UNIT III
Control
CONCEPT:
Ernest Dale in his book “Theory and Practice of Management” has stated that –
“The modern concept of managerial control envisages a system that not only provides a historical record of what has happened to the business as a whole but also pin points the reasons why it has happened and provides data that enable the chief executive or the departmental head to take corrective steps if he finds he is on the wrong track.”
Further, Koontz, O’Donnell and Weihrich have said-“Controlling as the measurement and correction of the performance of activities of sub-ordinates in order to make sure that enterprise objectives and the plans devised to attain them are being accomplished.”
Therefore, the managerial function of control implies measurement of actual performance comparing it with the standards set by plans and correction of deviations to ensure attainment of objectives according to plans.
Thus, control is an important function of management. It is an essential feature of scientific management. In fact much of the precision of managerial education is focused on the improvement of control techniques. It is generally used for putting restrains over the elements being controlled. In managerial terminology, control is ensuring work accomplishment according to plans. It is a process that guides activity towards some predetermined goals.
Definition:
(1) According to F. E. L. Brech, “Managerial control is checking current performance against pre-determined standards contained in the plans, with a view to ensuring adequate progress and satisfactory performances.”
(2) According to Henri Fayol -“In an undertaking control consists in verifying whether everything occurs in conformity with the plans adopted, the instruction issued and the principle established. Its object is to point out the weakness and error in order to rectify them and prevent occurrence. It operates on everything i.e., things, people and action.”
(3) Dalton E. McFarland has said -“Control in its managerial sense is the presence in a business of that force which guides it to a pre-determined objective by means of pre-determined policies and decision.”
Thus, we see that managerial control is fundamental management function that ensures work accomplishment according to plans. It is concerned with measuring and evaluating performance so as to secure the best results of managerial efforts.
PROCESS:
The top management initially must decide what elements of the environment and the organisation need to be monitored, evaluated and controlled. The four key areas to be monitored and controlled are – the macro environment, mission and objectives, the industry environment and internal operations.
Step # 1. Key Areas to be Monitored:
I. Macro-Environment:
One of the key areas to be monitored is the macro-environment of the company. This area should be focused first. Normally individual companies cannot influence the environment significantly. But the external environmental forces must be continuously- monitored as the changes in the environment influence the implementation of the plans of the company.
II. Mission and Objectives:
This includes modifying any one or more of the areas like company’s mission, objectives, plans, goals, strategy formulation and implementation. The modification depends upon the nature and degree of changes and shifts in the environment.
III. Industry Environment:
The manager also monitors and controls the industry related environment. The environmental forces may not be as they were planned. The changes in the environment may provide new opportunities or pose new threats. The plan, therefore, should be modified accordingly.
The industry environment of the future should be considered by the top management for the purpose of evaluation and control.
IV. Internal Operations:
The manager has to evaluate the internal operations continuously in view of the changes in the macro-environment and industry environment. The manager has to introduce changes in internal operations when changes in the environment affect the plans.
Step # 2. Establishing Standards:
Evaluating an organisational performance is normally based on certain standards. These standards may be the previous year’s achievements or the competitor’s records or the fresh standards established by the management. Qualitative judgements like the qualitative features of the product or service in the last year may be used.
Quantitative measures like Return on Investment (ROI), Return on sales may also be used for judging the performance. Companies should establish the standards for evaluating the performance of the strategies taking several factors into consideration.
The standards may include:
1. Quality of Products/Services.
2. Quantity of Products to be Produced.
3. Quality of Management.
4. Innovativeness/Creativity.
5. Long-term investment value.
6. Volume of sales and/or market share.
7. Financial soundness in terms of return on investment, return on equity capital, market price of the share, earning per share etc.
8. Community and environmental responsibility in terms of amount spent on community development, variety of facilities provided to the community, programmes undertaken for environmental protection and ecological balance etc.
9. Soundness of human resources management in terms of percentage of employee grievances redressed, employee satisfaction rate, employee turnover rate, industrial relations situation etc.
10. Ability to attract, develop and retain competent and skilled people.
11. Use of company’s assets.
12. Production targets, rate of capacity utilisation, design of new products, new uses of existing products, rate of customer complaints about the product quality, suitability of ingredients etc.
13. Corporate image among the customers and general public.
14. Market place performance.
15. Standards relating to the organisational variables include freedom and autonomy, level of control, responsibility, formal organisation and degree of formality and informal organisation scope for innovation and creativity.
Step # 3. Measuring Performance:
The manager has to measure the performance of various areas of the organisation before taking an action. Performance may be measured through quantitative terms or qualitative terms. Reports and statements help to measure the actual performance through quantitative terms and managerial observations help to measure performance through qualitative terms.
