Unit - 3
Combustion in SI and CI engines
SI Engines:
Conditions critical for combustion are:
- Some way of initiation combustion
- Stabilization and propagation of flame with within the combustion chamber SI engine flamable mixture provided via way of way of carburetor and combustion initiated via way of way of an electric powered powered spark
C8H18 + 12. Five O2 = 8CO2 + nine H2O
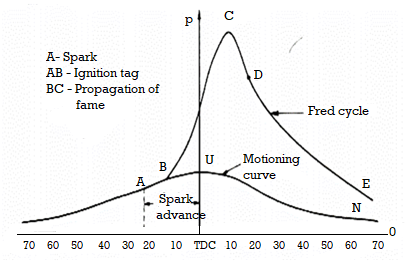
Fig.1. Combustion stages in S.I. Engine
Ignition Limit:
- Flame will propagate if temperature of burnt gases exceeds approx.
- 1500 K Relative fuel-air ratio lie among 0.five and 2.1
- Stoichiometric combination is 1:15 Fuel-air ought to be among 1:30 and 1:7
Stages of combustion in SI engine:
• Homogeneous combinations of vaporized fuel, air and residual gases.
• Electrodes temp. Exceeds 10,000֯C.
The useful resource of using a spark plug few stages earlier than the save you of compression.
This spark burns the few molecules of mixture with within the vicinity of spark hole and initiates the combustion method with the useful resource of using switch of warmth of molecules in neighborhood.
Once a flame is created, the development of this flame into the unburned mixture will rely on the rate of warmth switch the diverse flame and surrounding envelope of unburned mixture, temperature and pressure.
Though the mechanism of flame propagation is unknown however the presence of flame itself is the proof of chemical response the diverse fuel line and air.
To have a look at the combustion phenomenon of those engines the experiments were performed with the useful resource of using Ricardo the use of a quartz cylinder and using excessive pace photography. The effects are validated on pressure (p) and crank mind-set () diagram in Fig 1.
In Fig.1. Curse ABMN represents the motoring curve i.e. at the same time as the engine isn't always firing and ABCD represents the real combustion curse. Point A represents the component of ignition in which the spark is provided with the useful resource of using a spark plug.
The crank mind-set earlier than T.D.C. On the proper now spark is given is referred to as mind-set of spark advance.
Various tiers of combustion
Based at the experimental consequences the combustion in SI engines takes location in 3 tiers as follows:
1. Period of ignition Lag or practice phase.
2. Flame propagation phase.
3. After burning or flame termination phase.
1. Period of ignition lad or preparation.
The experimental consequences have demonstrated that there may be a positive c programming language of time most of the immediately of spark is given.
This time inters al corresponds to period AB and this era is known as ignition put off Ignition lag represents the period of preface reactions wherein the chain are customary as defined with in the chain response concept of combustion. The ignition lag relies upon the molecular shape of fueloline, temperature, strain, density, air-fueloline ratio and the share of residual gases with in the mixture.
2. Flame propagation section:
Once the self-maintaining flame seems at factor B, the flame travels outwards and burns the fueloline in air. Initially the fee of burning of fueloline and flame speeds are low with small fee of pressure rise. However because of the reality the combustion proceeds, the pressure and temperature continues on growing with warmth strength launch it surely is transferred from burned to unburned fee, the flame propagates sooner or later of the combustion chamber at excessive speeds. (Almost at consistent speed) with in the variety of (15-35) m/s.
3. After burning of flame termination section.
Actually combustion isn't finished at factor C eleven though it represents the very last contact of flame travel. It is because of the fact the burning continues because of left over fueloline and the association of dissociated gases present day with in the combustion chamber. This combustion past factor C continues sooner or later of the growth stroke and it is called as after burning representing the 1/3 diploma of combustion upto factor D. The flame pace decreases sooner or later of this section of combustion.
