Unit I
Indian Economic Environment
Concept:
Economic environment:
It is macroeconomic indicators that strategists study to influence their decisions. These indicators shape the health and well-being of the economy. These are determinants of a company's ability to make a profit and generate wealth. More important is the maximization of wealth, as it means maximizing profits and returning them to investments that generate more income.
Components:
The components of the economic environment are:
I. General economic situation:
The general economic situation that prevails in the economy is a determinant of economic prosperity and community well-being. These economic conditions are variables in which the amount of national income, per capita income, economic resources, income and wealth distribution, and economic development determine people's economic prosperity.
Revenue and its distribution determine the business outlook and therefore the business strategy. In an economy where it is low and per capita is relatively low, demand will decline. This pessimistic situation does not attract business people who invest in and execute manufacturing and marketing activities.
On the other hand, in an economy where the income of the economy is increasing, it leads to more and more investment and entry into industrial and marketing activities. In India, the backbone of the Indian economy, the Middle, is ready to increase income and invest in business.
Even NRI considers it beneficial to invest surplus income in this way, helping the Indian economy to become stronger and thus benefit from profits.
II. Economic system:
The economy is an arrangement that encourages the use of free resources to generate and distribute income, based on some accepted economic philosophies. Economy around the world is widely linked to Kabbalism, socialism, and communism as a hybrid economy called a pure variety or mixed economy.
India is the best example of a mixed economy, with the benefits of capitalism and socialism in one focus, eliminating the disadvantages of pure socialism or capitalism.
Capitalism gives maximum economic freedom in the management of economic activity, socialism talks about maximum domination by the state, mixed economy is freedom and the role of the state in which both the public and private sectors support each other. I have.
The collapse of the mighty nation formed in the early 20th century had to kick a bucket for a period of 100 years. Today, the Soviet Union is divided into small nations that were one of the greatest forces in the world linked to socialist ideology.
III. Economic policy:
It is the appropriate and timely economic policies adopted and implemented by the government that determine the fate of the state and its citizens. Think about India before 1991 and now. The Indian economy is on the verge of collapse and foreign exchange reserves were enough to pull another eight days.
It was a change in personality as a political leader and the brain behind them, together they freed India from control and opened the Indian economy to the whole world.
Private and public sector businesses that worked under the umbrella of protection were set up and faced the challenge of changing competition. Which foreign companies couldn't replace them as Indian players became global players?
IV. Economic growth:
Economic growth or development is the rise and maintenance of per capita income for all individuals who are members of the economy. It is economic growth, which represents increased consumer spending and lower pressure in the industrial sector, that provides more opportunities and enables businesses to withstand the severity of the threat. Other methods also apply. Declining economic growth and lower consumer spending will increase pressure and reduce profitability.
V. Interest rate:
Interest rates affect the demand for goods and services in the economy when they are purchased through borrowing. If interest rates are low, the demand for the product may be durable or non-durable. This gives Philip to a growing industry.
The opposite is true if the rate is high. Today, R.B.I is emerging at lowest interest rates to increase demand for durable and non-durable consumer goods, which will bring the Indian economy out of pessimism and tomorrow's rut.
The cost of capital also depends on interest rates. When they are getting capital at the lowest rates, the companies will encourage all companies to have ambitious plans and strategies in the case of borrowed funds.
VI. Exchange rate:
Exchange rates represent currency conversions to other currencies. It may be hard or soft. In 1991, the Indian Rupee was devalued to make Indian products cheaper in the global market to boost Indian exports. This was a great opportunity for all Indian exporters to export more commodities and reserves and earn forex.
Today, foreign exchange reserves are at a record high of Rs 200 billion, at least costly to boost quality production. Indian exporters do so only if they regularly understand and implement three strategies for export cost, export quality, and export volume. Therefore, it is the exchange rate that determines the fate of a country.
Importance of economic trends: Income; Savings and Investments, Industry; Trade and Balance of Payments, Money; Finance; Prices
Income
Income is the glide of cash to a person at a factor of time. Thus, earnings may be expressed as Real earnings=Money earnings/charge level.
Some standards of earnings are-
1. National earnings/ gross home product at marketplace charge: It is the sum overall of cash price of all of the very last items and offerings produces inside home territory of a rustic all through a monetary 12 months. Gross Domestic Product measures the mixture manufacturing of very last items and offerings taking vicinity in the home financial system all through a 12 months.
