Unit 1
Exploring the subject matter of economics
Economic is a study of ‘Choices’ or ‘Choice making’. Choice making is relevant for every individuals, families, societies, institution, area, state and nations and for the whole world. It also analyses how a society allocate the limited resources to achieve growth. The word’ Economics’ originates from a Greek word ‘Oikonomikos’. This Greek word has 2 parts – ‘Oikos’ means ‘Home’ and ‘Nomos’ means Management. Hence Economics means Home management.
Economics has emerged as high level of application due to its basic principle of ‘Choice making for optimization with the given resources of scarcity and surplus’.
Evolution in the definition of Economics
- Wealth definition (1776) by Adam Smith
- Welfare definition (1890) by Alfred Marshall
- Scarcity definition (1932) by Lionel Robbins
- Growth Definition (1948) by P.A. Samuelson
- Modern definition (2011) by A.C.Dhas
Modern definition of economics
Prof. A.C.Dhas defines economics as "The study of choice making by individuals, institutions, societies, nations and globe under conditions of scarcity and surplus towards maximizing benefits and satisfying the unlimited present and future needs.”
In short, the subject Economics is defined as the “Study of choices by all in maximizing production and consumption benefits with the given resources of scarce and surplus, for present and future needs.”
Characteristics
- It considers all the earlier definition of economics
- It covers both macro and micro aspects of economics
- It considers both production and consumption activities.
- It emphasizes Choice Making dimension of economics.
- It aims at obtaining maximum benefits with given resources
- It is suitable in conditions of both scarcity and surplus.
Importance of economic –
- Understand the function of economy – Microeconomic enables in understanding the function of free enterprise economy. It helps in taking major decision in the market economy.
2. Efficient employment of resources – The efficient utilization of scarce resources is the main problem faced by the government. Efficient employment of resources helps in economic development of the country. Micro economics helps in taking decision of efficient utilization of scarece and valuable resources.
3. Growth with stability – Microeconomic helps to achieve growth with stability. Developed economies finding difficulty in maintaining the growth with stability. While developing economy is making efforts for achieving growth.
4. A boon to business executive – Every business wants to increase the level of output and maximize their profit. Micro economics helps in estimating the total quantity of goods and services and the total costs involved for their manufacture.
5. Taxation – Micro economics helps in understanding the consequence of taxation. It explains how direct and indirect tax results in attainment of social welfare.
6. International trade - Micro economics helps in understanding the matter related to international trade, external trade, balance of payment, disequilibrium and the determination of foreign exchange rate.
7. Prediction – Micro economics helps in predicting the impact of government economic policies. Microeconomics analyses the causes and consequences of price determination by the government.
8. Construction of economic welfare – Micro economic emphasizes on study of economic welfare. To achieve maximum social welfare, micro economic suggest various alternatives for eliminating wastage of scarce resources..
Scope of economics
- Micro economics - This is considered to be basic economics. Microeconomics may be defined as that branch of economic analysis which studies the economic behavior of the individual unit, maybe a person, a particular household, or a particular firm.
The production of goods and services is based on allocation of scarce resources.
Efficient distribution of goods – this studies the matter relating to (a) Product pricing, (b) Factor pricing, (c) Economic welfare.
- Product pricing – it involves the determination of product price under monopoly, perfect competition, etc. considering demand, supply, cost production etc.
- Factor pricing - it involves the determination of price of factor inputs such as: land, labour, capital & organization in the form of rent, wage, interest & profit respectively.
- Economic welfare – it involves the study of maximum profit for producer and maximum benefit to consumer.
2. Macro economics - Macroeconomics may be defined as that branch of economic analysis which studies the behavior of not one particular unit, but of all the units combined together. Macroeconomics is a study in aggregates.
3. International economics - in order to conduct successful business dealings between countries with the advent of globalisation and cross-border integration, economic concepts are applied. Economic concepts can be used in areas, such as foreign trade (exports and imports), foreign exchange (trading currency), the balance of payments, and balance of trade.