Effect of various parameters on combustion
The various engine variables which affect the ignition lag are as follows:
Pressure and temperature:
At immoderate pressures the molecules are nearer and their rate of collisions will growth. The improved temperatures will growth the kinetic electricity of molecules which commonly generally tend to increase the rate of collisions and moreover the mobility of reaction. Therefore ignition lag reduces with improved temperatures. The effect of pressure and temperature on ignition lag is confirmed in Fig. 2.
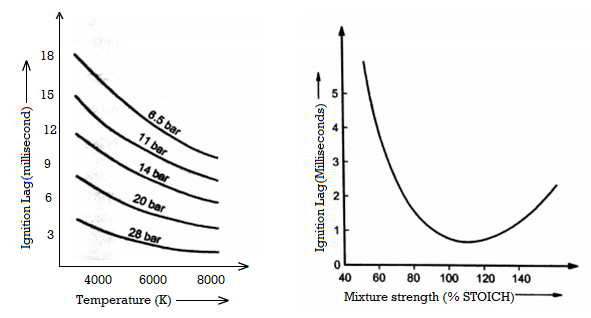
Fig.2. Effect of p,T on ignition lag , Fig 3. Effect of mixture on strength on ignition lag
Compression ratio:
Higher compression ratio will growth the pressure and temperature of the running substance. Therefore, the effect of improved compression ratio is much like improved pressure and temperature as noted above. At excessive pressures the molecules are closer and their fee of collisions will increase. It assist in forming the chain groups and decreases the ignition lag. The prolonged temperatures will increase the kinetic power of molecules which typically will be inclined to growth the fee of collisions and furthermore the mobility of reaction. Therefore ignition lag reduces with prolonged temperatures. The impact of pressure and temperature on ignition lag is tested in Fig. 2. Higher compression ratio will increase the pressure and temperature of the running substance. Therefore, the impact of prolonged compression ratio is just like prolonged pressure and temperature
Mixture strength:
It is decided that the ignition lag is minimum for about 10% rich combos as confirmed in Fig. 3.
Residual gases:
Therefore, higher the amount of residual gases in proportion to easy charge higher may be the length of ignition lag.
Nature of fuel:
The ignition lag is based upon on the chemical nature of the fuel. It is found that the fuels with higher self-ignition temperatures have fantastically higher length of ignition lag.
Speed:
It has no effect in terms of time period but it shows in terms of crank attitude turned. Therefore with higher speeds the ignition boom have to be increased.
Electrode gap:
The air hollow some of the electrodes of a spark plug is important from the component at reputation quo of nucleus of flame. If the electrode hollow is without a doubt too small, quenching of the flame nucleus might also rise up due to the fact the type of working with type of air-fuel ratio is reduced.
Abnormal Combustion:
When the 2 conditions of ordinary combustion do now not occur, the combustion method is atypical, causing engine damages or truly usual overall performance worsening and noise. There are types of atypical combustion in SI engines:
1) Surface ignition:
Combustion originates from some warm temperature spots with in the combustion chamber. The flame the front generated with the resource of the usage of ground ignition is actually much like the turbulent burning generated with the resource of the usage of a spark plug, Pre-ignition in most volatile because it help the ignition moment, therefore the useful art work output decrease, temperature and stress of the walking fluid This method is self-increasing, until some engine components collapse. This problem can be treatment with the resource of the usage of a proper format of the engine and using appropriate fine lubricant.
2) Knock:
The glowing rate vehicle mobile-ignites in advance than being reached with the resource of the usage of the flame the front large community increase of the gas line stress, causing a marvel wave to propagate from the vehicle mobile-ignition hassle thru the combustion chamber. Then the stress waves are time and again contemplated with the resource of the usage of the walls and they create an oscillatory stress style in region of time. Knock is the choice given to the metallic noise (a shape of hammering) produced with the resource of the usage of the vibrations of the engine components, excited with the resource of the usage of the ones stress oscillations. Knock intensity is based totally definitely upon on the amount of supply up-gas line mass that vehicle mobile ignites.
Engine parameters which influences knock tendency:
1) Compression ratio:
At immoderate compression ratios, even in advance than spark ignition, the gasoline-air combination is compressed to a immoderate pressure and temperature which promotes auto-ignition.
