UNIT 3
Flood
- Any flow that is comparatively high and that overtops the artificial banks in any reach of a stream could also be known as a flood
- Design of culverts, road and rail bridges, emptying works and irrigation diversion works, desires a reliable estimate of the food at the positioning involved.
- The maximum flood that any structure will safely pang known as the design flood"
- Because the magnitude of the look flood increase the opportunity cost of the structure additionally will increase however the chance of annual damages can decrease
- Magnitude of style food is set supported sustainable risk of exceed.
- With in the style flood estimates, reference manually created to the following:
(a) Common place project flood (SPF):
This is often the estimate of the flood doubtless to occur from the foremost severe combination of the meteorological and historiological conditions that are fairly characteristic of the catchment area being thought-about it excluding very rare combination
(b) Most probable flood (MPF):
This differs from the SPF therein it includes the very rare and harmful floods and is sometimes confined to spill style d terribly high genus Dams. The SPF is sometimes around 80 % of the MPF for the base
(c) Probable most precipitation (PMP):
The probable most precipitation (PMP) is outlined because the greatest or extreme precipitation of a given length that's physically possible over a station or basin
Depth area duration curve for PMP is usually derived by taking the result of maximum depth area duration analysis and adjusting them for maximum moisture change rate of moisture inflow and other hydrometeorological condition that would maximum the rainfall
PMP, once applied on the look unit hydrograph for the basin, can manufacture the MPF.
(d) Style flood:
It is the flood adopted for the look of hydraulic structure like spillways, bridge opening flood banks, etc. it should be the MPF or SPF or a flood of any desired return interval relying upon the degree of flood protection to be offered and price social science of construction of structures. The look flood is sometimes chosen when creating a analysis, the magnitude relation of profit to value could also be desired to be the most
The PMF is employed in things wherever the failure of the structure would lead to loss of life and casterophic harm and intrinsically complete security from potential floods in figure. On the opposite hand, SPF in typically used wherever the failure of a structure would cause lens severe damages. Typically, the SPF is concerning 40 % to 60 % of the PMF for constant catchment area.
The standards used for choosing the look for numerous hydraulic structures vary from one country to a different. The subsequent table provides a short outline of the rules adopted by CWC Asian country to pick style floods.
Key takeaways
Flood estimated time is depend on
- (a) Common place project flood (SPF):
- (b) Most probable flood (MPF):
- (c) Probable most precipitation (PMP):
- (d) Style flood:
The methods utilized in the estimation of the design flood will be classified as under
(1) Physical indication of past flood
(2) Envelope curves
(3) Empirical flood formulae
(4) Rational technique
(5) Unit hydrograph application
(6) Frequency analysis of applied math methods
(1) PHYSICAL INDICATIONS OF PAST FLOODS
By noting the flood Marks (native enquiry), depths, affluxes (heading of water close to bridge openings, or similar obstructions to flow), the utmost flood discharge could also be calculable.
(2) ENVELOPE CURVE
Areas having similar geo graphics options and atmospheric condition area unit classified along. All on the market information concerning discharges area unit compiled in conjunction with their several construction areas. Peak flood discharges area unit then planned against the emptying areas and a curve is drawn to hide or envelope the best planned points. Therefore for any geographic area, peak flood will be scan from the envelope curves. This technique offers a rough estimate of peak flood. Victimization this we have a tendency to cannot assign any come amount to the height worth.
Envelope curves area unit usually used for comparison solely a tie style floods got by alternative strategies, should be higher than those obtained from envelope curve
Following equation is usually used for enveloping curve of most floods throughout the globe
Q = 3010 A / (277 + A) 0.78
Where Q is in m3 /s, A is in km2
(3) EMPERICAL FORMULA
The simplest of the empirical relationships area unit those that relate the flood peak to the geographic area.
The various empirical formulas are:
Dickens Formula
Q p = C p A3/4
Where
Q p = maximum discharge
A = catchment area
C D = Dickens constant with value between 6 to 30
Dickens formula is used the central and northern parts of the country
Ryves Formula
Q p = C R A 2/3
Where Q p = maximum flood discharge
A = catchment area
C R = Ryves coefficient
It is in use in province and elements of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
C. = 6.8 for areas among 80 kilo meter from the east coast
= 8.5 for area unit as that are 80-160 kilo meter from the geographical region
= 10.2 for restricted areas close to hills
Inglis Formula
This formula relies on flood information of catchments in Western Ghats in geographic area, in ms is expressed
Q P = 124 A /√ (A + 104)
Where A within the catchment area in km², Q P is peak flow in m3/s
(4) RATIONAL METHOD
- We know that the utmost flood flow in made by sure downfall intensity that last for a time equal to or larger than the amount of concentration
- The concentration time is that the most time needed by the surface runoff to succeed in the basin outlet.
