Unit - 1
Basics of IC Engines
An inner combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a warm temperature engine wherein the combustion of a gas line takes area with an oxidizer (normally air) in a combustion chamber this is a vital a part of the on foot fluid go together with the drift circuit.
In an inner combustion engine, the growth of the excessive-temperature and excessive-strain gases produced thru combustion applies direct pressure to three hassle of the engine.
The pressure is completed normally to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. In primitive times, man’s muscle companies had been the primary deliver of electricity for work.
Then, animals had been knowledgeable and their electricity emerge as completed to perform super works.
Afterward, electricity conversion from one form to each unique emerge as introduced, using a device called ‘engine’. The engine is a mechanical problem that converts one form of electricity (mainly warmth electricity) into mechanical electricity. These sorts of engines are popularly said as ‘warmth engines’. Basically, engines are of types, i.e. E.C.Engine and I.C. Engine.
Both IC and EC engines are of types, i.e. Reciprocating and Rotary engine. A diesel engine is an example of it wherein the taking walks fluid is air. This engine is notably finished in automotive, aviation, electricity generation, etc. The engine consists of numerous components viz. Cylinder, spark plug, valves, piston, piston rings, connecting rod, crankshaft, and oil pan (sump).
Combustion, additionally called burning, is the fundamental chemical manner of liberating strength from a gas and air mixture. In an inner combustion engine (ICE), the ignition and combustion of the gas takes place in the engine itself. The engine then in part converts the strength from the combustion to work. The engine includes a set cylinder and a transferring piston.
There are varieties of inner combustion engines presently in production: the spark ignition gas engine and the compression ignition diesel engine. Most of those are 4-stroke cycle engines, which means 4 piston strokes are wanted to finish a cycle.
Spark ignition gas and compression ignition diesel engines range in how they deliver and ignite the gas. In a spark ignition engine, the gas is blended with air after which inducted into the cylinder all through the consumption manner. After the piston compresses the gas-air mixture, the spark ignites it, inflicting combustion.
Classification:
There are several types of engine based on different conditions they are as follows:
1. Number of strokes per cycle:
A) Four-stroke cycle engine:
This engine makes 4 piston strokes i.e. intake, compression, strength and exhaust to finish an walking cycle. The rotation angle of crankshaft should be 720 degree.
B) Two-stroke cycle engine:
As consistent with the name, this engine calls for piston strokes to complete an running cycle.
C) Six stroke cycle engine:
This engine is brought to make a few upgrades in traditional -stroke and 4-stroke engines. It will growth the general overall performance of fuel, reduces emissions, etc. In this engine, one of the cylinders makes strokes and others makes 4 strokes, in famous making six strokes consistent with cycle.
2. Nature of thermodynamic cycle:
A) Otto cycle engine
It consists of quasistatic and isentropic techniques and isochoric techniques. The engine which follows this thermodynamic cycle for operation is referred to as Otto cycle engine.
B) Diesel cycle engine
It is an idealized cycle for a diesel engine which incorporates isentropic processes, one isobaric process
C) Dual cycle engine
Dual cycle or mixed cycle or confined strain cycle is the combination of otto and diesel cycle. Heat addition is in component through constant amount and constant strain process.
3. Types of fuel used
A) Petrol or gasoline engine
This engine generates power with the useful resource of the usage of burning gasoline (or exceptional volatile liquid fueloline with similar properties) ignited with the useful resource of the usage of an electric powered powered spark.
B) Diesel engine
This engine makes use of diesel as fueloline, in which fueloline ignition takes location on its own, without any spark. Hence, compression of the inlet air combination takes location and then fueloline is injected.
C) Bi-fuel engine
This engine can run on each natural gasoline line and gasoline because of this it follows the natural gasoline line gadget and gasoline gadget i.e dual fuelling gadget. Hence the ones sorts of engines are called bi-gas or dual-gas engines.
4. Method of ignition
A) Spark ignition engine
In S.I engines, the ignition takes location with the help of a spark plug. This mechanical device referred to as spark plug ignites a mixture of air and fuel( charge) this is compressed and combusted with within the combustion chamber.
B) Compression ignition engine
A CI engine follows the auto-ignition or self-ignition system wherein fuel rate is ignited with the useful resource of the use of its private warm temperature of compression. Here, the air is inducted into the combustion chamber and compressed to quite immoderate pressure. Hence the compression ratio of this engine is immoderate (as a good deal as 22).
5. Number of cylinders
A) single-cylinder engine
It is a critical piston-cylinder configuration of an engine wherein fine one engine cylinder is used.