GDP=C+I+G+(X-M)
Where, C=consumption
I=earnings
G=Govt. Expenditure
X= export
M=import
2. Gross countrywide product (GNP): It is marketplace charge of all items and offerings produced in a 12 months via way of means of citizens of a rustic in the home territory in addition to abroad.
GNP=GDP+NFIA
3. Net countrywide product at marketplace charge (NNP): its miles the marketplace price of internet output of very last items and offerings produces via way of means of an financial system all through a 12 months and internet component earnings from abroad.
NNP=GNP-Depreciation
4. Personal earnings (PI): It refers to the whole cash earnings obtained via way of means of people and families of a rustic from all feasible reasserts earlier than direct taxes.
PI= NI-Corporate earnings taxes-undistributed company profits-social protection contribution+ Transfer payments.
5. Disposable earnings (DI): It is the earnings left with people after fee of direct taxes from non-public earnings.
DI= PI- direct taxes.
6. Per capital earnings: It is calculated via way of means of dividing the countrywide earnings of the united states via way of means of the whole populace of a rustic.
Per capital earnings= Total countrywide earnings/overall countrywide populace.
Savings and Investments
Savings
Savings is that a part of earnings that isn't always consumed. In different words,
S =Y –C
Where, S= Savings
Y= Income
C= Consumption
Investment
Investment is described as addition to the inventory of bodily capital (inclusive of machines, buildings, roads etc., i.e. something that provides to the destiny effective capability of the economic system) and modifications withinside the inventory (or the inventory of completed goods) of a producer. Investment choices with the aid of using producers, inclusive of whether or not to shop for a brand new machine, depend, to a massive extent, available in the marketplace fee of interest. However, for simplicity, we anticipate right here that corporations plan to make investments the equal quantity each year. We can write the ex-ante funding call for as
I = I/
Where I/is a high-quality steady which represents the autonomous (given or exogenous) funding withinside the economic system in a given year.
Industry
Industry refers to all monetary hobbies this is worried with primary, secondary and tertiary sports manufacturing of goods, extraction of minerals or the availability of services. Industries may be labelled on the idea of uncooked substances, length and ownership. For instance, fabric enterprise, car enterprise, meals processing enterprise etc.
On the basis of raw materials, ownership and size the industry is classified as depicted in figure 1
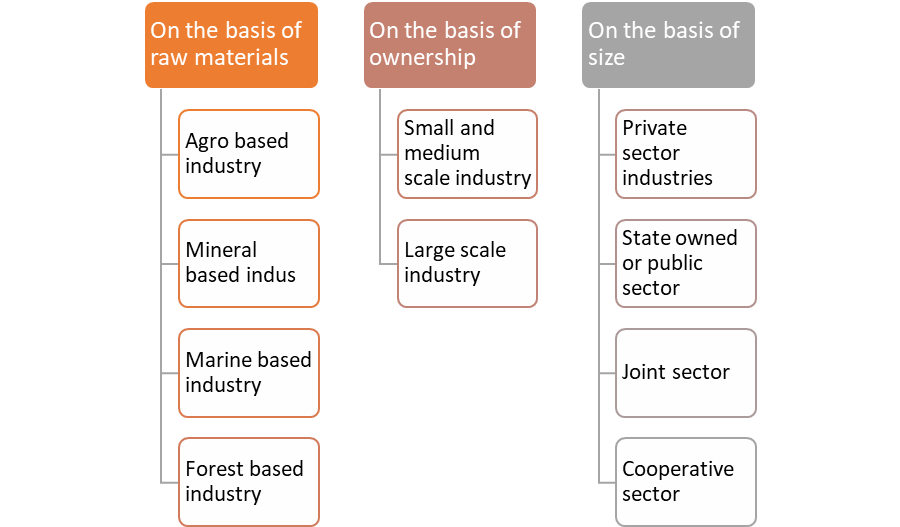
Figure 1: Classification of industry
a) On the idea of uncooked substances
1. Agro primarily based totally enterprise: It makes use of use plant and animal primarily based totally merchandise as their uncooked substances. For instance, meals processing, vegetable oil, cotton fabric, dairy merchandise and leather-based industries etc.
2. Mineral primarily based totally enterprise: Such industries make use of use mineral ores as their uncooked substances for the manufacture of some of different merchandise, including heavy machinery, constructing substances and railway coaches etc.
