UNIT 5
Water Wells
- A well is associate degree excavation or structure created within the ground by creating by removal, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, typically water.
- The oldest and commonest reasonably well could be waters well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The H2O is entailed by a pump, or victimization containers, like buckets, that area unit raised automatically or by hand.
- Water can even be injected back to the geological formation through the well. Wells were 1st created a minimum of eight thousand years a gone and traditionally vary in construction from an easy scoop within the sediment of a dry watercourse to the Iran, and therefore the step wells of Republic of India. Inserting a lining within the well shaft helps produce stability, and linings of wood or caning start a minimum of as way because the Iron Age.
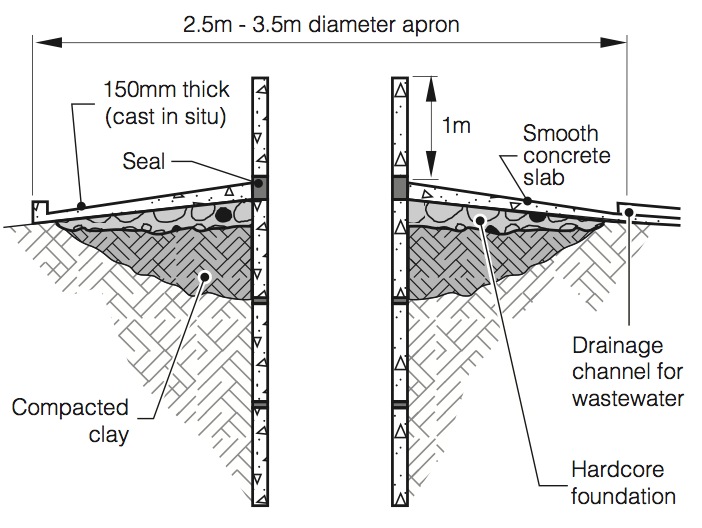
Fig. 1: Introduction of well construction
- Wells have historically been undone by hand creating by removal, as is that the case in rural areas of the developing world. These wells area unit cheap and low-tech as they use principally manual labor, and therefore the structure is lined with brick or stone because the excavation yields.
- A lot of trendy methodology known as caisson uses pre-cast ferroconcrete well rings that area unit down into the opening. Driven wells is created in loose material with a well hole structure, that consists of a hardened drive purpose and a screen of perforated pipe, when that a pump is put in to gather the water.
- Deeper wells are excavated by hand drilling ways or machine drilling, employing a bit in a very borehole. Trained wells area unit typically cased with a store-bought pipe composed of steel or plastic. Trained wells will access water at a lot of larger depths than mamma wells.
- Two broad categories of well area unit shallow or unconfined wells completed at intervals the upmost saturated geological formation at that location, and deep or confined wells, undone through associate degree tight stratum into associate degree geological formation below.
- A collector well is created adjacent to a fresh lake or stream with water percolating through the intervening material. The location of a well is designated by a hydro geologist, or groundwater surveyor.
- Water could also be pumped-up or hand drawn. Impurities from the surface will simply reach shallow sources and contamination of the availability by pathogens or chemical contaminants has to be avoided.
- H2O usually contains a lot of minerals in answer than surface water and will need treatment before being potable. Soil salination will occur because the groundwater level falls and therefore the close soil begins to dry out. Another environmental drawback is that the potential for to ooze into the water.
After the development of a pumping well, correct sanitary completion is critical to supply safe water needed for drinking and alternative functions. Totally different well completion operations usually needed for the wells created in loose formations area unit as follows (Todd, 1980):
- Placement of casing and well screens,
- Cementing/Grouting of casing, and
- Gravel packing.
However, the wells created in consolidated formations wherever the fabric close the well is stable, is left as open holes (i.e., uncased wells) into that groundwater will enter directly. Hence, the higher than well completion operations might not be needed for the wells created in consolidated formations. The main points of well construction in consolidated formation are found in archangel and Khepar (1999) and Sharma (2009).
Placement of Well Casing and Well Screen
(1) Types of Well Casing
Well casing could be a lining to take care of associate degree open vertical hole from ground surface to the geological formation. It seals out surface water and any undesirable quality groundwater and conjointly provides structural stability against caving materials outside the well. Materials used for construction of well casings area unit iron, alloyed or pure steel and Fe (Todd, 1980). Polyvinyl resin pipe is wide used as casing for shallow or deep, small-diameter observation wells. In cable tool drilling, the casing is driven into place, whereas in rotary drilling, the casing is smaller than the trained hole. Well casing usually involves: (i) surface casing, and (ii) pump-chamber casing.
(i) Surface Casing
It is put in from ground surface through higher strata of unstable or broken materials into a stable or comparatively tight material. Surface casing has many functions:
(a) It supports unstable materials throughout drilling,
(b) It reduces loss of drilling fluids,
(c) It facilitates installation or removal of alternative casing and
(d) It helps in inserting a sanitary seal and is a reservoir for a gravel pack.
(ii) Pump-Chamber Casing
It contains all the casing higher than the screen in wells of uniform diameter. The pump-chamber casing ought to have a nominal diameter a minimum of five cm larger than the nominal diameter of the pump bowls (Todd, 1980). Non-metallic pipes like ceramic clay, concrete, asbestos-cement, plastic, or fiberglass-reinforced plastic pipes area unit used wherever corrosion or incrustation could be a drawback.
(2) Placement of Well Screen
The method of putting in well screens is influenced by the look of the well, drilling methodology and therefore the issues encountered throughout drilling. The normally used ways for screen installation area unit (Todd, 1980; Raghunath, 2007): (i) pull-back methodology,
(ii) open-hole methodology,
(iii) bail-down methodology, and
(iv) Wash down methodology. A short description of those ways is given below.
(i) Pull-Back methodology
In this methodology, the casing is driven to the complete depth of the well. Thereafter, the screen is down within the casing and allowed to rest on rock bottom of the opening. The casing pipe is then force upward enough to show the complete length of the screen within the water bearing formation. The lead packer provided at the highest of the well screen is swollen by the wedge block so as to create a seal between the within of the casing and therefore the screen. This methodology is usually employed in cable-tool trained wells moreover as in rotary trained wells.
Key takeaways
Placement of well design
(1) Types of Well Casing
(i) Surface Casing
(ii) Pump-Chamber Casing
(2) Placement of Well Screen
(i) Pull-Back methodology
- Water-lifting devices area unit want to raise water to a height that enables users’ easy accessibility to water.