2) Engine pace:
At low engine speeds the flame pace is slow and thus the burn time is long, this consequences in more time for auto-ignition -at immoderate engine speeds there may be plenty much less warmth loss so the unburned gasoline line temperature is higher which promotes auto-ignition
3) Spark timing:
Maximum compression from the piston takes vicinity at TDC, developing the spark improve makes the surrender of combustion at TC (crank angle).
4) Engine layouts reducing knock tendency:
Compact combustion chamber shape - Central spark plug (symmetric flame propagation) - Hot spots near spark plug - Controlled fueloline motion
Factors affecting knocking:
- Temperature factors:
Increasing the temperature of the unburned mixture increase the possibility of knock in the SI engine we shall now discuss the effect of following engine parameters on the temperature of the unburned mixture:
i. Raising the Compression Ratio
Increasing the compression ratio will increase each the temperature and pressure (density of the unburned mixture). Increase in temperature reduces the postpone duration of the quit fuel line which in flip will increase the tendency to knock.
Ii. Supercharging
It additionally will increase each temperature and density, which growth the knocking tendency of engine.
Iii. Coolant Temperature
Delay duration decreases with growth of coolant temperature, reduced postpone duration growth the tendency to knock
Iv. Temperature Of The Cylinder And Combustion Chamber Walls:
The temperature of the quit fuel line relies upon at the layout of combustion chamber. Sparking plug and exhaust valve are freshest components with inside the combustion chamber and choppy temperature ends in pre-ignition and therefore the knocking.
2. Density Factors:
Increasing the density of unburnt aggregate will growth the opportunity of knock with inside the engine. The engine parameters which have an effect on the density are as follows:
Increased compression ratio growth the density Increasing the weight opens the throttle valve greater and as a result the density Supercharging growth the density of the aggregate Increasing the inlet stress will increase the general stress at some point of the cycle.
Advanced spark timing: amount of gasoline burnt in line with cycle earlier than and after TDC function relies upon on spark timing. The temperature of price will increase with the aid of using growing the spark enhance and it will increase with fee of burning and does now no longer permit enough time to the give up aggregate to expend the warmth and growth the knocking tendency
3. Composition factors:
i. Molecular Structure
The knocking tendency is markedly suffering from the kind of the gasoline used. The shape of the gasoline molecule has huge impact on knocking tendency. Increasing the carbon-chain will increase the knocking tendency and centralizing the carbon atoms decreases the knocking tendency. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have much less knocking tendency than saturated hydrocarbons.
Ii. Fuel-air ratio:
The maximum critical impact of gasoline-aft ratio is at the response time or ignition postpone. When the combination is almost 10% richer than stoichiometric (gasoline-air ratio =0.08) ignition lag of the stop fuel line is minimal and the speed of flame propagation is maximum. A too wealthy combination is especially powerful in reducing or putting off the knock because of longer postpone and decrease temperature of compression.
Iii. Humidity of air:
Increasing atmospheric humidity decreases the tendency to knock through reducing the response time of the gasoline.
Effects of knocking:
- Heat switch to the partitions of the combustion chamber is expanded with the aid of using engine knock.
- In this observe the have an impact on of knock onset and knock depth on the warmth flux is investigated with the aid of using inspecting over 10 000 man or woman engine cycles with a various diploma of knock.
- The warmness switch to the partitions changed into expected with the aid of using measuring the combustion chamber wall temperature in an SI engine below knocking conditions.
- The have an impact on of the air-gasoline ratio and the orientation of the oscillating cylinder pressure-relative to the combustion chamber wall-have been additionally investigated.
- It changed into discovered that knock intensities above 0.2 Mpa stimulated the warmth flux. At knock intensities above 0.6 Mpa, the height warmness flux changed into 2.five instances better than for a non-knocking cycle. The path of the oscillations did now no longer have an effect on the warmth switch.