B) Multi cylinder engine
Here, more than one cylinder tool is used. It is used to provide a more non-forestall waft of power. A well-known multi-cylinder engine includes four, six, and eight engines in various configurations.
6. Arrangement of cylinder
A) Horizontally opposed engine:
These engines have the cylinders configured in banks on every issue of a unmarried crankshaft. The specific names for this cylinder are Flat engines or “boxer” engines.
B) Vertical engine
The vertical engine is the engine in which the movement of the piston is vertical viz. Vertically up and down and the location of the crankshaft is under the cylinder.
C) v-type engine:
In this engine design, cylinders are placed at some mind-set. Due to the presence of mind-set in between, it office work a “v- shape”. This mind-set varies from 60 degrees to 90 degrees. Usually, even numbers of cylinders are used in this design. These are applied in high-give up sports activities sports bikes, high-give up cars, etc.
D) Radial engine
It resembles a celebrity engine, consequently called a well-known man or woman engine. This is reciprocating kind of engine.
E) In-line engine:
These engines also can moreover have 2, 3,4,5,6, or up to eight cylinders. This engine layout is traditional and pretty basic. Also referred to as instantaneously engine.
F) X engine:
When V engines are joined with the useful resource of the usage of a single crankshaft, we're capable of get an X engine. Thus, this engine is made from V engines. This engine has its private anciental Significance as they were applied in aircraft for the duration of the Second World War.
G) Opposed piston engine:
In this engine, pairs of pistons are co-axial which percent a single combustion chamber. The cylinder head is absent and the cylinder has its piston at its every ends.
H) W engine:
W engine is a kind engine in which greater than one (usually 3 or four) cylinder banks are used with the now not uncommon area crankshaft.
7. Cooling system
A) Air cooled engine
This shape of cooling engine is predicated upon on the amount of airflow all through their out of doors engine ground to take away the warm temperature dissipation. We make thin cooling fins to increase the ground area.
B) Water cooled engine
When water is used as a coolant in an internal combustion engine, then it is referred to as the water-cooled engine. This cooling tool works on the passing of water (as coolant) through furnished passages in engine blocks. We make water jackets, water pumps, and so on for this engine.
C) Oil cooled engine
It is another liquid-based totally completely cooling device engine in which engine oil acts as a coolant to reduce the warm temperature dissipation.
Advantages of I.C. Engine
• These engines are compact and required an awful lot an lousy lot an awful lot much less space.
• Initial rate of I.C. Engine is lower than E.C. Engine.
Components of IC Engine:
1. Cylinder block
For cooling of cylinder, a water jacket (for liquid cooling finished in most of cars) or fin (for air cooling finished in most of bikes) are placed at the outer factor of cylinder. At the better give up of cylinder, cylinder head and at the bottom give up crank case is bolted. So it's far made with the useful resource of the usage of immoderate grade solid iron. It is made with the useful resource of the usage of casting and commonly solid in a single piece.
2. Cylinder head
The top prevent of the engine cylinder is closed thru removable cylinder head. There are holes or ports at the cylinder head, one for intake of gas line and certainly considered one among a type for exhaust. Both the intake and exhaust ports are closed with the resource of the use of the two valves known as inlet and exhaust valve. The crucial characteristic of cylinder head is to seal the cylinder block and now no longer to permit get right of get admission to to and exit of gases on cover head valve engine. Cylinder head is normally made with the resource of the use of cast iron or aluminum. It is made with the resource of the use of casting or forging and normally in a unmarried piece.
3. Piston
A piston is acceptable to each cylinder as a face to collect gas line pressure and transmit the thrust to the connecting rod. It is a excessive mover withinside the engine. The number one function of piston is to provide tight seal to the cylinder through bore and slide freely withinside the cylinder. Piston should be slight and sufficient strong to cope with gas line pressure generated with the resource of the usage of combustion of gas. So the piston is made with the resource of the usage of aluminum alloy and occasionally it is made with the resource of the usage of solid iron because of the reality slight alloy piston expands extra than solid iron in order that they need extra clearances to the bore.
4. Piston rings
A piston ought to be a fairly unfastened suit withinside the cylinder so it could byskip freely withinside the cylinder. If the piston is simply too tight suit, it'd amplify as it had been given heat and may stick tight withinside the cylinder and if it's far too unfastened it'd leaks the vapor pressure. To provide an wonderful sealing suit and lots much less friction resistance a number of the piston and cylinder, pistons are prepared with piston earrings. They are split at one give up with a view to amplify or slipped over the give up of piston. A small stroke engine has piston earrings to provide particular sealing but a four-stroke engine has a further ring this is known as oil ring. Sometimes it's far made thru manner of manner of alloy spring steel.