- Lifting devices is wont to raise groundwater, rain hold on in associate degree underground reservoir, and watercourse water.
- Communities ought to be ready to select from a variety of water-lifting devices, and every possibility ought to be conferred with its benefits, disadvantages and implications.
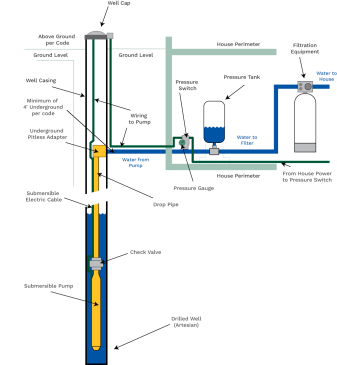
Fig. 2: Pumping equipment for water wells
- As an example, water lifting involves extra O&M activities and potential issues, compared to gravity systems, and therefore the latter area unit typically most well-liked if they're out there and applicable to true. The subsequent water-lifting devices area unit represented during this manual:
— Rope and bucket (loose through a block, or on a windlass);
— bucket pump;
— rope pump;
— suction plunger hand pump;
— dissent pump;
— deep-well piston pumps;
— deep-well diaphragm pumps;
— Centrifugal pump;
— Electrical submersible pump;
— Axial flow pump;
— Hydraulic pump pumps.
- There square measure different water-lifting devices that aren't delineates during this manual, like the progressing cavities pump, the manual diaphragm pump, the treadle pump and the chain pump. Different devices, like the air-lift pump, aren't enclosed as a result of they are not applicable to drinking-water provide systems.
1. Rope and bucket
The technology
- This device is principally used with hand-dug wells. A bucket on a rope is down into the water.
- Once the bucket hits the water it dips and fills, and is force up with the rope. The rope is also control by hand, run through a block, or wound on a lifting device.
- Sometimes, animal traction is employed together with a block. Improved systems use a rope through a block, and 2 buckets – one on every finish of the rope.
- For water but ten m deep, a lifting device with a hose running from very cheap of the bucket to a spout at the aspect of the well will be used. However, the hygiene of this method is poorer, albeit the well is protected.
- Initial cost: From US$ half dozen for a plastic bucket and five m of rope, to US$ one hundred fifty with a lifting device.
- Range of depth: 0–15 m (or a lot of sometimes).
Yield: 0.25 liter /s at ten m.
Area of use: everywhere the globe.
Main O&M activities
- The bucket is down and raised by playing out and pull within the rope, or by rotating the lifting device. Care should be taken to forestall the rope or bucket from becoming back feculent. Preventive maintenance consists of greasing the bearings of the lifting device or block.
- Little repairs square measure restricted to reparation holes within the bucket and hose, reconnecting the hinge of the bucket, and fixing the lifting device bearings or handle.
- All little repairs will be done by native individuals, and with tools and materials accessible within the community or space. Major repairs and replacements primarily encompass replacement the bucket, hose, rope, or half or all of lifting device.
- Woven nylon ropes might last for 2 years, however coiled nylon or sisal ropes last solely a number of months. A good-quality hose might last for over 2 years, and most buckets last a year (depending on the fabric and quality).
- Once individuals use their own rope and bucket, no further organization is needed. For community wells, a community committee sometimes organizes the upkeep and cleansing of the well, maintenance of the lifting device, etc.
2. Bucket pump
The technology
- The bucket pump is principally employed in trained wells. It consists of a lifting device over a one hundred twenty-five metric linear unit PVC tube, down that a narrow bucket with a valve within the base is lowered into the water on a sequence.
- Once the bucket hits the water, the valve opens and therefore the water flows in. Once the bucket is raised, the valve closes and therefore the water is preserved within the bucket.
- To unleash the water, the pump operator rests the bucket on a water discharger that opens the valve within the base. The windlass bearings square measure made from wood. Initial cost: calculable beginning value is US$ eighty.
Range of depth: 0–15 m.
Yield: comparatively low and depends on well depth.
Trademarks: Developed by national leader works
Area of use: Zimbabwe et al.
Main O&M activities
- To operate a bucket pump, rotate the handle of the lifting device and let the bucket meet up with the steel head.
- Each adults and youngsters will operate the pump. Preventive maintenance consists of lubricating the wood bearings of the lifting device, checking the bats and bolts, and checking that the valve is functioning.
- The pump and its setting ought to be unbroken clean, and therefore the well ought to be disinfected frequently. Minor repairs encompass replacement the valve washers and repairing links within the chain.
- Broken links within the chain will be repaired with steel wire. If the chain has fallen into the tube well it will be hooked out with an extended piece of wire.
- A serious demand is repairing very cheap of the bucket, which may be done domestically by or smith. At some stage, the chain, the bucket or the bearings of the lifting device can get to get replaced.
- A neighborhood craftsman is also required to repair or replace the lifting device system. Usually, village committee square measure shaped to drill or dig the well, and install the pump.
3. Rope pump
The technology
- The basic components of a rope pump square measure a block wheel higher than the well, a pipe age from below the water level to associate outlet slightly below the wheel, and a rope with rubber or plastic washers.
- The rope comes up through the pipe, over the wheel, backtrack into the well and into very cheap of the pipe, finishing the loop. Once the wheel is turned, the washers move upwards and elevate water into the pipe towards the outflow.
- Different components square measure associate underwater rope guide that directs the rope and washers into the pipe, and a frame that holds the block wheel. The rope pump will be created at village level victimization wood, rope and PVC tube (or bamboo canes with the centre bored out).
- In Central American nation, native industries turn out associate improved style of rope pump that contains a metal wheel and frame, industry-made washers, and a guide block of concrete with ceramic and PVC tubes.
- Concerning 25000 of those pumps are put in Central American nation. Water will be upraised from as deep as fifty m and raised to five m higher than ground level. Special models with 3-inch boreholes, and power-driven by windmills, bicycles, animal traction, electric motors or little gas engines, provide smart results.
Initial cost: US$ 15–35 for a conventional model and US$ ninety for a billboard model with
Piping (1995 knowledge, Nicaragua)
Range of depth: 0–50 m.
Yield: 0.6 liter /s at ten m, 0.15 liter /s at fifty m.
Area of use: In rural and urban areas of Central American nation, Bolivia, Indonesia, Ghana, Burkina face and different countries.
Construction: native manufacturers/artisans.
Main O&M activities
- The rope pump may be operated by men, girls or kids. Turning the handle of the pulley-block wheel makes the water rise.
