Unit 5
Banking Innovations
Debit card
A debit card is a payment card that makes payments by deducting money directly from a consumer’s checking account, rather than on loan from a bank. Debit cards offer the convenience of credit cards and many of the same consumer protections when issued by major payment processors such as Visa or Mastercard.
There are two types of debit cards that do not require the customer to have a checking or savings account, as well as one standard type.
- Standard debit cards draw on your bank account.
- Electronic benefits transfer (EBT) cards are issued by state and federal agencies to allow qualifying users to use their benefits to make purchases.
- Prepaid debit cards give people without access to a bank account a way to make electronic purchases up to the amount that was preloaded onto the card.
Advantages of Using Debit Cards
Debit cards can have both upsides and downsides, just like credit cards.

- Avoid debt
A debit card draws on money the user already has, eliminating the danger of racking up debt. Retailers know people usually spend more when using plastic than if they were paying cash. By using debit cards, impulsive spenders can avoid the temptation of credit and stick to their budget. This can help keep you out of high-interest debt.
2. Fraud protections
In addition, some debit cards—particularly those issued by payment processors, such as Visa or Mastercard—are starting to offer more of the protections enjoyed by credit card users. The key is reporting fraud or theft as soon as you realized it has occurred. Your liability for fraudulent purchases is determined by the time frame in which it’s reported. Waiting too long to let the bank know that your card has been used for unauthorized purchases could result in you being held responsible for some or all losses.
3. No annual fee
Though many credit cards charge an annual fee, debit cards don’t. There’s also no fee for withdrawing cash using your debit card at your bank’s ATM. Credit cards, on the other hand, can charge a cash advance fee plus a steep interest rate for that convenience. You may, however, pay other fees to maintain your checking account.
Disadvantages of Using Debit Cards
Similar to credit cards, the biggest downsides of using debit cards involve credit score impacts and cost.
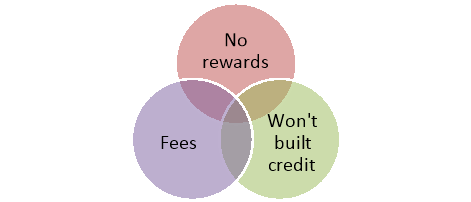
No rewards
Unless you have a rewards checking account, you won't earn any points, miles, or cash back on purchases made with your debit card. Because rewards can save you money, depending on how you redeem them, you could be missing out if you only spend with a debit card.
Won’t build credit
Building good credit means demonstrating to lenders that you can responsibly repay the money you borrow. When you’re spending with a debit card that’s linked to your bank account, you don’t have the opportunity to do that, so using a debit card alone won’t help you establish or build a credit history.
Fees
Though debit cards don’t have annual fees, you may pay other fees to have a checking account. Those can include monthly maintenance fees, overdraft fees if you overspend from your account, returned item fees, and foreign ATM fees if you use your debit card at another bank or financial institution’s machine.
Credit card
A credit card is a card issued by a financial institution, typically a bank, and it enables the cardholder to borrow funds from that institution. Cardholders agree to pay the money back with interest, according to the institution’s terms. Credit cards are issued in the following variety of categories:
- Standard cards simply extend a line of credit to their users for making purchases, balance transfers, and/or cash advances and often have no annual fee.
- Premium cards offer perks such as concierge services, airport lounge access, special event access, and more, but they usually have higher annual fees.
- Rewards cards offer cash back, travel points, or other benefits to customers based on how they spend.
- Balance transfer cards have low introductory interest rates and fees on balance transfers from another credit card.
- Secured credit cards require an initial cash deposit that is held by the issuer as collateral.
- Charge cards have no preset spending limit but often don’t allow unpaid balances to carry over from month to month.
Internet Banking
Internet Banking, also known as net-banking or online banking, is an electronic payment system that enables the customer of a bank or a financial institution to make financial or non-financial transactions online via the internet. This service gives online access to almost every banking service, traditionally available through a local branch including fund transfers, deposits, and online bill payments to the customers. Internet banking can be accessed by any individual who has registered for online banking at the bank, having an active bank account or any financial institution. After registering for online banking facilities, a customer need not visit the bank every time he/she wants to avail a banking service. It is not just convenient but also a secure method of banking. Net banking portals are secured by unique User/Customer IDs and passwords.
