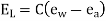Unit - 1
Introduction to Hydrology
- The word hydrology has been derived from Greek words ‘Hydro’. i.e., water and ‘logos’ i.e., technology. So, it's far a technology of water.
- It is defined as “A technology which offers with the properties, distribution and circulate of water at the ground of the land, withinside the soil, withinside the underlying rocks and additionally withinside the ecosystem normally withinside the form of moisture or water ecosystem commonly withinside the form of vapour and withinside the form of water droplets withinside the path of rain falls or withinside the robust form of snow debris at some point of snows fall.”
- C.O. Sister and E.F barter have described the technology of hydrology as “A technology which gives with the approach of governing the depletion and replenishment of water reassets of the land regions of the earth.”
- Hydrology is an applied technology utilized by the usage of many people running in top notch fields for the development of the human beings.
Key Takeaways:
The word hydrology has been derived from Greek words ‘Hydro’. i.e., water and ‘logos’ i.e., technology. So, it's far a technology of water.
First Step
- Due to picture graph voltaic radiation called as insulation i.e., in coming sun radiation.
- The oceanic and the water at the land floor get heated and get transformed into vapour.
Second step
- The vapour being lighter is lifted up withinside the ecosystem so the air has this vapour called as moisture starts cooling down and so it begins controlling.
- It reduces the sporting cap potential of air to maintain the moisture and it turns into moisture saturated i.e., no extra moisture it could maintain. This diploma is known as degree of condensation.
Third Step
- Due to the pushing of air from the earth floor, this saturated air continues to be driven withinside the upward path to make it although cooler and although greater compact to minimize its potential lesser than actuality accessible wetness. This additional moisture is reborn into tiny rain drops. That tempt the dirt particles to create it visible is understood as clouds
Fourth step
- The moisture carrying clouds are carried by victimization the winds toward the land surface. If it's a craggy location the clouds are however raised up to extend the dimension of the raindrops and that they begin falling down spoken as rainfall.
Fifth step
- The fresh water obtained on the surface starts Moving towards the slopes, to form the strolling water or streams, which eventually meet the oceans. The rainwater noninheritable on the floor identical times percolates (it depends upon the type of rock, if it's porous the water percolates) to structure the bottom water. It in addition comes back on the ground within the structure of springs to structure a floor circulation to achieve the ocean.
- The rain water noninheritable on the surface, that is obvious and have non porous rock: forms lakes or tanks. The cycle is finished once the ocean or surface water comes back will the planet floor to start the primary stage of geophysics ice. It starts off evolved obtaining reworked from the liquid nation to the vaporific state.
- Once the water is obtained within the structure of sturdy kingdom i.e., snow, it in addition undergoes the equal cycle. When the system is fast the vapor directly gets reborn into strong snow particles.
- It's spoken as sublimation. This befell once the temperature of the wetness saturated air is a smaller amount than O Cie. Not up to the melting point temperature. Within the temperature and in the arctic zones on the planet it causes rainfall.
- As noted on top of the hydro cycle is achieved in six states. Which may be expressed via the usage of technical nomenclature these methods are as follows:
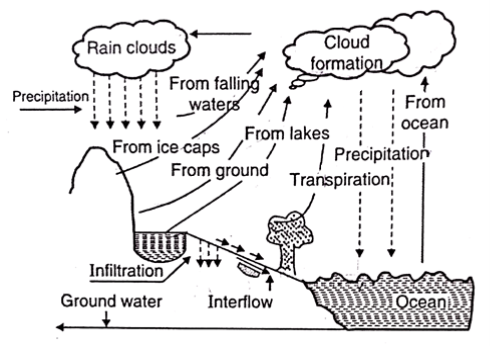
Fig 1: Descriptive representation of hydrological cycle
The processes involved in hydrological cycle are as follows:
- Evaporation: it's procedure of conversion of the liquid or sturdy water our bodies into the ocean state
- Precipitation: system of the conversion of the water vapor within the atmosphere in the liquid structure water of the stable structure autoimmune disorder hail or snow or frost.
- Interception: Interceptions the fugitive retention of rain by manner of the foliage of vegetation.
- Infiltration: Infiltration is that the movement of water into the soil of the earth’s surface.
- Percolation: Percolation is the movement of water from one soil zone to a decrease soil one.
- Transpiration: Transpiration is that the soil moisture haunted via the roots of a plant and discharged into the surroundings through the foliage by victimisation evaporation.
- Storage: Storage is the volume of water that receives saved in flavourer depressions of a basin.
- Runoff: Runoff is the volume of water drained by manner of a stream at the outlet of a structure.
Key Takeaways:
Hydrology is the technology that gives with the occurrence, circulate and distribution of water of the earth and its ecosystem.
- The hydrology i.e., the science that deals with the movement of water on the surface of the earth in the form of surface-flow and floods.
- India, being an agrarian country, the water plays an important role in the economic development of the country. So, the main application of this science is to the farmers.
- The duration amount of water which would be available for irrigation purpose is determined by the subject of Hydrology.
- E.g., in North-India, due to plain region and perennial rivers the runoff is greater than in south India. This has affected the yields and total agricultural products in North and South India.
- As it also deals with floods the subject of hydrology is important for the settlements along the bank of the rivers to provide safety and to reduce the economic losses.
IMD (Indian Meteorological Department):
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is an enterprise of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India. It is the predominant enterprise liable for meteorological observations, climate forecasting and seismology. IMD is based in Delhi and operates masses of remark stations throughout India and Antarctica. Regional places of work are at Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, Nagpur, Guwahati and New Delhi.
- IMD is likewise one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization. It has the obligation for forecasting, naming and distribution of warnings for tropical cyclones withinside the Northern Indian Ocean region, together with the Malacca Straits, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
- In 1686, Edmond Halley posted his treatise at the Indian summer time season monsoon, which he attributed to a seasonal reversal of winds because of the differential heating of the Asian landmass and the Indian Ocean. The first meteorological observatories have been set up in India with the aid of using the British East India Company. These protected the Calcutta Observatory in 1785, the Madras Observatory in 1796 and the Colaba Observatory in 1826. Several different observatories have been set up in India throughout the primary 1/2 of the nineteenth century with the aid of using numerous provincial governments.