- When pumping, the wheel needs to be command for a flash to empty the water within the riser and to stop the washers from being force back within the pipe, which might cause additional wear.
- The location and also the pump should be unbroken clean. Betting on use and also the kind of bearings, the shaft bearings should be lubricated a minimum of once per week. The pulley-block wheel and different elements of the pump have to be compelled to be checked often and glued, as necessary.
- The rope should even be checked for excessive wear. Users ought to listen to the pump performance and report issues. Most issues occur with the rope or washers obtaining stuck or slippery over the pulley-block wheel. Each six months to three years, the rope ought to get replaced (which takes regarding hour). Every few years, the washers ought to be revived.
- The piping lasts for a minimum of six years and, betting on the development, maintenance and use, the frame and pulley-block wheel of the pump will last from six to twelve years.
- The rope guide ought to last for many years and to vary it, the rising main ought to be taken out (which may be done by hand by some people). All repairs may be administrated by the users themselves, typically with the help of a craftsman for attachment.
- Rope pumps square measure utilized by communities or individual households. The upkeep wants square measure easy, however frequent, and users have to be compelled to make sure that they're administrated which their pump is unbroken in smart operating condition.
- Hygiene is additional vital than with several different forms of pump, significantly once the pump is employed communally. In such cases, it's vital that the users organize effective measures for guaranteeing smart practices.
4. Suction plunger hand pump
The technology
- A suction plunger hand pump has its cylinder and plunger (or piston) situated on top of the water level, typically inside the pump stand itself. These pumps should be set by gushing water on the plunger.
- On the up-stroke of the plunger, the pressure within the suction pipe is reduced and gas pressure on the water outside pushes the water up into the pipe.
- On the down-stroke, a check valve at the body of water of the suction pipe closes and water passes the plunger through an opened plunger valve. With future stroke, the plunger valve closes and also the water is upraised up by the plunger and flows out at the highest of the pump, whereas new water flows into the suction pipe.
- The operational depth of this sort of hand pump is restricted is restricted pressure and also the effectiveness of the plunger seals to regarding seven m baffled level, less at higher altitudes. Initial cost: From US$ thirty five (Thailand, 1985), together with ten m atomic number 26 drop pipe and a foot valve, to US$ 185 for a Wasp pump in Republic of India (1983 value while not a suction pipe)
Range of depth: 0–7 m.
Yield: 0.4–0.6 liter /s at seven m.
Area of use: Rural and low-income square measure as wherever groundwater tables are inside seven m of the surface.
Main O&M activities
- The operation begins with priming the pump, by gushing clean water on the plunger through the highest of the pump stand. Pumping is finished by moving the handle up and down, typically whereas standing beside the pump (with an oarsman pump, the user sits).
- Most suction hand pumps may be simply operated by men, girls and kids. Suction pumps square measure comparatively simple to take care of, since most or all of the moving elements square measure on top of ground level.
- Maintenance will usually be done by a village caretaker or by the users themselves, exploitation easy tools, and basic spare elements and materials (however, many brands can't be fully maintained at native level).
- The fundamental skills required for preventive maintenance (e.g. Greasing, dismantlement the pump stand, replacement spare elements, etc.) may be instructed to pump caretakers quickly (from some hours to some days, betting on the quality of the system, materials used, etc.).
- Preventive maintenance consists of greasing the bearings hebdomadally, inspecting the inside of the pump stand once a month, and inspecting the complete pump stand once a year.
- Most of this work may be done by one or 2 folks, however additional folks could also be required once pump elements have to be compelled to be upraised out of the well or borehole.
- Throughout these inspections, smaller repairs (replacement of washers, etc.) could also be necessary. For major repairs (e.g. Broken rising main, cracks within the attachment of metal parts), additional extremely delicate folks and specialized tools and materials could also be required.
- Several suction hand pumps square measure family pumps and square measure cared for by one family. For communal pumps, the user cluster or community can be would like an area committee to arrange O&M tasks, together with creating major repairs. Personal enterprises typically play role in playing repairs and marketing spare elements.
Key takeaways
Water-lifting devices area unit want to raise water to a height that enables users’ easy accessibility to water.
Lifting devices is wont to raise groundwater, rain hold on in associate degree underground reservoir, and watercourse water.
The subsequent water-lifting devices area unit represented during this manual:
Rope and bucket (loose through a block, or on a windlass);
Bucket pump;
Rope pump;
Suction plunger hand pump;
Dissent pump;
Deep-well piston pumps;
Deep-well diaphragm pumps;
Centrifugal pump;
Electrical submersible pump;
Axial flow pump;
Hydraulic pump pumps.
- Regular maintenance of your well is needed to confirm the continued safety of your water and to watch for the presence of any contaminants.
- The National spring water Association provides info to assist you schedule a well water checkup external, otherwise you will learn “How to urge info on Wells wherever You Live”, below. If you continue to have queries, take a glance at the H2O list.
- According to the National spring water Association, here square measure some steps you'll be able to go for facilitate shield your well:
- Wells ought to be checked and tested ANNUALLY for mechanical issues, cleanliness, and also the presence of sure contaminants, like coli form bacterium, nitrates/nitrites, and the other contaminants of native concern, (for example, arsenic and radon).
Fig. 3: Maintenance of well
- Well water ought to be tested over once a year if their square measure perennial incidents of epithelial duct malady among manage members or guests and/or a modification in style, odor, or look of the H2O.
- All venturesome materials, like paint, fertilizer, pesticides, and fuel, ought to be unbroken far from your well.
- When combination chemicals, don't place the hose within the blending instrumentation, as this could siphon chemicals into a household’s water system.
- Consult an expert contractor to verify that there's correct separation between your well, home, waste systems, and chemical storage facilities.
- Always check the well cowl or well cap to confirm it's intact. The highest of the well ought to be a minimum of one foot on top of the bottom.
- Once your well has reached its serviceable life (usually a minimum of twenty years) have a certified water well driller and pump installer call in the prevailing well and construct a brand new well. For additional info visit “Finding a Contract or External” (National spring water Association).
- Groundwater typically appearance crystal clear, however before drinking it, care should be taken to form positive it does not contain dissolved chemicals that might be harmful.
- Just because you've got a well that yields lots of water does not imply you'll be able to plow ahead and simply take a drink. As a result of water is such a superb solvent it will contain millions of dissolved chemicals. And since groundwater moves through rocks and submerged soil, it's loads of chance to dissolve substances because it moves. For that reason, groundwater can usually have additional dissolved substances than surface water can.
