Unit 1
Introduction to computer
Definition
Being a modern-day kid you must have used, seen, or read about computers. This is because they are an integral part of our everyday existence. Be it school, banks, shops, railway stations, hospital or your own home, computers are present everywhere, making our work easier and faster for us. As they are such integral parts of our lives, we must know what they are and how they function. Let us start with defining the term computer formally.
The literal meaning of computer is a device that can calculate. However, modern computers can do a lot more than calculate. Computer is an electronic device that receives input, stores or processes the input as per user instructions and provides output in desired format.
Input-Process-Output Model
Computer input is called data and the output obtained after processing it, based on user’s instructions is called information. Raw facts and figures which can be processed using arithmetic and logical operations to obtain information are called data.
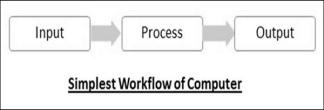
The processes that can be applied to data are of two types −
- Arithmetic operations− Examples include calculations like addition, subtraction, differentials, square root, etc.
- Logical operations− Examples include comparison operations like greater than, less than, equal to, opposite, etc.
The corresponding figure for an actual computer looks something like this −
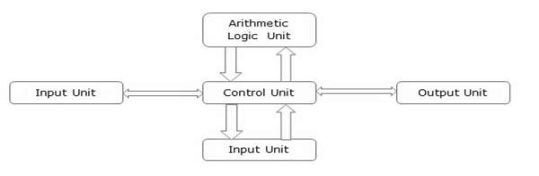
The basic parts of a computer are as follows −
- Input Unit− Devices like keyboard and mouse that are used to input data and instructions to the computer are called input unit.
- Output Unit− Devices like printer and visual display unit that are used to provide information to the user in desired format are called output unit.
- Control Unit−As the name suggests, this unit controls all the functions of the computer. All devices or parts of computer interact through the control unit.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit−This is the brain of the computer where all arithmetic operations and logical operations take place.
- Memory− All input data, instructions and data interim to the processes are stored in the memory. Memory is of two types – primary memory and secondary memory. Primary memory resides within the CPU whereas secondary memory is external to it.
Control unit, arithmetic logic unit and memory are together called the central processing unit or CPU. Computer devices like keyboard, mouse, printer, etc. that we can see and touch are the hardware components of a computer. The set of instructions or programs that make the computer function using these hardware parts are called software. We cannot see or touch software. Both hardware and software are necessary for working of a computer.
Advantages of Using Computer
Now that we know the characteristics of computers, we can see the advantages that computers offer−
- Computers can do the same task repetitively with same accuracy.
- Computers do not get tired or bored.
- Computers can take up routine tasks while releasing human resource for more intelligent functions.
Disadvantages of Using Computer
Despite so many advantages, computers have some disadvantages of their own −
- Computers have no intelligence; they follow the instructions blindly without considering the outcome.
- Regular electric supply is necessary to make computers work, which could prove difficult everywhere especially in developing nations.
Booting
Starting a computer or a computer-embedded device is called booting. Booting takes place in two steps −
- Switching on power supply
- Loading operating system into computer’s main memory
- Keeping all applications in a state of readiness in case needed by the user
The first program or set of instructions that run when the computer is switched on is called BIOS or Basic Input Output System. BIOS is a firmware, i.e. a piece of software permanently programmed into the hardware.
If a system is already running but needs to be restarted, it is called rebooting. Rebooting may be required if a software or hardware has been installed or system is unusually slow.
There are two types of booting −
- Cold Booting− When the system is started by switching on the power supply it is called cold booting. The next step in cold booting is loading of BIOS.
- Warm Booting− When the system is already running and needs to be restarted or rebooted, it is called warm booting. Warm booting is faster than cold booting because BIOS is not reloaded.
The first counting device was used by the primitive people. They used sticks, stones and bones as counting tools. As human mind and technology improved with time more computing devices were developed. Some of the popular computing devices starting with the first to recent ones are described below;
Abacus
The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer. It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago.
It was a wooden rack which has metal rods with beads mounted on them. The beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules to perform arithmetic calculations. Abacus is still used in some countries like China, Russia and Japan. An image of this tool is shown below;

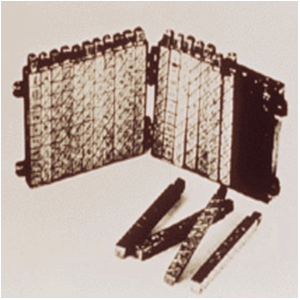
Napier's Bones
It was a manually-operated calculating device which was invented by John Napier (1550-1617) of Merchiston. In this calculating tool, he used 9 different ivory strips or bones marked with numbers to multiply and divide. So, the tool became known as "Napier's Bones. It was also the first machine to use the decimal point.
Pascaline
Pascaline is also known as Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine. It was invented between 1642 and 1644 by a French mathematician-philosopher Biaise Pascal. It is believed that it was the first mechanical and automatic calculator.
Pascal invented this machine to help his father, a tax accountant. It could only perform addition and subtraction. It was a wooden box with a series of gears and wheels. When a wheel is rotated one revolution, it rotates the neighbouring wheel. A series of windows is given on the top of the wheels to read the totals. An image of this tool is shown below;

Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel
It was developed by a German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz in 1673. He improved Pascal's invention to develop this machine. It was a digital mechanical calculator which was called the stepped reckoner as instead of gears it was made of fluted drums. See the following image;

Difference Engine
In the early 1820s, it was designed by Charles Babbage who is known as "Father of Modern Computer". It was a mechanical computer which could perform simple calculations. It was a steam driven calculating machine designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables.

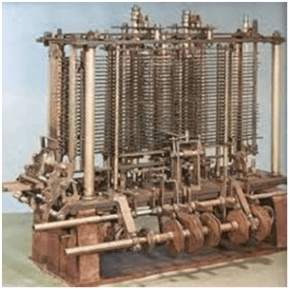
Analytical Engine
This calculating machine was also developed by Charles Babbage in 1830. It was a mechanical computer that used punch-cards as input. It was capable of solving any mathematical problem and storing information as a permanent memory.
Tabulating Machine
It was invented in 1890, by Herman Hollerith, an American statistician. It was a mechanical tabulator based on punch cards. It could tabulate statistics and record or sort data or information. This machine was used in the 1890 U.S. Census. Hollerith also started the Holleriths Tabulating Machine Company which later became International Business Machine (IBM) in 1924.

Differential Analyzer
It was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930. It was an analog device invented by Vannevar Bush. This machine has vacuum tubes to switch electrical signals to perform calculations. It could do 25 calculations in few minutes.
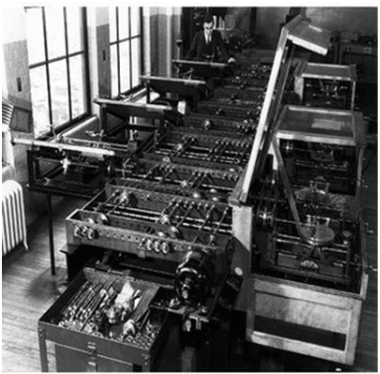
Mark I
The next major changes in the history of computer began in 1937 when Howard Aiken planned to develop a machine that could perform calculations involving large numbers. In 1944, Mark I computer was built as a partnership between IBM and Harvard. It was the first programmable digital computer.

