fireworks responded "no". The rest of interviewed said "yes". That shows that there should be absolute ban on selling fireworks to children as it may be very harmful and dangerous for them.
Conclusion On the basis of the findings above, it would seem that majority of people find fireworks dangerous and they would claim a definite ban on selling them, especially to children. People also do not trust displays of fireworks which should be banned. They also suggests that government should take some actions to restrict laws associated fireworks and sale of fireworks.
Trip Report
A trip report is an informative document provided to one’s supervisor after their business travel. It includes the collection of events during the trip, the expenditure accrued during the trip and information regarding the purpose of the trip.
A trip report should be curated with the following elements in mind:
1. Purpose: The purpose of a trip report is to justify the purpose of the trip and the money that was spent by the travelling individual. Because trip reports provide proof of expenses, it is imperative that they are accurate and provide a clear explanation of the trip.
2. Audience: Trip reports are targeted towards one's immediate supervisor; however, the report may become a portion of a larger report, or it may be forwarded to other managers, accountants, and even CEOs. Trip reports eventually provide company accountants with information for yearly reports, projected annual budgets, and crucial information for tax filing.
3. Mode: While trip reports can be written as a letter, memo, or e-mail, you should remember that trip reports are official documents that should always be written in a formal tone. Whichever mode of communication that you choose or that you are instructed to use as a means for providing your information, you should plan, organize, and write your report following the convention of business genre and following correct writing conventions (grammar, punctuation, and usage).
It is essential to organise and structure the trip report into different headings and subheadings so as to make it easily readable.
4. Formatting and Elements of the Report:
A. Subject line: On the subject line, you should include the destination, purpose, and date of the trip.
B. Statement of purpose: The first line of the text of your report should be your statement of purpose or the purpose of the trip—be specific. Depending upon your position in the company, it may be necessary to include the name of the person who approved the travel.
C. Introductory summary: The summary can be divided into sections, depending upon the reason for the trip. In each section, you should elaborate so that your company will have information for a follow-up trip.
I. Contains the reason for the trip.
II. Who you met. You should always provide full names, titles, and conversations
That related to your trip.
III. What you accomplished. A work trip is planned for achieving a specific task which should be mentioned in detail.
D. Summary of actions: A description of the events that took place on the trip.
E. Depending on the report, you may be asked to provide recommendations based on your findings from the trip.
F. Outcomes: Describe any results of the trip.
G. Spreadsheet: Provide a detailed list of expenditures, and photo copied receipts. (Do not highlight the receipts. Highlighting can impair the quality of the copy.)
Complaint Report
Many companies encourage the use of complaint reports as the proper method of formally stating a complaint. These reports are usually used to address unsatisfactory transactions or conditions concerning a company. Writing a complaint report properly is key to getting your concern heard and the problem remedied.
A complaint report consists of the following elements:
The Heading
The heading part follows the format given below:
TO: (The individual or company to whom the complaint is addressed)
FROM: (The individual registering the complaint)
DATE: (Current Date)
SUBJECT: (The main purpose summed up in one sentence)
The Body
The body must contain an introduction where you should write the purpose of your report and what is the primary concern of the report. It should then include the main subject, in this case the complaint. The issue at hand should be properly discussed and you should try to provide reasonable solutions to the problem. The tone should not be aggressive at it would make it more difficult to find a suitable resolution to your grievances. The concluding sentence should sum up the report in 2-3 sentences, try to reiterate the key points you have mentioned earlier and try to suggest a few measures that would help in solving your issue.
Joining Report
A joining report is a report written to the immediate supervisor or manager in the event of returning to work after a leave or vacation. These reports are the shortest kinds of report only intimating the supervisor of one’s return to the job. A joining letter on the other hand refers to a letter written by an individual to confirm his position where he is newly appointed to work at an organisation.
There is no set format for a joining report but it can follow the template given below:
JOINING REPORT
I hereby report myself for duty after returning from leave from this day on ……………….. (forenoon/
Afternoon).
I have availed the following kinds of leave.
Earned leave for ……………………….. Days (from ……………… to ………… )
Half Pay leave for ……………………… days (from ……………… to ………… )
Commuted leave (MC) for ……………... Days (from ……………… to ………… )
EOL (with/without MC for …………days (from ……………… to ………… )
With permission to prefix/suffix holidays on ……………………..)
Signature: ……………
Name in block letter:
Designation: ………….
Laboratory Report
A laboratory report is a formal, analytical and concise record of an experiment. The discussion of the experiment, the various procedures and the subsequent results obtained should be clear and specific enough that a reader could easily replicate the experiment. One of the main purposes of writing a laboratory report is to communicate the work done in the laboratory to the management on a regular basis. Another reason for writing a laboratory report is to record an experiment for the future and archive it.