5. Connecting rod
It converts the reciprocating movement of the piston into rotary movement of crankshaft. There are give up of connecting rod; one is called massive give up and first rate as small give up. Big give up is set up to the crankshaft and the small give up is set up to the piston via way of manner of use of piston pin. The connecting rods are fabricated from nickel, chrome, and chrome vanadium steels. For small engines the fabric can be aluminum.
6. Crankshaft
The crankshaft mounts in bearing so it is able to rotate freely. The shape and duration of crankshaft is predicated upon on the huge range and affiliation of cylinders. It is commonly made through manner of manner of metallic forging, but some makers use particular varieties of cast-iron consisting of spheroidal graphitic or nickel alloy castings which is probably much less high-priced to offer and characteristic suitable issuer life.
7. Engine bearing
Anywhere there may be rotary motion with within the engine, bearings are needed. Bearings are used to assist the transferring parts. The crankshaft is supported through manner of method of bearing. The connecting rod big forestall is set up to the crank pin on the crank of the crankshaft through manner of method of a bearing. The primary characteristic of bearings is to reduce friction amongst the ones transferring parts. In an IC engine sliding and rolling sorts of bearing used. The sliding type bearing which is probably at some point called bush is discover to attach the connecting rod to the piston and crankshaft. They are split in case you need to permit their assembly into the engine. The rolling and ball bearing is used to assist crankshaft so it can rotate freely. The regular bearing half of is made of metallic or bronze decrease lower back to which a lining of fantastically smooth bearing material is applied.
8. Crankcase
The fundamental body of the engine at which the cylinder are related and which includes the crankshaft and crankshaft bearing is referred to as crankcase. It serves due to the fact the lubricating tool too and sooner or later it's far referred to as oil sump. All the oil for lubrication is located in it.
9. Valves
To manage the inlet and exhaust of inner combustion engine, valves are used. The big sort of valves in an engine relies upon at the big sort of cylinders. Two valves are used for every cylinder one for inlet of air-gas line aggregate withinside the cylinder and special for exhaust of combustion gases. The valves are geared up withinside the port on the cylinder head via way of manner of use of robust spring. This spring maintain them closed. Both valves usually open inwards.
10. Spark plug
The crucial feature of a spark plug is to behavior a excessive functionality from the ignition device into the combustion chamber to ignite the compressed air gas line mixture. It is prepared on cylinder head. The spark plug includes a metal shell having electrodes that are insulated from every tremendous with an air gap. When excessive functionality contemporary-day deliver to spark plug it leaping from the deliver electrode and produces the crucial spark.
11. Injector
Injector is generally applied in compression ignition engine. It sprays the gas into combustion chamber at the surrender of compression stroke. It is ready on cylinder head.
12. Manifold
The crucial function of manifold is to supply the air gas mixture and collects the exhaust gases further from all cylinder. In an internal combustion engine manifold are used, one for intake and distinctive for exhaust. They are commonly made thru manner of approach of aluminum alloy.
13. Camshaft
Camshaft is applied in IC engine to manipulate the opening and very last of valves at proper timing. For proper engine output inlet valve must open at the end of exhaust stroke and closed at the end of intake stroke. So to modify its timing, a cam is discover this is oval in shape and it exerts a strain on the valve to open and release to close. It is strength via the timing belt which drives via crankshaft. It is located at the top or at the bottom of cylinder.
14. Gudgeon pin or piston pin
Those are hardened steel parallel spindles ready through the piston bosses and the small give up wood or eyes to allow the connecting rods to swivel. It connects the piston to connecting rod. It is made hollow for lightness.
15. Pushrod
Pushrod is used while the camshaft is placed at the bottom give up of cylinder. It incorporates the camshaft motion to the valves which might be placed at the cylinder head.
16. Flywheel
The vital function of flywheel is to rotate the shaft in a few unspecified time withinside the destiny of preparatory stroke. It moreover makes crankshaft rotation greater uniform.
Two Stroke, Four Stroke Engine and Engine Parts:
Two Stroke Engines:
A -stroke engine plays all of the same steps, however in best piston strokes. The best -stroke engines try this with the useful beneficial useful resource of the use of the use of the crankcase and the bottom of the moving piston as a sparkling rate pump. Such engines supply the brilliant name "crankcase-scavenged -strokes.