- When a storm continues on the far side concentration fifty a part of the construction would be tributary to the runoff at outlet and thus it represents condition peak runoff.
- The runoff rate love this condition given by
Q = CAI
Where A within the space of the construction, I is the intensity of downfall and C is a runoff constant to account for the abstractions from the downfall
- The intensity of downfall used ought to a period adequate to concentration time and desired return amount as obtained from IDE curve , I .e rainfall intensity corresponding to a duration of time of concentration (t c) and probability of chance P(T = 1/P)
RAINFALL INTENSITY
The rainfall intensity corresponding to period time of concentration) and therefore the desired probability of exceed P (I. e return period T=1/F) may also be found then the rainfall-frequency period relationship using the formula
I t c, p = K T X /t c + a) m
In which K, a, x and m area unit constant
TIME OF CONCENTRATION (t c)
Time of concentration will be calculated victimization the subsequent formula
US practice
For small emptying basins, the time of concentration is close to adequate to the lag time of the height flow. Thus
t c = t p = C t L (LL c a /√S)n
Where
t c = time of concentration in hours.
L = basin length measure along the water course from the basin divide to the gauging station in km.
L c a = distance along the main water course from the gauging station to center of water shed in km
S = basin slop
C I Land n is unit basin constant
KIRPICH EQUATION (1940)
t c= 0.01947 L 0.77 S -0.385
t c= time of concentration (minutes)
L = most length of travel of water in meter
S = slope of the catchment
∆ H = difference in elevation between the most remote point on the catchment and the outlet
RUNOFF COEFFICIENT
C = runoff/ rainfall = runoff coefficient = impermeable factors
If totally different, completely different parts of construction have different runoff constant then is calculated as
C = C1 A1 + C2A2 + C3A3 +......../A1 +A2 +A3 +......
Where C I = Runoff constant touching on space A i etc.
The rational formula is found to be suitable for peak allowed prediction is small catchment up 50 km2 in areas. It find considerable application is urban drainage design and in the design of small culverts and bridge
(5) UNIT HYDROGRAPH METHOD
The unit hydrograph technique is wont to predict the height smart hydrograph if the rain manufacturing the flood, infiltration characteristics of the structure and therefore the applicable unit hydrograph area unit out there. For style food extreme rain scenario area unit used style storm). The unit hydrograph of the structure within the operated upon by the planning storm penetrate the specified flood hydrograph.
Key takeaways
Methods of estimation of design flood
(1) Physical indication of past flood
(2) Envelope curves
(3) Empirical flood formulae
- Dickens formula
- Ryves formula
- Inglis formula
(4) Rational technique
(5) Unit hydrograph application
(6) Frequency analysis of applied math methods
- Frequency analysis makes use of the determined knowledge within the past to p hour food events along sides their possibilities and come period
- For frequency analysis and adequate and correct knowledge of previous usually records of lunar module than twenty years shouldn't be employed in frequency analysis.
- Dams, diversion, urbanization and alternative land changes intro in knowledge phenomenon the information must be changed to bring it at par with the present condition of the structure
What data should be used for analyzed
- If data for 50 yrs are available then in that 50 yrs may be the flood may have come 200 times. But for analysis purpose we do not take all the 200 data into account. Data selected for analysis are
(a) Data of annual series
(b) Data of partial series
- If peak discharge of 2, 5, 7, 10 etc are organized in decreasing order of magnitude we have a tendency to get annual aeries. Fall flood on top of a worth is take into account, we have a tendency to get partial knowledge series.
- For data regarding flood of fairly frequent prevalence, in is needed throughout the development amount of an oversized dam (4-6 yrs ), partial varies re the most effective whereas, for the up way food, the annual series area unit most popular
- Hence usually for flood of huge return, interval (I .e larger than twenty time period, or in other words flood exceed probability <= 0.05) annual knowledge serious in used and for all return interval (4-5 yrs) partial knowledge arise that is used.
In our course we will concentrate only on annual data series
Annual series square measure organized in descending order of magnitude and rank no. In a minded to every with rank m = 1 for highest discovered flood and lots of record) for lowest discovered flood. The come backs amount in calculated forever event victimization Weibull's formulae.
T r = (n+1)/m
Where T r = return period in year
m = order no.
n = no. Of period of time of records
Return period represent the AVG no of years within which given event will be equal or exceeded
Probability of exceed = 1 / T r = P
If graph is plot between flood magnitude and its return period in simple plane co-ordinates, the plot is named as probability or an empirical distribution
This graph could also be work out or interpolated to get the design flood of any specific return period. We may also plot flood magnitude (y-axis, easy scale) and return period (X - axis log scale) and use it for extrapolation
[This curve might yield line plot)
However, the extrapolation for big return period may yield erroneous results. Hence for longer return period, theoretical probabilities have to be used the most commonly used distribution is
(a) Gumble's distribution
(b) Log Pearson type 3 distribution.