4. Public finance - Public finance refers to how government raises its resources to meet the growing expenditure. Economic concepts are applied to assess the government’s collection of taxes from the users of public goods as well as expenditure on production and distribution of these goods to the general public
5. Welfare economics - To analyze the growth and development of low-income countries economic theories and concepts are used. In the developed countries this help in improving the living standard of people by understanding their needs for various facilities and utilities, such as health and education facilities and good working conditions.
6. Health economics - Economic concepts are also applicable in assessing the problems faced in promoting health in different countries. These concepts help the government in making decisions for defining appropriate health packages and programs for the general public.
7. Environmental economics - To analyze the utilization and depletion of natural resources economic concepts are used. Moreover, they are applied to study the impact of increasing ecological imbalance on society.
8. Urban and rural economics - the scope of economics covers the analysis of different urban issues such as crime, education, public transit, housing, and local government finance in urban development. Economics can be used to analyze the shortage of natural resources, obtain the best price for production, study constraints of productivity, adapt to climate change, etc in rural development.
Key takeaways –
- Microeconomics may be defined as that branch of economic analysis which studies the economic behavior of the individual unit, maybe a person, a particular household, or a particular firm.
- Macroeconomics is a study in aggregates
In every country resources are limited. Government, individual, businesses focuses on how to allocate scarce resources to satisfy the growing needs. This is the basic economic problem.
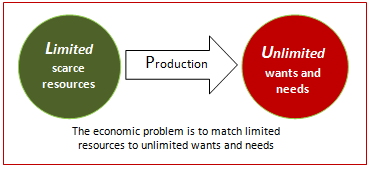
The problem of scarcity –
We live in a world of scarcity. People want and need variety of goods and services. This applies equally to the poor and the rich people. It implies that human wants are unlimited but the means to fulfil them are limited. At any one time, only a limited amount of goods and services can be produced. This is because the existing supplies of resources are extremely inadequate. These resources are land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship.
Limited resources are of 3 ways ;
- Land – natural resources
- Labour – Human resources
- Capital – Physical resources
The problem of choice –
Since we live in a world of scarcity, a society can produce only a small portion of goods and services that its people want. Thus, scarcity of resources gives rise to the fundamental economic problem of choice. Since the society cannot produce enough goods and services to satisfy all the wants of its people, it has to make choices.
Choice involves sacrifice since the decision to produce one good requires a decision to produce less of some other good. Thus every society is faced with the basic problem of deciding what it is willing to sacrifice to produce the goods it wants the most.
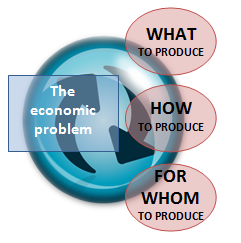
Human wants are unlimited and instable. The resources needed to satisfy the wants are scarce. Thus scarcity of resources leads to economic problems of the nation. Price mechanism plays an important role in answering the following question about the economy.
What to produce
When the resources are limited, what does the society do. It determines which goods and services it wants to produce and in what quantity. This involves the allocation of scarce resources to produce a final product. Since the resources is limited, the society decides which goods to produce such as wheat, cloth, etc. And also determines the quantity (How many kilos of wheat, how many million metres of cloth, etc) required to produce. Thus the production of goods and services depends on the preference of the society. If the society gives more preference to consumer goods now than capital goods, then consumer goods will have less preference in the future and capital goods will have more preference in the future.
How to produce
This problem refers to selection of appropriate technique of production, it means how to combine resources to produce goods and services at minimum cost and in more efficient way.
The technique which involves less capital and more labor is called labor intensive mode of production.
The technique which involves more capital and less labor is called as capital intensive mode of production
Thus the society should focus on using resources in such a way which results in maximum output at minimum cost
For example, how much land, labour, capital should be used to produce car, motor, etc
From whom to produce
This problem refers to the problem of distribution, ie how the consumer and capital goods to be distributed among the society. The income of the people determines the distribution of goods in the society. The more the income, the greater the quantity of goods is purchased in the market.
Sometimes government intervention leads to shortfall in the supply of goods and services.
Producer sells goods at a price to consumer and consumer receives income for their services from the producer. The allocation of consumer, luxury goods depends on the distribution of income. A rich person will purchase more luxury goods. A poor person will focus more on purchasing basic consumer goods.