Features of Internet Banking
Here are some of the best features of internet banking:
- Provides access to financial as well as non-financial banking services
- Facility to check bank balance any time
- Make bill payments and fund transfer to other accounts
- Keep a check on mortgages, loans, savings a/c linked to the bank account
- Safe and secure mode of banking
- Protected with unique ID and password
- Customers can apply for the issuance of a chequebook
- Buy general insurance
- Set-up or cancel automatic recurring payments and standing orders
- Keep a check on investments linked to the bank account
Advantages of Internet Banking
Given below are some advantages/benefits of Internet Banking available for all the users-
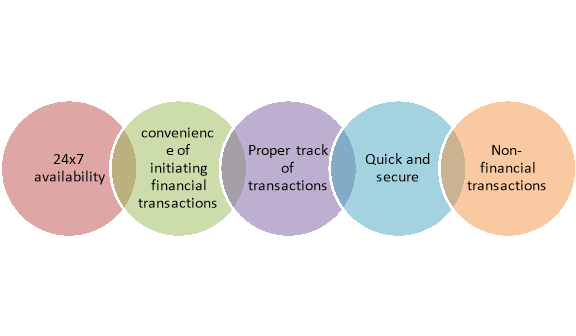
Figure: Advantages of internet banking
- 24×7 Availability: Internet banking, unlike usual banking hours, is not time-bound. It is available 24×7 throughout the year. Most of the services available online are not time-restricted. Users can check their bank balance, account statements and make fund transfers anytime instantly.
- Convenience of initiating financial transactions: Internet banking is largely preferred because of the convenience that it provides while fund transfer and bill payments. Registered users can use almost all the banking services without having to visit the bank and standing in queues. Financial transactions such as paying bills and transferring funds between accounts can easily be performed anytime as per the convenience of the user.
- Proper Track of Transactions: Acknowledgement slips are provided by the bank after transactions which have a high possibility of getting misplaced. However, with internet banking, it becomes very easy to track the history of all the transactions initiated by the user. Transactions and fund transfers made online are organised in the ‘Transaction History’ section along with other details such as payee’s name, bank account number, the amount paid, the date and time of payment, and remarks.
- Quick and Secure: Net banking users can transfer funds between accounts instantly, especially if the two accounts are held at the same bank. Funds can be transferred via NEFT, RTGS or IMPS as per the user’s convenience. One can also make bill payments, EMI payments, loan and tax payments easily. Moreover, the transactions, as well as the account, are secured with a password and unique User-ID.
- Non-financial Transactions: Besides fund transfer, internet banking allows the users to avail non-financial services such as balance check, account statement check, application for issuance of cheque book, etc.
Digital Banking
Digital banking is also termed as E-banking or Electronic Banking. It refers to all the forms of banking services and transactions performed through electronic means. It allows individuals, institutions and businesses to access their accounts, transact business, or obtain information on various financial products and services via a public or private network, including the internet.
Popular Types of E-banking Services in India
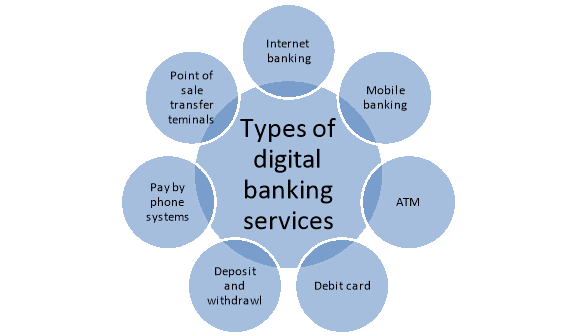
Figure: Types of digital banking services
- Internet Banking: It is the type of electronic banking service which enables customers to perform several financial and non-financial transactions via the internet. With internet or online banking or net-banking, customers can transfer funds to another bank account, check account balance, view bank statements, pay utility bills, and much more.
- Mobile Banking: This electronic banking system enables customers to perform financial and non-financial transactions via mobile phone. Most of the banks have launched their mobile banking applications available on Google Playstore and Apple App Store. Just like the net-banking portal, customers can use the mobile application to access banking services.
- ATM: Automated Teller Machines (ATM) is one of the most popular types of e-banking. ATMs allow customers to withdraw funds, deposit money, change Debit Card PIN, and other banking services. To make use of an ATM, the user must have a password. Banks charge a nominal fee from the customers on every transaction made after crossing the specified limit of free transactions if the transaction is done from any other bank’s ATM.