Generations of Computers
A generation of computers refers to the specific improvements in computer technology with time. In 1946, electronic pathways called circuits were developed to perform the counting. It replaced the gears and other mechanical parts used for counting in previous computing machines.
In each new generation, the circuits became smaller and more advanced than the previous generation circuits. The miniaturization helped increase the speed, memory and power of computers. There are five generations of computers which are described below;
First Generation Computers
The first generation (1946-1959) computers were slow, huge and expensive. In these computers, vacuum tubes were used as the basic components of CPU and memory. These computers were mainly depended on batch operating system and punch cards. Magnetic tape and paper tape were used as output and input devices in this generation;
Some of the popular first generation computers are;
- ENIAC ( Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
- EDVAC ( Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
- UNIVACI( Universal Automatic Computer)
- IBM-701
- IBM-650
Second Generation Computers
The second generation (1959-1965) was the era of the transistor computers. These computers used transistors which were cheap, compact and consuming less power; it made transistor computers faster than the first generation computers.
In this generation, magnetic cores were used as the primary memory and magnetic disc and tapes were used as the secondary storage. Assembly language and programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN, and Batch processing and multiprogramming operating systems were used in these computers.
Some of the popular second generation computers are;
- IBM 1620
- IBM 7094
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1108
Third Generation Computers
The third generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs) instead of transistors. A single IC can pack huge number of transistors which increased the power of a computer and reduced the cost. The computers also became more reliable, efficient and smaller in size. These generation computers used remote processing, time-sharing, multi programming as operating system. Also, the high-level programming languages like FORTRON-II TO IV, COBOL, PASCAL PL/1, ALGOL-68 were used in this generation.
Some of the popular third generation computers are;
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- PDP(Personal Data Processor)
- IBM-370/168
- TDC-316
Fourth Generation Computers
The fourth generation (1971-1980) computers used very large scale integrated (VLSI) circuits; a chip containing millions of transistors and other circuit elements. These chips made this generation computers more compact, powerful, fast and affordable. These generation computers used real time, time sharing and distributed operating system. The programming languages like C, C++, DBASE were also used in this generation.
Some of the popular fourth generation computers are;
- DEC 10
- STAR 1000
- PDP 11
- CRAY-1(Super Computer)
- CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer)
Fifth Generation Computers
In fifth generation (1980-till date) computers, the VLSI technology was replaced with ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration). It made possible the production of microprocessor chips with ten million electronic components. This generation computers used parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software. The programming languages used in this generation were C, C++, Java, .Net, etc.
Some of the popular fifth generation computers are;
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook
- UltraBook
- ChromeBook
Computer scan is broadly classified by their speed and computing power.
Sr.No. | Type | Specifications |
1 | PC (Personal Computer) or Micro-Computers | It is a single user computer system having a moderately powerful microprocessor. It is termed as a computer that is equipped microprocessor as its CPU. |
2 | Workstation | It is also a single user computer system, similar to the personal computer, however, has a more powerful microprocessor. |
3 | Mini-Computer | It is a multi-user computer system, capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously. |
4 | Main Frame | It is a multi-user computer system, capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously. Software technology is different from minicomputer. |
5 | Super-Computer | It is an extremely fast computer, which can execute hundreds of millions of instructions per second. |
PC (Personal Computer)

A PC can be defined as a small, relatively inexpensive computer designed for an individual user. PCs are based on the microprocessor technology that enables manufacturers to put an entire CPU on one chip. Businesses use personal computers for word processing, accounting, desktop publishing, and for running spreadsheet and database management applications. At home, the most popular use for personal computers is playing games and surfing the Internet.
Although personal computers are designed as single-user systems, these systems are normally linked together to form a network. In terms of power, nowadays high-end models of the Macintosh and PC offer the same computing power and graphics capability as low-end workstations by Sun Microsystems, Hewlett-Packard, and Dell.
Workstation

The workstation is a computer used for engineering applications (CAD/CAM), desktop publishing, software development, and other such types of applications which require a moderate amount of computing power and relatively high-quality graphics capabilities.
Workstations generally come with a large, high-resolution graphics screen, a large amount of RAM, inbuilt network support, and a graphical user interface. Most workstations also have mass storage device such as a disk drive, but a special type of workstation, called diskless workstations, comes without a disk drive.
Common operating systems for workstations are UNIX and Windows NT. Like PC, workstations are also single-user computers like PC but are typically linked together to form a local area network, although they can also be used as stand-alone systems.
Minicomputer
It is a midsize multi-processing system capable of supporting up to 250 users simultaneously.

Mainframe
The mainframe is very large in size and is an expensive computer capable of supporting hundreds or even thousands of users simultaneously. Mainframe executes many programs concurrently and supports much simultaneous execution of programs.

Supercomputer
Supercomputers are one of the fastest computers currently available. Supercomputers are very expensive and are employed for specialized applications that require an immense amount of mathematical calculations (number-crunching).

For example, weather forecasting, scientific simulations, (animated)graphics, fluid dynamic calculations, nuclear energy research, electronic design, and analysis of geological data (e.g. In petrochemical prospecting).
Computer systems consist of three components as shown in below image: Central Processing Unit, Input devices and Output devices. Input devices provide data input to processor, which processes data and generates useful information that’s displayed to the user through output devices. This is stored in computer’s memory.
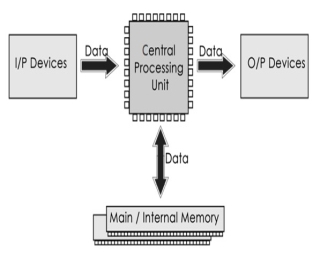
Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is called "the brain of computer" as it controls operation of all parts of computer. It consists of two components: Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), and Control Unit.
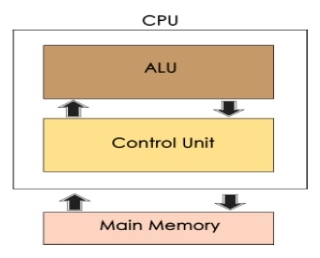
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Data entered into computer is sent to RAM, from where it is then sent to ALU, where rest of data processing takes place. All types of processing, such as comparisons, decision-making and processing of non-numeric information takes place here and once again data is moved to RAM.
Control Unit
As name indicates, this part of CPU extracts instructions, performs execution, maintains and directs operations of entire system.
Functions of Control Unit
Control unit performs following functions −
- It controls all activities of computer
- Supervises flow of data within CPU
- Directs flow of data within CPU
- Transfers data to Arithmetic and Logic Unit
- Transfers results to memory
- Fetches results from memory to output devices
Memory Unit
This is unit in which data and instructions given to computer as well as results given by computer are stored. Unit of memory is "Byte".
1 Byte = 8 Bits
All types of computers follow the same basic logical structure and perform the following five basic operations for converting raw input data into information useful to their users.
S.No. | Operation | Description |
1 | Take Input | The process of entering data and instructions into the computer system. |
2 | Store Data | Saving data and instructions so that they are available for processing as and when required. |
3 | Processing Data | Performing arithmetic, and logical operations on data in order to convert them into useful information. |
4 | Output Information | The process of producing useful information or results for the user, such as a printed report or visual display. |
5 | Control the workflow | Directs the manner and sequence in which all of the above operations are performed. |
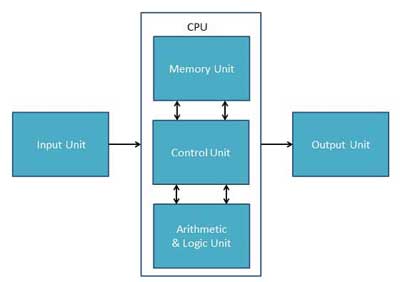
Input Unit
This unit contains devices with the help of which we enter data into the computer. This unit creates a link between the user and the computer. The input devices translate the information into a form understandable by the computer.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU is considered as the brain of the computer. CPU performs all types of data processing operations. It stores data, intermediate results, and instructions (program). It controls the operation of all parts of the computer.
CPU itself has the following three components −
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
- Memory Unit
- Control Unit
Output Unit
The output unit consists of devices with the help of which we get the information from the computer. This unit is a link between the computer and the users. Output devices translate the computer's output into a form understandable by the users.
Input Devices
Following are some of the important input devices which are used in a computer −
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Joy Stick
- Light pen
- Track Ball
- Scanner
- Graphic Tablet
- Microphone
- Magnetic Ink Card Reader(MICR)
- Optical Character Reader(OCR)
- Bar Code Reader
- Optical Mark Reader(OMR)
Keyboard
Keyboard is the most common and very popular input device which helps to input data to the computer. The layout of the keyboard is like that of traditional typewriter, although there are some additional keys provided for performing additional functions.

