Unit - 3
Vehicles And Their Specifications
Automobile is a vehicle driven by an internal combustion engine and it is used for transportation of passengers and goods on the ground. Automobile can also be defined asvehicle which can move by itself.
Automobile Classification
- Based on Number of Wheels
- Two Wheelers: Motorcycle, Scooters
- Three Wheelers: Auto-Rikshaw, Tempo
- Four Wheelers: Car, Truck, Bus
2. Based on Use of automobiles
- Mopeds: Vehicle with pedals having engine 50cc and speed less than 50Km/hr.
- Motorcycle:Vehicle with gears having engine 50cc and speed more than 50Km/hr.
- Car: Vehicle with passenger capacity 1 to 8 seats.
- Bus:Vehicle with passenger capacity more than 10 seats.
- Truck: Vehicle for Transporting Goods.
3. Based on Purpose
- Passanger Vehicles: Cars, Buses
- Goods Vehicles: Tempo, Trucks
4. Based on Capacity
- Light Motor Vehicles: Cars, Buses
- Heavy Motor Vehicles: Buses, trucks
5. Based on Fuel
- Petrol Vehicles: Motorcycle, Car
- Diesel Vehicles: Bus, Truck
- Electric Vehicles: Electric Car
- Hybrid Vehicles: Hybrid Car
6. Based on Transmission
- Manual Transmission: Manual Gear Shifting
- Automatic Transmission: AutomaticGear Shifting
7. Based on Side Drive
- Left Hand Drive: American Vehicles
- Right Hand Drive: Indian Vehicles
COMPONENTS OF I.C. ENGINE
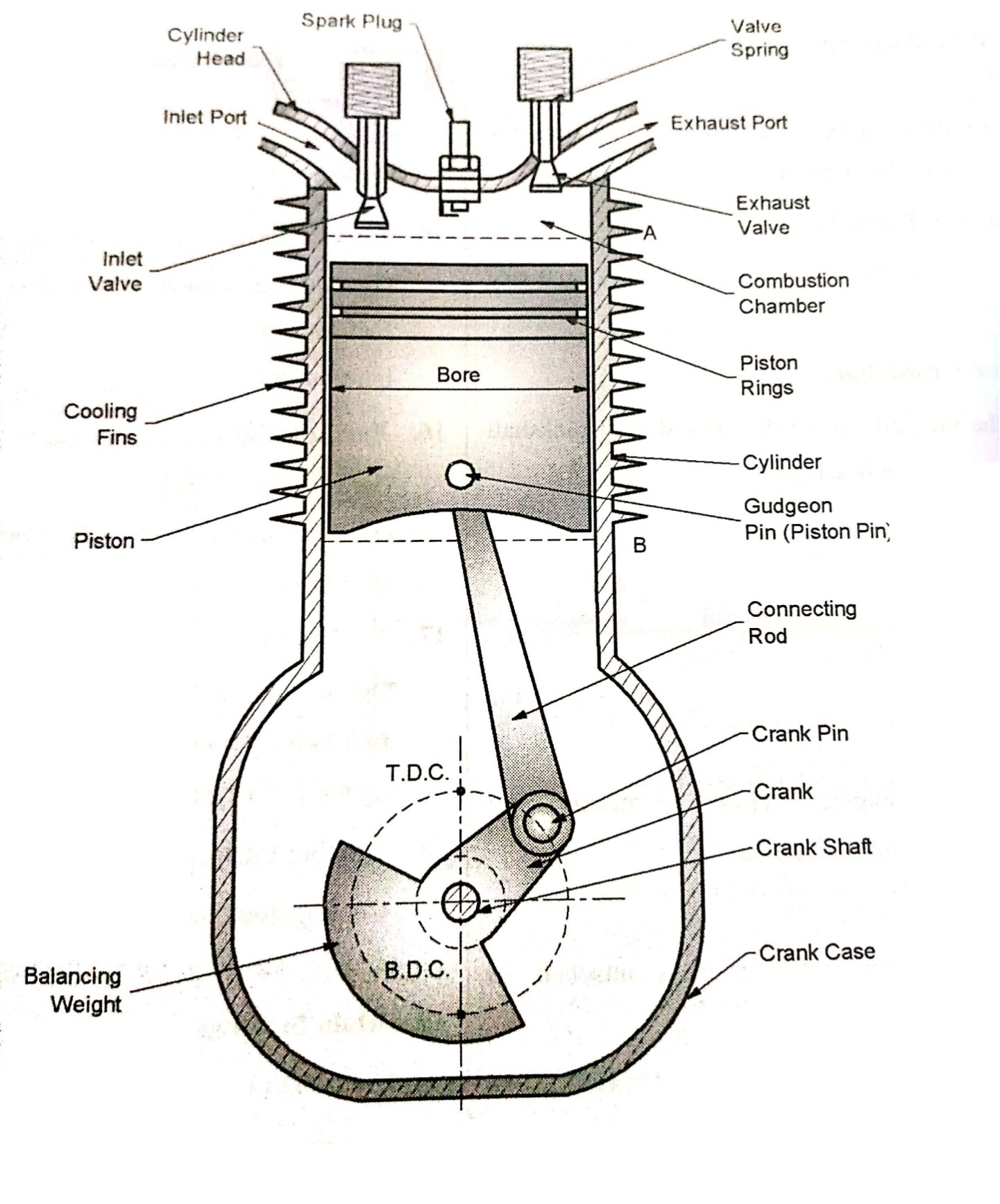
- Cylinder:
Combustion of fuel takes place inside of cylinder. Cylinder must with pressure of 70bar and temperature of 2500°C.
2. Cylinder Head:
Cylinder head is to cover the top end of cylinder. It also provides space for valve mechanism and spark plug.
3. Piston:
Piston transmits gas force to crank through the connecting rod. It reciprocates inside of cylinder.
4. Piston Rings:
Prevents the leakage of gas to crank case. Upper ring is called Compression Rings and lower rings are called as Oil rings.
5. Connecting Rod:
One end of connecting rod is connected to piston with piston pin and other end is connected to crank through crank pin. It converts reciprocating motion of piston into rotary motion of crankshaft.
6. Gudgeon Pin (Piston Pin):
Connects piston and small end of connecting rod.
7. Crank and Crankshaft:
Crank is integral part of crankshaft. Crankshaft is supported in main bearings.
8. Crank Pin:Connects connecting rod to crank.
9. Crankcase:
Crankshaft and main bearings are placed in crankcase. Bottom of engine is closed by means of oil sump, which carries lubricating oil.
10. Flywheel:
It is heavy rotary mass attached to crankshaft. Function is to control the cyclic fluctuations of torque of engine.
11. Inlet Valve:Controls entry of charge in cylinder.
12. Exhaust Valve:Discharges exhaust gases from cylinder.
13. Spark Plug:Provides spark for combustion of fuel in S.I. Engine.
14. Fuel Injector:Injects the fuel to cylinder with high pressure in C.I. Engine.
15. Cooling Fin:Increases heat transfer rate for cooling of cylinder.
16. Main Bearing:Supports crankshaft.
Any vehicle specification is based on the following parameters.
- Engine Specification
- Fuel Type
- Engine Type
- Bore dia. x Stroke length
- Displacement Volume (CC)
- Swept Volume (Vs)
- Clearance Volume (Vc)
- Maximum Power (BHP @ rpm)
- Maximum Power (N-m @ rpm)
- Number of Cylinders
- Valves per Cylinder
- Fuel Supply System
- Compression Ratio
2. Fuel Consumption
- Fuel Tank Capacity
- Mileage
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Gear
- Brakes Specification
- Front brake
- Rear Brake
- Suspension Specification
- Front Suspension
- Rear Suspension
6. Wheel Specification - Type of wheel – spoke or alloy
7. Tyre Specification
- Aspect ratio
- Load Index
- Steering (in case of four wheelers)
- Battery Specification
- Voltage
- Ampere-Hour Rating
- Body Dimensions
- Kerb Weight
- Gross weight
- Wheel Base
- Ground Clearance
- Total length of vehicle
- Maximum width of vehicle
- Maximum height of vehicle
- Boot Space(in case of four wheelers)
- Track – Front and Rear(in case of four wheelers)
- Overhang(in case of four wheelers)
- Engine Specifications
- Fuel Type
Type of fuel used may be petrol, CNG, LPG or diesel.
2. Engine Type
It informs whether the engine is Four stroke or Two stroke engine& whether the engine is Air cooled or water cooled engine.
3. Bore x Stroke
Inside diameter of cylinder is called as Bore while Distance travelled by piston when it moves from TDC to BDC is called as Stroke.
4. Displacement Volume (CC)
Total volume of air –fuel admitted by cylinder during suction stroke is called as displacement volume. It is also the total cylinder volume of engine measured in cubic centimeter.
5. Swept Volume (Vs)
Volume swept by piston when it moves from one end (TDC) to other end (BDC) is called as Swept Volume.
6. Clearance Volume (Vc)
Volume between piston reaches TDC, at that position, the volume between piston top surface and cylinder head is called as Clearance Volume.
7. Maximum Power (BHP @ rpm)
As the Engine speed increases power output of engine increases. It becomes maximum at some engine Speed and it reduces as engine speed further increases.Thus, it is the maximum power that the engine can develop at some value of engine RPM.
8. Maximum Power (N-m @ rpm)
Engine speed increases the output torque of engine increases. It becomes maximum at some engine speed and it reduces as engine speed further increases. Thus, it is the maximum torque that the engine can develop at some value of engine RPM.
9. Number of Cylinders
It specifies whether the engine is having only one cylinder or Number of cylinders used in engine. i.e. single cylinder engine or multi cylinder engine.
10. Valves per Cylinder
It specifies Number of valves used in each cylinder of the engine.