- Debit Cards: Almost every person owns a debit card. This card is connected to your bank account and you can go cashless with this card. You can use your debit card for all types of transactions, the transaction amount is debited from your account instantly.
- Deposit and Withdraws (Direct): This service under e-banking offers the customer a facility to approve paychecks regularly to the account. The customer can give the bank an authority to deduct funds from his/her account to pay bills, instalments of any kind, insurance payments, and many more.
- Pay by Phone Systems: This service allows the customer to contact his/her bank to request them for any bill payment or to transfer funds to some other account.
- Point-of-Sale Transfer Terminals: This service allows customers to pay for the purchase through a debit/credit card instantly.
ATM
The full form of ATM is Automated teller Machine, it is an electro-mechanical machine which consists of automated banking platforms that allow clients to perform smooth transactions without the assistance of a branch representative or teller. A debit card or credit cardholders should be able to withdraw cash at most ATMs.
ATMs are beneficial, allowing clients to conduct fast self-service transactions such as cash withdrawals, deposits, bill payments and account-to-account transfers. Fees are usually paid out for cash withdrawals by the bank where the account is held, by the ATM operator, or both. Some of these charges can be avoided by using an ATM which is operated directly by the account holding bank.
ATMs are recognized in different parts of the world as ABM (Automated Bank Machines), or Cash Machines.
Basic Parts of ATM
The ATM is easy to use. It contains input and output tools, allowing people to deposit or withdraw money comfortably. Underneath are the essential output and input devices of an ATM.
Input device
- Card reader – Card reader recognizes the card data stored on the ATM card in the magnetic stripe, which is located on the back. The account details are collected by the card reader and sent to the server, once the card is inserted in the specified location. Cash dispenser allows the cash to be dispensed based on account information and the commands obtained from the user server.
- Keypad – Keypad helps the user with the requested data from the machine such as personal ID number, cash amount, receipt needed or no needed and other information. In the encrypted form, the PIN is sent to the server.
Output Devices
- Speaker – Speaker is available in the ATM to generate the audio input when a button is pressed.
- Display Screen – Displays details on the screen concerning the transaction. It indicates the steps of cash withdrawal, one by one in order. The screen may be CRT or LCD.
- Receipt Printer – A receipt shows you information about the transactions printed on it. It informs you of the time and date of the transaction, balance and withdrawal amount, etc.
- Cash Dispenser – Cash dispenser is the ATM ‘s essential output tool as it hands out the cash. The highly accurate sensors provided in the ATM allow the cash dispenser to administer the appropriate cash amount as the consumer needs.
Key Takeaways
- A debit card is a payment card that makes payments by deducting money directly from a consumer’s checking account, rather than on loan from a bank.
- A credit card is a card issued by a financial institution, typically a bank, and it enables the cardholder to borrow funds from that institution.
Electronic fund transfer is an organised digital platform that facilitates transfer of funds electronically. The electronic fund transfers are made through MICR, RTGS, NEFT, DEMAT, SWIFT. Such types of EFTs are discussed below-
MICR
MICR (magnetic ink character recognition) is a technology used to verify the legitimacy or originality of paper documents, especially checks. Special ink, which is sensitive to magnetic fields, is used in the printing of certain characters on the original documents. Information can be encoded in the magnetic characters. The use of MICR can enhance security and minimize the losses caused by some types of crime. If a document has been forged - for example, a counterfeit check produced using a colour photocopying machine, the magnetic-ink line will either not respond to magnetic fields, or will produce an incorrect code when scanned using a device designed to recover the information in the magnetic characters. Even a legitimate check can be rejected if the MICR reader indicates that the owner of the account has a history of writing bad checks.

RTGS
The acronym 'RTGS' stands for Real Time Gross Settlement, which can be explained as a system where there is continuous and real-time settlement of fund-transfers, individually on a transaction by transaction basis (without netting). 'Real Time' means the processing of instructions at the time they are received; 'Gross Settlement' means that the settlement of funds transfer instructions occurs individually. The RTGS system is primarily meant for large value transactions. The minimum amount to be remitted through RTGS is ₹ 2,00,000/- with no upper or maximum ceiling.
With effect from July 01, 2019, the Reserve Bank has waived the processing charges levied by it for RTGS transactions. Banks may pass on the benefit to its customers.