Control of Knocking:
1. Controlling Temperature with Fuel
- When you’ve completed baking, you open the oven and pull the cake out to cool, the air in the over is a hundred and eighty levels C, so the cake and the metal cake tin are each a hundred and eighty levels but setting your fingers with inside the a hundred and eighty air doesn’t burn you.
- In this situation the air is a quite negative conductor of warmth, so it doesn’t burn you, the tin conducts warmth thoroughly and consequently it burns the pores and skin out of your fingers and the cake is someplace in between.
- We are setting each air and gas internal but, as we understand from our cake cooking example, air does now no longer behavior warmth thoroughly at all.
- The gas then again is a far higher conductor of warmth so the greater gas we placed with inside the greater warmth we are able to take away from the combustion chamber each engine cycle whilst the exhaust valve opens.
2. Controlling Pressure with Ignition
Timing Detonation because of over-superior ignition timing takes place while the spark fires too early (an excessive amount of advance) which reasons the flame the front to begin propagating from the spark plug outwards as ordinary however due to the fact the spark became began out too early, cylinder strain (from compression) builds at a fee extra than the flame velocity can propagate.
3. Controlling knock
- With knock detection prepared the ECU is 1/2 of manner to tracking and stopping engine harm because of detonation. There is continually a diploma of history noise with inside the engine that we need a good way to clear out
- . This history noise will range with engine RPM and engine load and it the challenge of the ‘knock threshold map’ to clear out it out.
- The knock threshold map need to be three or four dB better than the history noise in any respect load and RPM points.
- An clean manner to test that is to setup a rolling strip graph that suggests Knock Threshold (that’s the price you've got with inside the map) and knock sensor level (that’s the uncooked sign coming from the knock sensor) and run the engine.
The format of a combustion chamber for a spark Ignition Engine includes the shape of the combustion chamber. Due to this format, the combustion chamber has a remarkable have an effect on on engine overall performance. In this article, we are going to talk approximately the Different sorts of combustion chambers for SI Engines. The essential objectives and importance of the combustion chamber is to provide the following objectives.
• Smooth Engine operation
• High energy output and thermal efficiency
This can be completed with the resource of the use of the locate the spark plug at the correct position, proper Cooling of the spark plug and the exhaust valves area. High electricity output and thermal overall performance can be finished with the resource of the use of developing a immoderate degree of turbulence and sucking more amount of charge to achieve immoderate volumetric overall performance, improved antiknock characteristics, compact design. Most of those can be finished with the resource of the use of a suitable combustion chamber for the engine. There are wonderful varieties of combustion chambers for SI engines. Let’s communicate them in detail.
Different types of combustion chambers for SI Engines
- T-Head type
- L-Head type
- I-Head type
- F-Head type
T-Head Type
This sort of combustion chambers changed into used with withinside the early levels of the engine’s development. In this sort of combustion chamber, the knocking tendency is greater due to the distance at some point of the combustion chamber is long. There is want of cam shafts for the 2 valves. It is every one of a kind downside.
L-Head type
In this L-Head kind combustion chamber, you may see each inlet and the exhaust valve can be at the identical component operated via way of way of the identical camshaft.
This reason the shortage of pace and coffee turbulence effects with withinside the gradual combustion process. To keep away from this we've were given Ricardo’s turbulent head layout for the L-Head combustion chamber (Right component picture).
I-Head type
It is overhead type of combustion chamber. We can keep away from the thermal screw ups via way of way of keeping the modern exhaust valve with withinside the head in preference to the cylinder.
F-Head type
As you may see the F-Head kind combustion chamber with withinside the above diagram, One exhaust valve is with withinside the cylinder head, the inlet valve with withinside the aspect, and the spark plug is with withinside the cylinder head. Again this has the identical downside because of the reality the T-Head kind combustion chamber as the 2 valves want to be operated through specific camshafts.
Combustion is a machine of the quick chemical reaction amongst fueloline and the air. In IC Engine, there are exceptional levels of combustion for exceptional engines. In this post, we are going to recognition on levels of combustion in CI engine. Stages of combustion in SI engine are honestly exceptional than the CI engines.