Gumble's method
As per Gumble's method
X T = X + K 6n-1
Where
X T = value of variate with a return period of T
X = mean value of variate
n= no. Of years of record
6 n-1 = standard deviation of the sample of size n
6 n-1 = √ [summation (X-mean of X) 2 /n-1]
K = frequency factor
K = y T - y a / S n
Y T = reduce variate = - [In In (T/ T-1)
Y n = mean of reduce variate
S n = standard deviation of reduced variate
Y n and S n are function of n .Table is available for y n and S n against n hence S n and y n will be obtained from table
However if n is large
Y n = 0.577
S n = 1.2825
Normally for n > 50 also same time we use y n = 0.577, S n = 1.2825 without much error) thus the step concerned are:
1. Assemble the discharge data and note the sample size n. Here the annual flood value is the variate X. Find X and  n-1 for the given data
n-1 for the given data
2. Using tables determine y n and S n for given n
3. Find y T for a given T.
4. Find K.
5. Determination the required X T
- Floods square measure one amongst the foremost harmful natural hazards in Italia, inflicting several damages in term of economic losses and fatalities. It's crucial, beneath circumstances, having the ability to predict the magnitude of those events so as to mitigate the flood risk.
- During this work perform a versatile flood frequency analysis supported a region of influence approach to estimate the relation between flood peak discharge and therefore the come backs amount relative to the Pescara geographic area.
- We have a tendency to used four variables to assess the hydrological homogeneity of the water basins: annual cumulated precipitation; average slope of the water basin, slope of the flood length curve and an index considering the breadth operate and therefore the average slope of the catchment’s main watercourse.
- We have a tendency to elect the homogenized water basins in line with the chosen variables and that we verified their homogeneity with the Hosking and Wallis take a look at.
- Assumptive a generalized extreme price distribution of the annual peak flow discharge, we discover that the regional flood frequency curve yields lower discharge values compared to the frequency curve calculated solely with the native discharge values.
- We have a tendency to additionally realize that the region of influence of the analyzed water basin doesn't show sensible applied math homogenized characteristics, indicating that additional acceptable variables square measure required.
3.6.1 DESIGN STORM
- Coastal protection structures can typically be styled to with stand wave attack by the intense design storm. The severity of the storm (i.e. come back period) is chosen seeable of the appropriate level of risk of injury or failure. A style storm consists of a style wave condition, a style water level, and a period. (As outlined in wordbook of Coastal nomenclature By Washington Department of Ecology)
- A theoretical extreme storm whose wave's coastal protection structures can typically be designed to resist. The severity of the storm is chosen seeable of the appropriate level of risk of injury or failure. A style STORM consists of a style WAVE condition, a style water level and a period. (As outlined in wordbook of Coastal nomenclature
- By The u .s. Army) the eighty fifth score 24-hour storm depth, supported native historical rain records. (As outlined in Water Quality Management set up, By County of Riverside, California) rain quantity and distribution in area and time, accustomed verify a style flood or style peak discharge. (As outlined in wordbook of meteorologic Terms, By yankee meteorologic Society)
- However, in summary, "Design Storm" is: A essential rain event that's used for assessing the flood hydrograph of an explicit come back amount is termed "design rainfall". Because the quantity of the planning rain corresponds to rare frequencies, they need high values of rain depth or intensity which is why the planning rain is sometimes termed as "design rainstorm" or just "design storm". In summary, style Storm is hyetograph, or time distribution, of the planning rain over a particular period. A style storm is synthesized from items of maximum rain taken from several actual storm events in region.
- The term style storm is employed to visit a rain hyetograph that's believed to possess the characteristics that are essential to the protection of the project. A style storm is an artificial distribution supported characteristics inherent to an intensity-duration-frequency curve or AN actual hyetograph that caused major flood injury within the past, and also the policymakers try to forestall such damages within the future.
3.6.2 DESIGN FLOOD
Definition of design flood:
- Design flood is that the worth of the instant peak discharge adopted for the look of a selected project or any of its structures. Additionally to the issues of the flood characteristics, frequencies and potentiality of the tributary geographical region on top of the structure, social, economic and alternative non-hydrologic issues that area unit seemingly to own influence area unit thought-about in account a style flood.