3. Marine primarily based totally enterprise: Such industries use merchandise from the ocean and oceans as uncooked substances. Industries processing sea meals or production fish oil are a few examples
4. Forest primarily based totally enterprise: Such industries make use of utilise wooded area produce as uncooked substances. The industries related to forests are pulp and paper, pharmaceuticals, furnishings and homes are a number of the examples.
b) On the idea of length
1. Small and medium industries: Such industries make much less investment. For instance village and cottage industries like handloom and handicraft, brass metallic enterprise.
2. Large scale industries: Such industries make large investment. For instance, car enterprise, telecommunication enterprise etc.
c) On the idea of ownership
1. Private enterprise: Such industries are owned and operated via way of means of people or a set of people. For instance, Reliance industries ltd.
2. Public/ kingdom owned enterprise: The public quarter industries are owned and operated via way of means of the government. For instance, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, SAIl etc.
3. Joint quarter: Such industries are owned and operated via way of means of the kingdom and people or a set of people. For instance, MarutiUdyog Limited.
4. Co-operative: Such industries are owned and operated via way of means of the manufacturers or providers of uncooked substances, employees or both. For instance, Anand Milk
Union Limited, AMUL milk etc.
Factors affecting area of enterprise
Some of the important factors that affect the location of industry are highlighted in figure 2-
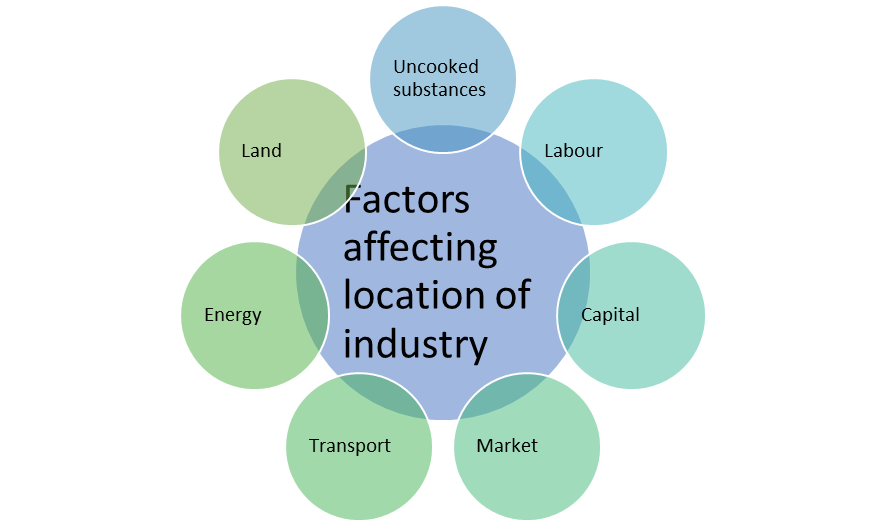
Figure 2: Factors affecting location of industry
1. Availability of uncooked substances:
Availability and get admission to uncooked substances impacts on area of an enterprise. Labour industries are positioned wherein reasonably-priced labour is to be had, Iron and Steel industries are positioned Jamshedpur due to wealthy in iron ore.
2. Availability of labour
It impacts on area of labour extensive enterprise due to the fact the enterprise can get massive range of labour at low cost. For instance, Bangladesh, India etc. has many labour extensive industries.
3. Accessibility to capital
Easy and handy accessibility to credit score for start-ups and current industries ends in advertising of extra industries. Govt. Of India commenced to release many schemes for advertising of industries. For instance, MUDRA loan, start-up India, make in India etc.
4. Market gets admission to
Industry will localise in the ones regions it could without difficulty get admission to the marketplace. It will assist them to continue to exist and develop withinside the marketplace.
5. Transport
There must be desirable conversation and transportation hyperlink for transporting the goods to the marketplace vicinity from the vicinity of manufacturing.
6. Availability of energy
Energy like electricity, gas, net etc. must be to be had withinside the vicinity wherein the enterprise is positioned.
7. Availability of land
An enterprise wishes massive property to installation its manufacturing unit. Thus an enterprise will discover in the ones regions wherein massive location of land is to be had.