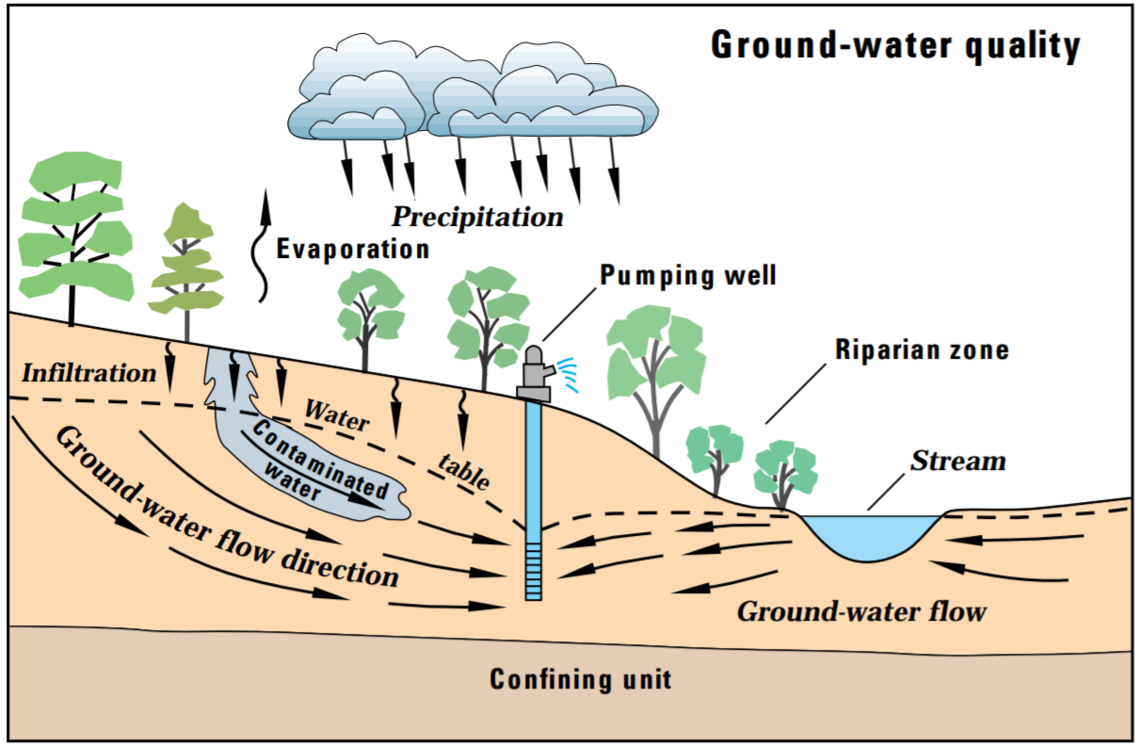
Fig. 4: Ground water quality
- Even though the bottom is a superb mechanism for filtering out particulate, like leaves, soil, and bugs, dissolved chemicals and gases will still occur in giant enough concentrations in groundwater to cause issues. Underground water will get contaminated from industrial, domestic, and agricultural chemicals from the surface. This includes chemicals like pesticides and herbicides that several owners apply to their lawns.
- Contamination of groundwater by road salt is of major concern in northern areas. Salt unfolds on roads to soften ice, and, with salt being thus soluble in water, excess Na and chloride is definitely transported into the submerged groundwater.
- The foremost common water-quality downside in rural water provides is microorganism contamination from septic tanks, that square measure usually utilized in rural areas that do not have a sewage-treatment system.
- Effluent (overflow and leakage) from a tank will percolate (seep) right down to the formation and perhaps into a homeowner's own well. Even as with urban water provides, chlorination could also be necessary to kill the damaging bacterium.
- Groundwater will contain sulfide or different present chemicals. Groundwater additionally could contain fossil oil, organic compounds, or different chemicals introduced by humans' activities. Contaminated groundwater will occur if the well is found close to land that's used for farming wherever sure styles of chemicals square measure applied to crops, or close to a gasoline station that features a unseaworthy vessel.
- Outpouring from septic tanks and/or waste-disposal sites can also contaminate groundwater. A tank will introduce bacterium to the water, and pesticides and fertilizers that course into farmed soil will eventually find self in water drawn from a well. Or, a well might need been placed in land that was once used for one thing sort of a garbage or chemical dump website. In any case it is wise have your H2O tested for contaminates.
- Over five hundredth of the U.S. Population depends on groundwater for potable. Groundwater is additionally one amongst our most significant sources of water for irrigation. Sadly, groundwater is liable to pollutants.
- Groundwater contamination happens once semi synthetic merchandise like gas, oil, road salts and chemicals get into the groundwater and cause it to become unsafe and unfit for human use.
- Materials from the land's surface will move through the soil and find yours self within the groundwater. For instance, pesticides and fertilizers will notice their means into groundwater provides over time. Road salt, toxicant substances from mining sites, and used oil additionally could ooze into groundwater.