11. Fuel Supply System
Fuel supply system such as MPFI- Multi Point Fuel Injection can be used in four-wheeler petrol vehicle. CRDI- Common Rail Diesel Injection is also the fuel supply system that is generally used by four-wheeler diesel vehicle. Most of the two-wheeler uses carburetor device to supply petrol to the engine.
12. Compression Ratio
It is the ratio of total volume of cylinder to clearance volume.
B. Fuel Consumption:
- Fuel Tank Capacity (liters)
It is the total volume fuel in liters that can be filled in fuel tank of any vehicle.
2. Mileage (kmpl)
It is measured in Kilometers per liter of fuel consumed under ideal conditions. It is nothing but the distance covered by any vehicle by consuming 01 liter of fuel.
C. Transmission:
- Clutch:
Type of clutch used in the vehicle may be multiplate wet Clutch in case of two wheelers and Single plate dry clutch in case of four wheelers.
2. Numberof Gears
No. Of gears may vary according to type of vehicle i.e 3,4,5 etc.
D. Braking
Types of brakes used in the vehicle may be disk brake or drum brake.
Front: Drum or Disk brake
Rear: Drum or Disk brake
E. Suspension
Front:Telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers or spring loaded hydraulic damper. (2 -Wheeler)
Rear:Telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers or spring loaded hydraulic damper. (2 -Wheeler)
Four Wheeler:Mac Pherson Strut type shock absorber with coil spring OR Coupled Torsion Beam Axle with Coil Spring
F. Wheels
Wheel Type used specifies the type of rim used to mount the tyres. It may be Spoke wheels or alloy wheels.
G. Tyre Specifications:
- Aspect ratio:
Itis defined as the ratio of height of tyre section to width of tyre section.
2. Load Index
It indicates maximum load carrying capacity of tyre when driven at maximum speed.Load index of 84 shows that maximum load carrying capacity of tyre is 500kg when driven at maximum speed.
H. Steering:
Type of Steering used: Hydraulic or Electric Power Steering.
I. Battery
- Voltage: 12V or 18V or 24V
- Ampere-Hour Rating: 2.5Ah or 5Ah or 7.5Ah
J. Body Dimension
- Kerb Weight
It is weight of vehicle with all parts and all necessary operating consumables without passengers and cargo.
2. Gross Weight
It is weight of vehicle with all parts and all necessary operating consumables with passengers and cargo.
3. Wheel Base
It is the distance between centers of front and rear wheels of vehicle.
4. Ground Clearance
It is the distance between the ground surface and lowest part of the vehicle.
5. Total length of vehicle
6. Maximum width of vehicle
7. Maximum height of vehicle
8. BootSpace (in case of four wheelers)
It is the volume space available in car to keep the luggage.
9. TRACK (in case of four wheelers)
FrontTrack: Distance between the centerline of front wheels.
RearTrack: Distance between the centerline of rear wheels.
10. Overhangs (in case of four wheelers)
It is the lengths of a road vehicle which extend beyond the wheelbase at the front and rear.Overhang are Front Overhang and Rear Overhang.
AUTOMOBILE ENGINE SPECIFICATION:- Maruti Suzuki Celerio
Parameter | Specification |
Fuel Type | Petrol/CNG |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4-Stroke, BS 4 Petrol Engine |
Bore x Stroke | 73mm x 89.4mm |
Displacement (CC) | 998 |
Maximum Power | Petrol Mode: 50 kW @6000 rpm CNG Mode: 43.5 kW @6000 rpm |
Maximum Power | Petrol Mode: 90 N-m @3500 rpm CNG Mode: 78 N-m @3500 rpm |
Number of Cylinders | 3 |
Valves per Cylinder | 4 |
Fuel Supply System | MPFI- Multi Point Fuel Injection |
Compression Ratio | 10.3:1 |
Sample specifications of Bajaj CT 110&Hero Extreme Sportare given below.
- AutomobileVehicle Specifications of BAJAJ CT 110
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Petrol | |
Engine Type | Single cylinder, Air Cooled, 4-Stroke, Petrol Engine. | |
Bore x Stroke | 50 mm x 58.8mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 115 | |
Maximum Power | 6.3 kW (8.6 PS) @ 7000 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 9.81 N-m @ 5000 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 1 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 2 | |
Fuel Delivery | Carburetor | |
Compression Ratio | 10 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 10.5 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity | 2 L | |
Mileage | 91 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 4 , Manual Constant Mesh Gear Box | |
Clutch | Wet , MultiPlate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | 130 mm Drum | |
Rear | 110 mm Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | Telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers 125 mm | |
Rear | SNS - Spring in Spring, 100 mm | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 18 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 2.75 X 17 P, Semi-knobby tread pattern | |
Rear Tyre | 3.00 X 17 P, Semi-knobby tread pattern | |
8. Battery | ||
Voltage | 12V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 3 Ah | |
9. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 116 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 1235 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 170 mm | |
Length | 1945 mm | |
Width | 752 mm | |
Height | 1072 mm | |
2. Automobile Vehicle Specifications of HERO EXTREME SPORT
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Petrol | |
Engine Type | Air Cooled, 4 - Stroke Single Cylinder OHC | |
Bore x Stroke | 57.3 mm x 57.8 mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 149.2 | |
Maximum Power | 11.64 KW (15.6 BHP) @ 8500 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 13.50 N-m @ 7000 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 1 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 2 | |
Fuel Delivery | CV Type with Carburetor Controlled Variable Ignition | |
Compression Ratio | 10 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 12.1 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity | 1.5 L | |
Mileage | 65 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 5 , Manual Constant Mesh Gear box | |
Clutch | Wet , MultiPlate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | 240 mm Disc | |
Rear | 110 mm Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | Telescopic hydraulic shock absorber | |
Rear | Rectangular Swing Arm with 5 step Adjustable Gas Reservoir Suspension | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 18 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 80 / 100 x 18 - 47 P Tubeless | |
Rear Tyre | 110 / 90 x 18 - 61 P Tubeless | |
8. Battery | ||
Voltage | 12V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 4 Ah | |
9. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 147 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 1325 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 163 mm | |
Length | 2100 mm | |
Width | 780 mm | |
Height | 1080 mm | |
Sample specifications of & are given below.
- Automobile Vehicle Specifications of HUNDAI CRETA 1.6 SX Option Diesel
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Diesel | |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4 - Stroke | |
Bore x Stroke | 73 mm X 71.5 mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 1582 | |
Maximum Power | 128 bHp @ 4,000 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 259.87 N-m @ 1500-3000 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 4 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 4 | |
Fuel Delivery | CRDi with VGT | |
Compression Ratio | 15 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 55 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity | - | |
Mileage | 20.5 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 6-Speed Automatic | |
Clutch | Dry, Single plate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | Disc | |
Rear | Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | McPherson Strut with Coil Spring | |
Rear | Couple Torsion Beam Axle with Coil Spring | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 17 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 215/60 R17 Steel Tubeless | |
Rear Tyre | 215/60 R17 Steel Tubeless | |
8. Steering | ||
Power Steering | Yes | |
Steering Type | Adjustable | |
9. Battery | ||
Voltage | 18 V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 7 Ah | |
10. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 1398 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 2590 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 190 mm | |
Length | 4270 mm | |
Width | 1780 mm | |
Height | 1665 mm | |
Boot Space | 400 L | |
Gross Weight | 1455 kg | |
Front Track | 1490 mm | |
Rear Track | 1480 mm | |
Minimum Turning Radius | 5.3 m | |
Seating Capacity | 5 | |
Front Overhang | 150 mm | |
Front Overhang | 120 mm | |
2. Automobile Vehicle Specifications of MARUTI SUZUKI SWIFT LXI
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Petrol | |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4 - Stroke | |
Bore x Stroke | 73 mm X 71.5 mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 1197 | |
Maximum Power | 81.8 bHp @ 6000 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 113 N-m @ 4200 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 4 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 4 | |
Fuel Delivery | MPFI | |
Compression Ratio | 11 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 37 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity |
| |
Mileage | 22 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 5-Speed Manual | |
Clutch | Dry Single Plate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | Disc | |
Rear | Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | McPherson Strut with Coil Spring | |
Rear | Couple Torsion Beam Axle with Coil Spring | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 14 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 165/80 R14 Tubeless | |
Rear Tyre | 165/80 R14 Tubeless | |
8. Steering | ||
Power Steering | Yes | |
Steering Type | Adjustable Electric | |
9. Battery | ||
Voltage | 18V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 7 Ah | |
10. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 880 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 2450 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 163 mm | |
Length | 3840 mm | |
Width | 1735 mm | |
Height | 1530 mm | |
Boot Space | 268 L | |
Gross Weight | 1315 kg | |
Front Track | 1530 mm | |
Rear Track | 1530 mm | |
Minimum Turning Radius | 4.8 m | |
Seating Capacity | 5 | |
Front Overhang | 150 mm | |
Front Overhang | 120 mm | |
- Automobile Vehicle Specifications of VOLVO 9400 14.5 M
Parameter | Specification |
1.Engine | |
Fuel Type | Diesel |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4-Stroke, Diesel Engine. |
Bore x Stroke | 73mm x 89.4mm |
Displacement (CC) | 10.8L |
Maximum Power | 410 BHP @ 2000 rpm |
Maximum Power | 1980 N-m @ 2000 rpm |
Number of Cylinders | 6 |
Valves per Cylinder | 2 |
Fuel Delivery | CRDI |
2. Fuel Consumption | |
Fuel Tank Capacity | 600 L |
3.Transmission | |
Number of Gears | 12 Speed Automatic |
Clutch | Dry Single plate |
4. Braking | |
Front | Disk Brake with Electronic braking System |
Rear | Disk Brake with Electronic braking System |
5. Suspension | |
Front | Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECS) |
Rear | Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECS) |
6. Wheels | |
Wheel Size | 18 inch |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels |
7. Tyres | |
Front Tyre | 295/80 R 22.5Tubeless |
Rear Tyre | 295/80 R 22.5Tubeless |
8. Steering | |
Power Steering | Yes |
Steering Type | Adjustable Electric |
8. Dimension and Weight | |
Kerb Weight | - |
Wheel Base | 8350 mm |
Ground Clearance | 209 mm |
Gross Weight | 22200 kg |
Front Track | 2054 mm |
Rear Track | 1837 mm |
Minimum Turning Radius | 11.54 m |
Seating Capacity | 54 |
Length | 14500 mm |
Width | 2600 mm |
Height | 3600 mm |
Front Overhang | 2620 mm |
Rear Overhang | 2830 mm |
1. Engine
- Fuel type: The diesel engines have higher thermal efficiency compared to petrol engines. Therefore, diesel vehicles give better fuel economy compared to petrol vehicles.