Trade and Balance of Payments
Balance of payment (BOP)
The stability of bills (BoP) facts the transactions in items, offerings and belongings among citizens of a rustic with the relaxation of the sector for a certain term generally a year. There are essential debts withinside the BoP — the modern account and the capital account.
The classification of BOP is shown in figure 3
Figure 3: Classification of BOP
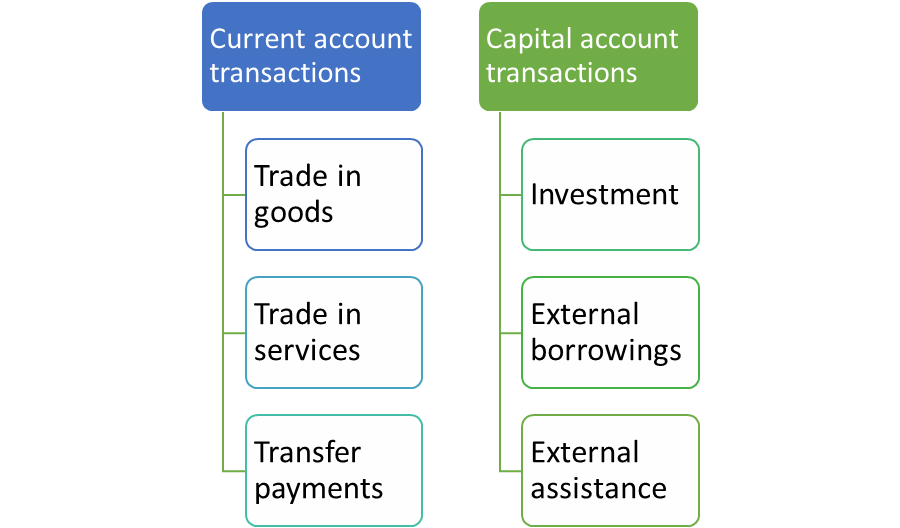
a) Current account transactions:
It refers to the ones forex transactions which does now no longer purpose modifications withinside the asset and legal responsibility role of the country. Current Account is the document of change in items and offerings and switch bills. A surplus modern account manner that the kingdom is a lender to different international locations and a deficit modern account manner that the kingdom is a borrower from different international locations.
i. Trade in items consists of exports and imports of items.
Ii. Trade in offerings consists of aspect profits and non-aspect profits transactions.
Iii. Transfer bills are the receipts which the citizens of a rustic get for ‘free’, while not having to offer any items or offerings in go back. They encompass gifts, remittances and grants.
b) Capital account transactions:
It refers to the ones forex transactions which purpose modifications withinside the asset and legal responsibility role of the country. For example, buy of asset in overseas country, go back of mortgage, External business borrowings etc. It encompass the components-
a. Foreign direct funding and overseas portfolio funding.
b. External borrowings via debt, mortgage from different international locations, global economic companies.
c. External aids like Govt. Aid, intergovernmental mortgage, bilateral mortgage etc.
Balance of Trade (BOT)
It shows the distinction among a rustic's imports and its exports of visible/merchandised objects. Balance of change is the biggest element of a rustic's stability of bills. Debit objects of BOT encompass imports, overseas aid, and home spending overseas and home investments overseas. Credit objects of BOT consist of exports, overseas spending withinside the home economic system and overseas investments withinside the home economic system. When exports are more than imports than the BOT is beneficial and if imports are more than exports then its miles unfavourable.
Difference between BOP and BOT
- Meaning
The balance of payments is the difference between payments and total revenues of a particular economy over a particular period of time, while the trade balance is the difference between imports and exports of a particular economy over a particular period of time.
b. Range
The trade balance captures all visible and invisible economic transactions in the world. The trade balance, on the other hand, captures the value of all import and export goods.
c. Economic view
The trade balance gives a big picture of the strength of a particular economy, while the trade balance gives a partial view based on imports and exports.
d. Capital transfer
The balance of payments includes capital transfers, but the trade balance does not include capital transfers.
e. Transaction
The balance of payments records transactions that occur in connection with both goods and services transactions, while the trade balance records transactions that occur in connection with goods only.
f. Calculation mode
The balance of payments is calculated by adding up the reserve balance, current account balance, and capital account balance. On the other hand, the trade balance is the value of exports minus the value of imports.
g. Net effect
On the balance of payments, the net impact is always zero. However, in the trade balance, the net effect is either positive, negative, or zero.