Production, sales, profitability, staff cost etc. can be measured through quantitative terms and quality of the product, employee’s performance, attitude etc. can be measured through qualitative terms.
Step # 4. Compare Performance with Standards:
Once the performance of different aspects of the organisation is measured, it should be compared with the predetermined standards. Standards are set to achieve the already formulated organisational goals and plans. Organisational standards are yardsticks and benchmarks that place organisational performance in perspective.
The manager should set standards for all performance areas of the organisation based on organisational goals and strategies. Normally, the standards vary from one company to the other company. Further, they also vary from time to time in the same company. The standards developed by General Electric Company can be used as model standards.
These standards include:
i. Profitability Standards:
They include how much gross profit, net profit, return on investment, earning per share, percentage of profit to sales, the company should earn in a given time period.
ii. Market Position Standards:
These standards include total sales, sales region-wise and product-wise, market share, marketing costs, customer service, customer satisfaction, price, customer loyalty shifts from or to other organisation’s products etc.
iii. Productivity Standards:
These standards indicate the performance of the organisation in terms of conversion of inputs into output. These standards include capital productivity, labour productivity, material productivity etc.
iv. Product Leadership Standards:
They include the innovations and modifications in products to increase the new uses of the existing product, developing new products with new uses etc.
v. Human Resources Standards:
These standards include providing competitive salaries, benefits and different aspects of quality of work life. They also include human resources performance, productivity, turnover rates, absenteeism rates providing challenging and creative jobs etc.
vi. Employee Attitude Standards:
They include employees’ favourable attitude towards the nature of work, organisation, salaries, benefits, working environment, quality of work life, treatment by superiors etc.
vii. Social Responsibility Standards:
All organisations discharge their responsibilities towards different sections of the society. These standards are related to the services of organisations towards community, government, employees, suppliers, creditors etc.
viii. Standards Reflecting Balance between Short-Range and Long-Range Goals:
Short- range and long-range strategies should be balanced successfully. Standards in these areas should bring balance between these two goals.
Step # 5. Take No Action, if Performance is in Harmony with Standards:
If the performances of various organisational areas match with the standards, the manager need not take any action. He should just allow the process to continue. However, he can try to improve the performance above the standards, if it would be possible, without having any negative impact on the existing process.
Step # 6. Take Corrective Action, if Necessary:
Managers should take necessary corrective action, if performance is not in harmony with standards. If the deviation is positive i.e. performance is above the standards continuously, revises the standards. On the contrary, if performance is below standard, take steps to improve the performance.
The managers compare the performance with standards. If they find any deviation between the standards and performance, they should take corrective action to bridge the gap between the standards and performance.
Causes of Deviations:
It is very easy to conclude that someone made a mistake, when deviations are identified. But the deviations maybe the result of an unexpected move by a competitor, or changes in external environment.
Therefore, the manager should consider the following before making a decision, in this regard:
1. Was the cause of deviation internal or external?
2. Was the cause random, or should it have been anticipated?
3. Is the change temporary or permanent?
4. Are the present plans still appropriate?
5. Does the organisation have the capacity to respond to the change needed?
Corrective Action:
Corrective action may be defined as change in a company’s operations to ensure that it can more effectively and efficiently reach its goals and perform its established standards.
Plans that do not achieve standards produce three possible responses viz.:
(i) To revise plans,
(ii) To change standards and
(iii) To take corrective action in the existing process without changing standards and plans.
Change in plans may require a ‘fine tuning’ of the existing strategy or complete changes in plans. If it is realised that the existing standards are unrealistic under the present conditions, the manager should reset the standards taking the existing conditions into consideration.
Corrective action may be as simple as to increase the price or may be as complex as change the chief executive officer. Deviations require re-examination of the company’s mission, objectives, and relationship to its environment, internal strengths, weaknesses and plans. After having an idea of the process of control, now we shall study the types of control. Now, we shall discuss the control techniques.
Key Takeaways:
1. The managerial function of control implies measurement of actual performance comparing it with the standards set by plans and correction of deviations to ensure attainment of objectives according to plans.
2. The top management initially must decide what elements of the environment and the organisation need to be monitored, evaluated and controlled.
Effective Control System (9 Principles of Designing Effective Control System)
Effective Control System (9 Principles of Designing Effective Control System)Managers are responsible for controlling in the organization and a manager must improve the effectiveness of the organization’s control system; as can do a great deal to improve the effectiveness of their control systems.
Controlling is the last step of management where how the implemented plan is working is assessed and evasive actions are taken.
9 principles of the effective control system are;
To design an effective control system without error for the organization; these 9 principles must be followed. They are more than just principles.
These are guidelines for managers for designing a control system that works.