Format
Although most laboratory reports will include the following sections, some experiments will require a
Different format. All reports should be tailored so as to meet the requirements laid down by the experiment.
Abstract: The abstract should contain a brief informational synopsis of your experiment. It is advisable to keep the abstract under 200 words. While writing the abstract, assertive or declarative sentences should be used rather than writing a long descriptive prose.
Introduction: Here the background of the experiment which is to be undertaken is explained in a few lines. The introduction should explain the objectives you hope to achieve from the experiment. When appropriate, the background should indicate theoretical predictions.
Procedures (or Methods): This section includes a detailed set of instructions of how the experiment is ought to be conducted. Each instruction should be so precise that the reader should be able to replicate it if he so desired. There should be no ambiguity and error when it comes to numbers and quantities. All statistical information should be well organised.
Results and Discussion (sometimes presented as separate sections): This section must convey results relevant to the goals of the experiment. Here the analysis of the results obtained from the experiment must be carried out along with its implications. All possible sources of error should be acknowledged with potential solutions if any. Results can also be presented in the form of graphs and tables if the experiment needs it.
Conclusions: Here you should place the specific results acquired into the context of the experiment as a whole. The discussion section should serve as sufficient conclusion if the experiment and report is short. Remember to evaluate the results you obtained in light of the objectives stated in the introduction.
Appendices: This section must include the information which is too extensive or tangential to warrant inclusion in the main body of the report, but necessary as procedural or analytical evidence.
C.V
If you’re pursuing opportunities in academia or looking for work outside India, it’s important to create a Curriculum Vitae (CV). This document will provide employers with a highly detailed account of your professional and educational history to decide whether to move you forward to the next step in the hiring process.
A curriculum vitae, an abbreviation for C.V, is a Latin term meaning “course of life”. It is a detailed professional document highlighting a person’s experience and accomplishments. Employers often require a CV when considering applications. Therefore, a C.V shares an overview of your career history, education, relevant awards and honours, scholarships, grants, research, projects and publications.
A curriculum vitae may also include professional references as well as coursework, fieldwork, hobbies and interests relevant to your profession. While curating a C.V, you might also choose to add a personal profile that lists your skills and positive attributes to ensure employers have a well-rounded view of your personality and achievements.
Contents of a C.V
While a CV should be specific to one background and tailored to the job for which one is applying, there are several steps you can take to ensure you write an effective CV. Most CVs include the following information:
- Contact information
- Academic history
- Professional experience
- Qualifications and skills
- Awards and honours
- Publications
- Professional associations
- Grants and fellowships
- Licenses and certificates
- Volunteer work
- Personal information (optional)
- Hobbies and interests (optional)
CV Template
Below is a basic template you can follow when formulating your CV:
[Your Name]
[Address, phone number, email address]
Professional summary
[Here, introduce yourself, highlight your best qualifications and explain why you’re a fit for the job]
Education
[Title of degree] [GPA] [Dates attended]
[School name]
[Title of dissertation or thesis]
Work experience
[Job title] [Dates of employment]
[Name of employer] [City and state of employer]
[description of your responsibilities and accomplishments]
Skills
[relevant skills]
Personal interests
[Short paragraph on your personal pursuits]
Community service
[Position held or job performed] [Dates of service]
[Organization] [City and state of organization]
[Accomplishment]
Publications
[Authors with your name in bold] [Year of publication] [Title of article] [Publishing journal]
Awards and honours
[Name of award] [year]
Writing a CV
Below are the seven basic steps for writing a CV:
1. Create a header with contact information
The header should be at the top of the page and must always include your name, phone number and email address so employers immediately know who you are and how to reach you.
2. Write a professional summary
Your professional summary must be a short bio that introduces you to the reader. This section should also sum up your highest qualifications and explains your ideal career path.
3. Detail your education
Since a CV is often used for the academic job search process, it’s important to include a section on your educational history. Provide a list of your academic achievements in reverse chronological order, with your most recent degree first. Include both degrees you’ve earned and those you’re pursuing.
4. Provide your work experience
In this section, provide details of all your practical workplace experience so your prospective employer can see your career path, including:
- Full-time and part-time employment
- Internships
- Research projects
- Lab work
- Volunteer work
- Field experience
Try to include the title of your position, the name and location of your employer and employment dates. After this, list two to three bullet points that explain your job duties.
5. List your relevant skills
If you possess any abilities that apply to the potential job, such as foreign languages or a type of software, list them here. Formulate a list of skills that relate to the job description to make yourself a more desirable candidate and include them here.
