UNIT 3
Public Expenditure growth and effect, Wagener’s law of increasing Expenditure
Expenditure incurred by central, state and local government for the benefit of the society as a whole is called public expenditure.
Public expenditure can be defined as,” the expenditure incurred by public authorities like central, state, and local governments to satisfy the collective social wants of the people is known as public expenditure”.
Public expenditure includes
- Public spending on education, health, security,etc
- Maintenance of government defense, police, civil servants
Causes of growth of public expenditure
- Income elasticity and increase in per capita income:
According to Musgrave, a rising share of public expenditure in national income is associated with a rise in per capita income. Thus, increase in per capita income will result in increase in public expenditure. The demand for goods and services rises with the rise in income and result in payment of tax and more spending in public welfare.
2. Welfare state:
The 21st century modern state is a welfare state. The modern government focuses on socio economic uplift of masses. Various socio economic programs are organized to promote the welfare of the society. Government spends huge money on economic development. Government spends tremendously on the welfare activities by providing various social security benefits, health, education, etc. In the form of transport, electricity, etc social and economic infrastructures are built.
3. Defense expenditure:
In modern times, tremendous growth of public expenditure can be attributed to threats of war. The threat of war has not vanished and thus large amount of financial resources are allocated for defense. Due to the invention of nuclear weapons, international situation is uncertain and insecure and result in rise in defense expenditure. The expenditure includes war materials, maintenance and growth of armed forces, naval and air wings, expenses on the development of military art and practice, pensions to retired war personnel, interests on war debt, cost of rehabilitation, etc.
Peacock and Wiseman have referred to the ‘displacement effect’. During war government finds increasing taxes easy way to increase government revenue. The displacement effects are supplemented by a ‘scale hypothesis’, i.e., adoption of new social welfare schemes by the government on a permanent basis.
4. Resource mobilization and ability to finance:
Government increases the methods of taxation and its ability to finance public expenditure increases. Public sector investment can be increases through more taxation, public debt, foreign aid, etc.
5. The population effect
Growth in population will naturally increase the government expenditure. Rising population leads to solving problems of food, unemployment, housing and sanitation. Every year state spends more on family planning campaigns to control the population growth.
6. Transportation and communication:
The state also focusing on expansion of trade and commerce. Thus the governments have to maintain efficient transportation system. Transportation is a public utility, the government provides cheap transportation. Sometimes government transportation runs at loss due to high maintenance and expansion. Lot of government revenue are spent on constructing new railway lines, new roads, national highways, bridges and even canals for smooth transportation at different areas.
7. The planning effect
In less developed country, government focuses on economic development of the country. Thus when the government plans for expanding the role of public sector, then public expenditure tends to increase.
8. The rural development effect:
The government spends more and more for the development of rural areas. It adopts schemes like community development projects and other social measures. Hence the public expenditure rises.
9. The urbanization effect
In modern times, the spread of urbanization result in increase in public expenditure. In urban sector expenses on water supply, electricity, provision of transport, maintenance of roads, schools and colleges, traffic controls, public health, parks and libraries, playgrounds, etc is increasing rapidly.
10. The role of democracy and socialism:
Democratic country like India increased the public expenditure very much. Expenses on elections are increasing. The number of minister and executive officers are also increasing. To create favorable image in public, ruling party launches new policies and programmes to achieve social objective.
- Effect on production
The effect of public expenditure on production can be examined by the following:-
- Ability to work, save and invest: public expenditure on education, health, communication, increases the people’s productivity at work and therefore their income rises. Rise in income saving also increases investment and capital formation.
- Willingness to work, save and invest: public expenditure sometimes has adverse effect in people willingness to work. Government benefits such as unemployment allowances old age pension, insurance benefits, sickness benefit, medical benefit, etc. may reduce the desire to work
- Effect on allocation of resources among different industries and trade: government expenditure many times encourages investment on a particular industry or region. For ex, to promote export, governments provide tax benefit to attract investment in such industry. Similarly, to promote a particular region government provide incentive to attract investment.
2. Effects on distribution
In favor of poor people public expenditure enables redistribution of income. It helps to improve the capacity of poor to consume. The government provides welfare programs like free education, healthcare, housing to improve the standard of poor people.
3. Effects on economic growth
The government allocates income in various sectors like agriculture, industry, transport, communication, education, health, etc to achieve growth of the economy. Government aims at maintaining balanced economic growth. To develop backward region, government allocate more resources. This helps in reducing inequality and balanced economic growth.
4. Effects on economic stability
Public expenditure acts as a tool to control instability. Economic instability results in depression, recession and inflation. During deflation public expenditure are increased. On the other hand, during inflation public expenditure is reduced. Thus control of money supply brings price stability.
German political economist Adolf Wagner propounded a principle Wagner’s law known as law of increasing state spending. The theory states that economic development of a nation will result in the increase in the activity of public sector.
Definition
Wagnar's law states that "as the economy develops over time, the activities and functions of the government increase".
According to Adolph Wagner, "Comprehensive comparisons of different countries and different times show that among progressive peoples (societies),with which alone we are concerned; an increase regularly takes place in the activity of both the Central Government and Local Governments, constantly undertake new functions, while they perform both old and new functions more efficiently and more completely. In this way economic needs of the people to an increasing extent and in a more satisfactory fashion, are satisfied by the Central and Local Governments."
A Wagner law is applicable to modern government in which the state is interested in expanding public sector of the economy. Wagner states that function of the state increases extensively and intensively.
Intensive means expansion of traditional function of the state. Extensive increase the welfare function.
According to Wagner, the following reason increases the expenditure of public.
- Expansion of traditional function
Traditional function includes defense, justice, law and order and provision of social overheads. The traditional functions have increased gradually. In modern times defense expenditure has expanded and became sophisticated. The maintenance of sophisticated weapons, men and material has increased in modern times. Similarly areas of administration and government machinery have become more expensive.
2. Coverage of new functions
New function included expanding in various fields of welfare to enrich the cultural life of the society. The government increases expenditure on education, public health, low cost housing, subsidized provision of food, agricultural inputs, etc
3. Expanding sphere of public goods
Government is focusing on expanding the public goods. Government stated investing to areas like irrigation and flood control projects, construction and maintenance of public parks, provision of education and health care facilities, creation of economic overhead capital etc.,. This leads to heavy investment in public enterprises.
Graphic Presentation of the Wagner Hypothesis
The modern formulation of Wagner’s law is that “as per capita income rises in industrializing nations, their public sector will grow in relative importance”
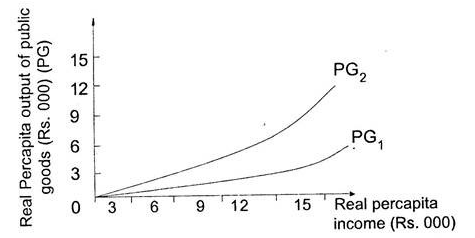
In the above figure, x axis shows real per capita income and Y axis shows real per capital output of public goods.
Line PG1 represents a circumstance where real income increases due to economic development of the society. While public sector remains constant of the economic production. Line PG2 depicts Wagner hypothesis which states that increase in the income due to economic development in the society. Similarly, real per capita output of public goods is expanding overtime. The income elasticity of expenditure for public goods is elastic.
Sources
1. Public finance in theory Baltic - Musgrave
2. Public Finance Department and Developing countries - Dr. S.K. SINGH
Http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.493.7556&rep=rep1&type=pdf