- In addition, price of diesel is less compared to petrol. Hence, customers with heavy usage of vehicle, prefer diesel vehicles.
- However, diesel vehicles have higher initial as well as maintenance cost compared to petrol vehicles.
- So, if initial cost is a prime consideration, petrol vehicles are preferred; whereas if running cost is a prime consideration diesel vehicles are preferred.
- Displacement, maximum power and maximum torque: All three parameter indicate the power of an engine.
2. Fuel Efficiency and Performance:
- Mileage (kmpl): Higher the mileage, lower is the running cost of the vehicle.
- Top Speed and Acceleration: User prefer vehicles with higher top speed and higher acceleration or pick up.
3. Transmission System:
- Type of transmission: Now a days, type of transmission is one of the most important comparison parameter. Because of ease and comfort of driving, many user prefer vehicles with automatic transmission over Vehicles with manual transmission.
- Number of gears:Vehicles with more number of gears give more number of speed ranges.
4. Braking System:
- Disc brakes give better braking effect compared to drum brakes. Therefore Vehicles with disc brakes are preferred over vehicles with drum brakes.
5. Suspension System:Better type of suspension system gives comfort to Passengers.
6. Steering:
- Power Steering:The vehicles reduce the efforts required for steering the vehicle.
- Steering Adjustments:now days, in many high end cars, steering is provided with telescopic and tilt adjustments. The vehicles with such adjustments enhance the driving comfort.
7. Dimensions:
- GroundClearance:The vehicles with high ground clearance reduce the possibility of underbody striking, the road while driving on rough roads or off roads.
- However, higher ground clearance means higher center of gravity which reduces the stability of vehicle.
- Boot Space: Higher boot space means higher space for the storage of luggage.
- SeatingCapacity:The seating capacity is one of the most important comparison parameters while selecting the vehicle.
8. Cost, Safety and Comfort Parameters are also considered for Comparison of Vehicles.
- These includes
- On road price
- Aesthetics
- Maintenance cost
- Warranty
- Driver and passenger safety devices
- Interior of vehicle Infotainment system.
Need of Electrical Vehicles:
- With current rate of oil production and consumption, the oil reserves on the earth will not last for more than 50 years.
- The automobile manufactures all over the world are looking for alternative energy sources for vehicles because of following reasons
- Fast depletion of crude oil reserves
- Increasing crude oil prices
- High pollution due to vehicles
- Increasing cost of vehicles due to new pollution control norms.
Types of Electric Vehicles
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
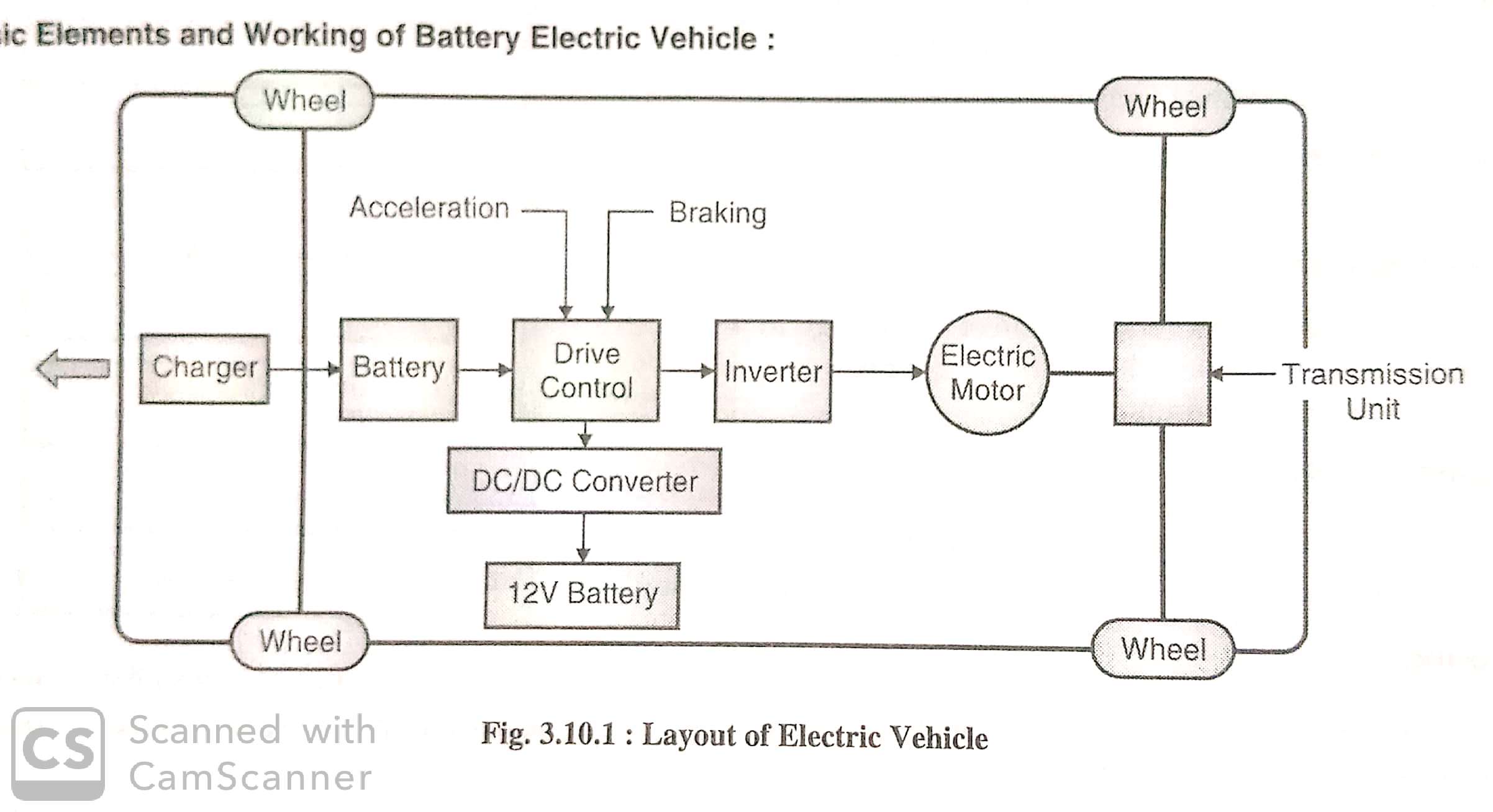
Figure: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Battery electrical vehicles are an automobile propelled by one or more electric motors using the energy stored in rechargeable battery. It consist of following components.
- Charger: The charger gets electricity supplied by electric grid and charges the battery of the vehicle.
- Rechargeable Battery: The rechargeable battery is charged through the charger. The battery may be Lead-acid battery, Nickel-metal hydride battery or Lithium-ion battery.
- The distance travelled by electric vehicle depends upon the energy storage capacity of the battery which ranges between 30 kWh to 150 kWh.
- Drive Control Unit: The drive control unit controls the supply of electric current from battery to inverter.
- Inverter: Inverter converts D.C. Supply of battery to A.C. Supply if AC Motor is used. If DC Motor is used in vehicle then inverter is not required.
- Electric Motor: A.C. Motor or D.C. Motor drives the transmission unit. It convert electrical energy into mechanical energy in the form of rotations.
- Transmission Unit (Gear box): The transmission unit drives the rear wheels.
Advantages of Battery Electric Vehicles
- Pollution free.
- Less Noise.
- Simple in design.
- Low running cost.
- Low maintenance cost.
Disadvantages of Battery Electric Vehicles
- Limited travelling range
- High initial cost
- Battery life is short
- Low speed
- Charging station non-availability.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) or hybrid vehicle is an automobile propelled by two power sources: (i) Electric motor driven by rechargeable battery and (ii) I.C. Engine.
- Hybrid electric vehicle is a progressive transformation from conventional automobile vehicle powered by only I.C. Engine to battery electric vehicle powered by only electric motor.
- Hybrid electric vehicle minimizes the drawbacks of conventional I.C. Engine powered automobile vehicle and retains the advantages of conventional I. C. Engine powered automobile vehicle.
- Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles:
- Series Hybrid Vehicles
- Parallel Hybrid Vehicles
1. Series Hybrid Vehicles
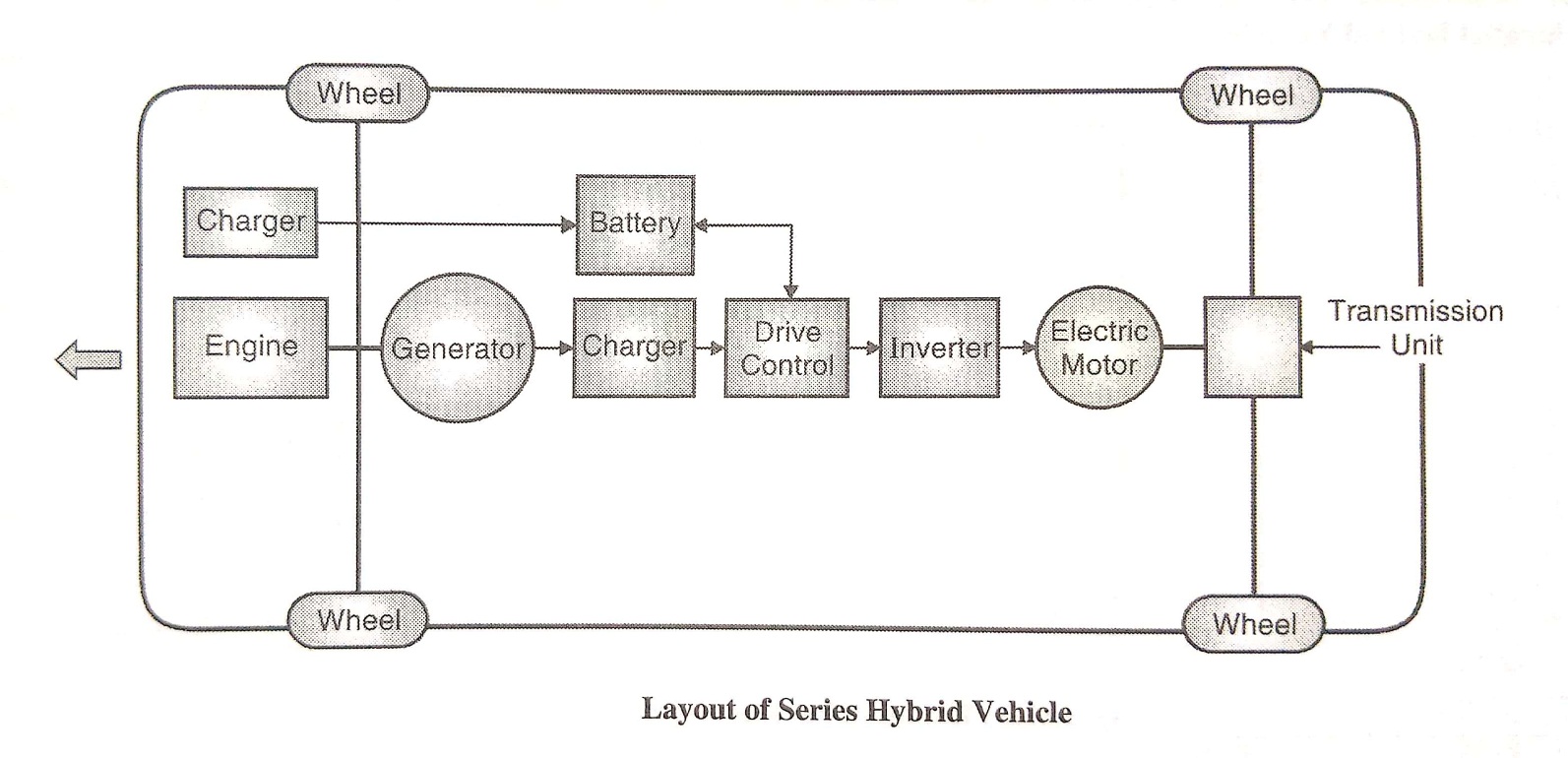
Figure: Series Hybrid Vehicles
- In series hybrid vehicles electric motor is the only means of providing the power to the wheels through transmission unit (gear box). The electric motor receives electric power form either from rechargeable battery or generator run by I.C. Engine.
- The computer assisted drive control unit decides the quantity of power to come from the battery and the IC engine generator.
- The excess electric power from generator is used to charge the battery. In addition, during braking, the electric motor acts as a generator and uses the regenerative braking energy to charge the battery. The battery is charged through charger form electric grid. In series hybrid vehicle, engine is of smaller capacity; because it has to meetonly partial power requirement. The battery is more powerful.
2. Parallel Hybrid Vehicles
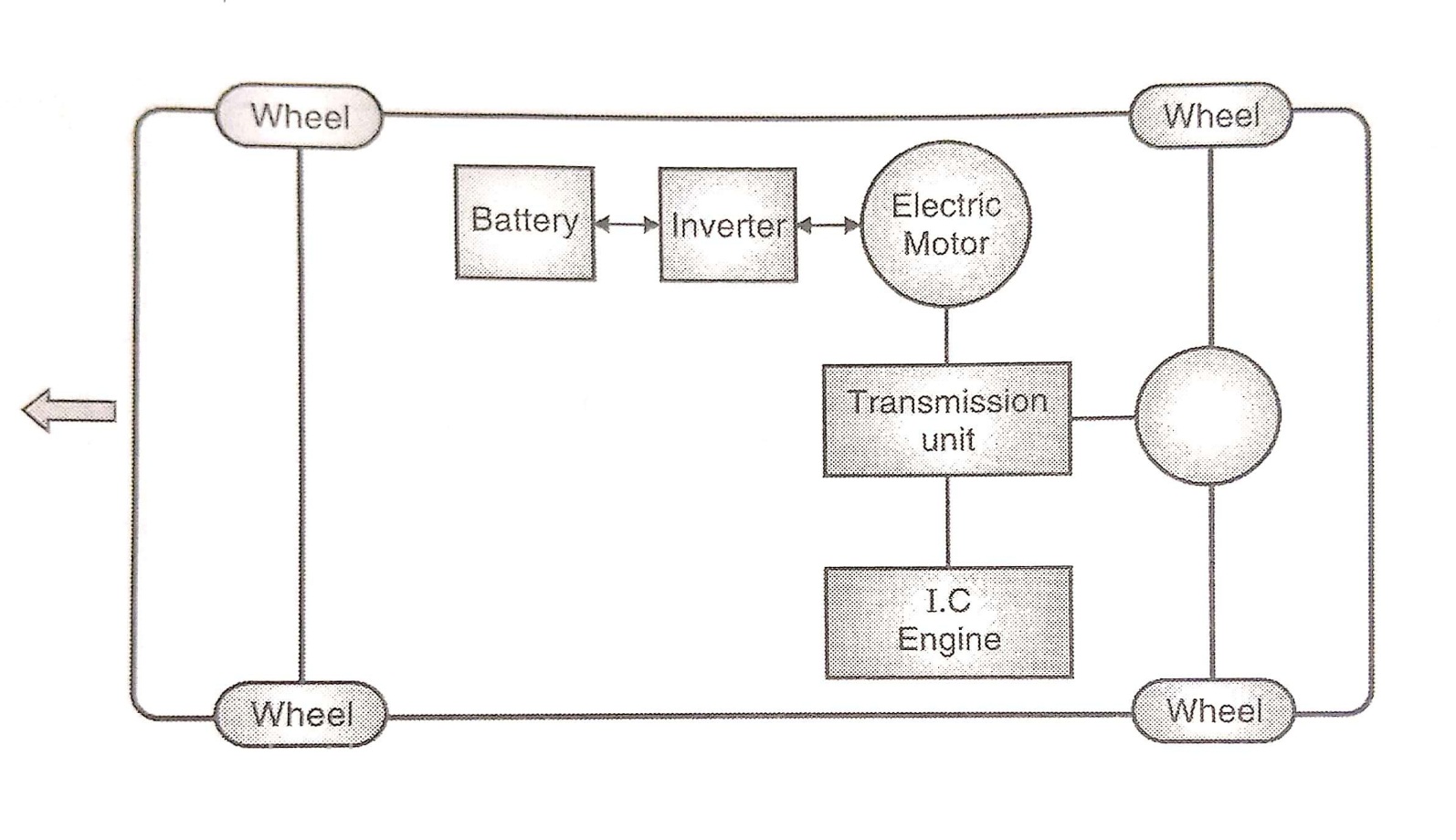
Figure: Parallel Hybrid Vehicles
- In parallel hybrid vehicles, the I.C. Engine as well as electric motor drives the wheels through the transmission unit.
- When power demand is low, the electric motor acts as a generator and utilizes the excess power form I.C. Engine to charge the battery.
- In addition, during braking also, the electric motor acts as a generator and uses the regenerative braking energy to charge the battery.
- In parallel hybrid vehicles, engine is of higher capacity as compared to series hybrid vehicles. However, parallel hybrid vehicles use a smaller capacity battery compared to series hybrid vehicles.
Advantages of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- Large travelling Range
- Environment friendly.
- Regenerative braking
- Light weight
Disadvantagesof Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- High initial cost
- Battery life is short
- Less Power
- High maintenance cost
Specifications Electric Vehicle
Parameter | Specifications |
1. Electric Motor | |
Type | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor |
Maximum Power | 134 hp (100 kW) |
Maximum Torque | 395 N-m |
2. Battery | |
Type | Lithium-Ion Polymer, 327 V |
Capacity | 39.2 kWh |
A.C. Charging 230 V (0-100 %) | Approx. 6 h 10 |
D.C. Charging (0-80%) | Approx. 57 min |
Driving Range | 452 km |
The overall cost of vehicle includes many parameters. Some of them are as follows.
- Type of Engine: According to the type of engine or its capacity the cost of vehicle changes. For high power engines, the cost of vehicle is very high.
- Safety Features: If a vehicle includes safety features like air ABS, air bag etc. then the cost of vehicle increases. It also depends on the number of airbags in a vehicle.
- Material of vehicle (Raw material): The material of vehicle is one of the important factor in cost analysis. For high grade material the cost of vehicle increases rapidly. Now-a-days some parts of vehicle are replaced by fiber parts to reduce the cost of vehicle.
- Production Method: Some manufactures like BMW, Audi etc. use fully automatic machines for production of vehicle. This increases accuracy and finishing of vehicle. But this increases the cost of vehicle. Hence as per the production method the cost of vehicle changes.
