Unit 1
Introduction to Communication Systems
Introduction to the communication system
The telegraph was invented in 1844. [ Morse Patent ]
The telephone was invented in 1876. [ Bell Patent ]
In 1887 radio was invented [ Hertz invent ]
In 1895 Marconi demonstrates wireless telegraphy.
1923 : Television is invented.
1948 : Transistor is invented.
1954 :Color television broadcasting begins
1969 : The internet is invented.
1983 : First cellular telephone system becomes operational.
1989 : GPS is used for commercial and personal applications.
1989 : www is invented.
1998 : The first commercial use of digital / high definition television takes place.
Simplex is one way communication.
Duplex is two-way communication.
Telegraph used Morse code whereas radio telegraphy used an international code of dots and dashes.
The most commonly used digital code in communications is the American Standard code for information interchange [ ASCII ].
Putting the original voice, video or digital signals directly into the medium is referred to as baseband transmission.
Eg : telephone and intercom communications systems. In some computer network ie digital signals are applied directly to coaxial cables for transmission to another computer.
To transmit baseband signals by radio, modulation techniques must be used. Techniques using modulation are referred to as broadband.
Modulation is the process of having a baseband voice, video or digital signal modify another higher frequency signal called the carrier.
In AM, the baseband signal varies the amplitude of the higher frequency carrier signal.
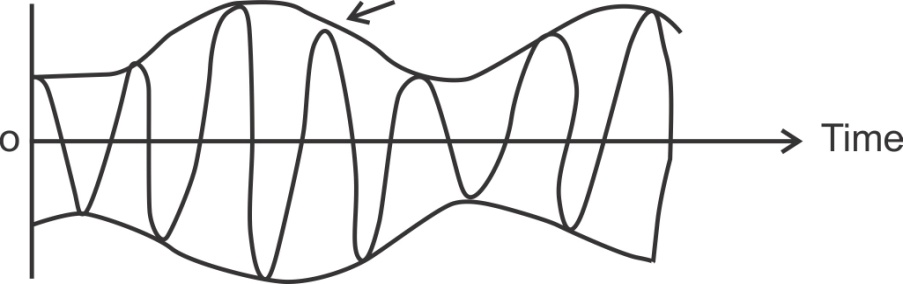
Fig.1: AM wave
In FM the baseband signal varies the frequency of the carrier.
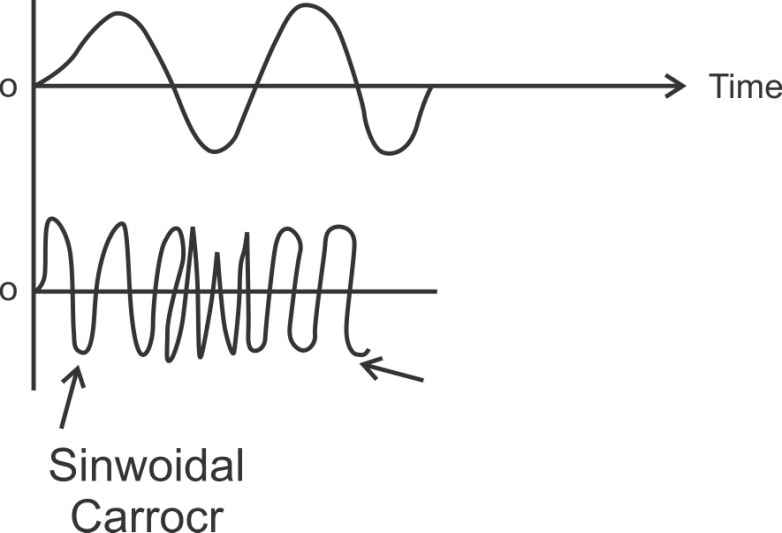
Fig:2: FM wave
Shifting the phase of the carrier in accordance with the i/p modulating signal produces phase modulation ( PM ). Phase modulation produces FM so a PM signal looks like the FM.
Electromagnetic signals are also referred to as radio freqn( Rf ) waves.
The electromagnetic spectrum used in electronic communication
The ionosphere refracts radio waves making long distance communication possible for some frequencies at certain times.
The visible range is approximately 8000 Ao ( red ) to 4000 Ao ( violet ).
Light wavelengths are usually expressed in terms of angstroms ( Ao ).
An angstrom is one ten thousandth of a micron.
Light is widely used for various kinds of communications. The great advantage of light wave signals is that their very high frequency gives them the ability to handle a tremendous amount of information. That is the bandwidth of the baseband signals may be very wide.
Audio signals are not transmitted by electromagnetic waves because
1> Antennas would be too long.
2> Simultaneous transmission would interfere.
HF signals are also called share waves.
Freqn above 1 GHz are called microwave.
Any broadcasting audio signals upto 5 KHz may be transmitted.
Government also established the Federal communication’s Commission [ FCC ] which is a regulatory body whose sole purpose is allocating spectrum space, issuing licences, setting standards & policing the airwaves.
The FCC controls all telephone & radio communications in this country & in general regulates all electromagnetic emissions.
The national telecommunications and information administration [ NTIA ] performs a similar function for government & military services.
Block diagram of communication system

Fig. 3 Block diagram of elements of communication (ref 3)
Information Source
It produces a message that is analog in nature, i.e., the output of the information source is a continuous signal.
Analog carrier source
Sine wave is used as a carrier signal which will help in analog modulation.
Analog modulation
The carrier signal is superimposed with the message signal and then the modulated signal is obtained which is also analog in nature.
Communication channel
The analog modulated signal is transmitted via the communication channel towards the receiver end after addition of the requisite power levels.
Analog demodulation
At the receiver end, the incoming modulated signal is passed through an analog demodulation process which extracts the analog message signal. The analog message is then passed onto the final destination.
Destination
The nature of signal starting from the information source till the final destination is analog.
Compare:

Key Takeaways:
Analog signals are used for analog communication and digital signals for digital communication.
Analog signals are used for long distance communication while digital communication for short distance.
References:
- “Electronic communication system”, by Kennedy, TMH
- “Communication system”, by haykin wiley
- “Communication system”, by bruce carison, TMH
- “Modern digital and analog communication”, B.P. LATHI, Oxford