- The term “design flood” is employed to denote the most flood flow that might be passed while not harm or serious threat to the steadiness of engineering structures. It's thus, necessary to specify volume and amount of flood flow which will flow down in conjunction with the height flow. Thus, style flood hydrograph is additionally totally puzzled out at the side of peak flow to facilitate style.
- The Probable most Flood (PMF) is that the flood that will result from the foremost severe combination of important earth science and hydrologic conditions thought-about physically potential within the region into account.
- The peak flow is calculable either by empirical formulae, envelope curves, unit hydrograph methodology, rational methodology or flood frequency analysis. Then considering social and economic issues the worth of the height flow is multiplied by applying a security factor.
- For major structures like massive dams it's not spare to think about style flood solely. It involves estimates of utmost flood like Probable most Flood (PMF). In account PMF try is formed to analysis the motor factors answerable for the assembly of flood with a read to incoming at a most crucial combination of earth science and hydrologic factors.
Among the factors manufacturing severe floods the vital ones area unit the following:
i. Prevalence of terribly intense storm.
Ii. Centering of the storm over the structure therefore on manufacture most runoff.
Iii. Important time sequence and movement of storm.
Iv. Pre valence of the storm at a time once the geographical region is already saturated by preceding precipitation.
Computation of style Flood Hydrograph:
Design flood hydrograph for emptying basins having but 5000 km2 space may be computed by adopting unit hydrograph methodology.
The steps concerned in its derivation may be summarized as follows:
(i) Choose or derive is important storm that is probably going to occur within the region.
(ii) Derive a mean or style unit hydrograph either mistreatment runoff knowledge or synthetically.
(iii) Calculate the number of effective precipitation which will result from the chosen important or style storm.
(iv)Get the precipitation amounts for time intervals up to the unit period of the look unit hydrograph from the depth period curve of the chosen storm.
(v) Regulate the sequence of increments of effective precipitation so it provides most crucial conditions of runoff. (Such adjustment could be for account PMF but, for style flood calculation solely, considering storm characteristics of the realm conservative sequence is taken).
(vi)Apply the effective precipitation increments with their adjusted sequence to the look unit hydrograph to get the full direct runoff hydrograph.
(vi)Add expected base flow throughout the look storm to the full direct runoff hydrograph to get the look flood hydrograph of total runoff.
In the case of emptying basins larger than 5000 km2 and in those smaller basins conjointly wherever completely different/ completely different} elements of the basin have wide different runoff characteristics, the full geographical region is sub-divided into sub-areas. Then for every sub-area separate unit hydrographs area unit derived.
From them flood hydrographs area unit determined for numerous sub-areas adopting the on top of mentioned procedure the sub-area flood hydrographs area unit then routed down the stream channel to the project website to finally work out the look flood hydrograph there.
Key takeaways
Design storm
Coastal protection structures can typically be styled to with stand wave attack by the intense design storm. The severity of the storm (i.e. come back period) is chosen seeable of the appropriate level of risk of injury or failure. A style storm consists of a style wave condition, a style water level, and a period. (As outlined in wordbook of Coastal nomenclature By Washington Department of Ecology)
Design flood
Design flood is that the worth of the instant peak discharge adopted for the look of a selected project or any of its structures. Additionally to the issues of the flood characteristics, frequencies and potentiality of the tributary geographical region on top of the structure, social, economic and alternative non-hydrologic issues that area unit seemingly to own influence area unit thought-about in account a style flood.
3.7.1 RISK FACTORS
- To increase the resilience against natural hazards and to cut back the vulnerability of municipalities, socio psychological models square measure urged to check risk perception and per received state as a result of completely different perceptions could lead to completely different risk-reducing responses.
- Not solely threats outlined by scientific discipline and economic issues however conjointly the social context and perspective square measure essential parameters to work out the foremost acceptable risk management approach (Renn, 2005), and therefore the models could deliver proof on however changes in beliefs foster reconciling behavior (Lindell et al., 1997, Paton et al., 2010).
- The survey provided proof that the socio psychometric framework functions a useful gizmo to analysis the choice creating and implementation method conjointly within the municipal public service context. This is often despite the actual fact that the amount of correlations could suffer as a results of the sample restrictions, i.e. the tiny size and therefore the diversity of the panel composition, and general method limitations as well as the completeness and integrity of the given answers, and therefore the bias of individual action and therefore the restricted power of the model to predict actual behavior (compare Grothmann and Reuss wig, 2006). Associate degree example is that the lack of applied mathematics important nations between the intention-signaling variable 'additional measures required' and therefore the four preventive 'responses' thanks to light focus of the investigated item. Seventy per cent of the panel square measure in favor of extra measures however meet the short, medium and long run, and while not shaping the way of response. Similarly, Lindell and speaker (2002) found the next correlation with intention than with actual changes. Despite these limitations, the model helped to achieve variety of sensible and new insights, which can foster native flood risk management and operations in future.