There are 4 one of a kind degrees of combustion in CI engine wherein right combustion of air and gasoline takes vicinity as follows:
- Ignition Delay Period
- Period of Uncontrolled Combustion
- Period of Controlled Combustion
- After Burning
1. Ignition Delay Period
After final touch of the vaporization approach, the preface reaction of the aggregate with in the combustion chamber starts off evolved. During the preface reaction, pressure into the cylinder starts off evolved developing with the release of energy at a slow rate. When physical delay completes, the time c programming language as tons because the fuel ignites and the flame of the combustion appears is known as chemical delay. Preflame reaction we referred to above is taking area at a few level withinside the chemical delay.
2. Period of Uncontrolled Combustion
After the above-referred to get rid of duration is over, the air and fueloline mixture will auto-ignite as they have got achieved their self-ignition temperature. The mixture of air and fueloline in CI engines is heterogeneous in comparison to homogeneous with in the SI engines. Due to this heterogeneous mixture, flames appear at more than one area in which the attention of the mixture is high. The collected fueloline in some unspecified time in the future of the get rid of is now started burning at a really rapid charge. It motives a upward push in in-cylinder stress and temperature. So, the higher the get rid of duration, the higher may be the charge of stress upward push. During this level, you can’t manipulate the amount of fueloline burning, that’s why this period is referred to as a duration of out of manage combustion. This duration is represented thru the curve CD with in the above figure.
3. Period of Controlled Combustion
When the accrued fuel sooner or later of the put off length without a doubt burned with within the length out of manage combustion, the temperature and pressure of the combination with within the cylinder are so immoderate that new injected That’s the motive we are able to control the rise of pressure into the cylinder with the resource of the usage of controlling the fuel injection rate. Therefore, this period of combustion is called a length of controlled combustion.
4. After Burning
This is the ultimate diploma out of the four tiers of combustion in CI engine.
The figure. Practically, the burning of the gas with in the combustion chamber remains to hold during the boom stroke. The important reason withinside the returned of its miles the affiliation of dissociated gases and unburnt gas. Therefore, this ultimate phase of combustion is known as After Burning. These are the four terrific tiers of combustion in CI engine.
It is just like Pre-Ignition, however it's miles different. This reasons a brief, however intense, spike in cylinder pressure. Detonation is likewise called an "Engine Knock", "Knocking", or "Pinging" due to the sound it makes. It is spontaneous process. Indication of Detonation in CI Engines:
• Knocking or pinging sound
• Drop in Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT)
• Broken piston jewelry and/or spark plugs
• Damage to the piston and/or valves
Detonation can be caused by several factors. A few common causes are:
Over-Advanced Ignition Timing
If Ignition Timing is definitely too a protracted manner advanced, the spark plug fires too soon. This motives the flame to surrender early. The closing fuel can detonate.
• Lean Air/Fuel Mixture A rich Air/Fuel Mixture runs cooler than a lean mixture. A lean mixture can get too heat and detonate.
• Too Much Compression motives heat. If the air/fuel mixture is compressed too an lousy lot, it can detonate.
• Engine Overheating Low coolant or a horrible water pump can cause the engine to overheat. Too an lousy lot heat can cause the air/fuel with in the chamber to detonate.
• Low Octane Fuel Octane Rating is a diploma of "knock resistance". Switching to higher grade fuel can help a knocking engine.
- Compression ratio: The pressure and temperature at the end of compression increases with increase in compression ratio.
- Supercharging:
- Increasing inlet temperature:
- Increase in load:
- Advancing the spark:
- Flame travel distance:
- Spark plug location:
- Engine size
Control Measures for detonation:
• Reduce power to a decrease setting.
- Increases the mixture
Types of combustion chambers for CI Engines
There are two different types of combustion chambers for CI Engines.
- Direct Injection type
- Indirect Injection type
Direct Injection type combustion chambers
Direct Injection type combustion chambers are also called the open type combustion chambers. This open type combustion chambers, the combustion chamber quantity may be positioned with in the cylinder. There are four format versions available in Direct Injection type combustion chambers. Those are
- Shallow depth chamber
- Hemispherical chamber
- Cylindrical chamber
- Toroidal chamber
1. Shallow depth chamber
As you may see the shallow depth chamber diagram, the depth of the hole area provided with in the piston is quite small and the diameter is large. Due to the large diameter, there is probably almost negligible squish.