- The Asiatic Society, based in Calcutta in 1784 and in Bombay in 1804, promoted the take a look at of meteorology in India. Henry Piddington posted nearly forty papers coping with tropical storms from Calcutta among 1835 and 1855 in The Journal of the Asiatic Society. He additionally coined the time period cyclone, which means the coil of a snake. In 1842, he posted his landmark thesis, Laws of the Storms.
- After a tropical cyclone hit Calcutta in 1864, and the following famines in 1866 and 1871 because of the failure of the monsoons, it turned into determined to organize the gathering and evaluation of meteorological observations beneath one roof. As a result, the India Meteorology Department turned into set up in 1875. Henry Francis Blanford turned into appointed the primary Meteorological Reporter of the IMD. In May 1889, Sir John Eliot turned into appointed the primary Director General of Observatories with inside the erstwhile capital, Calcutta. The IMD headquarters have been later shifted to Shimla in 1905, then to Pune in 1928 and eventually to New Delhi in 1944.
- IMD have become a member of the World Meteorological Organization after independence on 27 April 1949.The enterprise has received in prominence because of the importance of the monsoon rains on Indian agriculture. It performs a critical position in making ready the once a year monsoon forecast, in addition to in monitoring the development of the monsoon throughout India each season.
Key Takeaways:
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is an enterprise of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India. It is the predominant enterprise liable for meteorological observations, climate forecasting and seismology.
CWPRS (Central Water and Power Research Station):
- The Central Water and Power Research Station (CWPRS) Pune is the fundamental studies organization withinside the subject of hydraulic and allied studies as a subordinate workplace of the Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India and offers with planning, setting up and project particular studies and improvement research associated with optimizing designs of river, coastal, water garage and conveyance hydraulic structures.
Key Takeaways:
The Central Water and Power Research Station (CWPRS) Pune is the fundamental studies organization withinside the subject of hydraulic and allied studies as a subordinate workplace of the Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India and offers with planning, setting up and project particular studies and improvement research associated with optimizing designs of river, coastal, water garage and conveyance hydraulic structures.
MERI (Maharashtra Engineering Research Institute):
- Capacity assessment of the Reservoirs, crop identity and mapping, Land use Land Cover mapping, Green Cover mapping through faraway sensing Techniques and GPS and DGPS approach for Capacity evaluation of reservoirs.
- Works of Testing of Civil Engineering Materials and Suggestion of Remedial Measures to Field degree Problems of Water Resources Department and Public Works Department.
Key Takeaways:
Capacity assessment of the Reservoirs, crop identity and mapping, Land use Land Cover mapping, Green Cover mapping through faraway sensing Techniques and GPS and DGPS approach for Capacity evaluation of reservoirs.
CDO (A collateralized debt obligation):
- A collateralized debt obligation (CDO) is a form of based asset-subsidized security (ABS). Originally advanced as gadgets for the company debt markets, after 2002 CDOs have become automobiles for refinancing loan-subsidized securities (MBS).
- Like different non-public label securities subsidized via way of means of belongings, a CDO may be concept of as a promise to pay buyers in a prescribed series, primarily based totally at the coins go with the drift the CDO collects from the pool of bonds or different belongings it owns. Distinctively, CDO credit score hazard is commonly assessed primarily based totally on a chance of default (PD) derived from scores on the one’s bonds or belongings.
- The CDO is "sliced" into sections regarded as "tranches", which "catch" the coins go with the drift of hobby and major bills in series primarily based totally on seniority. If a few loans default and the coins accrued via way of means of the CDO is inadequate to pay all of its buyers, the ones withinside the lowest, maximum "junior" tranches go through losses first. The ultimate to lose fee from default are the safest, maximum senior tranches.
- Consequently, coupon bills (and hobby fees) range via way of means of tranche with the safest/maximum senior tranches receiving the bottom fees and the bottom tranches receiving the best fees to atone for better default hazard. As an example, a CDO would possibly difficulty the subsequent tranches so as of safeness: Senior AAA (every so often regarded as "top notch senior"); Junior AAA; AA; A; BBB; Residual.
- Separate unique cause entities—as opposed to the discern funding bank—difficulty the CDOs and pay hobby to buyers. As CDOs advanced, a few sponsors repackaged tranches into but any other iteration, regarded as "CDO-Squared", "CDOs of CDOs" or "artificial CDOs".
- In the early 2000s, the debt underpinning CDOs turned into typically diversified, however via way of means of 2006–2007—while the CDO marketplace grew to loads of billions of dollars—this had changed.
- CDO collateral have become ruled via way of means of excessive hazard (BBB or A) tranches recycled from different asset-subsidized securities, whose belongings had been normally subprime mortgages.
- These CDOs had been called "the engine that powered the loan deliver chain" for subprime mortgages, and are credited with giving creditors extra incentive to make subprime loans, main to the 2007-2009 subprime loan crisis.
Key Takeaways:
A collateralized debt obligation (CDO) is a form of based asset-subsidized security (ABS).
Hydrology Project Division:
- Hydrology is the medical look at of the movement, distribution, and control of water on Earth and different planets, consisting of the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability.
- A practitioner of hydrology is known as a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists analyzing earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and bodily geography.
- Using diverse analytical techniques and medical techniques, they accumulate and examine information to assist resolve water associated issues together with environmental preservation, herbal disasters, and water control.
- Hydrology subdivides into floor water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology consist of hydrometeorology, floor hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin control, and water quality, wherein water performs the crucial role.
- Oceanography and meteorology aren't protected due to the fact water is simplest one in all many essential components inside the one’s fields.
- Hydrological studies can tell environmental engineering, policy, and planning.
Key Takeaways:
Hydrology is the medical look at of the movement, distribution, and control of water on Earth and different planets, consisting of the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability.
NIH:
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the number one organization of the US authorities answerable for biomedical and public fitness studies. It turned into based withinside the overdue Eighties and is now a part of the US Department of Health and Human Services.
- The majority of NIH centers are placed in Bethesda, Maryland and different close by suburbs of the Washington metropolitan area, with different number one centers withinside the Research Triangle Park in North Carolina and smaller satellite tv for pc centers placed across the United States. The NIH conducts its personal medical studies via its Intramural Research Program (IRP) and presents foremost biomedical studies investment to non-NIH studies centers via its Extramural Research Program.