- The majority of the panel regarding worries is bothered about the potential temperature change effects on future floods as well as the connected consequences. The amount of perceived risk (some 70%) and therefore the worry a few potential threat to the municipality (66%) square measure high and as is that the demand for extra risk-reducing action (70%). The co relational statistics of pre pared variable with the 'worry' variable however the non significant relation with risk perception' points to the discrepancy of the psychological feature analysis of risk and therefore the emotional, emotional intention to cut back it (Sjöberg, 2000; Loewenstein et al., 2001). Plapp (2004) attributes the Roman deity crepancy to the additional personal warm heartedness of perceived worry in distinction with the additional purposeful live of perceived likelihood and severity.
- Given the panel composition of municipal consultants, public officers and decision-makers, and following the correlations, it's going to be hypothesized that traditional or technocratic responses like constructive rejection (dikes, retention), typically planned and determined by the higher authorities, square measure given the priority by the additional psychological feature risk attributes as well as future connected aspects of potential injury and acceptable safety standards.
- On the opposite hand, the sensory activity differentiation might presumably be implemented by the native context and responsibilities. As indicated by the correlations, the sensation of 'worry' may well be demanding for and resulting in additional domestically minded precautionary, 'damage-minimizing' and social capacity-building responses.
- An additional comprehensive definition of the psychological feature and emotional attributes of risk perception as already professional posed by Miceliet al. (2008) would possibly stimulate additional analysis within the relation of risk perception, hazard ready earth and risk-reducing behavior.
- It's going to conjointly stimulate a discussion concerning the responsibilities of municipalities within the flood safety chain and their adequate role within the general, basin wide call method of flood hindrance, a matter that's additional detailed within the paragraph shortly the institutional parts.
- The majority of the panel (55%) feels well ready to fulfill the results of additional frequent and severe floods in future, additional supported by the co relational statistics with the variable of outcome expectations 'trust within the applied con cepts and methods (Paton et al., 2010).
- The statement, however, appears to emphasize a rather optimistic safety feeling, given the correlations with the panel expectations of upper potential injury in future (33%), the high rating of 'worry' (66%), the request for extra protecting measures (70%) and therefore the correlation with the response cluster of constructive avoidance
- The optimistic judge may well be because of the official and political tint of the panel composition, resulting in the speculation of politically biased answers.
- Another rationalization is also the reliance on flood protection by higher authorities as indicated by the correlation with the 'trust' and 'focus' variables. Additional analysis is suggested into this side of absolutely perceived state.
- The low level of auditing (Table 3) suggests the existence of uncovered risks, and a municipal audit or benchmarking exercise appears a superb chance to match the target safety position and therefore the native standing of flood risk awareness and state.
- The social context has been introduced by the PADM model as a vital attribute touching the method by that preventive action is adopted (Lindell and Hwang, 2008). Just in case of the municipal representatives of this study, the institutional parts outline their role and responsibilities overflowing risk management.
- The correlations, additional detailed by verbal statements, recommend sure challenges and opportunities during this space. In general, the panel members appear to be glad with the data provision and therefore the institutional arrangements.
- The pronounced political focus puts the perceived worry into perspective, and - as conjointly urged by Paton et al. (2010) - the part of trust within the state-wide flood hindrance concept' could be a powerful support for self-efficacy and risk-reducing intentions.
- The interviews, however, place these positive findings into perspective even supposing in most cases, no important relations might be established.
- Various interviewees mentioned the complicated federal structure, split responsibilities and up to date body reforms as retarding factors for integrated and property flood risk management which a simpler interaction between the Federal States might deliver a broader perspective of the longer term risks and choices for associate degree integrated flood risk management Lindell associate degreed Perry (2000) mention the attribute of perceived responsibilities for protecting action an unfortunate omission of their earlier version of the PADM model, which has been addressed in additional recent studies (Arlikatti et al. 2007; Lindell and Perry, 2012).
- Terpstra and Gutteling (2008) yet known the attention of responsibility as a vital issue for effective flood risk management. Inclusion of a responsibility variable during this study couldn't establish statistically important correlations with cope variables or between the various actors. However, following the overall proposition that the next level of perceived responsibility for hindrance would result in additional active adjustment (Lindell and Perry, 2004).
- Additional targeted and representative studies on risk perception, cope appraisal and perceived responsibility square measure suggested to produce the required info on the role of municipalities and their "flood representatives, yet as their integration and weight within the general and regional call processes of future flood risk reduction ideas.