2. Hemispherical chamber
As you may see the hemispherical chamber, the depth to the diameter ratio can be various.
3. Cylindrical Chamber
In a few current diesel engines, this shape of combustion chambers modified into implemented. The Squish can be numerous with the resource of the use of numerous the intensity. Squash moreover can be controlled with the resource of the use of numerous the intensity.
4. Toroidal Chamber
This Toroidal chamber format is in particular centered to provide the powerful Squish along side the air moment. As the extra Squish, the mask needed on the inlet valve is small and there may be better utilization of oxygen.
Advantages of Direct Injection type combustion chambers
- Minimum Heat loss throughout the compression because of lower ground area to amount ratio results in better efficiency.
- The multi-hole nozzle can be possible and therefore tremendous atomization can be achieved.
Disadvantages of Direct Injection type combustion chambers
- High fueloline injection strain required. Hence complex format of fueloline injection system.
- Metering of fueloline should be accurate. Particularly for small engines. Indirect Injection type combustion chambers
One difficulty might be positioned with within the cylinder and the possibility difficulty might be with within the cylinder head. The gas line might be injected into the problem that is positioned with within the cylinder head. There are 3 version designs to be had in oblique Injection kind combustion chambers. Those are
- Swirl Chamber
- Pre-combustion chamber
- Air cell chamber
1. Swirl Chamber
This is likewise called the Ricardo swirl chamber. Swirl combustion chamber includes the round-fashioned chamber located with within the cylinder head separated from the engine cylinder. During the compression stroke, 50% of the air might be transferred to this swirl chamber. In this round fashioned swirl chamber, the gasoline line might be injected with the assist of a nozzle and the combustion might be initiated. The predominant disadvantage of this chamber is that the warmth loss is extra in comparison to the open combustion chambers.
2. Pre-combustion chamber
As you may see the above diagram of the Precombustion chamber. It includes the Prechamber associated with the principle chamber. This Prechamber quantity money owed for 40% of the general combustion space. During the compression stroke, the air is probably injected into the Prechamber the combustion is probably initiated in it. The charge of stress upward thrust and the most stress achieve withinside the direction of the combustion system is quite low than the open combustion chambers.
3. Air-Cell Chamber
In this combustion chamber, the clearance extent might be shared via way of manner of the 2 additives. The nozzle injects the gas line all through the primary combustion chamber place in the direction of the open neck the air mobileular. During the compression stroke, the primary chamber pressure might be extra than the strength mobileular pressure. When the temperature reaches excessive with in the critical chamber, The combustion will begins offevolved offevolved offevolved with in the critical chamber initially. In the strength, the mobileular includes the well-mixed charge, because of the warmth launch with in the critical chamber the excessive-pressure combustion debris will blow out via the small passages into the primary chamber. This excessive-tempo jet produces swirling movement with in the critical chamber thereby very well mixes the gas line with the air, consequently the combustion might be completed.
Advantages of indirect Injection type combustion chambers
The important benefit of the oblique injection combustion chambers are
- The direction of the spray isn't always that important
Disadvantages of indirect Injection type combustion chambers
- Poor bloodless beginning performance
- Specific fueloline intake is high.
References:
1. Obert E. F, “Internal Combustion Engines and Air Pollution”, Harper and Row Publication Inc. NY, 1973.
2. Heisler H, “Advanced Engine Technology”, Edward Arnold, 1995.
3. Heywood J. B, “Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals”, McGraw Hill Book Co. NY, 1989
4. Heldt P. M, “High Speed Combustion Engines”, Oxford & IBH publishing Co. India, 1985.
5. Stockel M W, Stockel T S and Johanson C, “Auto Fundamentals”, The Goodheart, Wilcox Co. Inc., Illinois, 1996.