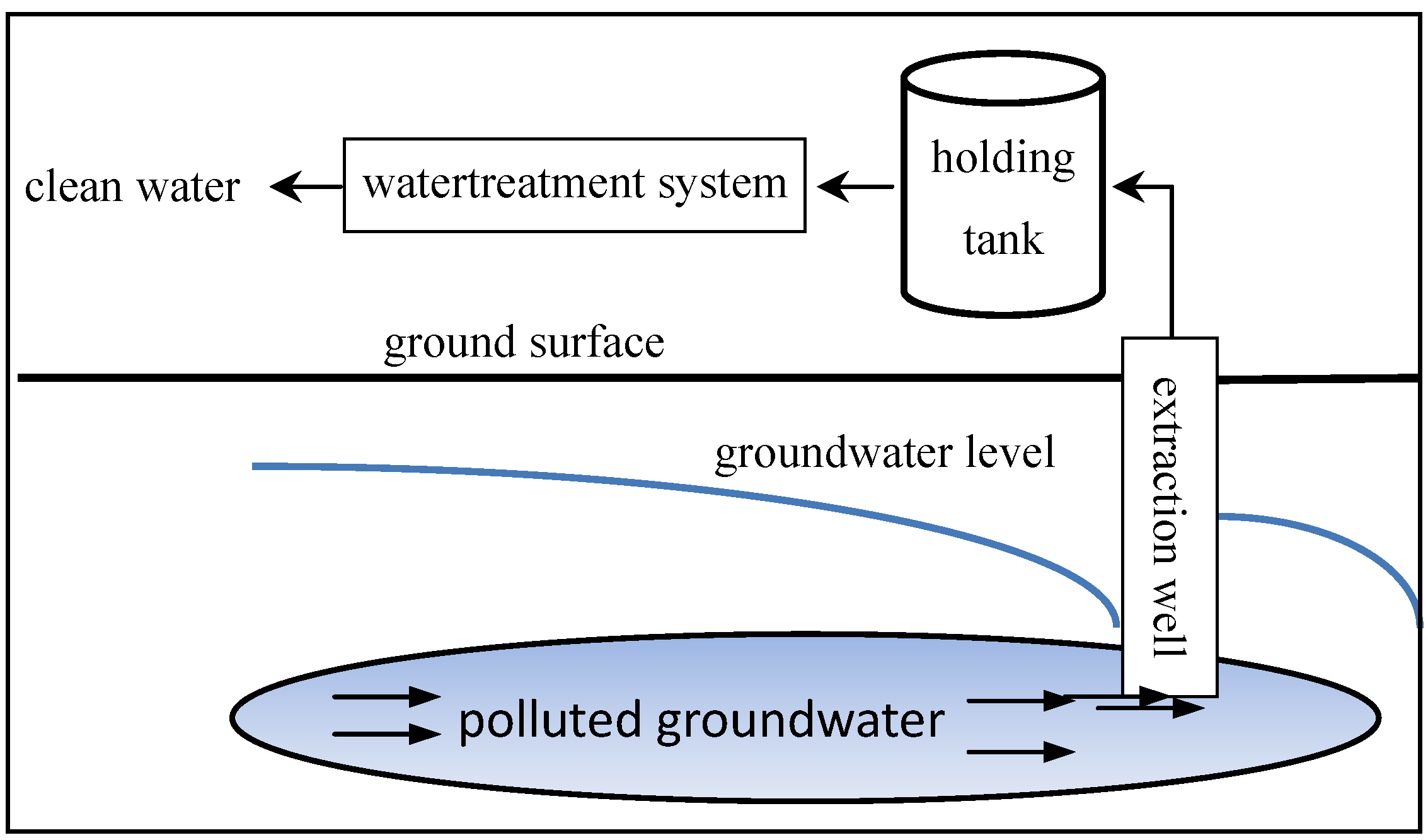
Fig. 5: Contaminated of groundwater and its control
- Additionally, it's doable for untreated waste from septic tanks and toxicant chemicals from underground storage tanks and leaky landfills to contaminate ground water.
POTENTIAL SOURCES OF GROUNDWATER CONTAMINATION
Storage Tanks
May contain gas, oil, chemicals, or alternative varieties of liquids and that they will either be higher than or below ground. There areas unit calculable to be over ten million storage tanks buried within the u. s. And over time the tanks will corrode, crack and develop leaks. If the contaminants get out and acquire into the groundwater, serious contamination will occur.
Septic Systems
On site waste product disposal systems utilized by homes, offices or alternative buildings that aren't connected to a town installation septic systems area unit designed to slowly drain away excrement underground at a slow, harmless rate. AN improperly designed, located, created, or maintained septic system will leak bacterium, viruses, manage chemicals, and alternative contaminants into the groundwater inflicting serious issues.
Uncontrolled unsafe Waste
In the U.S. Today, there areas unit thought to be over twenty,000 notable abandoned and uncontrolled unsafe waste sites and therefore the numbers grow once a year. Unsafe waste sites will cause groundwater contamination if there areas unit barrels or alternative containers parturition around that area unit packed with unsafe materials. If there's a leak, these contaminants will eventually build their means down through the soil and into the groundwater.
Landfills
Landfills area unit the places that our garbage is taken to be buried landfills area unit purported to have a protecting bottom layer to stop contaminants from moving into the water. However, if there's no layer or it's cracked, contaminants from the lowland (car battery acid, paint, manage cleaners, etc.) will build their means down into the ground water.
Chemicals and Road Salts
The widespread use of chemicals and road salts is another supply of potential groundwater contamination. Chemicals embrace merchandise used on lawns and farm fields to kill weeds and insects and to fertilize plants, and alternative merchandise utilized in homes and businesses. Once it rains, these chemicals will ooze into the bottom and eventually into the water. Road salts area unit utilized in the winter to place soften ice on roads to stay cars from slippery around. Once the ice melts, the salt gets washed off the roads and eventually lands up within the water.
Atmospheric Contaminants
Since groundwater is a component of the hydrologic cycle, contaminants in alternative elements of the cycle, like the atmosphere or bodies of surface water, will eventually be transferred into our groundwater provides.
Key takeaways
POTENTIAL SOURCES OF GROUNDWATER CONTAMINATION
Storage Tanks
Septic Systems
Uncontrolled unsafe Waste
Landfills
Chemicals and Road Salts
Atmospheric Contaminants
- Groundwater plays a basic role in human life. Despite its indispensable characteristics, it's unfortunate that groundwater is commonly related to low yield. The increasing demand for water and therefore the and also the value concerned in drilling boreholes therefore need the appliance and therefore the correct use of groundwater investigation techniques to find high yielding aquifers.
- A geology investigation involving AN electrical phenomenon technique employing a Schlumberger conductor array was conducted around dominion, a basement tract of southwestern African nation.
- Sixteen Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES) stations were applied across the study space employing a most current conductor separation of one hundred m.
- The geo electrical imaging from this study disclosed that the lithologies area unit divided into surface soil, lateritic soil, Sandy clay/clayey sand/clay/weathered rock and therefore the bedrock.
- Underwater geo electrical maps (overburden thickness, weatherworn layer iso thickness, weatherworn layer iso resistivity, bedrock relief, bedrock electrical phenomenon, and correlations from geo electric sections) were wont to generate info regarding the groundwater potential of the study space.
- It had been inferred that the (VESs one, 2, 8, 10, and 11) and therefore the southwestern (VESs thirteen and 14) regions area unit related to high groundwater yield. Boreholes are often trained to a mean depth of twenty-two.0 m (72.6 ft) on these axes.
- The groundwater potential of the northern (VES 5), central (VES 9), and southern (VES 12) elements of the study space were inferred to be of medium potential. The borehole drilling on these axes are often extended to the depth of thirty.0 m (99.0 ft), with medium groundwater yield.
- However, the northeastern (VES three and VES 4) and therefore the western (VESs half-dozen, 7, 15, and 16) zones area unit characterized by low groundwater potential. This gift study has been ready to notice the drillable zones and depths for optimum groundwater yield during a crystalline tract of dominion, Akure victimization VES.