- This fits conjointly with the overall plea of Lindell and Perry (2000) for additional analysis to explore the role of authorities, their relations to informal sources of expertise and public collaboration
3.7.2 SAFETY FACTORS
- Flash flooding is that the most venturous weather disaster within the u .s Flood causes power outages, harm infrastructure, trigger landslides, and might be deadly.
- Heavy precipitation during a short amount of your time causes water to rise chop-chop, elevating the chance of flooding. Flash floods occur with very little warning however flooding may also develop slowly when rain ceases.
- Though most of the people associate hurricanes with wind harm, flooding poses one among the largest threats from the storms. Cyclone physician in 2017 born sixty inches of rain in some components of American state, making large flooding hazards. In 2005, flooding from cyclone Katrina caused a majority of the harm once recent levees unsuccessful throughout the storm.
- Here are some safety tips to assist you steel oneself against rising water—and what to try to once a flood has begun
BEFORE A FLOOD
One of the largest ways that to safeguard yourself and your property is to organize prior to time
This includes:
- Avoid building during a flood plain space particularly at risk of flooding throughout serious rains.
- If you are doing sleep in a plain, think about shopping for flood insurance to assist with losses if, and when, a flood happens.
- Construct barriers (levees, beams, floodwalls) to prevent floodwater from coming into your home. Sandbags will offer a short lived dam in associate emergency.
- Seal walls in basements with waterproofing compounds to avoid ooze.
- Pay attention to weather forecasts. Once serious rain or storms are forecasted, hear the radio or t v for data on flooding risk.
- What’s worse a flood watch or warning? A watch means that flooding is feasible. A warning means that flooding is happening or can occur presently.
WHEN A FLOOD CLOSE TO HAND
- Have associate emergency set up and observe survival skills, like attention and the way to make clean water.
- Be prepared Assemble associate emergency kit just in case you would like to evacuate. Do not forget to incorporate necessary prescription medications and a little attention kit.
- Charge telephone batteries and any reusable batteries for flashlights. Get further batteries just in case power isn’t restored now.
- Heed evacuation warnings. If there's any risk of a flash flood, move now to higher ground. Follow applicable evacuation signs.
- If potential, herald out of doors article of furniture associated move vital things to a higher floor, on top of potential flood levels.
- Turn off utilities at the most switches or valves if tutored. Disconnect electrical appliances.
DURING A FLOOD
- Avoid low spots, like ditches, basements, or underpasses. These become very dangerous throughout a flash flood.
- Do not practice flooded areas. It is troublesome to inform however deep the water is and what lies beneath the water that might hurt you. Even shallow, moving water will cause you to fall.
- If you've got to steer in water, where potential, walk wherever the water isn't moving. Use a keep on with check the firmness of the bottom ahead of you.
- Do not drive into flooded areas. Remember: “Turn around, don’t drown.” If floodwaters rise around your automobile, abandon the automobile and move to higher ground only if you'll be able to do therefore safely.
- Do not bit electrical instrumentality if you're wet or standing in water.
Key takeaways
Risk factor
To increase the resilience against natural hazards and to cut back the vulnerability of municipalities, socio psychological models square measure urged to check risk perception and per received state as a result of completely different perceptions could lead to completely different risk-reducing responses.
The correlations, additional detailed by verbal statements, recommend sure challenges and opportunities during this space. In general, the panel members appear to be glad with the data provision and therefore the institutional arrangements.
Safety factor
Flash flooding is that the most venturous weather disaster within the u .s Flood causes power outages, harm infrastructure, trigger landslides, and might be deadly.
Heavy precipitation during a short amount of your time causes water to rise chop-chop, elevating the chance of flooding. Flash floods occur with very little warning however flooding may also develop slowly when rain ceases.
There are various type depend upon time
BEFORE A FLOOD
WHEN A FLOOD CLOSE TO HAND
DURING A FLOOD
- Flood routing in a very procedure whereby the form of cuckoo is set from the proverbial or assumed flood hydra another location on the stream is determined from know or assumed flood hydrology at a specific location on the stream
- As the discharge in a very stream because of flood hyperbolic will increase and therefore the amount of water in temporary storage within the channel will increase. Because the flood finder, this temporary storage depletes. As a result, a flood hydrograph moving down a channel has seen by elongated and peak gets reduced. The flood wave then is alleged to be attenuated. Similar is that the result of reservoir storage.
Flood routing is used as
(a) Establishing the flood pick at a downstream location (e. Prediction of flood).
(b) Establishing the result of construction of on food results as a result of construction of reservoirs of flood
(c) Determining the required levee height for flood protection
(d) Predicting the behavior of watercourse when a amendment has been worn out the channel conditions.