Keyboards are of two sizes 84 keys or 101/102 keys, but now keyboards with 104 keys or 108 keys are also available for Windows and Internet.
The keys on the keyboard are as follows −
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
Mouse
Mouse is the most popular pointing device. It is a very famous cursor-control device having a small palm size box with a round ball at its base, which senses the movement of the mouse and sends corresponding signals to the CPU when the mouse buttons are pressed.
Generally, it has two buttons called the left and the right button and a wheel is present between the buttons. A mouse can be used to control the position of the cursor on the screen, but it cannot be used to enter text into the computer.

Advantages
- Easy to use
- Not very expensive
- Moves the cursor faster than the arrow keys of the keyboard.
Joystick
Joystick is also a pointing device, which is used to move the cursor position on a monitor screen. It is a stick having a spherical ball at its both lower and upper ends. The lower spherical ball moves in a socket. The joystick can be moved in all four directions.

The function of the joystick is similar to that of a mouse. It is mainly used in Computer Aided Designing (CAD) and playing computer games.
Light Pen
Light pen is a pointing device similar to a pen. It is used to select a displayed menu item or draw pictures on the monitor screen. It consists of a photocell and an optical system placed in a small tube.

When the tip of a light pen is moved over the monitor screen and the pen button is pressed, its photocell sensing element detects the screen location and sends the corresponding signal to the CPU.
Track Ball
Track ball is an input device that is mostly used in notebook or laptop computer, instead of a mouse. This is a ball which is half inserted and by moving fingers on the ball, the pointer can be moved.

Since the whole device is not moved, a track ball requires less space than a mouse. A track ball comes in various shapes like a ball, a button, or a square.
Scanner
Scanner is an input device, which works more like a photocopy machine. It is used when some information is available on paper and it is to be transferred to the hard disk of the computer for further manipulation.

Scanner captures images from the source which are then converted into a digital form that can be stored on the disk. These images can be edited before they are printed.
Digitizer
Digitizer is an input device which converts analog information into digital form. Digitizer can convert a signal from the television or camera into a series of numbers that could be stored in a computer. They can be used by the computer to create a picture of whatever the camera had been pointed at.

Digitizer is also known as Tablet or Graphics Tablet as it converts graphics and pictorial data into binary inputs. A graphic tablet as digitizer is used for fine works of drawing and image manipulation applications.
Microphone
Microphone is an input device to input sound that is then stored in a digital form.

The microphone is used for various applications such as adding sound to a multimedia presentation or for mixing music.
Magnetic Ink Card Reader (MICR)
MICR input device is generally used in banks as there are large number of cheques to be processed every day. The bank's code number and cheque number are printed on the cheques with a special type of ink that contains particles of magnetic material that are machine readable.

This reading process is called Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR). The main advantages of MICR is that it is fast and less error prone.
Optical Character Reader (OCR)
OCR is an input device used to read a printed text.

OCR scans the text optically, character by character, converts them into a machine readable code, and stores the text on the system memory.
Bar Code Readers
Bar Code Reader is a device used for reading bar coded data (data in the form of light and dark lines). Bar coded data is generally used in labelling goods, numbering the books, etc. It may be a handheld scanner or may be embedded in a stationary scanner.

Bar Code Reader scans a bar code image, converts it into an alphanumeric value, which is then fed to the computer that the bar code reader is connected to.
Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
OMR is a special type of optical scanner used to recognize the type of mark made by pen or pencil. It is used where one out of a few alternatives is to be selected and marked.

It is specially used for checking the answer sheets of examinations having multiple choice questions.
Output Devices
Following are some of the important output devices used in a computer.
- Monitors
- Graphic Plotter
- Printer
Monitors
Monitors, commonly called as Visual Display Unit (VDU), are the main output device of a computer. It forms images from tiny dots, called pixels that are arranged in a rectangular form. The sharpness of the image depends upon the number of pixels.
There are two kinds of viewing screen used for monitors.
- Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)
- Flat-Panel Display
Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
The CRT display is made up of small picture elements called pixels. The smaller the pixels, the better the image clarity or resolution. It takes more than one illuminated pixel to form a whole character, such as the letter ‘e’ in the word help.

A finite number of characters can be displayed on a screen at once. The screen can be divided into a series of character boxes - fixed location on the screen where a standard character can be placed. Most screens are capable of displaying 80 characters of data horizontally and 25 lines vertically.
There are some disadvantages of CRT −
- Large in Size
- High power consumption
Flat-Panel Display Monitor
The flat-panel display refers to a class of video devices that have reduced volume, weight and power requirement in comparison to the CRT. You can hang them on walls or wear them on your wrists. Current uses of flat-panel displays include calculators, video games, monitors, laptop computer, and graphics display.

The flat-panel display is divided into two categories −
- Emissive Displays− Emissive displays are devices that convert electrical energy into light. For example, plasma panel and LED (Light-Emitting Diodes).
- Non-Emissive Displays− Non-emissive displays use optical effects to convert sunlight or light from some other source into graphics patterns. For example, LCD (Liquid-Crystal Device).
Printers
Printer is an output device, which is used to print information on paper.
There are two types of printers −
- Impact Printers
- Non-Impact Printers
Impact Printers
Impact printers print the characters by striking them on the ribbon, which is then pressed on the paper.
Characteristics of Impact Printers are the following −
- Very low consumable costs
- Very noisy
- Useful for bulk printing due to low cost
- There is physical contact with the paper to produce an image
These printers are of two types −
- Character printers
- Line printers
Character Printers
Character printers are the printers which print one character at a time.
These are further divided into two types:
- Dot Matrix Printer(DMP)
- Daisy Wheel
Dot Matrix Printer
In the market, one of the most popular printers is Dot Matrix Printer. These printers are popular because of their ease of printing and economical price. Each character printed is in the form of pattern of dots and head consists of a Matrix of Pins of size (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9) which come out to form a character which is why it is called Dot Matrix Printer.

Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Widely Used
- Other language characters can be printed
Disadvantages
- Slow Speed
- Poor Quality
Daisy Wheel
Head is lying on a wheel and pins corresponding to characters are like petals of Daisy (flower) which is why it is called Daisy Wheel Printer. These printers are generally used for word-processing in offices that require a few letters to be sent here and there with very nice quality.

Advantages
- More reliable than DMP
- Better quality
- Fonts of character can be easily changed
Disadvantages
- Slower than DMP
- Noisy
- More expensive than DMP
Line Printers
Line printers are the printers which print one line at a time.

These are of two types −
- Drum Printer
- Chain Printer
Drum Printer
This printer is like a drum in shape hence it is called drum printer. The surface of the drum is divided into a number of tracks. Total tracks are equal to the size of the paper, i.e. for a paper width of 132 characters, drum will have 132 tracks. A character set is embossed on the track. Different character sets available in the market are 48 character set, 64 and 96 characters set. One rotation of drum prints one line. Drum printers are fast in speed and can print 300 to 2000 lines per minute.
Advantages
- Very high speed
Disadvantages
- Very expensive
- Characters fonts cannot be changed
Chain Printer
In this printer, a chain of character sets is used, hence it is called Chain Printer. A standard character set may have 48, 64, or 96 characters.
Advantages
- Character fonts can easily be changed.
- Different languages can be used with the same printer.
Disadvantages
- Noisy
Non-impact Printers
Non-impact printers print the characters without using the ribbon. These printers print a complete page at a time, thus they are also called as Page Printers.
These printers are of two types −
- Laser Printers
- Inkjet Printers
Characteristics of Non-impact Printers
- Faster than impact printers
- They are not noisy
- High quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Laser Printers
These are non-impact page printers. They use laser lights to produce the dots needed to form the characters to be printed on a page.

Advantages
- Very high speed
- Very high quality output
- Good graphics quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Cannot be used to produce multiple copies of a document in a single printing
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are non-impact character printers based on a relatively new technology. They print characters by spraying small drops of ink onto paper. Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features.

They make less noise because no hammering is done and these have many styles of printing modes available. Color printing is also possible. Some models of Inkjet printers can produce multiple copies of printing also.
Advantages
- High quality printing
- More reliable
Disadvantages
- Expensive as the cost per page is high
- Slow as compared to laser printer
Memory
A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where data is to be processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is divided into large number of small parts called cells. Each location or cell has a unique address, which varies from zero to memory size minus one. For example, if the computer has 64k words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024 = 65536 memory locations. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535.
Memory is primarily of three types −
- Cache Memory
- Primary Memory/Main Memory
- Secondary Memory
Cache Memory
Cache memory is a very high speed semiconductor memory which can speed up the CPU. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory. It is used to hold those parts of data and program which are most frequently used by the CPU. The parts of data and programs are transferred from the disk to cache memory by the operating system, from where the CPU can access them.

Advantages
The advantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory is faster than main memory.
- It consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
- It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time.
- It stores data for temporary use.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory has limited capacity.
- It is very expensive.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory holds only those data and instructions on which the computer is currently working. It has a limited capacity and data is lost when power is switched off. It is generally made up of semiconductor device. These memories are not as fast as registers. The data and instruction required to be processed resides in the main memory. It is divided into two subcategories RAM and ROM.

Characteristics of Main Memory
- These are semiconductor memories.
- It is known as the main memory.
- Usually volatile memory.
- Data is lost in case power is switched off.
- It is the working memory of the computer.
- Faster than secondary memories.
- A computer cannot run without the primary memory.
Secondary Memory
This type of memory is also known as external memory or non-volatile. It is slower than the main memory. These are used for storing data/information permanently. CPU directly does not access these memories, instead they are accessed via input-output routines. The contents of secondary memories are first transferred to the main memory, and then the CPU can access it. For example, disk, CD-ROM, DVD, etc.

Characteristics of Secondary Memory
- These are magnetic and optical memories.
- It is known as the backup memory.
- It is a non-volatile memory.
- Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
- It is used for storage of data in a computer.
- Computer may run without the secondary memory.
- Slower than primary memories.
Motherboard
The motherboard serves as a single platform to connect all of the parts of a computer together. It connects the CPU, memory, hard drives, optical drives, video card, sound card, and other ports and expansion cards directly or via cables. It can be considered as the backbone of a computer.

Features of Motherboard
A motherboard comes with following features −
- Motherboard varies greatly in supporting various types of components.
- Motherboard supports a single type of CPU and few types of memories.
- Video cards, hard disks, sound cards have to be compatible with the motherboard to function properly.
- Motherboards, cases, and power supplies must be compatible to work properly together.
Popular Manufacturers
Following are the popular manufacturers of the motherboard.
- Intel
- ASUS
- AOpen
- ABIT
- Biostar
- Gigabyte
- MSI
Description of Motherboard
The motherboard is mounted inside the case and is securely attached via small screws through pre-drilled holes. Motherboard contains ports to connect all of the internal components. It provides a single socket for CPU, whereas for memory, normally one or more slots are available. Motherboards provide ports to attach the floppy drive, hard drive, and optical drives via ribbon cables. Motherboard carries fans and a special port designed for power supply.
There is a peripheral card slot in front of the motherboard using which video cards, sound cards, and other expansion cards can be connected to the motherboard.
On the left side, motherboards carry a number of ports to connect the monitor, printer, mouse, keyboard, speaker, and network cables. Motherboards also provide USB ports, which allow compatible devices to be connected in plug-in/plug-out fashion. For example, pen drive, digital cameras, etc.
Memory Units
Memory unit is the amount of data that can be stored in the storage unit. This storage capacity is expressed in terms of Bytes.
The following table explains the main memory storage units −
S.No. | Unit & Description |
1 | Bit (Binary Digit) A binary digit is logical 0 and 1 representing a passive or an active state of a component in an electric circuit. |
2 | Nibble A group of 4 bits is called nibble. |
3 | Byte A group of 8 bits is called byte. A byte is the smallest unit, which can represent a data item or a character. |
4 | Word A computer word, like a byte, is a group of fixed number of bits processed as a unit, which varies from computer to computer but is fixed for each computer. The length of a computer word is called word-size or word length. It may be as small as 8 bits or may be as long as 96 bits. A computer stores the information in the form of computer words. |
The following table lists some higher storage units −
S.No. | Unit & Description |
1 | Kilobyte (KB) 1 KB = 1024 Bytes |
2 | Megabyte (MB) 1 MB = 1024 KB |
3 | GigaByte (GB) 1 GB = 1024 MB |
4 | TeraByte (TB) 1 TB = 1024 GB |
5 | PetaByte (PB) 1 PB = 1024 TB |
Random Access Memory
RAM (Random Access Memory) is the internal memory of the CPU for storing data, program, and program result. It is a read/write memory which stores data until the machine is working. As soon as the machine is switched off, data is erased.