How efficiently are the resources being used – the society have to check whether the resources are used fully or not. In case resources such as manpower, land and capital are lying idle, the society has to find ways to utilize them fully.
Key takeaways –
- The economic problems involves what to produce, when to produce and from whom to produce
Economics studies how societies use their scarce resources to produce and distribute commodities to satisfy unlimited wants of its people. Goods and services are produced because they have ‘utility’ or the capacity to satisfy human wants. Production requires resources. Resources are broadly classified into land, labour, capital and enterprise. Since resources are scarce and have alternative uses, they have to be used optimally, that is, with minimum wastage. Use of scare resources involves rational choices. Economics is the science of choices. Thus the problem of scarcity and choices become the basis of economic analysis.
British economist, Lionel Robbins (1898 – 1984) stated, economic problem is concerned with scare resource which are unlimited. It is a problem of choice, a choice between ends and also a choice of using scarce resources between alternatives uses with the objective of maximizing satisfaction.
The subject matter of modern economics is generally divided into two parts: Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. The terms micro and macro are derived from Greek words ‘mikros’ and ‘makros’ meaning ‘small’ and ‘large’ respectively.
Microeconomics studies the economic behavior of individual decision making units such as consumers, resource owners, business firms and of small groups of individual units like industries and markets. In this connection, microeconomics examines the behavior of the industry with regard to determination of its product price, output and employment. It examines how prices of products and factors are determined and how resources are allocated among various uses. Microeconomics tends to offer a detailed treatment of one aspect of economic behavior but ignores interactions with the rest of the economy, in order to preserve the simplicity of the analysis. Macroeconomics has both theoretical and practical significance. Its principle and concepts are used by firms to make decision regarding pricing, marketing resources utilization and profit analysis.
Macroeconomics studies the functioning of an economy as a whole. It studies aggregate or collective behavior of a society in connection with economic choices. The main areas of study include national income, aggregate demand and supply, employment level, inflation, recession international trade. Macroeconomic analysis is extremely useful in formulation of economic policies by the government and monetary authorities. Business firms use macroeconomic data and analyses to formulate present and future business policies forecasting of future trends is an important part of applied macroeconomics.
Key takeaways - Economics studies how societies use their scarce resources to produce and distribute commodities to satisfy unlimited wants of its people.
Basic competitive models gives an answer of the control problems of an economy i.e., who makes the decision of what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce.
There are two participants in the market i.e. Producers and Consumers. In a competitive market there are a large number of buyers and sellers and thus they compete among themselves. Producers compete with each other by providing the desired products to the consumers at the lowest possible price and the consumers compete with one another by paying the price for the products they are willing to buy, while others may not be able to afford the product. This is known as the basic competitive model.
.
Basic assumptions of competitive models / features :
Rational self interested consumers
As consumer behavior assumes that there is a budget constraint through which the consumer makes a rational choice. Rational choice means given his budget constraint a consumer tries to maximize their satisfaction in a consistent manner.
Given their budget constraint, there will be opportunity set of goods and services. Opportunity set refers to the combination of goods and services that the consumer can buy with the given money income and prices of the goods and services. Thus, Rationality assumption about the behavior of consumer implies that they will make choice to promote their self interest.
Profit- Maximising Firms
Economists assume just like consumer the firms will also pursue their self interest in making choice. In terms of firm rational behavior means what goods will be produced and in what quantities and also how those products will be produced as guided by the motive of profit maximization. They also face the constraint of the limited resources.
Competitive market
In the basic competitive model the firm and the consumers do not have any market power to influence the prices of the goods and services they want to sell and buy. Under perfect competition there are large number of buyers and sellers and each firm and consumer is price taker.
The primary objective of all producer is to earn profit. Earning of profits from using resources owned by them also provides incentives to the firms and individuals to produce goods and services efficiently. The prices of goods and resources provides information to the individuals and firms about the relative scarcity of different goods and services.
Property Rights
There are different types of property which individuals and firms can privately own.
Real property: It includes land, buildings, capital equipments etc.
Financial Property: It includes shares and bonds, bank deposits etc.
Intellectual Property: It represents the products of creative effort and includes books written, audio etc.
Property rights should be enforced by the government for efficient use of all the resources, as with the advancement of technology it is a big challenge these days.