Matching controls to plans and position:
Control techniques should reflect the plans they are designed to follow. Managers need the information that will tell them how the plans for which they are responsible are progressing. Controls should also be tailored to positions, i.e. they may differ in between positions. Some control techniques, such as those involving standard hours and costs, budgets, and various financial ratios, have general application in various situations.
However, none of these techniques are completely applicable in any given situation. Managers should, therefore, be aware, of the critical factors in their plans requiring control, and they must use techniques and information suited to them. Controls should also reflect the place in the organization wherein responsibility for action lies, thereby enabling managers to correct deviations from plans.
Ensuring flexibility to control:
Flexibility is another essential characteristic of an effective control system. This means that the control system itself must be flexible enough to accommodate the change.
In other words, the controls should remain workable in the face of changed plans, unforeseen circumstances, or outright failures.
The illustration may be of an organization whose diverse product lines require 101 different raw materials. The company’s inventory control system must be able to manage and monitor the current levels of inventory for all the 101 materials.
When a change in the product line changes the number of raw materials needed, or when the required quantities of any of the existing materials change, the control system, should be able to accommodate the revised requirements.
Yet the seniors and probably other students with certain problems may simply have to take the course and they will be accommodated in its flexible computerized admission registration system.
Ensuring accuracy:
Control systems must also be accurate managerial decisions based on inaccurate information that may prove costly and harmful. If for example, sales estimates are artificially high, a manager might either cut advertising on the assumption that it is no longer needed or increase advertising to enhance the sale. In either case, the action may not be appropriate. Similarly, a manager, unaware of the hidden production cost, may quote a sales price much lower than is desirable. The accuracy of control systems goes a long way in preventing such damaging upshots.
Seeking objectivity of controls-
As far as possible the information provided by the control system should be objective. If on the other hand, controls are subjective, a manager’s or an executive’s personality may influence judgments of performance and make them less accurate. Thus, the control system should ideally provide objective information to the manager for evaluation and action.
Achieving the economy of controls:
A limiting factor of control: systems are their cost. So to be effective, controls must be worth their cost. Although it sounds simple, it is very difficult to accomplish. If tailored to the job and the size of the enterprise, control will probably be economical. To be precise, control techniques and approaches can be called efficient when they bring to light actual or potential deviations from plans with the minimum of cost.
Tailoring control to individual managers:
Control systems and information are, of course, intended to help individual managers carry out their function of control. If they are not of a type that a manager can or will understand, they will not be useful. What managers cannot understand they will not be useful; what managers cannot understand they will not trust; and what they do not trust they will not use.
Pointing up exceptions:
One of the best ways to make control effective is to make sure that it is designed to point up exceptions. Controls that concentrate on exceptions from planned performance allow managers to benefit from the time-honored exception principle and detect those areas that require their attention.
Fitting the system of control to the organizational culture
An effective control system must fit in with the organizational culture. For example; If employees have been managed without allowing them any participation in decision making, the sudden introduction of a permissive control system will hardly succeed.
On the other hand, in an organization where people have been allowed participation and freedom, the tight control system may fail to produce positive results.
Ensuring corrective action through the control:
An effective control system will disclose where failures are occurring and who is/are responsible for the failures and it will ensure that some corrective action is taken. Control is justified only if deviations from plans are corrected by an appropriate authority. Taking the proper corrective action necessitates sufficient authority to accomplish this task.
Conclusion-
An effective control system is important for an organization to run properly and achieve its goals. Any good control system will pass these 9 principles.
If any part of it is ignored; then controlling the organization’s resources will be very difficult for managers.
Control is a fundamental managerial function. Managerial control regulates the organizational activities. It compares the actual performance and expected organizational standards and goals. For deviation in performance between the actual and expected performance, it ensures that necessary corrective action is taken.
There are various techniques of managerial control which can be classified into two broad categories namely-
Traditional Techniques of Managerial Control
Traditional techniques are those which have been used by the companies for a long time now. These include:
1. Personal Observation
This is the most traditional method of control. Personal observation is one of those techniques which enables the manager to collect the information as first-hand information.
It also creates a phenomenon of psychological pressure on the employees to perform in such a manner so as to achieve well their objectives as they are aware that they are being observed personally on their job. However, it is a very time-consuming exercise & cannot effectively be used for all kinds of jobs.
2. Statistical Reports
Statistical reports can be defined as an overall analysis of reports and data which is used in the form of averages, percentage, ratios, correlation, etc., present useful information to the managers regarding the performance of the organization in various areas.
This type of useful information when presented in the various forms like charts, graphs, tables, etc., enables the managers to read them more easily & allow a comparison to be made with performance in previous periods & also with the benchmarks.