- As of 2013, the Intramural Research Program (IRP) had 1, two hundred fundamental investigators and extra than four,000 postdoctoral fellows in basic, translational, and scientific studies, being the biggest biomedical studies organization withinside the world, while, as of 2003, the extramural arm furnished 28% of biomedical studies investment spent yearly withinside the U.S., or approximately US$26.four billion.
- The NIH contains 27 separate institutes and facilities of various biomedical disciplines and is answerable for many medical accomplishments, such as the invention of fluoride to save you enamel decay, the usage of lithium to control bipolar disorder, and the introduction of vaccines towards hepatitis, Haemophilus influenzae (HIB), and human papillomavirus (HPV).
- In 2019, the NIH turned into ranked quantity withinside the world, at the back of Harvard University, for biomedical sciences withinside the Nature Index, which measured the biggest members to papers posted in a subset of main journals from 2015 to 2018.
Key Takeaways:
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the number one organization of the US authorities answerable for biomedical and public fitness studies. It turned into based withinside the overdue Eighties and is now a part of the US Department of Health and Human Services.
CWC:
- Central Warehousing Corporation is a statutory frame which changed into hooked up under ‘The Warehousing Corporations Act, 1962. Its goal is to offer reliable, cost-effective, value-added, included warehousing and logistics answer in a socially accountable and surroundings pleasant manner. It is a public warehouse operator hooked up with the aid of using the Government of India in 1957 to offer logistics guide to the rural sector.
- It operates 422 warehouses throughout India with a garage capability of 10 million tonnes. Services consist of food grain warehouses, business warehousing, custom bonded warehouses, box freight stations, inland clearance depots and air cargo complexes.
Function
- The Warehousing Corporation act, 1962: Subject to the provisions of this Act, the Central Warehousing Corporation may:
- Subscribe to the proportion capital of a State Warehousing Corporation;
- Act as agent of the Government for the functions of the purchase, sale, garage and distribution of agricultural produce, seeds, manures, fertilizers, agricultural implements and notified commodities; and
- Carry out such different features as can be prescribed.
- The Warehousing Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2011 has been proposed withinside the Lok Sabha with the aid of using the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution in search of to make Mini-Ratna corporation Central Warehousing Corporation (CWC) an impartial frame without authorities being a guarantor.
Key Takeaways:
Central Warehousing Corporation is a statutory frame which changed into hooked up under ‘The Warehousing Corporations Act, 1962. Its goal is to offer reliable, cost-effective, value-added, included warehousing and logistics answer in a socially accountable and surroundings pleasant manner.
- Precipitation is the fall of water in various forms on the earth from the clouds. The usual forms are rain, snow, sleet, glaze, hail, dew etc.
- Before studying the phenomenon of precipitation let us consider water vapours. Air in atmosphere can easily absorb moisture in the form water vapours. The amount of water vapours absorbed by air depends upon the temperature of air, the more is the temperature the more water vapours it can absorb.
- The water vapour exerts a partial pressure on the water surface called vapour pressure. The amount does water vapour present in air is indirectly expressed in terms of vapour pressure.
- If the evaporation continues, a state of equilibrium is reached when the air is fully saturated with vapour and therefore it cannot absorb more vapours. The vapours then exert a pressure which is known as saturation vapour pressure (es). es increase with increase in temperature.
- Let us consider a of parcel of air as temperature T and a vapour pressure (ea) indicated by pt. A. The saturation vapour pressure at that temperature is indicated by pt. B. The intercept BA = (es-ea) is called saturation deficit.
- If vapours are added to the parcel of air, the pt. A will move to pt. B when air is fully saturated.
- If the parcel of air is cooled at constant pressure but without the addition of more vapours, the pt. Moves horizontally towards pt. D and the air would be saturated when pt. D is reached. At that stage, the air would have a temperature called dew point temperature (T). Cooling of air beyond this pt. Would result in condensation or formation of mint.
- If neither the temperature not the pressure remains constant, the water evaporates freely and the pt. Moves to pt. C. In this case, water vapor rises but temperature falls. The temperature at pt C. Is called wet bulb temperature (T). The saturation vapour pressure is indicated by ew.
- Air in atmosphere can be cooled by many processes. However, adiabatic soling which occurs by a reduction of pressure through lifting of air masses is the main natural process.
Key Takeaways:
Precipitation is the fall of water in various forms on the earth from the clouds. The usual forms are rain, snow, sleet, glaze, hail, dew etc.
Depending upon the factors responsible for lining and cooling of alit there is following types of precipitation:
(1) Convective precipitation:
- It occurs due to heating of air. The air close to the earth surface gets heated, and item density decreases.
- Consequently, the air rises upwards in the atmosphere and it gets cooled adiabatically to form a cloud, precipitation caused by such clouds is called convective precipitation.
(2) Orographic Precipitation:
- Orographic rainfall occurs due to ascent of air forced by mountain barriers.
- The mountain barriers lying across the direction of air flow forces the moisture laden air to rise along the mountain slope. It results in cooling, condensation and precipitation.
(3) Cyclonic Precipitation:
- A cyclone is a large zone of low pressure which is surrounded by circular wind motion.
- Air tends low pressure zone from and displaces low pressure cyclonic precipitation to move into the surrounding area air upwards. Thus, occurs due to displacement of air in upwards direction due to pressure difference.
(4) Frontal Precipitation:
- It is a type of cyclonic precipitation. When two contrasting air masses (cold polar air mass and warm westerly air mass) coming from opposite directions converge along a line, a front is formed. The warm wind is lifted upward along this front where as cold air being heavier settles downward.
- Because the two types of fronts (warm and old) have different temperature and density, frontal precipitation occurs when they clash with each other.
- The various forms of precipitation are:
- Drizzle: If the size of water droplets is under 0.5mm, and its density is <0.01mm per hour, then it is called drizzle.
- Rain: If the size of the drops is more than 0.5m and when the droplet is about 6.25mm, it breaks up as they fall through the air causing rain.
- Glaze: When drizzle or rain freezes as it comes in contact with cold objects, it becomes a glaze.
- Sleet: Frozen raindrops formed when rainfall passes through the air at subfreezing temperature is known as sleet.
- Snow: Precipitation in the form of ice crystals resulting from sublimation.
- Snowflakes: Several ice crystals fused form snowflakes.
- Hail: Hail is a type of showery precipitation in the form of pellets or lumps of size greater than 8mm.
- The unit of measurement is cm or mm. It is measure for per sq. Cm of the land for a period of 24 hours. The instrument used to measure rainfall is called as Rain gauge i.e., gauging the rainwater.