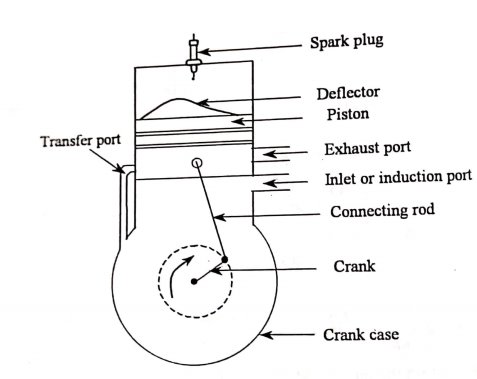
Fig: Two Stroke Engine
A consumption port of a few kind (cylinder wall port, reed valve or rotary disc valve) opens, permitting air to hurry into the crankcase thru a carburetor.
As the piston rises, it first covers the transfer ports, leaving most effective the exhaust port despite the fact that open. If there have been no way to prevent it, an entire lot of the easy charge may want to now be pumped out the exhaust. But there can be a clean way to prevent it—the use of exhaust pressure waves with within the exhaust. If we shape and length the exhaust pipe right, a reflected picture of the true pressure pulse, generated due to the fact the exhaust port opened, gets higher to the port certainly as easy charge is being pumped out of it. This pressure wave stuffs the easy charge once more into the cylinder certainly due to the fact the developing piston covers the exhaust port. Because fuel-air mixture is constantly being pumped with the resource of the use of the crankcase, it isn't sensible to lubricate piston and crank with the resource of the use of pumped circulating oil—it would be swept away with the resource of the use of the mixture rushing in and Therefore, we have to each combination a chunk oil with the fuel (2 to 4 percent) and inject it very sparingly into the bearings with a tiny metering pump. The reality that there can be so little oil dictates that such clean two-stroke engines have to lease rolling bearings, whose need for oil can be very small.
Advantages:
- Its mechanism should be simple to make.
- It is easy to start.
- It offers one electricity stroke according to revolution of the crankshaft. High electricity to weight ratio and massive electricity boost.
- It has no valves, so complex valve actuating mechanism now no longer required.
- It is mild weight, 30% lighter than the 4-stroke engine.
- It has few transferring parts, so compact and easy construction.
Disadvantages:
- Incomplete combustion, carbon deposit at the piston head and exhaust port.
- Unstable idling.
- Scavenging problems.
- Less green in phrases of gas economic system because of a part of the unburned fee is rejected in the course of switch phase.
- More put on and fragile than the four-stroke engine.
Four Stroke Engines:
A 4-stroke (furthermore 4-cycle) engine is an inner combustion (IC) engine wherein the piston completes 4 separate strokes on the identical time as turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the whole tour of the piston alongside the cylinder, in every direction. The 4 separate strokes are termed:

Fig. Four Stroke Engine
A 4-stroke (furthermore 4-cycle) engine is an inner combustion (IC) engine wherein the piston completes 4 separate strokes on the identical time as turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the whole tour of the piston alongside the cylinder, in every direction. The 4 separate strokes are termed:
1. Intake:
Also called induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins off evolved off evolved at top useless center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom useless center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve want to be with inside the open characteristic at the same time as the piston pulls an air-fuel line aggregate into the cylinder through manner of approach of producing vacuum stress into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in through manner of approach of the downward motion closer to the piston.
2. Compression:
This stroke begins off evolved at B.D.C, or without a doubt at the surrender of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel line aggregate in schooling for ignition at some stage in the strength stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed at some stage in this stage.
3. Combustion:
Also called strength or ignition. This is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke cycle. At this thing the crankshaft has completed a whole 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. (the surrender of the compression stroke) the compressed air-fuel line aggregate is ignited through manner of approach of a spark plug (in a fuel line engine) or through manner of approach of heat generated through manner of approach of immoderate compression (diesel engines), forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical art work from the engine to expose the crankshaft.
4. Exhaust:
Also known as outlet. During the exhaust stroke, the piston, once again, returns from B.D.C. To T.D.C. While the exhaust valve is open. This action expels the spent air-fuel mixture through the exhaust valve.
Engine parts:
- Engine block. The block is the main part of the engine.
- Pistons. Pistons pump up and down as the spark plugs fire and the pistons compress the air/fuel mix.
- Cylinder head.
- Crankshaft.
- Camshaft.
- Valves.
- Oil pan
- Conceptually, diesel engines carry out with the useful resource of the use of compacting air to immoderate pressure/temperature and then injecting a small amount of fuel line into this warmth compressed air.
- The immoderate temperature motives the small amount of tremendously atomized injected fuelling to evaporate.
- A -stroke engine incorporates processes:
- Compression stroke: The inlet port opens, the air-fuel line aggregate enters the chamber and the piston actions upwards compressing this aggregate.
- A spark plug ignites the compressed fuel line and begins off evolved off evolved the strength stroke.