- Research and development (R and D): It is a hidden cost of vehicle. It requires long time and number of technical people.
- Royalty: The innovations like ABS, Air bags, ESP etc. are all innovations by Bosch Company and not by car manufacturers. The manufacturers need to pay royalty to Bosch for using the technology.
- Dealer profit
- Insurance and taxation
- Availability of spare parts
- Advertisement (Posters, ads, campaigns etc.)
- Quantity of production
- Labour cost, etc.
References
1. Khan, B. H., “Non Conventional Energy Sources, Tata McGraw-Hill Publisher Co. Ltd.
2. Boyle, Godfrey, “Renewable Energy”,2nd Ed., Oxford University Press
3. Khurmi, R.S. ,and Gupta, J. K.,“A Textbook of Thermal Engineering”, S. Chand & Sons
4. Incropera, F. P. And Dewitt, D.P., (2007), “Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 6th Ed., John Wiley and Sons, USA
5. Groover,Mikell P., (1996), “Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing: Materials, Processes, and Systems”, Prentice Hall, USA
6. Norton, Robert L., (2009), “Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery”, Tata McGrawHill
7. Cleghorn, W. L., (2005), “Mechanisms of Machines”, Oxford University Press
8. Juvinal, R. C., (1994), “Fundamentals of Machine Component Design”, John Wiley and Sons, USA
9. Ganeshan, V., (2018), “Internal Combustion Engines”, McGraw Hill
10. Anderson, Curtis Darrel and Anderson,Judy, (2010), “Electric and Hybrid Cars: A History”, 2nd Ed., McFarland
Unit - 3
Vehicles And Their Specifications
Automobile is a vehicle driven by an internal combustion engine and it is used for transportation of passengers and goods on the ground. Automobile can also be defined asvehicle which can move by itself.
Automobile Classification
- Based on Number of Wheels
- Two Wheelers: Motorcycle, Scooters
- Three Wheelers: Auto-Rikshaw, Tempo
- Four Wheelers: Car, Truck, Bus
2. Based on Use of automobiles
- Mopeds: Vehicle with pedals having engine 50cc and speed less than 50Km/hr.
- Motorcycle:Vehicle with gears having engine 50cc and speed more than 50Km/hr.
- Car: Vehicle with passenger capacity 1 to 8 seats.
- Bus:Vehicle with passenger capacity more than 10 seats.
- Truck: Vehicle for Transporting Goods.
3. Based on Purpose
- Passanger Vehicles: Cars, Buses
- Goods Vehicles: Tempo, Trucks
4. Based on Capacity
- Light Motor Vehicles: Cars, Buses
- Heavy Motor Vehicles: Buses, trucks
5. Based on Fuel
- Petrol Vehicles: Motorcycle, Car
- Diesel Vehicles: Bus, Truck
- Electric Vehicles: Electric Car
- Hybrid Vehicles: Hybrid Car
6. Based on Transmission
- Manual Transmission: Manual Gear Shifting
- Automatic Transmission: AutomaticGear Shifting
7. Based on Side Drive
- Left Hand Drive: American Vehicles
- Right Hand Drive: Indian Vehicles
COMPONENTS OF I.C. ENGINE
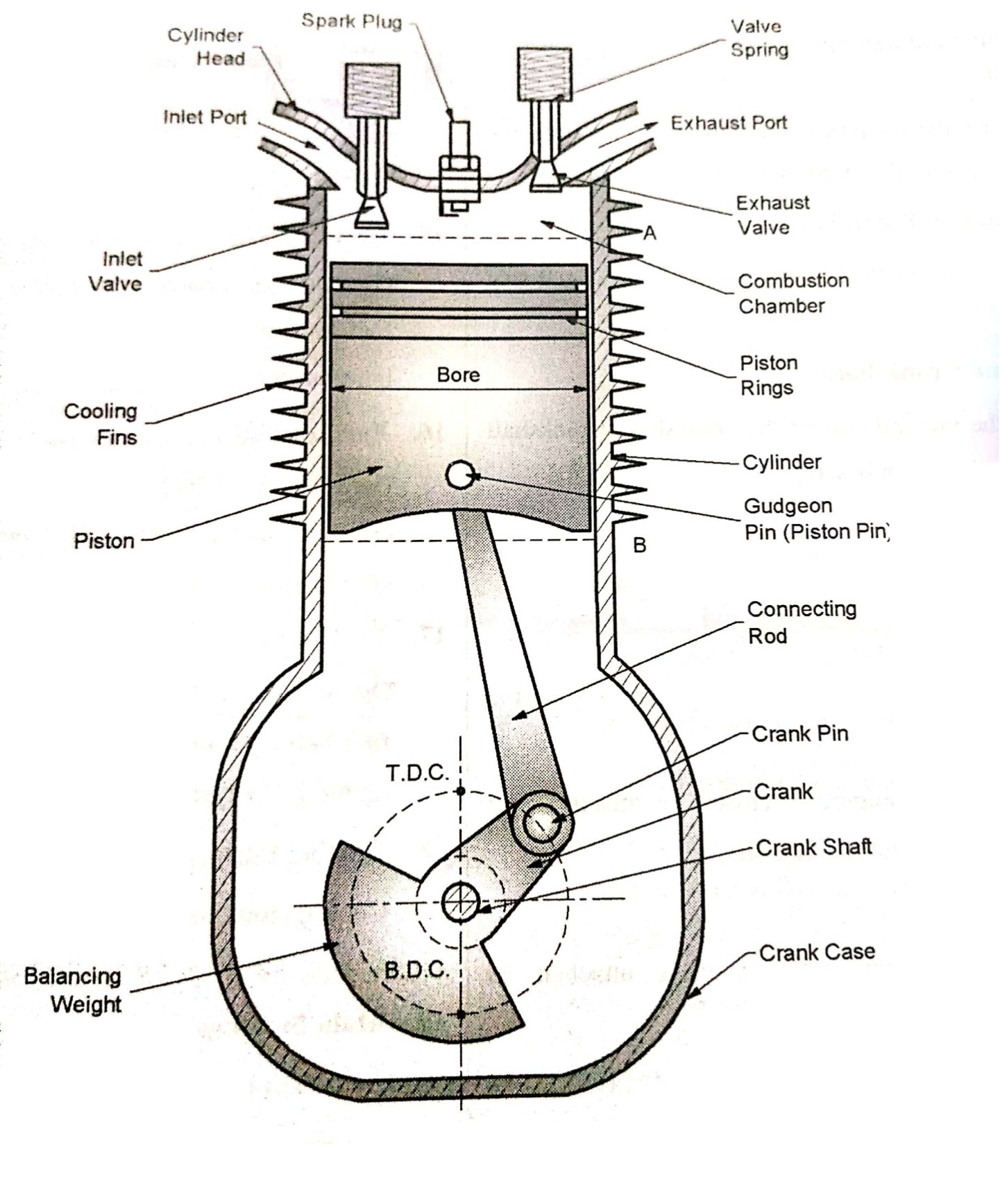
- Cylinder:
Combustion of fuel takes place inside of cylinder. Cylinder must with pressure of 70bar and temperature of 2500°C.
2. Cylinder Head:
Cylinder head is to cover the top end of cylinder. It also provides space for valve mechanism and spark plug.
3. Piston:
Piston transmits gas force to crank through the connecting rod. It reciprocates inside of cylinder.
4. Piston Rings:
Prevents the leakage of gas to crank case. Upper ring is called Compression Rings and lower rings are called as Oil rings.
5. Connecting Rod:
One end of connecting rod is connected to piston with piston pin and other end is connected to crank through crank pin. It converts reciprocating motion of piston into rotary motion of crankshaft.
6. Gudgeon Pin (Piston Pin):
Connects piston and small end of connecting rod.
7. Crank and Crankshaft:
Crank is integral part of crankshaft. Crankshaft is supported in main bearings.
8. Crank Pin:Connects connecting rod to crank.
9. Crankcase:
Crankshaft and main bearings are placed in crankcase. Bottom of engine is closed by means of oil sump, which carries lubricating oil.
10. Flywheel:
It is heavy rotary mass attached to crankshaft. Function is to control the cyclic fluctuations of torque of engine.
11. Inlet Valve:Controls entry of charge in cylinder.
12. Exhaust Valve:Discharges exhaust gases from cylinder.
13. Spark Plug:Provides spark for combustion of fuel in S.I. Engine.
14. Fuel Injector:Injects the fuel to cylinder with high pressure in C.I. Engine.
15. Cooling Fin:Increases heat transfer rate for cooling of cylinder.
16. Main Bearing:Supports crankshaft.
Any vehicle specification is based on the following parameters.
- Engine Specification
- Fuel Type
- Engine Type
- Bore dia. x Stroke length
- Displacement Volume (CC)
- Swept Volume (Vs)
- Clearance Volume (Vc)
- Maximum Power (BHP @ rpm)
- Maximum Power (N-m @ rpm)
- Number of Cylinders
- Valves per Cylinder
- Fuel Supply System
- Compression Ratio
2. Fuel Consumption
- Fuel Tank Capacity
- Mileage
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Gear
- Brakes Specification
- Front brake
- Rear Brake
- Suspension Specification
- Front Suspension
- Rear Suspension
6. Wheel Specification - Type of wheel – spoke or alloy
7. Tyre Specification
- Aspect ratio
- Load Index
- Steering (in case of four wheelers)
- Battery Specification
- Voltage
- Ampere-Hour Rating
- Body Dimensions
- Kerb Weight
- Gross weight
- Wheel Base
- Ground Clearance
- Total length of vehicle
- Maximum width of vehicle
- Maximum height of vehicle
- Boot Space(in case of four wheelers)
- Track – Front and Rear(in case of four wheelers)
- Overhang(in case of four wheelers)
- Engine Specifications
- Fuel Type
Type of fuel used may be petrol, CNG, LPG or diesel.