- The accuracy of the rainfall data is very important on the basis of this data (called as point data) the monthly or yearly arrange rainfall of that point is calculated for the purpose of the agricultural planning and other various types of economic planning.
- The intensity of rainfall is measure as mm per hour or can per day. To get correct data it is necessary to place the rain gauge at the correct place. Following points are considered while selecting the correct site for the rain gauge.
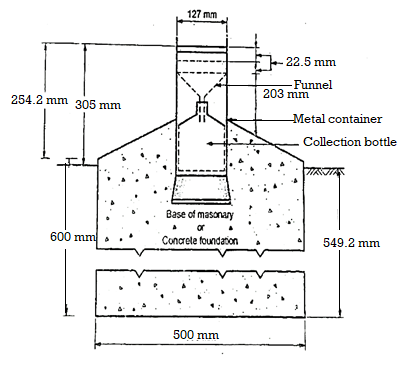
Fig: 2
Key Takeaways:
The unit of measurement is cm or mm. It is measure for per sq. Cm of the land for a period of 24 hours. The instrument used to measure rainfall is called as Rain gauge i.e., gauging the rainwater.
Non-recording type rain gauge:
- These rain gauges are very simple and are used only to collect the rain water, period of time i.e., 24 hours.
- The water collected in the rain gauge is measured by measuring jar and the record is maintained to get monthly total and monthly average rainfall of the rain gauge station.
- From the year 1969, IMD has introduced a new standardized by Indian Standard Institution (I.S.I) i.e., IS. 5225 - 1992 give the specifications of this rain gauge. It is called as "standard non-recording type rain gauge".
Self-recording type or Automatic type rain gauge:
- These rain gauges record the intensity of rainfall and also the time of the occurrence, in a form of a pentrace on a clock drives chart, from which the total amount of rainfall for a given period of time also can be determined.
- There are three different types of automatic type rain gauges as given below:
- Tipping bucket rain gauge
- Weighing type rain gauge
- Float type rain gauge
Key Takeaways:
Precipitation is the fall of water in various forms on the earth from the clouds. The usual forms are rain, snow, sleet, glaze, hail, dew etc.
- An automated climate station (AWS) is an automatic model of the conventional climate station, both to shop human labour or to permit measurements from far flung areas.
- An AWS will usually include a climate-evidence enclosure containing the information logger, rechargeable battery, telemetry (optional) and the meteorological sensors with a connected sun panel or wind turbine and established upon a mast.
- The unique configuration might also additionally range because of the cause of the device. [The device might also additionally file in close to actual time through the Argos System and the Global Telecommunications System, or shop the information for later recovery.
- In the past, automated climate stations had been regularly positioned in which power and verbal exchange strains had been available.
- Nowadays, the sun panel, wind turbine and cellular tele cell smartphone era have made it viable to have wi-fi stations that aren't linked to the electric grid or hardline telecommunications network.
Key Takeaways:
An automated climate station (AWS) is an automatic model of the conventional climate station, both to shop human labour or to permit measurements from far flung areas.
- Double mass curve method is used to detect the inconsistency in the rain gauge, due to some changes occurring in particular rain gauge station.
- In this method, a group of stations are chosen, their yearly rainfall values are recorded and these values are arranged in a reverse chronological order.
- The cumulative values of the doubtful station X(SPx), and the cumulative values of the group averages (SPav) are plotted on a graph.
- Finally, the precipitation values at station X prior to the period of change are then corrected by the relation:
Px’=Px(M’/M)
Where, Px’- corrected precipitation at station X.
Px- original recorded precipitation at station X.
M’- corrected slope of the double mass curve.
M- original slope of the double mass curve.
Key Takeaways:
Double mass curve method is used to detect the inconsistency in the rain gauge, due to some changes occurring in particular rain gauge station.
- As per the data collected by using rain gauge is used to calculate the total monthly rainfall of that region and on the basic of this data average monthly rainfall figures are calculated.
- These figures for all the months are represented by drawing bar for each month they are drawn to a given scale i.e., the 1 cm length of the bar represents 1cm rainfall. It is called as Bar graphs.
- We can prepare these bar graphs for 24 hrs. i.e.; each hourly rainfall will be shown by a different bar or Weekly bar graph where seven day's rainfall will be shown by seven separate bars or yearly bar graph which shows average monthly rainfall figures for all the twelve months or for a longer period bar graph which shows the average yearly rainfall for the last few years. (This type of data is used to project the expected rainfall of the coming year).
- If the rainfall data based on the rain gauge is plotted a graph paper by adding the previous days or week's months rainfall (cumulative value). We get a line graph.
- If the line graph is steep indicating sudden rise in the rainfall in the next day or week or a month, it indicates the intensity of the rainfall. e.g., At a given place, in the 1st week of July 50 mm rainfall is recorded.
- By using a suitable scale (vertical scale) this 50 mm rainfall will be shown by a dot (.). If in the next week, 150 mm rainfall is received the cumulative rule the next week's rainfall would be 50 + 150 = 200 mm and it also would be shown by another dot. The third- and fourth-week’s cumulative values of rainfall are 370 mm and 550 mm respectively. All these dots showing the rainfall record will be the joined by a smooth line. It is called as Mass curve.
Key Takeaways:
If the rainfall data based on the rain gauge is plotted a graph paper by adding the previous days or week's months rainfall (cumulative value). We get a line graph.
- A hyetograph is a bar graph showing the intensity of rainfall with time.
- The area under a hyetograph represents the total rainfall received in that period.

Fig 3: Hyetograph
- A 'Point rainfall' is indicated by a rain gauge. For a small area i.e., an area which is smaller than 50 sq.km; this point rainfall is considered as, the 'mean' or an average rainfall.
- If the area is large like a river basin, where there is a lot of variation in the receipt of annual rainfall a large number of rain gauge stations are installed, to calculate the mean or the average rainfall of 'that point' in the given river basin.
- Two methods are used to calculate the mean or the average rainfall or the precipitation of the given area; such as
- The Arithmetic mean or Average Method
- The Isohyetal method to calculate the mean or the Average.
Key Takeaways:
A 'Point rainfall' is indicated by a rain gauge. For a small area i.e., an area which is smaller than 50 sq.km; this point rainfall is considered as, the 'mean' or an average rainfall.