(e) Determining the adequate of spillway
The basic techniques utilized in flood routing are:
(1) Lumped routing (hydrologic routing)
(2) Distributed routing (hydraulic routing)
- In Lumped routing we discover out:
Q = f (t) at a given x-location
i.e. discharge as a operate of your time at any given x
- In distributed routing we discover out
Q = f(x)
I e, discharge as a operate of your time and area
- In lumped routing we use continuous equation
- In distributed routing we use continuously equation and momentum equation
1. Continuity equation
I - Q = d s/ d t
For small time increment ∆t
[(I1 + I2)/2] ∆ t - [(Q1 + Q2)/2] ∆ t = (S2 - S1)
2. In differential from the continuity equation for unsteady flow in a reach with no lateral inflow given by
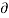 Q / ∂ X + T ∂ y / ∂ t = 0
Q / ∂ X + T ∂ y / ∂ t = 0
Where T = top surface width, y = depth of flow
3. Top momentum equation is given by
∂ y / ∂ X + V/g ∂ v/∂ t + 1/g ∂ v / ∂ t = so - SF
V = velocity of flow
So = bed slope
S f = energy line slope
3.10.1 HYDROLOGIC STORAGE ROUTING
- In storage routing we assume level pool routing concepts i.e the water level will be assumed horizontal
- In this case storage will be function of elevation only
S = S (h)
- This in level pool routing the inflow hydrograph known and at the same time the outflow elevation and storage elevation curve can be established we will have to find out outflow discharge Vs time or elevation Vs. Time or storage Vs time curve
- The outflow elevation and storage elevation relationship will be established as follows
The area at the reservoir site is survey and contour map is prepared. From this area enclosed various contour are plannimeter . Once the area enclose by contour are known the incremental volumes of water stored between any two successive contour can be determined using one of the following equation
∆ V = h/2 (A1 + A2)........... Trapezoidal formula
∆ V = h/3 (A1 + A2 + √ (A1 A2)) ............cone formula
∆ V = h/6 (A1 +4Am + A2) ...........Prismoidal formula
Where
A1 and A2 are the area corresponding to the successive contour and h is the difference between elevations.
- If these incremental accumulated up to any contour valves then the sum represent the storm volume of the reservoir upside elevation of that contour .Thus elevation storage relationship is established
3.10.2 ATTENUATION
During flood events, riparian buffers and wetlands can slow runoff and absorb excess water. This reduces peak flows and can lessen downstream flooding.
Key takeaways
The outflow elevation and storage elevation relationship will be established as follows
∆ V = h/2 (A1 + A2)........... Trapezoidal formula
∆ V = h/3 (A1 + A2 + √ (A1 A2)) ............cone formula
∆ V = h/6 (A1 +4Am + A2) ...........Prismoidal formula
- In a stream channel (river) a flood wave is also reduced in magnitude and prolonged in period id est. Attenuated, by storage within the reach between 2 sections,
- The storage within the reach are often divided into 2 parts-prism storage and wedge storage
- The degree that might be stored within the reach if the flow were uniform throughout, i.e., once water surface line is parallel to bed line e downstream water level is named prism storage and therefore the volume hold on between this line and the actual water surface profile because of outflow being completely different from influx into the reach is named 'wedge storage
- During rising storage volume in goodish whereas throughout falling as influx drops more rapidly than on wedge storage becomes negative.
- In the case of stream-flow routing the answer of the storage equation is a lot of sophisticated than within the case of reservoir routing, as a result of the wedge storage is concerned.
- While the storage in an exceedingly reach depends on each the influx and outflow, prism storage depends on the outflow alone (uniform flow condition) and therefore the wedge storage depends on the distinction of influx and outflow (I - 0)
- A standard technique of stream/channel flow routing within the Muskingum technique wherever the storage is expressed associate a operate of each influx and outflow within the reach as
S = k [Q + X (I - Q)]
- And this relationship is thought because the Muskingum equation. During this the parameter two is thought as coefficient issue it takes a price between zero and 0.5. The worth of x replay upon the paper of the wedge. When x= 0, clearly the storage could be a operate of discharge solely
I e S = K Q
- Such storage Iowa referred to as linear storage or linear (or reservoir kind storage).
- The constant K is referred to as storage-time constant and dimensions of your time. It's or so equal to the time of travel of a flood wave through the channel worth of K depends on the length of the reach and alternative roughness characteristics.
Note: By chasing arbitrary worth of x between 0-0.5 and Lydneyut accumulated storage as twenty one - Q)at, a graph is plotted between accumulated storage and [x I • (1- x)Q1asiordicate If nearly line is obtained, the corresponding value of x is that the correct worth and inverse slope of the on top of lives the K worth,
1. Structural methods:
(a) Flood control reservoirs - These areas unit of 2 sorts
- Detention reservoir - gated thence controlled outlet
- Retarding basin – un gated thence uncontrolled outlet
(b) Levees (flood embankments).