With a view to rationalise the service charges levied by banks for offering funds transfer through RTGS system, a broad framework of charges has been mandated as under:
a) Inward transactions – Free, no charge to be levied.
b) Outward transactions – ₹ 2,00,000/- to 5,00,000/- : not exceeding ₹ 24.50/-; (exclusive of tax, if any)
Above ₹ 5,00,000/- : not exceeding ₹ 49.50/-. (exclusive of tax, if any)
Banks may decide to charge a lower rate but cannot charge more than the rates prescribed by RBI.
The remitting customer has to furnish the following information to a bank for initiating an RTGS remittance:
- Amount to be remitted
- The account number to be debited
- Name of the beneficiary bank and branch
- The IFSC number of the receiving branch
- Name of the beneficiary customer
- Account number of the beneficiary customer
- Sender to receiver information, if any
Benefits of RTGS
RTGS offers many advantages over the other modes of funds transfer:
- It is a safe and secure system for funds transfer.
- RTGS transactions / transfers have no amount cap.
- The system is available on all days on 24x7x365 basis. There is real time transfer of funds to the beneficiary account.
- The remitter need not use a physical cheque or a demand draft.
- The beneficiary need not visit a bank branch for depositing the paper instruments.
- The beneficiary need not be apprehensive about loss / theft of physical instruments or the likelihood of fraudulent encashment thereof.
- Remitter can initiate the remittances from his / her home / place of work using internet banking, if his / her bank offers such service.
- The transaction charges have been capped by RBI.
- The transaction has legal backing.
NEFT
The NEFT is a nation wide payment system facilitating one-to-one funds transfer. It operates on a deferred net settlement (DNS) basis and settles transactions in batches. The settlement takes place with all the transactions received before a certain cut-off time. NEFT is not available on the bank holidays, RBI holiday and Sunday.
NEFT Features
- Minimum amount - Rs. 1
- Maximum amount - No limit, but generally RTGS is used for transfer of Rs 2,00,000
- Transaction charges - Not more than Rs 2.5/- plus service tax for any transfer up to Rs 10000, not more than Rs 5/- plus service tax between Rs 10000 and Rs 1 lakh, not more than Rs 15/- plus service tax between Rs 1 lakh and Rs 2 lakh and not more than Rs 25/- plus service tax for those above Rs 2 lakh.
- Timings - Available 24x7 , 365 days as the RBI has regularised that NEFT transactions will have round the clock availability on all days of the year and hence the bank customers can transfer funds through NEFT around the clock on all days including holidays.
Benefits of NEFT Transfer
- Available 24x7, 365 days.
- Funds transfer through NEFT is a safe and secure process.
- Funds get transferred very fast i.e. usually in a few minutes.
- You need not draw the physical cheque or send demand draft to the beneficiary for fund transfer from your account.
- The beneficiary will not have visit his bank branch to deposit the cheque/ DD in his account.
- No fear of loss/ theft of cheque/ DD.
- It saves cost and time.
- The customer can make intrabank as well as interbank payments.
- You get notified about the credit confirmation via SMS.
DEMAT
Demat Account is an account that is used to hold shares and securities in electronic format. The full form of Demat account is a dematerialised account. The purpose of opening a Demat account is to hold shares that have been bought or dematerialised (converted from physical to electronic shares), thus making share trading easy for the users during online trading. A Demat Account or Dematerialised Account provides the facility of holding shares and securities in an electronic format. During online trading, shares are bought and held in a Demat Account, thus, facilitating easy trade for the users. A Demat Account holds all the investments an individual makes in shares, government securities, exchange-traded funds, bonds and mutual funds in one place.
Dematerialisation is the process of converting the physical share certificates into electronic form, which is a lot easier to maintain and is accessible from anywhere throughout the world. An investor who wants to trade online needs to open a Demat with a Depository Participant (DP). The purpose of dematerialisation is to eliminate the need for the investor to hold physical share certificates and facilitating a seamless tracking and monitoring of holdings.
Features of Demat Account
1. Easy share transfers
Using a delivery instruction slip (also known as DIS) investors can transfer their securities. These slips make buying or selling shares more efficient and easier. These slips enable the investors to provide all the details that are required for the smooth execution of any transaction.
2. Hassel Free dematerialisation & rematerialisation
Demat account allows easy dematerialization and rematerialisation of all the physical certificates into electronic form and vice versa. To do these holders have to provide instructions to the depository participant or DP. Similarly, all-digital securities can be converted into physical certificates as well.
3. Loans against securities
There are many financial institutions that offer loans against securities that the borrower has in his demat account. You can use your securities as collateral while availing of loans by these financial institutions.