6. Include additional sections
CVs are typically longer than resumes so you can detail all the achievements relevant to the potential role. Add sections as needed to list all of your accomplishments, including:
- Publications
- Presentation and lectures
- Community service
- Grants, fellowships or scholarships
- Awards and honors
- Professional memberships
- Consulting work
- Fieldwork
- Study abroad experience
- Conferences
7. Describe your personal interests (optional)
You can choose to include a brief description of your hobbies and interests. Adding a few hobbies in this section may help you form a personal connection with the hiring manager.
Resume
A resume is a short document used to summarize the job search and qualifications of the prospective employer. The resume includes contact details for the job seeker, work experience, education, and the appropriate skills to support the job application.
Your renegotiation is a critical part of today's job application process. Writing a good resume is more important than ever now that online job posts tend to attract hundreds if not thousands of applicants. A refurbished, ready-to-start application will increase your chances of getting an interview while poorly written resumes may be lost at sea of applicants.
Resume vs. CV
Sometimes you will see the words go on and the CV is used interchangeably. They are not the same. The resume is a short documentary designed to market your professional skills while the cv contains an informative list of your expertise, of your courses, and other information.
C.V stands for curriculum ("course of life"). CVS are separate by design. Think of them as an encyclopaedia version of your professional life, taking your career history, education, credentials, relationships, publication and professionalism. They can extend well over three or four pages.
In the united states, CV’s are usually limited to professions with general positions where deep expertise is critical, such as academics, science and medicine. These CV’s are filled with extended education categories, work history, internships, gigs talk, teaching appointments, magazine publishing and other information that establishes trust.
Re-use across many industries and very short on just one or two pages. That's because the resume is not intended to capture all the details of your previous experience. Your resume should be designed and updated based on the details of each activity you use. Negative jobs in past jobs can be eliminated to save space and attract more attention to your used and accessible skills.
How to write the resume:
1. Select the resume format and the categories you need
2. Always include contact details, work experience, and education
3. Use traditional topics for high compliance
4. Apply practical skills directly to the job description
5. Replace basic tasks with impactful performance
6. Do not include an old goal statement or reference section
7. Preview and double-check what you wrote
8. Save as docx file (optional) or pdf.
If you think you are done, ask someone else to take care of you. Alternatively, take it to jobscan for a quick answer.
Contents of a Good Resume
At the very least, your startup should include your contact details, work experience, and education. Additional job summary sections, skills, volunteer work, and additional qualifications can be added when related to the job you work for.
The work ethic here is "worth it." remember that your resume is intended to quickly highlight the reasons why you are well prepared for the job. It is not intended to explain all the tasks you have done. Instead of simply listing your daily obligations from past activities, read the job listing and try to find the answer to each of the requirements listed. This is likely to get the attention of an employer who can only look at your return for a few seconds. It also broadens your application tracking system to apply to algorithms that help companies identify top candidates.
Below you will find out which parts of the restart to include in your startup and how to adapt to the job you are looking for.
Elements of a Resume
Contact information:
The title of your startup should include the following information:
- Name
- Phone number
- Location (city, country, zip code)
- Email address
- Linked profile url
It may seem obvious, but job seekers sometimes forget an important piece of contact information in this section. Double check and make it as easy as possible for employers to contact you for job interviews.
Phone number:
Enter a personal phone number, not a work number. Enter your city, state, and zip code (e.g. “seattle, wa 98104”). This is important as other applicant tracking systems allow employers to filter the candidates based on location. Employers will always start with local selectors first. If you are traveling from somewhere, write down your current location and your future location.
Email address:
Use a valid email address. An email address based around your name is correct, such as jackieromano12@email.com. Your "happy" email address may work well in your life, but the terms "beersnob88" or "biebersuperfan" may not be so clear. Even using a seemingly outdated email client - such as aol or hotmail - can harm your prospects. Consider creating a free gmail account for your search.
Linked Profile url:
If the employer is surprised by your qualifications, they will look at your online profiles. All job seekers should create a strong linkedin profile and include a url in their resume. This will make the life of the employer a little easier and help them to cross-check the claims on your resume.
Work experience:
Part of the work experience is the heart of your resume. Separate this category from a clear, existing topic, such as "work experience," "work experience," or "employment history." this will help guide employers towards your resume and ensure that the applicant tracking system (ats) is well defined.
Under the main heading, list each activity in chronological order. Each function should have its own sub-heading that includes the following information:
- Company
- Workplace
- Your job title
- Start and end dates
For example:
- Abc corporation, settle
- Distribution manager (01/2017-present)
The first things an employer looks for in your resume are the topics of the work you hold and the number of companies you've worked with. This format not only makes it easy for them to access that information, but our research has found that this sequence also provides greater ats compatibility.