2. Engine Type
It informs whether the engine is Four stroke or Two stroke engine& whether the engine is Air cooled or water cooled engine.
3. Bore x Stroke
Inside diameter of cylinder is called as Bore while Distance travelled by piston when it moves from TDC to BDC is called as Stroke.
4. Displacement Volume (CC)
Total volume of air –fuel admitted by cylinder during suction stroke is called as displacement volume. It is also the total cylinder volume of engine measured in cubic centimeter.
5. Swept Volume (Vs)
Volume swept by piston when it moves from one end (TDC) to other end (BDC) is called as Swept Volume.
6. Clearance Volume (Vc)
Volume between piston reaches TDC, at that position, the volume between piston top surface and cylinder head is called as Clearance Volume.
7. Maximum Power (BHP @ rpm)
As the Engine speed increases power output of engine increases. It becomes maximum at some engine Speed and it reduces as engine speed further increases.Thus, it is the maximum power that the engine can develop at some value of engine RPM.
8. Maximum Power (N-m @ rpm)
Engine speed increases the output torque of engine increases. It becomes maximum at some engine speed and it reduces as engine speed further increases. Thus, it is the maximum torque that the engine can develop at some value of engine RPM.
9. Number of Cylinders
It specifies whether the engine is having only one cylinder or Number of cylinders used in engine. i.e. single cylinder engine or multi cylinder engine.
10. Valves per Cylinder
It specifies Number of valves used in each cylinder of the engine.
11. Fuel Supply System
Fuel supply system such as MPFI- Multi Point Fuel Injection can be used in four-wheeler petrol vehicle. CRDI- Common Rail Diesel Injection is also the fuel supply system that is generally used by four-wheeler diesel vehicle. Most of the two-wheeler uses carburetor device to supply petrol to the engine.
12. Compression Ratio
It is the ratio of total volume of cylinder to clearance volume.
B. Fuel Consumption:
- Fuel Tank Capacity (liters)
It is the total volume fuel in liters that can be filled in fuel tank of any vehicle.
2. Mileage (kmpl)
It is measured in Kilometers per liter of fuel consumed under ideal conditions. It is nothing but the distance covered by any vehicle by consuming 01 liter of fuel.
C. Transmission:
- Clutch:
Type of clutch used in the vehicle may be multiplate wet Clutch in case of two wheelers and Single plate dry clutch in case of four wheelers.
2. Numberof Gears
No. Of gears may vary according to type of vehicle i.e 3,4,5 etc.
D. Braking
Types of brakes used in the vehicle may be disk brake or drum brake.
Front: Drum or Disk brake
Rear: Drum or Disk brake
E. Suspension
Front:Telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers or spring loaded hydraulic damper. (2 -Wheeler)
Rear:Telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers or spring loaded hydraulic damper. (2 -Wheeler)
Four Wheeler:Mac Pherson Strut type shock absorber with coil spring OR Coupled Torsion Beam Axle with Coil Spring
F. Wheels
Wheel Type used specifies the type of rim used to mount the tyres. It may be Spoke wheels or alloy wheels.
G. Tyre Specifications:
- Aspect ratio:
Itis defined as the ratio of height of tyre section to width of tyre section.
2. Load Index
It indicates maximum load carrying capacity of tyre when driven at maximum speed.Load index of 84 shows that maximum load carrying capacity of tyre is 500kg when driven at maximum speed.
H. Steering:
Type of Steering used: Hydraulic or Electric Power Steering.
I. Battery
- Voltage: 12V or 18V or 24V
- Ampere-Hour Rating: 2.5Ah or 5Ah or 7.5Ah
J. Body Dimension
- Kerb Weight
It is weight of vehicle with all parts and all necessary operating consumables without passengers and cargo.
2. Gross Weight
It is weight of vehicle with all parts and all necessary operating consumables with passengers and cargo.
3. Wheel Base
It is the distance between centers of front and rear wheels of vehicle.
4. Ground Clearance
It is the distance between the ground surface and lowest part of the vehicle.
5. Total length of vehicle
6. Maximum width of vehicle
7. Maximum height of vehicle
8. BootSpace (in case of four wheelers)
It is the volume space available in car to keep the luggage.
9. TRACK (in case of four wheelers)
FrontTrack: Distance between the centerline of front wheels.
RearTrack: Distance between the centerline of rear wheels.
10. Overhangs (in case of four wheelers)
It is the lengths of a road vehicle which extend beyond the wheelbase at the front and rear.Overhang are Front Overhang and Rear Overhang.
AUTOMOBILE ENGINE SPECIFICATION:- Maruti Suzuki Celerio
Parameter | Specification |
Fuel Type | Petrol/CNG |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4-Stroke, BS 4 Petrol Engine |
Bore x Stroke | 73mm x 89.4mm |
Displacement (CC) | 998 |
Maximum Power | Petrol Mode: 50 kW @6000 rpm CNG Mode: 43.5 kW @6000 rpm |
Maximum Power | Petrol Mode: 90 N-m @3500 rpm CNG Mode: 78 N-m @3500 rpm |
Number of Cylinders | 3 |
Valves per Cylinder | 4 |
Fuel Supply System | MPFI- Multi Point Fuel Injection |
Compression Ratio | 10.3:1 |
Sample specifications of Bajaj CT 110&Hero Extreme Sportare given below.
- AutomobileVehicle Specifications of BAJAJ CT 110
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Petrol | |
Engine Type | Single cylinder, Air Cooled, 4-Stroke, Petrol Engine. | |
Bore x Stroke | 50 mm x 58.8mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 115 | |
Maximum Power | 6.3 kW (8.6 PS) @ 7000 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 9.81 N-m @ 5000 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 1 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 2 | |
Fuel Delivery | Carburetor | |
Compression Ratio | 10 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 10.5 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity | 2 L | |
Mileage | 91 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 4 , Manual Constant Mesh Gear Box | |
Clutch | Wet , MultiPlate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | 130 mm Drum | |
Rear | 110 mm Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | Telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers 125 mm | |
Rear | SNS - Spring in Spring, 100 mm | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 18 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 2.75 X 17 P, Semi-knobby tread pattern | |
Rear Tyre | 3.00 X 17 P, Semi-knobby tread pattern | |
8. Battery | ||
Voltage | 12V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 3 Ah | |
9. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 116 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 1235 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 170 mm | |
Length | 1945 mm | |
Width | 752 mm | |
Height | 1072 mm | |
2. Automobile Vehicle Specifications of HERO EXTREME SPORT
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Petrol | |
Engine Type | Air Cooled, 4 - Stroke Single Cylinder OHC | |
Bore x Stroke | 57.3 mm x 57.8 mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 149.2 | |
Maximum Power | 11.64 KW (15.6 BHP) @ 8500 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 13.50 N-m @ 7000 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 1 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 2 | |
Fuel Delivery | CV Type with Carburetor Controlled Variable Ignition | |
Compression Ratio | 10 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 12.1 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity | 1.5 L | |
Mileage | 65 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 5 , Manual Constant Mesh Gear box | |
Clutch | Wet , MultiPlate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | 240 mm Disc | |
Rear | 110 mm Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | Telescopic hydraulic shock absorber | |
Rear | Rectangular Swing Arm with 5 step Adjustable Gas Reservoir Suspension | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 18 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 80 / 100 x 18 - 47 P Tubeless | |
Rear Tyre | 110 / 90 x 18 - 61 P Tubeless | |
8. Battery | ||
Voltage | 12V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 4 Ah | |
9. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 147 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 1325 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 163 mm | |
Length | 2100 mm | |
Width | 780 mm | |
Height | 1080 mm | |
Sample specifications of & are given below.