Valve Timing Diagram:
A valve timing diagram is a graphical illustration of the outlet and final of the consumption and exhaust valve of the engine, The commencing and final of the valves of the engine rely on the motion of piston from TDC to BDC, This relation among piston and valves is managed with the aid of using placing a he ordinary engine completes round one hundred thousand cycles in keeping with minute, as we understand there are wide variety of approaches concerned in a unmarried cycle (from the consumption of the air-gas combination to the exhaust of the combustion residual) of an inner which makes it essential to be prepared with an powerful gadget that may Synchronization between the steps of a cycle of the engine from the intake of air-fuel ratio to the exhaust of the combustion residual.
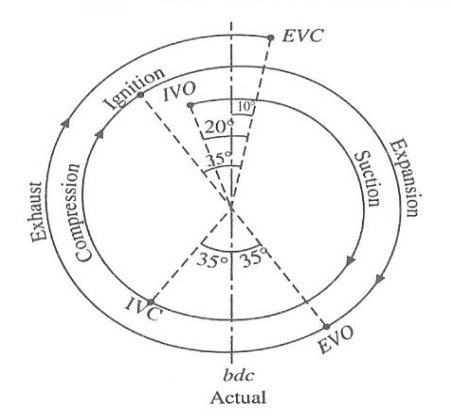
Fig: Valve Timing Diagram
- A valve timing diagram is a graphical instance of the outlet and final of the consumption and exhaust valve of the engine.
- The starting off and final of the valves of the engine rely on the motion of piston from TDC to BDC.
- This relation among piston and valves is managed with the beneficial aid of the use of putting a he ordinary engine completes round one hundred thousand cycles in step with minute, as we understand there are tremendous sort of strategies concerned in a unmarried cycle (from the consumption of the air-fuel line combination
Ideal Cycles:
Ideal cycles are simplified thermodynamic closed cycles to investigate the compression, combustion, and increase gadget in an engine with a focus on extraction of exertions from combustion of the fuel–air mixture. Fuel Air Cycle: theoretical cycle based totally absolutely on the actual houses of the cylinder contents is called the fuel – air cycle. The fuel – air cycle reflect on consideration on the following:
1- The actual composition of the cylinder contents.
2- The model with inside the correct warm temperature of the gases with inside the cylinder.
Ideal cycles have positive assumptions
Depending on the only you're studying yo may come upon situations like reversible process
- Isothermal warmth addition
- Constant pressure (isobaric)
- No interplay with surrounding/environment
- But in truth such situations do now no longer exist
- So whilst you plot a perfect cycle on a P-V or T-S scale you've got got may have immediately strains or best curves as a part of the plot.
But while you'll shape the cycle in actual lifestyles and plot it, you'll discover it won’t be best immediately strains and curves, it deviates from the suitable case due to the fact the assumptions we made don’t maintain actual in truth
Comparison of Ideal Cycles
In actual engines, SI engines have a compression ratio among 10:1 to 12:1 this cost is restricted because of engine knock CI engines have compression ratio better than 14:1 to offer temperature and stress required for self-ignition of the gas compression ratio of 16:1 to 18:1 is enough for efficiency, however used for enhancing ignition high-satisfactory excessive compression ratio will increase thermal and mechanical stresses.
Modern engines have compression ratios in the range 8 to 11, resulting in ideal cycle efficiencies of 56% to 61%.
Fuel Air cycle:
Theoretical cycle primarily based totally on the real residences of the cylinder contents is known as the fuel – air cycle.
The fuel air cycle think about the following:
- The real composition of the cylinder contents.
- The version withinside the unique warmth of the gases withinside the cylinder.
- The dissociation effect.
- The version withinside the wide variety of moles present withinside the cylinder because the stress and temperature change.
Assumption in Fuel Air cycle:
- All the tactics in (great) electricity cycles are internally reversible.
- Combustion approach is modeled with the resource of the usage of a heat-addition approach from an out of doors source.
These losses we known as warmness losses. C) Exhaust Blow-down Loss: Exhaust valve is thought to open at backside lifeless Centre (BDC) in case of best cycles even as in real engines 50 earlier than B.D.C.
References:
1. Obert E. F, “Internal Combustion Engines and Air Pollution”, Harper and Row Publication Inc. NY, 1973.
2. Heisler H, “Advanced Engine Technology”, Edward Arnold, 1995.
3. Heywood J. B, “Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals”, McGraw Hill Book Co. NY, 1989
4. Heldt P. M, “High Speed Combustion Engines”, Oxford & IBH publishing Co. India, 1985.
5. Stockel M W, Stockel T S and Johanson C, “Auto Fundamentals”, The Goodheart, Wilcox Co. Inc., Illinois, 1996.