Money
Money is a medium of alternate. In advance time barter device became prevailed for wherein items are exchanged with gods. But in a while cash is taken into consideration as a medium of alternate for its convenience. The function/functions of cash are-
1) It acts as a medium of alternate.
2) It acts as a handy unit of account.
3) It can act as a shop of value for individuals.
Demand for cash
People preference to keep cash stability extensively from motives-
1. The Transaction Motive:
The important cause for containing cash is to perform transactions. Suppose you earn Rs a hundred on the primary day of each month and run down this stability lightly over the relaxation of the month. Thus your coins stability at the start and stop of the month are Rs a hundred and 0, respectively. Your common coins preserving can then be calculated as (Rs a hundred + Rs 0) ÷ 2 = Rs 50, with that you are making transactions really well worth Rs a hundred in line with month. Hence your common transaction calls for cash is identical to 1/2 of your month-to-month profits, or, in different words, 1/2 of the cost of your month-to-month transactions. Consider, next, a -character financial system which includes entities – a corporation (owned through one character) and a employee. The corporation will pay the employee a income of Rs a hundred at the start of each month. The employee, in turn, spends this profits over the month at the output produced through the corporation – the best right to be had on this financial system. Thus, at the start of every month the employee has a cash stability of Rs a hundred and the corporation a stability of Rs 0. On the ultimate day of the month the photo is reversed – the corporation has accumulated a stability of Rs a hundred via its income to the employee. The common cash preserving of the corporation in addition to the employee is identical to Rs 50 each. Thus the overall transaction call for cash on this financial system is identical to Rs a hundred. The overall extent of month-to-month transactions on this financial system is Rs 200 – the corporation has offered its output really well worth Rs a hundred to the employee and the latter has offered her offerings really well worth Rs a hundred to the corporation. The transaction call for cash of the financial system is once more a fragment of the overall extent of transactions withinside the financial system over the unit length of time. In general, therefore, the transaction call for cash in an financial system, MdT,
Can be written in the following form
MdT= k.T
Where, T is the overall cost of (nominal) transactions withinside the financial system over unit length and okay is a nice fraction.
2. The Speculative Motive:
A person may also keep her wealth withinside the shape of landed property, bullion, bonds, cash etc. For simplicity, allow us to membership all sorts of property aside from cash collectively right into an unmarried class called ‘bonds’. Typically, bonds are papers bearing the promise of a destiny movement of financial returns over a sure length of time. These papers are issued through governments or companies for borrowing cash from the general public and they may be tradable withinside the marketplace. The fee of a bond is inversely associated with the marketplace charge of hobby. Different human beings have specific expectancies concerning the destiny actions withinside the marketplace charge of hobby primarily based totally on their personal facts concerning the financial system.
Speculations concerning destiny actions in hobby charge and bond expenses deliver upward push to the speculative call for cash. When the hobby charge could be very excessive anyone expects it to fall in destiny and as a result anticipates capital profits from bond-preserving. Hence human beings convert their cash into bonds. Thus, speculative call for cash is low. When hobby charge comes down, an increasing number of human beings count on it to upward push withinside the destiny and assume capital loss. Thus they convert their bonds into cash giving upward push to an excessive speculative call for cash. Hence speculative call for cash is inversely associated with the charge of hobby.
Assuming a simple form, the speculative demand for money can be written as
MdS= 
Where r is the market rate of interest and rmax and rmin are the upper and lower limits of r, both positive constants. It is evident from equation that asr decreases from rmax to rmin, the value of MdSincreases from 0 to α.
Finance
Finance may be defined as the art and science of managing money. It includes financial service and financial instruments. Finance also is referred as the provision of money at the time when it is needed.
According to Khan and Jain, “Finance is the art and science of managing money”.