- This approach calculates areal precipitation the usage of the mathematics suggests of all of the factor or areal measurements taken into consideration withinside the analysis.
- Rainfall recorded at every station is given a weightage primarily based totally at the region closest to the station Consider a catchment region with say, three rain gauge stations.
- Let there be three stations outdoor the catchment, however in its neighborhood. The catchment region is interested in scale and the location of those 6 stations are plotted on it.
- These 6 stations are joined that allows you to get a community of triangles. Perpendicular bisectors are interested in every of the edges of those triangles.
- These bisectors shape a polygon round every station. If the boundary of the catchment cuts the bisectors, then the boundary is taken because the outer restricts of the polygon.
- These bounding polygons are referred to as Thiessen Polygons. The region of those polygons is measured with a planimeter or through grid overlay.
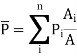
- This technique is taken into consideration advanced to the arithmetical averaging technique considering that a few weightage is assigned to every rain gauge station.
- Even rain gauge stations positioned out of doors the catchment are utilized in computing suggest precipitation.
Key Takeaways:
Rainfall recorded at every station is given a weightage primarily based totally at the region closest to the station Consider a catchment region with say, three rain gauge stations.
- The Isohyetel Method of computing mean Precipitation over an Area:
- To determine the mean precipitation this is the most accurate method. The Isohyet can be defined as, "It is the line which joins the points having same rainfall."
- This method is consisted of a map, drawn to a suitable scale of the given area. Which has the points marked of the rain gauge stations with the figures of their recorded rainfall.
- By using the interpolation technique, the isohyets are drawn by joining the points, of the rain gauge station having equal rainfall.
- Then the areas between two adjoining isohyets are calculated either by graphical techniques or by using the planimeter e.g. A₁, A₂ ….An etc.
- The mean value of the rainfall, which is indicated by two consecutive isohyets is the mean or the average rainfall of the inter isohyetal area, so, the mean or the average precipitation or the rainfall can be calculated by using the following formula.
- The mean Precipitation=

Key Takeaways:
The Isohyetel Method of computing mean Precipitation over an Area. To determine the mean precipitation this is the most accurate method. The Isohyet can be defined as, "It is the line which joins the points having same rainfall."
- DAD of a storm is carried to know the maximum amount of rainfall, within various durations, over the areas of different sizes. For that following step are taken
- A: The rainfall records are examined of the given region.
- B: The record of meteorologically similar region is examined.
- C: From the above records a list is prepared of the most severe storms, with their dates, occurrence and duration.
- D: Using such list, an ISO-hyetal map is prepared.
- E: By using the values of ISO-hyetal graphs are prepared, for different durations. i.e., one day rainfall, two days rainfall and three days rainfall.
Use of DAD:
- Although the most severe storm listed, may not reappear, but under the given rainfall-depths in the catchment area one can keep the people aware of the expected danger of floods and can reduce the losses; both human losses and economic losses.
Key Takeaways:
DAD of a storm is carried to know the maximum amount of rainfall, within various durations, over the areas of different sizes.
- Frequency evaluation has been growing for hydro-meteorological statistics together with rainfall, flood, and drought.
- Particularly, the copula has been used as a beneficial device for multivariate opportunity version which has no quandary on determining marginal distributions.
- The time-collection rainfall statistics may be characterized to rainfall occasion through inter-occasion time definition (IETD) and every rainfall occasion has a rainfall intensity and rainfall duration.
- In addition, non-stationarity in rainfall occasion has been studied currently because of weather extrade and fashion detection of rainfall occasion is crucial to decide the statistics has non stationarity or not.
Key Takeaways:
Frequency evaluation has been growing for hydro-meteorological statistics together with rainfall, flood, and drought.
- A 'Point rainfall' is indicated by a rain gauge. For a small area i.e., an area which is smaller than 50 sq.km; this point rainfall is considered as, the 'mean' or an average rainfall.
- If the area is large like a river basin, where there is a lot of variation in the receipt of annual rainfall a large number of rain gauge stations are installed, to calculate the mean or the average rainfall of 'that point' in the given river basin.
- Two methods are used to calculate the mean or the average rainfall or the precipitation of the given area; such as
- The Arithmetic mean or Average Method
- The Isohyetal method to calculate the mean or the Average.
Key Takeaways:
A 'Point rainfall' is indicated by a rain gauge. For a small area i.e., an area which is smaller than 50 sq.km; this point rainfall is considered as, the 'mean' or an average rainfall.
- To calculate the intensity of rainfall the following equation is used:
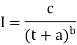
Where,
I = intensity of rainfall (un mm/per hour)
t = Duration of rain-fall (in minutes)
C, a, b = Constants for the specific area.
- The data generated is plotted on a graph paper to show the relation of intensity and duration on 'X' and 'Y' axis. The vertical scale indicates the maximum intensity of precipitation in mm/h and the horizontal scale indicates the time in hours.
- These points then are joined by a smooth line to form a curve. It is called as Intensity Duration Curve or Intensity-Duration graph.
If the data for a given area is
Equation No. 1
- The Maximum Annual Rainfall = 1.5x Average annual rainfall
Equation No. 2
- The Minimum Annual Rainfall = 0.60 × Average Annual Rainfall.
- Sometimes same specific point data is not available. e.g., in a region out of 50 rain gauge stations, some stations data for a long period is not available.
- In such cases, it is assumed that the rainfall data of 'n' rain gauge stations, for a period of one year is equivalent to the data of one rain gauge station for 'n' years and thus the study can be continued. This method is called as "The Station Year Method".
- The concept of Intersection is confined with a point at which two Lines or two different functions act at the same time but in different directions.
- Intersection of rainfall is a process, in which we receive the rainwater in different forms i.e., water liquid form or snow in solid form. When the rainwater is received on the surface of the earth, at that point of intersection, some of it gets evaporated, depending upon the temperature condition and dryness of the air.
- Some of it is percolated i.e., infiltration, which depends upon the type of surface rock. So, the usefulness of rainwater depends upon these two Intersecting parameters.
Key Takeaways:
The concept of Intersection is confined with a point at which two Lines or two different functions act at the same time but in different directions.
- Depression storage capacity is the ability of a particular area of land to hold water, in the pits or medium or large depressions.
- This type of storage prevents the surface water to flow in the downward direction. This capacity to hold water, mainly depends upon the rate of infiltration.