4. Freezing Demat accounts
Demat account holder can also freeze their demat account as per their convenience for a certain period. This is usually practiced when unexpected debit or credit into the account is to be prevented. By doing this the holder halt any money transferring into the demat account.
5. Multiple accessing options
For easy accessibility, you can access demat account via various modes. You can access your demat account via a computer, a smartphone, or any other type of smart device. All you need is a good internet connection for a better user experience.
6. SPEED E-Facility
When you trade using your demat account it offers faster transactions unlike your traditional method of trading. The National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) allows users to send instruction slips electronically rather than transferring physical slips to the DP. This requires lesser time and is more convenient and efficient.
7. Corporate benefits & actions
If the companies offer dividends, refunds, or interest to their investors, these benefits are automatically available to the Demat account holders. In addition, corporate actions like bonus issues, right shares, or stock split are automatically issued via Demat account of all the shareholders.
Benefits of Demat Account
- Easy to Hold
When it comes to maintaining physical certificates it is a very tedious job. Keeping track of their performance adds to the responsibility. Demat account holders make it more convenient to hold and track all their money and investments through a single account.
2. Immediate Updates
The client can find all the updates related to their account or stock prices in one place. Easy to access you can review stock performance from anywhere.
3. Lower Costs
When the traditional method was popular it involved physical certificates. These certificates required several additional expenses like stamp duty, handling charges, and other such expenses. Now that demat account eliminated holding of these physical certificates these extra expenses are eliminated as well.
4. Reduction in Delivery Risks
When everything becomes digitalized the risks of losing physical papers are eliminated. Hence it is better to hold your shares in a demat account than in the form of physical paper. It also eliminates the risk of forging documents when you maintain everything online. Demat account guarantees 100% safety and security of all the shares held in your demat account.
SWIFT
Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT) provides safe and secure financial transactions to their members. SWIFT was founded in Brussels in 1973. At the time of its establishment, it was supported by 239 banks in fifteen countries. SWIFT has evolved since 1973, and as of 2018, nearly half of the high-value cross-border payments worldwide have used the SWIFT network. As of 2015, SWIFT has linked more than 11,000 financial institutions in more than 200 countries and regions. SWIFT sends payment orders that need to be resolved with correspondent accounts owned by each other.
Swift payments are payments done through the network. Swift assigns each bank an eight- or 11-character long code, known as the bank identifier. It is similar to the IFSC code used for domestic interbank transfers, with Swift being used for international transfers. For example, if someone in India wants to send money to a person in the US, they would need the latter’s bank account number and the Swift code of the destination bank. The Swift code lets the US bank know of the transfer in real-time and eases its clearing.
SWIFT network has expanded over the years, and presently the following institutions use the system.
- Banks
- Securities Dealers
- Clearing Houses
- Exchanges
- Corporate Business Houses
- Brokerage Institutes
- Asset Management Companies
- Depositories
- Treasury Market Participants
- Foreign Exchange & Money Brokers
Key Takeaways
- Electronic fund transfer is an organised digital platform that facilitates transfer of funds electronically. The electronic fund transfers are made through MICR, RTGS, NEFT, DEMAT, SWIFT.
Case study
In India, digital banking started taking shape in the late 1990s with ICICI Bank being the first one to bring the service to their retail clients. Digital banking became mainstream only in 1999 as internet charges were reduced and there was increased awareness and trust with respect to the internet. It was only after the internet further developed and the costs came down, banks started serving a broader basket of products online.
As per a Deloitte research report on must-haves for a fully digital bank, each bank striving to become fully digital require the following as the key drivers for their success
- Option to order currency
- Customizable standing options
- Accounts linked to tax exemptions status
- Card blocking feature
- Innovation toward safety vaults
- Integration with stock market investment channels
- Financial management analytics
- Enable grouping of accounts of different banks
- Easily accessible assistance
A full-fledged replacement of physical branch banking with digital banking right now seems like a far-fetched dream. Digital banking comes in handy for recurring banking essential functions. However, customers prefer human interaction for more important and irregular decisions, such as while taking a loan or negotiating the terms of the loan.
References:
1. Gordon & Natarajan: Banking Theory Law and Practice, HPH
2. S. P Srivastava; Banking Theory & Practice, Anmol Publications
4. M. Prakash, Bhargavi VR: Banking law & Operation, Vision Book House.
5. Tannan M.L: Banking Law and Practice in India, Indian Law House