Profits and prices: Incentives and Information
Everyone works and saves for wages and interest respectively. If sufficient incentives are not given to them firms will not produce goods and services and bear risk of losing money. The prices of goods and services produced and cost incurred determines the price. Under perfect competition firms are the price takers and have no control over price. They can increase their profits by minimizing the cost of production. Thus profits serve as incentive for the firm to produce efficiently.
The price system working ensures that those individuals and firms will get goods who are willing and able to pay for them. Prices of goods and services indicate how much money individuals are ready to pay for them.
Key takeaways –
- In a competitive market there are a large number of buyers and sellers and thus they compete among themselves.
- Producers compete with each other by providing the desired products to the consumers at the lowest possible price and the consumers compete with one another by paying the price for the products they are willing to buy, while others may not be able to afford the product.
A quantity that can take on more than one value is called a variable. The line along which values of the x variable are measured is called the horizontal axis or x-axis. The line along which values of the y-variable are measured is called the vertical axis or y-axis. The point where the axes of a two-variable graph meet is the origin. A causal relationship exists between two variables when the value taken by one variable directly influences or determines the value taken by the other variable. In a causal relationship, the determining variable is called the independent variable; the variable it determines is called the dependent variable.
A curve is a line on a graph that depicts a relationship between two variables. It may be either a straight line or a curved line. If the curve is a straight line, the variables have a linear relationship. If the curve is not a straight line, the variables have a nonlinear relationship.
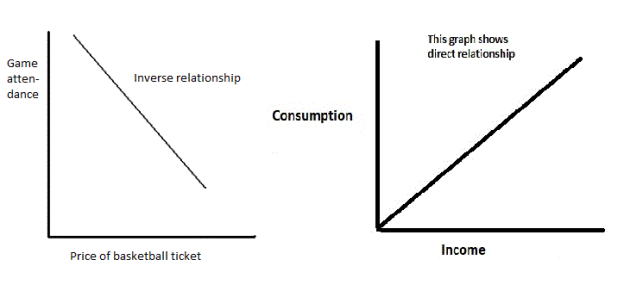
Two variables have a positive relationship when an increase in the value of one variable is associated with an increase in the value of the other variable. It is illustrated by a curve that slopes upward from left to right.
Two variables have a negative relationship when an increase in the value of one variable is associated with a decrease in the value of the other variable. It is illustrated by a curve that slopes downward from left to right.
The horizontal intercept of a curve is he point at which it hits the horizontal axis; it indicates the value of the x variable when the value of the y variable is zero. The vertical intercept of a curve is the point at which it hits the vertical axis; it shows the value of the y-variable when the value of the x-variable is zero. The slope of a line or curve is a measure of how steep it is. The slope of a line is measured by “rise over run”— the change in the y-variable between two points on the line divided by the change in the x-variable between those same two points.
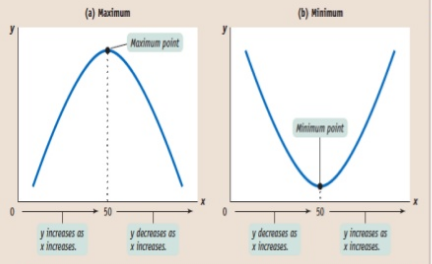
A non linear curve is the one in which the slope is not the same between every pairs of points. A nonlinear curve may have a maximum point, the highest point along the curve. At the maximum, the slope of the curve changes from positive to negative. A nonlinear curve may have a minimum point, the lowest point along the curve. At the minimum, the slope of the curve changes from negative to positive.
Key takeaways –
- A curve is a line on a graph that depicts a relationship between two variables.
REFERENCE
- Karl E. Case and Ray C. Fair, Principles of Economics, Pearson Education Inc., 8th Edition, 2007.
- N. Gregory Mankiw, Economics: Principles and Applications, India edition by South Western, a part of Cengage
- Learning, Cengage Learning India Private Limited, 4th edition, 2007.
- Joseph E. Stiglitz and Carl E. Walsh, Economics, W.W. Norton & Company, Inc., New York, International Student
- Edition, 4th Edition, 2007
- Arthashastra- Dr .Suman