Access time in RAM is independent of the address, that is, each storage location inside the memory is as easy to reach as other locations and takes the same amount of time. Data in the RAM can be accessed randomly but it is very expensive.
RAM is volatile, i.e. data stored in it is lost when we switch off the computer or if there is a power failure. Hence, a backup Uninterruptible Power System (UPS) is often used with computers. RAM is small, both in terms of its physical size and in the amount of data it can hold.
RAM is of two types −
- Static RAM (SRAM)
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Static RAM (SRAM)
The word static indicates that the memory retains its contents as long as power is being supplied. However, data is lost when the power gets down due to volatile nature. SRAM chips use a matrix of 6-transistors and no capacitors. Transistors do not require power to prevent leakage, so SRAM need not be refreshed on a regular basis.
There is extra space in the matrix, hence SRAM uses more chips than DRAM for the same amount of storage space, making the manufacturing costs higher. SRAM is thus used as cache memory and has very fast access.
Characteristic of Static RAM
- Long life
- No need to refresh
- Faster
- Used as cache memory
- Large size
- Expensive
- High power consumption
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
DRAM, unlike SRAM, must be continually refreshed in order to maintain the data. This is done by placing the memory on a refresh circuit that rewrites the data several hundred times per second. DRAM is used for most system memory as it is cheap and small. All DRAMs are made up of memory cells, which are composed of one capacitor and one transistor.
Characteristics of Dynamic RAM
- Short data lifetime
- Needs to be refreshed continuously
- Slower as compared to SRAM
- Used as RAM
- Smaller in size
- Less expensive
- Less power consumption
Read Only Memory
ROM stands for Read Only Memory. The memory from which we can only read but cannot write on it. This type of memory is non-volatile. The information is stored permanently in such memories during manufacture. A ROM stores such instructions that are required to start a computer. This operation is referred to as bootstrap. ROM chips are not only used in the computer but also in other electronic items like washing machine and microwave oven.

Let us now discuss the various types of ROMs and their characteristics.
MROM (Masked ROM)
The very first ROMs were hard-wired devices that contained a pre-programmed set of data or instructions. These kind of ROMs are known as masked ROMs, which are inexpensive.
PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory)
PROM is read-only memory that can be modified only once by a user. The user buys a blank PROM and enters the desired contents using a PROM program. Inside the PROM chip, there are small fuses which are burnt open during programming. It can be programmed only once and is not erasable.
EPROM (Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory)
EPROM can be erased by exposing it to ultra-violet light for a duration of up to 40 minutes. Usually, an EPROM eraser achieves this function. During programming, an electrical charge is trapped in an insulated gate region. The charge is retained for more than 10 years because the charge has no leakage path. For erasing this charge, ultra-violet light is passed through a quartz crystal window (lid). This exposure to ultra-violet light dissipates the charge. During normal use, the quartz lid is sealed with a sticker.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory)
EEPROM is programmed and erased electrically. It can be erased and reprogrammed about ten thousand times. Both erasing and programming take about 4 to 10 ms (millisecond). In EEPROM, any location can be selectively erased and programmed. EEPROMs can be erased one byte at a time, rather than erasing the entire chip. Hence, the process of reprogramming is flexible but slow.
Advantages of ROM
The advantages of ROM are as follows −
- Non-volatile in nature
- Cannot be accidentally changed
- Cheaper than RAMs
- Easy to test
- More reliable than RAMs
- Static and do not require refreshing
- Contents are always known and can be verified
Input Devices
Following are some of the important input devices which are used in a computer −
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Joy Stick
- Light pen
- Track Ball
- Scanner
- Graphic Tablet
- Microphone
- Magnetic Ink Card Reader(MICR)
- Optical Character Reader(OCR)
- Bar Code Reader
- Optical Mark Reader(OMR)
Keyboard
Keyboard is the most common and very popular input device which helps to input data to the computer. The layout of the keyboard is like that of traditional typewriter, although there are some additional keys provided for performing additional functions.

Keyboards are of two sizes 84 keys or 101/102 keys, but now keyboards with 104 keys or 108 keys are also available for Windows and Internet.
The keys on the keyboard are as follows −
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
Mouse
Mouse is the most popular pointing device. It is a very famous cursor-control device having a small palm size box with a round ball at its base, which senses the movement of the mouse and sends corresponding signals to the CPU when the mouse buttons are pressed.
Generally, it has two buttons called the left and the right button and a wheel is present between the buttons. A mouse can be used to control the position of the cursor on the screen, but it cannot be used to enter text into the computer.

Advantages
- Easy to use
- Not very expensive
- Moves the cursor faster than the arrow keys of the keyboard.
Joystick
Joystick is also a pointing device, which is used to move the cursor position on a monitor screen. It is a stick having a spherical ball at its both lower and upper ends. The lower spherical ball moves in a socket. The joystick can be moved in all four directions.

The function of the joystick is similar to that of a mouse. It is mainly used in Computer Aided Designing (CAD) and playing computer games.
Light Pen
Light pen is a pointing device similar to a pen. It is used to select a displayed menu item or draw pictures on the monitor screen. It consists of a photocell and an optical system placed in a small tube.

When the tip of a light pen is moved over the monitor screen and the pen button is pressed, its photocell sensing element detects the screen location and sends the corresponding signal to the CPU.
Track Ball
Track ball is an input device that is mostly used in notebook or laptop computer, instead of a mouse. This is a ball which is half inserted and by moving fingers on the ball, the pointer can be moved.

Since the whole device is not moved, a track ball requires less space than a mouse. A track ball comes in various shapes like a ball, a button, or a square.
Scanner
Scanner is an input device, which works more like a photocopy machine. It is used when some information is available on paper and it is to be transferred to the hard disk of the computer for further manipulation.

Scanner captures images from the source which are then converted into a digital form that can be stored on the disk. These images can be edited before they are printed.
Digitizer
Digitizer is an input device which converts analog information into digital form. Digitizer can convert a signal from the television or camera into a series of numbers that could be stored in a computer. They can be used by the computer to create a picture of whatever the camera had been pointed at.

Digitizer is also known as Tablet or Graphics Tablet as it converts graphics and pictorial data into binary inputs. A graphic tablet as digitizer is used for fine works of drawing and image manipulation applications.
Microphone
Microphone is an input device to input sound that is then stored in a digital form.

The microphone is used for various applications such as adding sound to a multimedia presentation or for mixing music.
Magnetic Ink Card Reader (MICR)
MICR input device is generally used in banks as there are large number of cheques to be processed every day. The bank's code number and cheque number are printed on the cheques with a special type of ink that contains particles of magnetic material that are machine readable.

This reading process is called Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR). The main advantages of MICR is that it is fast and less error prone.
Optical Character Reader (OCR)
OCR is an input device used to read a printed text.

OCR scans the text optically, character by character, converts them into a machine readable code, and stores the text on the system memory.
Bar Code Readers
Bar Code Reader is a device used for reading bar coded data (data in the form of light and dark lines). Bar coded data is generally used in labelling goods, numbering the books, etc. It may be a handheld scanner or may be embedded in a stationary scanner.

Bar Code Reader scans a bar code image, converts it into an alphanumeric value, which is then fed to the computer that the bar code reader is connected to.
Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
OMR is a special type of optical scanner used to recognize the type of mark made by pen or pencil. It is used where one out of a few alternatives is to be selected and marked.