- Automobile Vehicle Specifications of HUNDAI CRETA 1.6 SX Option Diesel
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Diesel | |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4 - Stroke | |
Bore x Stroke | 73 mm X 71.5 mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 1582 | |
Maximum Power | 128 bHp @ 4,000 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 259.87 N-m @ 1500-3000 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 4 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 4 | |
Fuel Delivery | CRDi with VGT | |
Compression Ratio | 15 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 55 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity | - | |
Mileage | 20.5 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 6-Speed Automatic | |
Clutch | Dry, Single plate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | Disc | |
Rear | Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | McPherson Strut with Coil Spring | |
Rear | Couple Torsion Beam Axle with Coil Spring | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 17 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 215/60 R17 Steel Tubeless | |
Rear Tyre | 215/60 R17 Steel Tubeless | |
8. Steering | ||
Power Steering | Yes | |
Steering Type | Adjustable | |
9. Battery | ||
Voltage | 18 V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 7 Ah | |
10. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 1398 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 2590 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 190 mm | |
Length | 4270 mm | |
Width | 1780 mm | |
Height | 1665 mm | |
Boot Space | 400 L | |
Gross Weight | 1455 kg | |
Front Track | 1490 mm | |
Rear Track | 1480 mm | |
Minimum Turning Radius | 5.3 m | |
Seating Capacity | 5 | |
Front Overhang | 150 mm | |
Front Overhang | 120 mm | |
2. Automobile Vehicle Specifications of MARUTI SUZUKI SWIFT LXI
Parameter | Specification | |
1. Engine | ||
Engine Fuel Type | Petrol | |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4 - Stroke | |
Bore x Stroke | 73 mm X 71.5 mm | |
Displacement (CC) | 1197 | |
Maximum Power | 81.8 bHp @ 6000 rpm | |
Maximum Power | 113 N-m @ 4200 rpm | |
Number of Cylinders | 4 | |
Valves per Cylinder | 4 | |
Fuel Delivery | MPFI | |
Compression Ratio | 11 : 1 | |
2. Fuel Consumption | ||
Fuel Tank Capacity | 37 L | |
Reserve Fuel Capacity |
| |
Mileage | 22 kmpl | |
3. Transmission | ||
Number of Gears | 5-Speed Manual | |
Clutch | Dry Single Plate | |
4. Braking | ||
Front | Disc | |
Rear | Drum | |
5. Suspension | ||
Front | McPherson Strut with Coil Spring | |
Rear | Couple Torsion Beam Axle with Coil Spring | |
6. Wheels | ||
Wheel Size | 14 inch | |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels | |
7. Tyres | ||
Front Tyre | 165/80 R14 Tubeless | |
Rear Tyre | 165/80 R14 Tubeless | |
8. Steering | ||
Power Steering | Yes | |
Steering Type | Adjustable Electric | |
9. Battery | ||
Voltage | 18V | |
Ampere hour Rating | 7 Ah | |
10. Dimension and Weight | ||
Kerb Weight | 880 Kg | |
Wheel Base | 2450 mm | |
Ground Clearance | 163 mm | |
Length | 3840 mm | |
Width | 1735 mm | |
Height | 1530 mm | |
Boot Space | 268 L | |
Gross Weight | 1315 kg | |
Front Track | 1530 mm | |
Rear Track | 1530 mm | |
Minimum Turning Radius | 4.8 m | |
Seating Capacity | 5 | |
Front Overhang | 150 mm | |
Front Overhang | 120 mm | |
- Automobile Vehicle Specifications of VOLVO 9400 14.5 M
Parameter | Specification |
1.Engine | |
Fuel Type | Diesel |
Engine Type | Water Cooled, 4-Stroke, Diesel Engine. |
Bore x Stroke | 73mm x 89.4mm |
Displacement (CC) | 10.8L |
Maximum Power | 410 BHP @ 2000 rpm |
Maximum Power | 1980 N-m @ 2000 rpm |
Number of Cylinders | 6 |
Valves per Cylinder | 2 |
Fuel Delivery | CRDI |
2. Fuel Consumption | |
Fuel Tank Capacity | 600 L |
3.Transmission | |
Number of Gears | 12 Speed Automatic |
Clutch | Dry Single plate |
4. Braking | |
Front | Disk Brake with Electronic braking System |
Rear | Disk Brake with Electronic braking System |
5. Suspension | |
Front | Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECS) |
Rear | Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECS) |
6. Wheels | |
Wheel Size | 18 inch |
Wheel Type | Alloy Wheels |
7. Tyres | |
Front Tyre | 295/80 R 22.5Tubeless |
Rear Tyre | 295/80 R 22.5Tubeless |
8. Steering | |
Power Steering | Yes |
Steering Type | Adjustable Electric |
8. Dimension and Weight | |
Kerb Weight | - |
Wheel Base | 8350 mm |
Ground Clearance | 209 mm |
Gross Weight | 22200 kg |
Front Track | 2054 mm |
Rear Track | 1837 mm |
Minimum Turning Radius | 11.54 m |
Seating Capacity | 54 |
Length | 14500 mm |
Width | 2600 mm |
Height | 3600 mm |
Front Overhang | 2620 mm |
Rear Overhang | 2830 mm |
1. Engine
- Fuel type: The diesel engines have higher thermal efficiency compared to petrol engines. Therefore, diesel vehicles give better fuel economy compared to petrol vehicles.
- In addition, price of diesel is less compared to petrol. Hence, customers with heavy usage of vehicle, prefer diesel vehicles.
- However, diesel vehicles have higher initial as well as maintenance cost compared to petrol vehicles.
- So, if initial cost is a prime consideration, petrol vehicles are preferred; whereas if running cost is a prime consideration diesel vehicles are preferred.
- Displacement, maximum power and maximum torque: All three parameter indicate the power of an engine.
2. Fuel Efficiency and Performance:
- Mileage (kmpl): Higher the mileage, lower is the running cost of the vehicle.
- Top Speed and Acceleration: User prefer vehicles with higher top speed and higher acceleration or pick up.
3. Transmission System:
- Type of transmission: Now a days, type of transmission is one of the most important comparison parameter. Because of ease and comfort of driving, many user prefer vehicles with automatic transmission over Vehicles with manual transmission.
- Number of gears:Vehicles with more number of gears give more number of speed ranges.
4. Braking System:
- Disc brakes give better braking effect compared to drum brakes. Therefore Vehicles with disc brakes are preferred over vehicles with drum brakes.
5. Suspension System:Better type of suspension system gives comfort to Passengers.
6. Steering:
- Power Steering:The vehicles reduce the efforts required for steering the vehicle.
- Steering Adjustments:now days, in many high end cars, steering is provided with telescopic and tilt adjustments. The vehicles with such adjustments enhance the driving comfort.
7. Dimensions:
- GroundClearance:The vehicles with high ground clearance reduce the possibility of underbody striking, the road while driving on rough roads or off roads.
- However, higher ground clearance means higher center of gravity which reduces the stability of vehicle.
- Boot Space: Higher boot space means higher space for the storage of luggage.
- SeatingCapacity:The seating capacity is one of the most important comparison parameters while selecting the vehicle.
8. Cost, Safety and Comfort Parameters are also considered for Comparison of Vehicles.
- These includes
- On road price
- Aesthetics
- Maintenance cost
- Warranty
- Driver and passenger safety devices
- Interior of vehicle Infotainment system.
Need of Electrical Vehicles:
- With current rate of oil production and consumption, the oil reserves on the earth will not last for more than 50 years.
- The automobile manufactures all over the world are looking for alternative energy sources for vehicles because of following reasons
- Fast depletion of crude oil reserves
- Increasing crude oil prices
- High pollution due to vehicles
- Increasing cost of vehicles due to new pollution control norms.
Types of Electric Vehicles
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)

Figure: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Battery electrical vehicles are an automobile propelled by one or more electric motors using the energy stored in rechargeable battery. It consist of following components.
- Charger: The charger gets electricity supplied by electric grid and charges the battery of the vehicle.
- Rechargeable Battery: The rechargeable battery is charged through the charger. The battery may be Lead-acid battery, Nickel-metal hydride battery or Lithium-ion battery.
- The distance travelled by electric vehicle depends upon the energy storage capacity of the battery which ranges between 30 kWh to 150 kWh.
- Drive Control Unit: The drive control unit controls the supply of electric current from battery to inverter.
- Inverter: Inverter converts D.C. Supply of battery to A.C. Supply if AC Motor is used. If DC Motor is used in vehicle then inverter is not required.
- Electric Motor: A.C. Motor or D.C. Motor drives the transmission unit. It convert electrical energy into mechanical energy in the form of rotations.
- Transmission Unit (Gear box): The transmission unit drives the rear wheels.
Advantages of Battery Electric Vehicles
- Pollution free.
- Less Noise.
- Simple in design.
- Low running cost.
- Low maintenance cost.
Disadvantages of Battery Electric Vehicles
- Limited travelling range
- High initial cost
- Battery life is short
- Low speed
- Charging station non-availability.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) or hybrid vehicle is an automobile propelled by two power sources: (i) Electric motor driven by rechargeable battery and (ii) I.C. Engine.
- Hybrid electric vehicle is a progressive transformation from conventional automobile vehicle powered by only I.C. Engine to battery electric vehicle powered by only electric motor.
- Hybrid electric vehicle minimizes the drawbacks of conventional I.C. Engine powered automobile vehicle and retains the advantages of conventional I. C. Engine powered automobile vehicle.
- Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles:
- Series Hybrid Vehicles
- Parallel Hybrid Vehicles
1. Series Hybrid Vehicles
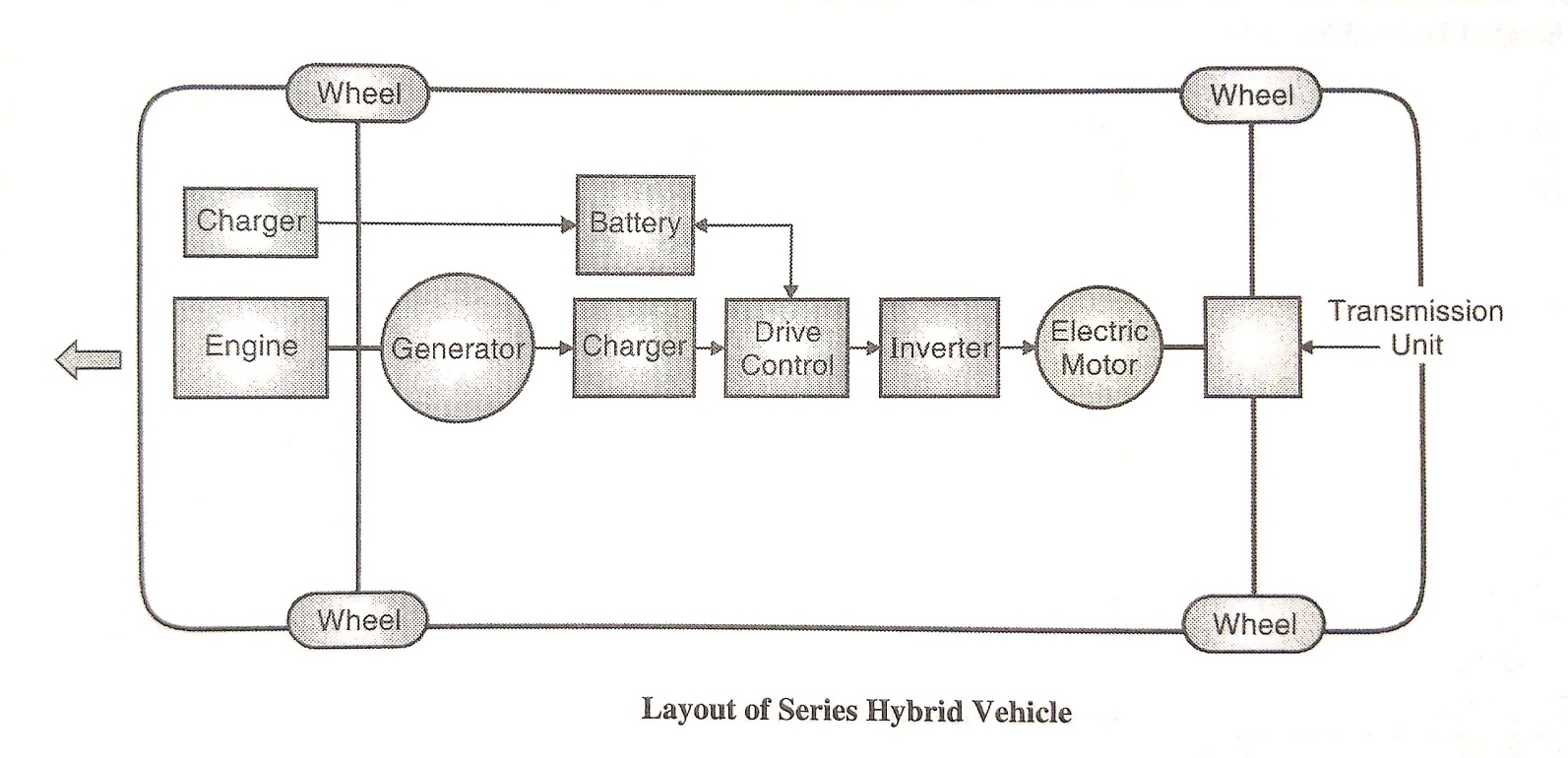
Figure: Series Hybrid Vehicles
- In series hybrid vehicles electric motor is the only means of providing the power to the wheels through transmission unit (gear box). The electric motor receives electric power form either from rechargeable battery or generator run by I.C. Engine.
