Unit – 2
Curves
(a) Linear method
(i) Offset from long chord
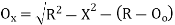
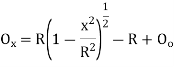
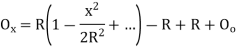
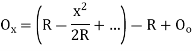

Where 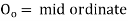
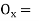 offset at some point P at distance x from midpoint D.
offset at some point P at distance x from midpoint D.
(ii) Perpendicular offset from tangent
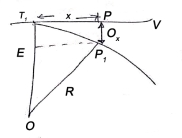
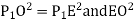
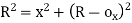
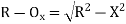
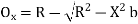
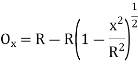
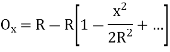
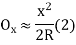
(iii) Radial offset from tangent:
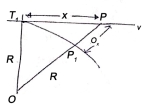
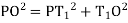
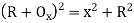
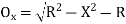
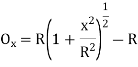
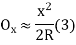
(iv) Successive Bisection of Arc or chord
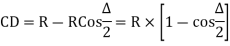
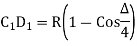
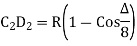
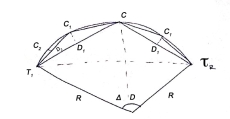
(v) By offset from chord produced

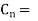 last sub chord
last sub chord
b) Angular method
i) Rankine's method of deflection angle
- It is generally used for setting out a circular curve of long length and large radius.
- It gives good result except then chords are long as compared to radius, so that variation between length of an Arc and its cord becomes considerable.
- It is used in highway and Railway
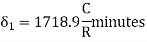
 = Tangential angle
= Tangential angle
C = chord length
(ii) Tachometric method
-It is similar to Rankine’s method of deflection angle.
- The theodolite at 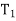 may be used as Tacheometric and Tacheometric observation are made.
may be used as Tacheometric and Tacheometric observation are made.
- Less accurate as compared to Rankins.
- Chaining is completely dispersed in this method.
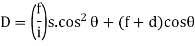
(For Incline and line of sight)
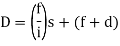
(For horizontal line of sight)
ii) Two theodolite method
- Convenient than any of to our method when ground is undulating rough and not suitable for Linear measurements.
- Two theodolites are used and linear measurement are completely eliminated.
- Hence, most accurate method.
- It is based on principle that angle between the tangent and chord is equal to angle subtended by chord in opposite segment.
- Time consuming method
- Most accurate method
- Highly expensive.
Reverse curve: -
When to normal circular curves of different or equal radii, have opposite in direction of curvature join together, the formed or resultant curve is known as reverse curve.
Uses: -
a) When angle between two straight line is very small.
b) When two straight line are parallel to each other.
Element of reverse curve
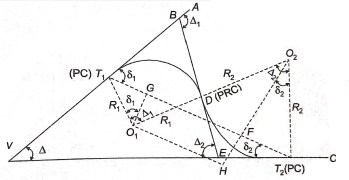
- VA and ucinclude deviation angle of .
.
- 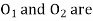 centres of two curves.
centres of two curves.
-  are radii of two curve.
are radii of two curve.
-  common tangent which is perpendicular to
common tangent which is perpendicular to 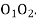
- Join 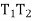 and draw
and draw 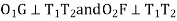
In ∆BVE,

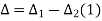
In 
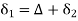
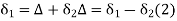
From (1) and (2)
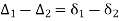
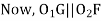
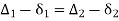
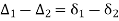
In, 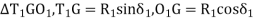
In,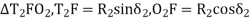
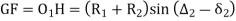
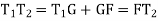
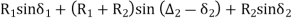
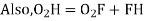
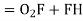
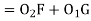
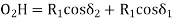
Also,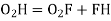
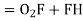
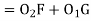
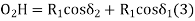

From (3) and (4)
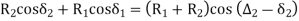
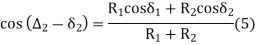
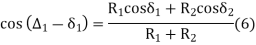
- It is a curve introduced between a simple circular curve industry tour between two simple circular curves.
- Also known as easement curve.
- Its videos, gradually changing from a finite to infinite value or vice versa.
- It is generally used in highway and Railway.
Length of transition curve: -
a) Method of arbitrary gradient: -
e = total super elevation provided at junction of transition curve with circular curve
L = ne
Where rate of super elevation is ∆ in n
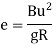
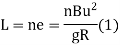
(b) Method of Time rate: -
 time rate of super elevation
time rate of super elevation


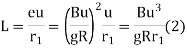
Method of rate of change of radial acceleration
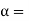 Rate of change of radial acceleration
Rate of change of radial acceleration
t is the time attained by radial acceleration (a)
a = 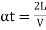


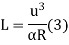
Super elevation or Cant:
It is defined as the raising of outer end of a road or outer rail over inner one.
h = super elevation = e
w = weight of vehicle
P = centrifugal force
g = acceleration due to gravity
R = radius of curve
G = gauge distance between rails
u = speed of vehicle
B = width of pavement
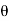 = Angle of super elevation
= Angle of super elevation
h = super elevation = e
w = weight of vehicle
P = centrifugal force
g = acceleration due to gravity
R = radius of curve
G = gauge distance between rails
u = speed of vehicle
B = width of pavement
 = Angle of super elevation
= Angle of super elevation
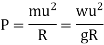
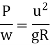