3. Break-even Analysis
Breakeven analysis is a technique used by managers to study the relationship between costs, volume & profits. It determines the overall picture of probable profit & losses at different levels of activity while analyzing the overall position.
The sales volume at which there is no profit, no loss is known as the breakeven point. There is no profit or no loss. Breakeven point can be calculated with the help of the following formula:
Breakeven point = Fixed Costs/Selling price per unit – variable costs per unit
4. Budgetary Control
Budgetary control can be defined as such technique of managerial control in which all operations which are necessary to be performed are executed in such a manner so as to perform and plan in advance in the form of budgets & actual results are compared with budgetary standards.
Therefore, the budget can be defined as a quantitative statement prepared for a definite future period of time for the purpose of obtaining a given objective. It is also a statement which reflects the policy of that particular period. The common types of budgets used by an organization.
Some of the types of budgets prepared by an organisation are as follows,
Modern Techniques of Managerial Control
Modern techniques of controlling are those which are of recent origin & are comparatively new in management literature. These techniques provide a refreshingly new thinking on the ways in which various aspects of an organization can be controlled. These include:
1. Return on Investment
Return on investment (ROI) can be defined as one of the important and useful techniques. It provides the basics and guides for measuring whether or not invested capital has been used effectively for generating a reasonable amount of return. ROI can be used to measure the overall performance of an organization or of its individual departments or divisions. It can be calculated as under-
Net income before or after tax may be used for making comparisons. Total investment includes both working as well as fixed capital invested in the business.
2. Ratio Analysis
The most commonly used ratios used by organizations can be classified into the following categories:
3. Responsibility Accounting
Responsibility accounting can be defined as a system of accounting in which overall involvement of different sections, divisions & departments of an organization are set up as ‘Responsibility centers’. The head of the center is responsible for achieving the target set for his center. Responsibility centers may be of the following types:
4. Management Audit
Management audit refers to a systematic appraisal of the overall performance of the management of an organization. The purpose is to review the efficiency &n effectiveness of management & to improve its performance in future periods.
5. PERT & CPM
PERT (programmed evaluation & review technique) & CPM (critical path method) are important network techniques useful in planning & controlling. These techniques, therefore, help in performing various functions of management like planning; scheduling & implementing time-bound projects involving the performance of a variety of complex, diverse & interrelated activities.
Therefore, these techniques are so interrelated and deal with such factors as time scheduling & resources allocation for these activities.
The term motivation is derived from the word ‘motive”. The word ‘motive’ as a noun means an objective, as a verb this word means moving into action. Therefore, motives are forces which induce people to act in a way, so as to ensure the fulfillment of a particular human need at a time. Behind every human action there is a motive. Therefore, management must provide motives to people to make them work for the organization.
Motivation may be defined as a planned managerial process, which stimulates people to work to the best of their capabilities, by providing them with motives, which are based on their unfulfilled needs.
“Motivation means a process of stimulating people to action to accomplish desired goods.” —William G. Scott
“Motivation is the process of attempting to influence others to do your will through the possibility of gain or reward.” — Flippo
Motivation is, in fact, pressing the right button to get the desired human behaviour. Motivation is no doubt an essential ingredient of any Organisation. It is the psychological technique which really executes the plans and policies through the efforts of others.
Following are the outstanding Features of the concept of motivation:
1. Motivation is a personal and internal feeling:
Motivation is a psychological phenomenon which generates within an individual.
2. Motivation is need based:
If there are no needs of an individual, the process of motivation fails. It is a behavioural concept that directs human behaviour towards certain goals.
3. Motivation is a continuous process:
Because human wants are unlimited, therefore motivation is an ongoing process.
4. Motivation may be positive or negative:
A positive motivation promotes incentives to people while a negative motivation threatens the enforcement of disincentives.
5. Motivation is a planned process:
People differ in their approach, to respond to the process of motivation; as no two individuals could be motivated in an exactly similar manner. Accordingly, motivation is a psychological concept and a complex process.
6. Motivation is different from job satisfaction:
He might choose the second alternative and succeed in getting promotion (goal achievement) thus, his need for promotion would be satisfied and he would start again for the satisfaction of a new need.
1. MASLOW’S NEED HIERARCHY THEORY:
It is probably safe to say that the most well-known theory of motivation is Maslow’s need hierarchy theory Maslow’s theory is based on the human needs. Drawing chiefly on his clinical experience, he classified all human needs into a hierarchical manner from the lower to the higher order.