- The computer assisted drive control unit decides the quantity of power to come from the battery and the IC engine generator.
- The excess electric power from generator is used to charge the battery. In addition, during braking, the electric motor acts as a generator and uses the regenerative braking energy to charge the battery. The battery is charged through charger form electric grid. In series hybrid vehicle, engine is of smaller capacity; because it has to meetonly partial power requirement. The battery is more powerful.
2. Parallel Hybrid Vehicles
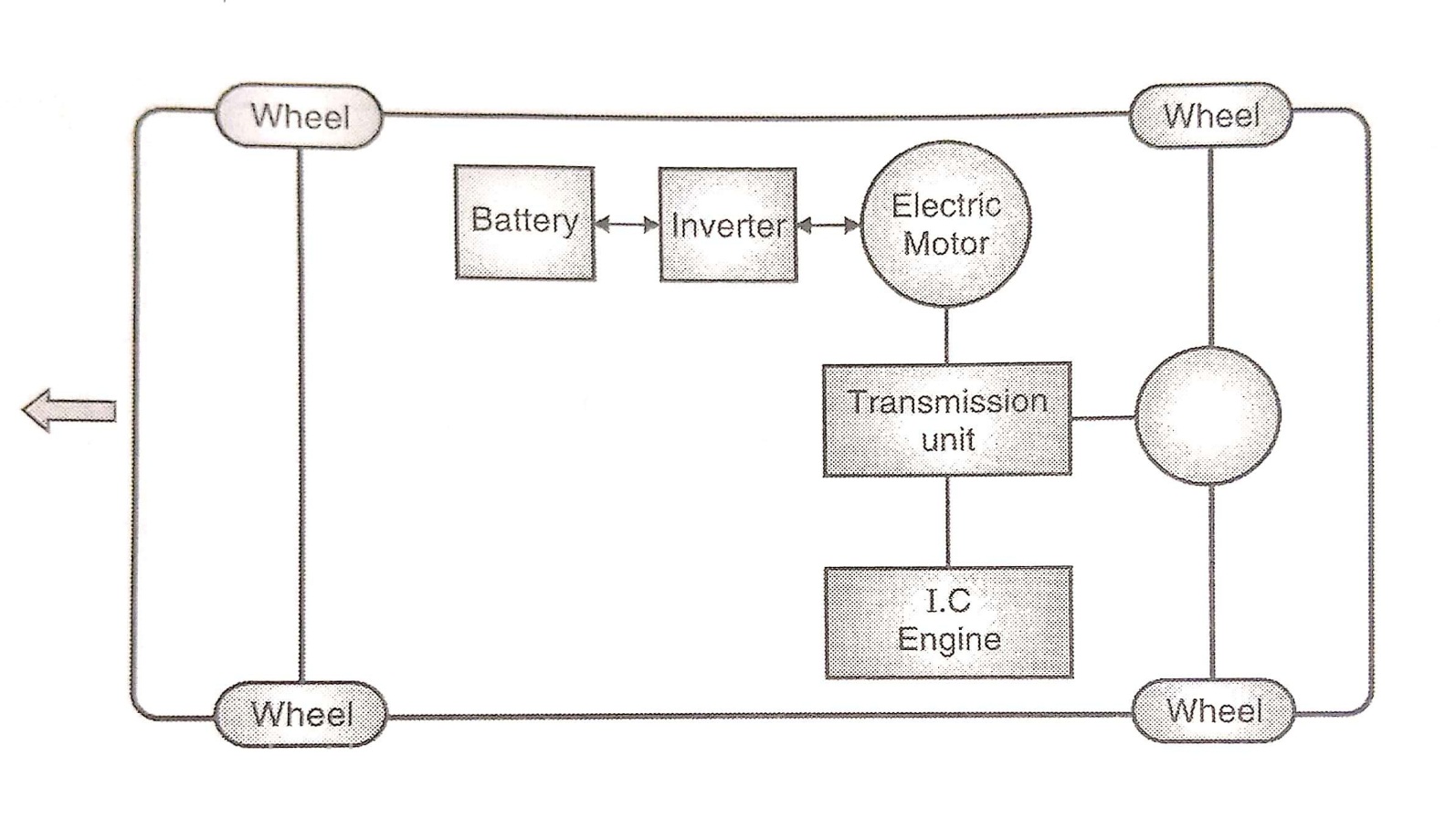
Figure: Parallel Hybrid Vehicles
- In parallel hybrid vehicles, the I.C. Engine as well as electric motor drives the wheels through the transmission unit.
- When power demand is low, the electric motor acts as a generator and utilizes the excess power form I.C. Engine to charge the battery.
- In addition, during braking also, the electric motor acts as a generator and uses the regenerative braking energy to charge the battery.
- In parallel hybrid vehicles, engine is of higher capacity as compared to series hybrid vehicles. However, parallel hybrid vehicles use a smaller capacity battery compared to series hybrid vehicles.
Advantages of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- Large travelling Range
- Environment friendly.
- Regenerative braking
- Light weight
Disadvantagesof Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- High initial cost
- Battery life is short
- Less Power
- High maintenance cost
Specifications Electric Vehicle
Parameter | Specifications |
1. Electric Motor | |
Type | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor |
Maximum Power | 134 hp (100 kW) |
Maximum Torque | 395 N-m |
2. Battery | |
Type | Lithium-Ion Polymer, 327 V |
Capacity | 39.2 kWh |
A.C. Charging 230 V (0-100 %) | Approx. 6 h 10 |
D.C. Charging (0-80%) | Approx. 57 min |
Driving Range | 452 km |
The overall cost of vehicle includes many parameters. Some of them are as follows.
- Type of Engine: According to the type of engine or its capacity the cost of vehicle changes. For high power engines, the cost of vehicle is very high.
- Safety Features: If a vehicle includes safety features like air ABS, air bag etc. then the cost of vehicle increases. It also depends on the number of airbags in a vehicle.
- Material of vehicle (Raw material): The material of vehicle is one of the important factor in cost analysis. For high grade material the cost of vehicle increases rapidly. Now-a-days some parts of vehicle are replaced by fiber parts to reduce the cost of vehicle.
- Production Method: Some manufactures like BMW, Audi etc. use fully automatic machines for production of vehicle. This increases accuracy and finishing of vehicle. But this increases the cost of vehicle. Hence as per the production method the cost of vehicle changes.
- Research and development (R and D): It is a hidden cost of vehicle. It requires long time and number of technical people.
- Royalty: The innovations like ABS, Air bags, ESP etc. are all innovations by Bosch Company and not by car manufacturers. The manufacturers need to pay royalty to Bosch for using the technology.
- Dealer profit
- Insurance and taxation
- Availability of spare parts
- Advertisement (Posters, ads, campaigns etc.)
- Quantity of production
- Labour cost, etc.
References
1. Khan, B. H., “Non Conventional Energy Sources, Tata McGraw-Hill Publisher Co. Ltd.
2. Boyle, Godfrey, “Renewable Energy”,2nd Ed., Oxford University Press
3. Khurmi, R.S. ,and Gupta, J. K.,“A Textbook of Thermal Engineering”, S. Chand & Sons
4. Incropera, F. P. And Dewitt, D.P., (2007), “Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 6th Ed., John Wiley and Sons, USA
5. Groover,Mikell P., (1996), “Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing: Materials, Processes, and Systems”, Prentice Hall, USA
6. Norton, Robert L., (2009), “Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery”, Tata McGrawHill
7. Cleghorn, W. L., (2005), “Mechanisms of Machines”, Oxford University Press
8. Juvinal, R. C., (1994), “Fundamentals of Machine Component Design”, John Wiley and Sons, USA
9. Ganeshan, V., (2018), “Internal Combustion Engines”, McGraw Hill
10. Anderson, Curtis Darrel and Anderson,Judy, (2010), “Electric and Hybrid Cars: A History”, 2nd Ed., McFarland