Under each subheading, include responsibilities and measurable outputs that are relevant to the job you are working on. Remember, you don't have to include all the activities that were part of your daily routine. Use your available space to highlight the skills and knowledge requested in the job description. Jobscan helps you decide exactly what skills are requested and whether or not you have highlighted them.
Education:
When you have a few years into your career, your education level may also be reduced under your resume.Unless you're using a profession that places more emphasis on education (such as academics, law, or medicine), most job seekers can escape by simply providing the following information on their resume:
• Agency name
• Stem
• School location
• Years visited
If you have just graduated from college, your education level surpasses your professional experience and includes many details. Skills developed in school are real skills that are important in the professional world. Recent rooms can include appropriate coursework, communities, organizations, and extracurriculars that strengthen their identity.
Activities:
98% of fortune 500 companies use applicant tracking systems (ats) to filter, filter, and enter applicants. Other atss, such as taleo, can automatically add your own content to the job description, allowing employers to focus only on the best "applicants". Employers are also looking at their application site to find keywords, such as "customer service," "accounts available," or "adobe photoshop."
Overloading or coming up as a search result is about adding complex skills and keywords to your resume. A good way to identify key skills in a list and search algorithms is to identify which skills are most prominent in the job description. Aligning these skills to your resume, where applicable, increases your chances of being selected for an interview
Strong skills should apply to all your resume capabilities. Entering the skills category for your startup is not a prerequisite, but it can help you have a natural place to list the essential skills in the job you work for. The dedicated skills section also makes your resume much easier for employers trying to quickly find out if you meet their needs.
If you are using the skills section, remember that the list of skills and keywords is not enough. Add context to these skills to your full potential so employers can believe. This includes factors such as projects you have used in skills, the number of years of experience in a given skill, or the level of your expertise.
Historical and free:
Some restart forms allow space for some optional components. Only use the category of awards or honors in your resume if it makes sense for the job you work for. Active reputations will improve your credibility while poor prizes simply distract you from your best titles. For example, decide to get a monthly career or get a great customer satisfaction rating for your department, but maybe not if you are a kart race expert in your free time.
Volunteer work and study:
The work you do as an active volunteer can add to your qualifications and skill set as all paid experience. Also, the word "works." highlight the volunteer work of your startup that uses the skills that apply to the job you work for. Carefully list voluntary organizations or affiliated organizations, such as political or religious organizations.
What you can leave from your view:
- Statement of note:
The statement of intent has been used as a standard for the restart and appears in other implementation templates. Traditionally, the purposeful statements were a brief introduction to the resume which explains why the submission is returned. For example, "purpose: to secure a position as a communications manager at a leading sales centre."
Including a purpose that you can restart these days can make you appear later. The job summary statement replaced the purpose of today's reboot. Any other information can serve as a cover letter.
While a statement of objectives describes your goals, a concise statement outlines how you can add value to the company.
- Examinations:
It is not necessary to write your directions in your resume unless otherwise stated in the job description. In addition, it is assumed that you have references, so there is no need to include "references available on request" either. Use the space you save to add additional skills and achievements.
- Soft skills:
When it comes to your resume, soft skills are not nearly as important as technical skills. That is because it is difficult to demonstrate within the context of a restart. For example, an employer will not take your name from you if you say "you work hard" or "you solve a problem." in fact, it looks like it's short.
Instead of simply writing soft skills, find opportunities to show off your interpersonal and behavioural skills. Achievements and measurable results are a great way to do this. For example, instead of saying "hard work," indicate in writing that you have completed x projects that are more than your department average.
- Gpa:
Only list your GPA as part of your continuing education program if you have recently graduated from college and have a good GPA, similar to a 3.5 or better with a 4.0 rating. There are a few exceptions. Some industries, as professionals, are waiting to see your GPA.
Length of your resume:
While a one-page start-up is sometimes considered to be the best, a two-page resume may be required after five or ten years of staffing, especially if all of your experience is relevant to the job you are pursuing. Managers sometimes have three or more pages running.
That said, your resume should not be longer than it should. Short, step-by-step resumes will easily be digested and highlight your most important skills. After writing your resume, try removing the excess fluff and inappropriate content to reduce your page count and draw your attention to your best titles. No matter how many pages you start, try putting your most impressive titles at the top of the first page with a summary or category of skills.
There are several different ways to format your resume. Choosing the right format will make the writing process easier. When choosing a format, consider the function you are using for it. The chronological, compositional, and functional styles of each work serve a specific purpose.