In essence, he believed that once a given level of need is satisfied, it no longer serves to motivate man. Then, the next higher level of need has to be activated in order to motivate the man. Maslow identified five levels in his need hierarchy. These are now discussed one by one:
1. Physiological Needs:
These needs are basic to human life and, hence, include food, clothing, shelter, air, water and necessities of life. These needs relate to the survival and maintenance of human life. They exert tremendous influence on human behaviour. These needs are to be met first at least partly before higher level needs emerge. Once physiological needs are satisfied, they no longer motivate the man.
2. Safety Needs:
After satisfying the physiological needs, the next needs felt are called safety and security needs. These needs find expression in such desires as economic security and protection from physical dangers. Meeting these needs requires more money and, hence, the individual is prompted to work more. Like physiological needs, these become inactive once they are satisfied.
3. Social Needs:
Man is a social being. He is, therefore, interested in social interaction, companionship, belongingness, etc. It is this socialising and belongingness why individuals prefer to work in groups and especially older people go to work.
4. Esteem Needs:
These needs refer to self-esteem and self-respect. They include such needs which indicate self-confidence, achievement, competence, knowledge and independence. The fulfillment of esteem needs leads to self-confidence, strength and capability of being useful in the organisation. However, inability to fulfill these needs results in feeling like inferiority, weakness and helplessness.
5. Self-Actualization Needs:
This level represents the culmination of all the lower, intermediate, and higher needs of human beings. In other words, the final step under the need hierarchy model is the need for self-actualization. This refers to fulfillment.
The term self-actualization was coined by Kurt Goldstein and means to become actualized in what one is potentially good at. In effect, self- actualization is the person’s motivation to transform perception of self into reality.
According to Maslow, the human needs follow a definite sequence of domination. The second need does not arise until the first is reasonably satisfied, and the third need does not emerge until the first two needs have been reasonably satisfied and it goes on. The other side of the need hierarchy is that human needs are unlimited. However, Maslow’s need hierarchy-theory is not without its detractors.
The main criticisms of the theory include the following:
1. The needs may or may not follow a definite hierarchical order. So to say, there may be overlapping in need hierarchy. For example, even if safety need is not satisfied, the social need may emerge.
2. The need priority model may not apply at all times in all places.
3. Researches show that man’s behaviour at any time is mostly guided by multiplicity of behaviour. Hence, Maslow’s preposition that one need is satisfied at one time is also of doubtful validity.
4. In case of some people, the level of motivation may be permanently lower. For example, a person suffering from chronic unemployment may remain satisfied for the rest of his life if only he/she can get enough food.
Notwithstanding, Maslow’s need hierarchy theory has received wide recognition, particularly among practicing managers. This can be attributed to the theory’s intuitive logic and easy to understand. One researcher came to the conclusion that theories that are intuitively strong die hard’.
2. MCGREGOR’S PARTICIPATION THEORY:
Douglas McGregor formulated two distinct views of human being based on participation of workers. The first basically negative, labeled Theory X, and the other basically positive, labeled Theory Y.
Theory X is based on the following assumptions:
1. People are by nature indolent. That is, they like to work as little as possible.
2. People lack ambition, dislike responsibility, and prefer to be directed by others.
3. People are inherently self-centered and indifferent to organisational needs and goals.
4. People are generally gullible and not very sharp and bright.
On the contrary, Theory Y assumes that:
1. People are not by nature passive or resistant to organisational goals.
2. They want to assume responsibility.
3. They want their organisation to succeed.
4. People are capable of directing their own behaviour.
5. They have need for achievement
What McGregor tried to dramatise through his theory X and Y is to outline the extremes to draw the fencing within which the organisational man is usually seen to behave. The fact remains that no organisational man would actually belong either to theory X or theory Y. In reality, he/she shares the traits of both. What actually happens is that man swings from one set or properties to the other with changes in his mood and motives in changing environment.
3. HERZBERG’S MOTIVATION HYGIENE THEORY:
The psychologist Frederick Herzberg extended the work of Maslow and proposed a replacement motivation theory popularly referred to as Herzberg’s Motivation Hygiene (Two-Factor) Theory. Herzberg conducted a widely reported motivational study on 200 accountants and engineers employed by firms in and around Western Pennsylvania.
He asked these people to explain two important incidents at their jobs:
(1) When did you feel particularly good about your job, and
(2) When did you feel exceptionally bad about your job? He used the critical incident method of obtaining data.