- The electrical phenomenon sounding is economical in characterization of aquifers for groundwater exploration.
- The overburden thickness varied from four.2 to 47.1 m. Weatherworn layer and broken bedrock represents the geological formation units.
- The geo electric sections supported the apparent electrical phenomenon data's interpretations and established the electrical phenomenon variations' pattern of the underwater.
- The analysis of aquifers' vulnerability to contaminants through geo electric parameters showed that the aquifers area unit safe from anthropogenetic pollution. This is often in agreement with the work of Adeyemo et al. (2016) that was administered at Ipinsa and Okeodu via Akure southwestern African nation. Their model showed that solely 100% of the study space is extremely liable to close to surface pollution.
- The analyses during this study have created the work to be qualitative and quantitative in nature. The exempted info in one scope is disclosed through the opposite scope that necessitate excusable conclusion. Once and for all, the thick overburden that corresponds to basement depression is related to high yield of groundwater.
- This zone that is grouping trough for groundwater would be the foremost economic zone for groundwater exploitation.
- Efforts geared toward guaranteeing adequate groundwater offer within the space ought to be targeted at zones wherever the bedrock is deep. Moreover, the regions of broken basement rocks and bedrock depression (thick overburden) area unit zones with high groundwater accumulation capability and area unit so suggested for extracting groundwater in substantial quantities.
An Introduction to Artificial Recharge
- One results of the growing competition for water is augmented attention to the employment of artificial recharge to reinforce spring water provides.
- Declared merely, artificial recharge could be a method by that excess surface water is directed into the ground—either by spreading on the surface, by mistreatment recharge wells, or by fixing natural conditions to extend infiltration—to make full a formation.
- Artificial recharge (sometimes referred to as planned recharge) could be a thanks to store water underground in times of water surplus to satisfy demand in times of shortage. Water recovered from recharge comes is allotted to non-potable uses like landscape irrigation or, less ordinarily, to potable use.
- Artificial recharge may also be wont to management brine intrusion in coastal aquifers, management land subsidence caused by declining spring water levels, maintain base flow in some streams, and lift water levels to scale back the value of spring water pumping.
- It is helpful to consider the complete artificial recharge operation as a water supply undergoing a series of treatment steps throughout that its composition changes. The constituents of potential concern rely not solely on the character of the supply water, however additionally on its treatment before recharge (pretreatment), changes that occur because it moves through the soil and formation (soil-aquifer processes), and treatment once withdrawal to be used (post treatment).
- This report discusses 3 kinds of supply waters having terribly completely different characteristics—treated municipal waste, storm water runoff, and irrigation come back flow—that are planned to be used in artificial recharge. Normally, every of those supply waters has to be subjected to some reasonably pretreatment before being introduced into the soil or formation.
- The precise pretreatment operations needed rely on the sort of supply water, the character of the recharge process, and also the supposed use of the recovered water.
- A basic assumption of this report is that waste want to recharge the bottom water should receive a sufficiently high degree of treatment before recharge therefore on minimize the extent of any degradation of native spring water quality, also on minimize the requirement for and extent of further treatment at the purpose of extraction.
- After pretreatment, the water is prepared for recharge, either through surface spreading and infiltration through the unsaturated zone or by direct injection into spring water.
- Recharge by infiltration takes advantage of the natural treatment processes, like biodegradation of organic chemical, that occur as water moves through soil. The standard of the water before recharge is of interest in assessing the potential risks related to human exposures to chemical toxicants and infective microorganisms that may be gift within the supply water.
- Though one will fairly expect that such constituents can typically be reduced throughout filtration through the soil, also as afterward within the formation, a conservative approach to risk assessment would assume that toxicants and microorganisms aren't fully removed and a few area units affected solely minimally before resultant extraction and use.
- Therefore, once recharge water is withdrawn later for one more purpose, it's going to need a point of post treatment, betting on its supposed use.
- Taking a systems perspective that encompasses all steps from pretreatment, through recharge, through transformation and transport, to extraction, this report assesses the problems and uncertainties related to the bogus recharge of spring water mistreatment supply waters of impaired quality.
- Specially, the report focuses on the methodologies and nature of the recharge systems and also the resultant impacts on the native spring water quality, particularly as those impacts might have an effect on public health following use of the recovered water. Economic, institutional, and regulative queries area unit examined also. First, this chapter presents a primer on artificial recharge of spring water to present the reader AN introduction to the philosophy and techniques of the sector.
Artificial Recharge
- Artificial recharge is that the method of spreading or poundage water on the land to extend the infiltration through the soil and percolation to the formation or of injecting water by wells directly into the formation. Surface infiltration system is wont to recharge unconfined aquifers solely.
- Confined formation is recharged with wells that penetrate the aquifer. Well recharge is additionally used for unconfined aquifers if appropriate land for infiltration systems isn't on the market.
- Artificial recharge is done mistreatment any surplus surface water. Once quality water is employed for recharge, the underground formations will act as natural filters to get rid of several physical, biological, and chemical pollutants from the water because it moves through.
- Often, the standard improvement of the water is really the most objective of recharge, and also the system is operated specifically mistreatment the soil and also the formation to produce further treatment to the supply water. Systems employed in this fashion area unit referred to as soil-aquifer treatment (SAT), or geo purification, systems.
- The water extracted from weekday systems typically is used while not any treatment to support recreation, landscape irrigation, and alternative non-potable functions. Potable use might need additional treatment.
- As a result of aquifers sometimes area unit abundant comer than vadose zones, the standard improvement of the water is far less within the formation than within the vadose zone.
- Thus, recharge mistreatment wells in confined aquifers can't be expected to supply major enhancements within the quality of the water. If low-quality water is to be used for well injection, it should be treated to satisfy the required reprocess qualities before injection.
- Additionally, adequate treatment of the water before recharge is important to scale back preventative of the recharge wells. A summary of sources of water, treatment choices, recharge systems, recovery techniques, and uses of the water once recovery.
Ground Water Level
- Another style criterion is that the bottom water level should be deep enough below the infiltration system that it doesn't interfere with the infiltration method.
- This demand applies to the mounding of the permanent water level caused by recharging, also on perked up spring water mounds which will kind over proscribing layers within the vadose zone.
- Wherever infiltration rates area unit controlled by the preventative layer (which is that the rule instead of the exception for basins and ponds), the water level should be a minimum of zero.5 m (1.6 ft) below the lowest of the basin.
