UNIT 1
Cost and Revenue
Cost analysis is concerned with determining the money value of input used for production which is called as overall cost of production.
Definition:
In economics, the Cost Analysis refers to the measure of the cost – output relationship, i.e. the economists are concerned with determining the cost incurred in hiring the inputs and how well these can be re-arranged to increase the productivity (output) of the firm.
Concepts of cost:
Types of cost are as follows-
- Nominal cost is the money value of cost of production. It is also called expenses of production. The expenses paid to the factors he employs in the process of production.
- The real cost are the pain and sacrifices of labour involved in the process of production.
2. Explicit and implicit cost –
3. Accounting cost and Economic cost –
4. Private cost and social cost –
5. Opportunity cost and actual cost –
6. Business cost and full cost –
7. Total, Average and Marginal cost –
8. Fixed cost and variable cost –
9. Direct and indirect cost –
10. Incremental and sunk cost-
Key takeaways –
The relationship between output and cost is expressed in terms of cost function. The companies use cost function to minimize cost and maximize production efficiently.
The following functions are applied to take decision-
- It is the full cost of producing any given level of output. The cost is divided into 2 parts-
- Total fixed cost does not vary with the level of output. For eg – land.
- Total variable cost changes directly with the output. For eg – labour.
- Average total cost is the total cost per unit of output.
- Average fixed cost is the fixed cost per unit of output.
- Average variable cost is the variable cost per unit of output.
3. Marginal cost:

Change in output
Relation between average cost and marginal cost:
Average cost can be worked out by dividing the total cost by total output.
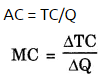
Likewise, marginal cost can also be calculated from total cost. The addition made to the total cost by producing one more unit of the commodity is called marginal cost. MC = TCn – TCn-1
When average cost falls, marginal cost also falls. In this case, marginal cost falls more rapidly than the average cost. That is why when marginal cost curve is falling; it is below the average cost curve.
When average cost rises, marginal cost also rises but marginal cost rises more rapidly than the average cost.
MC cuts AC at its lowest point : When average cost is minimum then marginal cost will be equal to it.
For a brief stretch, AC may continue to decline even when MC is rising : Shows that between points F and E, marginal cost is rising while AC continues to fall.
Mutual Interaction between MC and AC : When marginal cost is more than average cost, average cost has a tendency to rise. It seems as if marginal cost curve is pulling the AC curve upward. On the other hand, when MC is less than AC, it pulls the AC curve downward. When MC is equal to AC then the latter is constant.
Key takeaways –
Short run cost:
Short run cost is the cost where the quantity of one input is fixed and the quantity of other input varies. In this case, the land and machinery is fixed whereas the other factors such as labour and capital vary with time. Thus expansion is done in hiring more labour and increasing capital.
Definition:
In the words of Ferguson, “Total fixed cost is the sum of the ‘short run explicit fixed costs and implicit costs incurred by the entrepreneur.”
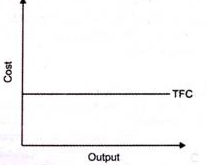
From the above figure , we can see TFC curve is horizontal to X axis.TFC remains constant with proportionate change in the output.
2. Total variable cost-
According to Ferguson, “total variable cost is the sum of amounts spent for each of the variable inputs used”
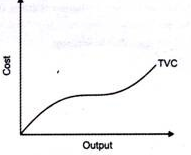
In the above figure, TVC changes with the change in the level of production
3. Total cost-
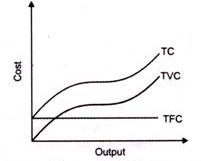
4. Average fixed cost (AFC)–
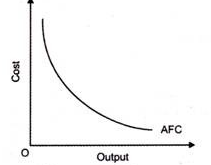
5. Average variable cost (AVC)-
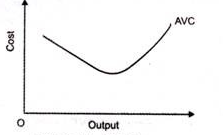
6. Average cost of production (AC)-
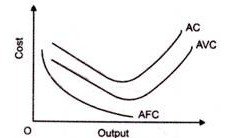
7. Marginal cost (MC)-
 Proportionate change in output
Proportionate change in output
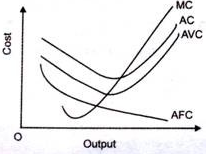
Long run cost:
In long run, all the factors of production vary. Long run is period in which all cost change as all the factors of production are variable. To produce at a lower cost in long run, the organization should have the ability to change the factors of production. There is no difference between TC and TVC as there is no fixed cost.
- It refers to the minimum cost at which a given level of output can be produced.
- Definition:
According to Leibhafasky, “the long run total cost of production is the least possible cost of producing any given level of output when all inputs are variable.”
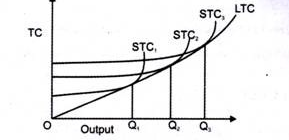
2. Long run average cost (LAC)-
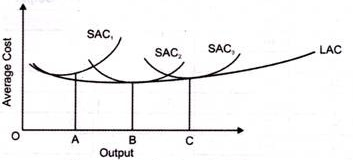
3. Long run marginal cost (LMC)-
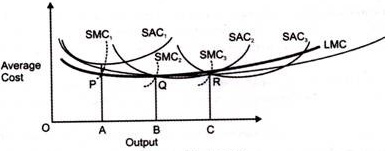
Key takeaways-
The term revenue refers to income obtained by the firm through sale of goods and services at different prices.
Definition:
In the words of Dooley, ‘the revenue of a firm is its sales, receipts or income’.
Revenue are of 3 types as given below-
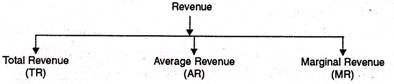
- Income received by the seller after selling the output is called total revenue.
- “Total revenue is the sum of all sales, receipts or income of a firm.” Dooley.
- TR = Q x P
Where,
TR – Total Revenue
Q – Quantity of sale (units sold)
P – Price per unit of output
2. Average Revenue:
Where, AR – Average Revenue, TR – Total Revenue – Total units sold
3. Marginal revenue:
Key takeaways-
References