The responses when analysed were found quite interesting and fairly consistent. The replies respondents gave once they felt good about their jobs were significantly different from the replies given once they felt bad. Reported good feelings were generally related to job satisfaction, whereas bad feeling with job dissatisfaction. Herzberg labeled the work satisfiers motivators, and he called job dissatisfies hygiene or maintenance factors. Taken together, the motivators and hygiene factors have become referred to as Herzberg’s two-factor theory of motivation
Herzberg’s motivational and hygiene factors are shown in the Table 17.1
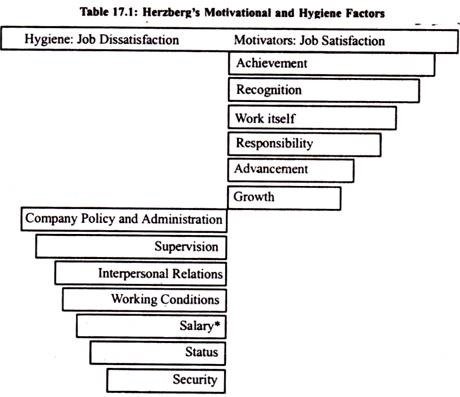
According to Herzberg, the other of satisfaction isn't dissatisfaction. The underlying reason, he says, is that removal of dissatisfying characteristics from a job doesn't necessarily make the job satisfying. He believes in the existence of a dual continuum. The other of ‘satisfaction’ is ‘no satisfaction’ and therefore the opposite of ‘dissatisfaction’ is ‘no dis-satisatisfaction’.
According to Herzberg, today’s motivators are tomorrow’s hygiene because the latter stop influencing the behaviour of persons once they get them. Accordingly, one’s hygiene could also be the motivator of another.
However, Herzberg’s model is labeled with the subsequent criticism also:
1. People have a tendency to take credit themselves when things go well. They blame failure on the external environment.
2. The theory basically explains job satisfaction, not motivation.
3. Even job satisfaction isn't measured on an overall basis. it's not unlikely that an individual may dislike a part of his/ her job, still thinks the job acceptable.
4. This theory neglects situational variable to motivate an individual.
Because of its ubiquitous nature, salary commonly shows up as a motivator also as hygiene.
Regardless of criticism, Herzberg’s ‘two-factor motivation theory’ has been widely read and a few managers seem untaminar together with his recommendations. the most use of his recommendations lies in planning and controlling of employees work.
Financial Incentives/ Techniques of Motivation:
Financial techniques refer to monetary rewards. Incentives are nothing but the inducements provided to employees in order to motivate them. There should be direct relationship between efforts and rewards, financial reward should be substantial in value and must be in parity with others.
Under -paying staff sends the message that your firm doesn’t value their work. Money is not a prime motivator but this should not be regarded as a signal to reward employees poorly or unfairly.
The financial incentives include:
1. Pay and Allowances:
It includes basic pay, grade pay, and dearness allowance; travelling allowance, pay increments, etc. Good pay and allowances help the organization to retain and attract capable persons.
However, good pay and allowances need not motivate all the people, especially who are enjoying security of job in government organizations and those for whom corruption is a way of life.
Some of the other issues are associated with bad attitudes, grievances, absenteeism, turnover, poor organizational citizenship, and adverse effect on employees’ mental and physical health.
2. Incentive Pay:
Incentive pay plans are meant to increase output, which can be measured quantitatively. For incentive plan targets, the employees must have confidence that they can achieve the targets.
3. Gain Sharing:
It is a reward system in which team members earn bonus for increasing productivity or reduce wastages. To illustrate, if the wastage is reduced from 5% to less the benefits may be shared equally with the team.
4. Profit Sharing:
It means sharing of profits with the employees by way of distribution of bonus. Profit sharing plan has its shortcomings – one, that it has become a regular feature in government departments irrespective of performance and two, it may have no relation with individual efforts.
5. Stock Options:
Many companies use employee stock options plans to compensate, retain, and attract employees. These plans are contracts between a company and its employees that give employees the right to buy a specific number of the company’s shares at a fixed price within a certain period of time.
Employees who are granted stock options hope to profit by exercising their options at a higher price than when they were granted. In India, stock options have primarily been used as a retention tool for a more selective group of employees.
6. Retirement Benefits:
It includes the accumulated provident fund, gratuity, leave encashment and pension. The provision of terminal benefits provides assurance to employees during the service for their future
Non-financial Incentives/Techniques:
Non-financial incentives do not involve money payments. These are also important in motivating employees as they bring in psychological and emotional satisfaction to them.
These include so many techniques. People do work for money-but they work even more for meaning in their lives. In fact, they work to have fun.
Some of the important non-financial incentives include:
1. Job security:
Nothing can motivate a worker, appointed temporarily, better than provision of job security. Even if a temporary worker puts in greater efforts, lack of job security will always pose a threat. If such a worker is given job security, he will be more committed to the organization.
2. Challenging work:
Workers, who are dynamic in nature, do not show preference for routine jobs. They are always ready to accept challenging assignments, challenge can be brought through mentoring, job redesigning – job enlargement and job enrichment. Understand the capabilities of every individual in the organization and accordingly assign him work.