It is specially used for checking the answer sheets of examinations having multiple choice questions.
Output Devices
Following are some of the important output devices used in a computer.
- Monitors
- Graphic Plotter
- Printer
Monitors
Monitors, commonly called as Visual Display Unit (VDU), are the main output device of a computer. It forms images from tiny dots, called pixels that are arranged in a rectangular form. The sharpness of the image depends upon the number of pixels.
There are two kinds of viewing screen used for monitors.
- Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)
- Flat-Panel Display
Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
The CRT display is made up of small picture elements called pixels. The smaller the pixels, the better the image clarity or resolution. It takes more than one illuminated pixel to form a whole character, such as the letter ‘e’ in the word help.

A finite number of characters can be displayed on a screen at once. The screen can be divided into a series of character boxes - fixed location on the screen where a standard character can be placed. Most screens are capable of displaying 80 characters of data horizontally and 25 lines vertically.
There are some disadvantages of CRT −
- Large in Size
- High power consumption
Flat-Panel Display Monitor
The flat-panel display refers to a class of video devices that have reduced volume, weight and power requirement in comparison to the CRT. You can hang them on walls or wear them on your wrists. Current uses of flat-panel displays include calculators, video games, monitors, laptop computer, and graphics display.

The flat-panel display is divided into two categories −
- Emissive Displays− Emissive displays are devices that convert electrical energy into light. For example, plasma panel and LED (Light-Emitting Diodes).
- Non-Emissive Displays− Non-emissive displays use optical effects to convert sunlight or light from some other source into graphics patterns. For example, LCD (Liquid-Crystal Device).
Printers
Printer is an output device, which is used to print information on paper.
There are two types of printers −
- Impact Printers
- Non-Impact Printers
Impact Printers
Impact printers print the characters by striking them on the ribbon, which is then pressed on the paper.
Characteristics of Impact Printers are the following −
- Very low consumable costs
- Very noisy
- Useful for bulk printing due to low cost
- There is physical contact with the paper to produce an image
These printers are of two types −
- Character printers
- Line printers
Character Printers
Character printers are the printers which print one character at a time.
These are further divided into two types:
- Dot Matrix Printer(DMP)
- Daisy Wheel
Dot Matrix Printer
In the market, one of the most popular printers is Dot Matrix Printer. These printers are popular because of their ease of printing and economical price. Each character printed is in the form of pattern of dots and head consists of a Matrix of Pins of size (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9) which come out to form a character which is why it is called Dot Matrix Printer.

Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Widely Used
- Other language characters can be printed
Disadvantages
- Slow Speed
- Poor Quality
Daisy Wheel
Head is lying on a wheel and pins corresponding to characters are like petals of Daisy (flower) which is why it is called Daisy Wheel Printer. These printers are generally used for word-processing in offices that require a few letters to be sent here and there with very nice quality.

Advantages
- More reliable than DMP
- Better quality
- Fonts of character can be easily changed
Disadvantages
- Slower than DMP
- Noisy
- More expensive than DMP
Line Printers
Line printers are the printers which print one line at a time.

These are of two types −
- Drum Printer
- Chain Printer
Drum Printer
This printer is like a drum in shape hence it is called drum printer. The surface of the drum is divided into a number of tracks. Total tracks are equal to the size of the paper, i.e. for a paper width of 132 characters, drum will have 132 tracks. A character set is embossed on the track. Different character sets available in the market are 48 character set, 64 and 96 characters set. One rotation of drum prints one line. Drum printers are fast in speed and can print 300 to 2000 lines per minute.
Advantages
- Very high speed
Disadvantages
- Very expensive
- Characters fonts cannot be changed
Chain Printer
In this printer, a chain of character sets is used, hence it is called Chain Printer. A standard character set may have 48, 64, or 96 characters.
Advantages
- Character fonts can easily be changed.
- Different languages can be used with the same printer.
Disadvantages
- Noisy
Non-impact Printers
Non-impact printers print the characters without using the ribbon. These printers print a complete page at a time, thus they are also called as Page Printers.
These printers are of two types −
- Laser Printers
- Inkjet Printers
Characteristics of Non-impact Printers
- Faster than impact printers
- They are not noisy
- High quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Laser Printers
These are non-impact page printers. They use laser lights to produce the dots needed to form the characters to be printed on a page.

Advantages
- Very high speed
- Very high quality output
- Good graphics quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Cannot be used to produce multiple copies of a document in a single printing
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are non-impact character printers based on a relatively new technology. They print characters by spraying small drops of ink onto paper. Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features.