(c) Channel improvement,
(d) Flood ways that (new channels), and
(e) Soil conservation
2. Non-structural methods
(a) Flood plain section and
(B) Flood warning, evacuation and relocation.
FLOOD CONTROL BY RESERVOIR
The purpose of a control reservoir is to briefly keep a portion of the food so the flood area unit planate out. The reservoir is also ideally located upstream of the realm to be protected and therefore the water discharge within the channel downstream at its safe capability All the influx into the reservoir in far more than the safe {channel capability data rate} in keep till the influx drop currently the data rate and the keep water is discharged to recover the storage capacity for consequent flood
DETENTION RESERVOIR
A detention reservoir consists of AN obstruction to a stream with AN uncontrolled outlet. These area units essentially tiny structures and operate to cut back the flood peak by providing temporary storage and by restriction of the outflow rate.
LEVEES
Levees conjointly referred to as dikes or flood embankments area unit stuff banks created parallel to the course of the stream to confine it to a set course and restricted cross-sectional dimension. The heights of levees are beyond the design flood levels with sufficient free board the confinement of the stream to a set path free giant of land type inundation and consequently harm
Masonry structure accustomed confined the stream in a very manner like levees area unit referred to as flood walls
FLOOD WAYS
Flood ways in {which} area unit natural or artificial channel into which a vicinity of the flood are amused throughout high stages
CHANNEL IMPROVEMENT
1. Widening or deepening of the channel to extend the cross sectional space
2. Reduction of the channel roughness by improvement of vegetation from the channel perimeter
3. Short circuiting of meander loops by cutoff channel resulting in raised slopes
Key takeaways
Factor control
1. Structural methods:
(a) Flood control reservoirs - These areas unit of 2 sorts
- Detention reservoir - gated thence controlled outlet
- Retarding basin – un gated thence uncontrolled outlet
(b) Levees (flood embankments).
(c) Channel improvement,
(d) Flood ways that (new channels), and
(e) Soil conservation
2. Non-structural methods
(a) Flood plain section and
(b) Flood warning, evacuation and relocation.
(a) Modified pulse method
(b)Goodrich method
(c) Standard 4th order Runge Kitts methods
Modified pulse methods
[(I1 +I2)/2]∆t - [(Q1 + Q2)/2] ∆t = S2 - S1
The only unknown in this are S2 and we. Hence we rearrange the term such that all unknowns are on one side and all unknown are on other side
[(I1 +I2)/2] ∆ t + [S1 - (Q1 ∆t)/2] = [S2 + (Q2 ∆ t)/2]
As storage and discharge both are function of elevation hence we find a relationship of [S + Q ∆t/2] and elevation
Thus we have Q = Q (H), S = S (H) and [S + Q ∆t/2] = f (H) are known
The various steps in the routing are
(1) For the 1st time interval ∆t
[(I1 + I2)/2] ∆t and [S1 - (Q1 ∆t)/2] are known, hence [S2 + (Q2 ∆ t)/2]is determined
(2) From the relationship of [S + Q ∆t/2] bra (H), H is found out .At the same time from H outlet discharge is found out using discharge elevation relationship.
(3) For the next time increment, [S1 - Q1∆t/2] at the beginning is found out from [(S2 + Q2∆t/2) - Q2∆t] and the procedure described above is repeated till the entire inflow hydrograph is routed
Goodrich method
[(I1 +I2)/2]∆t - [(Q1 +Q2)/2] ∆t = S2 - S1
(I1 + I2) + (2S1/∆t - Q1) = (2S2/ ∆t + Q2)
All terms in LHS is known, and that on RHS is unknown for a given time increment.
(2S/∆t + Q)2 is determined from above equation and from storage elevation discharge data (2S/∆t + Q)2 is known as a function of elevation
Hence discharge, elevation and storage at the end of time incremental known
For next time increment
[(2S/∆t + Q)2 - 2Q2] of previous time increment
= [(2S)/∆t - Q] for use as initial value of next time increment.
Key takeaways
(a) Modified pulse method
[(I1 +I2)/2]∆t - [(Q1 + Q2)/2] ∆t = S2 - S1
(b)Goodrich method
[(I1 +I2)/2]∆t - [(Q1 +Q2)/2] ∆t = S2 - S1
(I1 + I2) + (2S1/∆t - Q1) = (2S2/ ∆t + Q2)
(c) Standard 4th order Runge Kitts methods
References
- Techmax
- Groundwater Hydrology by Todd D K Wiley
- Irrigation Theory and Practice by Michael A M Vikas Publication House
- Engineering Hydrology by Ojha Oxford University