3. Recognition:
It is important that the employer recognizes hard work. Even a word of appreciation from him would motivate the employees to maintain the same level of performance or do even better. Employees ranked a personal ‘thank you’ as the most sought after form of recognition, followed by a handwritten note of appreciation from the boss.
4. Better job Titles:
Job titles do matter. Employees do show preference for certain designations. A salesman, for example, would like to be designated as a sales executive and a sweeper to be Sanitary Inspector.
5. Opportunities for Advancement:
There should never be a stagnation point for any employee during the prime time of his career. The employer must always provide opportunities for his employees to perform well and move up in the hierarchy.
6. Empowerment:
To stimulate an employee is his involvement in certain crucial decisions. For example, if the management decides to buy a new machinery for the factory, the workers’ viewpoints may be secured before making the final decision. The management should avoid unilateral decisions on such matters.
7. Competition:
The management can encourage healthy competition among the employees. This would, certainly, motivate them to prove their capabilities. The management can also rank the employees according to performance. Such of those employees who have performed very well may be given merit certificates.
8. Job Rotation:
By job rotation we mean that the employees will be exposed to different kinds of job. This certainly would break the monotony of employees. For example, in a bank an employee may work in the Savings Bank Section for sometime after which he may be posted to the cash section. Such a change not only motivates the employees to perform well but also prepares him to be versatile.
9. Lead by Example — be passionate and energetic:
Leaders should demonstrate the attitudes, values, actions, and mindsets that they want among their staff. Leaders are always considered as role models.
10. Encourage the use of humour and creativity:
Incorporating humour into the workplace can alleviate stress and create a more positive environment for everyone. Strategies to enhance humour include having a daily cartoon or joke sent to all staff via e-mail, encouraging laughter, finding fun in events that did not turn out as planned or expected etc.
11. Treat your people as human beings – neither inferior, nor superior:
Show trust and respect, motivate them for creativity, create a ‘safe-to-risk environment’, keep them informed of relevant developments inside the organisation, mistakes be treated as learning tools instead of blaming them, act as an advocate for their employees and be a visible champion for them, provide resources and support required by staff to complete their jobs, promote and provide two-way feedback, address stress and burnout, and implement work/life balance initiatives.
Meaning of Leadership
A Leader moves others to act while at the same time coordinating with the help of demonstration. They should be harmonious enough for others to follow their requests, and they should have the basic speculation aptitudes to realize the most ideal approach to utilize the assets available to an association. In business, administration is connected to execution, and any authority definition needs to consider.
In this way, while initiative isn't characteristically connected to benefit, the individuals who are seen as compelling Leaders in corporate settings are the ones who increment their organization's main concern. While there are individuals who appear to be normally invested with more administration capacities than others, anybody can figure out how to turn into a Leader by improving specific abilities. History is loaded with individuals who, while having no past initiative experience, have ventured to the front in emergencies and convinced others to follow their recommended game-plan. They had attributes and characteristics that helped them to venture into parts of authority. The terms administration and the managements will in general be utilized conversely, yet they're not the equivalent. Initiative requires characteristics that stretch out past administration obligations.
The two chiefs and directors need to deal with the assets available to them, however obvious initiative requires more. For instance, chiefs might possibly be depicted as moving by individuals working under them; however a Leader must move the individuals who follow them. Another distinction among Leaders and chiefs is that Leaders accentuate development regardless of anything else.
THE MAIN LEADERSHIP STYLES:
1. Autocratic or Authoritarian Style:
It is also known as leader centered style. Under this style of leadership there is complete centralization of authority in the leader i.e. authority is centered in the leader himself. He has all the powers to make decisions. There is no two ways communication, only downward communication is used.
It is leader who can only communicate, he cannot be communicated. He uses coercive measures. He adopts negative method of motivation. He wants immediate obedience of his orders and instructions. Any breach on the part of subordinates invites punishment. There is no participation from the subordinates in decision making. Leader thinks that he is the only competent person. Under autocratic style no time is wasted in two way communication for seeking opinion or advice. The task gets completed on time.
Edwin. B. Flippo has divided autocratic style of leadership into following three:
(a) Hard Boiled or Strict Autocrat:
He uses negative influence and expects that his orders should be obeyed by the employees immediately. Non compliance of his orders invites punishment. His outlook is “pay for performance”. He makes all decisions and does not reveal anything to anyone.
He is quite rigid on performance. This style is useful for newly employed or the employees having no experience. But this style should not be adopted when employees by nature are hard workers, experienced and understand their responsibility fully.