- Which depends upon the type of rock on the surface and its retaining capacity when the volume of water is more than the rate of evaporation and the rate of infiltration, it creates the surface runoff or the surface flow, which causes the origin of floods and also create the danger to the surface soil through the surface erosion.
- So, the depression storage is important as it provides water for various purposes and also it is eco-friendly as it reduces. The channel of over flooding and controls soil erosion.
Key Takeaways:
Depression storage capacity is the ability of a particular area of land to hold water, in the pits or medium or large depressions.
- Evaporation is one of the basic and important process in the function of Hydraulic cycle. In this process, due to solar radiation, during the day time the water in the liquid form is transformed into gaseous form called as moisture water vapour or humidity.
- The evaporation occurs on the surface of free water bodies, such as Oceans, Seas, lakes tanks and rivers. The water in the sub-soil also gets evaporated, and makes the soil-dry.
- It also occurs from plants and vegetation cover. It also appears in the areas covered by sheets of ice, in the polar areas.
Evaporation Process:
- The water is made up of a number of molecules. Each one of the molecules moves in different direction with different velocities. The velocity of the molecule depends upon the temperature.
- These molecules are attracted towards each other the force of attraction is proportionate to the mass and inversely proportionate to the distance square.
- If the mass is greater the point of attraction will be more and as the distance between two molecules goes on increasing the point of attraction goes on reducing. The molecules on the top are attracted by molecules below them.
- The molecules having more kinetic energy (through the heating process.) than the attraction in the down ward direction escape into the " atmosphere. This process is called as Evaporation.
- These escaped molecules while going up into the atmosphere carry some kinetic energy. So, evaporation is a cooling process.
- When molecules are pushed into the upward direction, some of them already in the air start coming down (decanting) and there is collision of these molecules moving in and out from the water surface.
- The evaporation is the net rate of movement of molecules to and from the water surface. When all t the rate of molecules coming towards the surface dive or water is more than the molecules moving from the water surface into the air, it is called as condensation.
- When the air near the water surface is very cool through the evaporation, the molecules are converted into solid form of snow.
- This process is called as sublimation. The evaporation is expressed in terms of the depth of the water per unit of area per unit of time. i.e.mm/m2/h.
Key Takeaways:
Evaporation is one of the basic and important process in the function of Hydraulic cycle. In this process, due to solar radiation, during the day time the water in the liquid form is transformed into gaseous form called as moisture water. Vapour or humidity.
The factors affecting evaporation are:
- Vapour pressure: The rate of evaporation is directly proportional to the difference between the saturation vapour pressure at the water temperature (ew) and the actual vapour pressure in the air (ea),
- Temperature: Rate of evaporation increases with an increase in temperature.
- Wind: The rate of evaporation increases up to critical wind speed, then further increase in wind speed does not affect the rate of evaporation.
- Atmospheric pressure: Decrease in atmospheric pressure, increases the rate of evaporation.
- Quality of water: As the concentration of solutes in the water increases, the rate of evaporation decreases.
- Size of the water body: The rate of evaporation is more in shallow water bodies compared to deep water bodies.
- To estimate the rate of evaporation from the surface of the water body, following methods have been introduced.
A: Water Budget Method
- To calculate the rate of evaporation following equation is used:
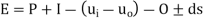
Where,
E = Evaporation
P= Precipitation
I= Surface inflow
ui = Under-ground inflow of water into the surface water (Through springs)
uo =Under-ground out flow of water from the surface water (through percolation)
0= Out flow of water (through irrigation canal)
Ds =Change in the storage
- If all the numerical data (accurate) is available the loss of water through evaporation can be calculated.
B: Energy Budget Method
- In this method, for a specific period of time, how much energy is received from the sun by the water is calculated and how much energy is utilized for the evaporation is calculated to know the accurate evaporation. For this, the following equation is used.
Q₁ = QR ±Qs + QE
Where Q1= Total energy received from the solar radiation
QR= Total energy reflected by to the atmosphere through the reflection
Qs = Change in the energy in the stored water
QE = Energy required for evaporation
- In this QS, may be
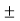 or - because in same case the energy may be added or may be reduced (through the utilization of energy).
or - because in same case the energy may be added or may be reduced (through the utilization of energy). - In this equation if all the figures are available QE i.e., energy required for evaporation can be calculated. The actual evaporation can be calculated if the following information is available.
- Latent heat of evaporation
- Temperature of water
- Atmospheric pressure.
C: Mass Transfer Method
- This method is based on the determination of the mass of the water-vapour transferred from the water surface to the atmosphere. So, this method is also called as vapour flow approach or Aerodynamic approach.
- In this method, both the boundary layer theory and the continuous mixing theories have been used. It is assumed that the wind velocity in the upward direction is logarithmic and the atmosphere is adiabatic.
- This method is based on the determination of the mass of the water-vapour transferred from the water surface to the atmosphere. So, this method is also called as vapour flow approach or Aerodynamic approach.
- In this method, both the boundary layer theory and the continuous mixing theories have been used. It is assumed that the wind velocity in the upward direction is logarithmic and the atmosphere is adiabatic.
- The equation used to calculate the evaporation is as follows:
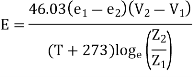
Where, E = Evaporation in mm/per hrs.
Z₁, Z₂ = Arbitrary levels above the mater surface levels in m.
e1, e2= The vapour pressure at Z1, Z2, in mm/of Hg
V₁, V₂ = Wind velocity at Z₁, Z2, in km/per hour
T= Average temperature in OC between Z₁, Z2
Key Takeaways:
There are three types of methods:
- Energy Budget Method
- Water Budget Method
- Mass Transfer Method
- The water from the surface is lost in the form of evaporation (it comes back in the form of precipitation, to complete the cycle but not necessarily in the same region from where it has been evaporated.)
- Another way to lose the surface water is through the plants and trees.
- The plants absorb the water from the soil, through their roots for their growth. Minerals and salts (soluble) also are absorbed from the soil and water is used as a medium to get these nutrients.
- The decomposers in the soil provide these nutrients to the plant. The plants create their own food through the solar energy (it is called as photosynthesis). This plant food is used by the consumers e.g., grass, Leaves, Fruits grains etc. so the natural cycle of flow energy is based on the function of Eva-transpiration.