- This distance sometimes is capable keep the highest of the capillary fringe below the basin bottom, so infiltration rates aren't restricted by underlying spring water.
- Where there's no preventative layer, there's additional hydraulic continuity between the water within the infiltration system and also the spring water.
- In this case, the vertical distance between the water surface and also the spring water table (at a long way from the ponds wherever most of the mound has dissipated) ought to be a minimum of double the dimension of the infiltration system (Bouwer, 1990).
- Thus, wherever spring water levels area unit high, most infiltration rates is obtained solely with long, slim streams or basins spaced an appropriate distance apart.
- Where waters of impaired quality area unit used for recharge by surface infiltration systems, it's going to be fascinating to stay water levels sufficiently low to form Associate in nursing adequate unsaturated zone below basin bottoms for aerobic processes and virus removal. Projected American state rules, as an example, need a minimum depth to water of three m (9.8 ft) below the basins (Hultquist et al., 1991).
- Alternative infiltration systems, however, like those within the dunes of Netherlands for pretreatment of Rhine water for potable use, operate basically within the water zone with no unsaturated conditions.
- Also, wherever wells area unit trained getting ready to streams or lakes to ''pull" surface water through the formation for treatment before drinkable treatment (bank filtration systems), the processes conjointly manifest itself fully below the bottom groundwater level.
- Thus, there's no normal for minimum depth to water below infiltration basins for adequate quality improvement of waters of impaired quality.
- Groundwater levels area unit declining across the country as our withdrawals exceed the speed of aquifers to naturally fill up themselves, referred to as recharge. One methodology of dominant declining water levels is by victimization artificial groundwater recharge.
- The USGS monitors wells to judge the impact of groundwater depletion and recharge, and provides important data to people who rely on groundwater resources.
BACKGROUND
- Artificial recharge is that they observe of accelerating the quantity of water that enters Associate in nursing formation through human-controlled suggests that.
- As an example, groundwater will be unnaturally recharged by redirecting water across the land surface through canals, infiltration basins, or ponds; adding irrigation furrows or mechanical device systems; or just injecting water directly into the subsurface through injection well.
- Actual groundwater recharge happens as precipitation falls on the land surface, infiltrates into soils, and moves through pore areas right down to the groundwater level. Natural recharge can also occur as surface-water outflow from rivers, streams, lakes, and wetlands.
- Artificial recharge will be done through injection of water through wells. This methodology typically is applied to recharge deep aquifers wherever applications of water to the land surface do not seem to be effective at recharging these aquifers.
AQUIFER STORAGE AND RECOVER
- Aquifer storage and recovery may be a water-storage technique applied by water-resource managers and scientists worldwide. Basically, it involves storage of obtainable water through wells completed into aquifers, with ulterior retrieval from these same wells throughout dry periods. Recovery of water hold on in these wells greatly advantages environmental, agricultural, and concrete uses.
Key takeaways
An Introduction to Artificial Recharge
- One results of the growing competition for water is augmented attention to the employment of artificial recharge to reinforce spring water provides.
- Declared merely, artificial recharge could be a method by that excess surface water is directed into the ground—either by spreading on the surface, by mistreatment recharge wells, or by fixing natural conditions to extend infiltration—to make full a formation.
Artificial Recharge
- Artificial recharge is that the method of spreading or poundage water on the land to extend the infiltration through the soil and percolation to the formation or of injecting water by wells directly into the formation. Surface infiltration system is wont to recharge unconfined aquifers solely.
- Confined formation is recharged with wells that penetrate the aquifer. Well recharge is additionally used for unconfined aquifers if appropriate land for infiltration systems isn't on the market.
Ground Water Level
- Another style criterion is that the bottom water level should be deep enough below the infiltration system that it doesn't interfere with the infiltration method.
Background
- Artificial recharge is that they observe of accelerating the quantity of water that enters Associate in nursing formation through human-controlled suggests that.
Aquifer storage and recover
- Aquifer storage and recovery may be a water-storage technique applied by water-resource managers and scientists worldwide
- Rooftop Rain Water gathering is that the technique through that rain water is captured from the roof catchments and hold on in reservoirs. Harvested rain water will be hold on in sub-surface water reservoir by adopting artificial recharge techniques to satisfy the social unit wants through storage in tanks.
- Although fresh water gathering has been enforced altogether the Urban native Bodies, it's currently felt that there's a desire to change a number of the structures. The recharge bore wells and open wells have currently established to be a lot of made to recharge deep fractures, fissures. Hence, the individual households could also be advocated to observe the methodologies.
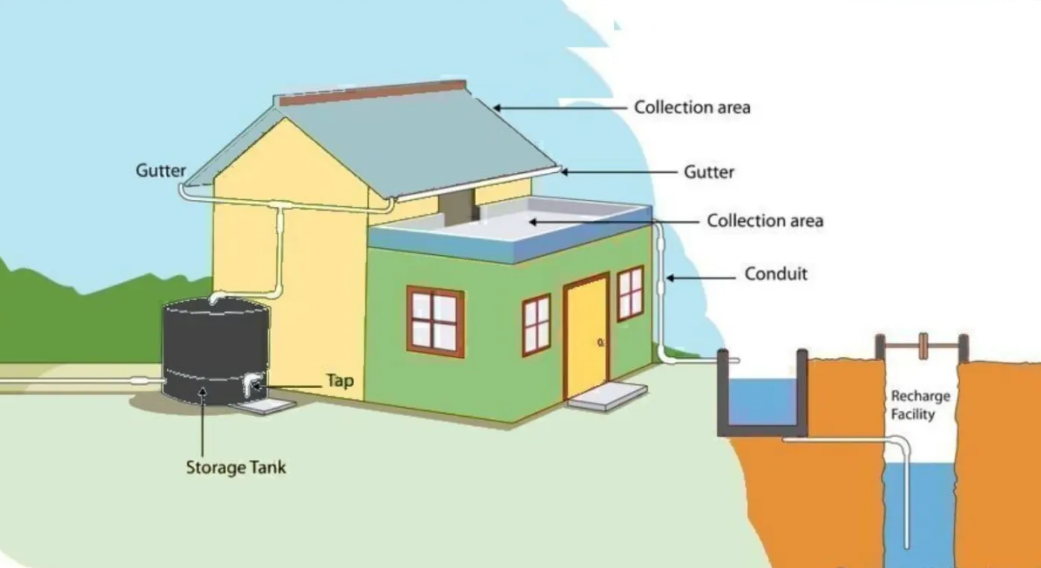
Fig. 6: Roof top rainwater harvesting
- In top gathering, the roof becomes the catchments, and therefore the fresh water is collected from the roof of the house/building. It will either be hold on during a tank or amused to artificial recharge system. This methodology is a smaller amount costly and extremely effective and if enforced properly helps in augmenting the water level of the world.