They make less noise because no hammering is done and these have many styles of printing modes available. Color printing is also possible. Some models of Inkjet printers can produce multiple copies of printing also.
Advantages
- High quality printing
- More reliable
Disadvantages
- Expensive as the cost per page is high
- Slow as compared to laser printer
Computer Block Diagram
Mainly computer system consists of three parts that are central processing unit (CPU), Input Devices, and Output Devices. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is divided into two parts again: arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and the control unit (CU). The set of instruction is in the form of raw data.
A large amount of data is stored in the computer memory with the help of primary and secondary storage devices. The CPU is like the heart/brain of the computer. The user does not get the desired output, without the necessary option taken by the CPU. The Central processing unit (CPU) is responsible for the processing of all the instructions which are given by the user to the computer system.
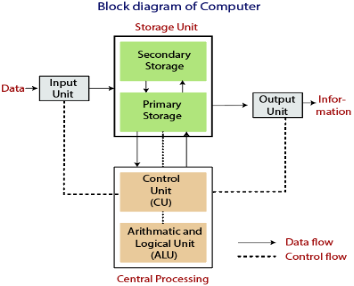
Fig: Block Diagram of the computer.
The data is entered through input devices such as the keyboard, mouse, etc. This set of instruction is processed by the CPU after getting the input by the user, and then the computer system produces the output. The computer can show the output with the help of output devices to the user, such as monitor, printer, etc.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- Storage Unit
- ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
- Control Unit
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The computer system is nothing without the Central processing Unit so, it is also known as the brain or heat of computer. The CPU is an electronic hardware device which can perform different types of operations such as arithmetic and logical operation.
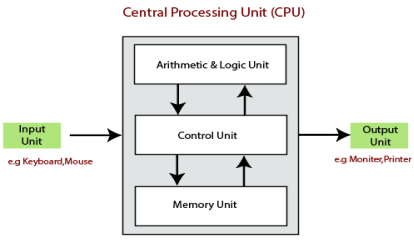
The CPU contains two parts: the arithmetic logic unit and control unit. We have discussed briefly the arithmetic unit, logical unit, and control unit which are given below:
Control Unit
The control unit (CU) controls all the activities or operations which are performed inside the computer system. It receives instructions or information directly from the main memory of the computer.
When the control unit receives an instruction set or information, it converts the instruction set to control signals then; these signals are sent to the central processor for further processing. The control unit understands which operation to execute, accurately, and in which order.
Arithmetic and Logical Unit
The arithmetic and logical unit is the combinational digital electronic circuit that can perform arithmetic operations on integer binary numbers.It presents the arithmetic and logical operation. The outputs of ALU will change asynchronously in response to the input. The basic arithmetic and bitwise logic functions are supported by ALU.
Storage Unit
The information or set of guidelines are stored in the storage unit of the computer system. The storage unit provides the space to store the data or instruction of processed data. The information or data is saved or hold in computer memory or storage device. The data storage is the core function and fundamental of the computer components.
Components of Computer System
The hardware and software exist on the computer. The information which is stored through the device is known as computer software. The hardware components of the computer system are related to electronic and mechanical parts, and the software component is related to data and computer programs. Many elements are connected to the main circuit board of the computer system called a “motherboard.”
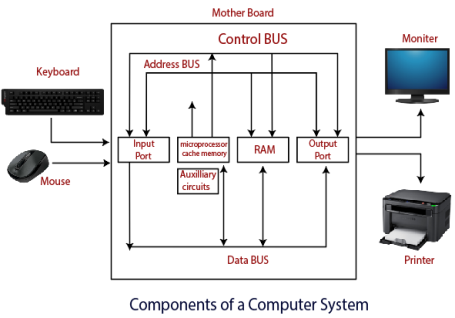
- Processor.
- Main Memory.
- Secondary Memory.
- Input Devices.
- Output Devices.
These are mainly five components of the computer system. The computer hardware, computer software, and liveware exist in the element of the computer system.
Processor
The processor is an electric circuitry within the computer system. The Central processing unit is the central processor or main processor of the computer system. The processor carries out the instructions of the computer program with the help of basic arithmetic and logic, input/output operations.
Main Memory
The Random Access Memory is the main memory of the computer system, which is known as RAM. The main memory can store the operating system software, application software, and other information. The Ram is one of the fastest memory, and it allows the data to be readable and writeable.
Secondary memory
We can store the data and programs on a long-term basis in the secondary memory. The hard disks and the optical disks are the common secondary devices. It is slow and cheap memory as compare to primary memory. This memory is not connected to the processor directly.
It has a large capacity to store the data. The hard disk has a capacity of 500 gigabytes. The data and programs on the hard disk are organized into files, and the file is the collection of data on the disk. The secondary storage is direct access by the CPU; that’s why it is different from the primary storage.
The hard disk is about 100 times the capacity of the main memory. The main difference between primary and secondary storage is speed and capacity. There are several large blocks of data which are copied from the hard disk into the main memory.
Input Devices
The user provides the set of instruction or information to the computer system with the help of input devices such as the keyboard, mouse, scanner, etc. The data representation to the computer system is in the form of binary language after that the processor processes the converted data. The input unit implements the data which is instructed by the user to the system.
We can enter the data from the outside world into the primary storage as the input through input devices. The input devices are the medium of communication between the outside world and the computer system. There are some important features of input devices which are given below:
- The input devices receive or accept the data or instruction from the user, who exist in the outside world.
- These devices convert the data or instruction into the machine-readable form for further processing.
- The input device performs like the connection between the outside world and our computer system.
- The keyboard and mouse are common examples of input devices.
- When the whole procedure is finished, we get the desired output from the output devices such as monitor, printer, etc.
Output Devices
The output devices produce or generate the desired result according to our input, such as a printer, monitor, etc. These devices convert the data into a human-readable form from binary code.
The computer system is linked or connected to the outside world with the help of output devices. The primary examples of output devices are a printer, projector, etc. These devices have various features which are given below:
- These devices receive or accept the data in the binary form.
- The output devices convert the binary code into the human-readable form.
- These devices produce the converted result and show to the user.
The computer memory holds the data and instructions needed to process raw data and produce output. The computer memory is divided into large number of small parts known as cells. Each cell has a unique address which varies from 0 to memory size minus one.
Computer memory is of two types: Volatile (RAM) and Non-volatile (ROM). The secondary memory (hard disk) is referred as storage not memory.
But, if we categorize memory on behalf of space or location, it is of four types:
- Register memory
- Cache memory
- Primary memory
- Secondary memory
Register Memory
Register memory is the smallest and fastest memory in a computer. It is not a part of the main memory and is located in the CPU in the form of registers, which are the smallest data holding elements. A register temporarily holds frequently used data, instructions, and memory address that are to be used by CPU. They hold instructions that are currently processed by the CPU. All data is required to pass through registers before it can be processed. So, they are used by CPU to process the data entered by the users.
Registers hold a small amount of data around 32 bits to 64 bits. The speed of a CPU depends on the number and size (no. Of bits) of registers that are built into the CPU. Registers can be of different types based on their uses. Some of the widely used Registers include Accumulator or AC, Data Register or DR, the Address Register or AR, Program Counter (PC), I/O Address Register, and more.
Types and Functions of Computer Registers:
- Data Register: It is a 16-bit register, which is used to store operands (variables) to be operated by the processor. It temporarily stores data, which is being transmitted to or received from a peripheral device.
- Program Counter (PC): It holds the address of the memory location of the next instruction, which is to be fetched after the current instruction is completed. So, it is used to maintain the path of execution of the different programs and thus executes the programs one by one, when the previous instruction gets completed.
- Instructor Register: It is a 16-bit register. It stores the instruction which is fetched from the main memory. So, it is used to hold instruction codes, which are to be executed. The Control Unit takes instruction from Instructor Register, then decodes and executes it.
- Accumulator Register: It is a 16-bit register, which is used to store the results produced by the system. For example, the results generated by CPU after the processing are stored in the AC register.
- Address Register: It is a 12-bit register that stores the address of a memory location where instructions or data is stored in the memory.
- I/O Address Register: Its job is to specify the address of a particular I/O device.
- I/O Buffer Register: Its job is to exchange the data between an I/O module and the CPU.
Cache Memory
Cache memory is a high-speed memory, which is small in size but faster than the main memory (RAM). The CPU can access it more quickly than the primary memory. So, it is used to synchronize with high-speed CPU and to improve its performance.
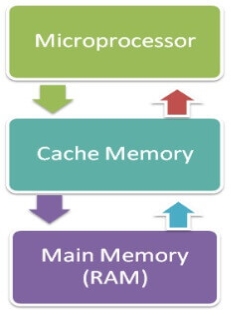
Cache memory can only be accessed by CPU. It can be a reserved part of the main memory or a storage device outside the CPU. It holds the data and programs which are frequently used by the CPU. So, it makes sure that the data is instantly available for CPU whenever the CPU needs this data. In other words, if the CPU finds the required data or instructions in the cache memory, it doesn't need to access the primary memory (RAM). Thus, by acting as a buffer between RAM and CPU, it speeds up the system performance.
Types of Cache Memory:
L1: It is the first level of cache memory, which is called Level 1 cache or L1 cache. In this type of cache memory, a small amount of memory is present inside the CPU itself. If a CPU has four cores (quad core cpu), then each core will have its own level 1 cache. As this memory is present in the CPU, it can work at the same speed as of the CPU. The size of this memory ranges from 2KB to 64 KB. The L1 cache further has two types of caches: Instruction cache, which stores instructions required by the CPU, and the data cache that stores the data required by the CPU.
L2: This cache is known as Level 2 cache or L2 cache. This level 2 cache may be inside the CPU or outside the CPU. All the cores of a CPU can have their own separate level 2 cache, or they can share one L2 cache among themselves. In case it is outside the CPU, it is connected with the CPU with a very high-speed bus. The memory size of this cache is in the range of 256 KB to the 512 KB. In terms of speed, they are slower than the L1 cache.
L3: It is known as Level 3 cache or L3 cache. This cache is not present in all the processors; some high-end processors may have this type of cache. This cache is used to enhance the performance of Level 1 and Level 2 cache. It is located outside the CPU and is shared by all the cores of a CPU. Its memory size ranges from 1 MB to 8 MB. Although it is slower than L1 and L2 cache, it is faster than Random Access Memory (RAM).
How does cache memory work with CPU?
When CPU needs the data, first of all, it looks inside the L1 cache. If it does not find anything in L1, it looks inside the L2 cache. If again, it does not find the data in L2 cache, it looks into the L3 cache. If data is found in the cache memory, then it is known as a cache hit. On the contrary, if data is not found inside the cache, it is called a cache miss.
If data is not available in any of the cache memories, it looks inside the Random Access Memory (RAM). If RAM also does not have the data, then it will get that data from the Hard Disk Drive.
So, when a computer is started for the first time, or an application is opened for the first time, data is not available in cache memory or in RAM. In this case, the CPU gets the data directly from the hard disk drive. Thereafter, when you start your computer or open an application, CPU can get that data from cache memory or RAM.
Primary Memory
Primary Memory is of two types: RAM and ROM.
RAM (Volatile Memory)
It is a volatile memory. It means it does not store data or instructions permanently. When you switch on the computer the data and instructions from the hard disk are stored in RAM.
CPU utilizes this data to perform the required tasks. As soon as you shut down the computer the RAM loses all the data.
ROM (Non-volatile Memory)
It is a non-volatile memory. It means it does not lose its data or programs that are written on it at the time of manufacture. So it is a permanent memory that contains all important data and instructions needed to perform important tasks like the boot process.
Secondary Memory
The secondary storage devices which are built into the computer or connected to the computer are known as a secondary memory of the computer. It is also known as external memory or auxiliary storage.
The secondary memory is accessed indirectly via input/output operations. It is non-volatile, so permanently stores the data even when the computer is turned off or until this data is overwritten or deleted. The CPU can't directly access the secondary memory. First, the secondary memory data is transferred to primary memory then the CPU can access it.
Some of the secondary memory or storage devices are described below:
1) Hard Disk:
It is a rigid magnetic disc that is used to store data. It permanently stores data and is located within a drive unit.