- The water absorbed by the plant, is again discharged into the atmosphere in the form of vapour. So, the plants also are the important parts of the hydrological cycle.
- This process is called as Transpiration or Eva transpiration (out of the total water consumed by a plant only 1% is used for its growth and 99% of the water is sent back into the air in the form of vapour through the process of transpiration).
Factors which Affect the Process of Transpiration:
In fact, almost all the factors which affect the process of evaporation have the same type of effect on the process of transpiration. In addition to these the following factors also have an impact on the process of transpiration
Sunlight
- The growth of the plant depends upon the availability of sunlight.
- The equatorial and tropical regions in the world have very thick plantation growth and so more: the plants more will be the transpiration and more sunlight more the plants so the cycle of plant growth affects the rate of transpiration.
Moisture in the soil
- Plants get the water from the soil moisture, so if the soils are moist and have more water-holding capacity, the transpiration rate will be more e.g., in the dry sandy soils of deserts having, a little or almost no moisture have less plantation and hence less transpiration.
Stage of plants growth
- The growth of any plant is faster in the early parts of its life faster the growth more will be the water requirement, so in the early state of plant growth the rate of transpiration is always greater than in the later stage of the plant.
- The growth of the plant also has seasonal variation e.g., the deciduous plants, stand their leaves during the hot-dry summer season (to reduce the rate of evaporation) while in the rainy season they get new leaves and the growth rate increases. This seasonal variation in the plant growth also affects the rate of transpiration.
Measurement of Transpiration:
- It can be measured in terms of the changes in the depth of water which has been transmitted daily monthly or yearly.
- It can be accurately measured by using photometer. It is a large vessel which has been filled with soil and one or more plants are rooted into the soil. The surface of the soil is sealed to prevent any loss of water through soil evaporation.
- The vessel soil plant and to seal etc. and accurately weighted and after a given period the whole material is again weighted
- The loss of weight is the loss of water in the form of vapour which has been escaped through the process of transpiration. A small size photometer having water only is called as photometer.
Reduction in the Transpiration:
- For conservation of water, it is necessary to reduce the losses of water through the process of transpiration. Following methods are used to control the transpiration.
- By using a film produced by the chemicals (we already have discussed the method and use of such film to conserve the surface water of a reservoir.)
- By harvesting plants
- By using improved irrigation methods i.e., drip irrigation sprinklers etc.
- By removing the plants moving no economic importance and which are not productive.
- The loss of water through the transpiration can be expressed by using a ratio. It is called as Transpiration ratio (TR). It is ratio of the total weight of the water which has been transpired by a plant during its total growth to the weight of the dry-matter produced.
- It has no dimension. Each plant has different TR e.g., Rice has the TR between 300 and 600 while wheat has the TR between 600 and 800.
- As already seen from the field of any crop or plant. It is difficult to calculate the loss of water separately i.e., the loss through evaporation and the loss through transpiration, so it is put together and this combined figure which indicate. The water loss is called as Evapo-transpiration.
If an adequate quantity of water is available for evaporation and transpiration the combined process is known as Potential Evapo transpiration (PET). The actual Evapo transpiration (AET) is always lesser than PET (PET > AET).
The Measurement of Evapotranspiration:
- Two methods are used to measure the AET, which are as follows:
A: Lysimeter:
B: Inflow-outflow measurements
A: Lysimeter
- It has a tank which is circular shape. The diameter of the tank varies between 600 mm and 3000 mm. The machine is buried into the group up to its top and it is filled with the soil. A plant is planted in it.
- The tank is filled with water to its capacity. The following equation is used to calculate AET of the plant.
P+W=O+AET+
Where,
P = Precipitation during the period of observation
W = Water supplied;
0= Water Drained
AET= Actual Evapo-transpiration
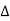 S =Change in the soil-moisture in the lysimneter.
S =Change in the soil-moisture in the lysimneter.
Disadvantages:
- These lysimeter are costly.
- The total process needs a very long period of time.
B: Inflow-Outflow Measurements
- This method is useful for a very large area i.e., an extensive field area up to 100 ha.
- An accurate account of the inflow of water i.e., the water supplied to the field, is kept up to date.
- The inflow can be rainwater, canal water or the unused, extra water is also measured. The difference between these two would be the Evapo-transpiration.
Disadvantages:
- The theory of this method is very accurate but in reality, it is very difficult to measure the inflows and the outflows.
- Estimating water requirement of vegetation is one of the primary desires for crop making plans on a farm and for making plans of any irrigation project.
- In designating water use through vegetation, evaporation and transpiration are mixed into one time period evapotranspiration (ET) as it's miles tough to split those losses in cropped fields.
- Evapotranspiration become calculated from distinctive methods, however Modified Penman technique is used for crop water requirement because of its resemblance with the real area overall performance the use of HYMOS for the have a look at vicinity of Pench Project.
- The real Evapotranspiration for the Kamthi-Khairi is decided through the evaluation of the concurrent file rainfall and different climatological elements from the watershed.
Key Takeaways:
Estimating water requirement of vegetation is one of the primary desires for crop making plans on a farm and for making plans of any irrigation project.
- The process of infiltration can be defined as "It is an entry and movement of water through the land surface into the substrate."
- The process of percolation and the process of infiltration are always taken as one process only. It is not true. The infiltration includes the entry of water into the soil surface and its movement.
- While percolation is the movement of water under gravity. Through these processes are closely related technically they are different. Infiltration is followed by percolation.
Process of Infiltration:
- The rain water gets divided into three different processes i.e. A part of it gets evaporated. A part 2 of it runs along the slopes due to the gravitational force it is called as run-off and the rest of the water which gets saturated on the surface of land tries to move in the vertical direction.
- Through the tracks, faults and through the voids between the soil particles. It is called as infiltration.
- The rate at which the water goes down to the sub surface is called as Infiltration rate. In the beginning the rate is high due to easy penetration and dryness of soil but as it goes further down the rate of infiltration gets reduced. The unit of measurement of the rate of infiltration is mm/per hr.
Key Takeaways:
The process of infiltration can be defined as "It is an entry and movement of water through the land surface into the substrate."
- Infiltration capacity, or infiltration charge is the capacity of the way speedy or how sluggish soil and rocks soak up rain.
- The charge through which soils and rocks can soak up sparkling fallen rain or water from irrigation structures is associated with the soil content, grain length and if there may be any cowl from vegetation.