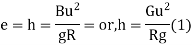
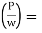 Centrifugal ratio
Centrifugal ratio
Formula for elements of a simple circular curve
a) Relation between degree and radius of curve.
Arc definition / Chord Definition: -
Arc definition of degree of curve: According to this, degree of curve in the central angle subtended by an arc of length of 20m or 30 m.
If R = radius of curve
D = degree of curve as per arc definition for 30m arc length.
D° = 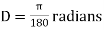
Q (radians) = 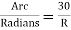
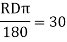
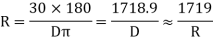
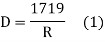
For 20 mm length
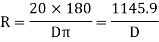
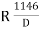 (2)
(2)
(b) length of curve
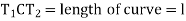

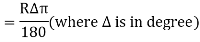
If a 30m arc or chord definition is used


If a 20 m arc or chord definition is used.

(c) Length of tangent: -
Tangent length (T) = 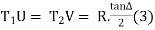
(d) long chord length
Length of long chord (L) 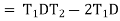
From 
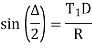
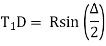
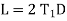
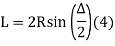
(e) Apex distance: -
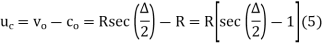
(f) Mid ordinate: -

(a)Total Tangent Length
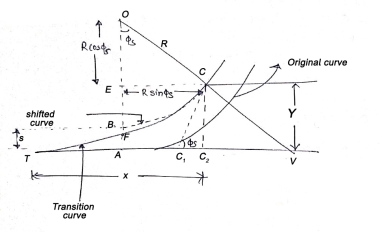
Tangent length 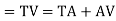
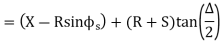
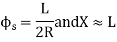
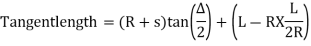

(b) Length of long chord
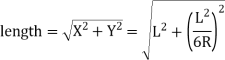
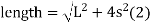
(c) Total length of curve
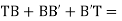 Total length of curve
Total length of curve
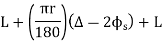
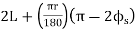 =Total length (3)
=Total length (3)
(d) Apex distance E
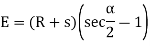

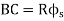
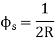
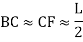
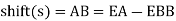
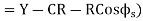




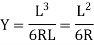
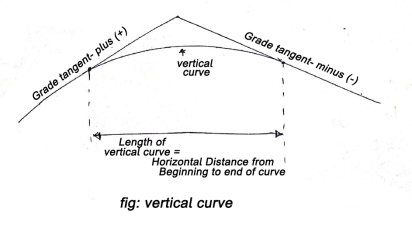
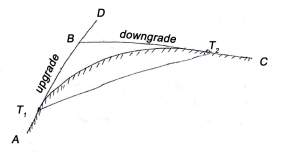
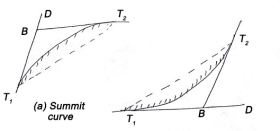
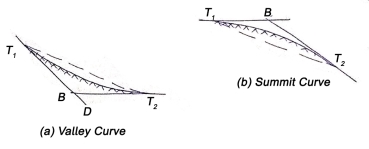
These are curves in a vertical plane, used to join two intersecting grade lines.
A vertical summit curve is provided when a rising grade join a falling grade and a vertical curve is provided when a falling grade joins a rising grade.
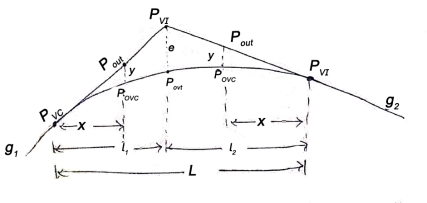
PVC – point of vertical curvature place where curve begins
PVT – point of vertical tangency, where curve end.
PVI – point of vertical intersection, where grade tangents intersect.
POVC - point on vertical curve applies to any point on parabola
POVT - point on vertical tangent, applies to any point on other tangent
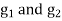 are grade tangent at PVC and PVT respectively.
are grade tangent at PVC and PVT respectively.

(a) Length of vertical curve
L = algebraic difference of two grades/ rate of change of grade
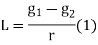
(b) Change of end of curve
PVT = change of intersection point + half the length
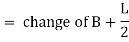
Types of vertical curves
iii) Upgrade followed by a downgrade
iv) Upgrade followed by another upgrade
v) A downgrade followed by an upgrade
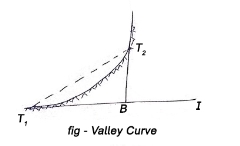
vi) A downgrade followed by another downgrade
References:
1 Madhu, N, Sathikumar, R and Satheesh Gobi, Advanced Surveying: Total Station, GIS and Remote
Sensing, Pearson India, 2006.
2 Manoj, K. Arora and Badjatia, Geomatics Engineering, Nem Chand & Bros, 2011
3 Bhavikatti, S.S., Surveying and Levelling, Vol. I and II, I.K. International, 2010 4 Chandra, A.M., Higher
Surveying, Third Edition, New Age International (P) Limited, 2002.
5 Anji Reddy, M., Remote sensing and Geographical information system, B.S.
6 Arora, K.R., Surveying, Vol-I, II and III, Standard Book House, 2015.