The figure 4 shows that finance can be classified into two major parts:
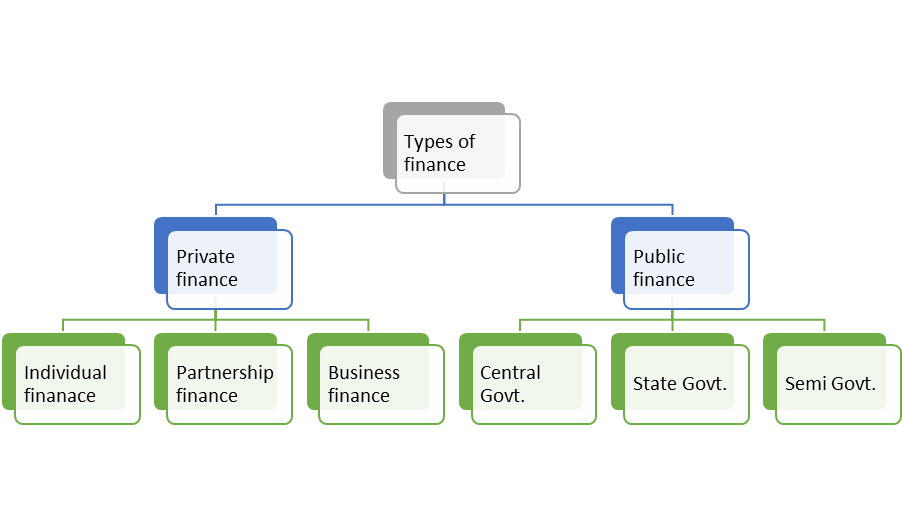
Figure 4: Types of finance
a) Private finance:
Private finance includes the individual, firms, business or corporate financial activities to meet the requirements.
1) Individual/personal finance is concerned managing one’s savings and investment. It covers budgeting, banking, insurance, mortgages, investment, tax, retirement planning etc. of an individual.
2) Partnership firm finance refers to the managing of savings and investment of partnership firm.
3) Business finance is concerned with planning, acquisition and control of funds/capital of business concern. Different sources of business finance are shares, debentures, bonds, borrowings from financial institutions etc.
b) Public finance:
Public Finance which concerns with revenue and disbursement of Government such as Central Government, State Government and Semi-Government Financial matters.
1) Government revenues are income of government earned from income tax, corporate tax, GST, non-tax items like fees, fines, royalty etc.
2) Public expenditure is the money spent by government entities on infrastructure, defence, education, health, housing, administration etc.
Key takeaways:
- The general economic situation that prevails in the economy is a determinant of economic prosperity and community well-being.
- Revenue and its distribution determine the business outlook and therefore the business strategy.
- The economy is an arrangement that encourages the use of free resources to generate and distribute income, based on some accepted economic philosophies.
- Private and public sector businesses that worked under the umbrella of protection were set up and faced the challenge of changing competition. W
- Interest rates affect the demand for goods and services in the economy when they are purchased through borrowing.
- Today, foreign exchange reserves are at a record high of Rs 200 billion, at least costly to boost quality production.
- Income is the glide of cash to a person at a factor of time.
- Personal earnings (PI): It refers to the whole cash earnings obtained via way of means of people and families of a rustic from all feasible reasserts earlier than direct taxes.
- Investment is described as addition to the inventory of bodily capital (inclusive of machines, buildings, roads etc., i.e. something that provides to the destiny effective capability of the economic system) and modifications withinside the inventory (or the inventory of completed goods) of a producer.
- Industry refers to all monetary hobbies this is worried with primary, secondary and tertiary sports manufacturing of goods, extraction of minerals or the availability of services.
- The public quarter industries are owned and operated via way of means of the government.
- Industry will localise in the ones regions it could without difficulty get admission to the marketplace.
- The stability of bills (BoP) facts the transactions in items, offerings and belongings among citizens of a rustic with the relaxation of the sector for a certain term generally a year.
- The balance of payments is the difference between payments and total revenues of a particular economy over a particular period of time, while the trade balance is the difference between imports and exports of a particular economy over a particular period of time.
- The important cause for containing cash is to perform transactions. Suppose you earn Rs a hundred on the primary day of each month and run down this stability lightly over the relaxation of the month.
- A person may also keep her wealth withinside the shape of landed property, bullion, bonds, cash etc. For simplicity, allow us to membership all sorts of property aside from cash collectively right into an unmarried class called ‘bonds’.
- Finance may be defined as the art and science of managing money. It includes financial service and financial instruments.
- Individual/personal finance is concerned managing one’s savings and investment. It covers budgeting, banking, insurance, mortgages, investment, tax, retirement planning etc. of an individual.
- Public Finance which concerns with revenue and disbursement of Government such as Central Government, State Government and Semi-Government Financial matters.
Reference:
- Agrawal, A.N. : Indian Economy
- Dutta, R.& Sunderam, K. P.M. : Indian Economy