- Rooftop Rain Water gathering will be done at any building, massive or little, wherever every of the subsequent kind a locality of the RWH structure. The RWH system chiefly carries with it geographical region, transportation, flushing and filter media (Sand gravel filter/Charcoal filter). The roof prime fresh water is collected and hold on for direct use or it will be recharged the water level.
Roof prime Rain Water gathering (RRWH) Print
Rainwater gathering Menus
About
Methods of RWH
Documents
Gallery
Video
Contact North American nation - RWH
Roof prime Rain Water gathering (RRWH)
- Although fresh water gathering has been enforced altogether the Urban native Bodies, it's currently felt that there's a desire to change a number of the structures. The recharge bore wells and open wells have currently established to be a lot of made to recharge deep fractures, fissures. Hence, the individual households could also be advocated to observe the methodologies.
- In top gathering, the roof becomes the catchments, and therefore the fresh water is collected from the roof of the house/building. It will either be hold on during a tank or amused to artificial recharge system. This methodology is a smaller amount costly and extremely effective and if enforced properly helps in augmenting the water level of the world.
- Rooftop Rain Water gathering will be done at any building, massive or little, wherever every of the subsequent kind a locality of the RWH structure. The RWH system chiefly carries with it geographical region, transportation, flushing and filter media (Sand gravel filter/Charcoal filter). The roof prime fresh water is collected and hold on for direct use or it will be recharged the water level.
1. RRWH for direct use
Suitable roof
Gutter to gather water from the roof
Down pipe to divert water from gutter to vessel
A pre-collection filter
Storage tank
2. RRWH for groundwater recharge
The fresh water collected from the top will be used for recharging the groundwater aquifers by varied styles of structures to confirm percolation of fresh water within the ground rather than exhausting removed from the surface.
Open well
Bore well
Recharge pit
Recharge trench
Recharge shaft
Percolation tanks
Activities to be taken up/Design/Methods
- Rooftop Rain Water gathering systems will offer smart quality of potable water, if the planning options made public below area unit taken into account:
- The substances that get in the creating of the roof ought to be non-toxic and with chemicals inert.
- Roof surfaces ought to be sleek, laborious and dense since they area unit they are easier to wash and are less seemingly to be broken and un harness materials/ fiber into the water.
- Roof painting isn't sensible since most paints contain poisonous substances and should peel off.
- No overhanging trees ought to be left close to the roof.
- Nesting of birds on the roof ought to be prevented.
- All gutter ends ought to be fitted with a wire mesh screen to stay out leaves, etc.
- Appropriate arrangement for discarding the primary flow of rain ought to be created.
- A soak away channel ought to be designed at water retailers and a screened overflow pipe ought to be provided.
- The vessel ought to have a decent fitting roof that excludes lightweight, a top and a flushing pipe at the bottom of the tank (for standing tanks).
- There ought to be a reliable sanitary extraction device like a gravity faucet or a pump to avoid contamination of the water within the tank.
- There ought to be no risk of contaminated waste matter flowing into the tank (especially for tanks put in at ground level).
- Water from alternative sources, unless it's a reliable supply, shouldn't be empty into the tank through pipe connections or the top.
Maintenance
- Roof high structure tanks, like all water supply systems, demand periodic management and maintenance to make sure reliable and quality water supply. If the assorted parts of the system are not often cleansed, water use isn't properly managed, issues don't seem to be known or necessary repairs not performed, the roof structure system will cease to produce reliable and sensible quality water. Following could be a program of maintenance and management needs which will give a basis for monitoring and checking:
- During the time of year, the total system (roof structure, gutters, pipes, screens, first flush and overflow) ought to be checked before and when every rain and ideally cleansed when each dry amount prodigious a month.
- At the top of the season and simply before the primary shower of rain is anticipated, the vessel ought to be clean and flushed of all sediment and detritus (the tank ought to be refilled afterward with many cm of fresh water to stop cracking). Timely service (before the primary rains area unit due) of all tank fixtures, as well as replacement of all worn screens and pairing of the outlet faucet or pump.
- The runoff water collected from roof A-one will by artificial means recharge and augment the depleting well water resources particularly within the urban areas, wherever the natural recharge has diminished significantly. The area unit as having depth to water level larger than eight m below ground level and underlain by leaky strata is appropriate for artificial recharge.
Design
- The design involves thought of knowledge on hydrological and hydro geological aspects and hydro earth science parameters. The background information to be collected is as given below:
- Layout arranges of the realm.
- Demarcation of the roof, paved and open areas.
- Delineation of storm water drains and flow of storm water.
- Details of the present well water abstraction structures in and round the neighborhood of the project web site.
- Computation of the runoff for recharge. Except the higher than mentioned parameters. Choice of applicable recharge structure depends on the provision of house for construction of recharge structures and invert levels of storm water drains at inlets to recharge structures.
- Whereas making ready the recharge theme, depth and form of the storage facility in recharge structure depends on the provision of runoff, depth of storm water evacuation and house availableness in a neighborhood. The recharge theme as ready may be got vetted by applicable authorities/TWAD to include suggestions for improvement.
- The most appropriate recharge structures for roof high rain water gathering are:
Recharge pits
Recharge trenches
Recharge through dry or operational dug wells
Recharge through abandoned/existing tube wells
Recharge wells, etc.
Key takeaways
- Rooftop Rain Water gathering is that the technique through that rain water is captured from the roof catchments and hold on in reservoirs. Harvested rain water will be hold on in sub-surface water reservoir by adopting artificial recharge techniques to satisfy the social unit wants through storage in tanks.
Maintenance
- Roof high structure tanks, like all water supply systems, demand periodic management and maintenance to make sure reliable and quality water supply. If the assorted parts of the system are not often cleansed, water use isn't properly managed, issues don't seem to be known or necessary repairs not performed, the roof structure system will cease to produce reliable and sensible quality water. Following could be a program of maintenance and management needs which will give a basis for monitoring and checking:
Design
- The design involves thought of knowledge on hydrological and hydro geological aspects and hydro earth science parameters.
References
- Techmax
- Groundwater Hydrology by Todd D K Wiley
- Irrigation Theory and Practice by Michael A M Vikas Publication House
- Engineering Hydrology by Ojha Oxford University