(b) Benevolent Autocrat:
He uses positive influences and develops effective human relations. He is known as paternalistic leader. He showers praise on his employees if they followed his orders and invites them to get the solutions of the problems from him.
He assumes the status of a parent. He feels happy in controlling all the actions of his subordinates. He wants complete loyalty from his subordinates. He hates disloyalty and punishes disloyal employees. He takes all the decisions and does not want any interference from anyone. This style of leadership is useful only when subordinates do not want to take any responsibility and wants close supervision.
(c) Manipulative Autocrat:
He is manipulative by nature and creates a feeling in the minds of his subordinates and workers that they are participating in decision making process. Like the two other types he also makes all decisions by himself. Non compliance of his orders invites punishment.
2. Democratic or Participative Style:
This style of leadership is also known as group centered or consultative leadership. Under this style leaders consult the group and solicit their opinion and participation from the following in decision making process. Democratic leaders confer authority on the group and after their consultation decisions are taken.
Leaders under this style encourage discussion by the group members on the problem under consideration and arrive at a decision by consensus. Two way communication channels are used. Participation or involvement in decision making process is rewarded. Under this style positive motivation techniques are used.
Exchange of ideas among subordinates and with the leader is given encouragement. Human values get their due recognition. Leaders give more freedom to their subordinates and invite to share responsibility.
Subordinates are asked to exercise self control. Leaders do not delegate authority to subordinates to make decisions but their opinions are sought before arriving at a decision. Under this style subordinates feel that their opinions are honoured and they are given importance and not feel neglected. The leaders delegate responsibility according to experience and knowledge of the subordinates.
Cooperation of subordinates are sought that lead to creativity. This increases the productivity too. This is a very effective style where the subordinates are talented and qualified. It develops a sense of confidence among subordinates and they derive job satisfaction by working under participative leader. It improves quality of decision as it is taken after due consideration to valued opinions of the talented subordinates.
This style of leadership is not free from demerits. It takes more time to arrive at a decision. It is less effective if participation from the subordinates is for name sake. Consulting others while making decisions go against the capability of the leader to take decisions. Leader has to waste lot of time in pursuing subordinates. If employees refuse to work as a team with other members of the group renders the style of leadership ineffective.
3. Laissez-faire or Free Rein Style:
Under this style of leadership there is virtual absence of direct leadership. It is, therefore, known “as no leadership at all.” There is complete delegation of authority to subordinates so that they can make decisions by themselves. There is free flow of communication.
Subordinates have to exercise self control. They also have to direct their activities. It is people oriented style of leadership in true sense of the term. Leader gives free hand to his followers or subordinates. Absence of leadership may have positive and sometimes negative effects.
Free rein leadership may be effective if members of the group are highly committed. The negative aspect creates blemishes on the leader himself because of his incompetency in leading his people. It casts aspersions on the leader. However, this style of leadership provides chance for competent members of the group to fulfill and attain self actualization needs.
It gives chance to take initiative to the member. It gives chance for open discussion and creativity to all. It has free work environment. Members feel insecure and develop frustration for lack of specific decision making authority.
This style of leadership suffers a setback when some member of the group refuses to cooperate. It cannot take proper decision. It may lead to chaos and confusion. This style may work effectively when the subordinates are highly competent, able to exercise self control and can have the capacity to take decisions.
4. Bureaucratic Style:
Under this leadership the behaviour of leader is determined by rules, regulations and procedure. These rules and regulations are followed by the leader and the subordinates both. No one can escape. Hence, the management and administration has become a routine matter. This is apathetic to the employees because they know that they cannot do anything in this regard. It is the rules that determine their minimum performance. Rules allow work without participation and without committed to work. A lot of paper work is involved. Rules lead to red tapism. This style of leadership centres round the rules.
5. Manipulative Style:
As the name suggests the leader manipulates the employees to attain his objectives. Manipulative leader is quite selfish and exploits the aspirations of the employees for his gains. He knows very well the needs and desires of the employees but he does very little to fulfil them. He views these needs and desires as a tool to fulfill his aims. Employees do not trust such leader. He has to face the resentment of the employees at times.
6. Paternalistic Style:
The paternalistic style of leadership maintains that the fatherly attitude is the right one for better relationship between the manager and the employees. All are working together like a family. According to this style of leadership more benefits are to be provided to make the employees happy and extract maximum output from them. It believes in the concept that the happy employees work better and harder.
7. Expert Leadership Style:
The expert leadership style emerged as a result of complex structure of modern organisations. The leadership is based on the ability, knowledge and competence of the leader. He handles the situation skillfully with his talent. The employees feel relieved as they are working under a person who is expert and can handle the situation ably without any problem. But the expert may fail to handle the situation which does not belong to the area of his expertise.
Key Takeaways:
References-