Unit 1
Indian Business Environment
Business environment refers to the environment within which a business organisation operates. The business environment composed of internal environment and external environment. The internal factors are plans and policies, employees, value system, physical resources, corporate culture, organisational structure etc. which can be controlled by the organisation by adopting appropriate measures. The external factors are economic, social, political, legal, demographic etc. which cannot be controllable by the organisation. All these internal and external factors influence the working of the organisation. Any change in the business environment also leads to changes in plans, policies and working mechanism of business organisations. For example, introduction of GST requires the business houses to register under GST Act to get the benefit of input tax credit. The business environment is highlighted in figure 1

Figure 1: Business Environment
Some of the important characteristics of business environment are-
1) It is the composition of internal and external environment. Internal environment are controllable and external environment are not controllable by the organisation.
2) It is dynamic in nature and keeps on changing.
3) It is unpredictable because the changes occur in the environment due to happening of natural events and also man-made events.
4) It varies from place to place depending on its location, culture, society, demography, political stability, governance etc.
5) It influence on organisational plans and policy, objectives, working mechanism etc.
Key takeaways-
1) Business environment refers to the environment within which a business organisation operates. The business environment composed of internal environment and external environment.
The components of business environment are depicted in figure 2-
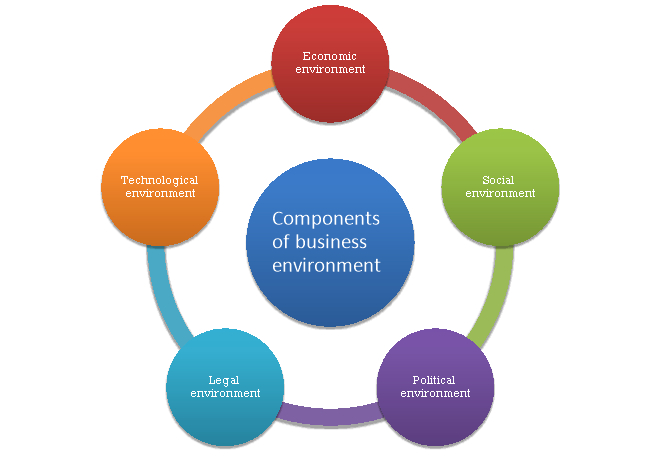
Figure 2: Components of business environment
The economic environment of business refers to economic system of a country as well as the world. It consist of the following elements-
a) Economic Conditions: It includes gross domestic product, per capita income, markets for goods and services, availability of capital, foreign exchange reserve, growth of foreign trade, strength of capital market etc. All these help in improving the pace of economic growth.
(b) Economic Policies: It includes-
(i) Industrial policy,
(ii) Fiscal policy,
(iii) Monetary policy,
(iv) Foreign investment policy,
(v) Export –Import policy (Exim policy).
(c) Economic System: There are three types of economic systems, viz., (i) Capitalist economy; (ii) Socialist economy; and (iii) Mixed economy.
2. Sociocultural environment
It refers to the environment that includes social factors like customs, traditions, values, beliefs, poverty, literacy, life expectancy rate etc. The social structure and the values that a society cherishes have a considerable influence on the functioning of business firms. For example, during festive seasons there is an increase in the demand for new clothes, sweets, fruits, flower, etc. Due to increase in literacy rate the consumers are becoming more conscious of the quality of the products. Due to change in family composition, more nuclear families with single child concepts have come up. This increases the demand for the different types of household goods.
3. Political environment
This includes the political system, the government policies and their attitude towards the business and industrial sector. The political stability, their ideology, beliefs, values etc. influences the business organisation. The LPG policy, demonetisation, GST etc. are some of the examples of policy formulated by different government from time to time that influences the industrial sector of our country.
4. Legal environment
This refers to set of laws, regulations, which influence the business organisations and their operations. Every business organisation has to obey, and work within the framework of the law. Some of the important legislations that concern the business enterprises include:
(i) Companies Act, 1956.
(ii) Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
(iii) The Factories Act, 1948.
(iv) Industrial Disputes Act, 1972.
(v) Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972.
(vi) Industries (Development and Regulation) Act, 1951.
(vii) Prevention of Food Adulteration Act, 1954.
(viii) Essential Commodities Act, 2002.
(ix) The Standards of Weights and Measures Act, 1956.
(x) Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969.
(xi) Trade Marks Act, 1999.
(xii) Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986.
(xiii) Consumer Protection Act, 1986.
(xiv) Environment Protection Act.
(xv) Competition Act, 2002.
Besides, the above legislations, the following are also form part of the legal environment of business.
5. Technological environment
Technological environment include the methods, techniques and approaches adopted for production of goods and services and its distribution. In the modern competitive age, the pace of technological changes is very fast. Hence, in order to survive and grow in the market, a business has to adopt the technological changes from time to time. For example, technology changes bring changes from traditional banking to online banking, traditional shopping to online shopping, offline education to online education etc.
6. Demographic environment
This refers to the size, density, distribution and growth rate of population. All these factors have a direct bearing on the demand for various goods and services. A company market their products depending on the target population. For example a country where population rate is high and children constitute a large section of population, then there is more demand for baby products. Again, The high rise of population indicates the easy availability of labour. These encourage the business enterprises to use labour intensive techniques of production.
Key takeaways-
1) The external factors are economic, social, political, legal, demographic etc. which cannot be controllable by the organisation.
Some of the significances of business environment are discussed below-
1. Business opportunities
The business environment is full of opportunities. The business organisations need to carefully scan the business environment and its recent changes to capture the opportunities for business. The advancement of information technology creates opportunities for online banking, e-learning apps, online shopping sites etc.
2. Helps to utilize useful resources
Careful scanning of your business environment can help you leverage the useful resources for business needs. This helps businesses track these resources and convert them into goods and services.
3. Dealing with change
Businesses needs to be aware of the on-going changes in their business environment, including changing customer requirements, new trends, new government policies, and technological changes. If the business is aware of these regular changes, they can provide a response to address those changes.
4. Planning support
It provides adequate information to the existing business houses for further planning for changes in the organisation to cope up with the changes in the business environment.
5. Helps to improve performance
Companies that scan the environment thoroughly not only address the changes presented, but also thrive with them. Adapting to external forces helps businesses improve performance and survive in the market.
6. Image Building: Environmental understanding helps the business organisations in improving their image by showing their sensitivity to the environment within which they are working. For example, in view of the shortage of power, many companies have set up Captive Power Plants (CPP) in their factories to meet their own requirement of power.
7. Meeting Competition: It helps the firms to analyse the competitors’ strategies and formulate their own strategies accordingly.
8. Identifying Firm’s Strength and Weakness: Business environment helps to identify the individual strengths and weaknesses in view of the technological and global developments.
Key takeaways-
1) Importance of business environment are business opportunities, helps to utilize useful resources, improvement of performance, image building, competition, identify firms’ strength and weaknesses.
References-