- If a soil's infiltration charge is insufficient, because of a bodily barrier, loss of soil aeration or if its miles saturated, runoff occurs.
- This is correlated to the hydraulic conductivity of the soil close to the surface. It may be measured with a unique device known as an infiltrometer.
- Both gravity and capillary movement are the 2 forces which motive infiltration. The infiltration charge may be decided through the traits of a soil primarily based totally on its transmission charge via the soil and its garage capacity.
- For example, coarse, sandy soils have big areas permitting water to infiltrate at a quick charge.
- Vegetation and organic existence inclusive of worms and precious bugs also can usefully resource in developing greater porous soils, however additionally shield it from runoff while there may be extra water present.
- In contrast, soils which might be bad in natural and organic existence do now no longer have excessive porosity and therefore, runoff is greater common at the side of excessive erosion rates. This may be negative to flora and soil existence.
Key Takeaways:
Infiltration capacity, or infiltration charge is the capacity of the way speedy or how sluggish soil and rocks soak up rain.
Based on the functions these infiltrometers can be classified as:
- Flooding-type Infiltrometers
- Sprinkling type infiltrometer
A: Flooding type infiltrometers
- These can be further sub-divided into two as,
- Single-tube flooding infiltrometer.
- Double-tube flooding infiltrometer.
1. Single-tube infiltrometer:
- It consists of a metal tube having its diameter between 250mm and 300 mm. And having both of the ends open.
- The length of the tube is 600 mm; out of which 500 mm. Part of the tube is kept under the ground level and 100 mm. Part of the tube is kept above the ground level.
- While placing the tube in the soil care is taken to have minimum disturbance to the present soil structure.
- In this tube the water is added from the top opening and the level of water is constantly maintained.
- The amount of water used the duration period and the depth of the water which has infiltrated in the soil is measured to know the rate of infiltration. For this a pointer gauge is used to show the water level accurately.
2. Double-tube infiltrometer:
- It’s in case of a single-tube infiltrometer, the water may flow sideways, so two tubes are used their diameters vary between 300 and 600 mm.
- They are driven 150 mm. In the ground keeping 100 mm. Part of the length of these tubes above the ground level.
- Outside these tubes a metal ring is used to avoid the side and the border effects.
- The procedure of providing water to the single tube is followed here also to maintain the water level in both the tubes. As the quantity of water, which has been put into this tube is known it is easy to calculate the rate of infiltration.
Key Takeaways:
Based on the functions these infiltrometers can be classified as:
- Flooding-type Infiltrometers
- Sprinkling type infiltrometer
- The Horton technique describes how infiltration capability declines because the precipitation occasion advances and is primarily based totally on producing runoff while rainfall depth exceeds the infiltration capability.
- In addition, the changed Horton's equation describes the restoration of infiltration capability all through dry periods. Both variations are most effective legitimate while precipitation depth exceeds the infiltration capability.
- They determined the following:
- Surface runoff came about for occasions with much less than 1-12 months go back duration for clayey soils, and from 10-12 months go back duration for sandy soils. That is due to the fact the relative infiltration capability of clayey soil usually is much less than 50% on the onset of an occasion, because the drying duration is plenty slower.
- Variation of runoff values is related to variant of preliminary conditions (infiltration capability on the begin of the vent), soil kind and occasion go back duration.
- Both soil sorts decreased the simulated runoff peaks and volumes as compared with impervious surfaces.
Key Takeaways:
The Horton technique describes how infiltration capability declines because the precipitation occasion advances and is primarily based totally on producing runoff while rainfall depth exceeds the infiltration capability.
- The rate of infiltration is very important because it is, a one hand a wastage of surface water but on the other hands, it is the way to increase the level of ground water, which also is used for domestic purpose as well as for commercial purpose through the dug well, tube well and springs etc.
- To make is easy to understand, the rate of infiltration of water is assumed to be same at all the depths, in the soil in fact the rate of infiltration. Never remains equal at the top layer of soil it is always greater than at the lower layers. By assuming uniform rate, we can calculate this rate of infiltration by using following methods.
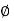 Index:
Index:
- It is the most common method to express the rate of infiltration. For this the following equations are used,

Or 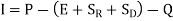
Where, P= Precipitation;
E = Evaporation.
SR = Surface retention (through, interception and depression storage)
SD = Surface detention (after a while it also flows as a surface run off)
Q = Surface runoff;
I= Rate of Infiltration
[If we neglect the effects of E, SR, and SD]
- The simple equation can be formed as,
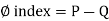
- If we deduct the amount of water taken away from the total precipitation by the way of run-off. We can calculate the rate of infiltration. Fig.is a graphical expression of the above mentioned
 index.
index.
W Index:
- If all the abstractions i.e., evaporation surface retention, surface retention, surface detention etc. are considered, W index can be used to express the rate of infiltration.
- It is expressed as,
W Index =P- (E+SR +SP +Q)
- So, W index is always lesser than
 index.
index.
Wmin Index:
- It is an expression which indicates the minimum rate of infiltration. It is observed when uniform stage is reached after the stabilization is attained. It is expressed as,
- Wmin=
 index (after the stage of stabilization)
index (after the stage of stabilization)
fAV:
- It is slight modification of index. In is assumed that in a storm, there is very low or no precipitation. The process of infiltration is still in progress, due to the effects of the early receipt of a heavy precipitation.
- This situation can be expressed graphically as shown below.
- So, it is provision for infiltration when there is no actual precipitation. As shown in the Fig. No rainfall is observed between 4 and 5 hrs. But a heaving rainfall has been observed during the previous hours i.e., 3 to 4, so this extra amount of water is adjusted during the no rainfall period. It has been seen that FAy is slightly less than AV index.
Key Takeaways:
The rate of infiltration is very important because it is, a one hand a wastage of surface water but on the other hands, it is the way to increase the level of ground water, which also is used for domestic purpose as well as for commercial purpose through the dug well, tube well and springs etc.
References:
1. A textbook of Hydrology, Dr. P. Jaya Rami Reddy, USP Publisher
2. Irrigation, Water Resources and Water Power Engineering, P.N. Modi.
3.Irrigation and Water Power Engineering, Dr. Purnima and Dr. Pande
4. Irrigation Engineering, Bharat Singh, Nem Chand & Bros. India
5.Irrigation Engineering, H.M Raghunath, Wiley