The hard disk is also known as a hard drive. It is a rigid magnetic disc that stores data permanently, as it is a non-volatile storage device. The hard disk is located within a drive unit on the computer's motherboard and comprises one or more platters packed in an air-sealed casing. The data is written on the platters by moving a magnetic head over the platters as they spin. The data stored on a computer's hard drive generally includes the operating system, installed software, and the user's files and programs, including pictures, music, videos, text documents, etc.
Components of Hard Drive:
The main components of a hard drive include a head actuator, read/write actuator arm, read/write head, platter, and spindle. A circuit board, which is called the disk controller or interface board, is present on the back of a hard drive. It allows the hard drive to communicate with the computer.
2) Solid-state Drive:

SSD (Solid State Drive) is also a non-volatile storage medium that is used to hold and access data. Unlike a hard drive, it does not have moving components, so it offers many advantages over SSD, such as faster access time, noiseless operation, less power consumption, and more.
As the cost of SSD has come down, it has become an ideal replacement for a standard hard drive in desktop and laptop computers. It is also suitable for notebooks, and tablets that don't require lots of storage.
3) Pen drive:

Pen drive is a compact secondary storage device. It is also known as a USB flash drive, thumb drive or a jump drive. It connects to a computer via a USB port. It is commonly used to store and transfer data between computers. For example, you can write a report using a computer and then copy or transfer it in the pen drive. Later, you can connect this pen drive to a computer to see or edit your report. You can also store your important documents and pictures, music, videos in the pen drive and keep it at a safe place.
Pen drive does not have movable parts; it comprises an integrated circuit memory chip that stores the data. This chip is housed inside a plastic or aluminium casing. The data storage capacity of the pen drive generally ranges from 2 GB to 128 GB. Furthermore, it is a plug and play device as you don't need additional drives, software, or hardware to use it.
4) SD Card:

SD Card stands for Secure Digital Card. It is most often used in portable and mobile devices such as smartphones and digital cameras. You can remove it from your device and see the things stored in it using a computer with a card reader.
There are many memory chips inside the SD card that store the data; it does not have moving parts. SD cards are not created equal, so they may differ from each other in terms of speed, physical sizes, and capacity. For example, standard SD cards, mini SD cards, and micro SD cards.
5) Compact Disk (CD):

Compact Disk is a portable secondary storage device in the shape of a round medium disk. It is made of polycarbonate plastic. The concept of CD was co-developed by Philips and Sony in 1982. The first CD was created on 17 August 1982 at the workshop of Philips in Germany.
In the beginning, it was used for storing and playing sound recordings, later it was used for various purposes such as for storing documents, audio files, videos, and other data like software programs in a CD.
Physical characteristics of a CD/ Structure of CD:
A standard CD is around 5 inches in diameter and 0.05 inches in thickness. It is made of a clear polycarbonate plastic substrate, a reflective metallic layer, and a clear coating of acrylic plastic. These thin circular layers are attached one on top of another as described below:
- A polycarbonate disc layer at the bottom has the data encoded by creating lands and pits.
- The polycarbonate disc layer is coated with a thin aluminium layer that reflects the laser.
- The reflective aluminium layer is coated with a lacquer layer to prevent oxidation in order to protect the below layers. It is generally spin coated directly on the top of the reflective layer.
- The label print is applied on the lacquer layer, or artwork is screen printed on the top of the disc on the lacquer layer by offset printing or screen printing.
How Does a CD Work?
The data or information is stored or recorded or encoded in CD digitally using a laser beam that etches tiny indentations or bumps on its surface. The bump is called a pit, which represents the number 0. Space, where the bump is not created, is called land, and it represents the number 1. Thus, the data is encoded into a compact disc by creating pits (0) and lands (1). The CD players use laser technology to read the optically recorded data.
6) DVD:

DVD is short for digital versatile disc or digital video disc. It is a type of optical media used for storing optical data. Although it has the same size as a CD, its storage capacity is much more than a CD. So, it is widely used for storing and viewing movies and to distribute software programs as they are too large to fit on a CD. DVD was co-developed by Sony, Panasonic, Philips, and Toshiba in 1995.
Types of DVDs:
DVDs can be divided into three main categories which are as follows:
- DVD-ROM (Read-Only): These types of DVDs come with media already recorded on them, such as movie dvds. As the name suggests, data on these discs cannot be erased or added, so these discs are known as a read-only or non-writable DVD.
- DVD-R (Writable): It allows you to record or write information to the DVD. However, you can write information only once as it becomes a read-only DVD once it is full.
- DVD-RW (Rewritable or Erasable): This type of discs can be erased, written, or recorded multiple times.
Memory Units
Memory units are used to measure and represent data. Some of the commonly used memory units are:
1) Bit: The computer memory units start from bit. A bit is the smallest memory unit to measure data stored in main memory and storage devices. A bit can have only one binary value out of 0 and 1.
2) Byte: It is the fundamental unit to measure data. It contains 8 bits or is equal to 8 bits. Thus a byte can represent 2*8 or 256 values.
3) Kilobyte: A kilobyte contains 1024 bytes.
4) Megabyte: A megabyte contains 1024 kilobytes.
5) Gigabyte: A gigabyte contains 1024 megabyte.
6) Terabyte: A terabyte contains 1024 gigabytes.